
Malignant skin
tumors
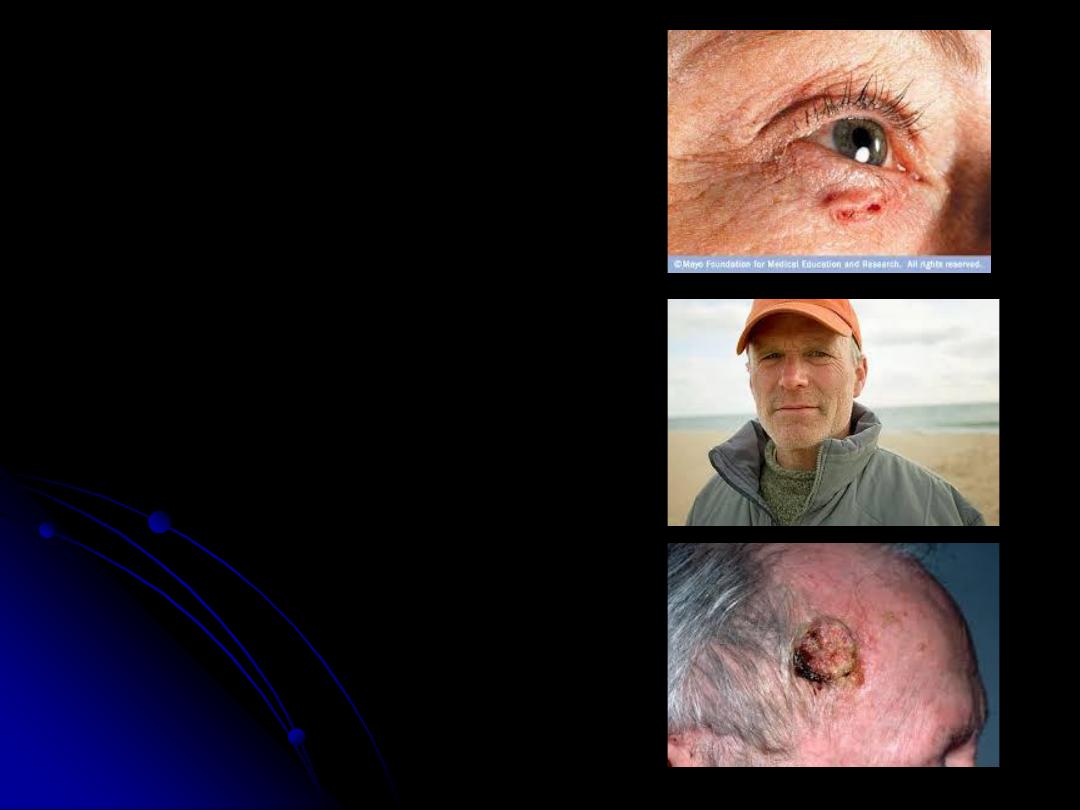
Basal Cell Carcinoma
---------------------------------
-The commonest skin cancer.
-Typically affects individuals between the age of 40
and 79 years.
- more than 50% are males.
- more than 85% occur in the head and neck region.
Common site in the face is above the line joining the
angle of the mouth and the ear lobe. Most common
site of presentation is the medial canthal area on the
lower lid.
- more common in sun exposed parts of the body.
- more in fair(white)skin peoples.
- common in those who spend long time working
outdoors like farmers and sailors (chronic
accumulative sun exposure).
- UV light type B(in sun light) has a role as
carcinogenic factors.
- basal cell carcinoma usually grow slowly, but
locally invasive and penetrate deeper tissues, so it is
called rodent ulcer. Metastasis is rare.
- The patient gives a history of “spot” that fails to
heal.
