Soft tissue masses ,sinus and fistula
Prof. Alaa JamelMRCSI CABS
Soft tissue masses ,sinus and fistula
Sinus; it’s a blind end tract lined by granulation tissue which connects a cavity (usually an old abscess ) with an epithelial surface , it produces a serious or purulent discharge , its eithercongenital or acquired .
congenital sinus arise from ruminant of embryonic ducts that persist instead of obliterated .
Congintal sinuses
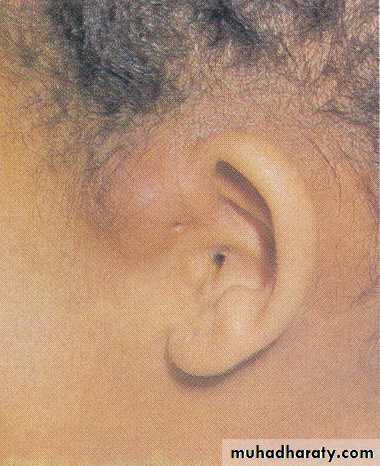
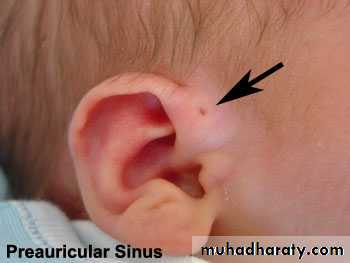
Priauricular sinuses; may be unilateral or bilateral .Umbilical sinuses;
Urchal sinus; This occurs when the urachus did not seal close to the umbilicus and leads to a blind ending tract from the umbilicus into the urachus called a sinus.
Clinical features;
• *It may be a symptomatic .
• *but it may have tendency to infection which may lead to persistent discharge,
• *pain if there is a swelling.
Common acquired sinuses;
Post surgical and perineal sinuses;mainly due to suture sinus (non absorbable suture material act as a focus of infection).
Or may occur after anastemotic leaks or
post surgical intra abdominal abscess>
Perianal sinus; which occur after procto coloctomy which more commonly occur with crohn's disease.
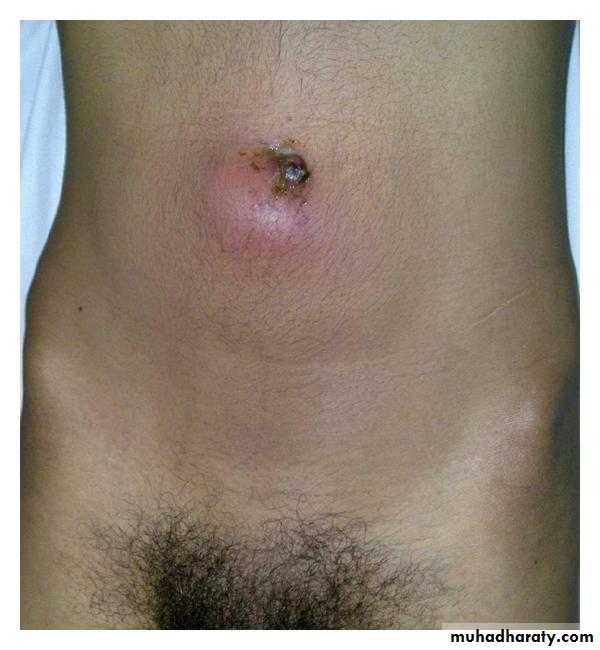
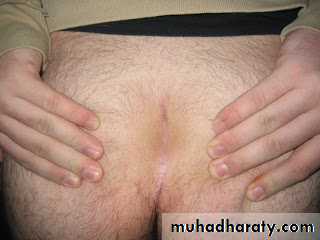
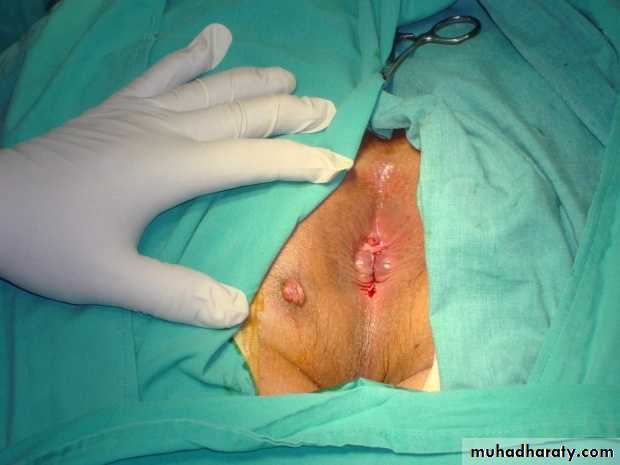
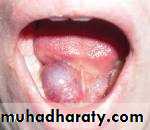
Pilonoidal sinus; (P.N.S)
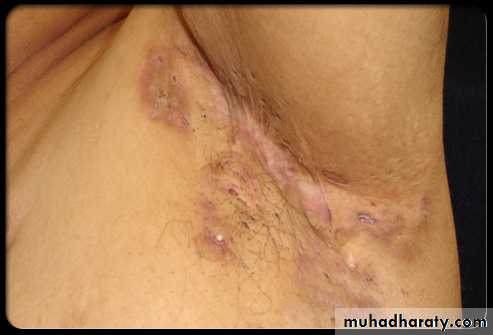
Hydradenitis supurativa; abnormal of apocrine sweet gland of the body which found in axilla . groin and perineum and around the nipple.
