
ا
ﻻ
ﺳ
ﺎﺘ
ذ
ﻟا
ﺪ
ﻛ
ﺘ
ﻮ
ر
ﻋ
ﻼ
ء
ﺣ
ﺴ
2
ن
ﺣ
ﻴ
ﺪ
ر
ا5
6
78

Objectives
1- To know the aetiology of lung cancer
2- To know how lung cancer can present
3- To know how to reach the diagnosis
4- To know the main lines of treatment

Aetiology
Cigarette smoking is the most common cause.(responsible for 90%
of cases) . Risk is proportional to amount of smoking and content
of tar. Death rate from the disease in heavy smokers is 40 times
more than non smokers . Risk decreases slowly after cessation . 1 in
2 smokers dies from smoking related disease.
Passive smoking is responsible for 5%
Exposure to radon
A number of industrial materials are associated with lung cancer
More common in urban than rural area due to atmospheric
pollution.



pathology
Lung cancer arise from bronchial epithelium or mucous
gland .
Symptoms occur early when tumor involves large
bronchus.
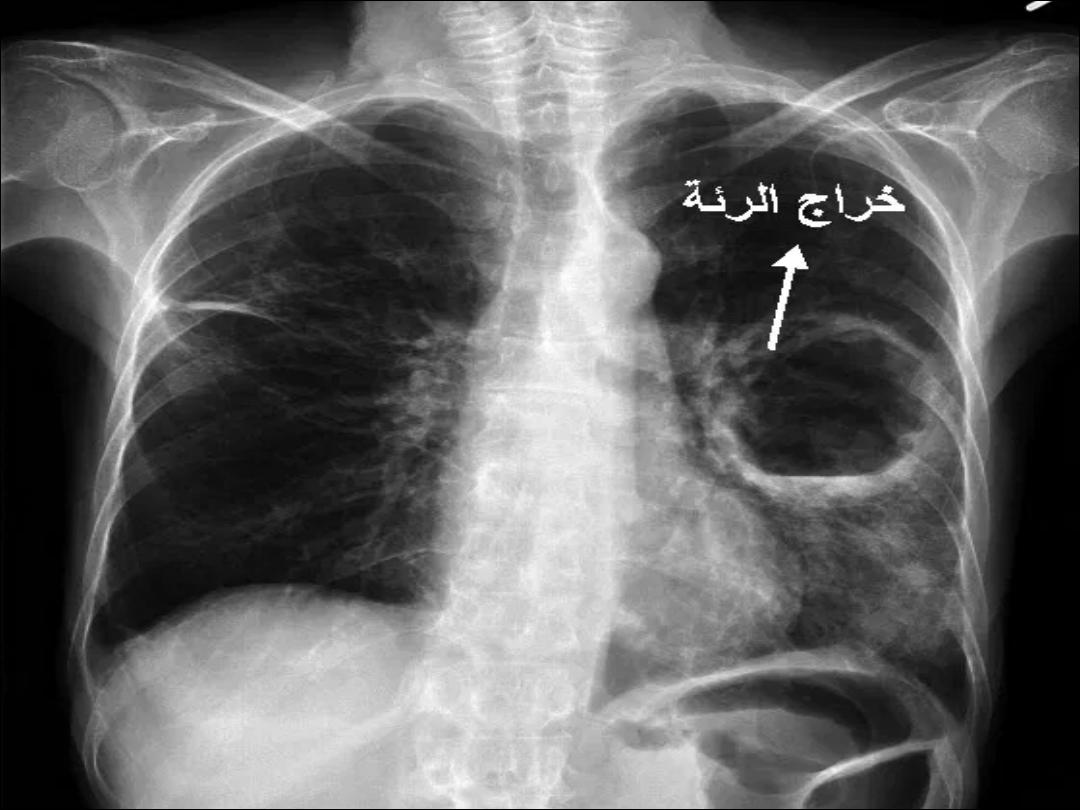
Peripheral tumor grows slowly and can reach large size
with cavitation ( resemble lung abscess) with little or no
symptoms

Common cell types in lung cancer
Cell type
1-Adenocarcinoma 35-40%
2-Squamous 25-30%
3-Small-cell 15%
4-Large – cell 10-
15%

Clinical features
Local symptoms
1- Cough….most common early symptom , usually dry ,
can be productive when associated with infection . A
change in character of smokers cough should attract the
attention to investigate for lung cancer
2- Hemoptysis…. especially in central tumor. Hemoptysis
in smokers should attract the attention to investigate
lung cancer

3- Bronchial obstruction ….. the clinical and radiological
manifestation depend on the site and extend of the
obstruction , any infection and coexisting lung disease.
Complete obstruction result in collapse with shortness of
breath , mediastinal shift , dullness percussion notes . Partial
obstruction results in monophonic wheeze that fails to clear
with cough and impair drainage resulting in infection ,
recurrent pneumonia at same site or poorly responding
pneumonia raises possibility of underlying pathology
including lung cancer . Strider ( a harsh inspiratory sound )
occurs when larynx , trachea is narrowed by tumor or
compression by malignant lymph node ( sub carinal or
paratracheal ) .

4-Breathlessness… caused by collapse or pneumonia
or by tumor causing large pleural effusion or by
compressing phrenic nerve resulting in
diaphragmatic paralysis
-

