

It developes when a woman's
immune system is sensitized to
foreign erythrocyte
surface antigen
.
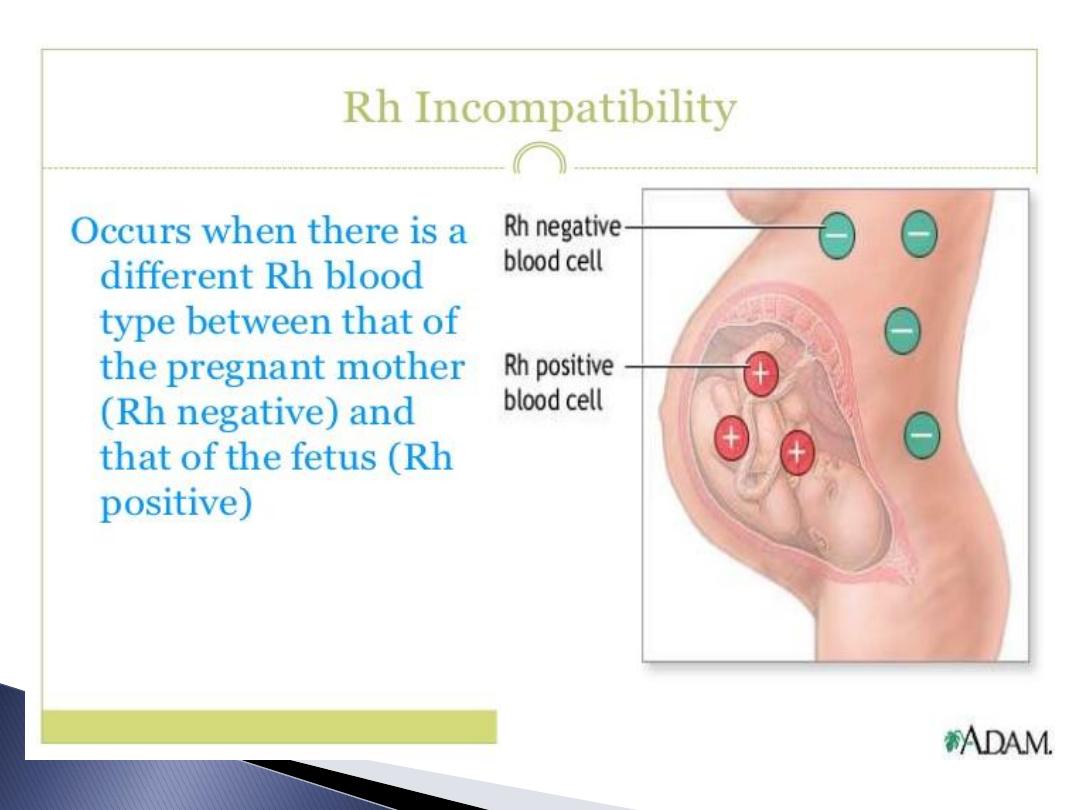
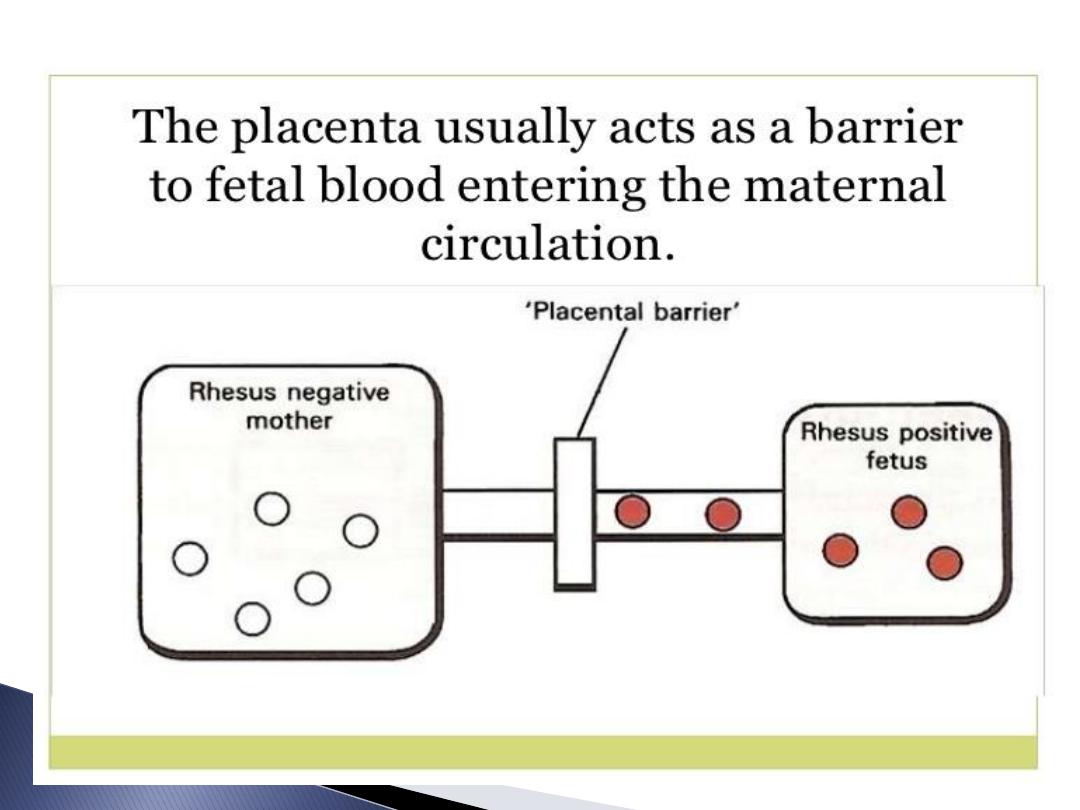

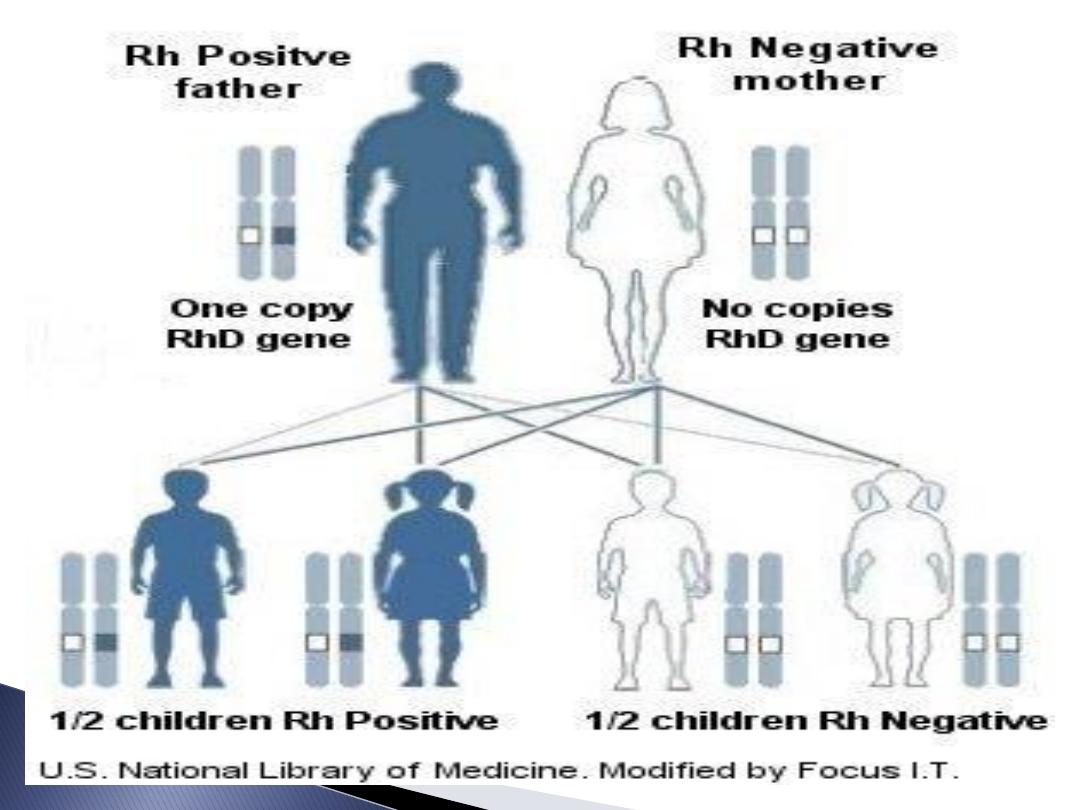
