
Bone Tumors
Tikrit University
College of Medicine
Department of Radiology
MSK Series

Before to start: you should
know certain bony

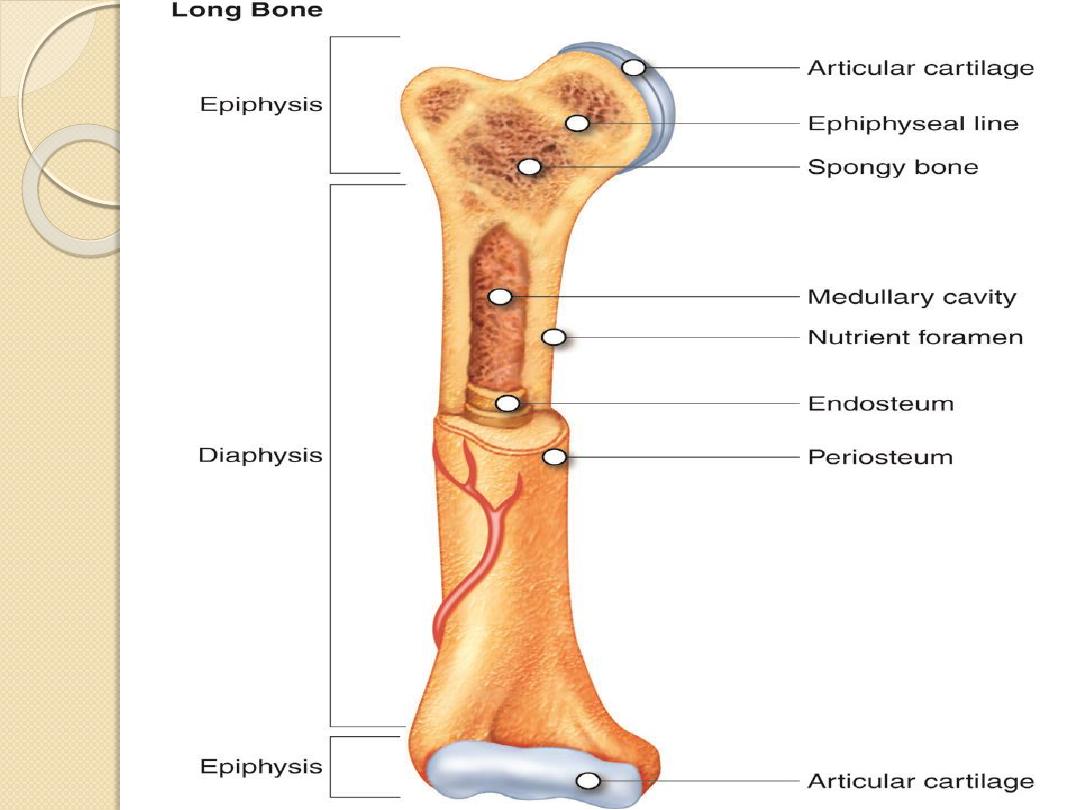
Terminology
Diaphysis - shaft
Metaphysis
Epiphysis
Epiphyseal plate (Growth plate) (Physis).
Periosteum.
Cortex.
Endosteum.
Medullary cavity.
Articular.
Subarticular.

Radiological modalities in bone lesions
Plain X-Ray – very very helpful.
CT.
MRI.
Bone scintigraphy (Static & Dynamic).
US – limited use.
Intervention (Diagnostic & Therapeutic).

Types of bony lesions
Infections.
TUMORS – our lecture-.
Metabolic disorders.
Hematologic diseases.
Vascular abnormalities.
Traumatic injuries.
Congenital anomalies.

