Introduction to Fractures
Dr. Wahby GhalibCABMS, FJMC, MRCS
Wahby Ghalib
2Fracture : breakage in the structural continuity of bone
Wahby Ghalib3
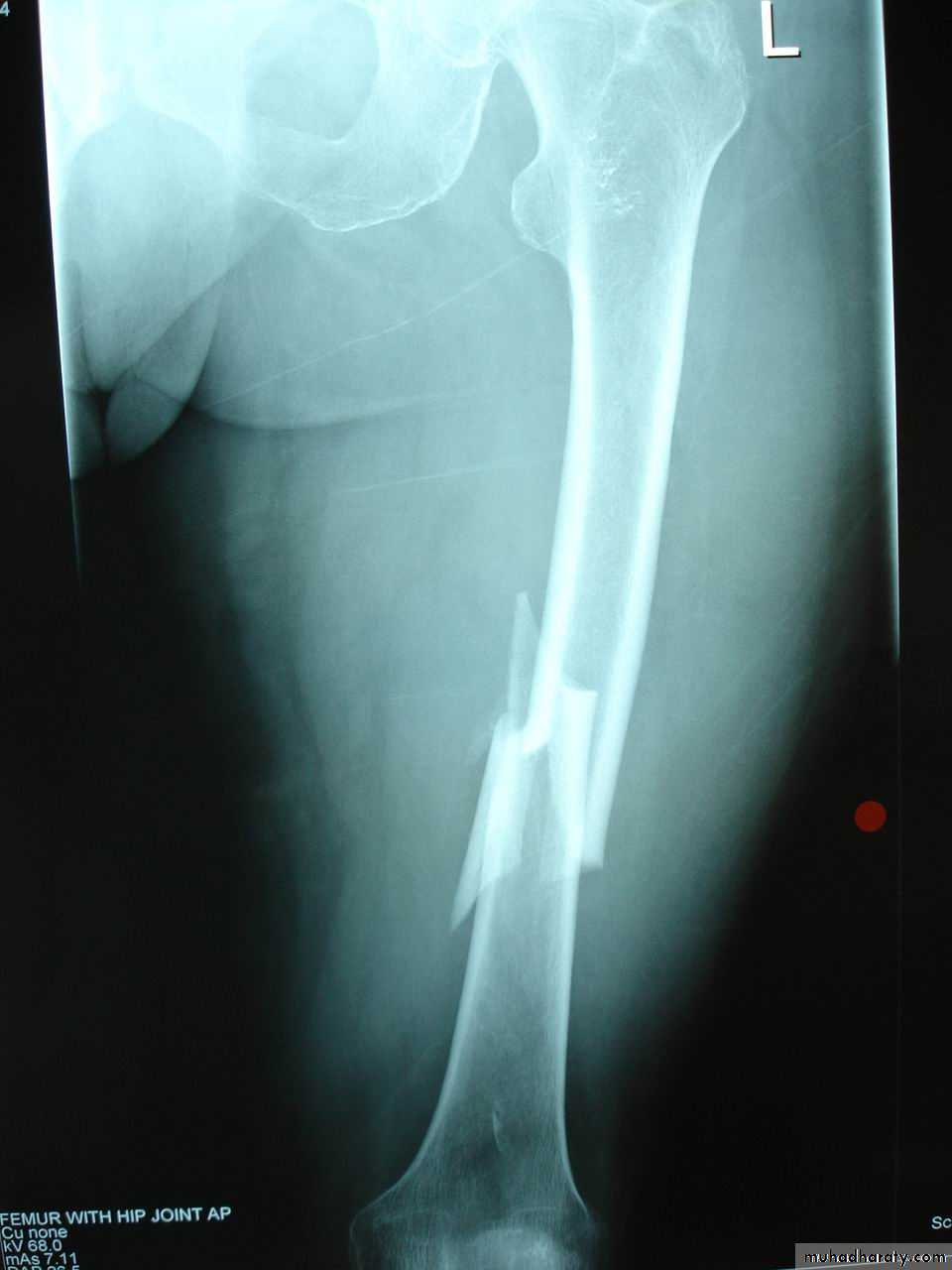
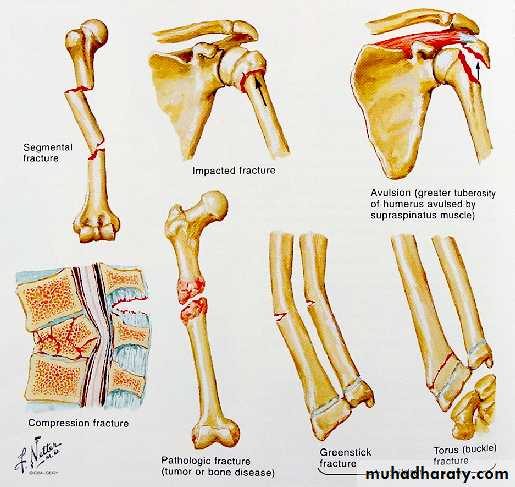
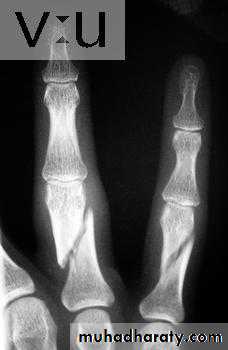
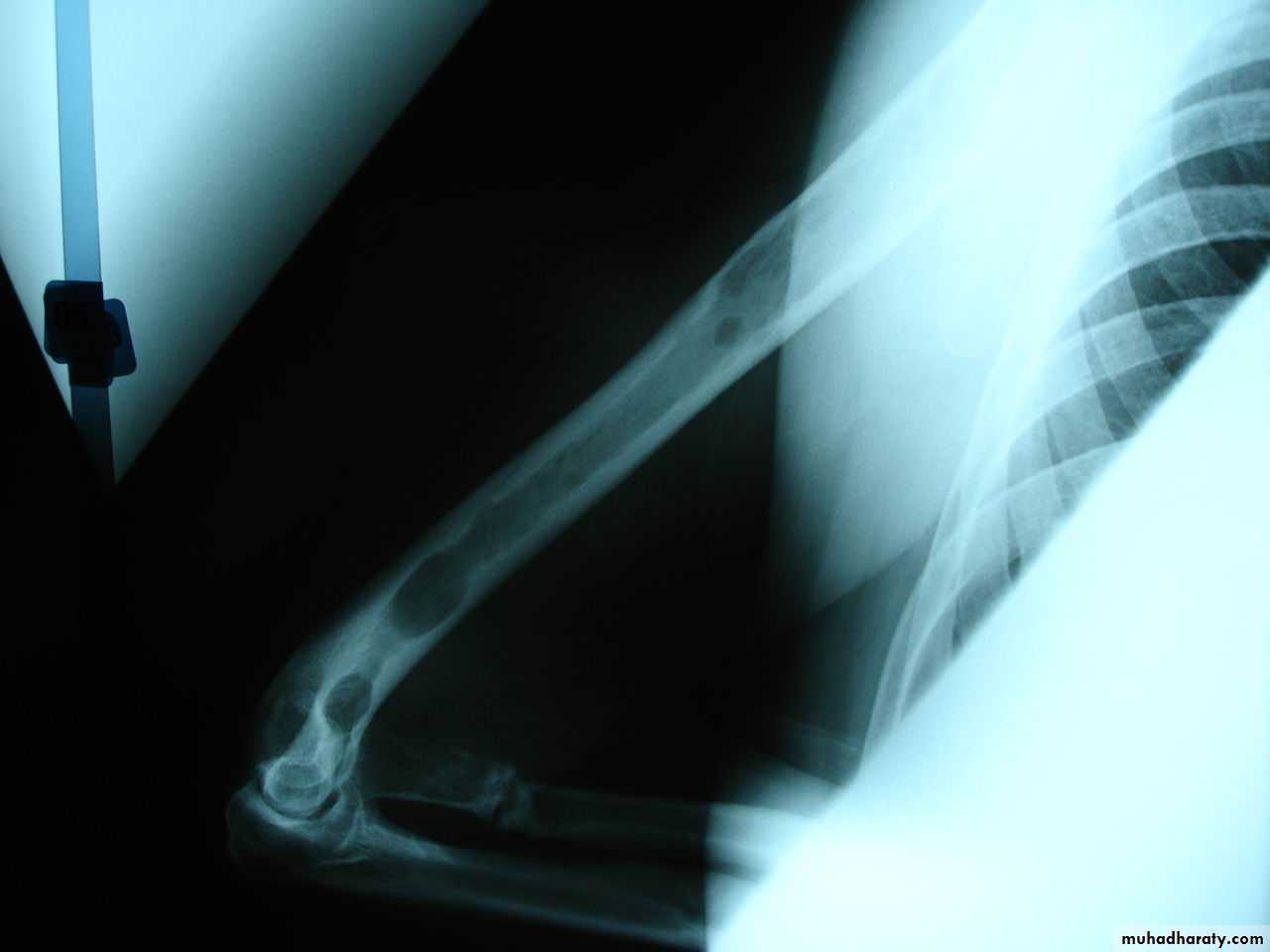
Comminuted fracture
# with more than two fragments
Comminution is caused by severe violence
union is delayed
Wahby Ghalib
4Wahby Ghalib
5Wahby Ghalib
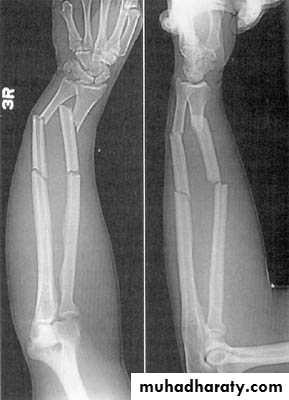
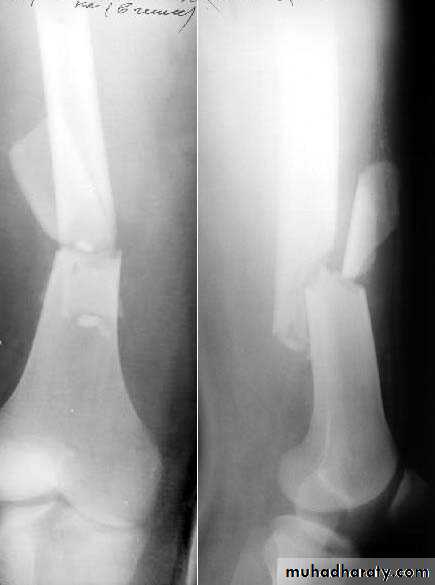
6Segmental fracture
The bone is fractured at more than one level
Wahby Ghalib
7Wahby Ghalib
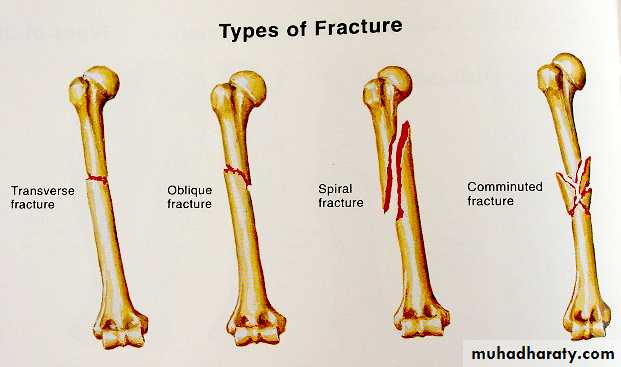
8Types
Transverse : tension or direct force
