}
If a hazardous substance or work process
cannot be eliminated or substituted, then
enclosing it so workers are not exposed to
the hazard is the next best method of
control.
}
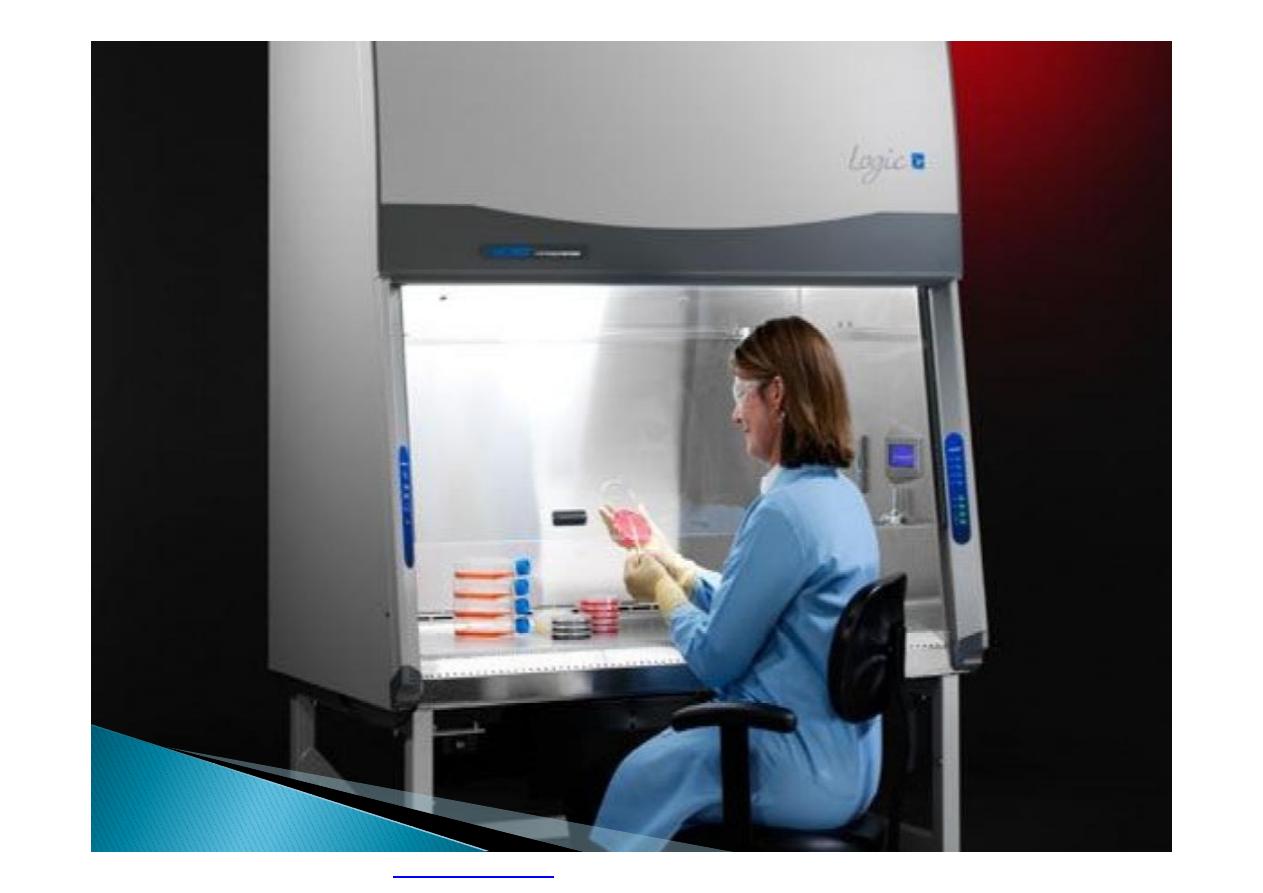
Many hazards can be controlled by partially
or totally enclosing the work process.
}
Highly toxic materials that can be released
into the air should be totally enclosed, usually
by using a mechanical handling device or a
closed glove system that can be operated
from the outside
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Whole areas of a plant can be “enclosed” by
requiring workers to operate those areas
from a control room.
