stomach
ProfDr alaa jamel
Cabs,FACS ,mrcsi .mbchb
Stomachch. Site,shape, size,ext.feature,orfice,
It’s the widest &most distensible part of the git.
Site its lie obliquely in the lf hypochondrium ,epigastric and umbilical regionsShape; j shape but its shape depend on
1- the degree of its destension
2- the body built short and obese more horizontal
3- the phase of respiration ; more vertical with inspiration
4- position of the body ; vertical on standingSize ;it mean capacity 2 liters in adult
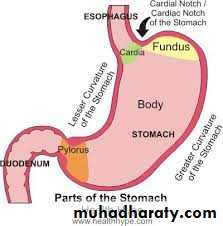
External feature ; it has 2 orfices cardiac and pyloric
2 borders lesser and greter curviture
stomach
2 surfaces ant.superior and post.inferior
3 parts fundus ,body and pyloric partsorfices of the stomach;
Cardiac orfice;
its more fixed part, position, it lie behind 7th costal cartilage ,1 inch from median plain
Relations ant .lf lobe of liver
Post. diaphragm
;
G.e junction has no anatomical sphincter
Its closed by physiological sphincter which depend on
A-acute angle between stomach and esophagus
B- sphincter action of fiber of RT crus of diaphragm which encircle the lower end of esophagus.
Sphincter
C- the thick mucosal fold of the lower end of esoph.
D- contraction of circular muscle fiber in the lower end of oesoph.
So why occur of gastro esophageal reflex diseases?
;less fixed end
Site trans pyloric plane L1
Its connect with duodenum
Pyloric orifice indicated by
A-pyloric constriction( circular groove)
B- prepyloric vein of mayo
This vein important it connect rt gastric vein with rt g.epiploic vein
C- felling of thickness of pyloric sphincter
Pyloric orfice
Anterior quadrate lobe of liver
Posterior neck of pancreaspyloric region has a true anatomical sphincter
Relations;
Lesser curvature; angular notch in its lower part.
It give attachment to the lesser omentum
Its related to the lf and rt gastric vessels and gastric l.n which runs on lesser omentum.
Borders of stomach
Cardiac notch at gejRelation;
It give attachment to 3 ligaments from above down word;
1- gastrophrenic ligament from fundus
2-gastrosplenic ligament from uper part of greater curvature to the spleen.
Greater curviture
3-Greater omentum ;
From lower part of greater curvatureIts related to the rt and lf gastro .epiploic vessels and l.n
Fudus;
Body;
Pyloric region which consist of
*pyloric antrum
* pyloric canal
* sphincter.
Parts of the stomach
;
Ant.sup. Completely cover by peritoneum
Post.inf covered by peritoneum of lesser sac except small area closed to the cardiac orifice (bare area of stomach)
Suface of stomach
;
1-Fundus; diaphragm which separate from the pericardium and heart
2-Ant. Sup. surface ; related to diaphragm ,lf costal margin , lf lobe of liver ,ant. abdominal wall
3-post.inf.surface; related to the stomach bed
Relation of stomach
Lf side stractuers ;
Spleen, lf crus of diaphragm, lf suprarenal gland, lf kidney, .
Transverse stracture;
Splenic artery, body of pancreas , transverse mesocolon, transverse colon
Pyloric end related anterior to the quadrate lobe of liver
Posteriorly related to neck of pancreas and lesser sacPost. Relation of stomach bar area related to the lf crus of diaphragm.
1- lesser omentum;
2- greater omentum3- gastrosplenic ligament(ferom upper 1/3 of greater curvature
4- gastrophenic ligament;(from fundus to the diaphragm)
Ligaments of stomach
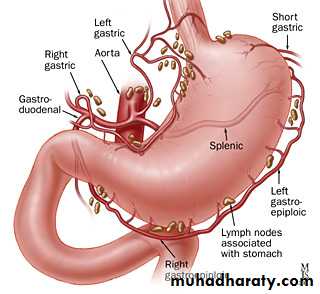
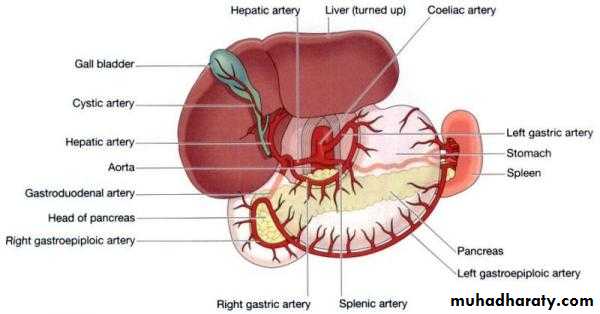
Blood supply1- lf gastric art.largest art. Of stomach
2-rt gastric art.branch from hepatic art.lower lesser curvature3-lf gastro epiploic art. Along greater curv.(splenic)
4- rt gastro epiplo.art –gastrodud.art---hepatic art.
