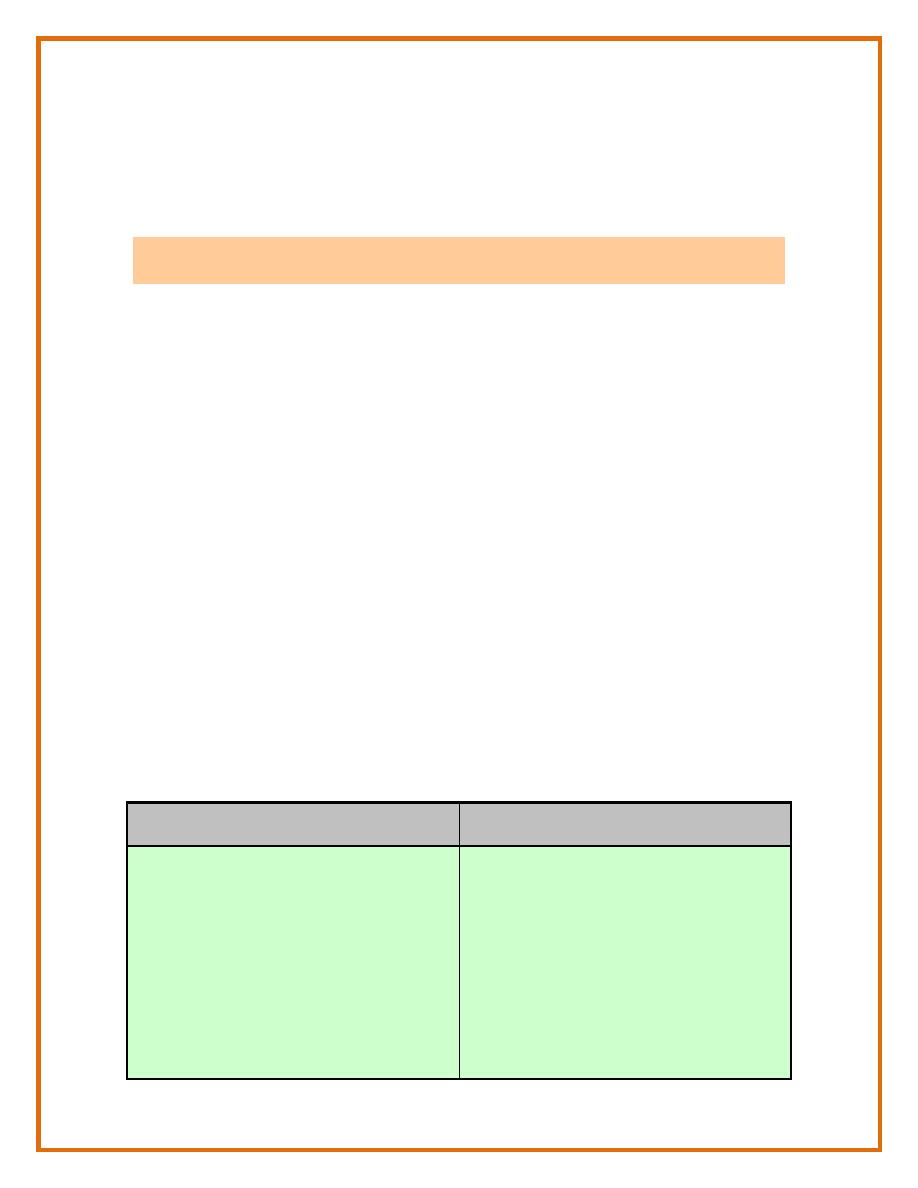
Growth and development
L2+L3
Assist Prof Dr.Raid Kareem
The 1
st
Year
Most full-term infants regain their birthweight by the age of 10 days .