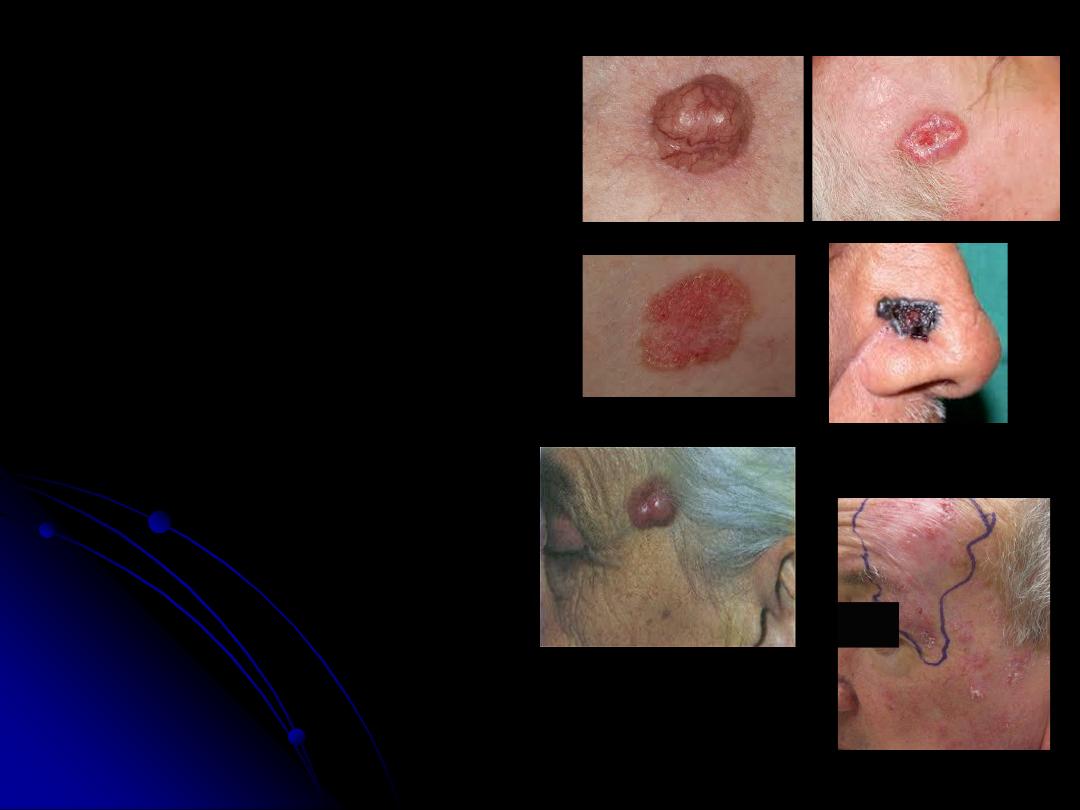
- There are
5 clinical types of BCCs
:
1.
Nodular
. typical presentation as
a nodular appearance with a pearly
rolled edge and telangiectatic
vessels.
2.
Superficial
.
3.
Cystic
.
4.
Pigmented
.
5.
Morphic
.
-Differential diagnosis; Squamous
cell carcinoma, solar keratosis,
Malignant melanoma.
- Diagnosis by history, clinical
examination and biopsy.
