Investigations of the Cardiovascular system
1At the end of this lecture, you should be able to appreciate
The usefulness of each investigation in diagnosing cardiac diseaseEach type of investigation clarifies and detects a certain aspect of cardiac pathology
Non-invasive investigations are increasingly replacing the old, invasive techniques.
Rapidly evolving methods of investigation because of the advances achieved in technology
Investigations of the CVS
BNP, TroponinElectrocardiography
Radiology
Echocardiography
CT imaging
MRI
Cardiac catheterization
Radionuclide imaging
3
BNP, Pro-BNP
Peptide released from the atria in response to stretch
Very sensitive for the diagnosis of congestive heart failure
Levels fall with improvement of heart failure on treatment, rise with worsening
4
Troponin
Protein contained within cardiac muscleReleased when cardiac muscle is injured e.g. ischemia or inflammation
Very useful in the diagnosis and follow up of patients with acute coronary syndrome
5
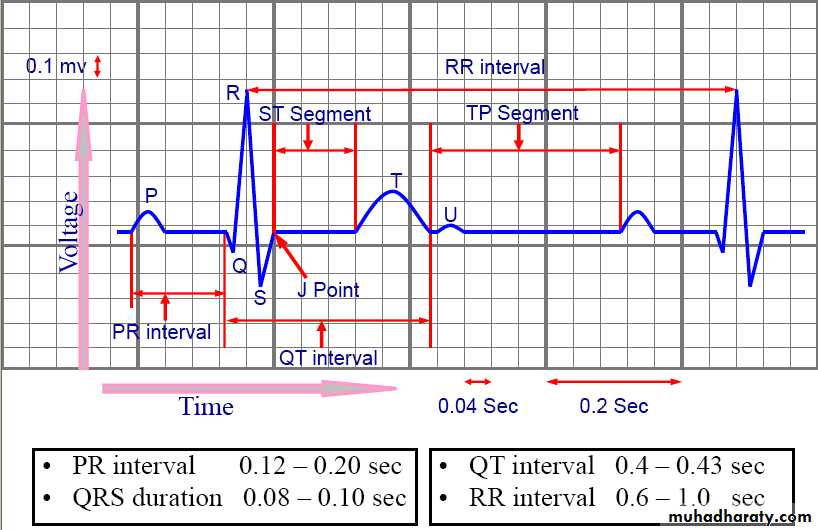
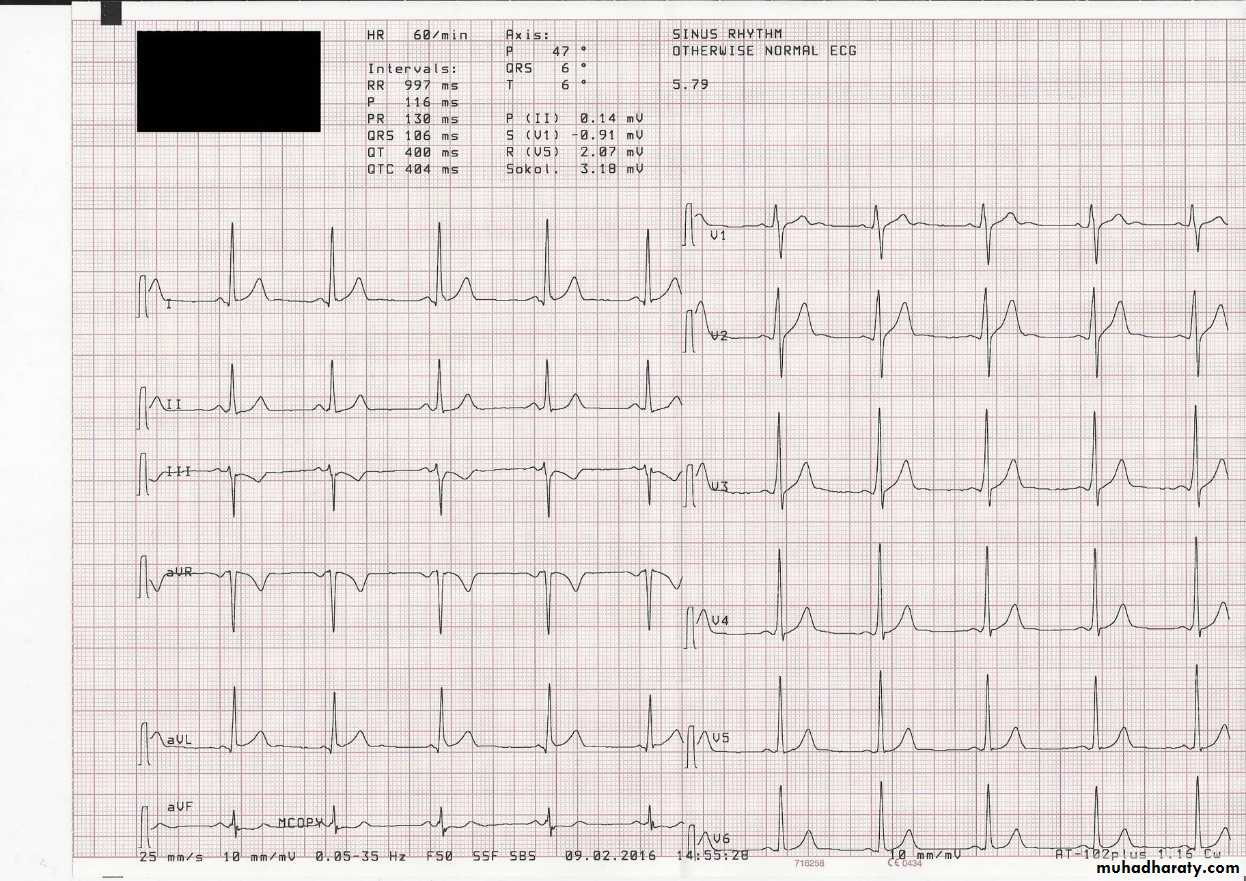
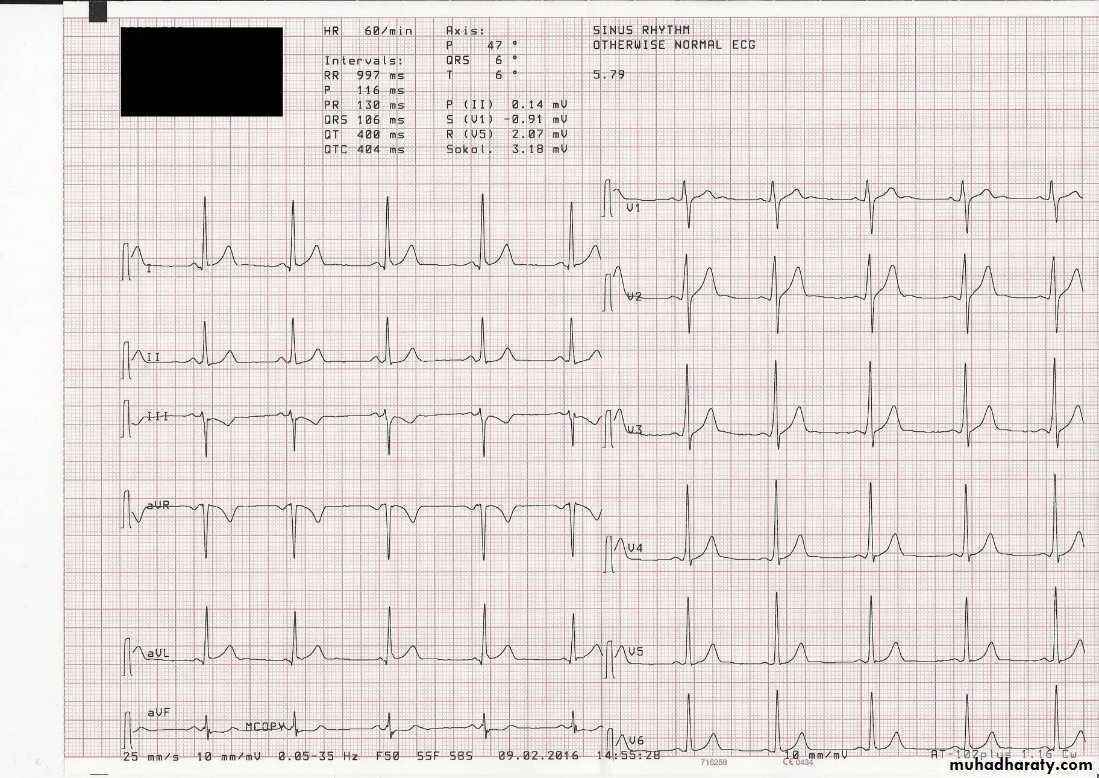
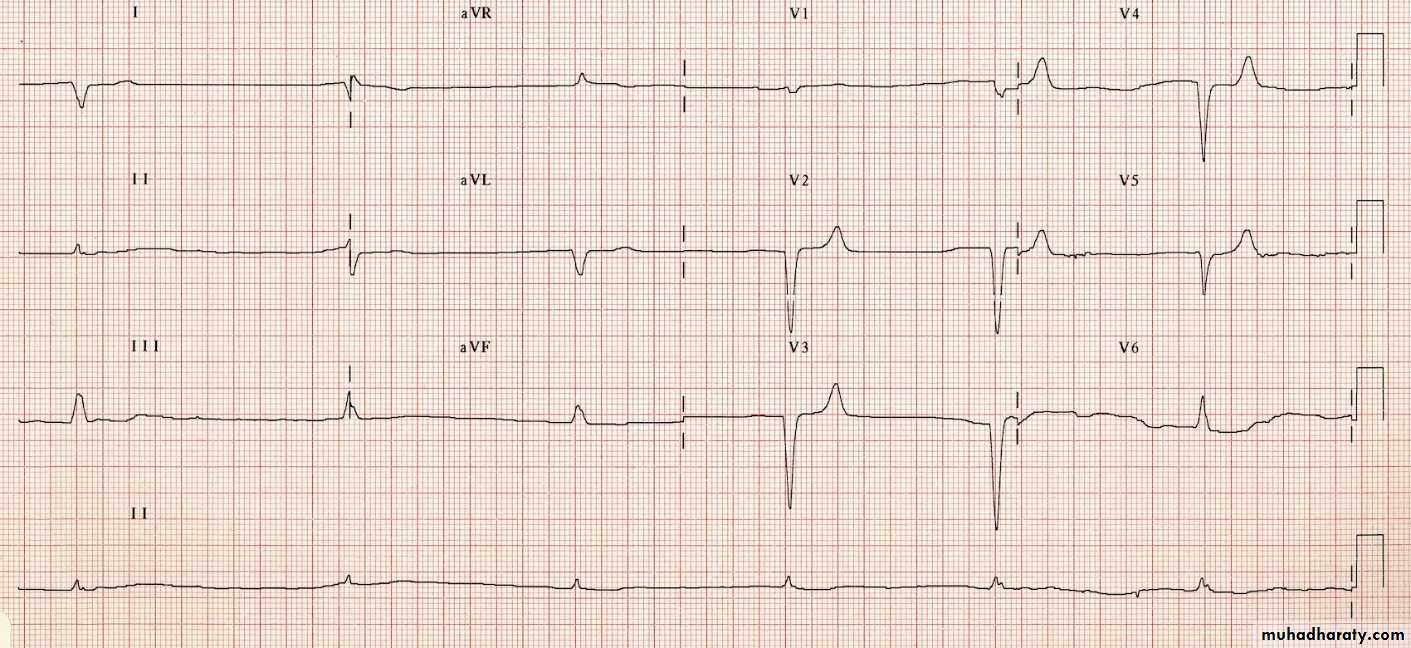
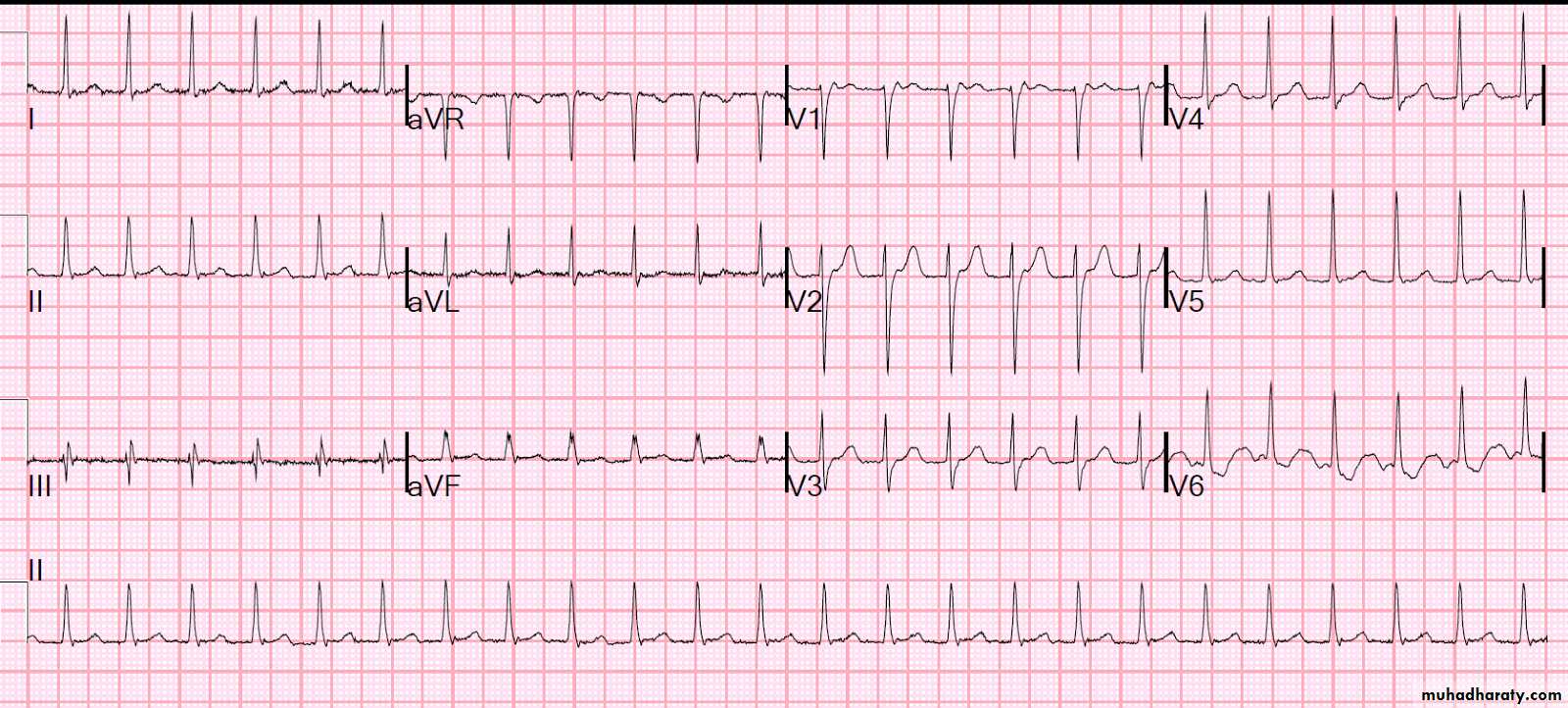
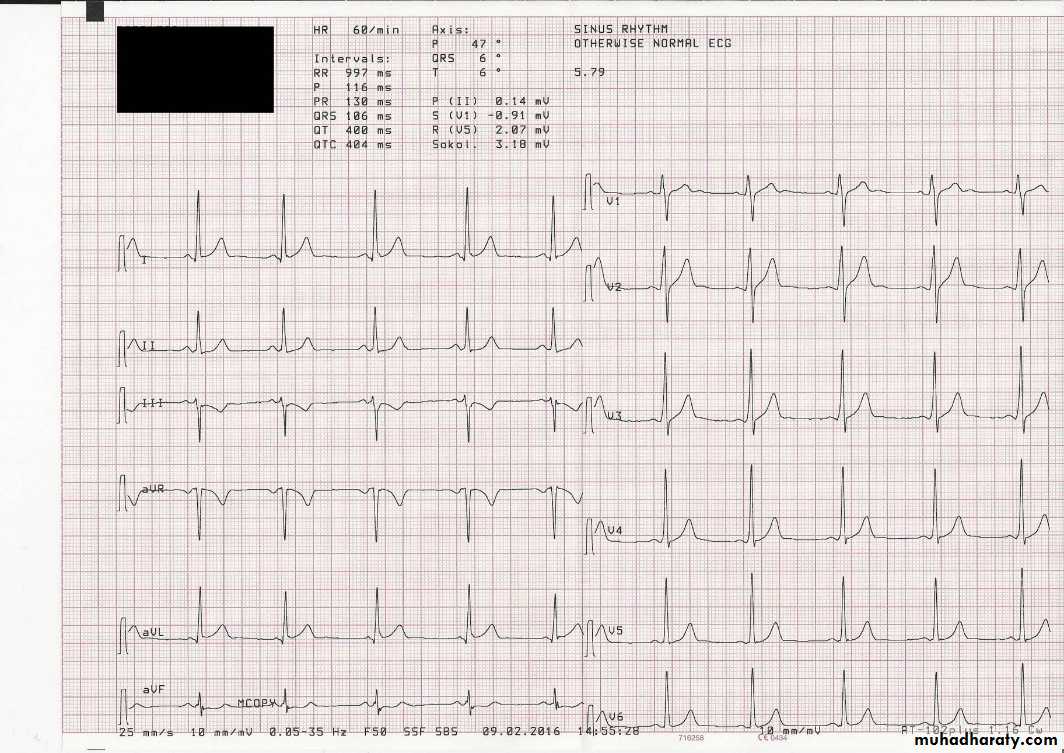