Blood supply of stomach;
5- short gastric arts.– splenic art.to the fundus through gastrosplenic art.Venous drainage;
To the portal vein
Lf &rt gastric vein to the portal vein
Lf gastro epiplo. and short gastric vein to splenic vein
Rt gastro epiplo.to the sup mesenteric vein
All lymph daring to the coeliac l,n through
Supragastric l.n,infragastic l,n and pancreaticosplenic l.nLymphatic drainage;
;
Sympathatic fibers;arise from spinal cord segments from T6 to T10
Runs along or via gastric & gastroepiploic arteries
Function;1- motor to pyloric sphincter but inhibitory to the rest of stomach musculature
2- chief pathway for pain sensation from stomach
Nerve supply
From vagus
Ant. gastric nerve continuation of lf vagus supply ant. surface of stomach down to the pylorus
Post. gastric nerve continuation of RT vagus
Supply post surface of stomach except the pylorus .it give branch to cealiac plexus
Function; motor to the gastric wall &secretory to gastric juice
Parasympathatic fiber
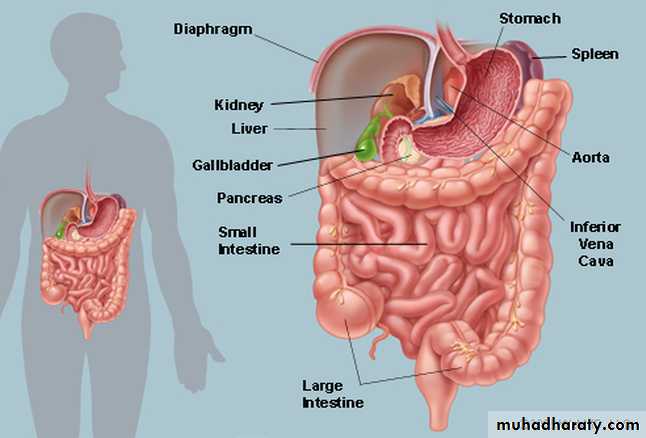
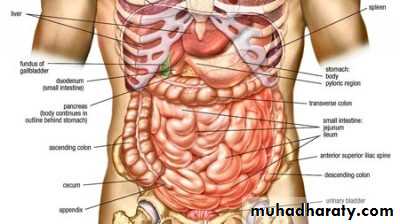
Position: in the infra colic compartment of the greater sac occupying the central & lower parts of the abdomen.
Relations: it is surrounded by the curve of the large intestine & covered anteriorly by the greater omentum & the ant. abdominal wall.
Beginning: at the pyloroduodenal junction.Termination: at the ileocaecal junction where it joints the caecum.
Length & Parts: it is 6 meters (20feet) long & is formed by 3 parts.
Small intestine
1. Duodenum: the first 10 inches & fixed to thepost. Abdominal wall.
2. Jejunum: follows the duodenum. It is 8 feet long and forms the proximal 2/5 of the small intestine.
3. Ileum: next to the jejunum. It is 12 feet long and forms the distal 3/5 of the small intestine. It ends by joining the caecum at the ileocaecal
valve.
N.B. both jejunum & ileum have a mesentery attaching them to the post. Abd. Wall.
It is the shortest, widest & the most fixed part of the small intestine.
Site: in the epigastric & umbilical regions, above the level of the umbilicus. It is applied to the post. abd.wall against the upper 3 lumbar vertebrae.
Shape: C-shaped loop surrounding the head of pancreas.
Begins: at the pyloric end of the stomach ½ inch to the right of the median plane.
Ends: at the duodenojejunal flexure 1 inch to the left of the median plane.
Duodenum
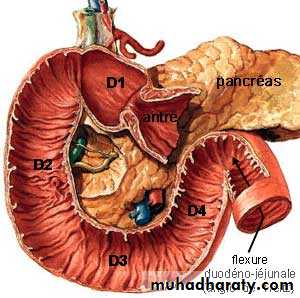
Length & Parts: it is 10 inches long & is divided into 4 parts:
1st Part (superior) 2 inches long & lies opposite the 1st L. vertebra.2nd part (descending) 3 inches long & extends from L1 to L3 vertebra.
3rd Part (horizontal) 4 inches & lies at the level of L3 vertebra.
4th Part (ascending) 1 inch & ascends from the level of L3 to L2.