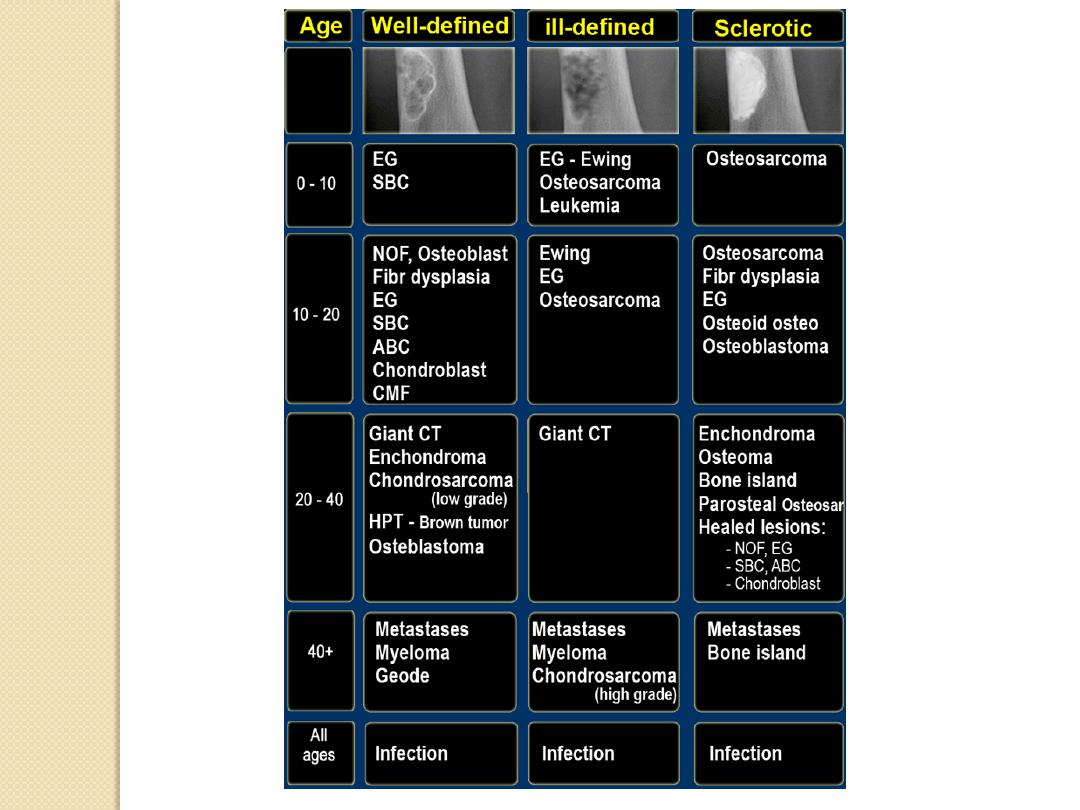
How to approach the lesion
to reach the diagnosis ?
CLINICAL
Age
Gender
Clinical history
RADIOLOGICAL
Site: cortical or Medullary?
Site: diaphysis, metaphysis or epiphysis?
Matrix of the lesion (lytic / sclerotic)
Behavior of the lesion (destructive or not?)
Transitional zone (wide? Narrow?)
Soft tissue component?

How to describe the lesion
USE THE FOLLOWING APPROACH
A well
define
/
ill define
Expansile
/
non expansile
Osteolytic / Sclerotic
Lesion is seen at the
Epiphysis
/
metaphysis
/
diaphysis
Of the RT/LT (bone name)
Associated with
Type of periosteal reaction.
NEW
Pattern of cortical bone destruction/thinning.
NEW
Large / small Soft tissue component / internal
septation or not.