Butterfly fragment : bending
Short oblique : compression
Long oblique : indirect force
Spiral : twisting
Wahby Ghalib
9
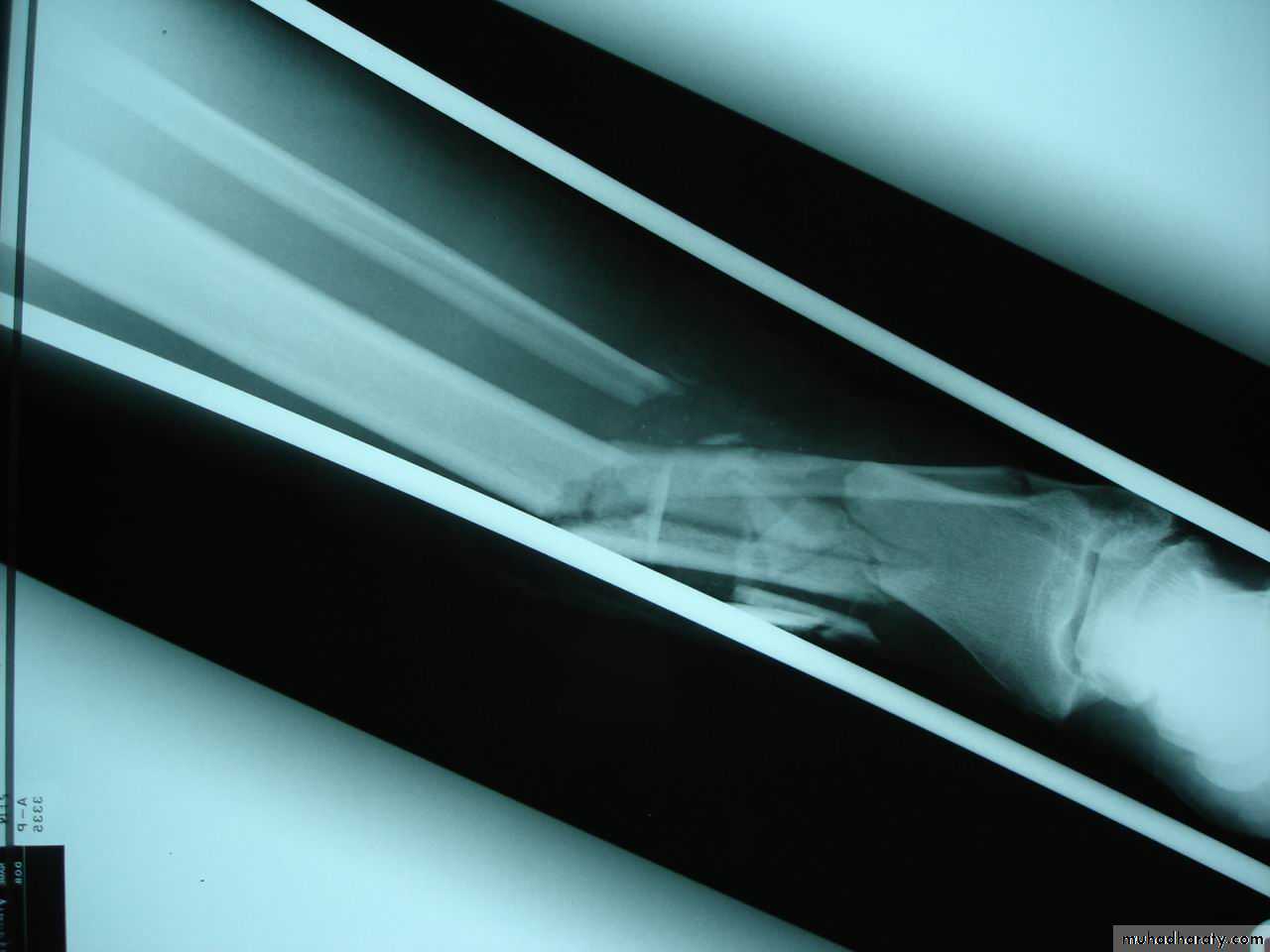
Avulsion # : bone fragment is pulled off bone by ligament or muscle
Wahby Ghalib10
Wahby Ghalib
11Wahby Ghalib
12Wahby Ghalib
13Wahby Ghalib
14Wahby Ghalib
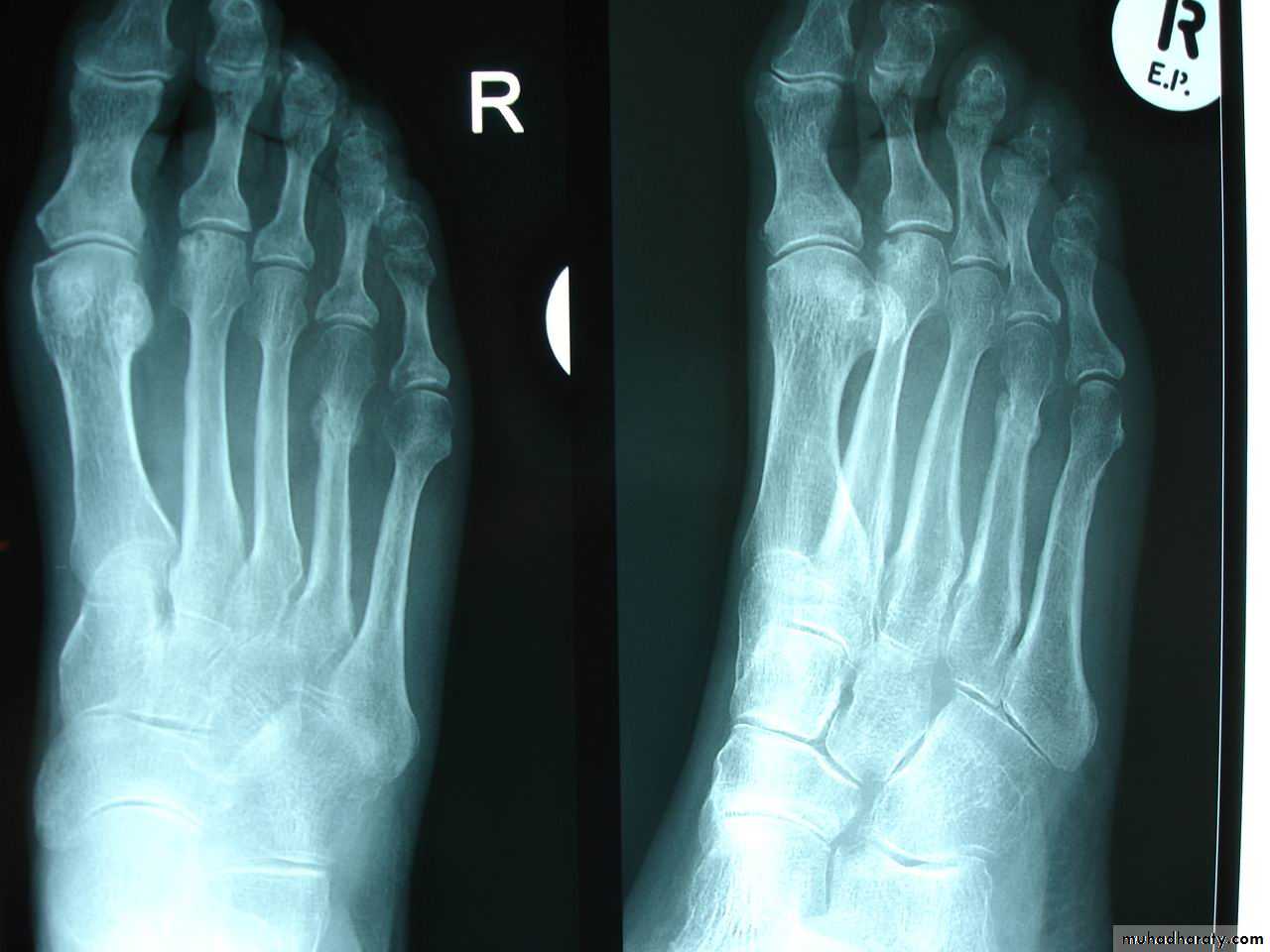
15Special types in children
Green-stick # : one cortex fractured & the opposite is compressed
Buckle fracure
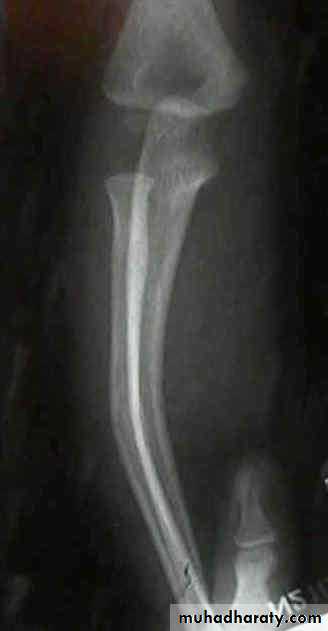
Plastic deformation
Wahby Ghalib
16Wahby Ghalib
17Wahby Ghalib
18Torus fracture
Wahby Ghalib
19Forces
Direct & indirect
Low & hi energy
The state of local soft tissues is very important for fracture healing