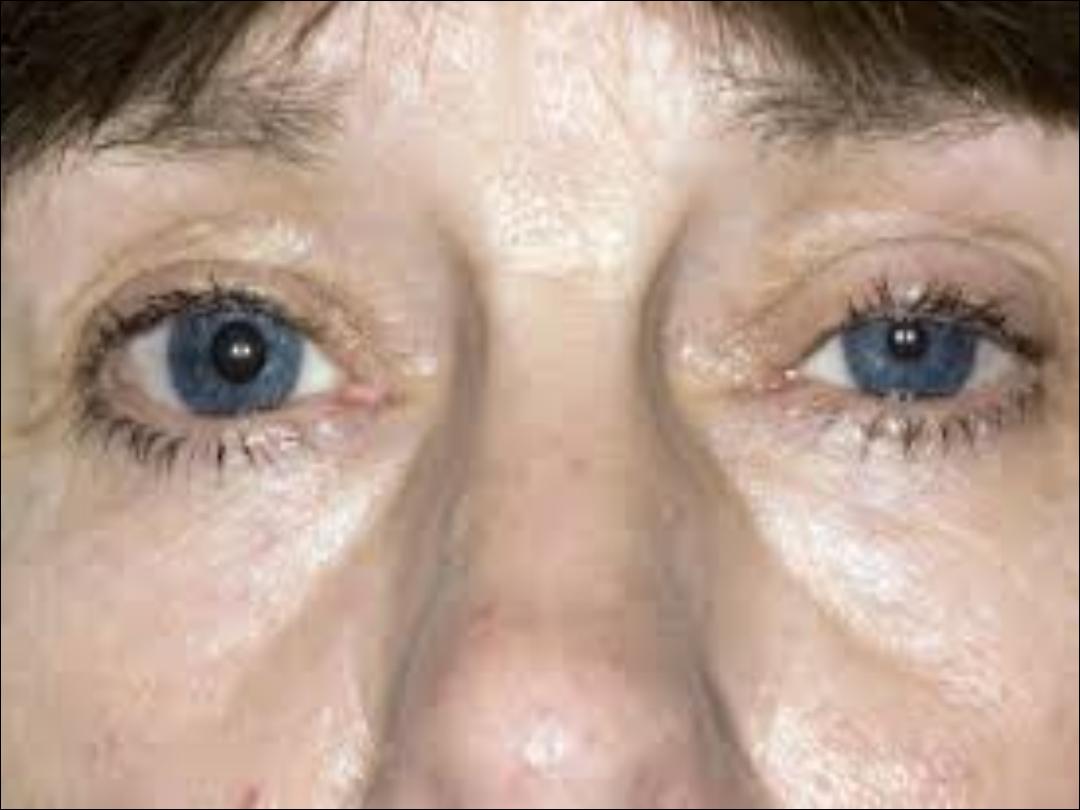
5- Pain and nerve entrapment…pleural chest pain
usually reflects pleural invasion( although it can occur in
distal infection ).Inter costal nerve involvement results
in chest pain. Cancer in lung apex can result in horner
syndrome( involvement of sympathetic trunk resulting
in miosis , ipsilateral ptosis , enophthalmia , and
hypohidrosis ). Pancost tumor( pain in inner aspect of
the arm with small muscle wasting of the hand due to
involvement of brachial plexus in apical lung tumor).

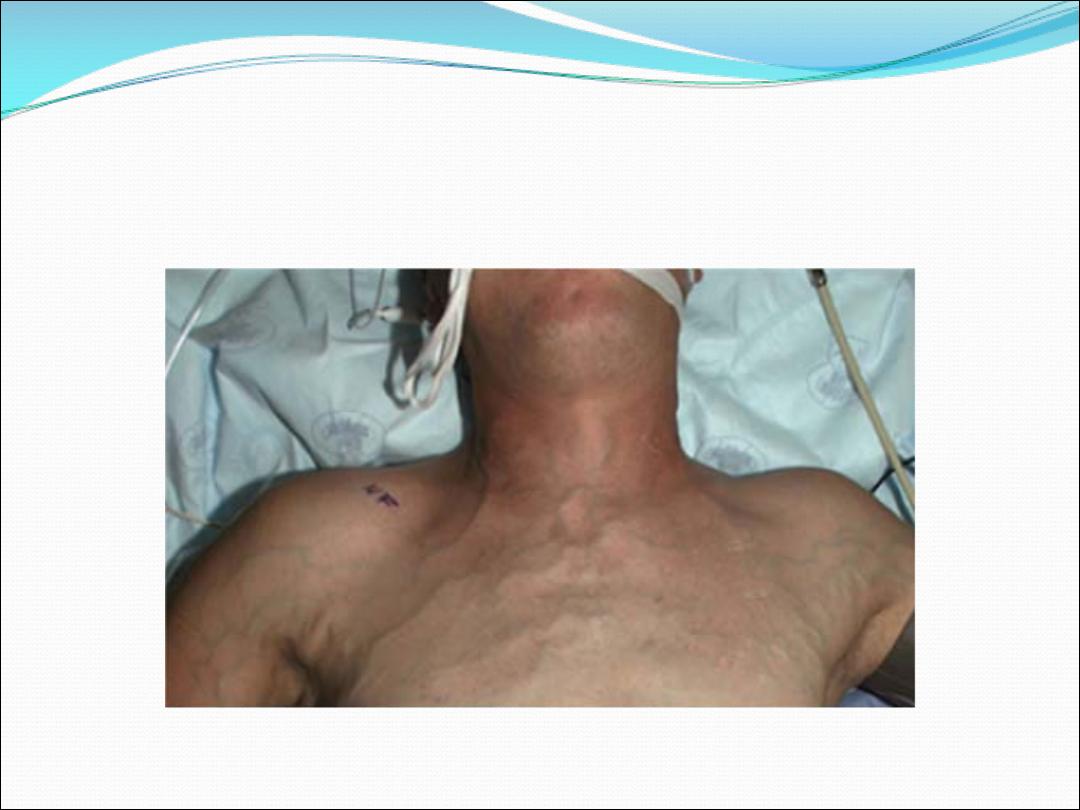
6- Mediastinal spread … involvement of esophagus
result in dysphagia , spread to pericardium result in
arrhythmia and pericardial effusion Superior vena cava
obstruction by tumor results in suffusion and swelling
in neck and face with conjunctival odema , headache
and dilated veins in chest wall. Left recurrent
laryngeal nerve can be involved by left hilar tumor
resulting in vocal cord paralysis( bovine cough )
.Tumor can spread to supraclavicular nodes, biopsy
from these nodes can reach the diagnosis

Metastatic spread
To liver result in jaundice . To bone result in bone pain .
To brain result in focal neurological defects ,fits ,
personality changes . To adrenal gland and to skin
result in skin nodule . Anorexia and weight loss usually
reflect metastatic spread