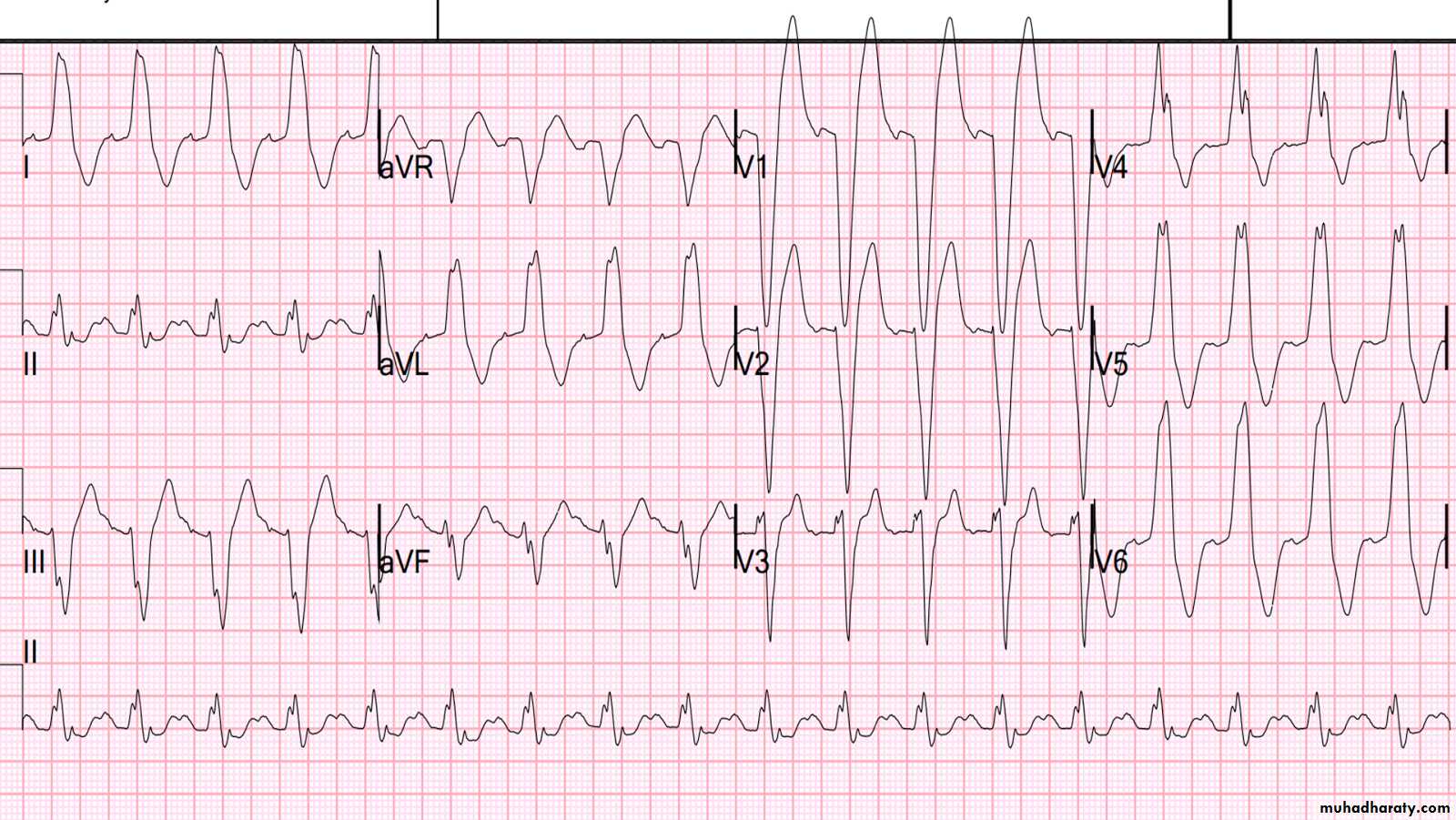
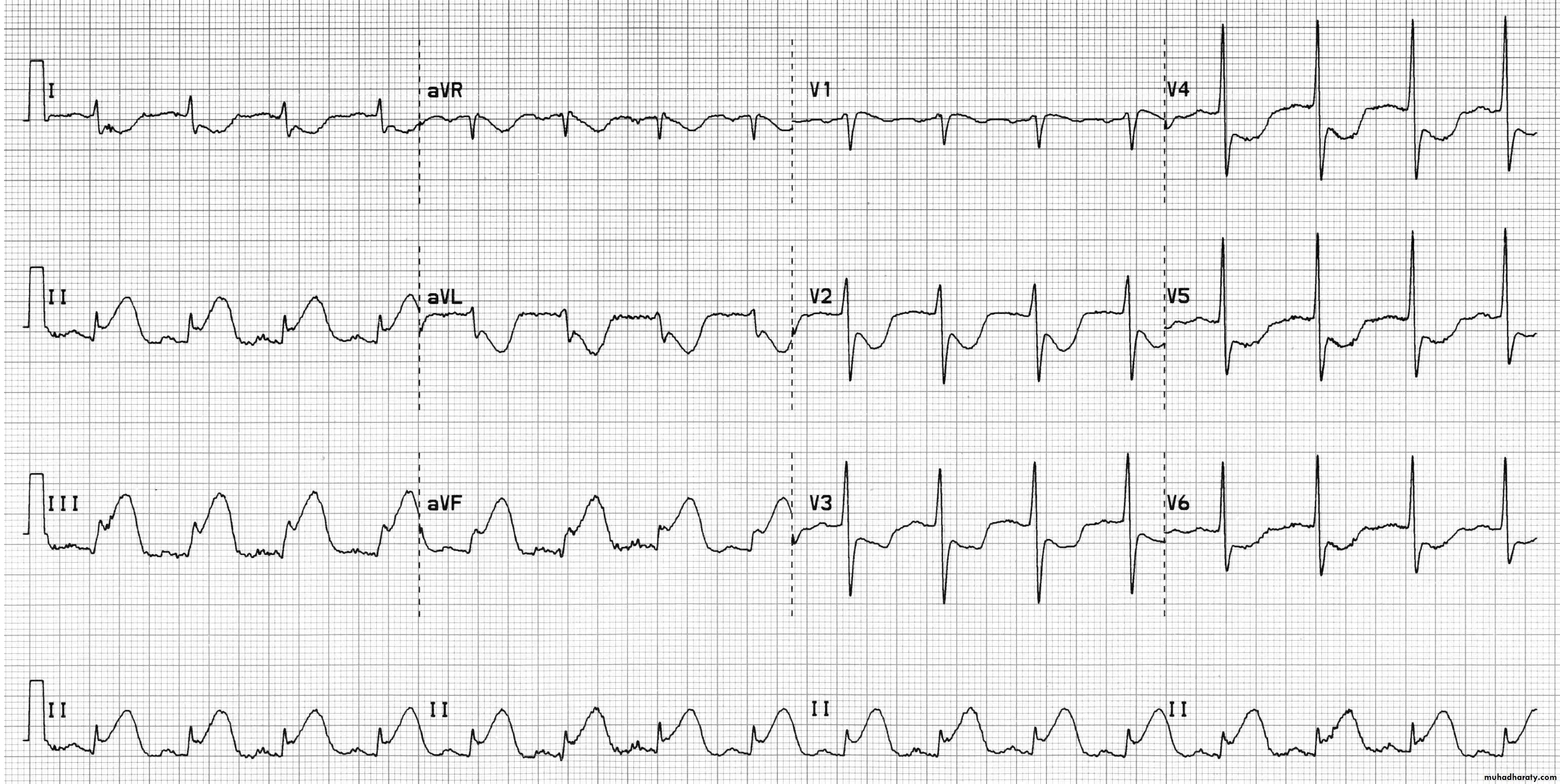
Electrocardiography (ECG)
uses:To determine heart rhythm
Status of the conducting system
To diagnose myocardial ischemia or infarction
Chamber enlargement and hypertrophy
Effects of drugs & metabolic disorders (electrolyte imbalance, acidosis, etc.)
