1
Fluoride
د. ريا جاسم النعيمي
Fluoride has been found to be a very important element in the prevention of
dental caries , this has been proved by epidemiological ,experimental and
clinical studies .
Fluoride is a trace element ( found in a very low concentration) which is
about 1ppm (this is equal to 1 mg / liter ). In nature the conc. Of fluoride may
reach levels up to 10,000 ppm ,it is found in sea water , rivers , rocks , ground ,
soil ,vegetables.
Historical Background
In 1901 Dr . Frederick Mckay arrived in Colorado springs, he noticed that
many of his patients, especially those who lived in the area had a permanent
stain on their teeth called by the residents Colorado Stain .
In 1912 Mckay discovered that people from parts of Naples in Italy had a
dental pecularity known locally as denti di chiae this mottling of the teeth was
the same feature as that found in Colorado springs.
In 1931 Churchill who was a chemist found that the cause of the mottled
enamel was due to high levels of fluoride in the water supplies that was
analyized.
In 1933 Dean studied the relationship between the severity of mottled enamel
and fluoride concentration in water supplies . Ainsworth also in 1933 reported
that caries experience in high fluoride areas was markedly lower than caries in
other districts with low fluoride content .

2
Dean with his researches found that maximum reduction in caries occurred
when concentration of fluoride was 1ppm , at this conc. Fluoride causes
sporadic instances of the mildest forms of dental flourosis of no practical
esthetic significance .
Artificial water fluoridation was started in 1945 , the experiment was carried
out by Dr. Dean in Grand Rapids which was the experimental town and
Muskegon was the control town ( DMFT was the same in both cities in 4 -16
year olds ) .Sodium fluoride was added to the water supply of Grand Rapids
,after 6 ½ years DMFT rates where measured , the children of Grand Rapids
had almost half the DMFT of Muskegon , other cities began to start water
fluoridation .
Sources of fluoride intake
The main sources are :
1-Water: In some areas the conc. Of fluoride in water may reach up to 10
ppm some areas in North Iraq also have high conc. It is present in an ionic
state .
2-Food : food also is one source of fluoride ,its concentration in food is
affected by conc. Of fluoride present in the water,it is present in soil ,
fertilizers , sea food, fish.
3-Drugs:some drugs contain fluoride like diuretics, floursteroids, general
anesthesia, fluoridated products like mouth rinses , gel , tablets and tooth paste.
4-Pollution:also considered as a source of fluoride specially in areas of
industries, as there is an increase of fluoride in the water, soil , the conc. May
reach to 25 -1000 times normal .

3
Metabolism of fluoride
Absorption
Fluoride is mainly absorbed by the GIT (intestine and stomach ), about
85 – 97 % of fluoride ingested is absorbed , the bioavalibiaty of fluoride is
important for its absorption that the fluoride must be in an ionic form as the
bonded fluoride is removed by urine and feces .
Absorption 100% in case of water
Absorption 50-80% in cases of food
Factors affecting absorption of fluoride from the GIT
.
1-Presence of food in the stomach may affect the absorption of fluoride
because this food act as a physical barrier for absorption of fluoride ions from
the GIT.
2-Presence of other elements in the stomach that fluoride may bind to like
calcium , magnesium , phosphate , aluminium leading to decrease in the ionic
form of fluoride leading to decrease absorption of fluoride ions ( that is why in
case of fluoride toxicity the patient is given milk because calcium in milk will
bind to fluoride leading to decrease fluoride absorption .
3-Types, solubility of the fluoridated dental product ex NaF absorption from
the GIT is faster than sodium monoflourophosphate , so absorption of NaF is
faster.
4-Acidity of the stomach which is an important factor that increase fluoride
absorption because of presence of acidity which lead to increase dissociation of
ionic fluoride, increasing the rate of absorption of fluoride from the GIT.