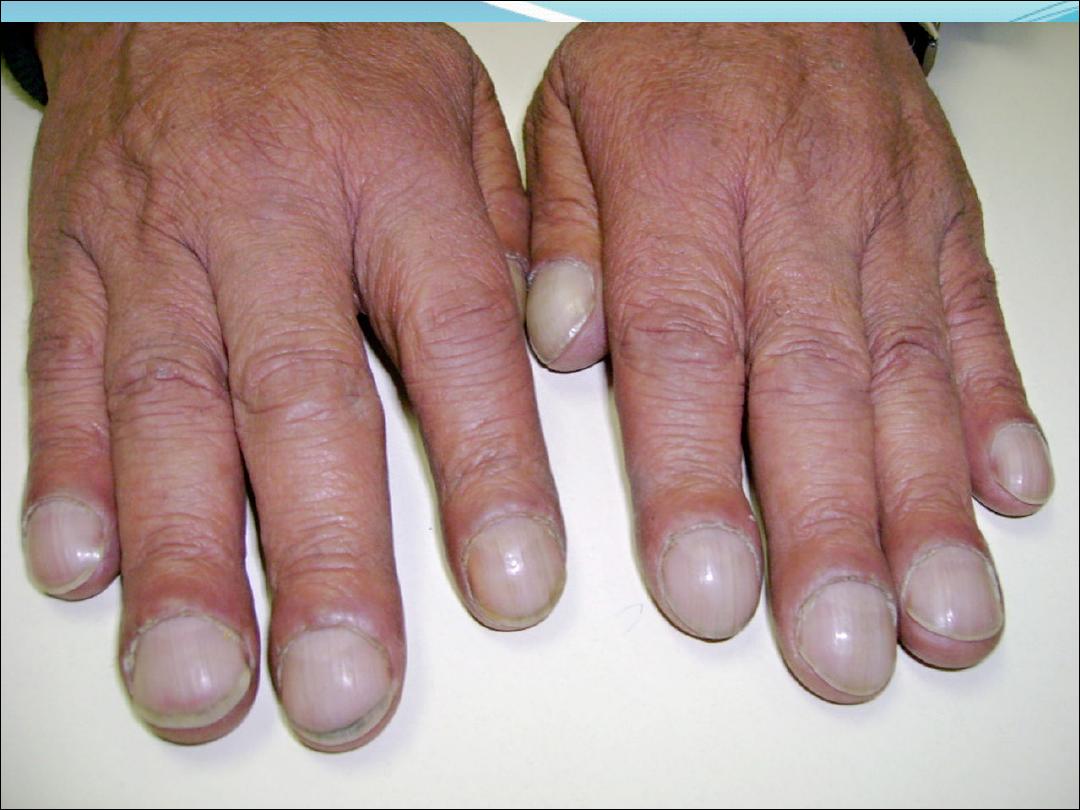
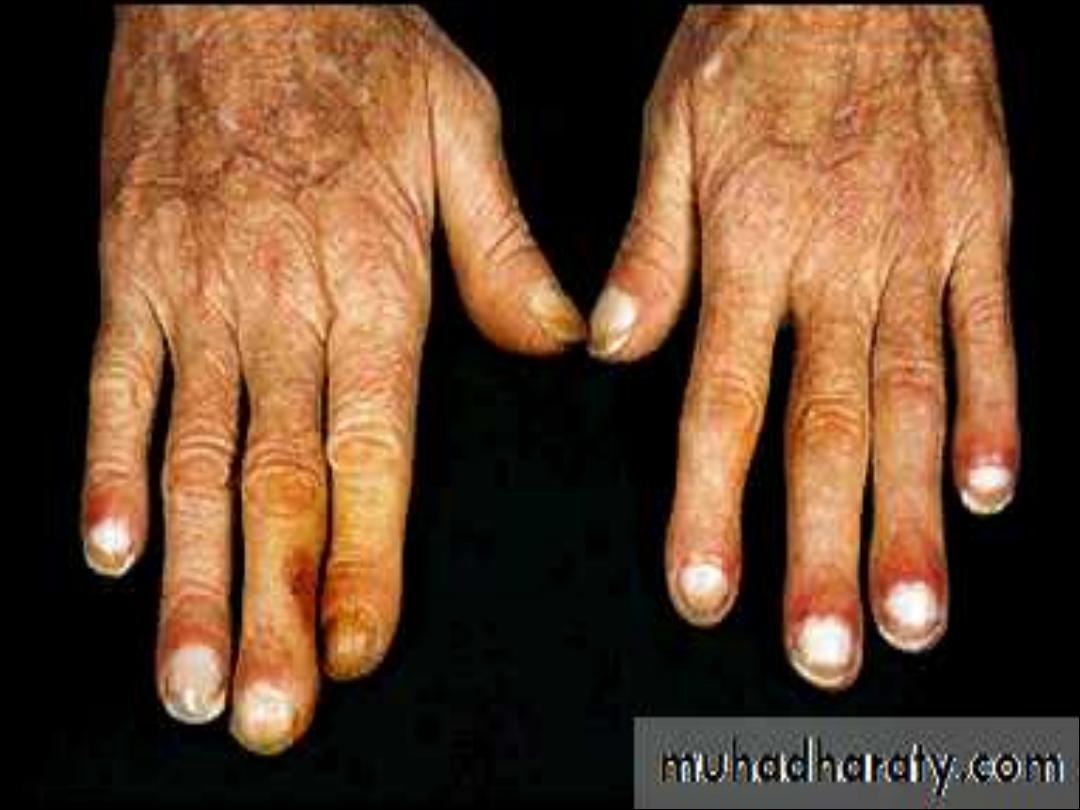
Finger clubbing due to over growth of the soft tissue of
terminal phalanx cause increase nerve curvature and
nail bed fluctuation
Hyper trophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy ( painful
swelling of the distal radius , ulna , tibia and fibula due
to subperiosteal new bone formation

Non metastatic extra pulmonary effects
1- endocrine …. ACTH , ADH( associted with small cell
cancer) , hyper calcemia due to secreation of
Parathyroid like peptite ( associated with squamous cell
carcinoma ) , carcinoid syndrome , gynecomastia
2- neurological …. Polyneuropathy , myelopathy ,
cerebellar degeneration , mysthenia
3- others ….digital clubbing, hypertrophic pulmonary
osteoarthropathy , nephrotic syndrome, polymyositis ,
eosinophilia

