BENIGN SKIN
TUMOR
Benign tumor
: grows by
expansion without invasion of
the extra-cellular matrix .
Malignant
tumor(cancer):
grows by
invasion into the extra-cellular
matrix.
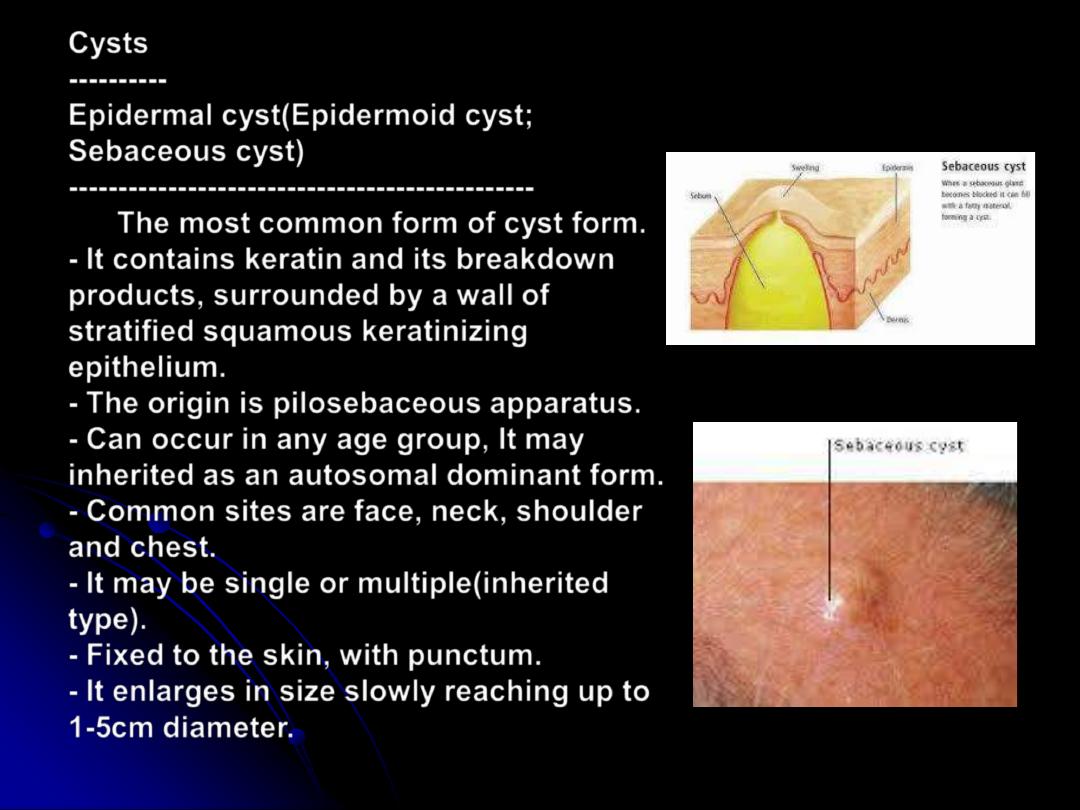
Cysts
----------
Epidermal cyst(Epidermoid cyst;
Sebaceous cyst)
-----------------------------------------------
The most common form of cyst form.
- It contains keratin and its breakdown
products, surrounded by a wall of
stratified squamous keratinizing
epithelium.
- The origin is pilosebaceous apparatus.
- Can occur in any age group, It may
inherited as an autosomal dominant form.
- Common sites are face, neck, shoulder
and chest.
- It may be single or multiple(inherited
type).
- Fixed to the skin, with punctum.
- It enlarges in size slowly reaching up to
1-5cm diameter.
