Genodermatosis

Neurofibromatoses
relatively common, 1 in 3000
Autosomal dominant
There are two main types:
1.
Von Recklinghausen
’s
neurofibromatosis (NF1; 85% of all
cases)
2.
Bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis
(NF2)

NF1
Cause
Mutation of NF1 gene, localized to
chromosome 17q11.1.
The NF1 gene is a tumour suppressor gene,
the product of which, neurofibromin, interacts
with the product of the RAS proto-oncogene.
This may explain the susceptibility of NF1
patients to a variety of tumours.
Inheritence as autosomal dominant trait
about half of index cases have no preceding
family history.

Clinical features
The physical signs include the following.
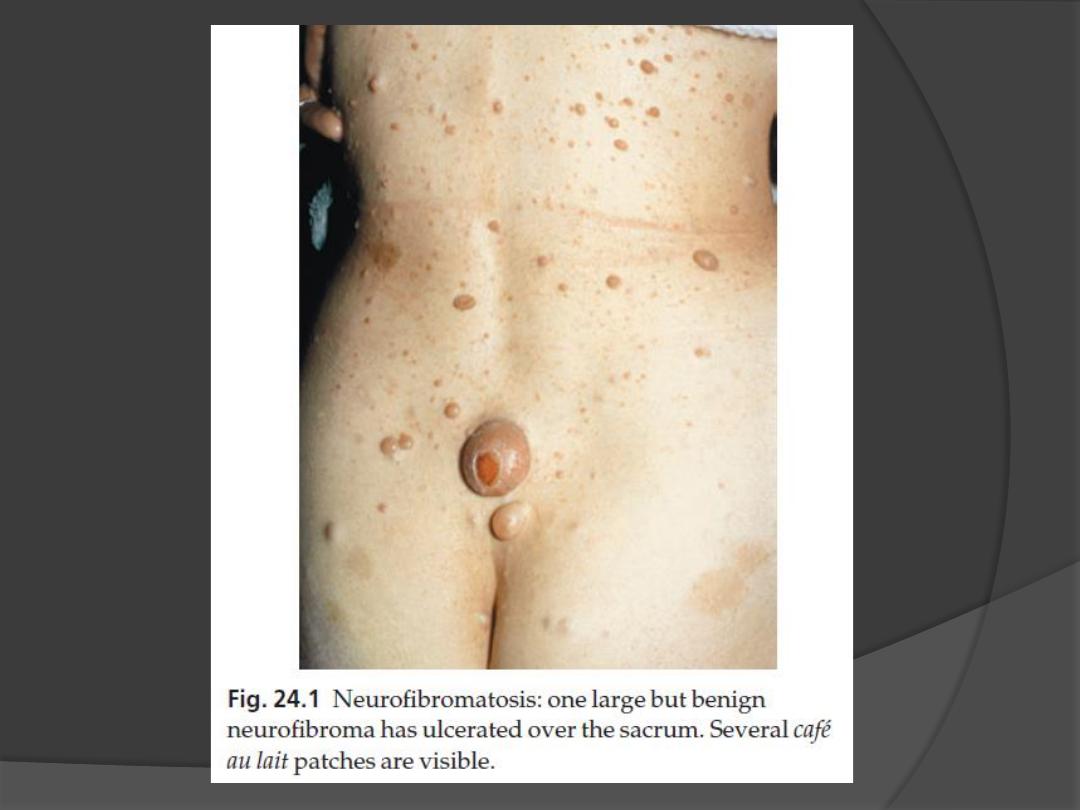