}
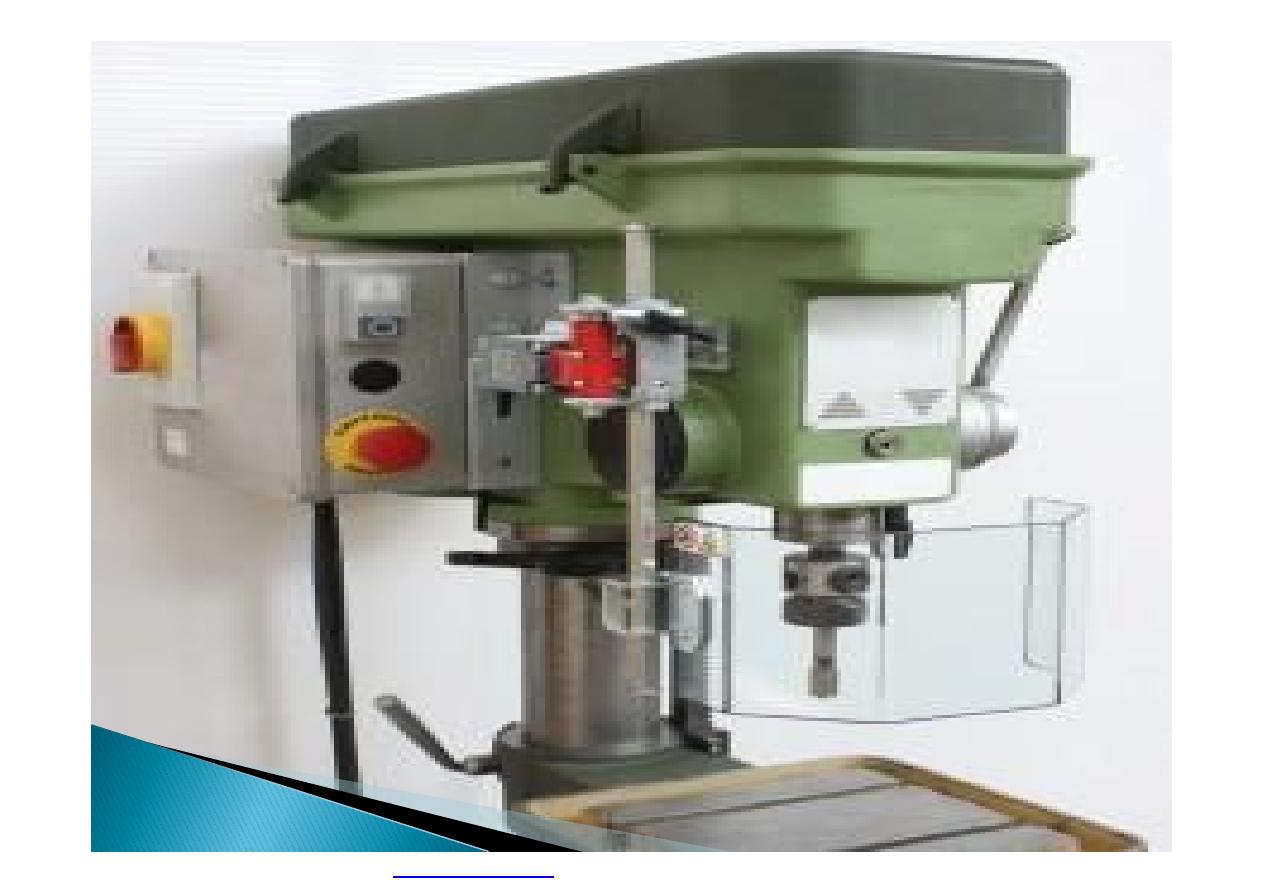
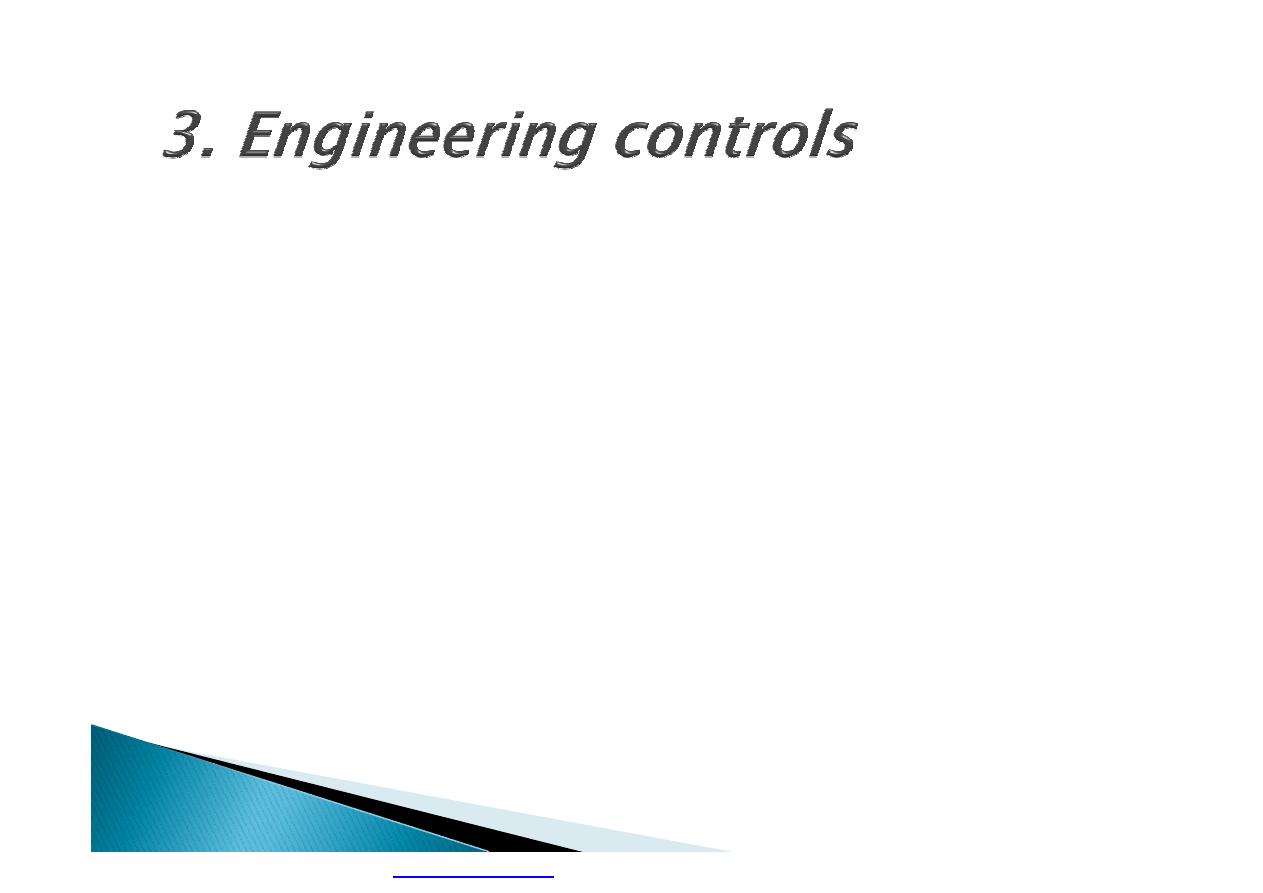
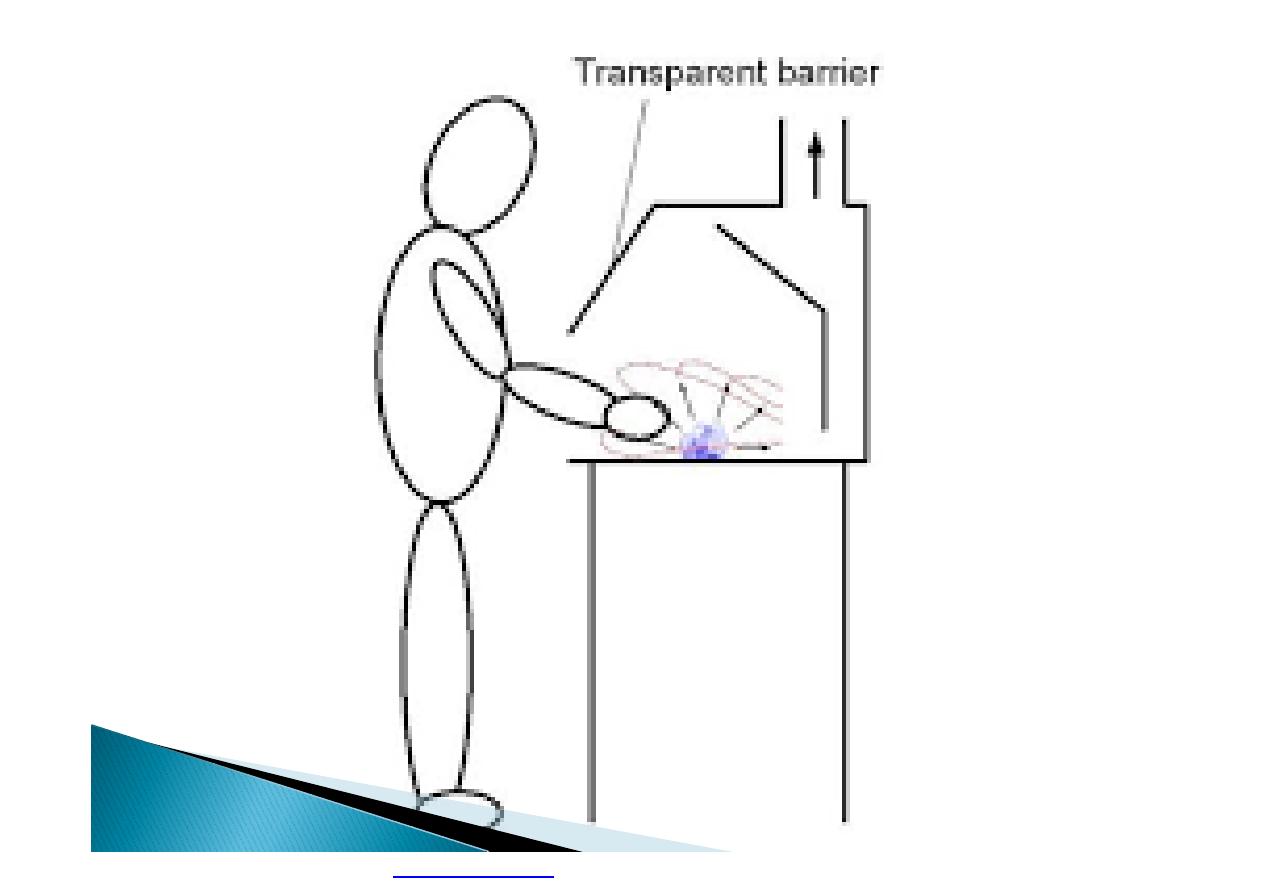
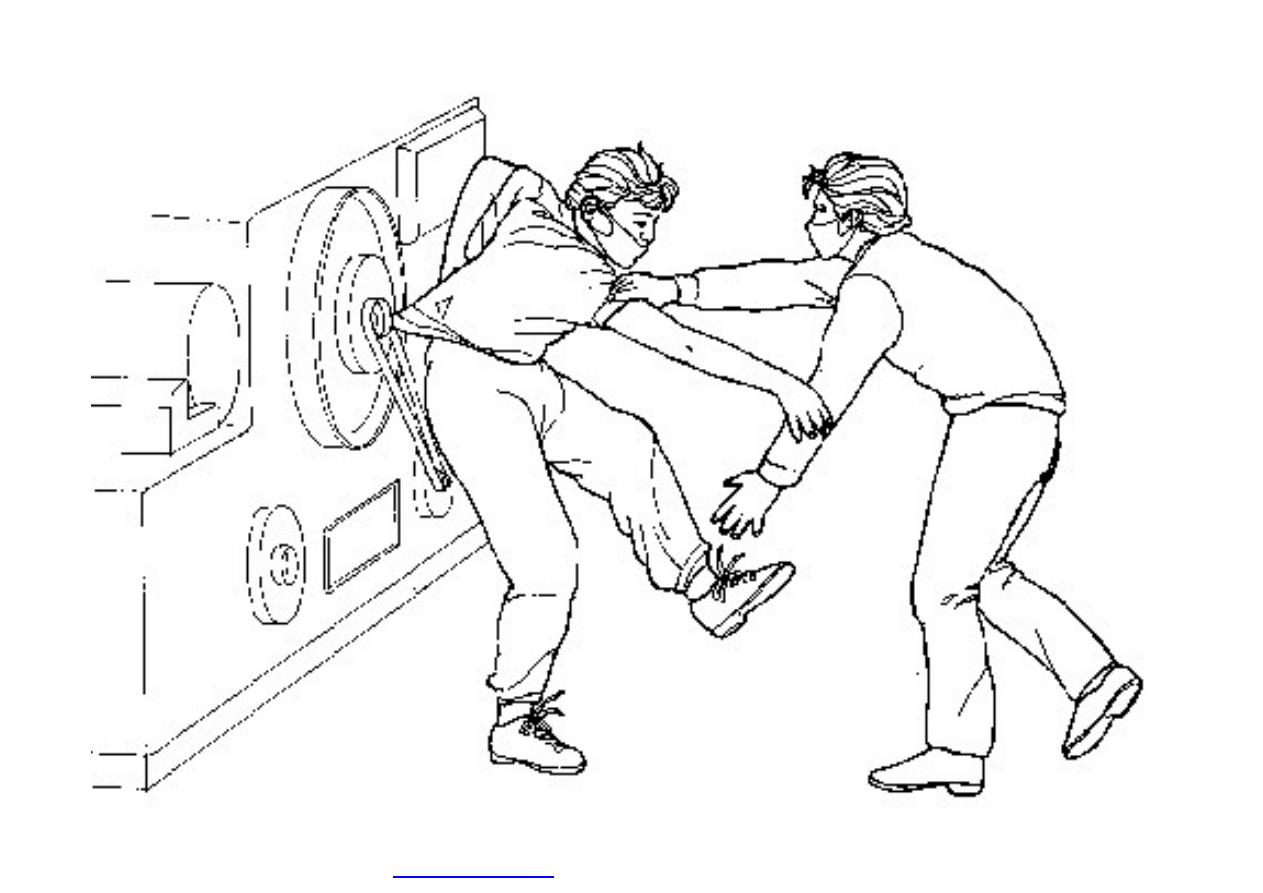
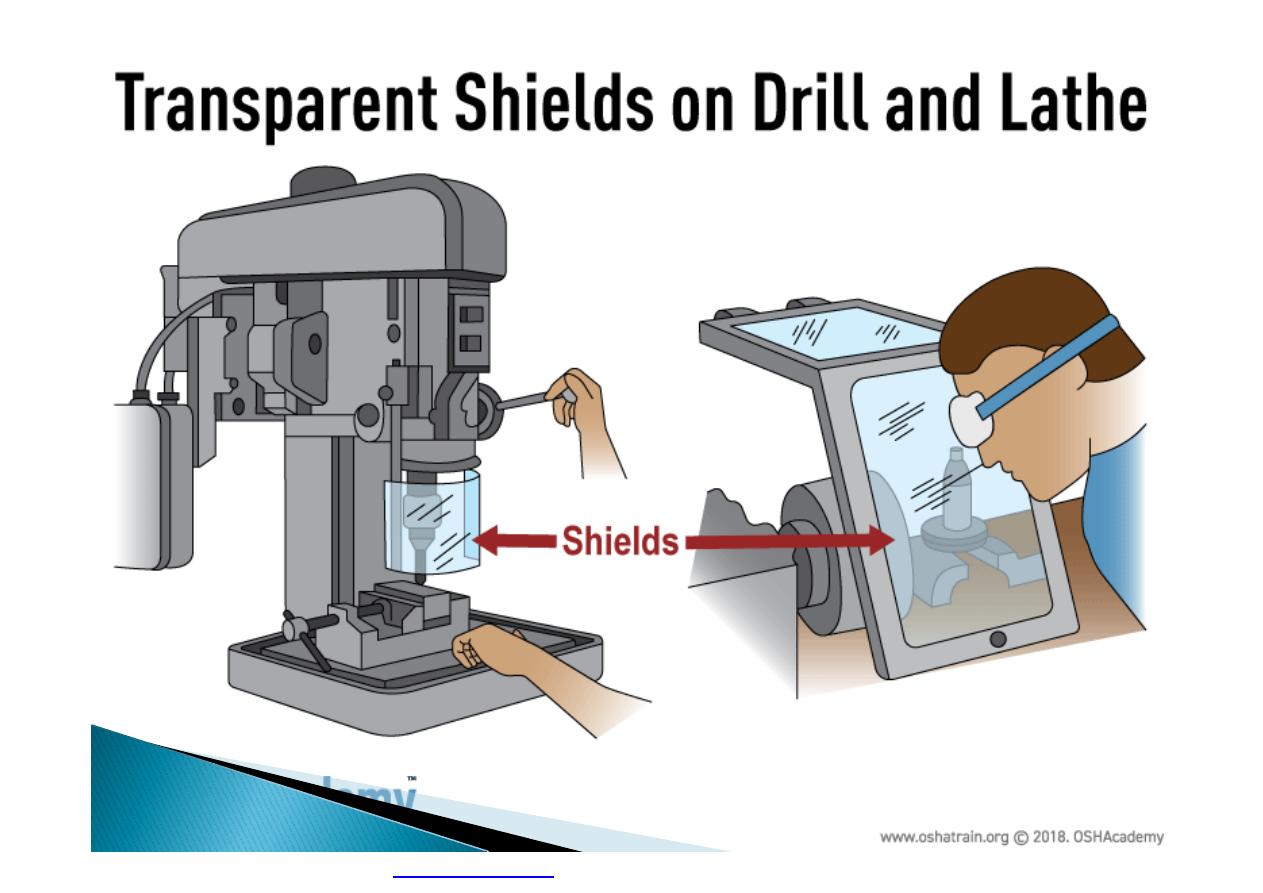
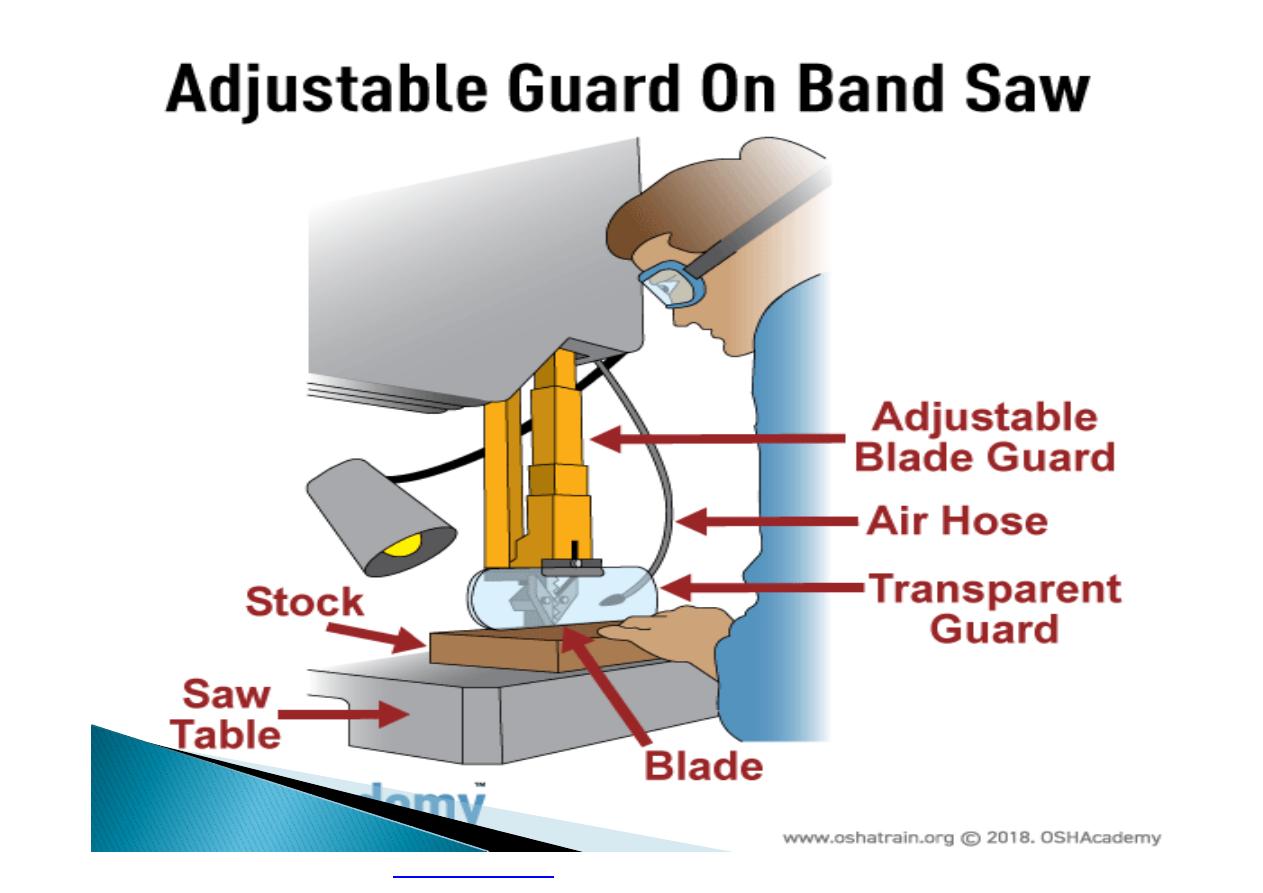
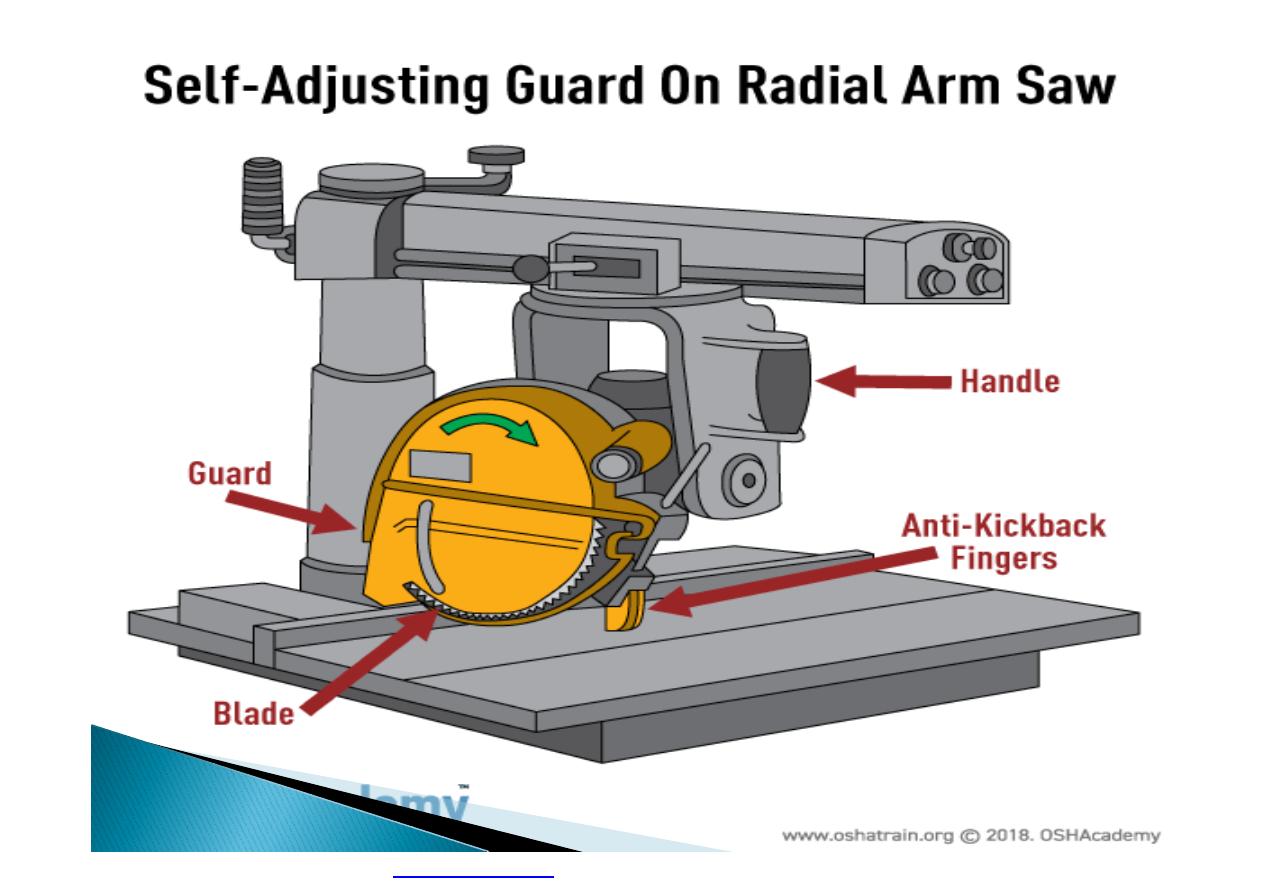
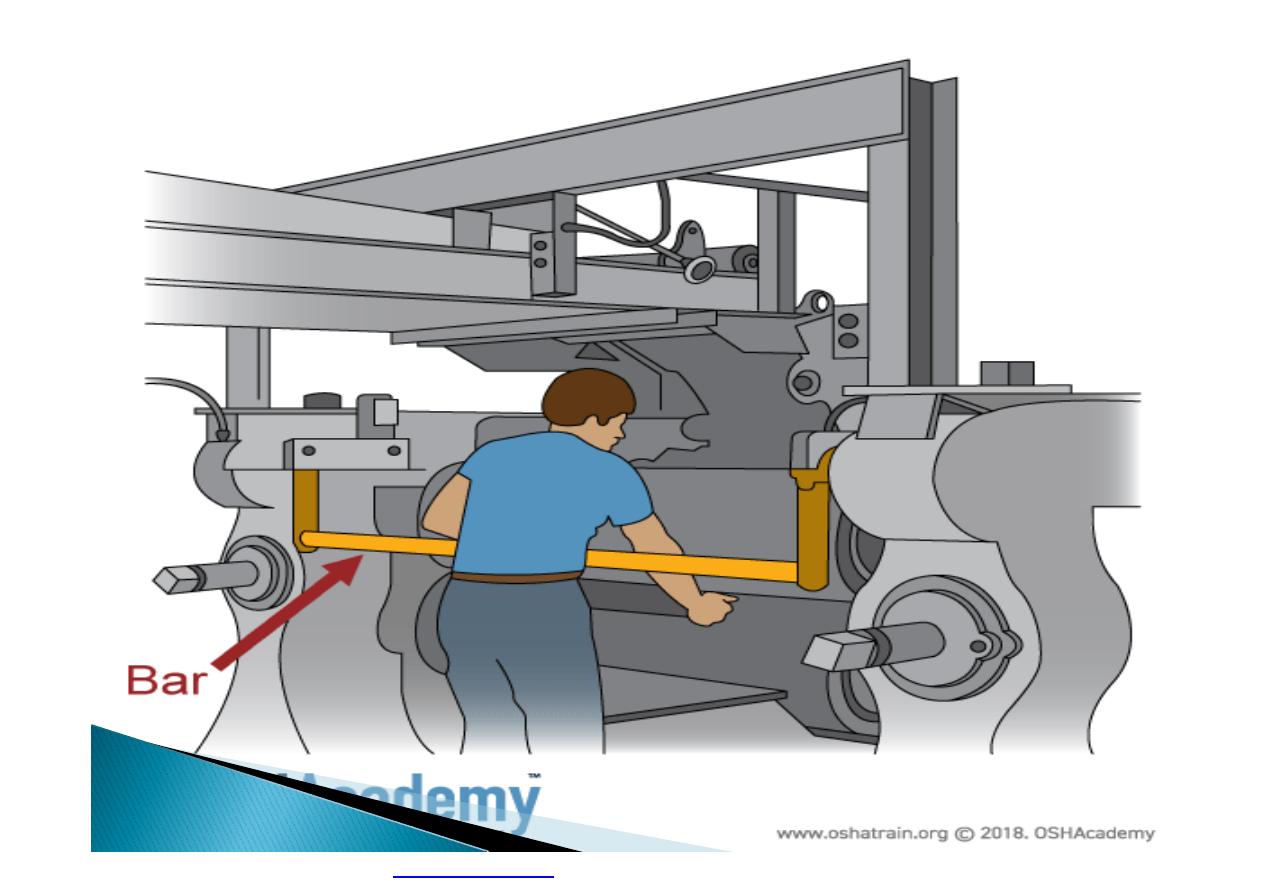
