
Chronic diarrhea
Diarrhea lasting more than 2 weeks considered chronic.
The outcome of
diarrhea depends on its cause and ranges from benign conditions such as
toddler's diarrhea, to severe congenital diseases such as microvillus
inclusion disease that can lead to irreversible intestinal failure and
ultimately death.
Common causes :
1- infancy ;
Post gastroenteritis malabsorption syndrome , cows milk / soy protein
intolerance , secondary disaccharidase deficiency , cystic fibrosis .
2- childhood :
Chronic non specific diarrhea , secondary disaccharidaes deficiency ,
Giardiasis , Post gastroenteritis malabsorption syndrome, celiac disease ,
cystic fibrosis .
3- adolescence :
Irritable bowel syndrome , inflammatory bowel disease , giardiasis ,
lactose intolerance .
Postenteritis syndrome is a clinical-pathologic condition in which
small intestinal mucosal damage persists after acute gastroenteritis.
Sensitization to food antigens, secondary disaccharidase deficiency, or
an infection or reinfection with an enteric pathogen is responsible for
postenteritis syndrome. A change of the gut microflora due to the
infectious agent and/or antibiotic therapy can contribute to
postenteritis diarrhea.
Other rare causes
Defects in the genes of the Na+/H+ and the Cl−/HCO3− exchangers
are responsible for congenital Na+ and Cl− diarrhea, respectively.
congenital chloride diarrhea; The consequent defect in bicarbonate
secretion leads to metabolic alkalosis and acidification of the intestinal
content
Patients with congenital sodium diarrhea show similar clinical
features because of a defective Na+/H+ exchanger in the small and
large intestine, leading to massive Na+ fecal loss and severe acidosis.
Evaluation of children having chronic diarrhea .
Phase 1 : history and physical examination . If the child have history of
excessive drink of carbonated drink or fruit juice more than 150 ml/kg/24
h. with normal growth and height , this is chronic non specific diarrhea
If the patient ingest non absorbable nutrient in excessive amount such as
sorbitol, dietary adjustment need to be made.

Then do stool exam ; bacterial culture should be done, gross examination
of stool; if blood or mucous in stool it indicates inflammation of colon.
Carbohydrate malabsorption; by analysis of stool for ph if less than 5 or
the presence of reducing substance .
The stool should be sent for electrolyte and osmolality if secretary
diarrhea is considered. Stool should be examined for ova and parasite
such as giardia and ameba.
phase 2 : if phase 1 has failed to revile a cause pass to phase 2.
-sweat chloride test to rule out cystic fibrosis.
-72 hours stool collection for fat determination.
-stool should be checked for Mg sulfate or phenolphthalein if the diarrhea
secondary to ingestion of laxative ( factitious diarrhea ).
Phase 3 investigations :
Endoscopic studies for small bowel and colonic biopsies
-barium study and barium enema to rule out anatomic lesion.
Phase 4 ;
Hormonal study for vasoactive intestinal poly peptide and gastrin assay.