1. Café au lait patches
Six or more (light brown oval macules, usually developing in the first
year of life.
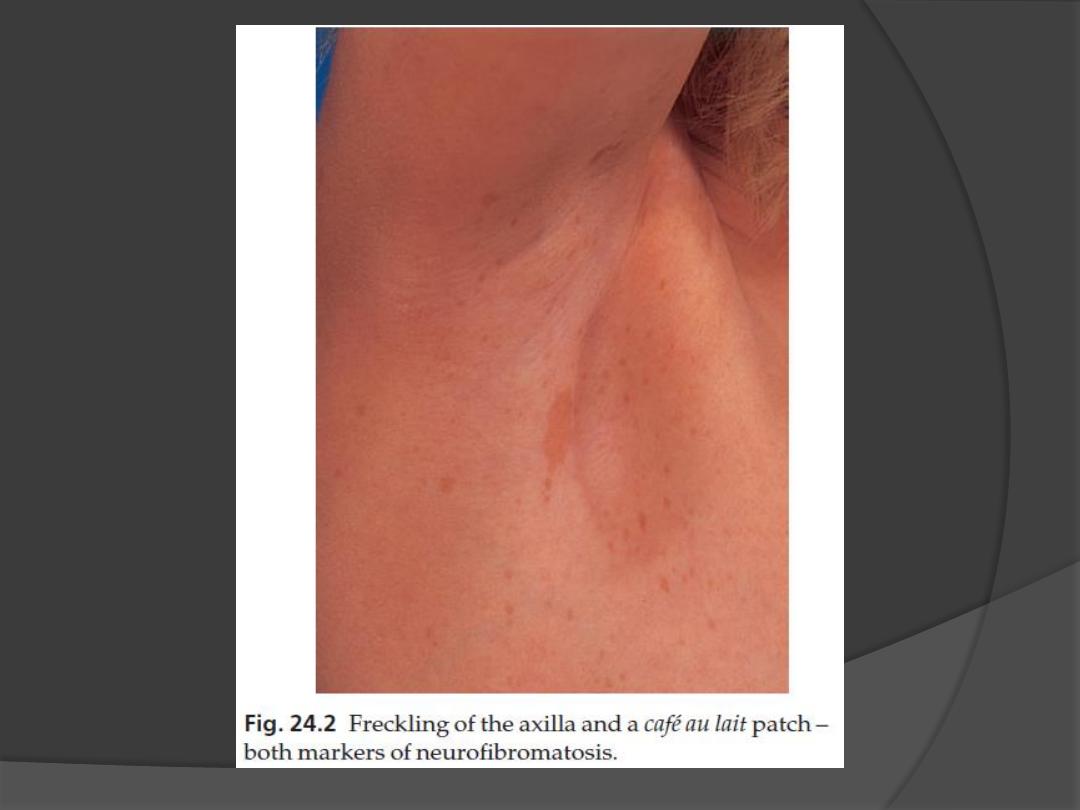
2. Axillary freckling
in two-thirds of affected individuals (Crowe
’s sign).
3. Neurofibromas
Any number
some small and superficial, others larger and deeper
Most are dome-like nodules, but others are irregular raised plaques.
Some are firm, some soft and compressible through a deficient dermis
(
‘button-hole’ sign); others feel ‘knotty’ or ‘wormy’.
may not appear until puberty and become larger and more numerous
with age.
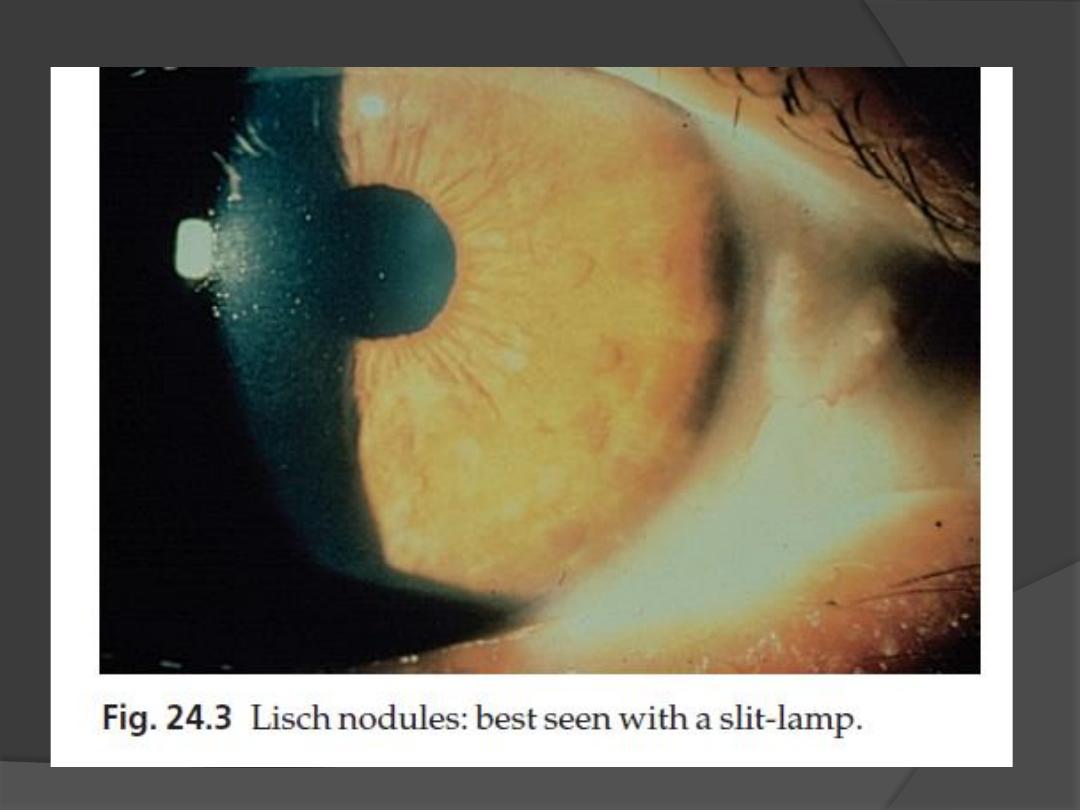
4. Lisch nodules
Small circular pigmented hamartomas of the iris, appear in early
childhood.