Infants regain or exceed birthweight by 2 wk of age and should grow at
approximately 30 g (1 oz)/day during the 1st mo . This is the period of
fastest postnatal growth. The full term infants generally doubles birthweight
by 4-5 mo , and triples it by 1 year . The premature infant is likely to gain
about 6-7 kg in the 1
st
yr , which is about the average gain for full-term
infants . The length of the normal infant increases during the 1
st
yr by 25 –
30 cm. There is an increase in subcutaneous tissue in the early months of life
reaches its peak at about 9 mo .
The anterior fontanel may increase in size after birth but generally
diminishes after 6 mo and may become effectively closed between 9 and 18
mo . The posterior fontanel is usually closed to palpation by 4 mo .
Formulas for Approximate Average Height and Weight of
Normal Infants and Children :
— Weight
Kilograms
— At birth
— 3 – 12 mo
— 1 – 6 yr
3.25
age ( mo ) + 9
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
2
age ( yr ) x 2 + 8
— 7 – 12 yr
age ( yr ) x 7 – 5
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
2
— Height
Centimeters
— At birth
— At 1 yr
— At 4 yr
— At 2 – 12 yr
50
75
100cm
age ( yr ) x 6 + 77
Head circumference ( normally 34 – 35 cm at birth ) increases to
approximately 44 cm by 6 mo and to 47 cm by 1 yr (2cm/mo. in 1
st
3 mo. ,
1cm/mo. in 2
nd
3 mo. and 0.5cm/mo. in the next 6 mo.) . The head
circumference is slightly larger than that of the chest at birth , but the two
measurements become equal by the end of the first year .
The first deciduous teeth erupt in most children between 5 and 9 mo . The
first to appear are the lower central incisors , followed by the upper central
and then the upper lateral incisors . By the age of 1 yr most children have 6 –
8 teeth .
First 3 months of Life
By 12 wk there is some control of the head as the infant is drawn to a
sitting position . When held in ventral suspension, the newborn infant will be
in a posture of flexion of head and extremities around the supporting hand .
By 1 mo of age the infant will raise the head momentarily to the plane of the
body , and by 2 mo he or she will start to sustain the head in that plane . By
3 mo the head will be raise above the plane of the body , and the legs will be
extended as well .
In the first days of life infants visually fixate best on those objects that are
placed close to or moved through their line of vision . They may maintain
fixation with movement of the eyes and head to nearly 90 degrees to either
side of the midline . By 2 mo of age a supine infant will be follow an object
presented 90 degrees from the midline through an arc of 180 degrees . A
fully developed social smile becomes manifest usually between 4-6 wk of
age . The infant who does not have a social smile by the age of 8 – 12 wk
should be regarded as possibly seriously .
3 – 6 Months :
By the age of 3 mo an infant in the prone position on a firm surface is
generally able to raise the head and chest with the arms extended . When the
infant of 4 mo is pulled from a supine to a sitting position , the head is
brought up without lag ; At 5 – 6 mo of age the infant begins to roll over , at
first from the prone to the supine position and then in the reverse direction .
By 4 mo the infant becomes more adept at making contact with objects
brought within reach and often brings them to the midline and to the mouth
for visual and oral exploration . By 6 – 6 1/2 mo most infants can grasp a
large object such as a rattle and transfer it from hand to hand . By 4 mo they
begin to laugh aloud at pleasurable social contacts . By the end of the 6
th
mo
normal infants have developed clear preferences for social contact with the
persons giving them the most care . Total sleep requirements are
approximately 14-16 hr/24 hr, with about 9-10 hr concentrated at night and 2
naps/day.