Clues by Appearance of Lesion
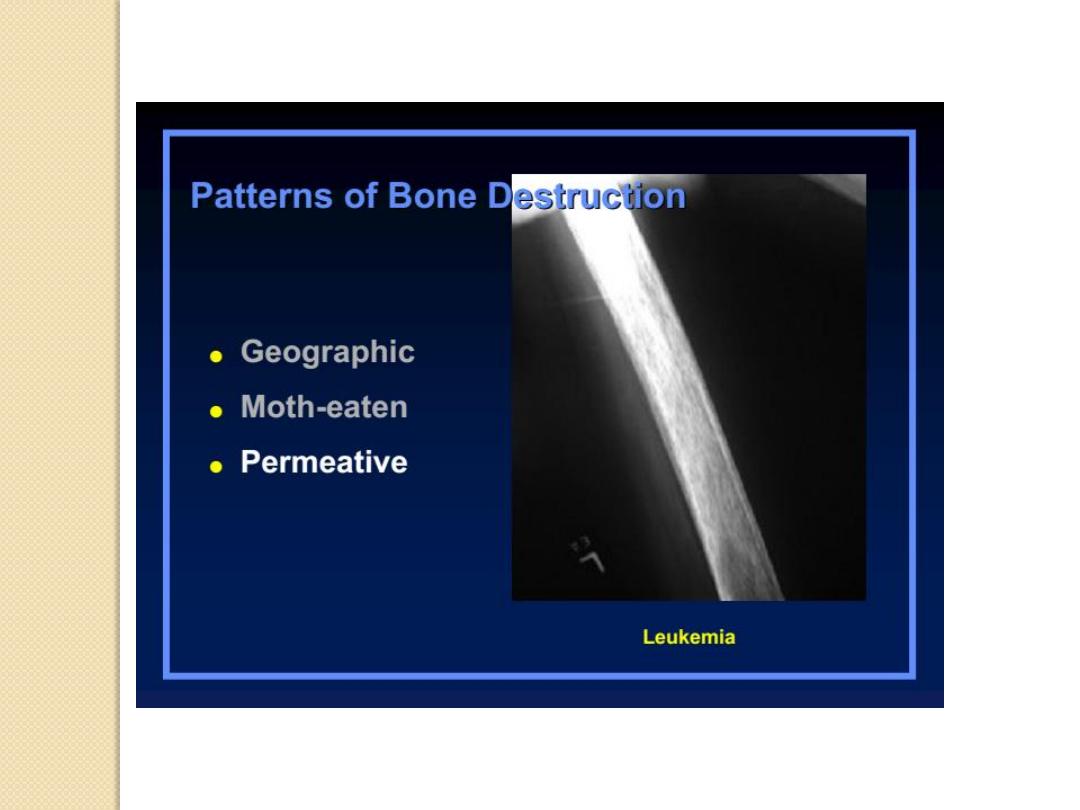
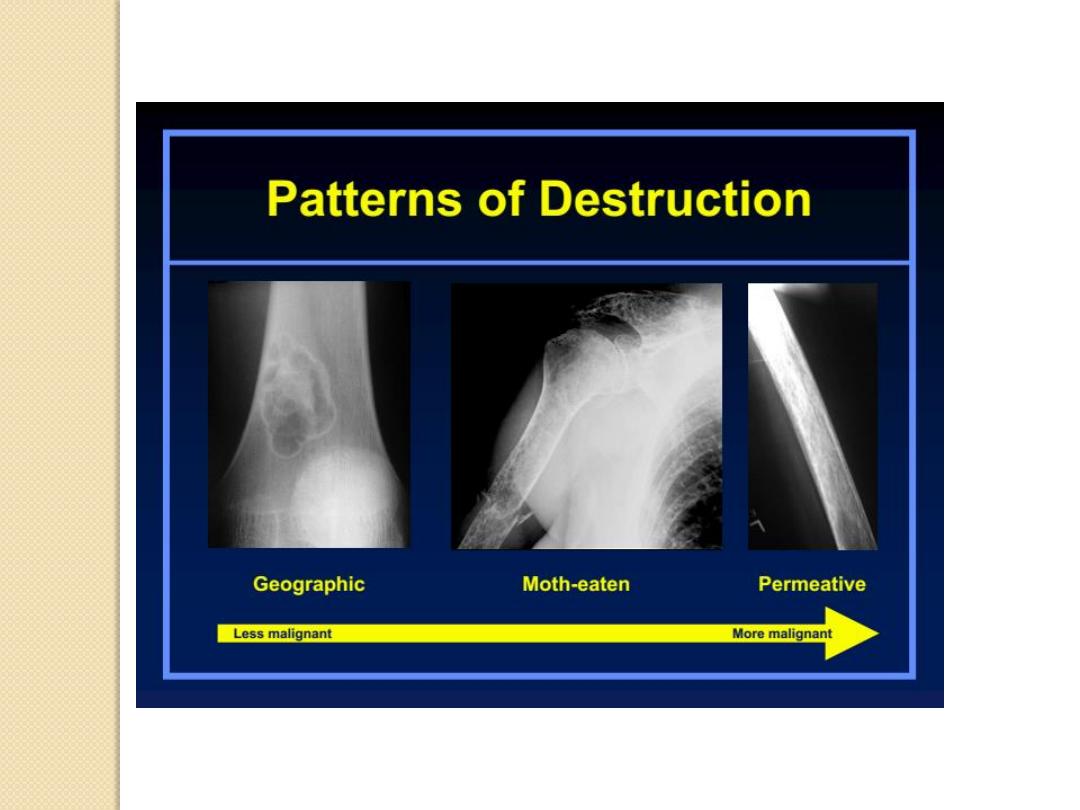