4
Distribution
After absorption , fluoride is going to be distributed in the body with in 10
minutes , fluoride in plasma increase with in an hour it will reach its peak, it
returns to its normal value with in 11- 15 hours.
Fluoride mainly distributed to the calcifying tissue ( bone ,teeth) so flouride is
described as calcified tissue seeker, fluoride bonds to bone in reversible
manner, because of remodeling process of the bone ,but in teeth fluoride bond
is irreversible once it is incorporated to the tooth because there is no
remodeling process in the teeth.
Excretion
Flouride is excreted through kidneys, some of the bonded fluoride unabsorbed
is removed in the feaces, a low concentration is excreted in sweat, also a low
concentration is excreted in sweat , also low concentration 0.01 – 0.04 ppm is
excreted in saliva .
Storage of Fluoride
Fluoride is stored in the hard tissue bone and teeth, deposition in bone is due to
normal physiological process, there are certain factors that control the amount
of fluoride deposite:
1-Age of the individual .
The younger the person , the more fluoride is deposited in bones .
2-Concentration of Fluoride :
Flouride uptake and deposition increases with increasing the conc. Of fluoride
in the water.
3-Duration of fluoride intake :
In the first years of age there will be more deposition, but this is not continuous
to all life, it reaches a certain level then all the fluoride intake is excreted in

5
urine, this level is called the steady state level in which there is no more
deposition of fluoride in bone because of saturation of the bone with fluoride
and then all of it is excreted in urine .
Fluoride content of dentin and enamel is considerably lower than that found in
bone for the same individual, dentin is found to contain 4 times more fluoride
than enamel , the highest conc. Of fluoride in dentin is found adjacent to the
odontoblastic layer ,the conc. Of fluoride on the outer layer of enamel is about
4 -5 times higher than layers.
Fluoride Toxicity
There are 2 types of fluoride organic and inorganic .
Inorganic fluoride :is non toxic unless is taken in high dose , it is present in
natural food and water either soluble as Naf or insoluble as CaF2.
Organic fluoride : this type is toxic like flouro-acetate and flourocarbonate and
phosphate .
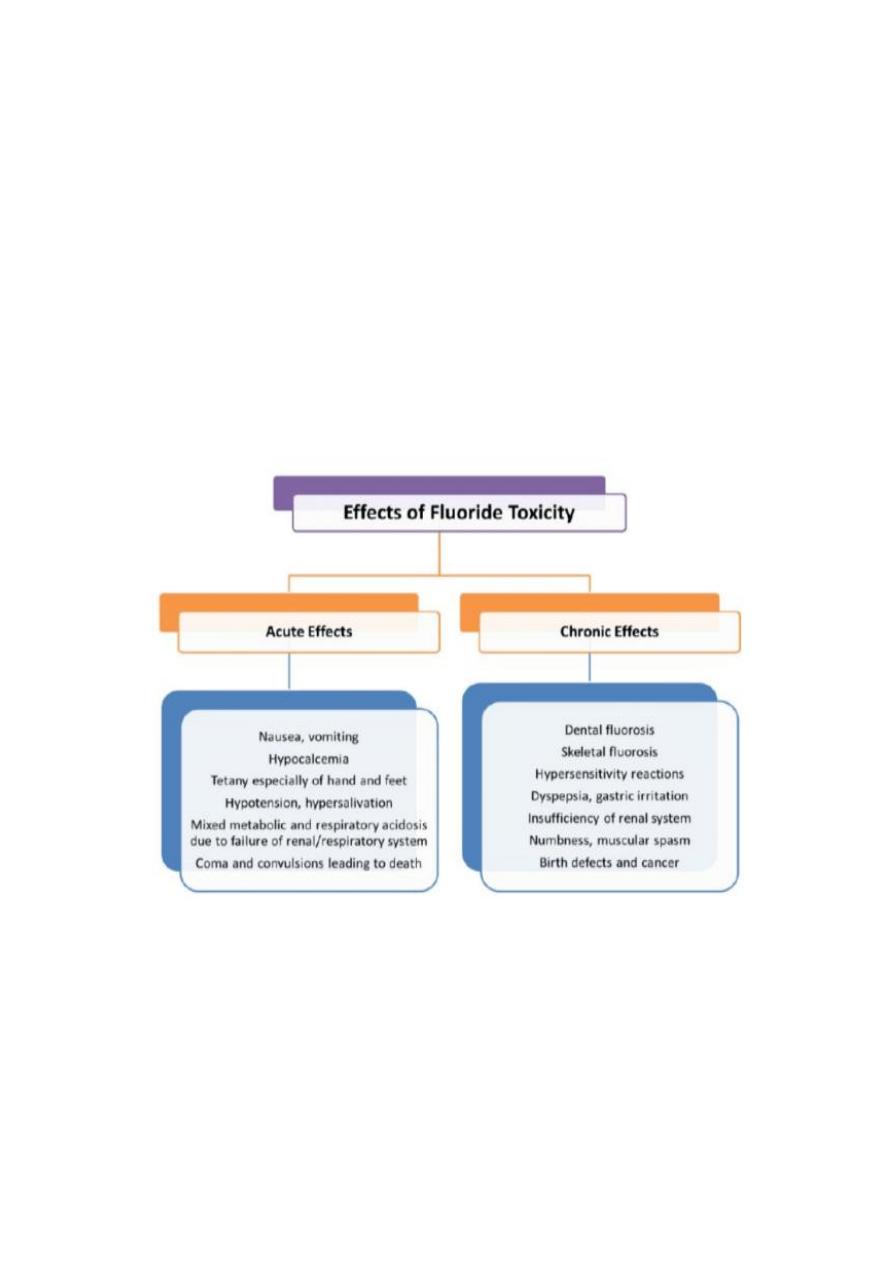
Chronic toxicity of fluoride
Long continuous exposure with excessive amount of fluoride may lead to
skeletal changes as skeletal flourosis or called osteosclerosis and exostosis
which is often associated with out symptoms but in sever cases pain and
deformity may occure and also if exposure through tooth development occure
then dental flourosis will develop mottled enamel .
High levels of naturally occurring fluoride causes a crippling bone disease
. Skeletal fluorosis, in its extreme form, currently
affects millions of people living in India, China, and other poorer countries