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Exercise ECG
In patients with angina, the resting ECG may be normalThe principle of the test is to stress the heart and observe for ECG changes of ischemia
ECG and BP are continuously recorded while the patient is exercising on a bicycle or a treadmill
13
Ambulatory ECG Monitoring (Holter)
Continuous recording of ECG over 24 hours or more
Used to detect transient episodes of ischemia or arrhythmia which can rarely be captured during routine, ordinary ECG recording
14
Imaging
The principle of imaging is to reconstruct a three-dimensional structure out of a group of two dimensional images:Silhouette imaging: various structures are overlapped over each other e.g. CXR, angiography, nuclear imaging
Tomographic imaging: a group of sections through the structure to be examined e.g. echo, CT, MRI
15
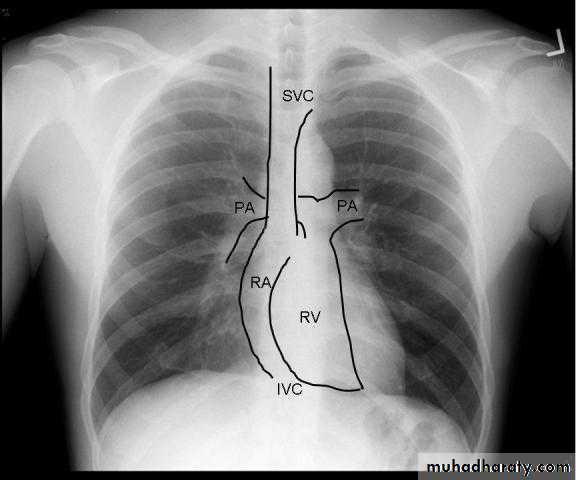
Radiology of the Heart
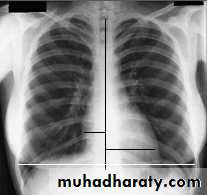
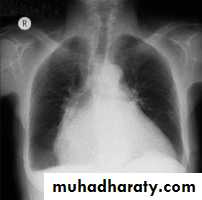
Chest X-ray: Postero-anterior view (PA view):Size of the heart
Shape of the heart
Specific chamber enlargement
Status of the pulmonary circulation
16
Radiology of the Heart
Cardiac size:Cardio-thoracic ratio (CTR):
Normally < 0.5
Enlargement of the heart (cardiomegaly):