-
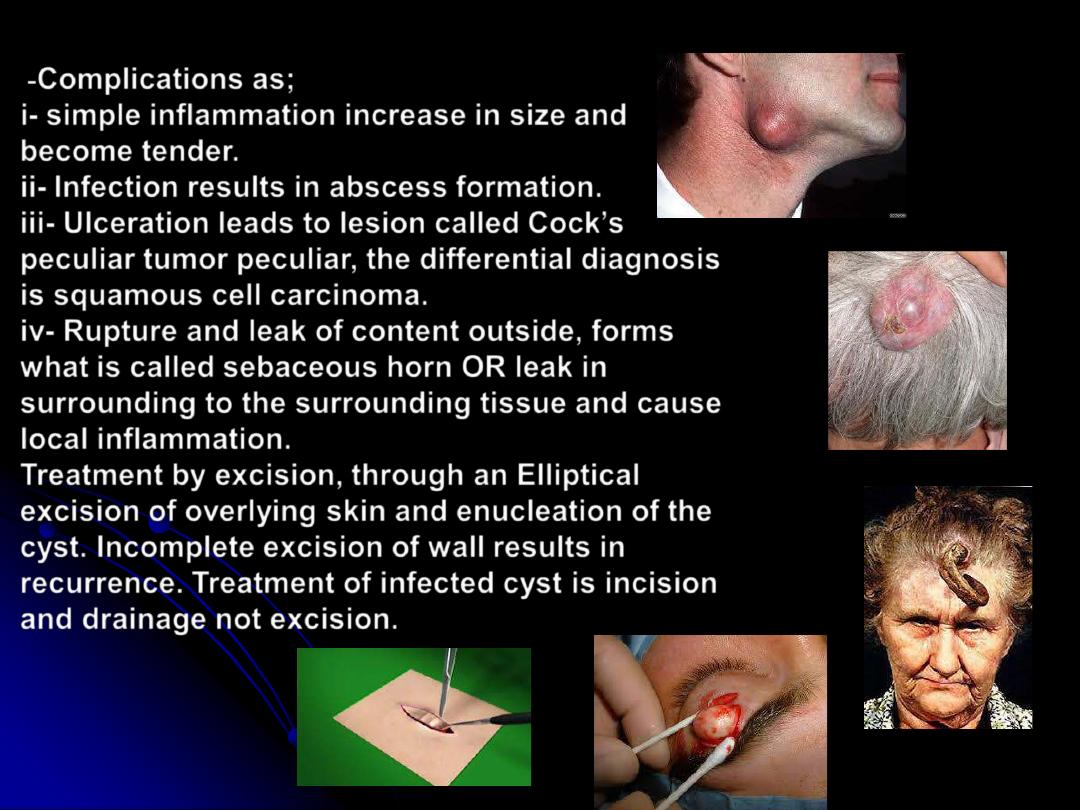
Complications as;
i- simple inflammation increase in size and
become tender.
ii- Infection results in abscess formation.
iii- Ulceration leads to lesion called Cock
’
s
peculiar tumor peculiar, the differential diagnosis
is squamous cell carcinoma.
iv- Rupture and leak of content outside, forms
what is called sebaceous horn OR leak in
surrounding to the surrounding tissue and cause
local inflammation.
Treatment by excision, through an Elliptical
excision of overlying skin and enucleation of the
cyst. Incomplete excision of wall results in
recurrence. Treatment of infected cyst is incision
and drainage not excision.
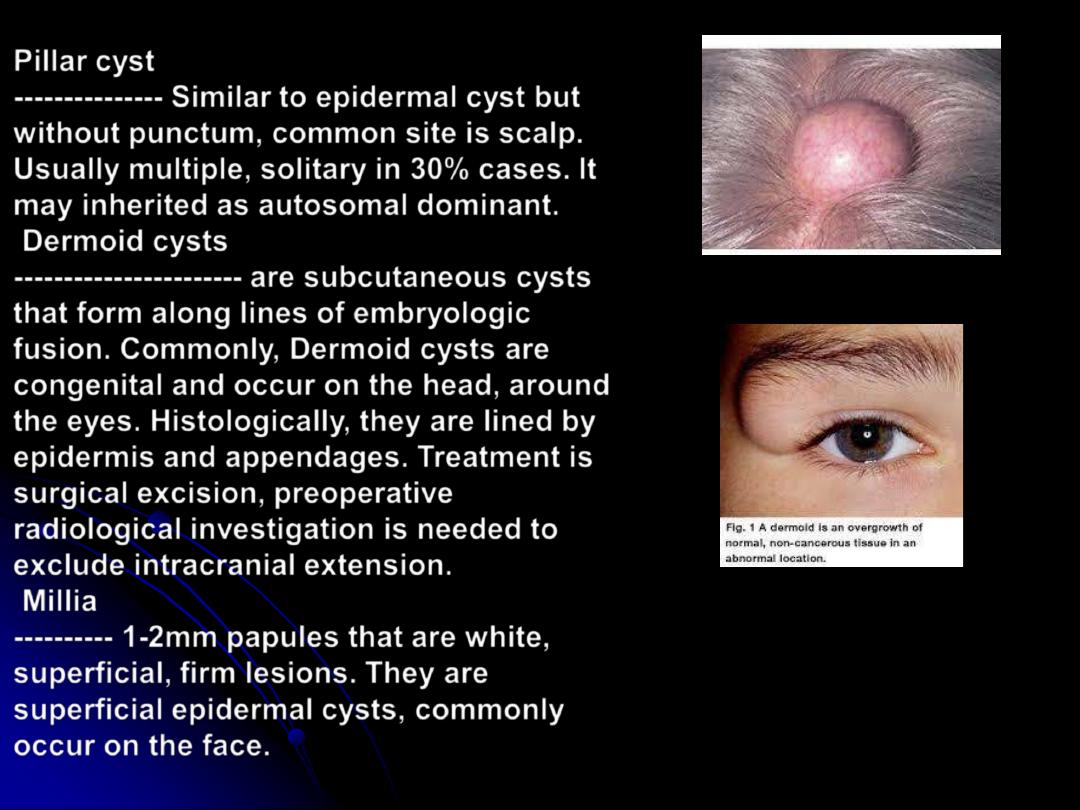
Pillar cyst
--------------- Similar to epidermal cyst but
without punctum, common site is scalp.