Patterns of Bone Destruction
Periosteal Reactions
Tumor Matrix
Expansile Lesions of Bone
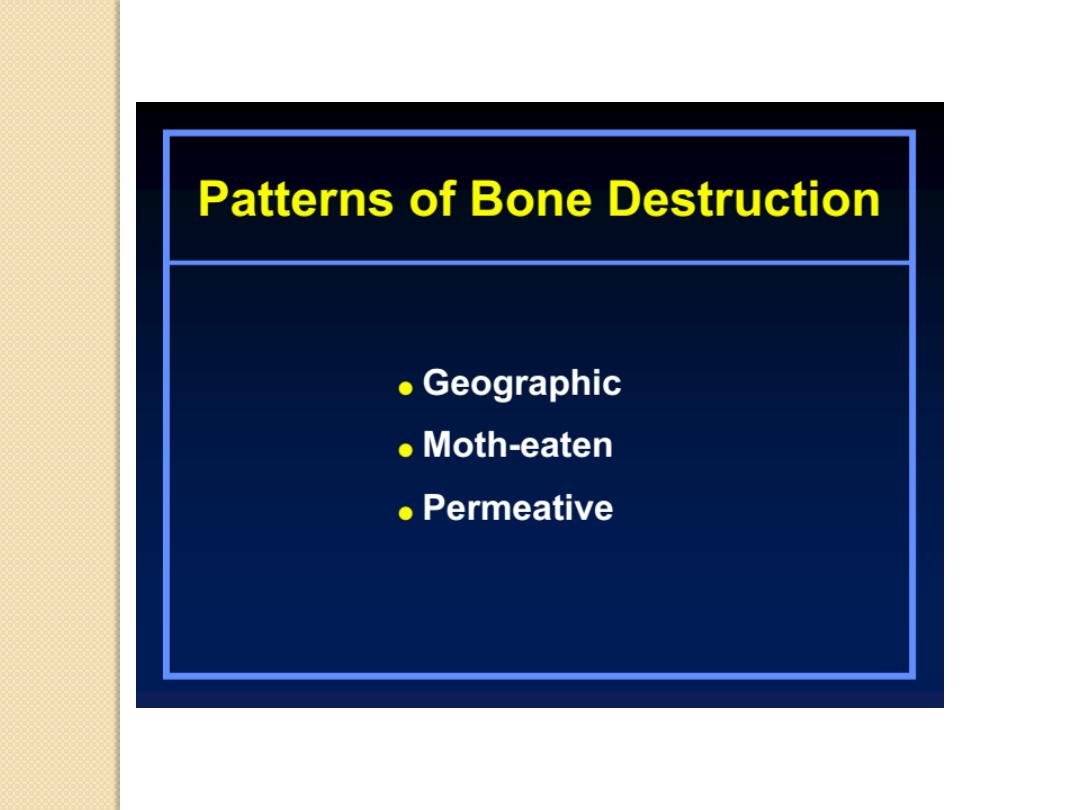