Wahby Ghalib
20
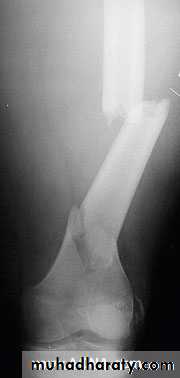
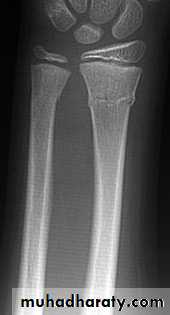
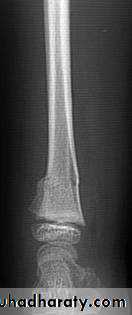
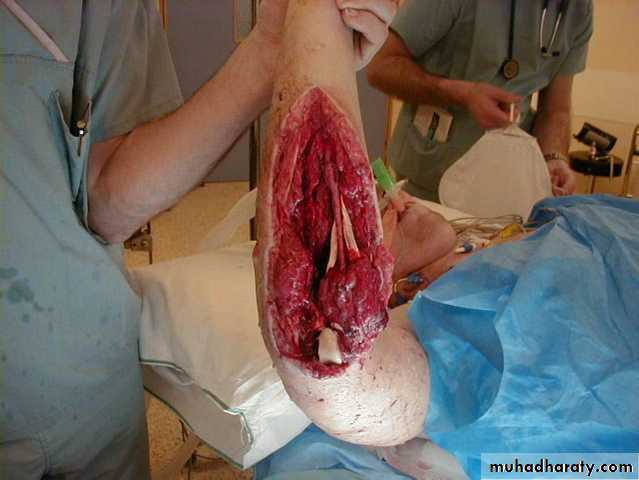
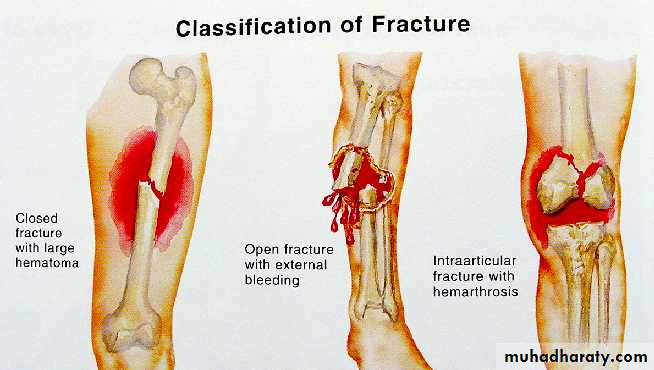
Open (compound) fracture
There is communication between the # and the exterior (disruption of skin, intestine)
↑ Risk of infection
Wahby Ghalib
21Wahby Ghalib
22Wahby Ghalib
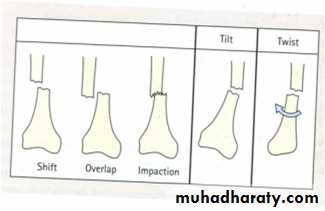
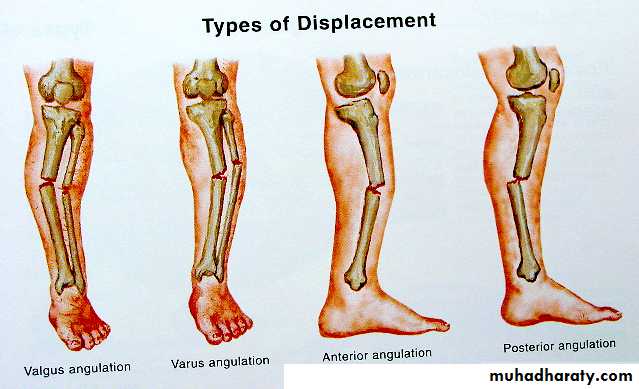
23Displacement
Shift (translation)
Tilt (angulation)
Twist (rotation)
Overlap
Impaction
Distraction
Wahby Ghalib
24
Wahby Ghalib
25Wahby Ghalib
26Unstable fracture
# that is displaced or has the potential to displace
Wahby Ghalib