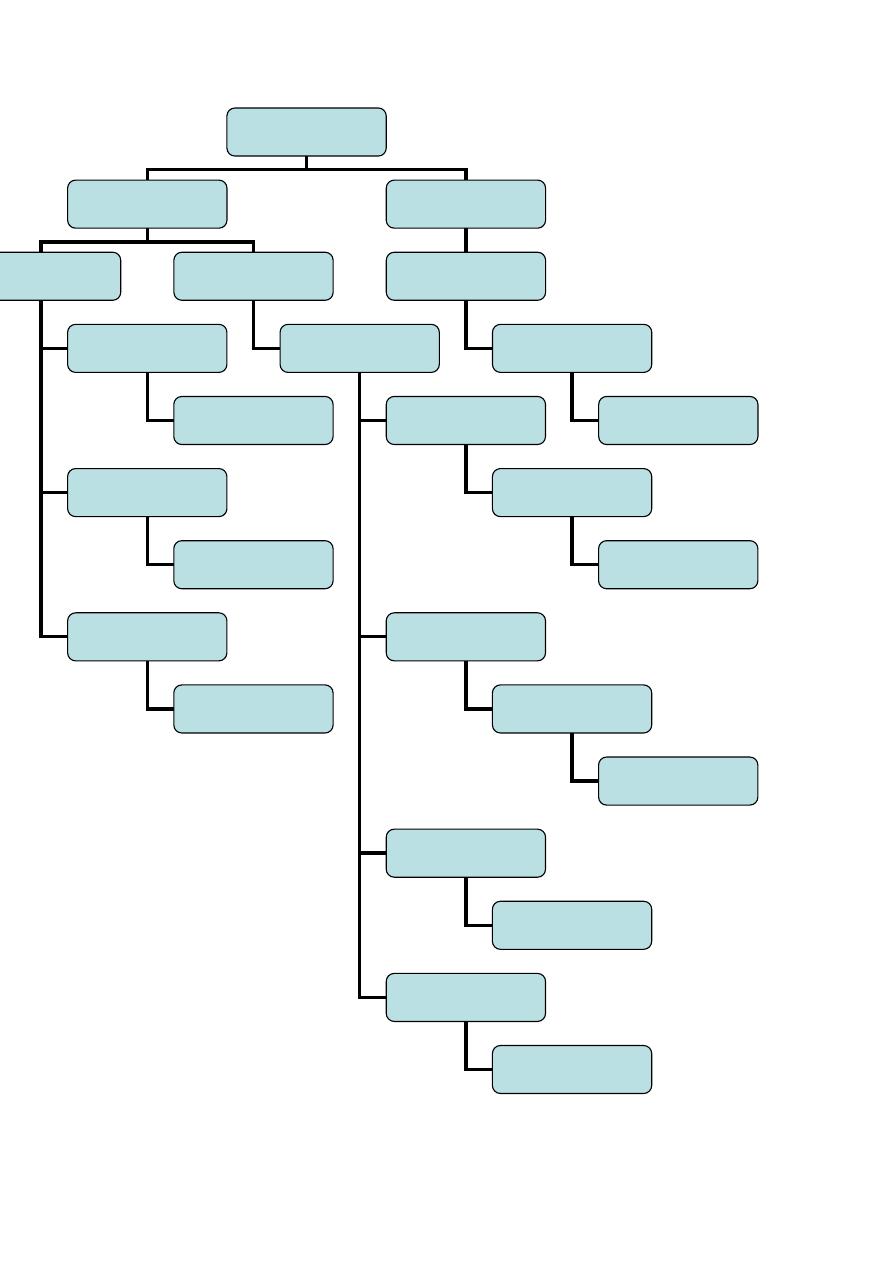
Chronic
diarrhea
Wt and ht is
normal and no fat
in the stool
Wt loss
Stool show fat
Chronic non
specific diarrhea
Diarrhea related to
carbohydrate
intake
Low fat intake
Excessive intake of
carbonated fluid
Excessive intake of
fruit juice
Increase fat intake
to 40%
Decrease fluid
intake to less than
90 cc / kg /24 h
Decrease intake of
fruit juice
Carbohydrate
malabsorption
Sucrose
intolerance
Lactose
intolerance
Monosaccharide
(glucose –
galactose )
Excessive sorbitol
ingestion
Decrease sucrose intake ,
add sucrosidase
Decrease lactose intake ,
add lactase tablet
Fructose is beast
alternative (formula
contain fructose )
Decrease sorbitol intake white
grape juice is beast
alternative
If no improvement
give sucrose free diet
If no improvement give
lactose free diet
Malabssorption
syndrome
Diagnostic test
Specific treatment

Treatment :
chronic non specific diarrhea.;
occur in generally well appearing toddler 1-3 year of age ( toddler
diarrhea ) the diarrhea is often brown and watery , at times containing un
digested food particles , if the child fluid intake more than 150 cc/kg/ 24
h fluid intake should be reduced to 90 cc/kg/24 h , parent note that
patient irritable in the first two days of fluid restriction however this
result in decrease stool frequency and volume .
if the history suggest the child take more fruit juice reduction in the
offending juice correct diarrhea . sorbitol sugar is found in apples , pear
can cause diarrhea in toddler , white grape juice is best alternative .
