
High risky pregnancy
مدرس المادة
م
.
د
.
ميادة كامل محمد
رعاية صحية اولية المرحلة الخامسة

Overview
•
In a high-risk (at-risk) pregnancy, the mother, fetus, or neonate is at
increased risk of morbidity or mortality before or after delivery
•
Pregnancy places additional physical and emotional stress on a
woman’s body
•
Health problems that occur before a woman becomes pregnant or
during pregnancy may also increase the likelihood for a high-risk
pregnancy
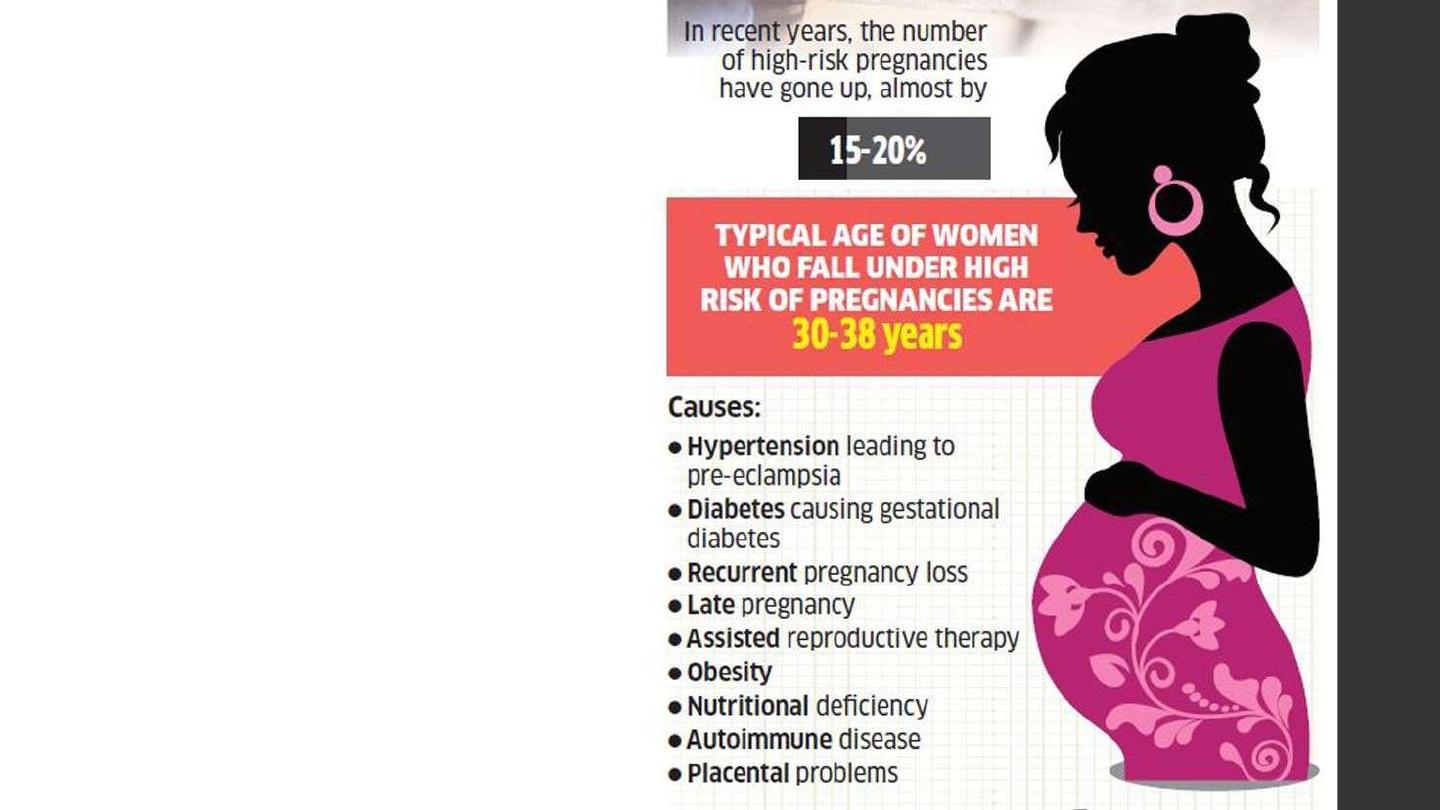