Investigations
The aim is to establish the diagnosis ,
know cell type and extent of the disease
1-Imaging : including chest x- ray and CT
scan ( may reveal mediastinal spread
and helpful for planning biopsy
procedures
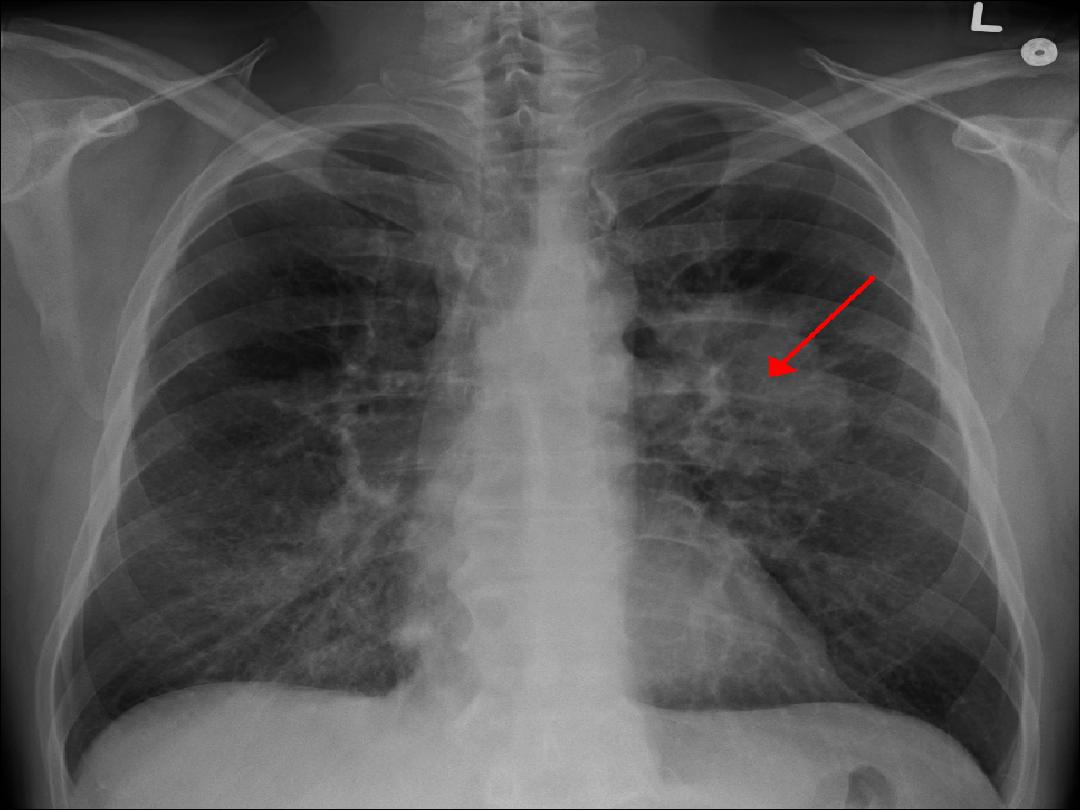