Usually multiple, solitary in 30% cases. It
may inherited as autosomal dominant.
Dermoid cysts
----------------------- are subcutaneous cysts
that form along lines of embryologic
fusion. Commonly, Dermoid cysts are
congenital and occur on the head, around
the eyes. Histologically, they are lined by
epidermis and appendages. Treatment is
surgical excision, preoperative
radiological investigation is needed to
exclude intracranial extension.
Millia
---------- 1-2mm papules that are white,
superficial, firm lesions. They are
superficial epidermal cysts, commonly
occur on the face.
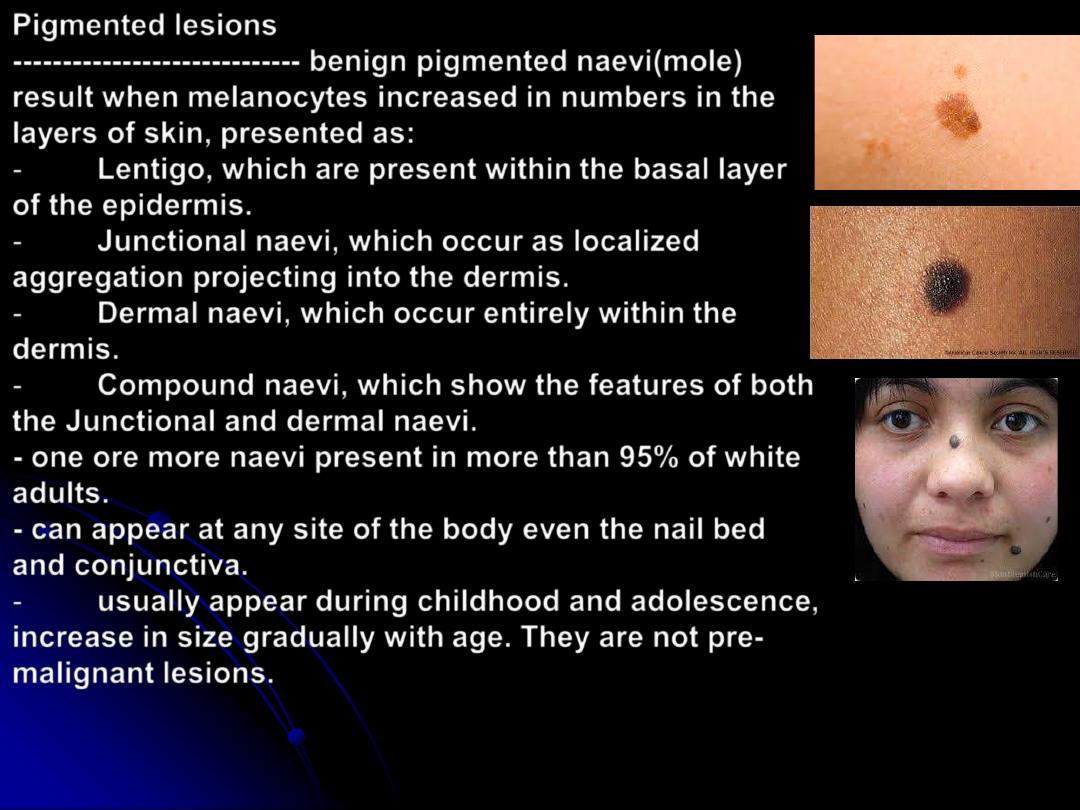
Pigmented lesions
-----------------------------
benign pigmented naevi(mole)
result when melanocytes increased in numbers in the
layers of skin, presented as:
-
Lentigo, which are present within the basal layer
of the epidermis.