High risk factors of pregnancy and
their management at an ANC clinic
•
Complications can occur during pregnancy and affect the health and survival of the
mother and the fetus
•
Every pregnant woman must receive at least 4 checkups during pregnancy
•
Registration and 1st check-up within 12 weeks, 14-26 weeks, 28-32 weeks and 36-40
weeks)
•
Proper history should be elicited and complete general physical, systemic and
abdominal examinations performed during each ANC visit

High Risk Conditions of pregnancy
not to be missed
•
Severe anemia (Hb <7 mg/dL)
•
Pregnancy induced hypertension, pre-eclampsia, pre-eclampsic toxemia
•
Syphilis/HIV positive
•
Gestational diabetes mellitus
•
Hypothyroidism
•
Young primi (less than 20 years) or elderly gravida (more than 35 years)
•
Twin/multiple pregnancy

High Risk Conditions of pregnancy
not to be missed
•
Malpresentation
•
Previous LSCS
•
Low lying placenta, placenta previa
•
Positive bad obstetric history (H/O still birth, abortion, congenital
malformation, obstructed labor, premature birth etc.)
•
Rh negative
•
Patient with history of any current systemic illness(es)/past history of
illness

Warning signs to be explained to
each pregnant woman
•
Fever >38.5ºC/for more than 24 hours
•
Headache, blurring of vision
•
Generalized swelling of the body and puffiness of face
•
Palpitations, easy fatigability and breathlessness at rest
•
Pain in abdomen
•
Vaginal bleeding / watery discharge
•
Reduced fetal movements
Hypertensive disorders
of pregnancy
•
Hypertensive disorders complicate around 10% of pregnancies
•
Hypertension is defined as BP >=140/90 in two consecutive
readings at any time of pregnancy

Types of hypertensive disorders in
pregnancy
•
Chronic Hypertension
Hypertension that antedates the pregnancy or present before 20 weeks of
gestation
It can be complicated by pre-eclampsia when there is proteinuria as well.
•
Pregnancy induced hypertension
Hypertension after 20 weeks of pregnancy
•
Pre-eclampsia
May present with any symptoms of headache, blurring of vision,
epigastric pain or oliguria and oedema
When the blood pressure is >=140/90 but <160/110 recorded 4-6 hrs apart,
associated with proteinuria > 3 gm/dl in a 24hrs specimen or with
proteinuria trace, 1+ or 2+

Types of hypertensive disorders in
pregnancy
•
Severe pre-eclampsia
The blood pressure is >= 160/110 with proteinuria 3+ or 4+
•
Eclampsia
Eclampsia is the occurrence of generalized convulsion(s), usually
associated with background of pre-eclampsia during pregnancy, labour
or within seven days of delivery
However, it can occur even in normotensive women
Convulsions with >=140/90 and proteinuria more than trace

Likely complications of hypertensive
disorders of pregnancy
Maternal
HELLP syndrome
ARDS
Renal failure
Pulmonary edema
DIC
Fetal
IUGR
IUD
Fetal distress
Prematurity
Anemia during pregnancy
and in the postpartum period
•
Prevalence of Anemia in pregnant women in India is 58.7%
•
Anemia is defined as Hb level < 11g/dl in pregnancy or immediate post partum
period
•
Anemia is grouped as mild (10-10.9g/dl), moderate (7-9.9 g/dl), severe (< 7 g/dl)
•
Iron deficiency anemia is the commonest

Complications due to anemia in
pregnancy
Maternal
Cardiac failure
Susceptibility to infections
Preterm labour
PPH
Sub-involution
Failing lactation
DVT
Fetal
IUGR
Anemia of newborn
Prematurity