If Rh-ve woman married Rh +ve husband
got pregnant with Rh +ve foetus ,so
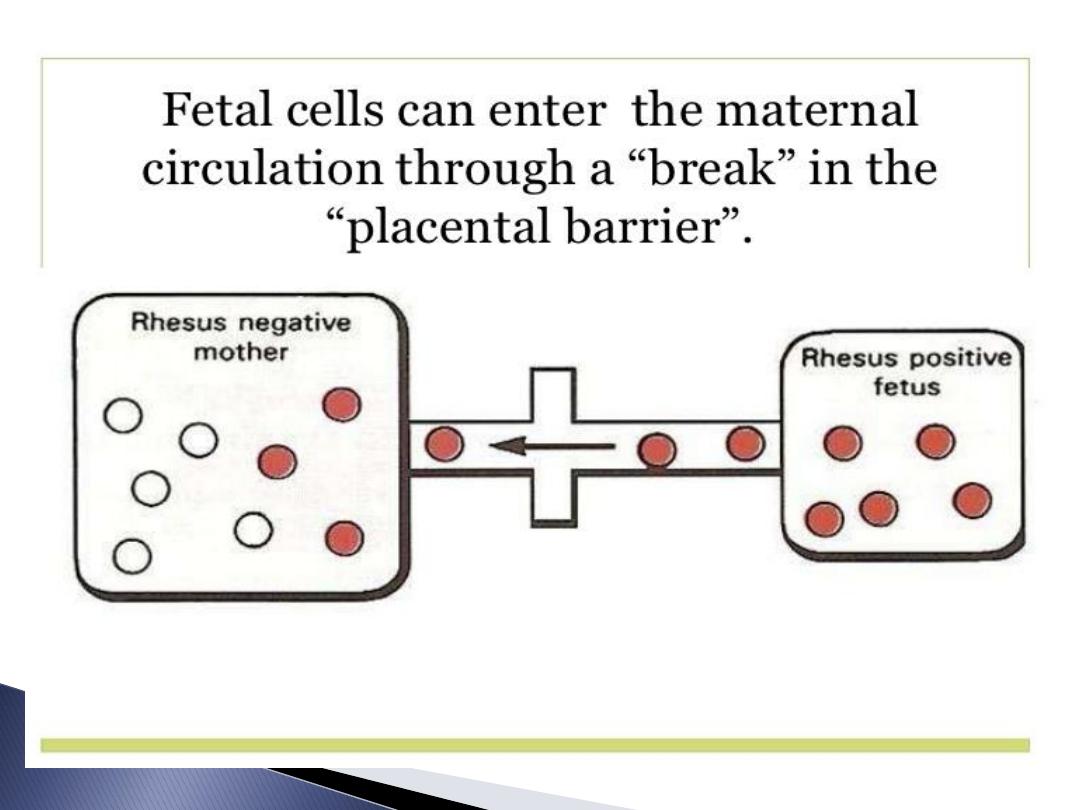
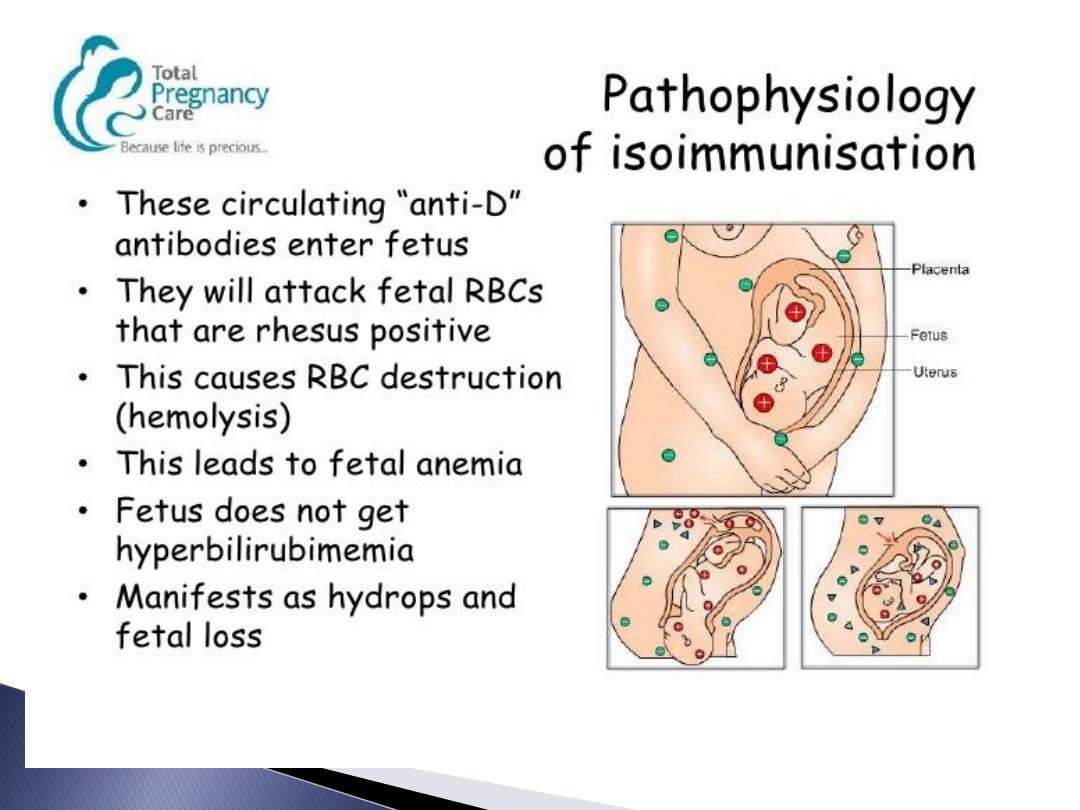
foetal RBC leak to maternal circulation
