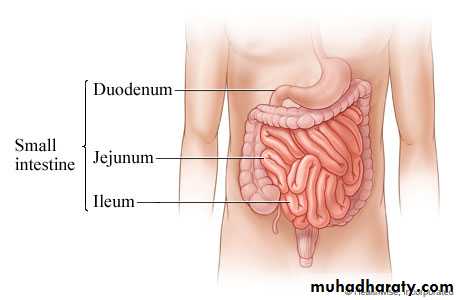
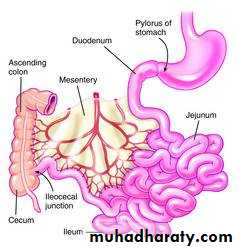
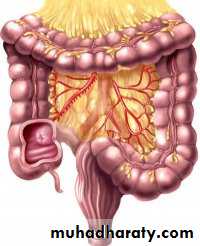
Differences between Jejnum & Ileum
1. Length juj 2/5 8 feet2. Site umblical region
3. Lumen wider4. Wall thicker , thick mucosa and muscle
5. Circular folds of mucosa are numorousThe juj.arteries anastemosis together forming 2 arcades (simple art.arcades) while ilium forming 3,4 or even 5 arcades.
Peyres patches (aggregation of lymphoid follicles in sub mucosa)abscent in juj.
At operation juj wall felt as douple layer.
Definition: it is a peritoneal fold enclosing the free part of the small (jejunum & ileum) & connecting it to the post. Abdominal wall.
Shape: fan-shaped fold having broad free border & narrow attached border:
(a) Free border: is 6 meters (20feets) long & encloses the jejunum & ileum.
(b) Attached border: (Root of mesentery): 6 inches long & 6 inches away from the free border (depth).
Mesentery of Small Intestine
- It is attached to the post. Abdominal wall extending from the duodenojejunal flexure (on the left side of L2) to ileocecal junction (above the Rt. Sacroiliac joint).
- Its attachment follow a curved course with its concavity directed to the Rt. Side.
- The root crosses 6 structures on the post. Abd. wall. (2 parts of duodenum, 2 large vessels & 2 muscles) :
1. The 3rd part of duod. 2. the 4th part of duod.
3. Abdominal aorta 4. Inferior vena cava
5. Rt. Psoas major m. 6. Rt. Iliacus m.
Mesentery of Small Intestine ..
Contents of the mesentery:
1. Coils of jejunum & ileum in the free margin of the mesentery.2. Superior mesenteric artery & its branches:
- It runs downwards & to the Rt. In the root of mesentery.
- It gives 12-16 jejunal & ileal branches which run between the 2 layers of the mesentery to reach the coils of small intestine in the free border.
- Its branches anastomose together forming arterial arches.
- Contents of the mesentery ..
3. Sup. Mesenteric V. & its tributaries:
- Runs in the root of mesentery on the Rt. Side of the sup. Mesenteric artery.
- Receives tributaries corresponding to the branches of the sup. Mesenteric a.
- It ends by joining Splenic vein to form portal vein.
4. Lymphatics & 3 raws of mesenteric L.Ns.
(a) Small lymph nodes near the intestine in the free border.
(b) Medium-sized L.Ns in the middle of the mesentery
(c) Large L.Ns: lie along the sup. Mesenteric vessels,
- Contents of Mesentery ..
5. Dense plexuses of autonomic nerve fibers around the arteries.6. Extraperitoneal fatty tissue
Ileocaecal valve
It is the valve which guards the opening of the ileum into the caecumSite & surface anatomy: it lies in Rt. Iliac fossa at the point of junction between Rt. Lat. Vertical plane & the intertubercular plane.
Structure: it has 2 lips (upper&lower) & 2 frenula (Rt&Lt)
Function: it regulates the passage of ileal contents into the cecum & prevents reflux from cecum to ileum.
Mechanism: it closes actively by symp. Stimulation & passively by distention of cecum.
Begning ; from iliocecal valve in the rt iliac fossa and end at anal orfice .
About 5 feet (1.5) meters in length
Parts ; caecum and appendix---ascending colon –rt(colic hepatic flexure –transverse colon –lt colic(splenic) flexure—descending colon – pelvic colon (sigmoid)--- rectum and anal canal.
Large intestin
Differences between large and small intestine
Large intestine ch. By1- appendices epiploicae small peritoneal sac filled with fat scattered over the surface of large bowel except caecum ,appendix and rectum
2- taenia coli longitudinal muscle fiber absent in appendix and rectum
3- saculation ( hustration),it occur because length of tania coli is shorter than the true length of large intestin.
4-diameter.
5- site
Site in rt iliac fossa above the lateral half of inguainal ligament.