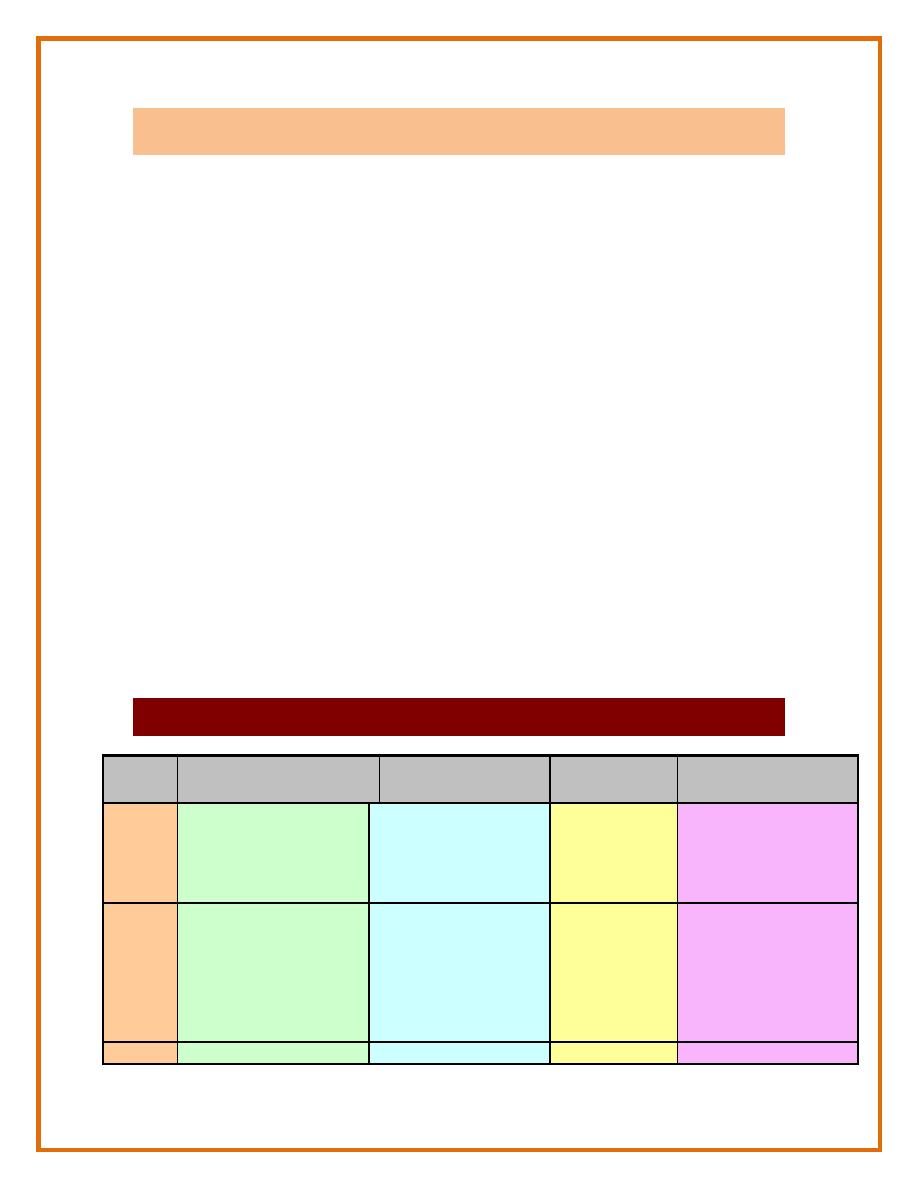
6 – 12 Months :
The ability to sit unsupported (6-7 mo), and by 8 – 9 mo they are able to
assume a sitting position without help . By 9 – 10 mo most infants have
learned to creep or to crawl. They are often able at 8-9 mo to stand steadily
for a short time as long as their hands are held , and by 9 mo may be able to
take some steps with both hands held .
Between 6 and 9 mo the radial – palmar grasp becomes clearly . The
index finger is used to poke at objects by 9 mo . And at this time the thumb
and forefinger can be brought into sufficiently accurate apposition to permit
a pellet to be picked up with a pincer motion . At 9 mo an infant may be able
to release an object on request . At 9 mo the infant can wave bye-bye.