LV dilatation and dysfunction
Pericardial effusion
17
18
19
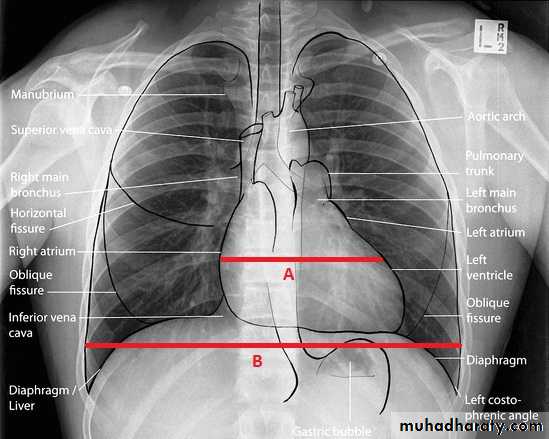
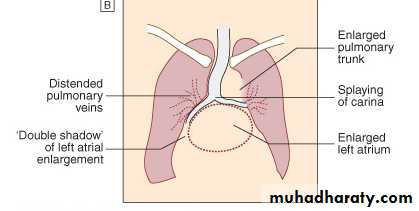
Radiology of the Heart
Left atrial enlargement:Straight heart border (LA appendage)
Widening of the carinal angle
Double contour of the right heart border
20
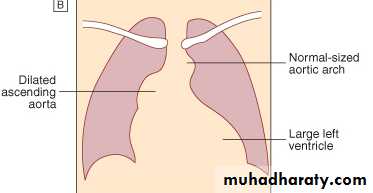
Radiology of the Heart
LV enlargement:Enlarged cardiac silhouette
Prominent left heart border
21
Radiology of the Heart
RV enlargement:Cardiomegaly
Straightening of the left heart border
Apex displaced upwards
Right atrial enlargement:
Prominence of the right border of the heart
22
Radiology of the Heart
Lung fields:Congestion & edema in patients with left heart failure
Increased blood flow (prominent arteries and veins) in shunt lesions
Oligemic lungs in pulmonary stenosis
Pleural effusions in advanced heart failure
23
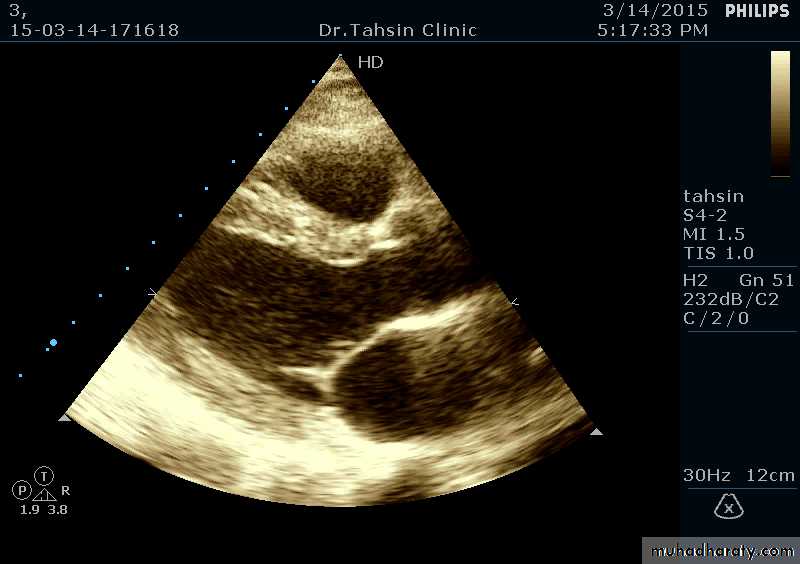
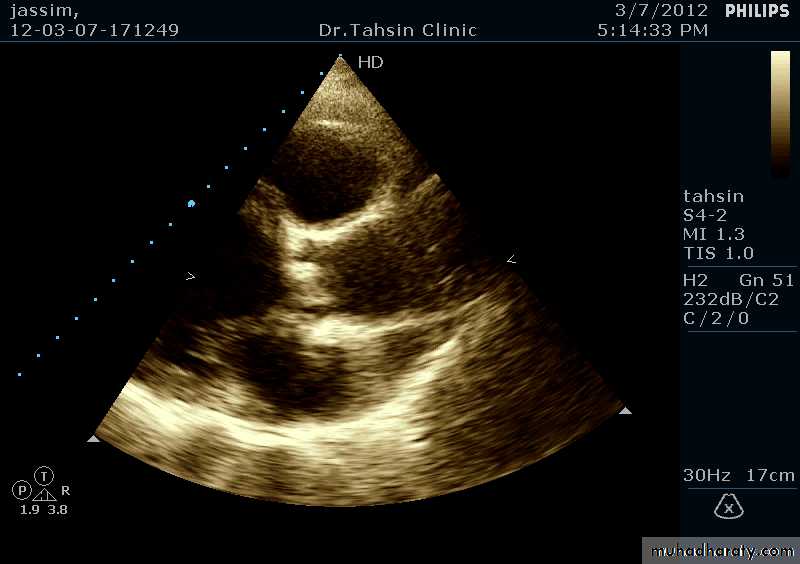
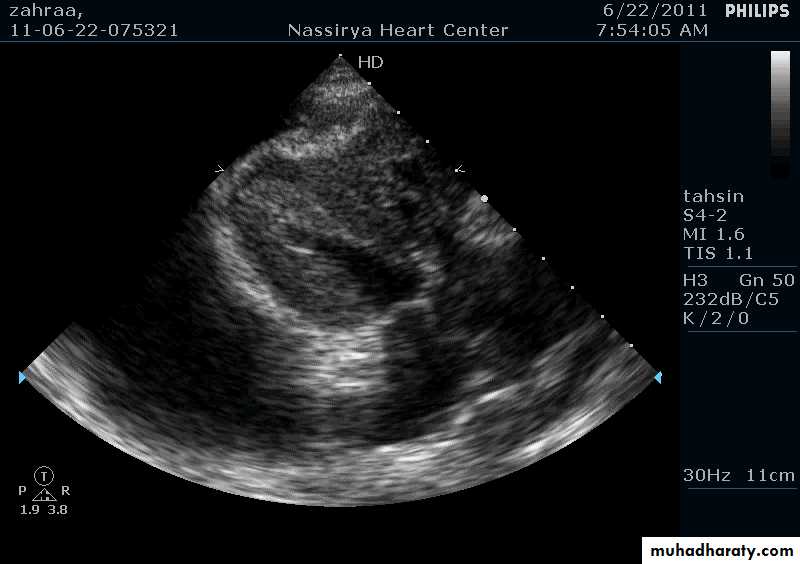
Two Dimensional Echocardiography
Ultrasound beam passing through the heart generates cross sectional images or “slices” of the heartVarious structures can be seen in real time
24
25
Two Dimensional Echocardiography indications
Assessment of LV functionDiagnosis & quantitation of severity of valvular lesions