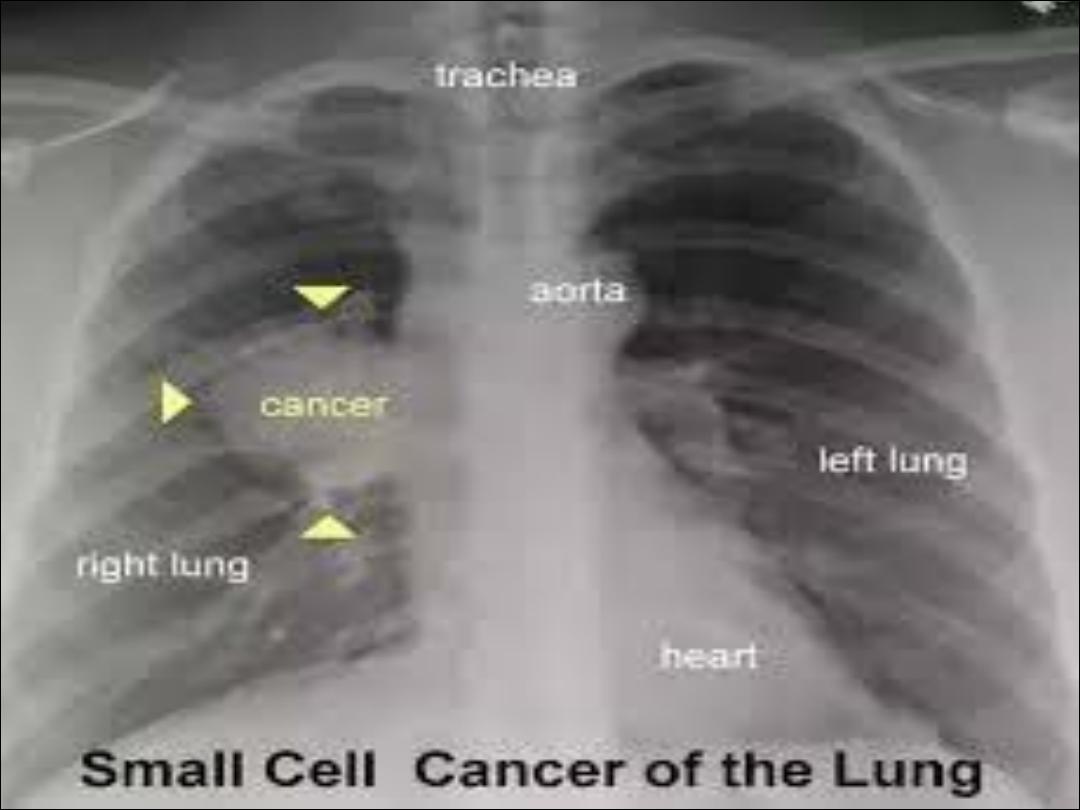
Chest x- ray may show :
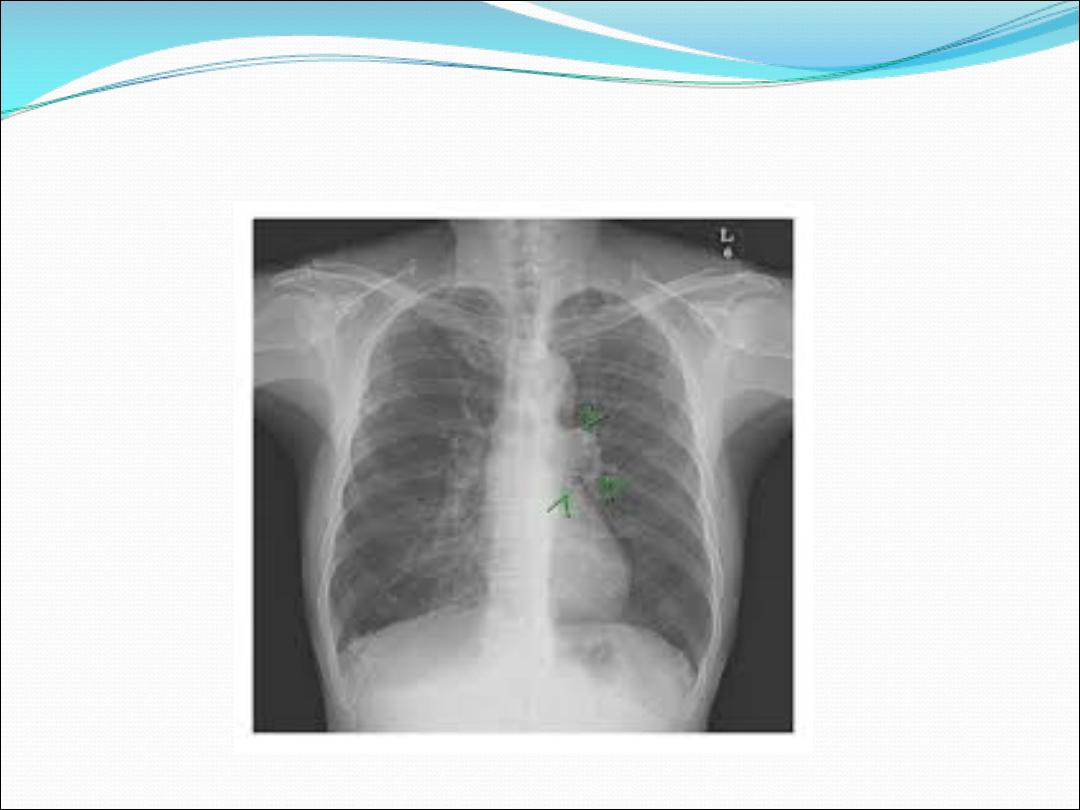
1-Unilateral hilar enlargement may
be mass or lymph node
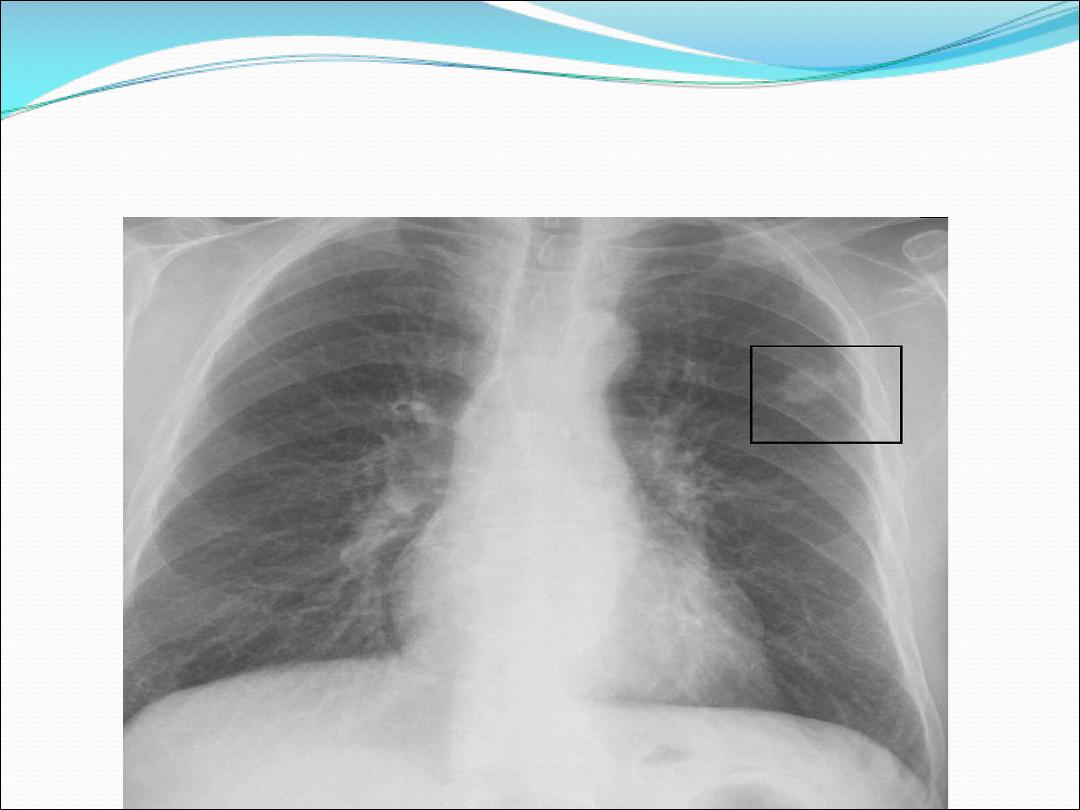
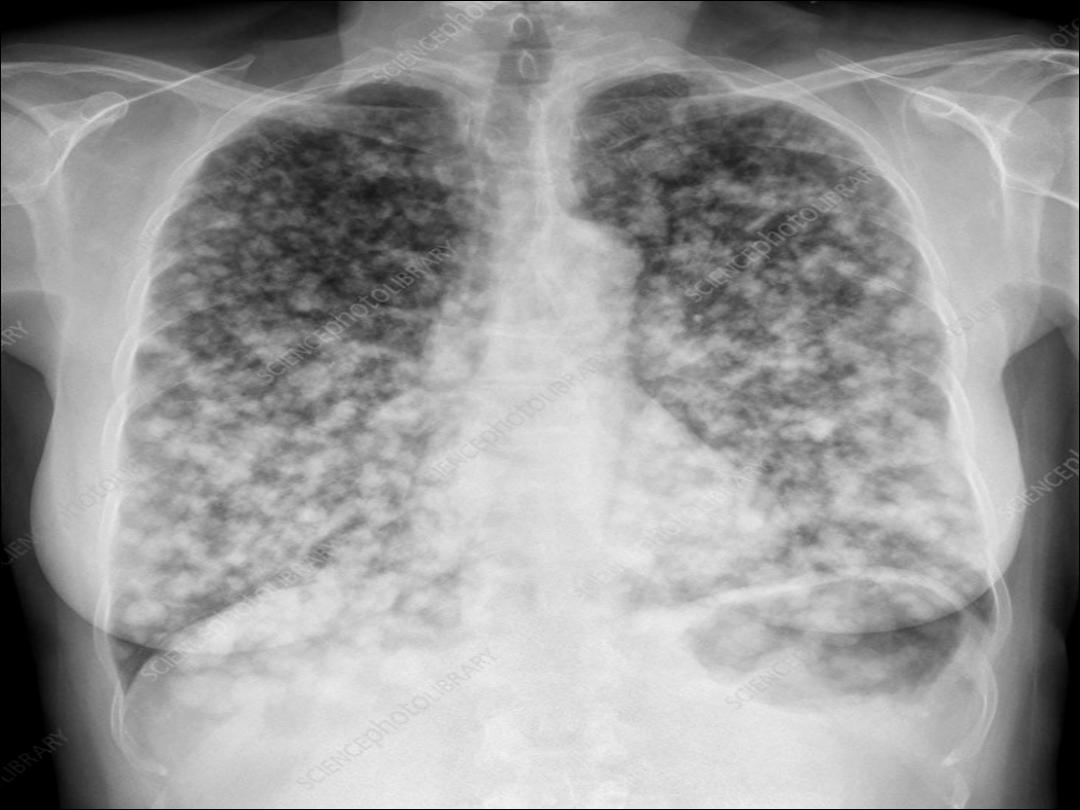