-
Junctional naevi, which occur as localized
aggregation projecting into the dermis.
-
Dermal naevi, which occur entirely within the
dermis.
-
Compound naevi, which show the features of both
the Junctional and dermal naevi.
- one ore more naevi present in more than 95% of white
adults.
- can appear at any site of the body even the nail bed
and conjunctiva.
-
usually appear during childhood and adolescence,
increase in size gradually with age. They are not pre-
malignant lesions.
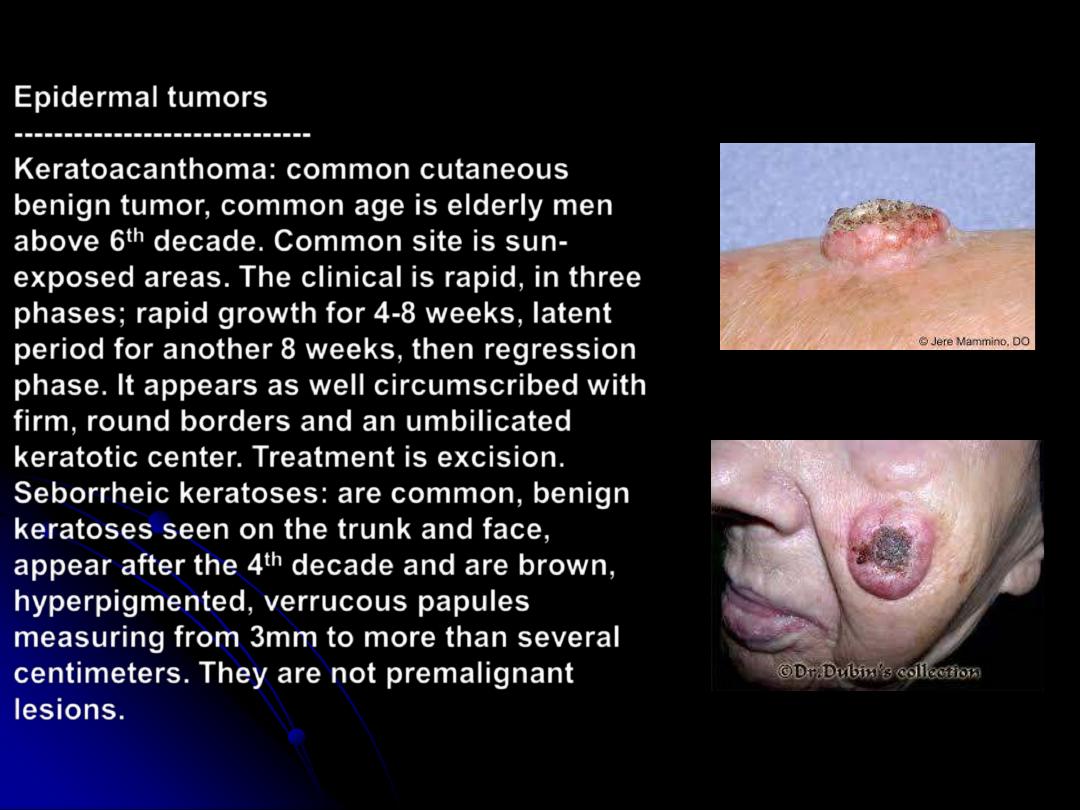
Epidermal tumors
------------------------------
Keratoacanthoma: common cutaneous
benign tumor, common age is elderly men
above 6
th
decade. Common site is sun-
exposed areas. The clinical is rapid, in three
phases; rapid growth for 4-8 weeks, latent
period for another 8 weeks, then regression
phase. It appears as well circumscribed with
firm, round borders and an umbilicated
keratotic center. Treatment is excision.
Seborrheic keratoses: are common, benign
keratoses seen on the trunk and face,
appear after the 4
th
decade and are brown,
hyperpigmented, verrucous papules
measuring from 3mm to more than several
centimeters. They are not premalignant
lesions.

Callosities
: are thickened or
hardened parts of skin. They are
commonly occur on pressure or
friction areas like the hand and feet,
so they may be occupational.