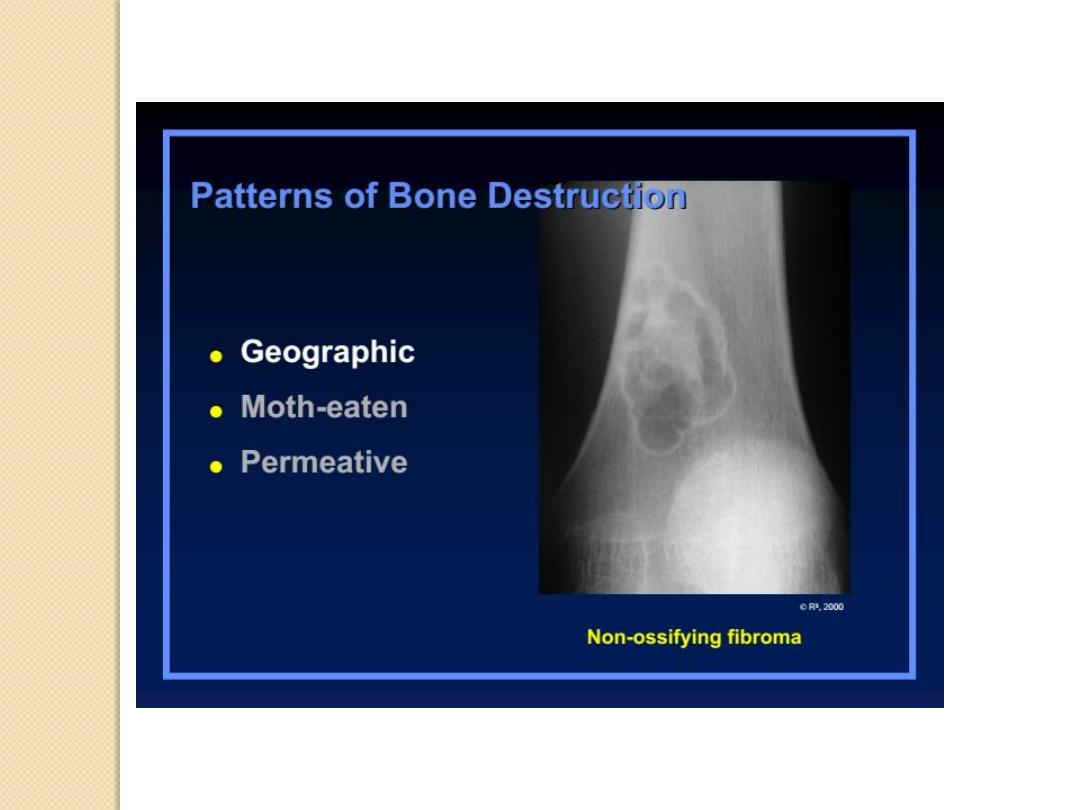


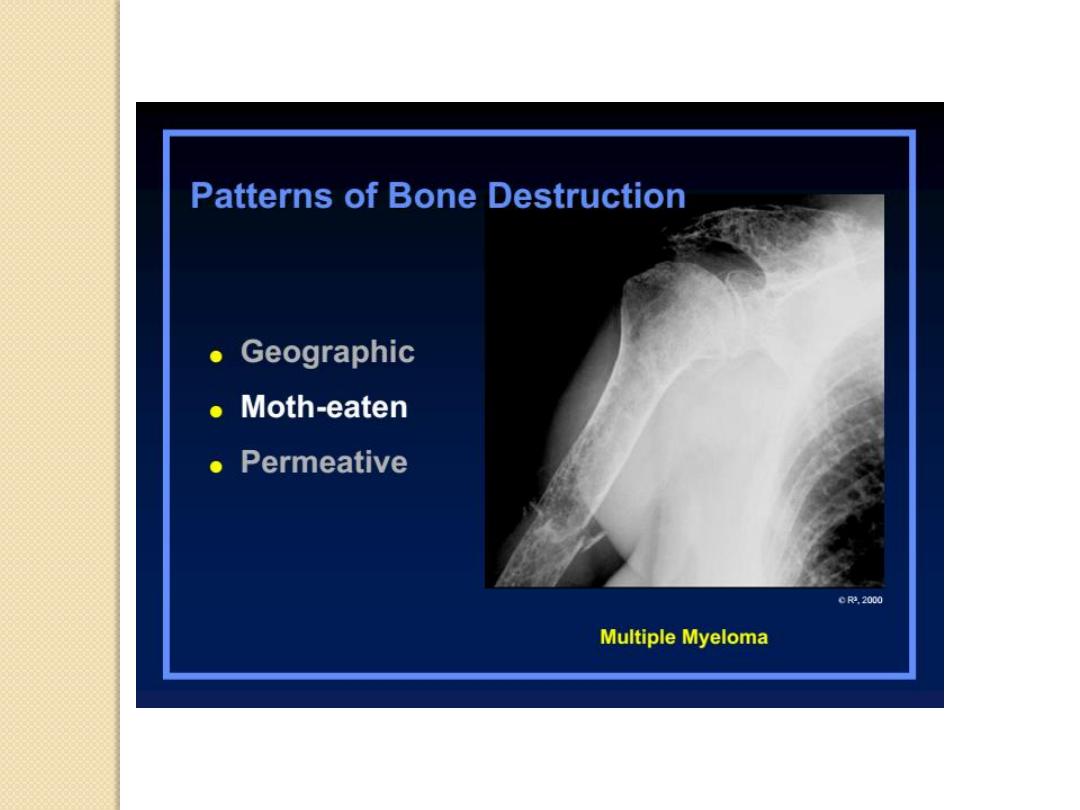

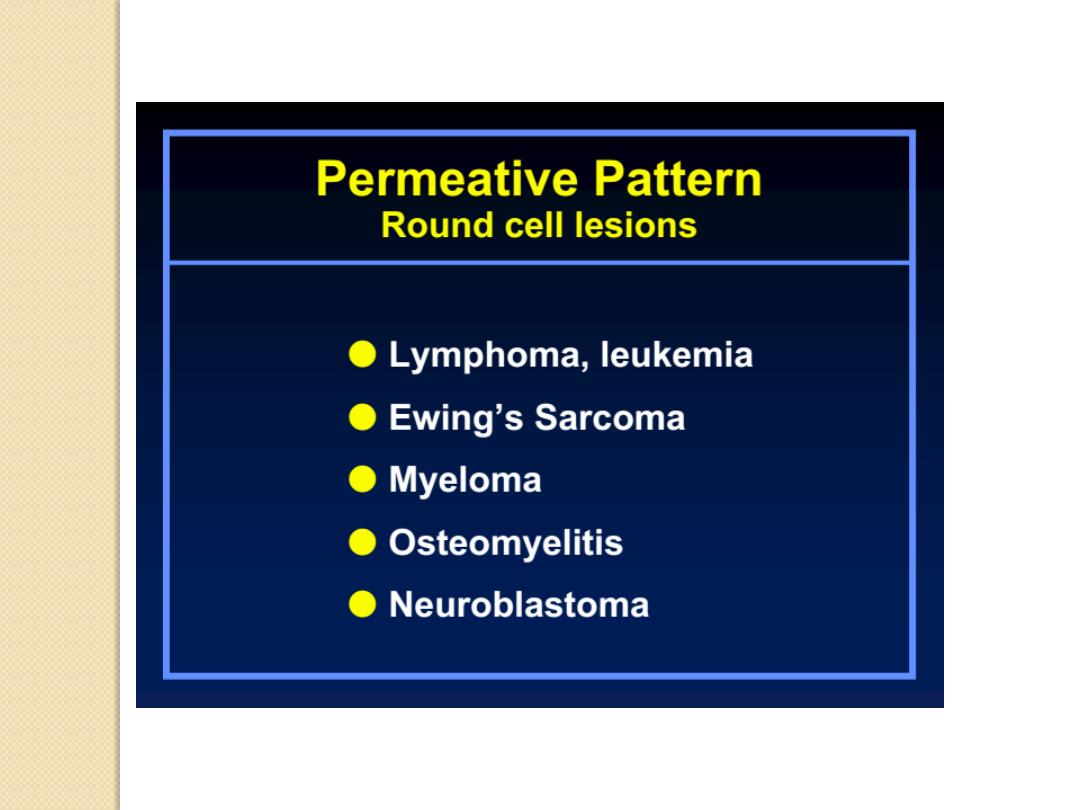