Identification of vegetations
Identifying the source of systemic embolism
Detection of pericardial effusion
26
27
28
29
30
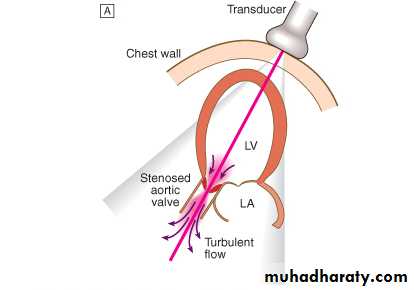
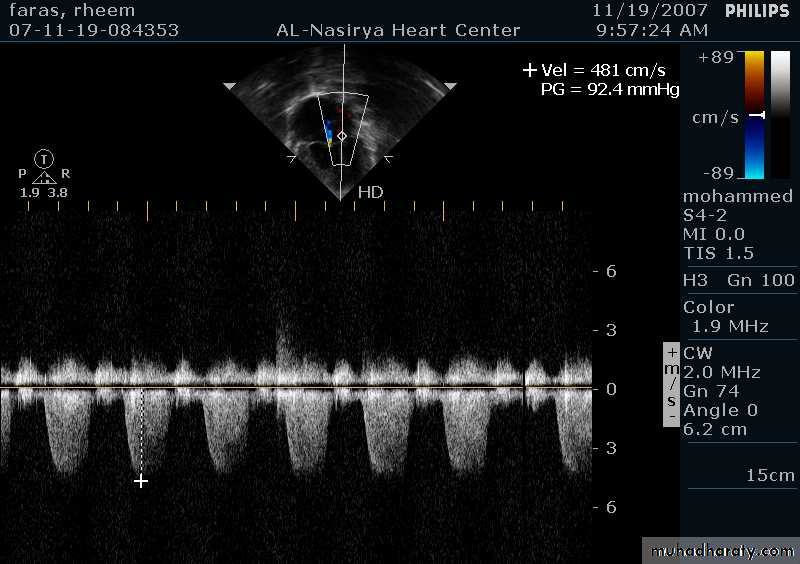
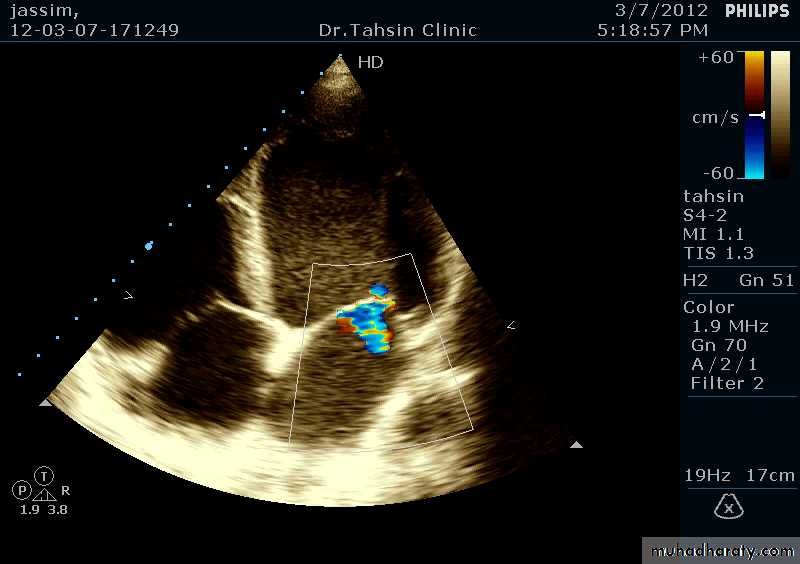
Doppler Echocardiography
Sound waves reflected from moving RBCs undergo frequency shiftThe faster the blood velocity , the greater the frequency shift
The direction of moving blood determines whether the reflected signal is positive or negative
31
32
33
Doppler Echocardiography
The derived signal can be plotted graphically against timeOr, color can be assigned for the reflected signal and superimposed over the 2D image (color flow mapping)
34
3-Dimentional Echocardiography
35
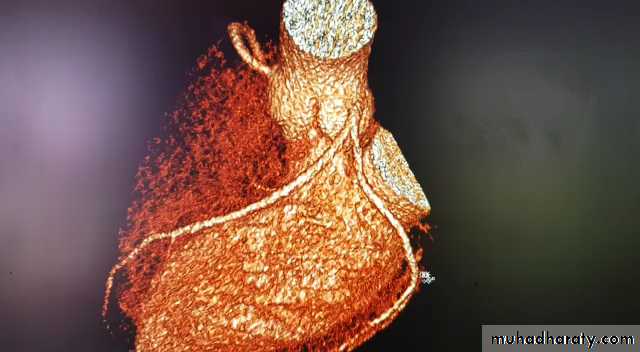
Other non-invasive imaging:CT and MRI
Chambers of the heartThe great vessels
The pericardium
Diseases of the aorta
The pulmonary arteries
Non-invasive imaging of the
coronary arteries
36
37
Invasive investigation: cardiac catherization
A small tube (catheter) is passed into the heart via a peripheral artery or vein under fluoroscopic guidancePressure can be measured, flow volumes calculated, radiographic dyes can be infected to outline the specific chamber or vessel (angiography)
38