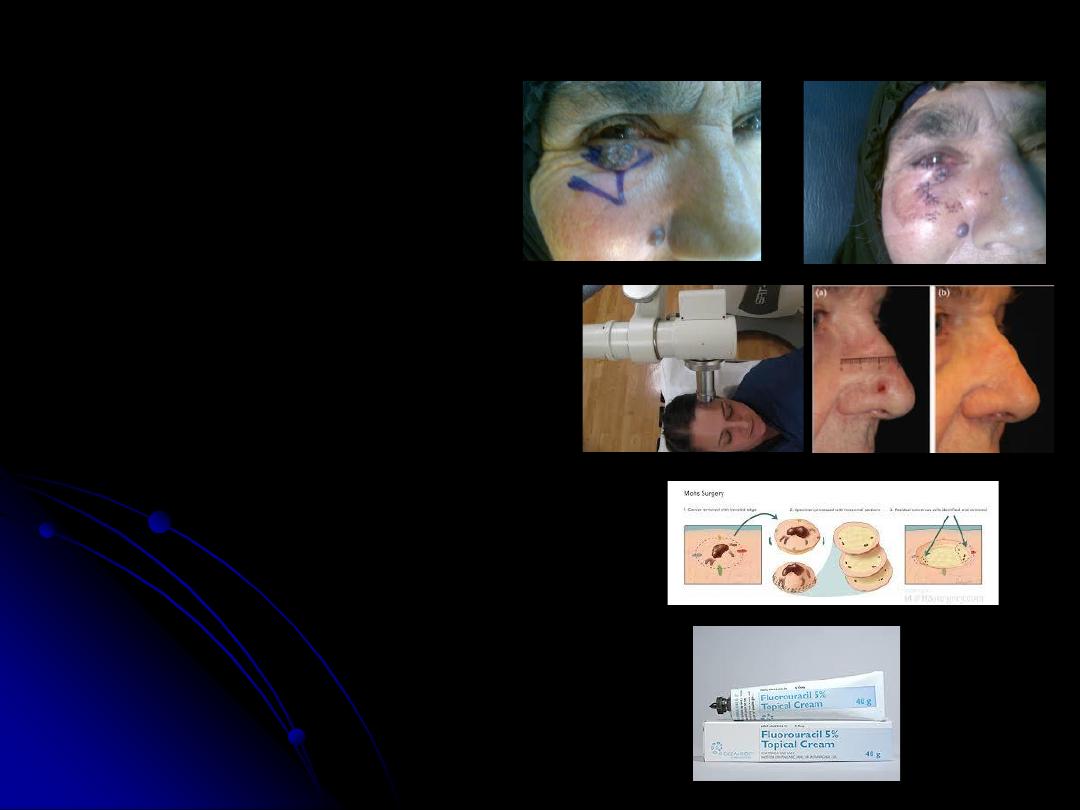
-
Treatment:
1.
Surgery
as excision of tumor
with safe margin of 2-5mm.
2.
Radiotherapy
.
3.
Laser
.
4.
Cryosurgery
.
5.
Mohs’ surgical technique
.
6.
Curettes and
electrodessication
.
7.
Chemotherapy as 5 flouro
Uracil.(5FU).
- The recurrence rate is less
than 10% in all modalities of
treatments except with
chemotherapy is about 20%. In
case of Recurrent BCC the
recurrence rate is about 34%.
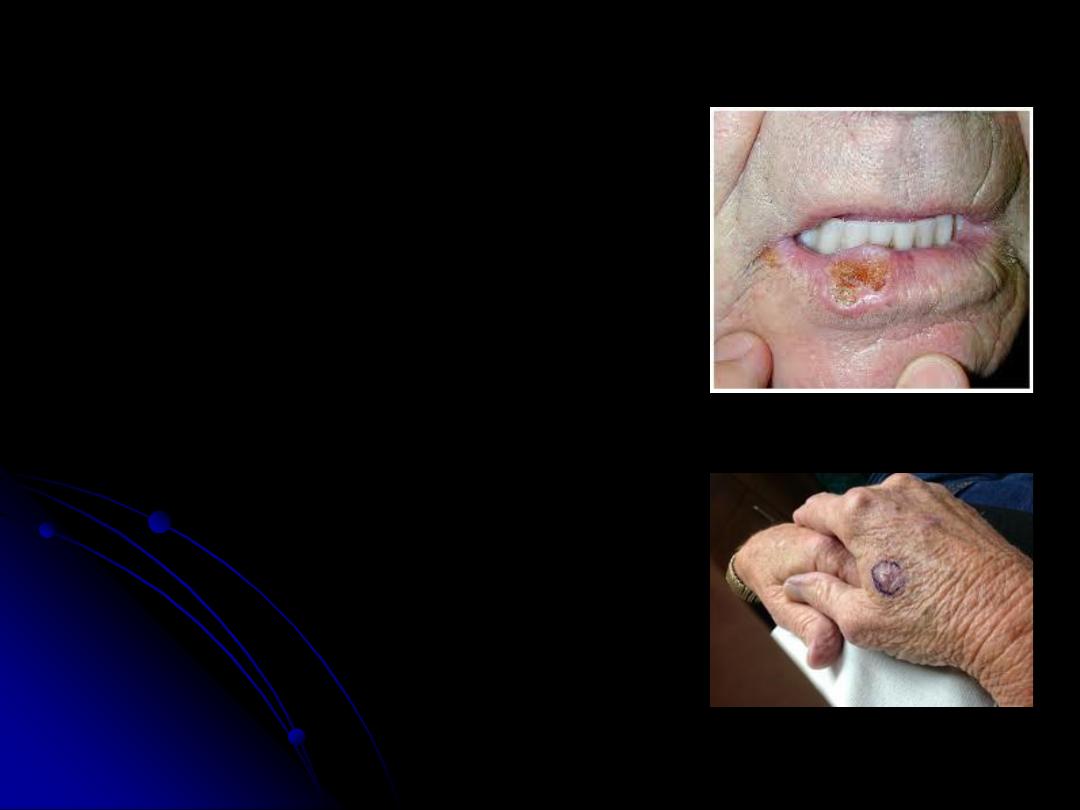
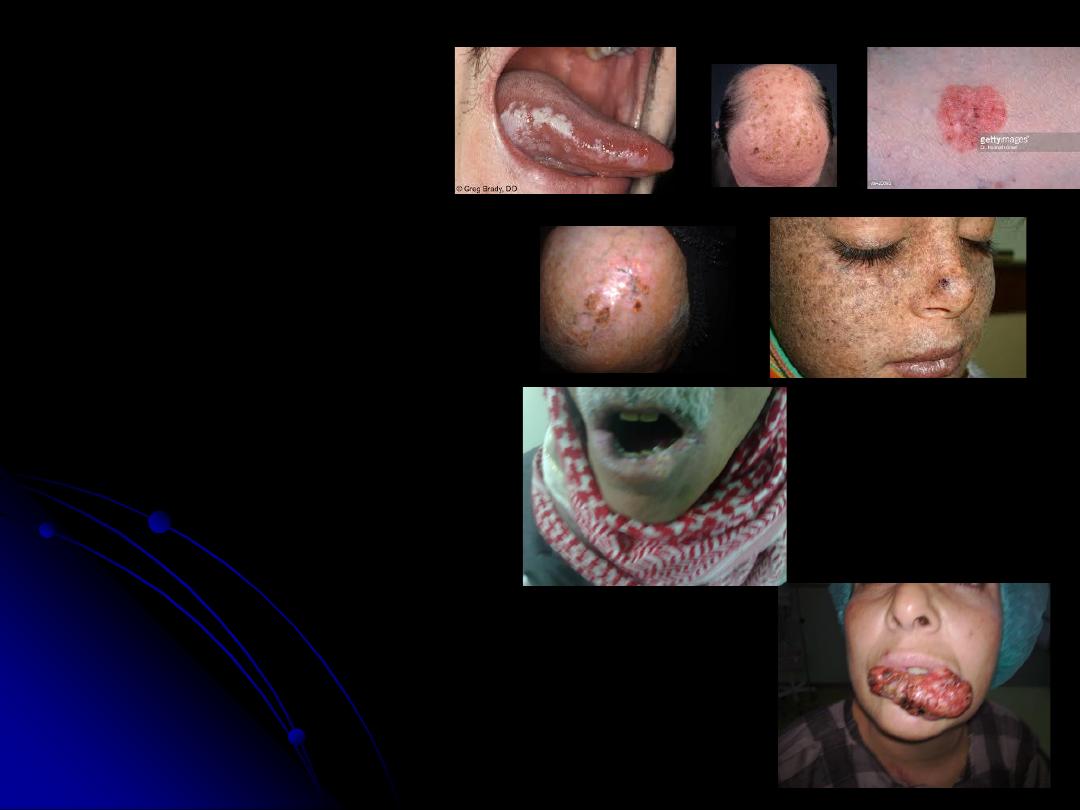
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-cell of origin is the keratinocytes(keratinizing
epithelium, spindle cells) .
-Etiology;
1. solar radiation: chronic accumulative exposure
to sun light (UV type B),so it is common in those
working outdoors for long periods as farmers &
sailors, & it is common in sun exposed parts of the
body mainly face & hands, in the face the common
site is the area below the line joining the angle of
the mouth and the earlobe, 95% of SCC occur in
the lower lip.