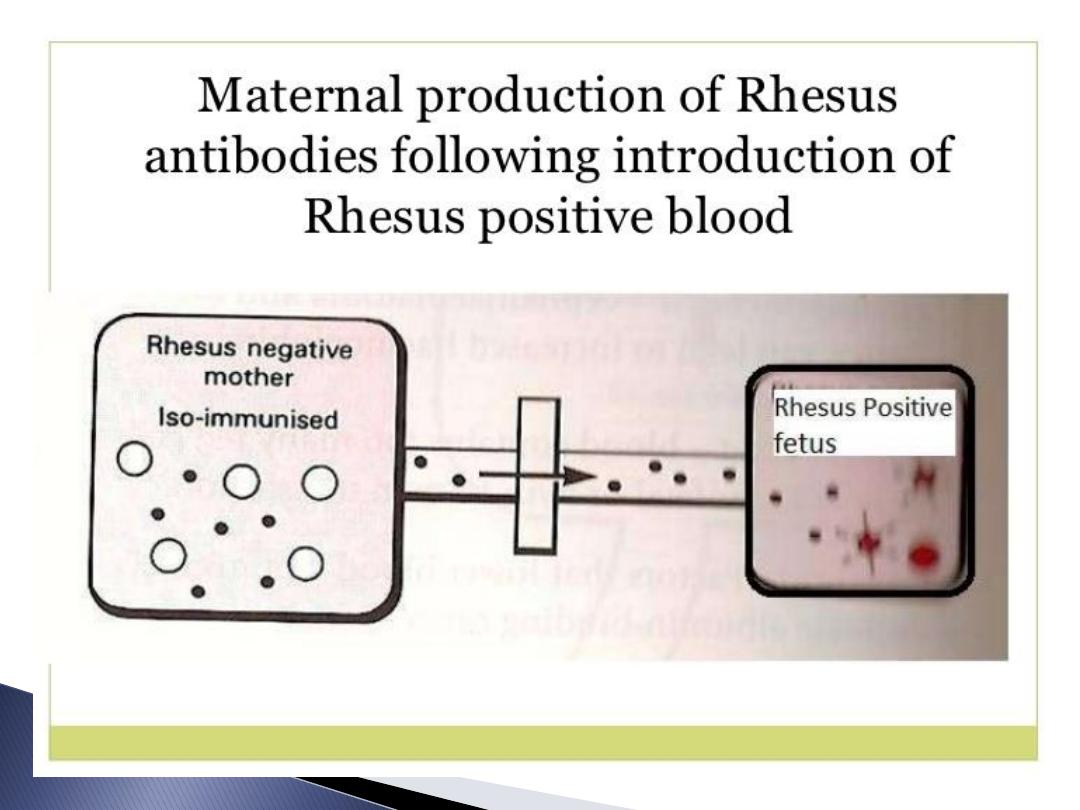
recognised as antigen so forming
Antibodies return to foetal circulation
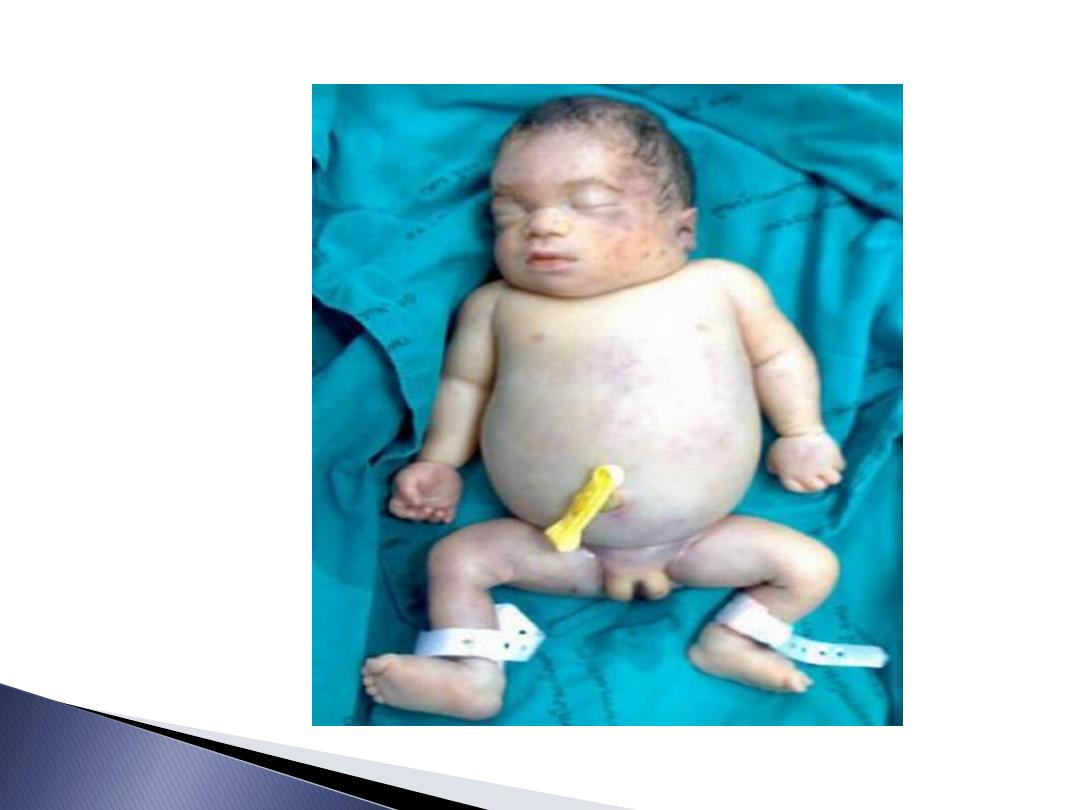
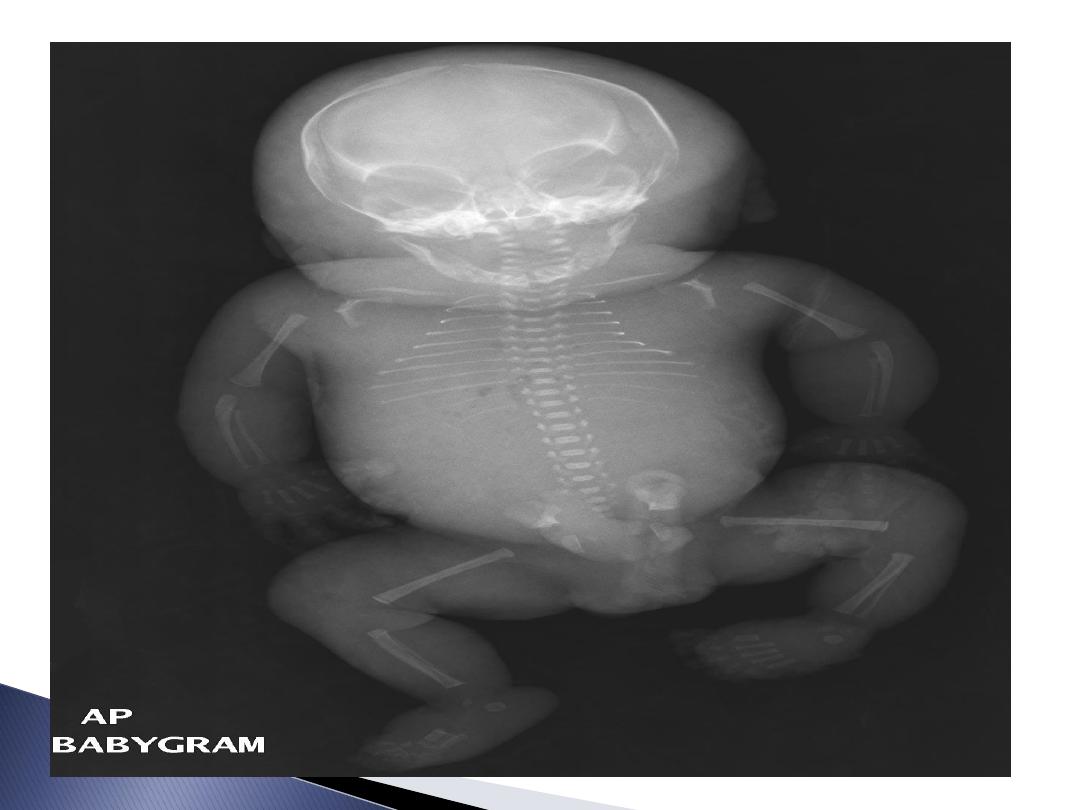