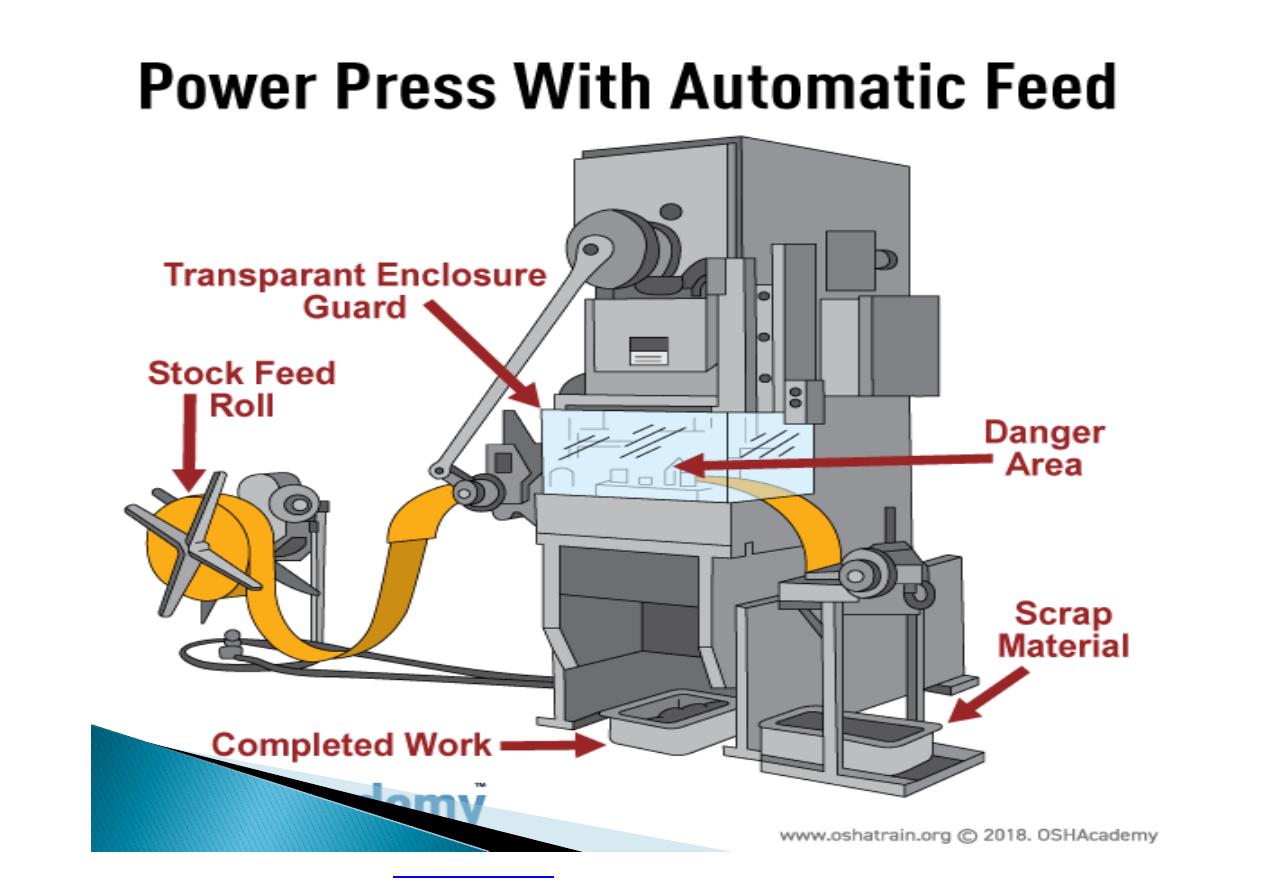
Machine guarding is another form of
enclosure that prevents workers from coming
into contact with dangerous parts of
machines.
}
Some of the areas of a machine that can
injure the worker are: the point of operation
pinch-points; sharp areas, such as blades;
exposed electrical components, which can