27Clinical features
Look : swelling, deformity, ecchymosis
Feel : tenderness
Move : loss of function
abnormal movement
crepitus
Wahby Ghalib
28
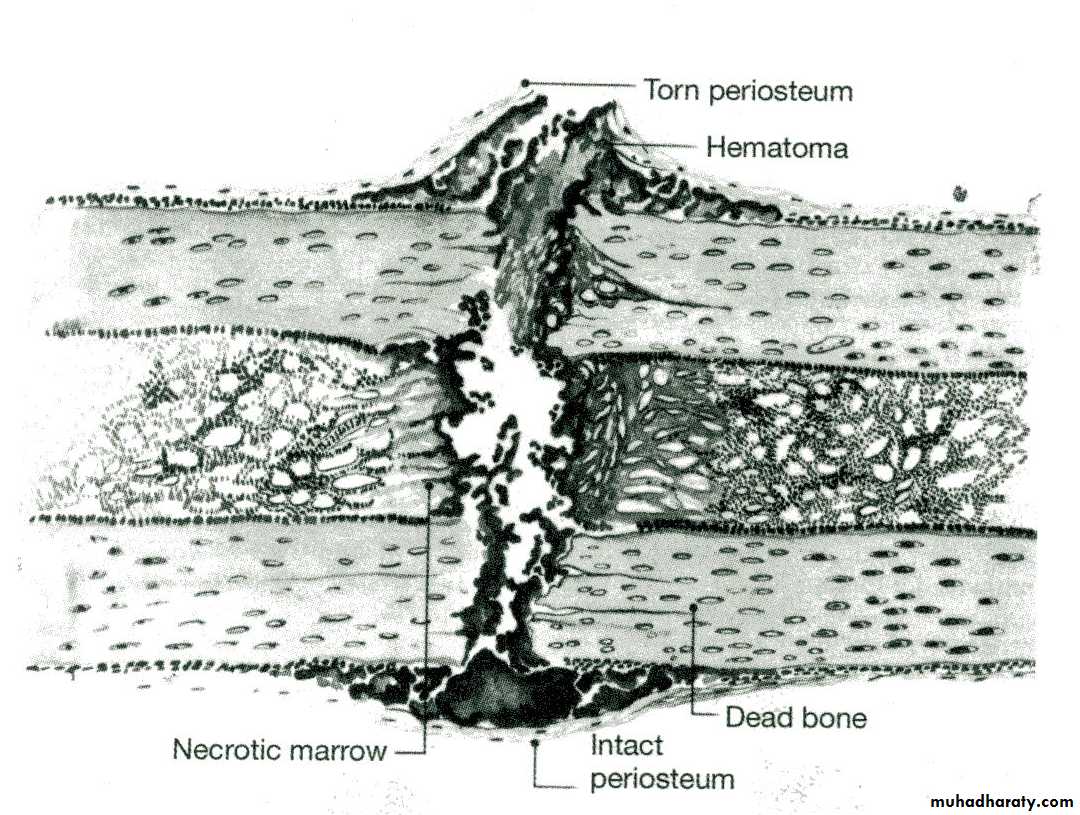
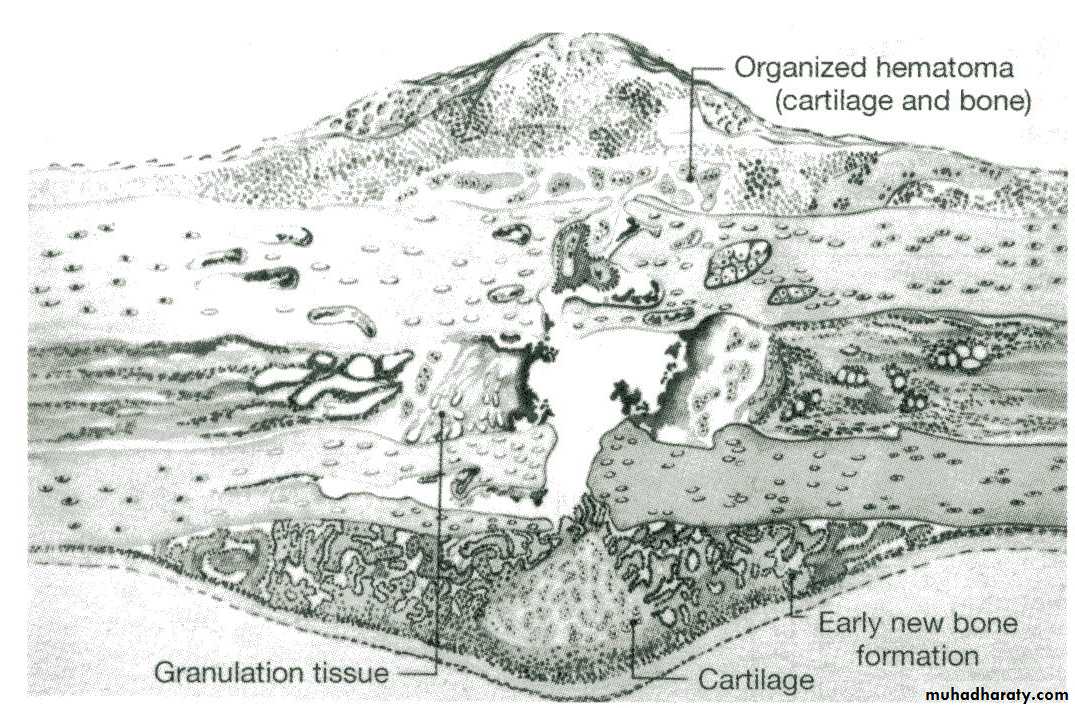
Healing
Haematoma formation
Inflammation & granulation t.
Callus
Woven bone
Lamellar bone
Remodelling
Wahby Ghalib
29Wahby Ghalib
30Wahby Ghalib
31Union & consolidation
• Union
• Consolidation
• Healing
• Incompete
• Complete
• Callus
• Calcified
• Ossified
• Tendeness
• Yes
• No
• XR
• # visible, fluffy callus
• # invisible, callus well defined
• Put stress
• No
• Yes
Wahby Ghalib
32
Perkin`s rule
Spiral # in upper limb unites in 3 w
consolidation x 2