By 12 mo , the pincer will be executed without ulnar support . Between 6
and 12 mo the infant's behavior becomes more imitative . A major milestone
is the achievement at about 9 mo of object permanence (constancy), the
understanding that objects continue to exist, even when not seen. At 12 mo a
child may enter into very simple games with a toy such as a ball
developmental milestones ( table below )
Age
Gross motor
Vision / fine
motor
Hearing /
speech
Personality / social
6 wks
Symmetrical limb
movements .
Ventral-head in line
with body briefly .
Supine-fencing posture.
Fixed and follows to
90 .
Turns to light .
Grasp reflexes .
Cries / Coos
Startles to
noise .
Smiles
3
months
Moves limbs
vigorously .
Head control.
Back-lumber curvature
only .
Prone-lifts upper chest
up .
Fixes and follows to
180 .
Plays with own
hands .
Holds rattles placed
in hands .
Quietens to
mother's
voice .
Turns to
sound .
Laughs and squeals .
6
Sits with support .
Palmar grasp .
Turns to
Laughs and screams .
months
Lifts chest up on
extended arms .
Rolls frond to back .
Downward parachute .
Transfers objects .
Shakes rattle .
Mouths objects .
quiet sound .
Says vowels
and
syllables .
Not shy .
9
months
Tripod sits-rights self if
pushed and can reach
for toy steadily .
Rolls to standing .
Stands holding on .
Forward parachute .
Reaches for small
objects .
Rolls balls .
Points with index
finger .
Early pincer grasp
Looks for fallen
objects .
Releases toys .
Distraction
hearing test .
Says mama ,
dada (non-
specifically)
Chews biscuit .
Stranger anxiety .
Play peek-a-boo .
Understands no and
bye-bye .
12
months .
Cruises around
furniture .
Walks if held , may take
few steps
unsupported .
Neat pincer grip .
Casting objects .
Banges cubs
together .
Known
name .
Understands
simple
commands .
Says few
words .
Drink from a cup .
Finger-feeds .
Waver bye-bye .
Find hidden objects .
15
months
Broad-based gait .
Kneels .
Pushes wheeled toy .
Sees small objects .
Tower of 2 bricks .
To and fro scribble .
2 – 6 words .
communicate
s wishes and
obeys
commands .
uses cup and spoon .
18
months
steady purposeful walk .
Runs , squats .
Walks carrying toy .
Pushes / pulls .
Creeps downstairs .
Circular scribble
points to pictures in
book .
Turns pages of book .
Hand preference .
6 – 20 words
Points to named body
parts .
Feeds independently .
Domestic mimickry .
Symbolic plays alone .
Takes off socks and
shoes
2 years
Kicks balls .
Walks up and down
stairs holding on .
Tower of 6 bricks .
Copies vertical line .
2 – 3 word
sentences .
Uses pivotal
grammar .
Uses
question
words .
Feeds with fork and
spoon .
Begins toilet
training .
Temper tantrums .
3 years
Walks up stairs 1 foot
per step , down with
2 .
Walks on tip-toe .
Throws ball .
Pedals tricycle .
Tower of 9 bricks .
Builds train and
bridge with bricks .
Copies circle .
Gives first
and last
name .
Knows sex .
Recognizes
colours .
Pure tone
audiometry .
Washes hands and
brushes teeth .
Eats with fork and
spoon ( + / -knife ) .
Make believe play .
Likes hearing and
telling stories .
4 years
Walks up and down
stairs 1 foot per step .
Hops .
Builds steps of
bricks .
Copies cross .
Counts to 10
or more .
Able to undress .

Draws man .
5 years
Skips .
Catches ball .
Runs on toes .
Copies triangle .
Asks how
and when .
Uses
grammatical
speech .
Uses knife and fork .
Able to put on
clothes and do large
buttons .
Developmental quotient ( DQ ) :
To assess or have simple expression of deviation from norm , use DQ
Developing age
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ × 100
Chronological age
Normal = > 85
Abnormal < 70
70 – 85 = gray area and warrants close follow up ( important for cognitive
function and less for motor domain ) .