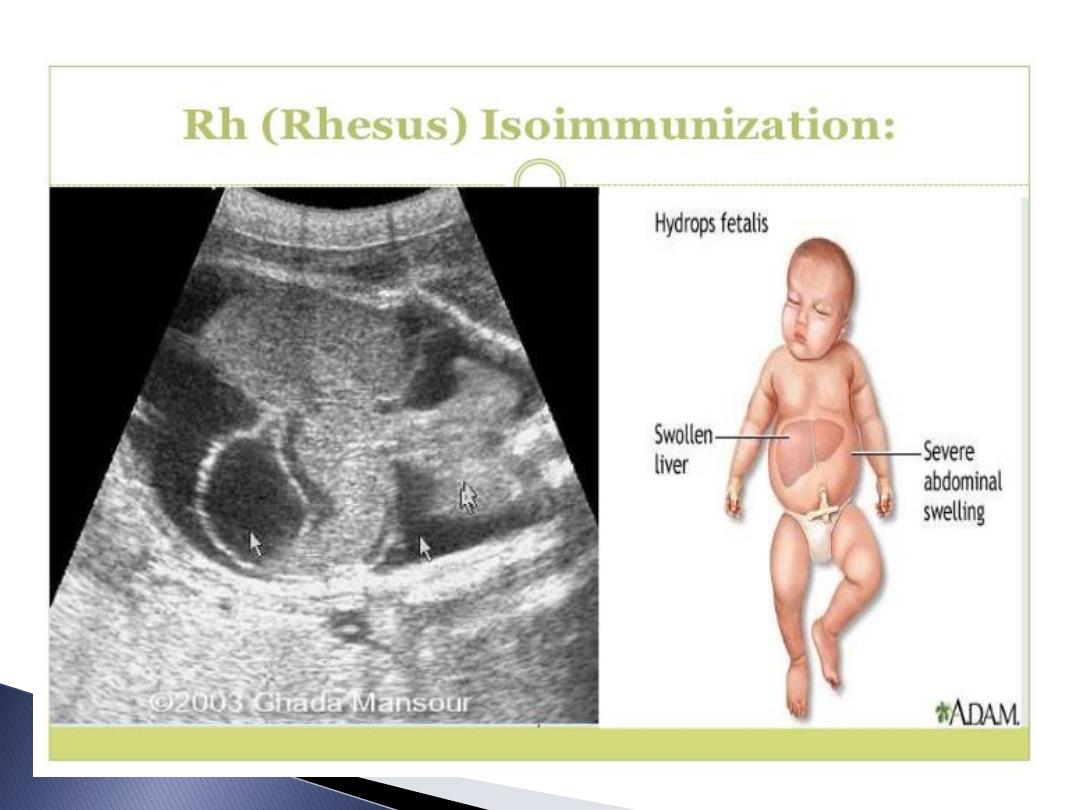
destroying foetal RBC lead to haemolysis
&anaemia if continued causing heart
failure and Hydrops fetalis

Circumstances at which sensitisation
develop:
During smooth uneventful pregnancy.
After miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Any obstetrical procedure.
Given mismatched blood.
Ante partum haemorrhage.
During delivery.
Failure of protection.
Not received
.

Diagnosis:
History:
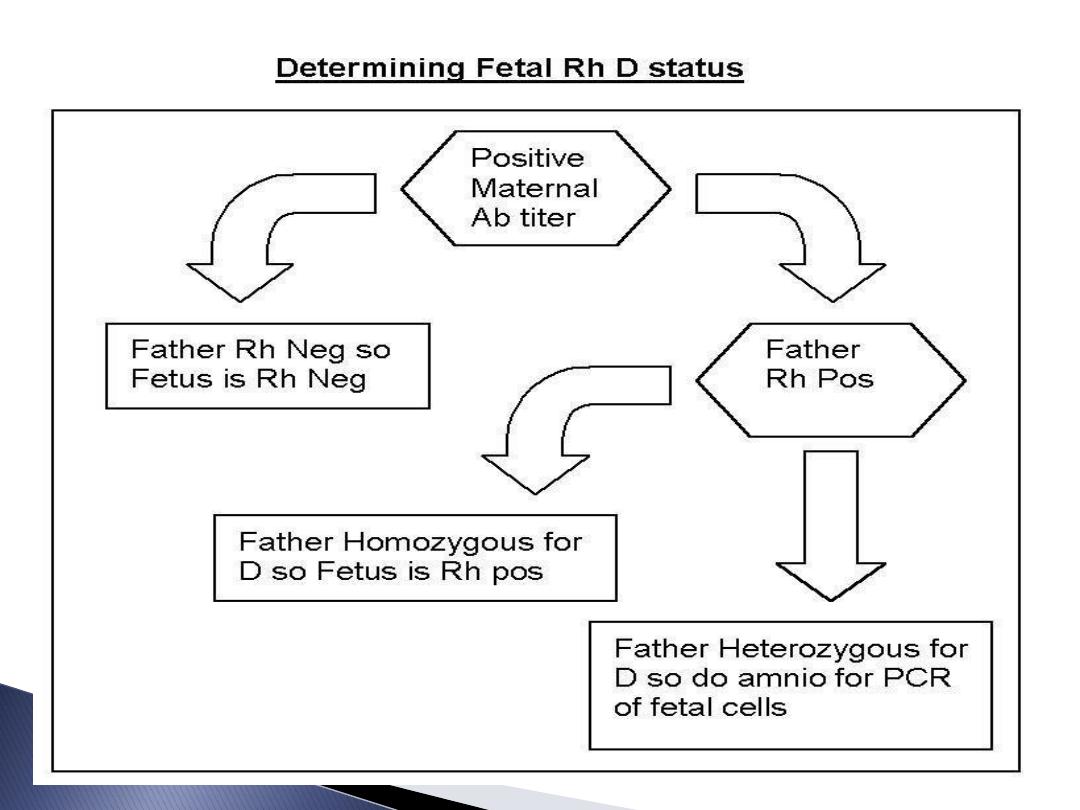
Bl. group & Rh of her & her husband.
Previous pregnancy losses & deliveries.
Received Anti –D or not in previous
pregnancy.
Any blood transfusion.
Neonatal exchange transfusion for the
neonate.
Physical Exam.:
General :
Abd. Exam.:

Investigations:
Blood group & Rh of the pregnant & her
husband
Indirect Coomb’s Test:
Done at booking &28 weeks of gestation
If its negative means no sensitisation.
If positive means sensitised.
If sensitised so perform Antibody Titer.
Ultrasound :
For dating and any abnormality.

Management of Rh-D Negative Non-
sensitized Patients :
- For prevention of sensitization:
Rh-immune globulin(Rh-IgG)* 500
IU(300 mcg covers 15 ml foetal cells) is
given at 28 -34 weeks' .
After delivery cord blood sent for Direct
Coomb’s test ,Hb, bilirubin level and
blood group& Rh.
If the antibody screen is negative a
second dose of Rh-IgG is given if the
infant is Rh-positive .
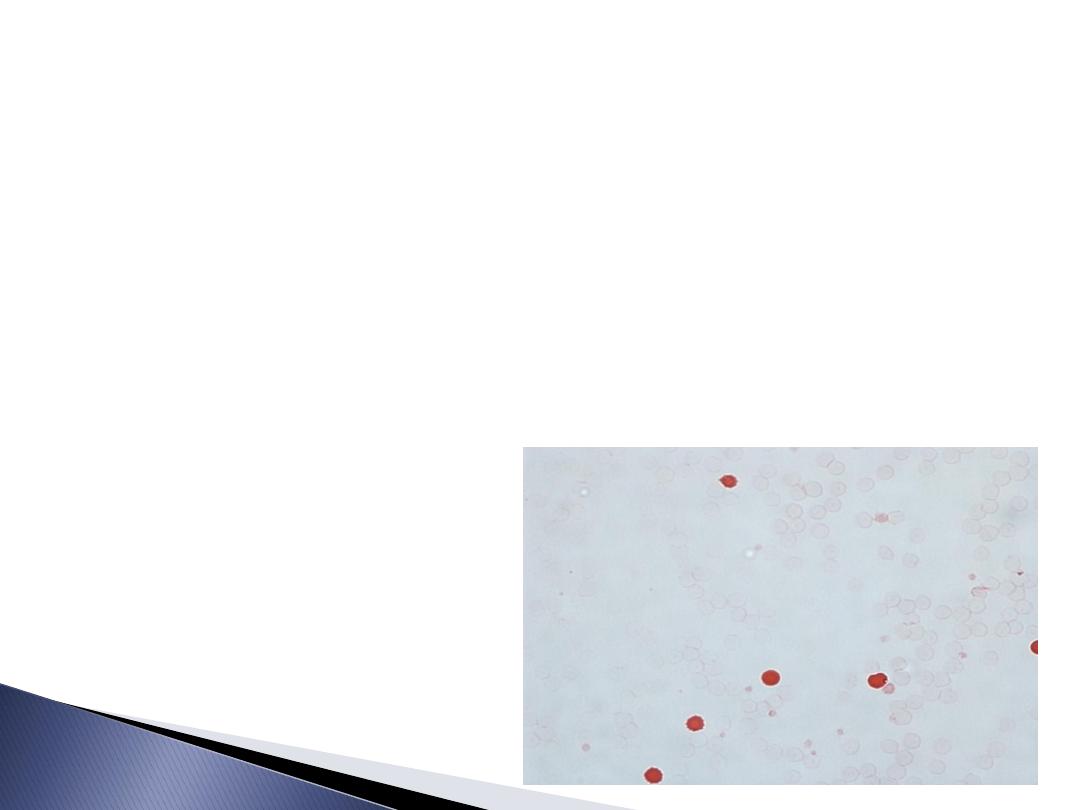

Kliehauer Test:
Its a test used to calculate the number of
foetal RBC in maternal circulation of Rh-
ve pregnant carries Rh +ve foetus.