2. chemicals as smoking &spicy food.
3.chronic ulcers & skin diseases as pressure ulcers,
osteomyelitis(with discharging sinus), old
scars(results in SCC called Marjolin’s ulcer),
radiation dermatitis, Discoid lupus erythematosis,
solar (actinic) keratosis,-----e.t.c.
4.hereditary factors: as SCC is common in those
with blue eyes &fair skin, also is common in those
with Xeroderma pigmentosa & Albinism.
-
Premalignant conditions
are;
1.
Leukoplakia
.
2.
Solar keratosis
.
3.
Bowen’s disease(SCC in situ).
4.
Radiation dermatitis
.
5.
Xeroderma pigmentosa
.
-Types:
Clinical types
:
1.Slow growing type
, verrucous nature,
exophytic. It is locally invasive & could
metastasize.
2.Rapid growing type
, nodular and
indurated. Early ulcerate with local
invasion & high rate of metastasis.
-
Histopathological types
:
1.Well differentiated type
with high
survival rate(CL.1).
2.poorly differentiated type
with poor
prognosis(CL.2).

-
Metastasis
: local invasion &
destruction, lymphatic, and
hematogenous metastasis.
-D.D.; solar keratosis,
Keratoacanthoma, BCC,
Chronic skin diseases.
-Diagnosis: history, clinical
examination & biopsy.
-Treatment: same modalities
used for BCC, but with surgery
the safe margin is 1cm in the
face & 7cm in other areas of the
body.
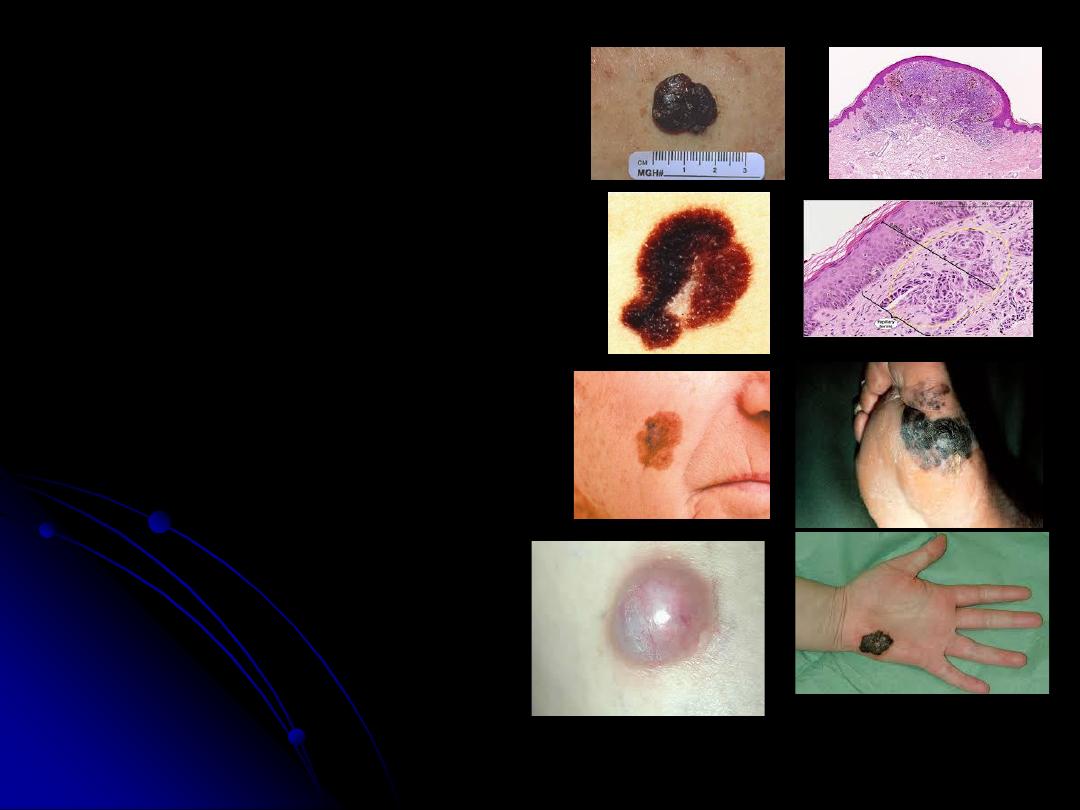
Malignant Melanoma
-cell of origin is Melanocytes.