cause electrical shock or burns; presses,
which can crush; rotating parts; flying chips
and sparks.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Isolation can be an effective method of
control if a hazardous job can be moved to a
part of the workplace where fewer people will
be exposed,
}
or if a job can be changed to a shift when
fewer people are exposed (such as a weekend
or midnight shift).
}
The worker can also be isolated from a
hazardous job, for example by working in an
air-conditioned control booth.
}
isolating the work process or the worker does
not eliminate the hazard, which means
workers can still be exposed
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Ventilation in the workplace can be used for
two reasons:
}
(1) to prevent the work environment from
being too hot, cold, dry or humid;
}
(2) to prevent contaminants in the air from
getting into the area where workers breathe.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Generally there are two categories of
ventilation:
1.
local exhaust ventilation
2.
general ventilation.
}
Ventilation should be used together with
other methods of control.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
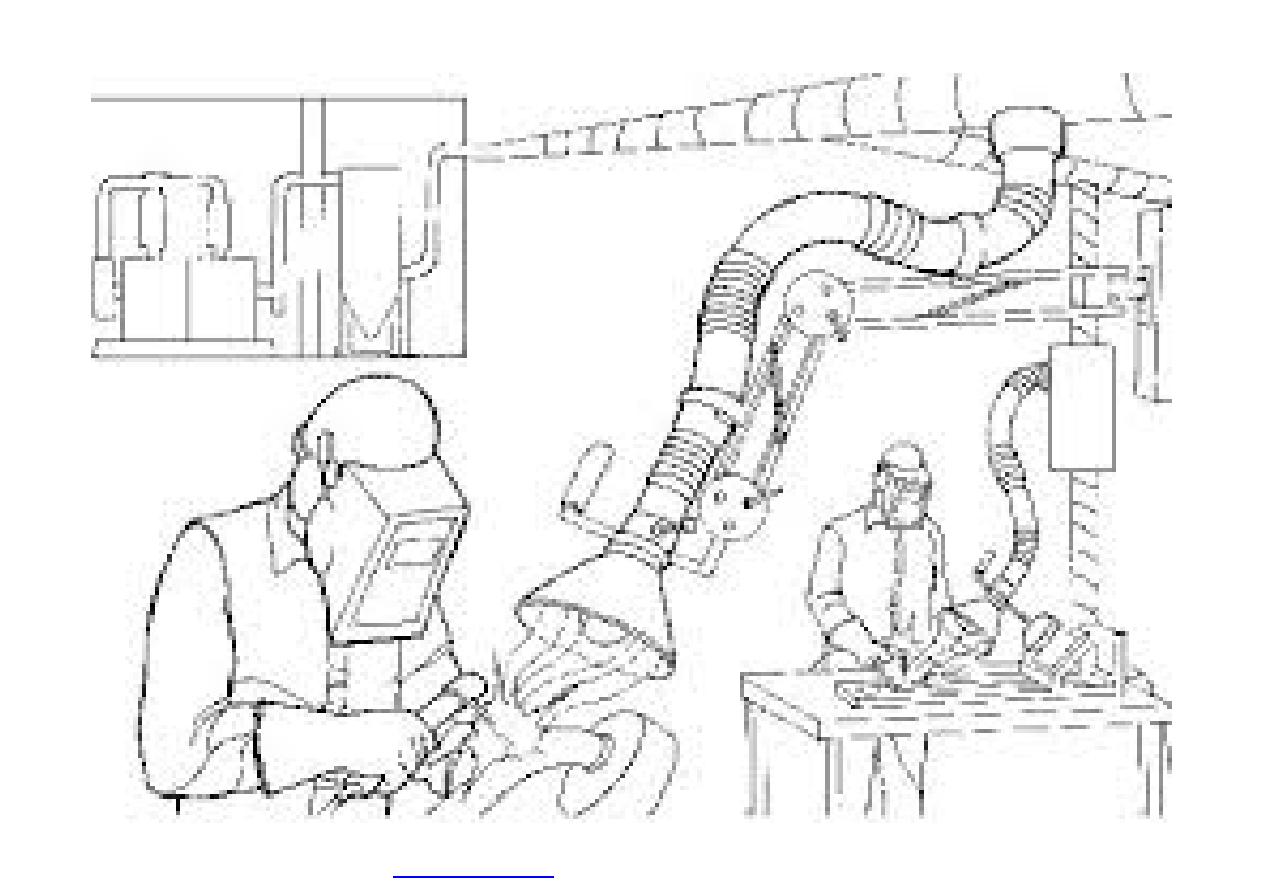
It usually uses suction, based on the principle of
a vacuum cleaner, to remove pollutants from the
air.