lower limb x 2
transverse # x 2
Healing is quicker in children
Wahby Ghalib
33XR
2 views
2 joints
2 limbs
2 injuries
2 occasions (scaphoid,FN, physis, stress #)
2 brains
Wahby Ghalib
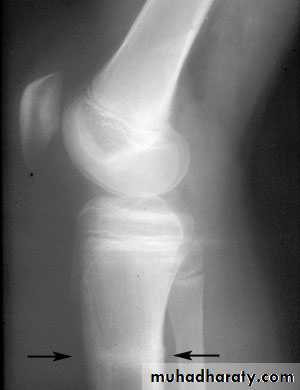
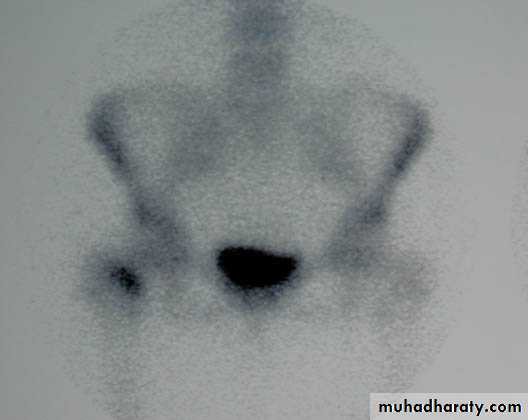
34Stress (fatigue) #
# that occurs in normal bone by repetitive stresses
> in athletes, ballet dancers & military recruits
Common sites: pars interarticularis of L5, FN, proximal tibial shaft, distal fibular shaft,calcaneum, MTBs
Wahby Ghalib
35
XR: early : -ve… few weeks : transverse defect ± periosteal new bone
Bone scanDDx: OM, OSa
Tx :immobilize & avoid painful activity
Wahby Ghalib
36Wahby Ghalib
37Wahby Ghalib
38Wahby Ghalib
39Pathlogical fracture