-etiology; sun light mainly type C.
-common in sun exposed parts.
-premalignant conditions are
naevi(different types), Lentigo maligna.
-Clinical types:
1. Suprerficial spreading type
. With
high 5-year survival rate(90%).
2.
Nodular type
. With 5-year survival
rate less than40%.
3.
Lentigo maligna melanoma
. Common
in old age people and sun exposed parts.
4.
Acral lentigenous melanoma
.
Common in black skin peoples,
mucocutaneous junctions(lips &
perianal areas), palm and sole.
5.
Amelanotic melanoma
.
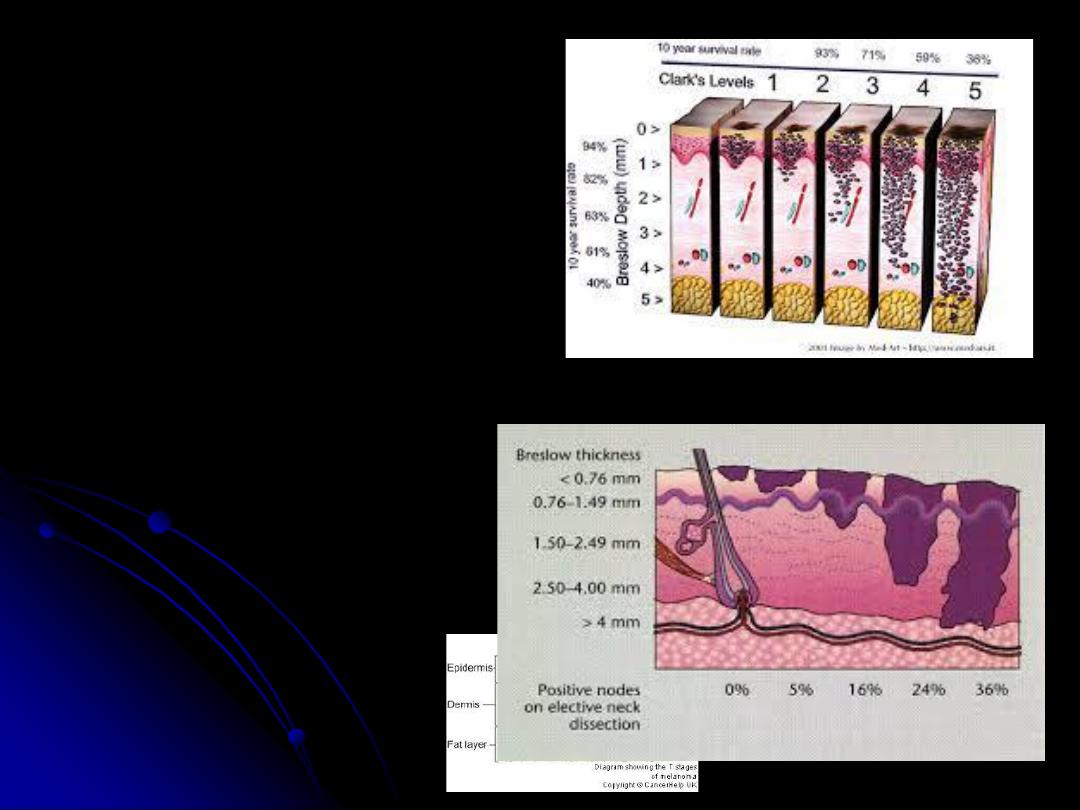
-
Histological grading
:
Clark’s levels
:
I
within the Epidermis.
II
within the papillary dermis.
III
at interface between
papillary and reticular dermis.
IV
at level of reticular dermis.
V
invades to the
subcutaneous tissue.
Breslow’s thickness(levels
):
-
less than
0.76
mm.