Surface anatomy atriangular area in rt iliac fossa bounded by
Above- intertubercular plain
below -Lateral ½ of inguinal ligament
Medialy – rt lateral vertical plan
Shape blind pouch 3 inch in length
caecum
Comminication
Above – medially –iliumPosteriomedial– appendix
Peritoneal covering completely cover
Relation
Anterior– ant .abd,wall, lower part of greater omentum..coil of small intestin
Posterior-- 2 muscles rt psoas major,,rt iliacus
2 nerve rt cut, n, of thigh,rt femoral n
2 vessels rt ext.iliac vessels& rt gonadal (test or ovarian)
Site –rt iliac fossa, attach to post. medial aspect of caecum 1 inch below iliocaecal valve
Size ½ -9 inch average 4 inch it’s the narrowest part of GIT
Shape worm like tube
appendixPertonial covering completely cover
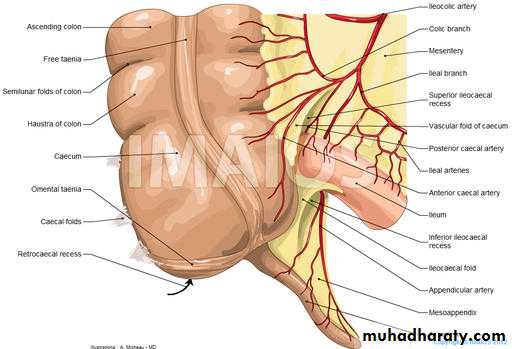
Mesoappendix ;
Its peritoneal fold which suspends the appendix
appendix
Contains of mesoappendix
1- app,vessels 2-lymphatic and l.n 3- autonomic nerve fiber 4- extrapertoneal fatty tissue.Position of appendix;
Retrocaecal 65%
Pelvic 31%
Preilial 1.5%
Post ilial 0.5%
Subcaecal 2%
Surface anatomy;
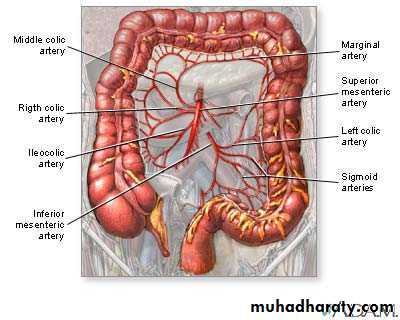
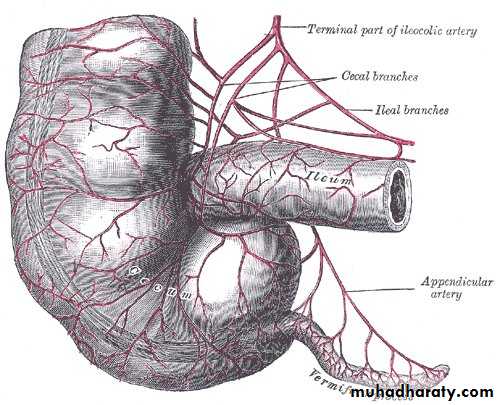
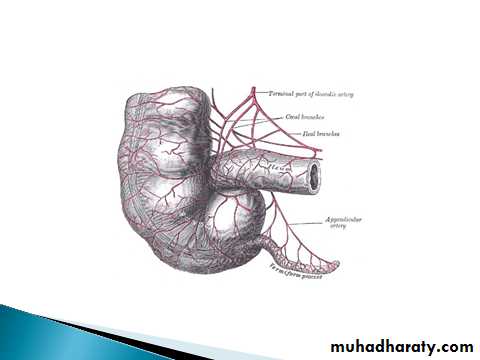
Mc Burney’s point; what?Arterial supply; appendicular artery branch from iliocolic artery. run through free border of mesoappendix till reach the tip of appendix (it end artery).
It accompanied with app. vein which drain to the sup. mesent,vein.
Lymphatic drainage; 1-to the append. ln
2-To the l.n along iliocolic art.
3-L.n along sup.mesentric artery
Nerve supply ;sympathetic from T10 segment via sup mesenteric plexus
Parasympathetic via vagus nerveApplied anatomy
Acute appendicitis common --why? 1- narrow lumen 2- rich in lymphoid tissue
Necrosis and rapture because of end artery
Pain start around umbilicus because T10
how reach to the base of appendix?
Ascending colon ;
site RT lumber regionBegning ;from caecum to the RTcolic flexure.
Taenia coli ; 1ant&2 post..
Pertonium ant.and sides only
Relation;
Anteriorly and laterally;
Ant. Abd. wall, rt border of greater omentum,, coil of ilium
Medially coils of ilium
Posteriorly; from above down word
Lower part of rt kidney
Origin of transverses abdomens
Quadrates lumborus muscle
Iliohypogastric and ilio inguinal nerve
Iliac crest and ilio lumber ligament
Iliacus muscle
Lateral cutnous nerve of the thigh
Blood supply rt colic and ascending branch of iliocolic artery
Site
Begning –rt hypochondirumEnd lf hypochond.