2- Peripheral pulmonary opacity
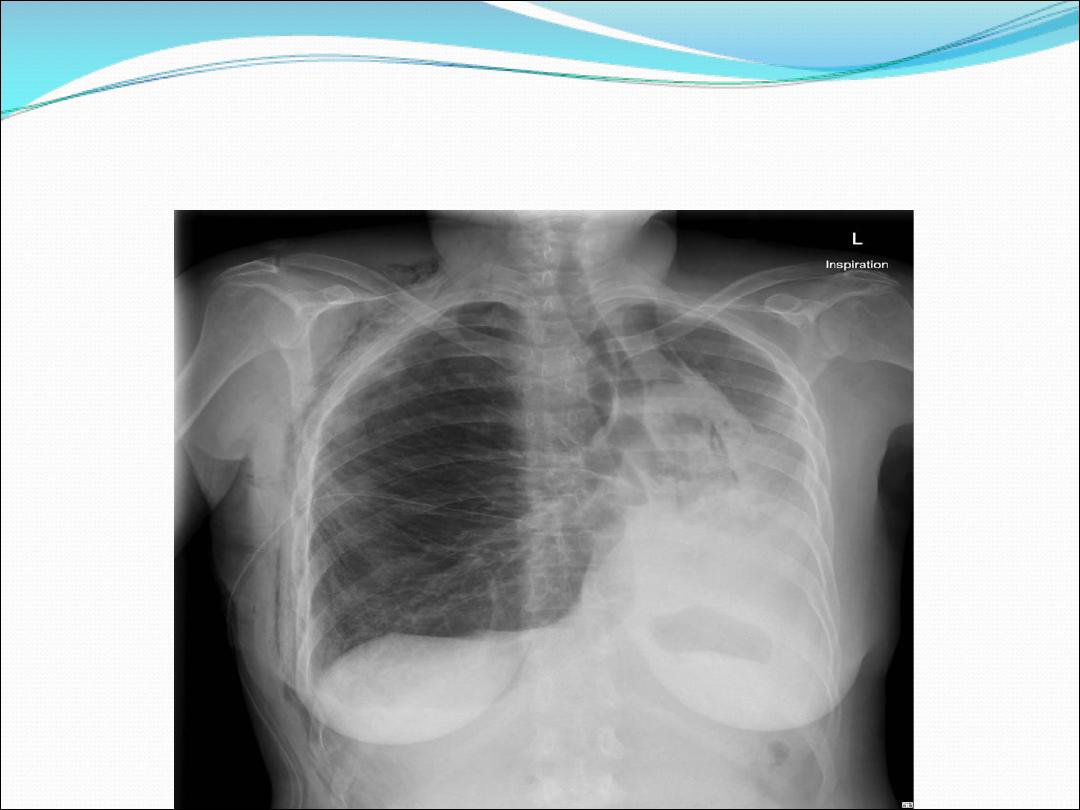
3- Lung , lobe or segmental
collapse
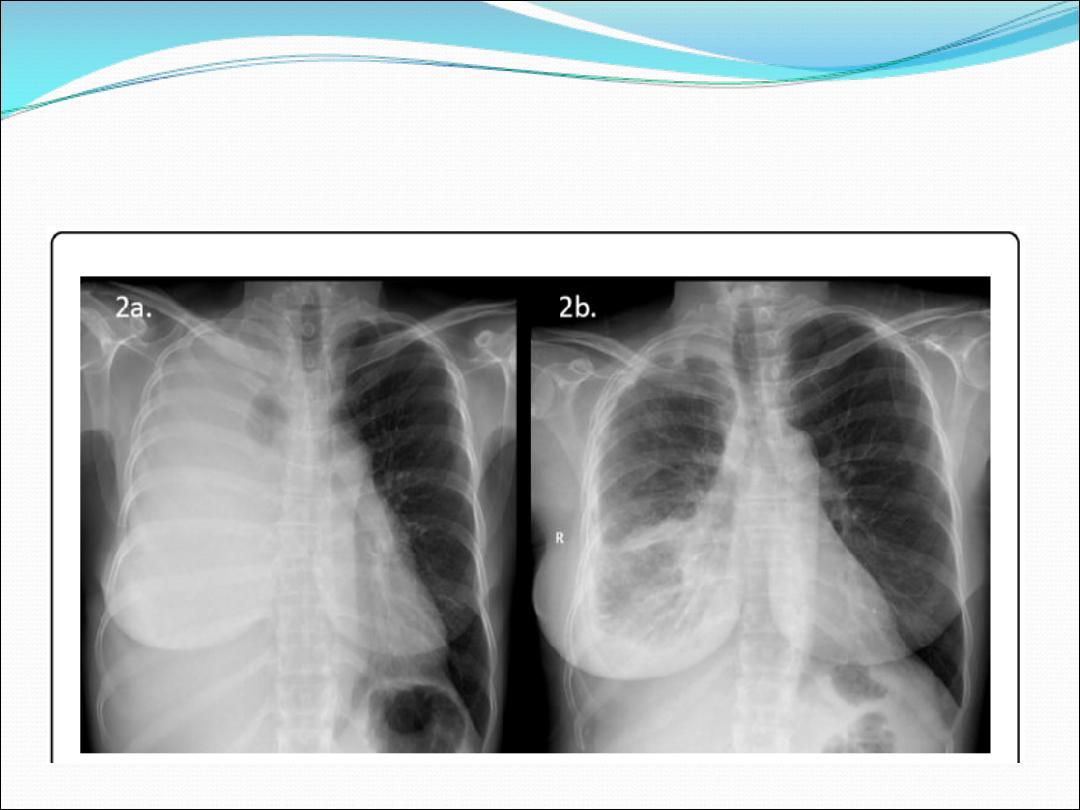
4- Pleural effusion
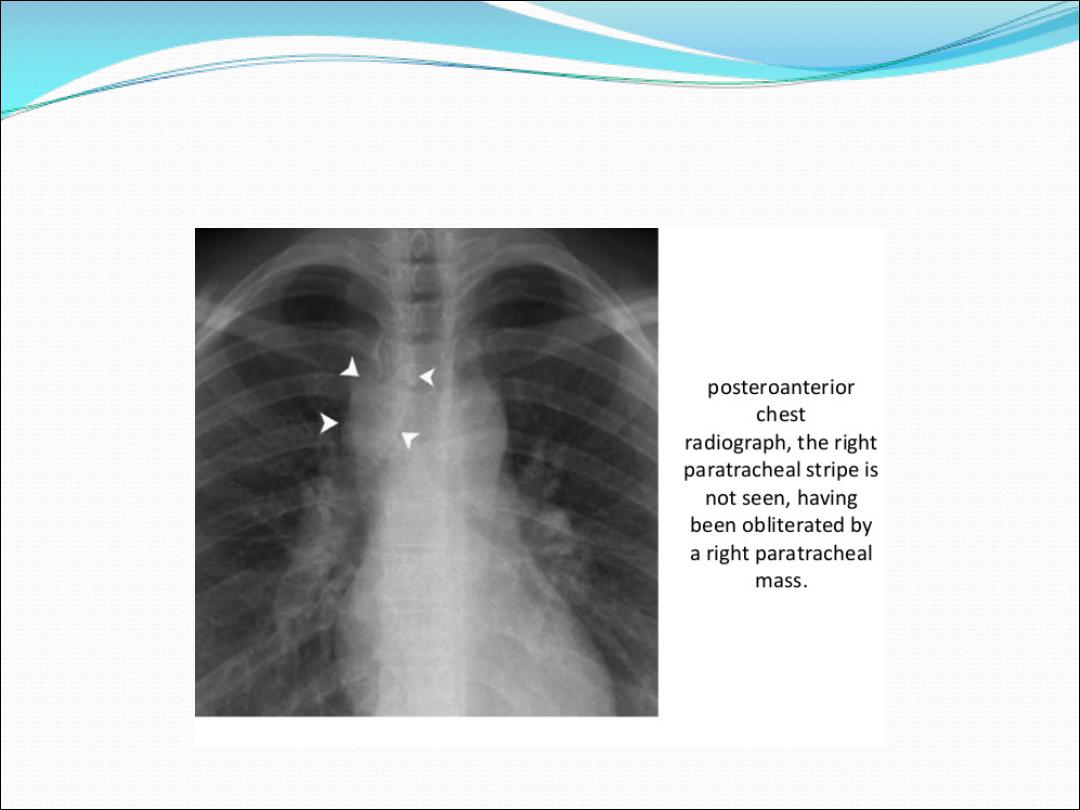
5-Paratracheal lymphadenopathy
