
P
ERINATAL AND POSTNATAL
CARE

W
ARM
U
P
What are the 3 Stages of Labor?
1. Contractions open the cervix
2. The baby is born
3. The placenta is expelled
T
HE BEGINNING OF LABOR
Lightening
Baby settles deep in the pelvis
Pressure on the upper abdomen is reduced
Mother gets anxious
Happens during the last few weeks of pregnancy for
the first pregnancy.
Women who have already had a baby, may happen
right before labor begins.

E
ARLY SIGNS OF
L
ABOR
The “Show” or “Bloody Show”
Few drops of blood or pinkish vaginal stain that
occurs when the mucus that plugs the uterus during
pregnancy dissolves.
May occur as early as a few days prior to birth.
Water Breaks
Trickle or gush of warm fluid from the vagina
This indicates that the amniotic sac has broken
Delivery should be within 24 to 48 hours

E
ARLY SIGNS OF
L
ABOR
Contractions
Tightening and releasing of the muscles of the uterus
Purpose: to push the baby against the cervix
Fetal Monitoring
Watching the unborn baby’s heart rate for indications
of stress
Usually done during labor and birth.
Most common method is an ultrasound.

S
TAGE
1: C
ONTRACTIONS OPEN
C
ERVIX
What Takes Place?
Contractions come at regular intervals.
How Long Does It Last?
First Child: 6 to 18 hours
Later Children: 2 to 5 hours

S
TAGE
2: T
HE
B
ABY IS
B
ORN
What Takes Place?
Contractions are stronger, pushing the baby through
the birth canal.
How Long Does It Last?
First Child: 1 to 2 hours
Later Children: 15 to 30 minutes

S
TAGE
3: T
HE
P
LACENTA IS
E
XPELLED
What Takes Place?
The placenta comes out.
How Long Does It Last?
10 to 30 minutes

B
REECH
P
RESENTATION OR
P
OSITION
Feet or butt first rather than the head
Babies may have a difficult time moving through
the pelvis area.
Doctors will decide whether a normal delivery is
possible.
Usually a cesarean birth is necessary.

C
ESAREAN BIRTH
Cesarean section or C-Section
Delivery of a baby through a surgical incision in
the mother’s abdomen.
Why:
Lack of normal progress during labor
Discover the baby is distressed or turned the wrong
way
Multiple births
Epidural or anesthesia is used
May need up to 6 weeks for full recovery

N
EWBORNS
A
PPEARANCE
Fontanel- soft spots or open space on the skull;
bones are not yet joined.
EX: Just above the forehead; back of the skull
Appearance: pointed or lopsided due to the passage
through the birth canal.
Eye Color changes – permanent at 3-6 months
Very Large Head- due to the size of the brain.
Milia- tiny, white bumps on baby’s nose and
cheeks.
Lanugo

P
HYSICAL
A
DJUSTMENTS
Circulatory System- Changing temperature.
Baby should be wrapped in a blanket and a knit cap
on their head.
Lanugo- fine, downy hair growing on newborns’
foreheads, backs, and shoulders.
Disappears soon after birth

B
ABY
’
S FIRST
B
ATH
Vernix- thick, white, pasty substance made up of
the fetus’s old skin cells and the secretions of skin
glands.
Protects baby from amniotic fluid

F
IRST
E
XAM
Apgar Scale- system rating the physical
condition of the newborn
Five Factors:
1.
Heart Rate
2.
Breathing
3.
Muscle Tone
4.
Response to Stimulation (crying)
5.
Skin Color
Rating for each factor 0 to 2
Normal Score 6 to 10

O
THER
M
EDICAL PROCEDURES
Hearing Test
Blood Test
Screen for diseases or disorders
Hepatitis B Vaccine