Evaluation of sinuses;
by**micro bacterial examination of the discharge. **Propping gently ,
**sinography ( who).
Treatment ;
depends on location of abscess cavity and eradicated otherwise recurrence either at the
same location or adjacent to it
fail to close if;
1-the cavity is in adequately drained2-its caused by specific chronic infection.
3-a foreign body is present in the bottom of the sinus
4- the cavity has epithiliazed
5- the cavity has undergone malignant changes
6- the surrounding tissue have poor vasculirized and or irradiated..
FISTULA
it’s a pathological connection between two epithelial surfaces, example
fistula between bowel and skin .
bowel and other loop of bowel
the bowel and bladder.
its usually lined by granulation tissue but can becomeepithilized.
Congental or aquird..
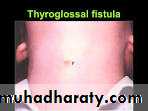
Common fistula seen in practice is fistula in ano due to purest of peranal abscess or in adequate drainage. Other example is thyroglossal fistula who it occur or tracheoesophageal fistulla?
Cyst;
Its a collection of fluid in a sac lined by endo-or epithelium which usually secretes the fluid.
We have 2 types true & false cysts .
what's the differences between them?
Classification;
True; its lined between endo or epithelium tissue .
False ; are the results of exudation or degeneration e.g. pseudo cyst of pancreas, cystic degeneration of tumour. Brain cyst ,encystic pleural effusions.
Classification;
Congenital; as sequestration dermoid cyst (lateral margin of eye brow)Acquired;
1- retention cyst , as sebaceous cyst due to blocking of execratory duct. Ranula (salivary gland) breast cyst2-Distension cyst; as thyroid or ovarian cyst occur due to distension closed cavity with the fluid
3-Neoplastic; cyst adenoma of the ovary
4-Parasitic cyst hydatid cyst
5-implantation ; dermoid cyst
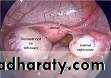
ranula
Dermoid of ovary
Clinical feature; the swelling is smooth, spherical which may be soft and fluctuated or may be tens which may be produce pain in the cyst or surround stricture , may be transilluminate if the fluid clear.
Effects; may compress surrounding stricture and may cause pain if complication occur.
Complication;
Infection, torsion , rapture, hemorrhage and calcification.
Treatments
Excisions ,drainage, marsupialization.Epidermoid cyst
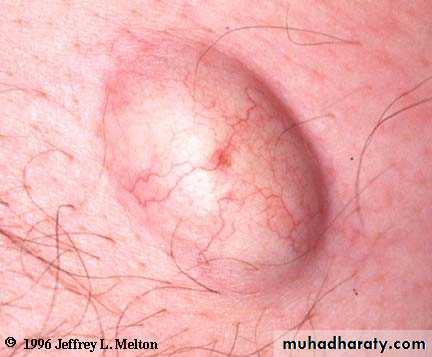
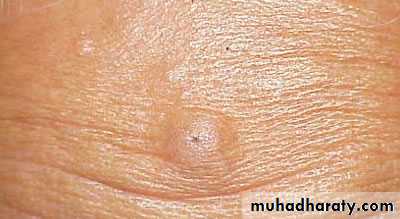
Also called sebaceous cyst ,pilar cyst .
it occur at any age groups but rarely in children . found in the hair bearing part of the body especially in the scalp, neck, scrotum, shoulder and back.
They can occur whenever the sebaceous gland found but not in palm or sole .why?
it vary in size from few millimeters up to 4 cm. its slow growing and usually a symptomatic , it rise from infundibular portion of hair follicle ,
Its more laible for infection why?.
90% arise in the scalp ,70 % multipleComplications
1-infection why more susceptible to infection? (Punctum) discharge foul smelling , cheesy material
2- malignant changes very rare or extremely rare reported at 1963
3- multiple cysts occur in gardener syndrome
4- pilar tumour , proliferation of epithelial lining cyst with ulceration give appearance like seq. cell carcinoma (cocks peculiar tumour).
Treatments;
Complete surgical execion with its contents through un elliptical incision including the punctum.
recur occur if a small portion of cyst lining left behind.