Size 18-20 inches
Taenia coli –2 ant .&1 post.
Pertonium; it completely covered with peritoneum except the rt 2 inch wher it adherent to the 2nd part of dued. and head of pancreas
It has transverse mesocolon
Transverse colon
Relation of transverse colon
Anterior sup. from rt to lfRt lobe of liver..gall bladder..great curvature of stomach…greater omentum.
Posterior from rt to lf
2nd part of dued…head of pancreas
Dj flexure &coil of jej.
Inferiorly…coil of small intestine
Blood supply; middle colic and ascending branches of upper lf colic art.
Rt and lf colic flexures
Position rt L2 ,,LF L1
Shape rt a blunt forming right angle lf sharp forming acute angle
Attachment to the diaphragm rt no lf yes through phrencocolic ligament.
Relation rt ant sup..rt lobe of liver,, post.inf.. Rt kidney medially 2nd part of duodenum
Lf ant.sup spleen and tail of pancreas
Post inf lf kid. and diaphragm
Medialy lf kidney
Blood supply; rt rt colic art.lf lf colic art.
Colic flexures
Site; in the lf lumber and lf iliac region ,start from lf colic flexure to the lf border of pelvic brim where it become pelvic colon(sigmoid)
Size 10-12 inch double length of ascending colon but narrow lumen.
Taenia coli; one ant .and 2 post, same ascending.
Peritonium cover in front and sides same ascending.
Descending colon
Relation; anterior and laterally ;
Ant. Abdominal wallLf border of greater omentium
Coil of small intestine
Medial relation;
coil of small intestine
Posterior relation;
It descend on the fallowing strictures;
Diaphragm
Lower lat part of the lf kidney
Origin of lf trans. abdominus m.
Lf quadretous lumborous m. and structures infront of it .a-subcostal n &vessels
B-iliohypogastric n.
C- ilioinguinal n.
Lf iliacus muscle & stracture related to it
A- lat. cutanous n . Of thigh B-femoral n.
Lf psoase major m & structure related to it
A-lf gonodal v.
B- lf genetofemoral n.
C- lf external iliac artery
Relation same ascending colon
Pelvic (sigmoid )colonSite ;in lf iliac fossa ,in pelvic cavity
Shape; s shape
Size ; 16 inches
Begins; infront of ext.iliac artery at the lf border of pelvic prim ,2 inch above the inguinal ligament.as a continuation of descending colon.
End ;opposite the 3rd sacral piece by becoming rectum.
`
Sup.and to the rt;
Coil of iliumInferior;
According to the sex
In female uterus
In male urinary bladder in both male and female
Posreiorly;
Sacrum and structure infront of it;(piriformis and sacral plexus)
Lf ureter
Lf internal iliac vessels
relations
Blood supply; lower lf iliac (sigmoid arteries)
Pertonial covering; completely covering
Has mesentry cold pelvic mesocolon connecting it to the post.abdominal wall.
Pelvic mesocolon
Its peritoneal fold attaching the pelvic colon to the upper part of the post. wall of pelvis.
Shape; inverted v shape having 2 limb
Lat. limb ascending
Med. limb descending.
Attachment;
A- lat. Limb attach to the med. side of lf ext. iliacB- medial limb attach to the front of sacrum till the 3rd sacral piece
C-The apex ; attach infront of the lf ureter.
Content of pelvic mesocolon;
1- segmoid colon in free margin
2- sigmoid artery;(lower lf colic)
3-sup.rectal v.
4- sympathetic fibers
5- extraperitonial fatty tissue
Caecum , ascending colon and rt 2/3 of transvese colon supply by sup.mesentric artery through iliocolic,rt colic.middle colic art.
Venous draing corrsponding
Lf 1/3 of trans.colon descending colon sigmoid supply by inf, mesentric art through upper and lower lf colic art.
Venous drainge corresponding
Blood supply of the colon
Marginal artery ;its an arterial arcade lying along the concavity of colon . Its formed by anastemosis of iliocolic, middle colic, upper and lower lf colic a.
Lymphatic drainge of colon
Pass through 4 groups of l.n
1- epicolic l.n on wall of colon
2- paracolic along inf. Border
3- intermediate l.n along the colic arteries
4- terminal l.n along the trunk of sup & inf mesenteric a. which continuous with para oartic l.n
70 years old with atrail fibrillation complaining from acute abdomen due to small bowel gangrene .from anatomical point of view why gangrenous bowel occur mostly
in small bowel not large bowel?