O
THER
H
OSPITAL
C
ARE
Weigh, measure, and dry baby
Apply antibiotic to baby’s eye
Inject Vitamin K to prevent rare bleeding
disorder
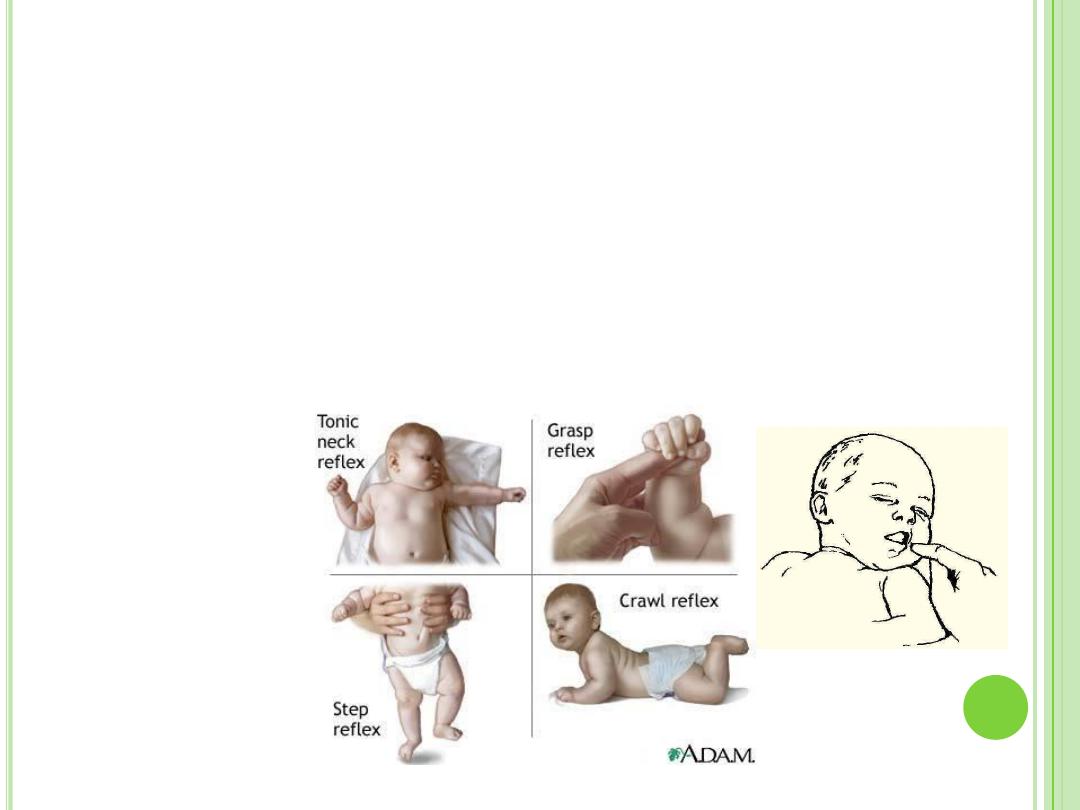
N
EWBORNS
R
EFLEXES
Instinctive automatic responses
Involuntary → voluntary
Sneezing & swallowing continue throughout life
Reflexes that last until voluntary control is
developed:
Rooting
Grasp
Startle
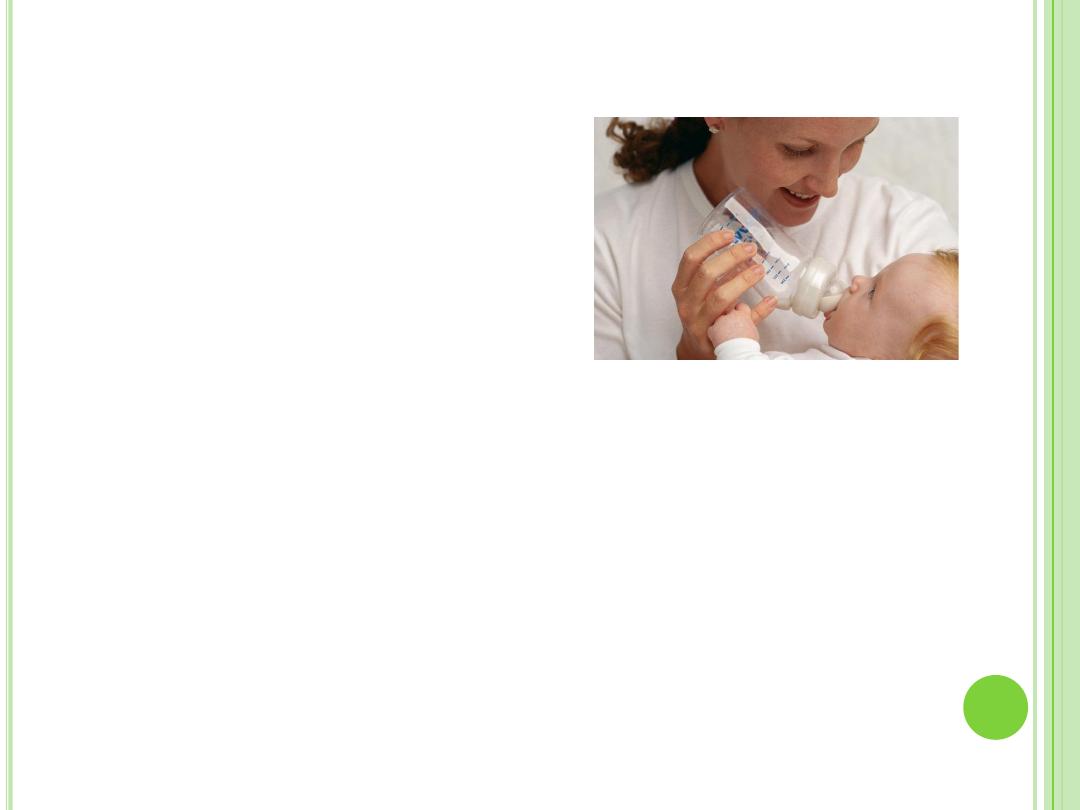