Corn
: is a horny induration of the
cuticle with a hard center, caused by
undue pressure, chiefly affecting the
toes and feet.
Wart
: is a dry , rough excrescence
on the skin. It is a virus-induced
tumor that undergoes spontaneous
resolution.
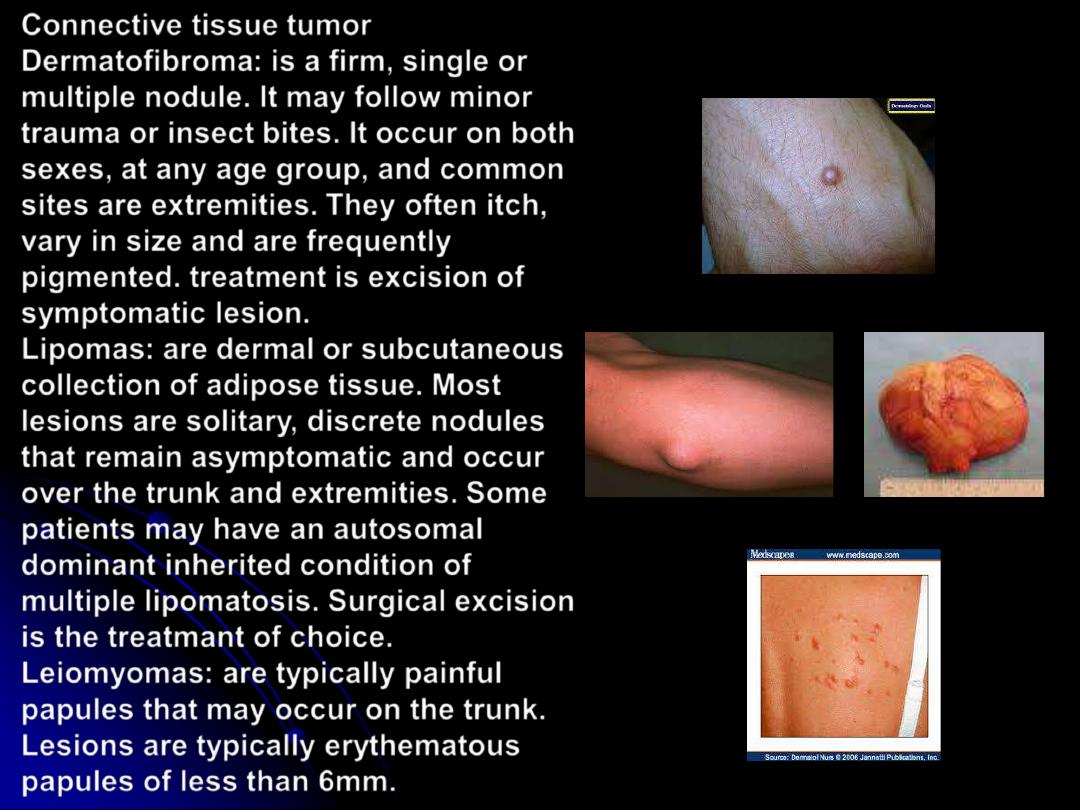
Connective tissue tumor
Dermatofibroma
: is a firm, single or
multiple nodule. It may follow minor
trauma or insect bites. It occur on both
sexes, at any age group, and common
sites are extremities. They often itch,
vary in size and are frequently
pigmented. treatment is excision of
symptomatic lesion.
Lipomas
: are dermal or subcutaneous
collection of adipose tissue. Most
lesions are solitary, discrete nodules
that remain asymptomatic and occur
over the trunk and extremities. Some
patients may have an autosomal
dominant inherited condition of
multiple lipomatosis. Surgical excision
is the treatmant of choice.
Leiomyomas
: are typically painful
papules that may occur on the trunk.
Lesions are typically erythematous
papules of less than 6mm.