Clinical features, cont.
Nearly all NF1 patients meet the criteria
for diagnosis by the age of 8 years, and
all do so by 20 years.
The usual order of appearance of the
clinical features is:
1.
café au lait macules
2.
axillary freckling
3.
Lisch nodules
4.
neurofibromas.

Clinical features, cont.
A segmental form of NF1 is caused by a
post-zygotic mutation.
Isolated neurofibromas are not
uncommon in individuals without
neurofibromatosis and are of little
consequence unless they are painful.

Complications
1.
A neurofibroma will occasionally change
into a neurofibrosarcoma
2.
Kyphoscoliosis
3.
Learning impairment
4.
Epilepsy
5.
Renal artery stenosis
6.
an association with
phaeochromocytoma

Management
Ugly or painful lesions, and any
suspected of undergoing malignant
change, should be removed.
The chance of a child of an affected
adult developing the disorder is 1 in 2
blood pressure checked regularly.

Tuberous sclerosis
uncommon condition, with a prevalence
about 1 in 12000 in children under 10
years
autosomal dominant trait
Fertility is reduced, so transmission
through more than two generations is
rare.

Cause
Inactivating mutations at two different
loci can, independently, cause clinically
identical tuberous sclerosis.
Both genes are tumour suppressors.
1.
(TSC1 on chromosome 9q34)
2.
(TSC2 on 16p13.3)
TSC2 gene mutations are responsible
for 80
–90% of cases.

Clinical features
The skin changes include the following.
1. Ash leaf macules
Small oval white patches
occur in 80% of those affected
may be the only manifestation at birth.
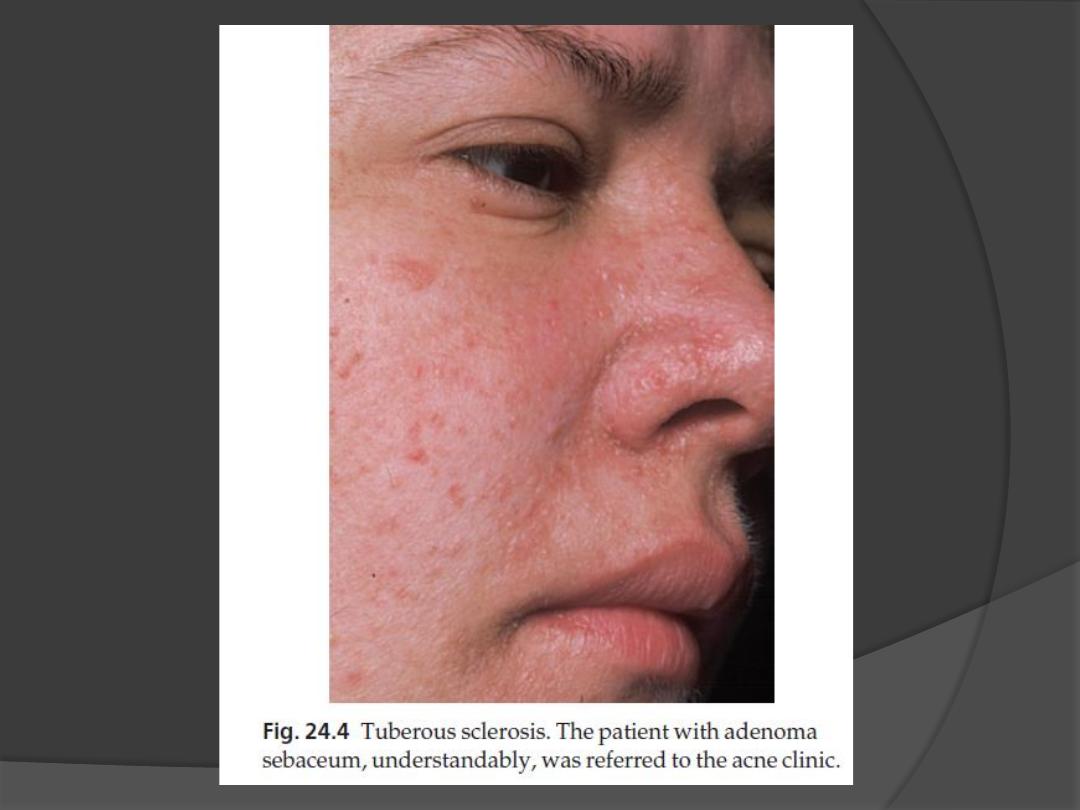
2. Angiofibromas (known as adenoma
sebaceum)
occur in 85% of those affected
develop at puberty as pink or yellowish
acne-like papules on the face, often around
the nose.