(show widening mediastinum )
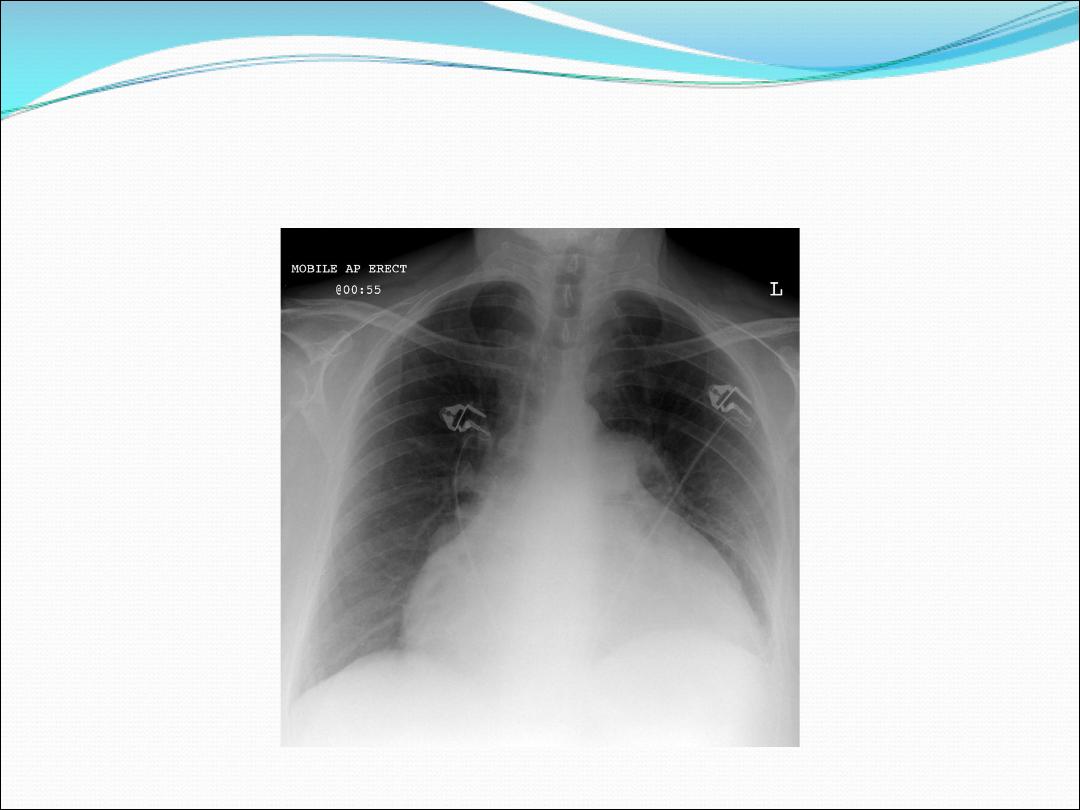
Malignant pericardial effusion
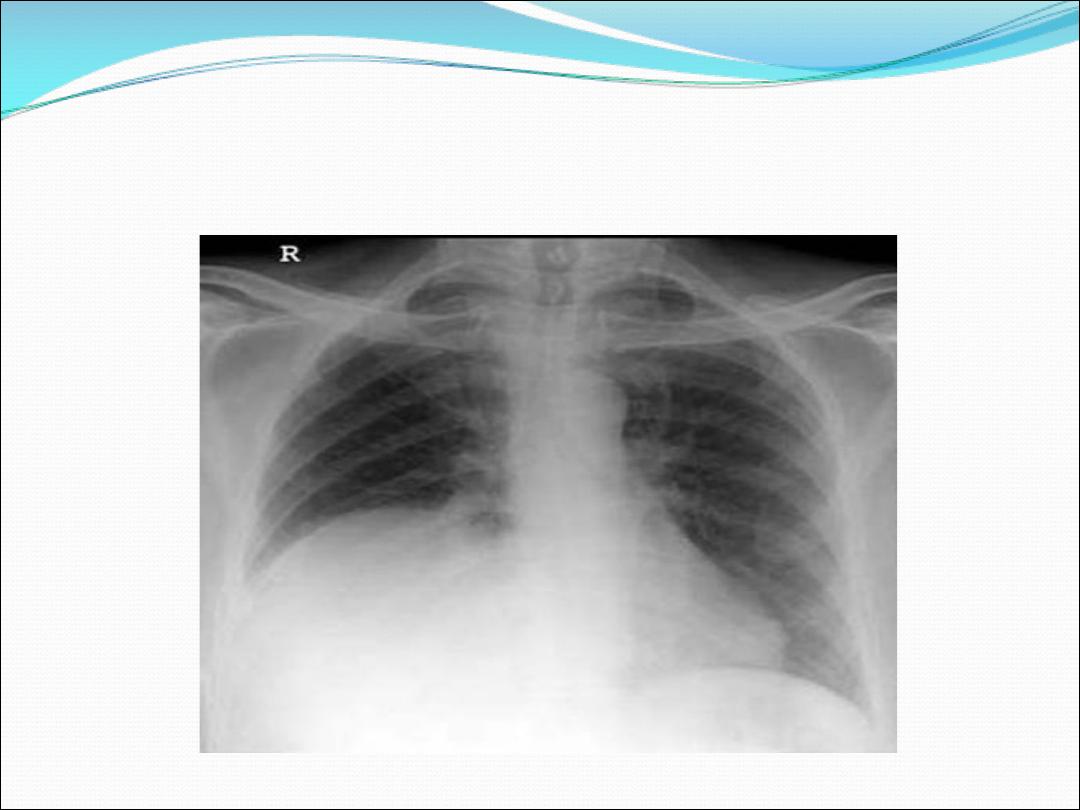
7- A rasied hemi diaphragm
(phrenic nerve palsy )
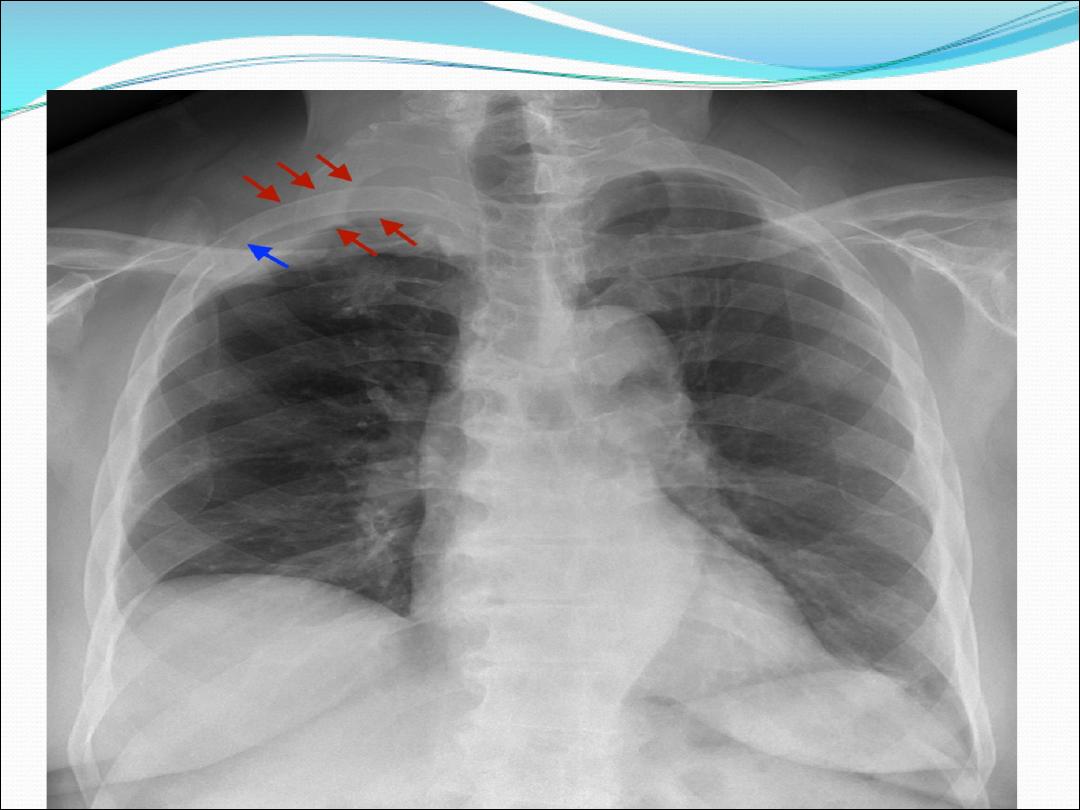
8- Osteolytic rib destruction