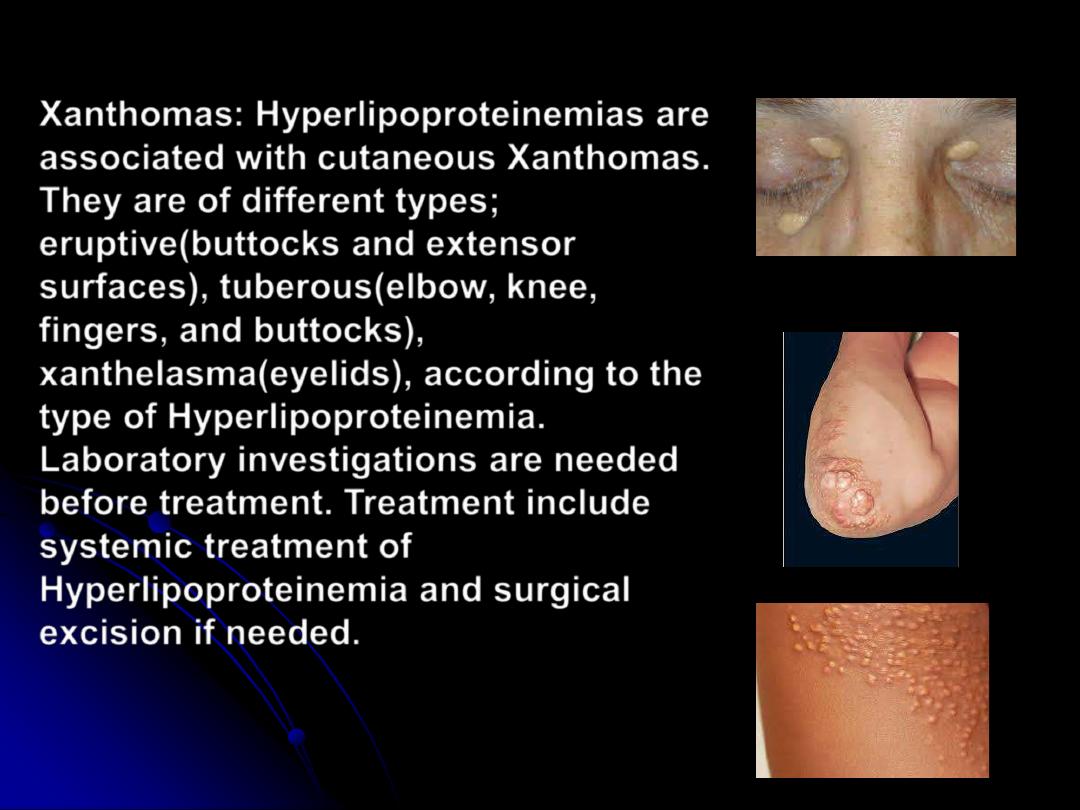
Xanthomas
: Hyperlipoproteinemias are
associated with cutaneous Xanthomas.
They are of different types;
eruptive(buttocks and extensor
surfaces), tuberous(elbow, knee,
fingers, and buttocks),
xanthelasma(eyelids), according to the
type of Hyperlipoproteinemia.
Laboratory investigations are needed
before treatment. Treatment include
systemic treatment of
Hyperlipoproteinemia and surgical
excision if needed.
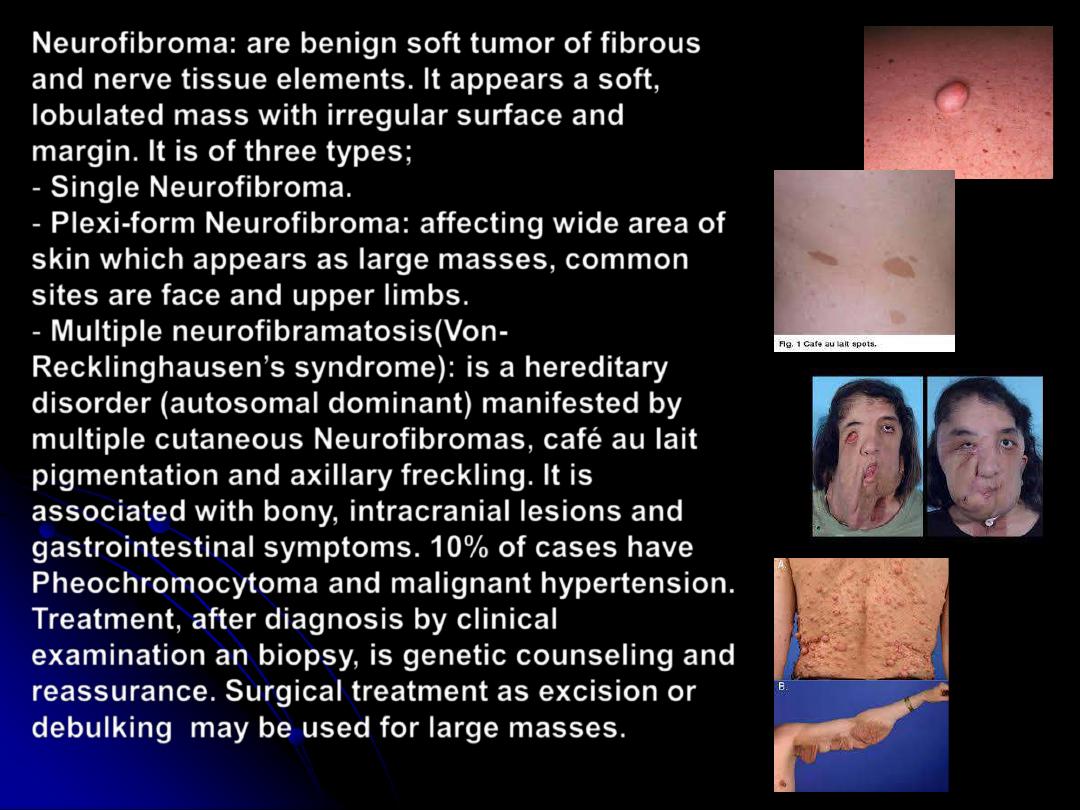
Neurofibroma
: are benign soft tumor of fibrous
and nerve tissue elements. It appears a soft,
lobulated mass with irregular surface and
margin. It is of three types;
-
Single Neurofibroma
.