}
Exhaust ventilation can include the use of flexible
piping.
}
The end of the pipe that draws in the
contaminants (the inlet) must be placed as close
as possible to the source of the hazard in order
to be effective.
}
Flexible piping is often used to draw welding
fumes away from the worker and to draw away
contaminants in work areas that are hard to
reach.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Which is generally used for keeping the
workplace comfortable.
}
It is one of the least effective methods of
controlling hazards but one of the most
commonly used.
}
The purpose of any general ventilation
system is to remove contaminated air and
replace it with “fresh” air.
}
This system does not really remove
hazardous agents from the air; it simply
reduces the amounts in the air to levels that
are considered “safe” for breathing.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

The effectiveness of a general ventilation
system depends on several things, including:
}
how quickly the hazardous agent is being
released into the air;
}
how much and how quickly fresh air is
coming in;
}
and how the contaminated air is being
removed.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Limiting the amount of time workers spend at
a hazardous job.
}
Used together with other methods of
control to reduce exposure to hazards.
}
changing work schedules (for example, two
people may be able to work for four hours
each at a job instead of one person working
for eight hours at that job);
}
giving workers longer rest periods or shorter
work shifts to reduce exposure time;
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
moving a hazardous work process to an area
where fewer people will be exposed;
}
changing a work process to a shift when
fewer people are working.
}
administrative controls only reduce the
amount of time workers are exposed to a
hazard and they do not eliminate exposures.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is the least
effective method of controlling occupational
hazards and should be used only when other
methods cannot control hazards sufficiently.
}
PPE can be uncomfortable, can decrease work
performance and can create new health and
safety hazards.
}
For example, ear protectors can prevent the
worker from hearing warning signals, respirators
can make it harder to breathe, earplugs may
cause infection, and leaky gloves can trap
hazardous chemicals against the skin.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Hot or humid working conditions decrease
the effectiveness of PPE. Under these
conditions, workers should take frequent
breaks and drink plenty of fluids.
}
If PPE does not fit well it may not protect the
worker; this is particularly important with
respirators.
}
All workers using PPE should be trained on
the proper use, maintenance and limitations
of PPE.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

a. General cleanliness
}
Keeping a clean and organized workplace
}
They will reduces the risk of fire and
accidents and cost effective.
}
At the same time, maintaining a pleasant
working environment can produce higher
productivity
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

b. Personal cleanliness
}
Personal hygiene (cleanliness) is also very
important as a method of controlling
hazards.
}
Employer should provide facilities so worker
can wash and/or take a shower every day at
the end of working shift
}
Eating and smoking away from the work area
help to prevent ingesting contaminants.
}
Worker should leave dirty clothes at work and
if necessary, washing work clothes done
separately not with the family wash.
}
So Worker does not take workplace hazards
home with him.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

C. first-aid facility
}
Every workplace should have first-aid facility
}
Every workplace should have as well adequate
personnel trained to provide first aid.
}
First-aid facilities and trained personnel are
important components of a healthy and safe
workplace.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

*
General control measures of occupational hazards :
1.
Elimination &/or substitution (most effective but
most difficult)
}
( substitute injections by administrating
medication through another route
}
(Usage of unleaded gasoline)
}
Replace flooring with more slip-resistant surface
2.
Isolation of the process . As in x ray room
3.
Total enclosure of the process.
4.
Shielding of the source or worker.
5.
Suppression of the emission .
6.
Locally applied exhausted ventilation.
7.
General ventilation .
10 October 2019
٩٢
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

6.
Reduce time of exposure (Work shift )
7.
Health education to the workers
(information, training and instruction) .
8.
Personal protective equipment.
9.
General cleanliness .
10.
Personal hygiene .
and
10 October 2019
٠٣
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

11. Maintaining control by:
a. pre employment exam
}
Provide a baseline data for further compare and
assessment.
}
to ensure that prospective employees can perform
their jobs safely and effectively.
}
No further deterioration of the health status of the
employee.
}
Adapt the work according to the capabilities of the
worker.
b. periodic medical exam
1.
Routine medical examination.
2.
After long absence medical examination.
3.
After any change in the process or the substances
used at the work
c. monitoring procedures .
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version