# that occurs with trivial trauma in a bone weekened by a pathologic process
e.g. osteoporosis, Paget`s d.,infection, & tumours
Wahby Ghalib
40Wahby Ghalib
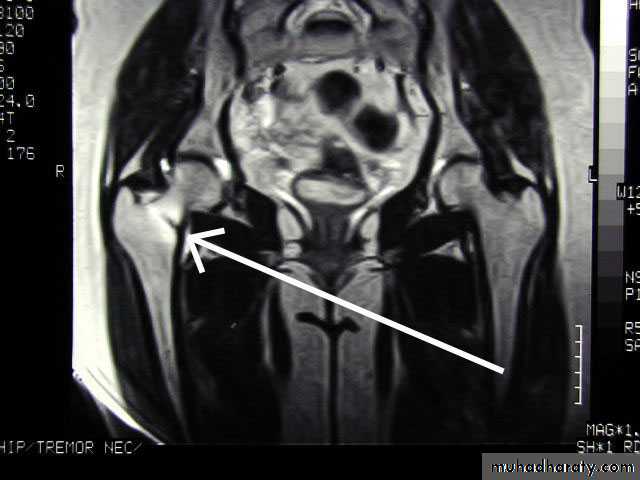
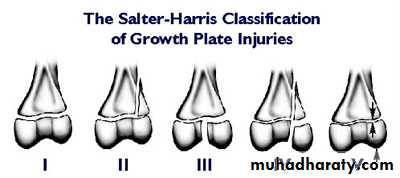
41Physeal injuries
10% of fractures in children
Salter - Harris classification:
1: separation of the epiphysis usually thru the calcified zone
2: separation of epiphysis & triangular piece of metaphysis
Wahby Ghalib
42
3: intra-articular # thru epiphysis then thru physis
4: intra-articular # thru epiphysis, physis, & metaphysis5: crushing of physis arrested growth
Wahby Ghalib
43Wahby Ghalib
44# may not be visible initially