Clinical features, cont.
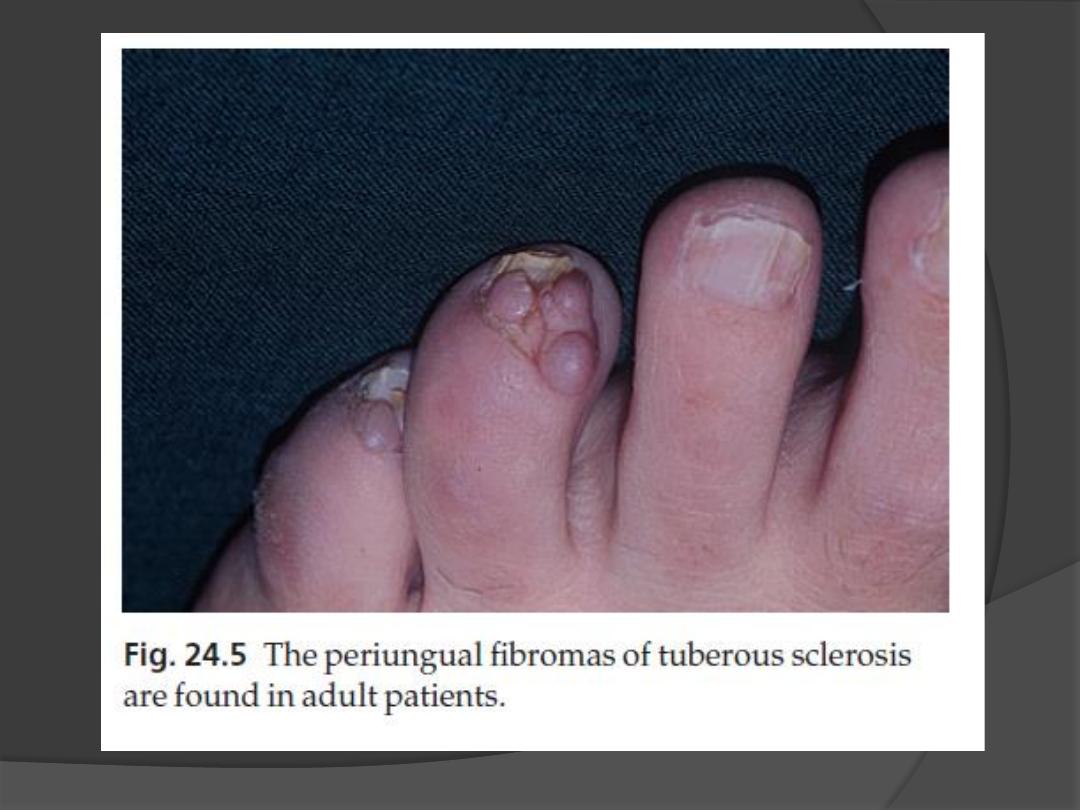
3. Periungual fibromas
occur in 50% of patients
develop in adult life as small pink sausage-
like lesions emerging from the nail folds.
4. Connective tissue naevi (
‘shagreen
patches
’)
Are seen in 40% of patients.
Cobblestone, somewhat yellow plaques
often arise in the skin over the base of the
spine.

Other features
may include:
1.
Epilepsy (in 75% of patients)
2.
Mental retardation (in 50% of patients)
3.
Ocular signs, including retinal phakomas
and pigmentary abnormalities (in 50% of
patients)
4.
Hyperplastic gums
5.
gliomas along the lateral walls of the
lateral ventricles (80% of cases) and
calcification of the basal ganglia
6.
Renal and heart tumours.