Biopsy and histopathology
More than 50% of tumors can be visualized and take
biopsy from them by flexible bronchoscoy. For
peripheral tumors that cannot be reached by
bronchoscopy , percutaneous lung biopsy by ultrasound
or CT scan guide is the preferred procedure ( with small
risk of pneumothorax ) . In patients who are unfit for
invasive procedure sputum cytology may show
malignant cells . If the patient has pleural effusion ,
pleural biopsy is the preferred procedure . The diagnosis
can be confirmed by biopsy from affected lymph node ,
liver , skin lesion or bone marrow

Staging to guide treatment
Patients with small cell cancer get metastasis early and
so these patients are not suitable for surgery . Non small
cell cancer patients needs to be investigated for extent of
disease to stage it and see it is operable or not , this
requires CT scan of chest to see local and mediastinal
metastasis ,combined CT and whole body PET is used to
detect metastasis. Head CT ,radionuclide bone scan
,liver ultrasound and bone marrow biopsy are done for
patients suspected to have metastases to these sites .
Physiological respiratory
tests are needed to asses
ability for aggressive treatment

Management
1- Surgical treatment : carries the best
hope for long term survival , 5 year
survival in stage one ( no metastasis) is
75%, and 50% in stage two
(involvement of ipsilateral lymph node ).
Lot of patients are not suitable for
operation either because of distant
metastasis or poor lung function or
comorbidity

Radiotherapy
Less effective than surgery but can improve
patients with localized disease and cannot do
surgery because of comorbidity and can be
combined with chemo therapy when there is
lymph node metastasis . The main role of
radio therapy is palliation of distressing
complication such as superior vena cava
obstruction , recurrent hemoptysis and
metastatic pain to chest wall or bone

Chemo therapy
The combination of chemo and radiotherapy
can prolong survival of small cell cancer from
3 months to one year . In non small cell cancer
chemo therapy is less effective , it can be
given prior to surgery and following surgery
can be given if there is nodal involvement ,
platinum based chemotherapy regimen offers
30% response rate in NSCLC

Laser therapy
Laser therapy through bronchscopy
can open air way in collapsed lung
due to tumor obstructing the
bronchus ( palliative treatment ) ,
Stent can be put to maintain airway
patency

Prognosis
The over all prognosis is poor ,
70% die with one year . The
best prognosis is with non
metastatic squamous cell
carcinoma amenable for
surgery