C
ARING FOR
N
EWBORNS
Feeding
Every 2-3 hours
Sleeping
Average of 15 hours per day
Exercise
Actively moving arms and legs to gain strength and
control
Safe, clean, and warm
Diaper and bathe
Close watch
N
EONATAL PERIOD
First month after the baby is born
Major adjustments for mother and baby.
Bonding- forming emotional ties between
parents and child.
Ways to Bond:
Touching the check
Holding the baby close
Talking to the baby
Singing
Breast feeding / Bottle feeding

B
RAIN
D
EVELOPMENT
Bonding helps with brain development.
During the first year, a baby’s brain cells are
making millions of connections.
Parents efforts to bond with the baby helps build
connections in the brain.
Interactions, such as holding or singing, help
strengthen the baby’s brain development.

B
REAST FEEDING
Colostrum-
A high calorie, high protein early breast milk.
Provides protection from illnesses; builds immunity.
Satisfies the baby’s appetite

J
AUNDICE
Condition that causes the baby’s skin and eyes to
look slightly yellow.
Occurs in more than 50% of newborns
Why: the liver cannot remove bilirubin
Bilirubin- a substance produced by the breakdown
of red blood cells.
Baby’s body is producing too much or not able to get
rid of it fast enough
If Jaundice is left untreated, it can damage the
nervous system
Treatment- newborn is placed under an
ultraviolet light that is absorbed by the baby’s
skin.

P
OST
N
ATAL
C
ARE OF THE
M
OTHER
New mothers have specific physical and
emotional needs
Doctor or nurse discuss these needs before mother
and baby go home
A general expectation is that by 6 weeks after birth a
woman's body will have recovered sufficiently from
the effects of pregnancy and the process of parturition

P
OSTNATAL
C
ARE
The time following the baby’s birth
Physical Needs:
Rest
Exercise- stretching and walking
Good Nutrition-
Medical Checkups- 4 to 6 weeks after birth
Emotions:
Confused
Mood Swings
Baby blues- crying, irritated, lonely, anxious, or sad
Postpartum depression- very sad, cry a lot, have
little energy, feel overly anxious or little interest in
baby.