6
where nutritional deficiencies (e.g.
) exacerbate fluoride's toxic
effects.
-Hypersensitivity reactions
-Gastric irritation
-Insufficiency of renal system
-Numbness and muscle spasm
-Birth defects and cancer
Acute Fluoride Poisoning
The lethal dose of fluoride is 3 – 5 gm of fluoride which is sufficient to kill
an adult when taken in a single dose ,approximately equivalent to 63 mg/kg of
body weight ,it is impossible for water containing 1mg/liter to cause lethal
effect .
Topical fluoride such as acidulated phosphate fluoride with a concentration of
1.23 % present in bottles of 250 millileter, so contains approximately 3 gm of
fluoride ,which is a potent lethal dose if the whole bottle is consumed quickly
by one person.
Main signs and symptoms of acute fluoride poisoning is abdominal pain ,
diarrhea , vomiting , painful spasms of the limbs , some patients suffering from
osteoparosis or pagets disease are treated with a daily dose of 20 -100 mg of
fluoride (NaF daily ), so if acute fluoride poisoning is suspected , the content
of the stomach is emptyed by a gastric levage or by giving an emetic drug ,
milk can be useful to reduce the amount of fluoride absorption .
7
First Aid Treatment For acute fluoride Poisoning
Milk or milk with eggs
Plenty of fluid including milk should be ingested
Lime water (CaOH)
Maalox (aluminum preparation)
Protects mucous membranes of upper GI from chemical burns
Contains calcium as a binder
Types of Fluorides
Fluoride has 2 types of effects systemic and topical depending on the delivery
method used, systemic fluoride provides a low concentration of fluoride to
teeth over a long period, it circulates in the blood stream and is incorporated in

8
the developing teeth, and after teeth erupt fluoride contacts teeth directly
through salivary secretions.
Topical fluorides are placed directly on the teeth ,some preparations provide a
high concentration of fluoride over a short time, topical fluoride allows
interaction of fluoride with minerals in the teeth.
Some fluoride preparations provide both topical and systemic effects ex
fluoride mouth rinse used swished to obtain topical effect and swallowed .Most
systemic fluorides have a topical effect but their primary effect is systemic.
Community water fluoridation
School water fluoridation
Dietary fluoride supplements
Systemic fluorides include
1. Community water fluoridation
2. School water fluoridation
3. Fluoridated salt
4. Fluoridated milk and fruit juice
5. Fluoridated tablets with/ without vitamins
6. Fluoride drops with/with out vitamins
7. Lozenges intended to be sucked slowly in mouth
8. Oral rinse supplements (swished and swallowed)