-
0.76-1.5
mm.
-
1.5-4
mm.
-
More than
4
mm.
Metastases
1. Locally invasive.
2. Lymphatic to the regional lymph nodes, melanoma in-
transit is a pigmented lesion between the original
lesion & the regional lymph nodes (which indicate
presence of malignant cells in lymphatic vessels).
3. Hematogenous
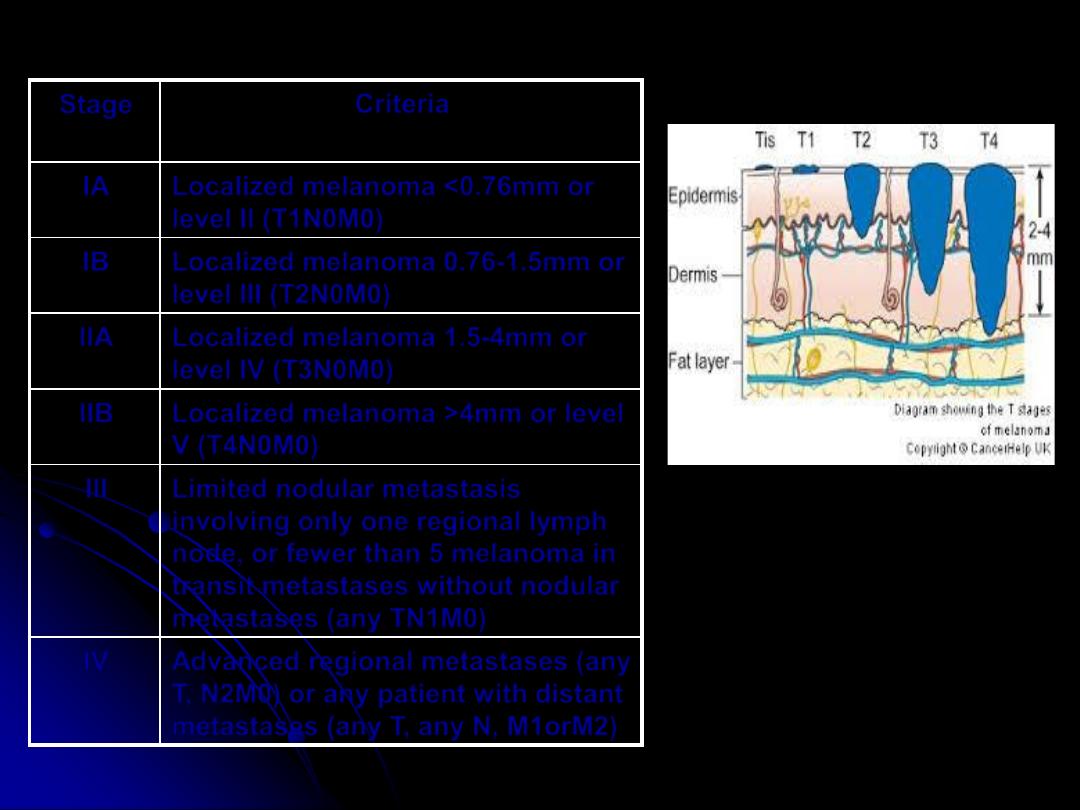
Criteria
Stage
Localized melanoma <0.76mm or
level II (T1N0M0)
IA
Localized melanoma 0.76-1.5mm or
level III (T2N0M0)
IB
Localized melanoma 1.5-4mm or
level IV (T3N0M0)
IIA
Localized melanoma >4mm or level
V (T4N0M0)
IIB
Limited nodular metastasis
involving only one regional lymph
node, or fewer than 5 melanoma in
transit metastases without nodular
metastases (any TN1M0)
III
Advanced regional metastases (any
T, N2M0) or any patient with distant
metastases (any T, any N, M1orM2)
IV
Staging: TNM Staging
D.D; pigmented BCC, Naevi.
Diagnosis; History, clinical
examination, and biopsy.
Treatment:
1.Surgical excision. safe margin
3cm.
2.Radiation.
3.Chemotherapy.
4.Immunotherapy.