Parts of duodenium
Length & Parts of duod.:
Peritoneal relations:
The duodenum is mostly retroperitoneal and fixed to the post.abd.wall except the following 2 mobile parts:1. The proximal 1 inch which is suspended by : a. lesser omentum: aboveb. greater omentum: below
2. The distal end which is attached to the right crus of the diaphragm by a fibro muscular band called the suspensory muscle of duodenum.
- Begins: as a continuation of the pylorus, ½ inch to the Rt. Of the median plane at the level of L1 (transpyloric plane).
- Course: it passes upwards, backwards & to the Rt. undercover of the quadrate lope of the liver.
- Ends: close to the neck of the gall bladder by curving downwards to become the 2nd part.
First Part of Duodenum
* Peritoneal connection:
- Its 1st inch is completely covered by peritoneum & and gives attachment to the lesser omentum above & greater omentum below.- Its 2nd inch is covered by peritoneum only infront & above.
Relations of the 1st partI. Anteriorly
1. Quadrate lope of liver
2. Neck of gall bladder
II. Superiorly
1. Epiploic foramen
2. Lesser omentum containing portal v., hepatic a. & C. bile duct.
III. Inferiorly
1. Head of pencreas
2. Greater omentum
IV. Posteriorly1.Neck of pencreas
2. C.B. duct, gastroduodenal a. & portal v.
Begins: at the level of L1 as a continuation of the 1st part.
Course: it descends vertically downwards infront of the hilum of the Rt. Kidney.
Ends: at the level of L3 by curving to the left to become the 3rd part.
Peritoneum: it is covered by peritoneum only anteriorly except its middle part which is devoid of peritoneum & is directly related to transverse colon.
2nd Part of Duodenum
Relation of 2nd part of duodenum:
(A) Anteriorly1. Rt. Lobe of liver 2. Transverse Colon3. Coils of jejunum(B) Posteriorly
1. The hilum of Rt. Kidney & adjoining part of ant. Surface.2. Rt. Renal vessels 3. Rt. Psoas major muscle
(C) Laterally
1. Fat infront of the right kidney
2. Rt. Colic flexure 3. ascending colon
(D) Medially:
1. Head of pencreas2. Ampulla of vater (hepato-pancreatic ampulla) opens in the posteromedial aspect of 2nd part of duodenum just below its middle.
3. Sup. & Inf. Pancreatico-duodenal vessels in the groove between head of pancreas & 2nd part of duodenum
3rd Part of Duodenum
Length: it is the longest part (4 inches long).
Course: it passes horizontally form Rt. To Lt. at the level of L3 vertebra.
Peritoneum: it is covered by peritoneum anteriorly and inferiorly.Relations:
A. Superiorly: head of pancreas B. Inferiorly: Coils of jejunumC. Anteriorly:1. Coils of jejunum 2. Root of mesentery 3. Sup. Mesenteric vesselsD. Posteriorly (from right to left):
1. Rt. Psoas major m. (separated from duodenum by the Rt. Ureter).
2. Inferior vena cava (separated from duodenum by the Rt. Gonadal vessels)
3. Abdominal aorta (separated from duodenum by the inf. Mesenteric artery).
4th part of Duodenum
Length: it is the shortest part (one inch long)Course: it ascends along the Lt. side of the vertebral column (from L3 to L2).
Peritoneum: it is covered by peritoneum anteriorly & to the left.Relations of the 4th part ..
(a) Anterolaterally: Coils of Jejunum.
(b) Medially (to the Rt.): 1. uncinate process of pancreas2. abdominal aorta
3. vertebral column
(c) Posteriorly:
1. med. Border of lt. psoas major M.
2. Lt. renal vessels
3. Lt. sympathetic chain
4. Lt Gonadal vessels
Termination of 4th part ..
It ends by curving forwards to form the duodeno-jejunal flexure on the Lt. side of L2.Suspensory muscle of duodenum
(Lig. Of Treitz)
- It is a fibromuscular band which suspends the duodenojejunal flexure.
- It arises from the Rt. Crus of diaphragm close to the esophagus.
- It descends behind the pancreas to be attached to post aspect of the duodenojejunal flexure & the 3rd & the 4th parts of duodenum.
- It contains striated & smooth muscle fibers & also elastic fibers.
Arterial supply of duodenum :
1. sup. pancreatico duodenal a. (branch of gastroduodenal a.)
2. inf. pancreatico duodenal a. (branch of sup. Mesenteric a.)
3. Branches from hepatic, Rt. Gastric, Rt. Gastroepiploic & supraduodenal arteries.
Venous drainage : into splenic, sup. Mesenteric & portal veins.
Lymphatic drainage : into pyloric, sup. Mesenteric & hepatic lymph nodes.
Nerve supply : sympathetic nerves from T9 & T10 and parasymp. Nerves from vagi pass through the coeliac plexus & accompany the arteries to duodenum