Each 5 foetal RBC correspond to 0.25 ml
of foetal maternal transfusion
.

10 mcg of anti-D IgG should be administered
for every millilitre of foetal blood in the
maternal circulation.
300-mcg dose is more than adequate for
covers haemorrhage volumes of up to 30
mLs.

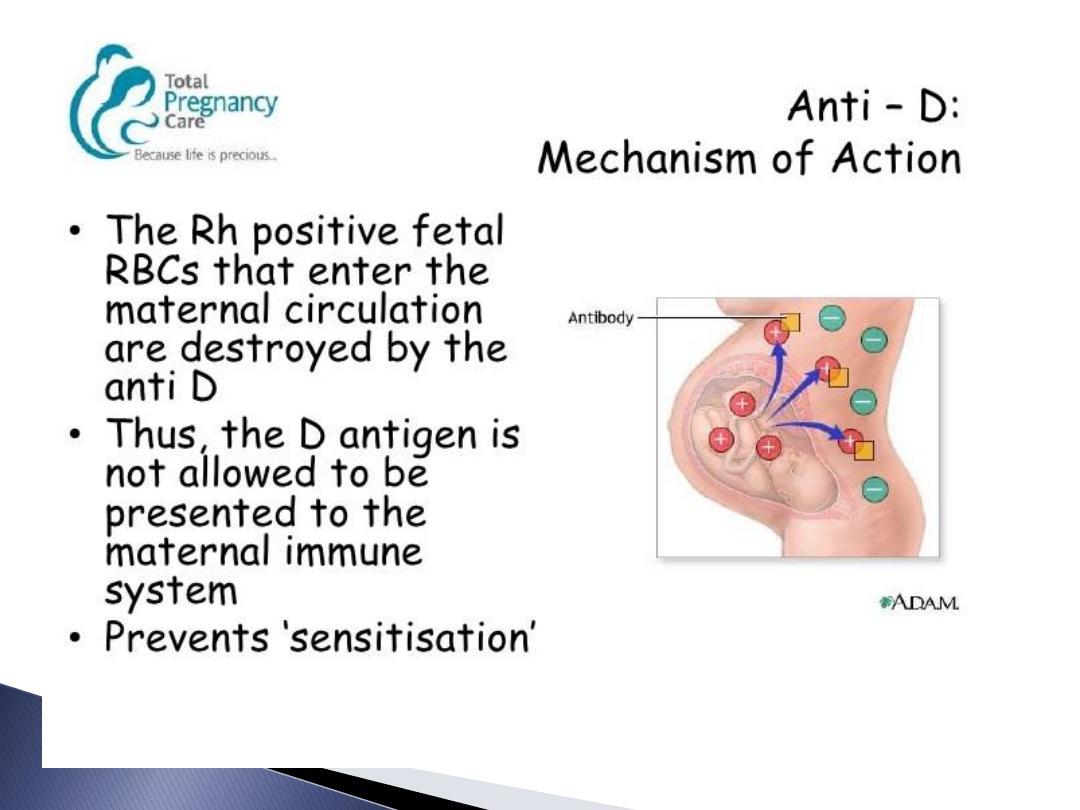
Anti-D:
*Rh-immune globulin is an antibody
that will help to remove any Rh positive
cells in the mother's blood. Rh-immune
globulin must be given before the
mother begins to produce her own
antibody to the Rh factor.

Indications For Giving Anti- D:
After Miscarriage :
- If pregnancy ended after 12 weeks of
gestation
- At any gestational age if any surgical or
medical termination of pregnancy.
After Ectopic pregnancy.
CVS.
FBS.
Ante partum haemorrhage.
Prophylaxis between 28 – 34 weeks of
gestation
Delivery whether normal or operative
delivery.

Management For First Sensitized
Pregnancy (no prior severely affected
pregnancy).
IAT titres of < 1:4 or less are managed
non-invasively with repeat antibody
titres every 2 - 4 weeks.
If the foetus is antigen negative then no
further testing is necessary.

If the foetus is antigen positive then the
pregnancy is followed with serial titres and
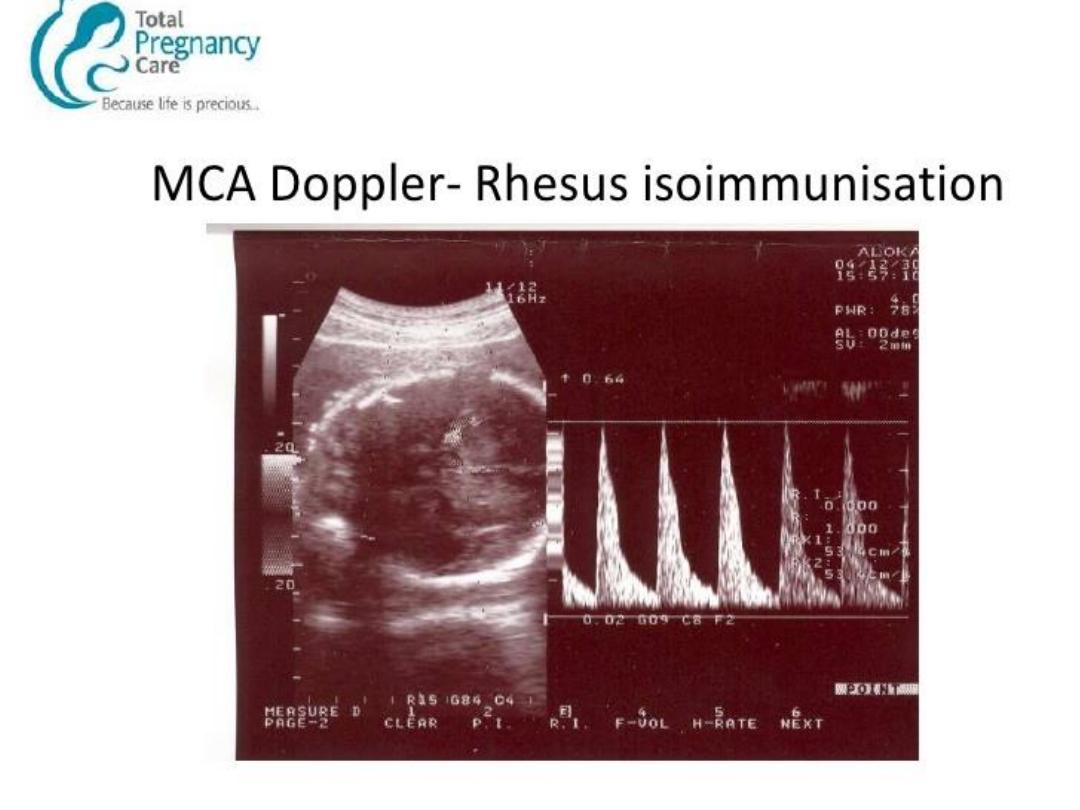
Doppler ultrasound ( MCA-PSV) as long as
titres remain below the "critical" value.