R
ECOVERY
A
FTER
C
HILDBIRTH
Physical Needs
Recover from pregnancy and birth
Regain fitness
About 12 pounds is lost during birth (baby, placenta, fluids)
4 pounds by the end of 1
st
week (water weight)
Takes a few months
Must take of herself in order to properly take care of
baby
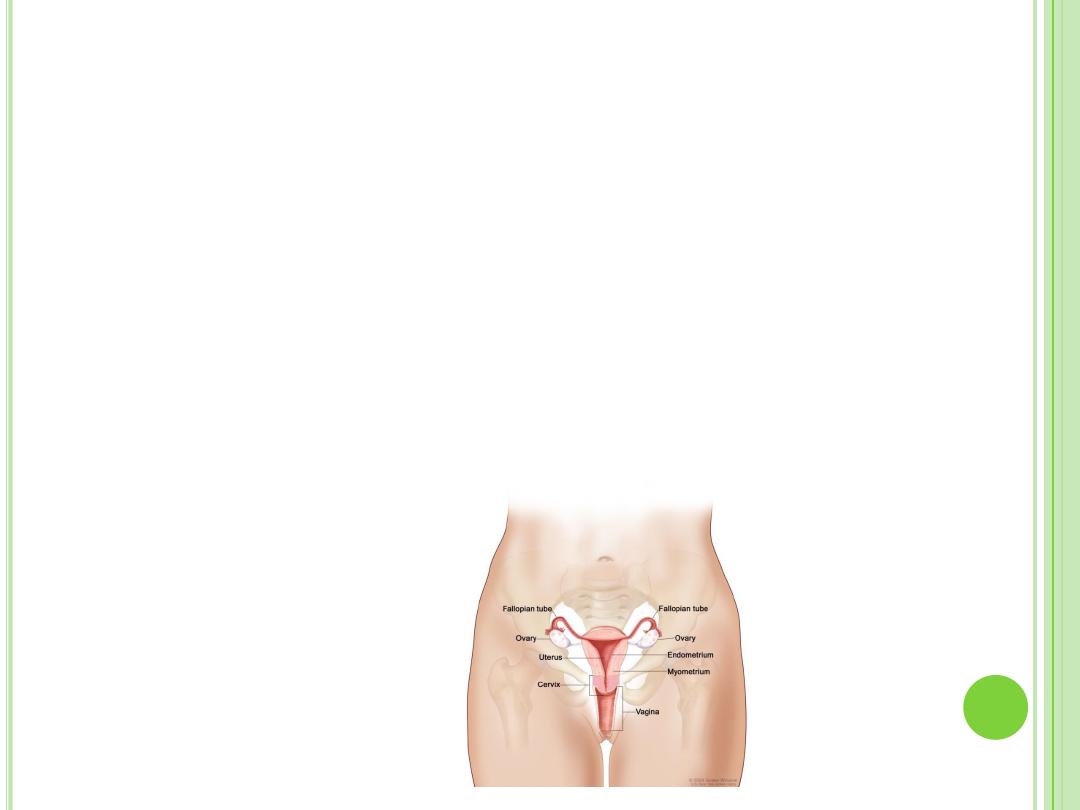
R
ECOVERY
A
FTER
C
HILDBIRTH
Uterus
Shrinks back to its previous size and location
May feel it contracting
As uterus shrinks, abdomen tightens
Fluid
Additional fluid stored during pregnancy
New mothers perspire more and urinate more to rid the
excess fluid

R
ECOVERY
A
FTER
C
HILDBIRTH
Physical Needs
Rest
Exercise to decrease body weight
Nutrition
Medical Checkup
4-6 weeks after birth
Postnatal checkup
Check uterus and any problems(PPH)

R
ECOVERY
A
FTER
C
HILDBIRTH
Postnatal Care (after childbirth)
Rest and sleep
Nutrition
Postnatal checkup
Exercise(pelvic floor)