-
Plexi-form Neurofibroma
: affecting wide area of
skin which appears as large masses, common
sites are face and upper limbs.
-
Multiple neurofibramatosis(Von-
Recklinghausen
’
s
syndrome): is a hereditary
disorder (autosomal dominant) manifested by
multiple cutaneous Neurofibromas, café au lait
pigmentation and axillary freckling. It is
associated with bony, intracranial lesions and
gastrointestinal symptoms. 10% of cases have
Pheochromocytoma and malignant hypertension.
Treatment, after diagnosis by clinical
examination an biopsy, is genetic counseling and
reassurance. Surgical treatment as excision or
debulking may be used for large masses.
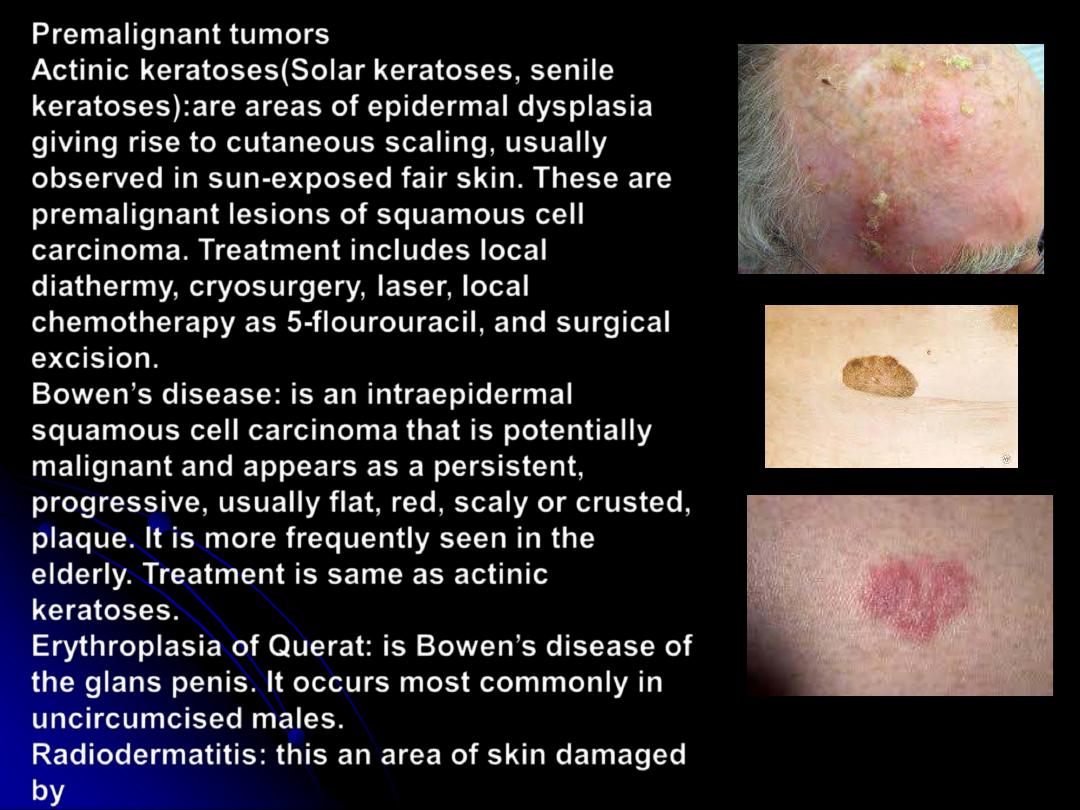
Premalignant tumors
Actinic keratoses(Solar keratoses, senile
keratoses):
are areas of epidermal dysplasia
giving rise to cutaneous scaling, usually
observed in sun-exposed fair skin. These are
premalignant lesions of squamous cell
carcinoma. Treatment includes local
diathermy, cryosurgery, laser, local
chemotherapy as 5-flourouracil, and surgical
excision.