If after 34 weeks and been more than 4 IU so
delivery is indicated.

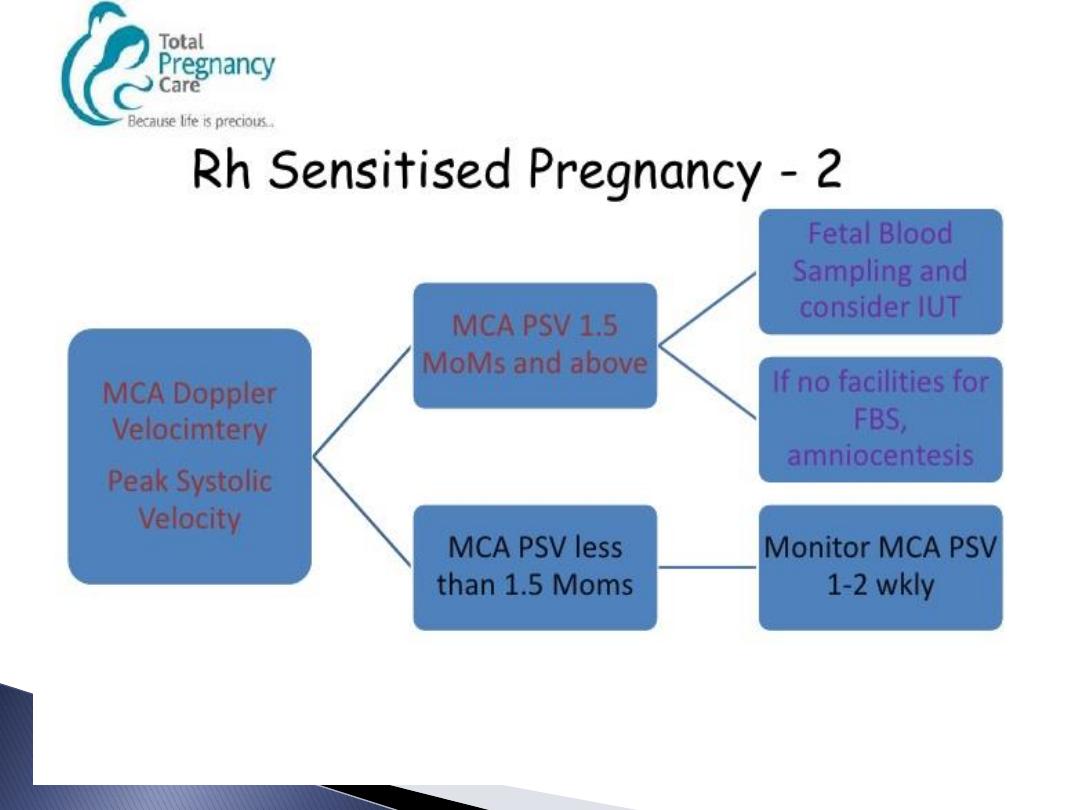
If MCA PSV rises above 1.5 MoM or
antibodies above 4 IU or history of
previous affected foetus refer for foetal
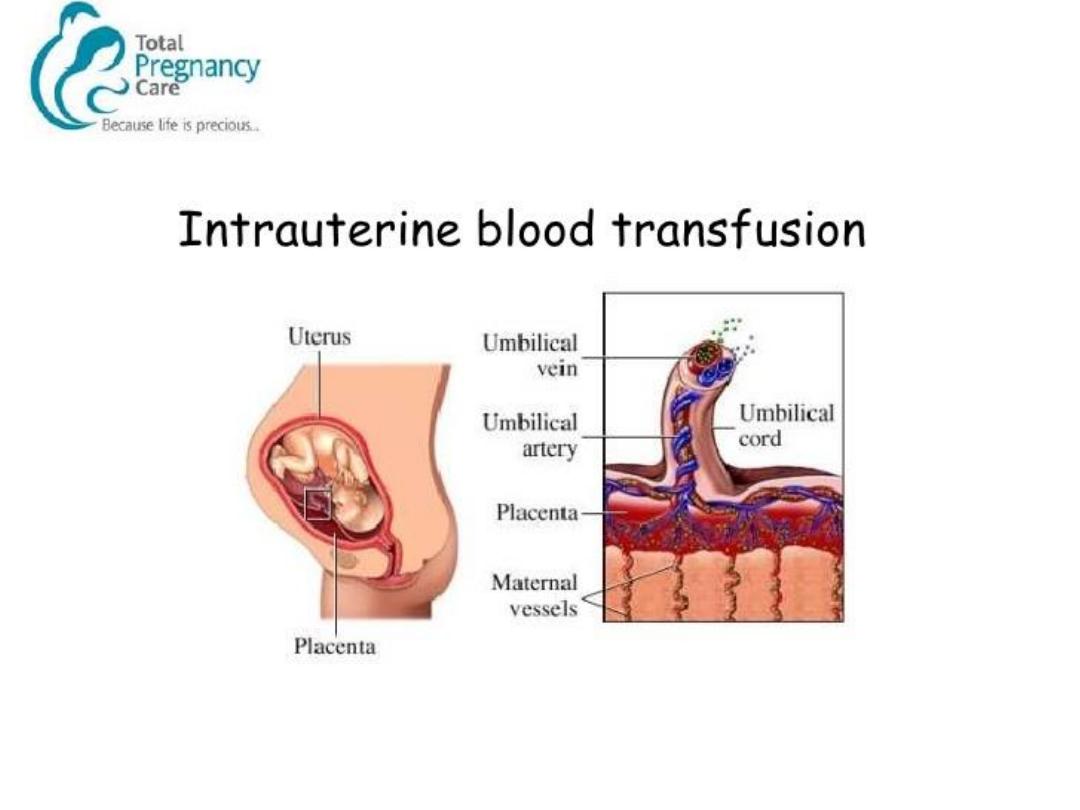
medicine unit for IUT.