The infants is able to make repetitive vowel sounds by 6 1/2 mo and by 8 mo
is likely to produce repetitive consonant sounds , such as ba-ba , ma-ma ,
and da-da . Children of 8-9 mo become attentive to the sounds of their own
names . Separation anxiety between the ages of 6 and 8 mo.
The 2
nd
Year
During the 2nd yr of life there is a further deceleration in the rate of growth:
the average child gains about 2.5 kg and about 12 cm. After 10 mo of age
there is often a decrease in appetite extending into the 2nd yr. The result is a
loss of some of the subcutaneous tissue. With the upright posture the mild
lordosis and protuberant abdomen appear that are characteristic of the 2nd
and 3rd yr of life.
The growth of the brain continues its deceleration during the 2nd yr.
Head circumference, which increased approximately 12 cm during the 1st
yr, increases only 2 cm during the 2nd yr. During the 2nd yr more teeth
erupt, making a total of 14 – 16. By 12 mo infants are generally able to walk
a few steps alone. By 18 mo the infant is able to run stiffly. At 18 mo the
infant can climb stairs of one hand is held; by 20 mo he or she is able to go
downstairs, one hand held.
By 24 mo children normally enter the "runabout" age. They are able to
move quickly from a safe environment into danger and need constant
surveillance. At 15 mo generally be able to put the pellet into a small bottle
by 18 mo is able dump it from the bottle.
By 15 mo the child is able to put a 1 – in cube on top of another in
response to a demonstration; by 18 mo be or she is able to make a tower of
four cubes and by 24 mo a tower of seven cubes. Vertical lines at 18 mo; by
24-30 mo the child imitates circular strokes and can make a horizontal line.
During the 2nd yr the child develops a sense of self as separate from other
person. The child normally has 10 words by 18 mo with the result that most
normal children by their second birthday are able to put three words
together. During the 2nd yr imitative behavior extends to person other than
the mother, including siblings. By 18 – 24 mo most children are able to
verbalize their toilet.
Preschool Years:
During the 3rd, 4th and 5th yr of life gains in weight and height are
relatively steady at approximately 2.0 kg and about 6-8 cm / per y. Most
children are lean in comparison with their earlier body configuration. The
healthy preschooler is slender and agile, with an upright posture. The
lordosis and protuberant abdomen of late infancy tend to disappear by the
4th yr. By 2 1/2 yr the deciduous teeth have usually erupted. Major
development occurs in the area of fine motor coordination. The preschooler
is an inquisitive learner and absorbs new concepts like a sponge absorbs
water.
Myelinazation of the spinal cord allows for bowel and bladder control to be
complete in most children by age of 3 years. The number of alveoli
continues to increase, reaching the adult number at about 7 years of age.
Alternation of feet in ascending stairs by 3 yr and alternation in
descending stairs by 4 yr. By 3 yr most children can stand for a short period
on one foot; by 5 yr they are generally able to hop on foot and soon to skip.
They can kick ball forward.

18 mo 20 mo 2.5 y 3 y 4 y 5 y 6 y
| __
By the age 3 yr the child can respond to the request to draw a person. The
first figures consist of a circular head with arms and legs attached as sticks.
During the next years the child adds the trunk. Draw persons with 2-4 parts
in 4 years, and at least 6 parts in 5 years.
The child in intuitive phase can count 10 or more objects, correctly name
at least four colors, and better understand the concept of time, and he knows
about things that used in everyday life, such as money, appliance, and foods.
During the 3rd yr the child puts short sentences together to sustain a brief
conversation. Vocabulary at 3 years comprises about 900 words. The
preschool child may acquire as many as 10-20 new words/ day and at age 5
usually has 2,100 words. They start to develops fluency.
By 3 yr most children can state their ages and whether they are boys or
girls. During the 3rd yr of life children more increasingly into play activities
in which other are involved, at first in parallel play (doing the same thing)
rather than in reciprocating actions or exchanges.