Pregnancy with Previous
Caesarean sections
•
About 15% of pregnancies suffer from major obstetric complications
that require emergency care
•
Nearly10% of the total delivery cases may require CS
•
In the past 35 years, the rate of cesarean section has steadily
increased from 5% to approximately 25%
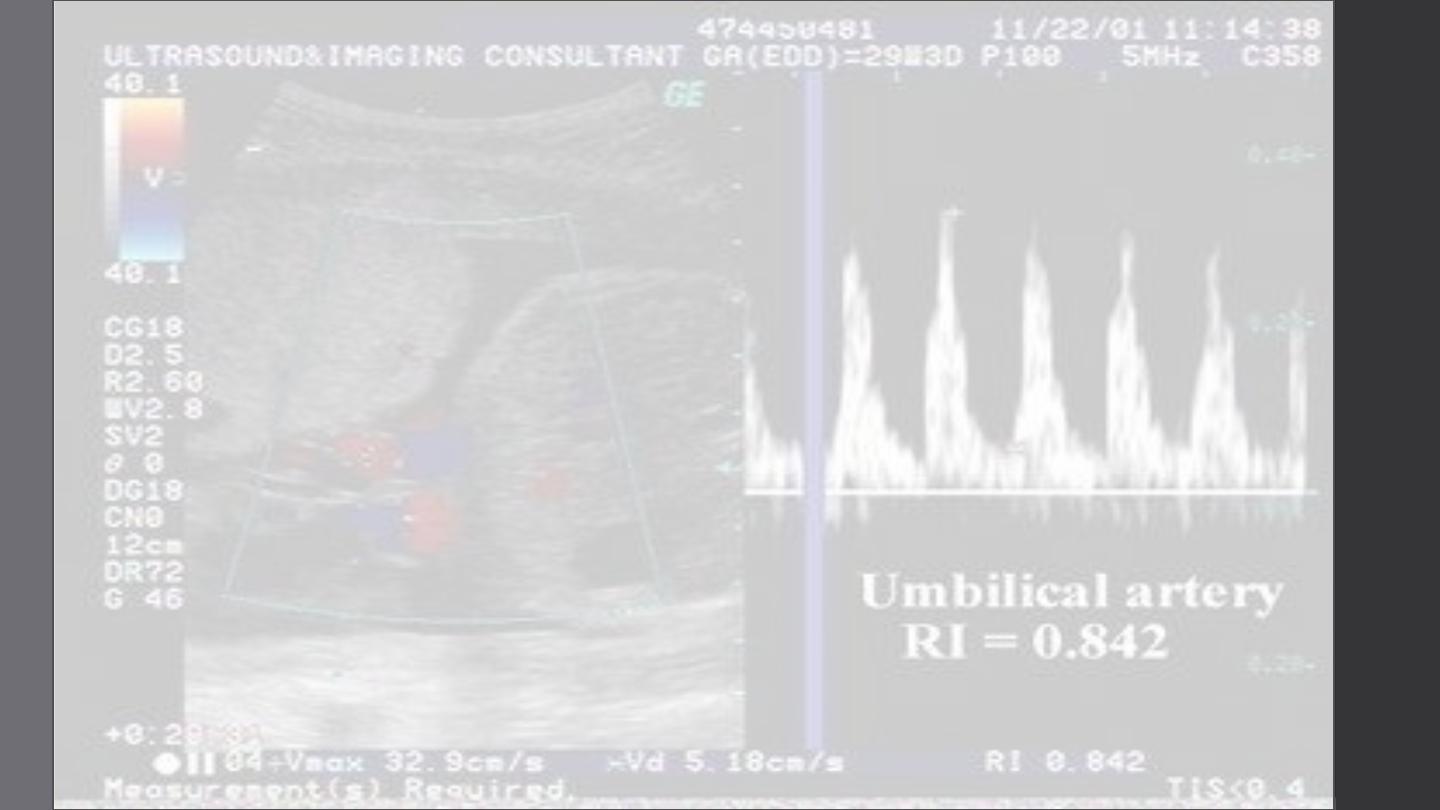
Intrauterine growth
retardation (IUGR)
•
It is referred to birth weight below the 10th percentile for the
gestational age caused by fetal, maternal or placental factors
•
The fetus is healthy but small for gestational age(SGA)