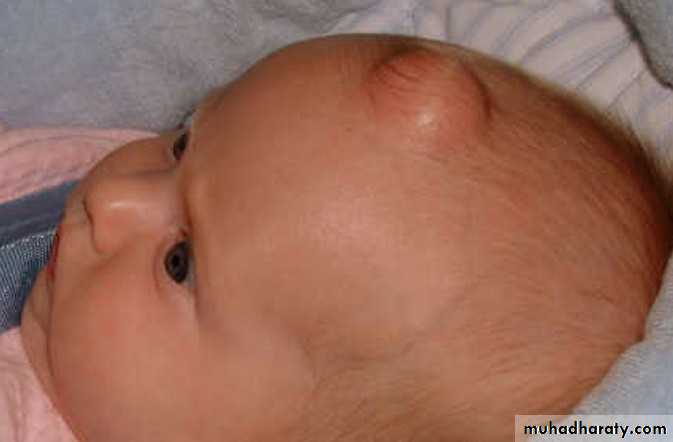
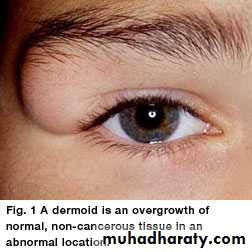
Dermoid cyst
Its deep to the skin ,which is lined by skin .Skin can become trapped in the subcutaneous tissue either during fetal development (congenital dermoid cyst ) or following an injury which force the skin in to the deeper tissues( acquired/implantation cyst)
Congental dermoid cyst (sequestration types)
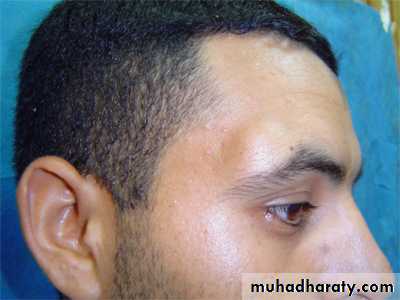
; it’s a subcutaneous cyst caused by developmental inclusion of epidermis along lines of fusion. Its lined by stratified sequamous epithelium but unlike epidermoid cyst the wall contains functioning (not keratenizing) epidermal appendages such as hair follicles sweet and sebaceous gland.Site ; more commonly found on the lateral and medial end of eye brow(external and internal angular dermoid), midline of the nose (nasal dermoid), midline of the neck.
By examination
It has smooth surface and well defined adges its soft and fluctuant but dose not transilluminated its not attached to the skin above it but appear to be fixed to the deeper structure. Surrounding skin and regional L.N usually normal except in infection causing painful regional l.n and may redness of skin.Complications;
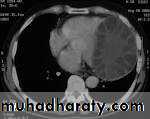
1-may cause bony depression and penetrate to the dura , meningeal penetration is a problem with midline dermoid not occur in internal or external angular dermoid. so need C.T SCAN before operation.Treatments by surgical excision if causing a troublesome.
Acquired (implantation) dermoid cyst;
It occur after a survival of a piece of skin forcibly implanted in to the subcutaneous tissues by an injury such as a small deep cut or stab injury, the pt may not remember the injury .histology is similar to congenital dermoid .Site ; occur in area subject to repeated trauma such as finger
Manangment ;
excision its commonly confused with sebaceous cyst but the presence of scar and old history of trauma is helpful in differentiation.Implantation dermoid cyst .
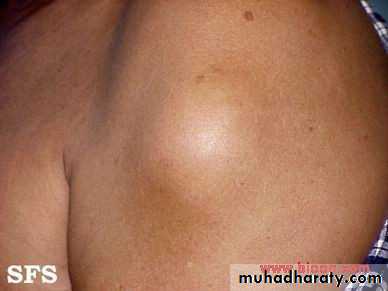
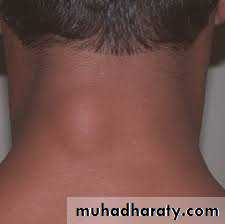
Lipoma;
Lipomo are hamartoma ( over growth of cell types normaly found in that organ) so it’s a clastur of mature fat cells that have become over active and distended with fat .its represent as a non tender lump ,lobulated ,smooth surface age are also lobulated and sliped away from the fingers( sliped sign). Its soft and flactulant why ?its not a fluid .
It occur any where when there is a fat but common on the back, shoulder, neck, forearm, trunk. its not occur in palm ,sole and the scalp why?( because fat is contained within dense fibrous septa)
Dercum's tumour; it’s a familial syndrome of multiple lipomata.
Lipoma in intestine more common in the cecum in large intestine although lipoma in large intestine are less common in small intestine. Tumour in intestine is submucous and more than half of cases cause intussusceptions.
Thank you
Prof.Dr.alaa jamel