Types 1 & 2 : good Px except around the kneeTypes 3 & 4: need perfect reduction & f/u for re-displacement
Wahby Ghalib
45Complications
Arrested growth
Accelerated growth
Asymmetrical growth
Wahby Ghalib
46
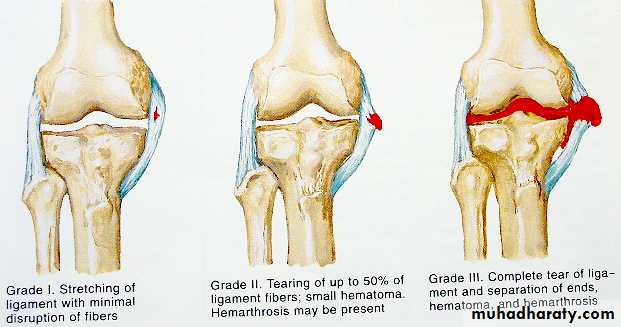
Ligament injuries
Sprain : stretching of ligament but it is still anatomically intact
Partial tear : more pain, joint is stable
Complete tear : less pain , joint unstable
Tx : partial immobilize & exercise
complete surgical repair
Wahby Ghalib
47Wahby Ghalib
48Joint injuries
Dislocation : complete loss of apposition of articular surfaces
Subluxation : partial loss
Fracture dislocation
Recurrent dislocation :chronic ligamentous & capsular injuries e.g. shoulder & patella
Habitual dislocation
Wahby Ghalib
49
Tx : reduction & immobilization
Wahby Ghalib50
Haemarthrosis : blood accumulates inside the joint
Objectives :Stressing the importance of managing fracture cases in general medical practice.
Clarification of the general principles of managing multitrauma cases.
Making the students familiar with the basic terms used in musculoskeletal traumatology.
Wahby Ghalib
51
Objectives :
Clarifying the basic principles of use of XR in case of fractures and dislocations.Developing basic skills to identify the severity of skeletal traumas so as to determine the line of management and the need to consult a senior.
Clarifying the special points in paediatric skeletal traumatology
Wahby Ghalib
52