Red cell for IUT should be O or ABO
compatible with the foetus CMV
negative , PCV 70 – 85%.It can be
repeated after 3-5 weeks.
Ab. Titre 4 or less than 4
Continue follow up by Ab.T. Every 2-4 weeks
Delivery at term
Ab. Titre above 4
MCA-PSV above 1.5 MO M.
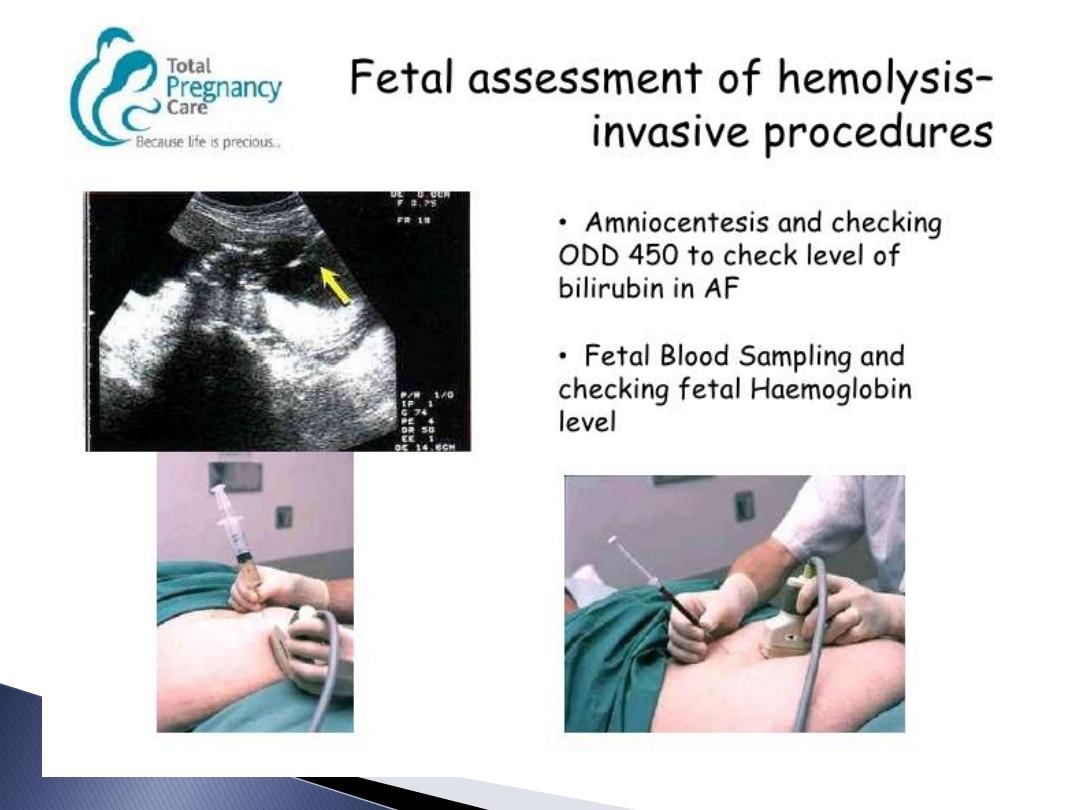
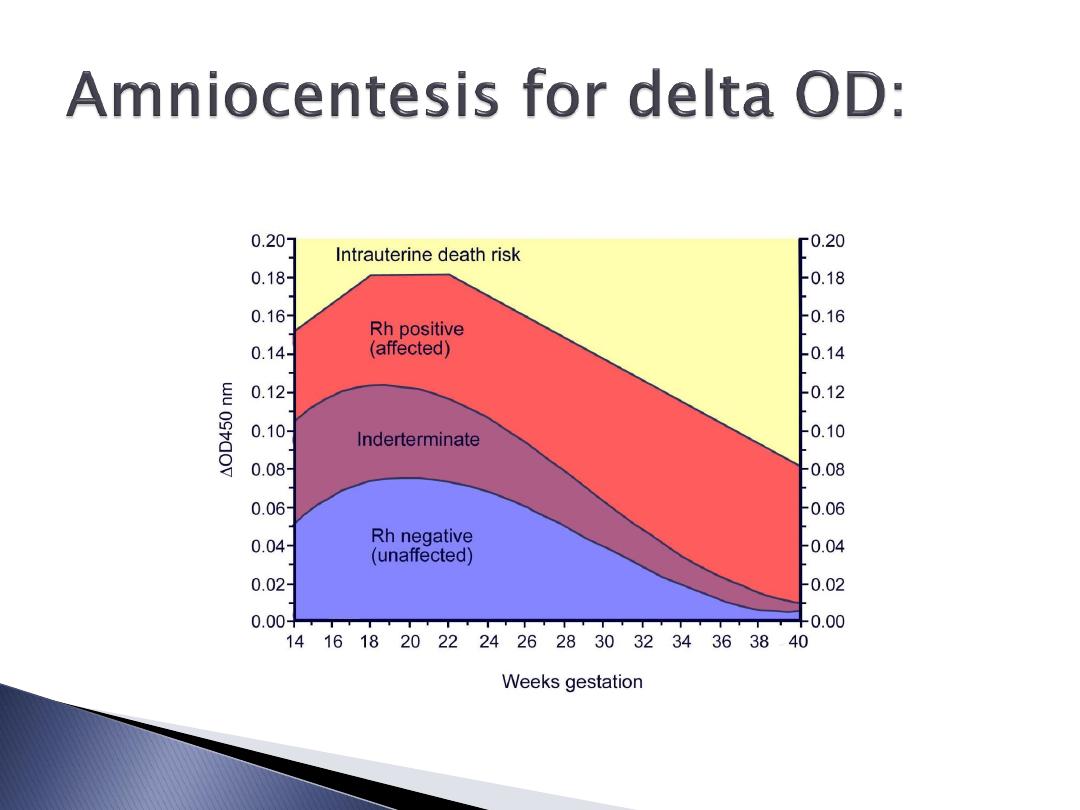
Indication of IUT or termination or Amniocentesis.