if the child fat intake is restricted by the parent the fat intake can increase
to 40% of the total calorie . in addition to treat the cause, during treatment
of chronic diarrhea should focus on providing adequate nutritional
support, also take attention to type and volume of fluid when used in
treatment, when use antibiotic therapy in bacterial overgrowth it should
be of broad spectrum; such as metronidazole, tetracycline,
chloramphenicol and ampicillin and for 2 weeks course, i.v. nutrition and
complete bowel rest for secretary diarrhea and lope amide and
somatostatin in primary villous atrophy.
⚫
In Rotavirus-induced severe and protracted diarrhea, oral
administration of human immunoglobulins (300 mg/kg) should be
considered.
⚫
Zinc supplementation is an important factor in both prevention and
therapy of chronic diarrhea, because it promotes ion absorption,
restores epithelial proliferation, and stimulates immune response.
Disaccharidase deficiency :
The disaccharidases are located on the brush border membrane surface of
small bowel , the most common is lactase deficiency, occasionally
congenital deficiency occur . but most often is the result from diffuse
acquired lesions of the intestinal epithelium such as infection or celiac
disease .
In older children and
adults late onset genetic lactase deficiency is the most common cause .
Clinical manifestation .
Watery osmotic diarrhea with stool PH less than 5.6 , contain excess
sugar and excoriate the buttocks , patient may bloating and borborygmi.
If the Disaccharide involved is a reducing sugar (lactose ) the standard
clinitest examination will be 2 + or greater in most cases. Disaccharidase
activity can be assayed in mucosal biopsy , breath hydrogen excretion

after an oral sugar load is a useful non invasive technique for detecting
disaccharide intolerance .
Treatment :
Consist of removal of milk from the diet , in most cases the elimination
need not be total . a lactase preparation is available as a tablet ingested
with meal . yogurt contains bacteria that produce lactase enzyme . thus
frequently tolerated by lactase deficient individual .
Glucose – galactose malabsorption :
More than 30 different mutation of the sodium / glucose transporter gene
have been identified to cause this rare autosomal recessive congenital
disorder . this transporter couples glucose and galactose to the sodium
gradient across intestinal and renal brush border . renal tubular epithelium
is affected to a lesser degree .
Clinical manifestation :
Osmotic diarrhea followed ingestion of glucose , breast milk or
conventional formula soon after birth because most dietary sugar are
polysaccharides or disaccharides with glucose and galactose moieties .
the patient may be bloated and if diarrhea persist dehydration and
acidosis can be sever , resulting in death , the stool is acidic and contain
sugar. the finding of positive reducing substance in a watery stool and
slight glycosuria despite low blood sugar level is highly suggestive of
Glucose – galactose malabsorption . and it also easily identified by using
breath hydrogen test , after ingestion of 0.5 g/kg glucose the breath
hydrogen rise to more than 20 PPM .
Treatment : Vigorous restriction of glucose and galactose . fructose the
only carbohydrate that can be given safely should be added to
carbohydrate – free formula in a concentration of 6 – 8% . diarrhea
immediately ceases when infants are given such a formula .
Arco dermatitis enteropathica :
It is due to zinc deficiency , early in life the patient experience rash
around mucocutaneous junctions ( mouth and anus ) and on the
extremities , alopecia , chronic diarrhea and sometime if not treated the
patient fail to thrive .serum zinc and alkaline phosphatase are low ,
intestinal biopsy show Paneth cell inclusion that disappear after
treatment.
Treatment :
Oral zinc sulfate 1-2 mg elemental zinc /kg / 24 h .causes rapid healing of
skin lesion and improvement of diarrhea.
Cows milk protein intolerance :

It present early in life with watery diarrhea and sometime with streak of
blood in the stool the infant may develop eczema , recurrent otitis media ,
respiratory wheeze and failure to thrive if not treated .
Treatment :
By avoiding the offending milk , prolong breast feeding decrease the
incidence of cows milk protein intolerance . sodium cromoglycate also
useful in treatment .