Bowen
’
s disease:
is an intraepidermal
squamous cell carcinoma that is potentially
malignant and appears as a persistent,
progressive, usually flat, red, scaly or crusted,
plaque. It is more frequently seen in the
elderly. Treatment is same as actinic
keratoses.
Erythroplasia of Querat
: is Bowen
’
s disease of
the glans penis. It occurs most commonly in
uncircumcised males.
Radiodermatitis: this an area of skin damaged
by
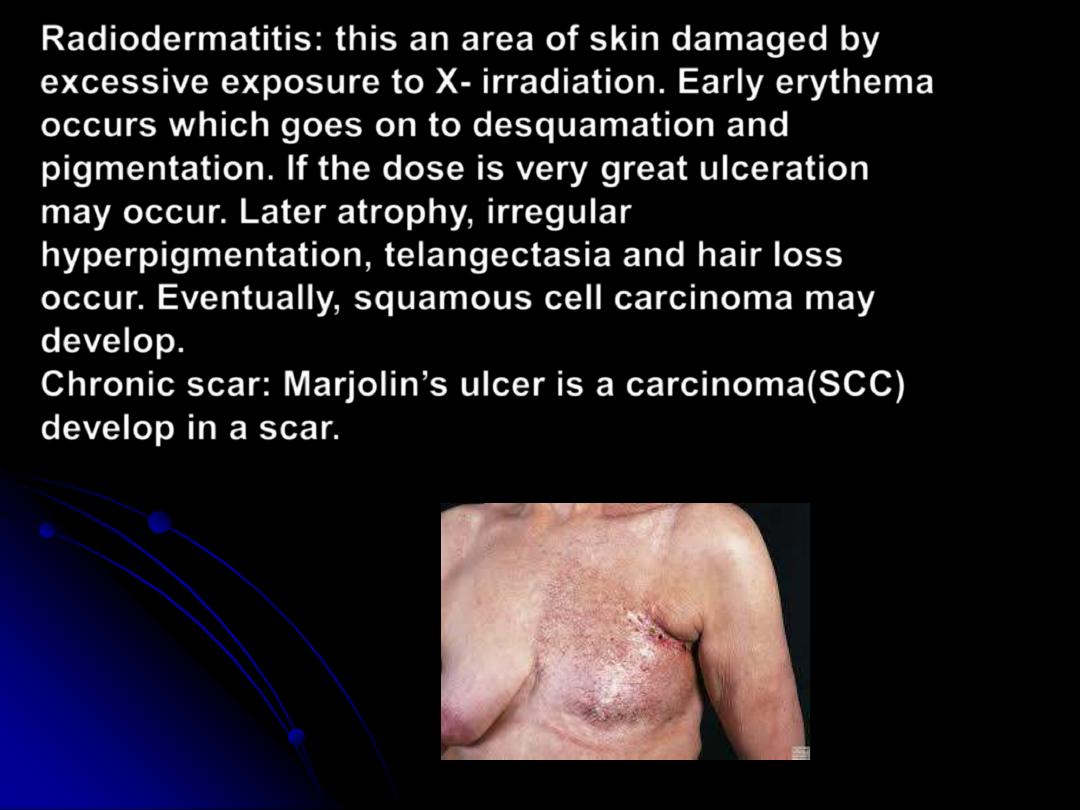
Radiodermatitis
: this an area of skin damaged by
excessive exposure to X- irradiation. Early erythema
occurs which goes on to desquamation and
pigmentation. If the dose is very great ulceration
may occur. Later atrophy, irregular
hyperpigmentation, telangectasia and hair loss
occur. Eventually, squamous cell carcinoma may
develop.
Chronic scar: Marjolin’s ulcer is a carcinoma(SCC)
develop in a scar.