Diagnosis and differential
diagnosis
Any baby with unexplained epilepsy
should be examined with a Wood
’s light
to look for ash leaf macules.
Skull X-rays and computed tomography
scans of CNS and kidneys.
The lesions of adenoma sebaceum (a
misnomer, as histologically they are
angiofibromas) may be mistaken for
acne.

Management
Genetic counselling
Facial angiofibromas may improve
cosmetically after electrodessication,
dermabrasion or destruction by laser but
tend to recur

Xeroderma pigmentosum
heterogeneous group of autosomal
recessive disorders, characterized by
the defective repair of DNA after its
damage by ultraviolet radiation.
rare, affecting about 5 per million in
Europe.

Clinical features, cont.
There are many variants but all follow the
same pattern.
1. The skin is normal at birth.
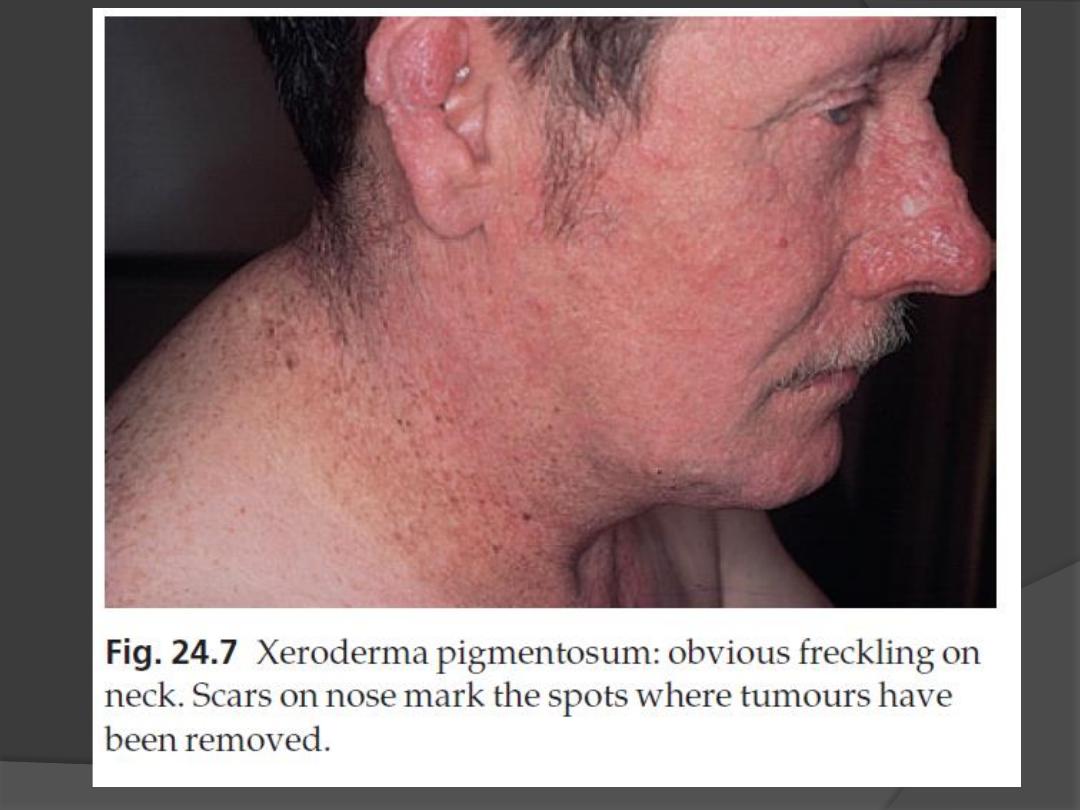
2. Multiple freckles, roughness and keratoses
on exposed skin appear between the ages
of 6 months and 2 years
3. Photosensitivity increases thereafter.
4. The atrophic facial skin shows
telangiectases and small angiomas.

Clinical features, cont.
5. Many tumours develop on light-damaged
skin: BCC, SCC, MM
Many patients die before the age of 20
years.
6. Eye problems are common and include
photophobia, conjunctivitis and ectropion.
7. The condition may be associated with
microcephaly, mental deficiency, dwarfism,
deafness and ataxia (De Sanctis
–
Cacchione syndrome).

Treatment
Strict avoidance of sunlight, the use of
protective clothing, widebrimmed hats
and of reflectant sunscreens and dark
glasses.
If possible, patients should not go out by
day.
Early and complete removal of all
tumours is essential.
Radiotherapy should be avoided