Moth-eaten




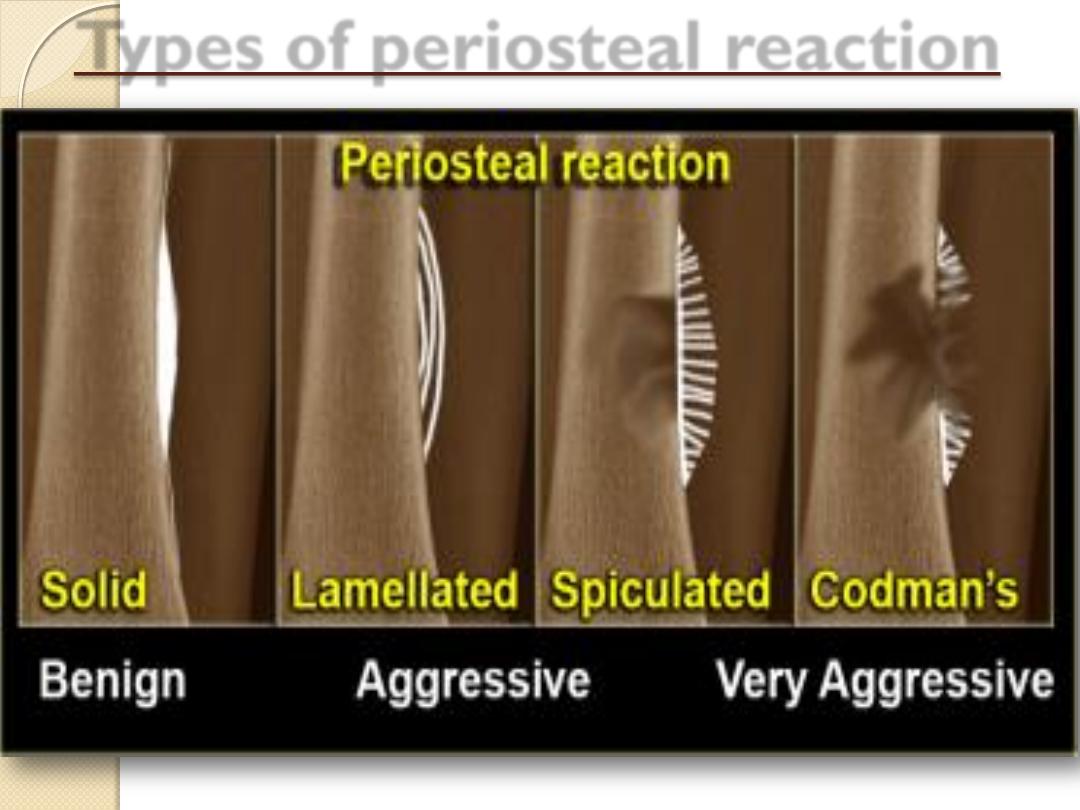
Periosteal Reactions
Benign
◦
None
◦
Solid
More aggressive or malignant
◦
Lamellated or onion peel
◦
Sunburst
◦
Codman’s triangle
Types of periosteal reaction
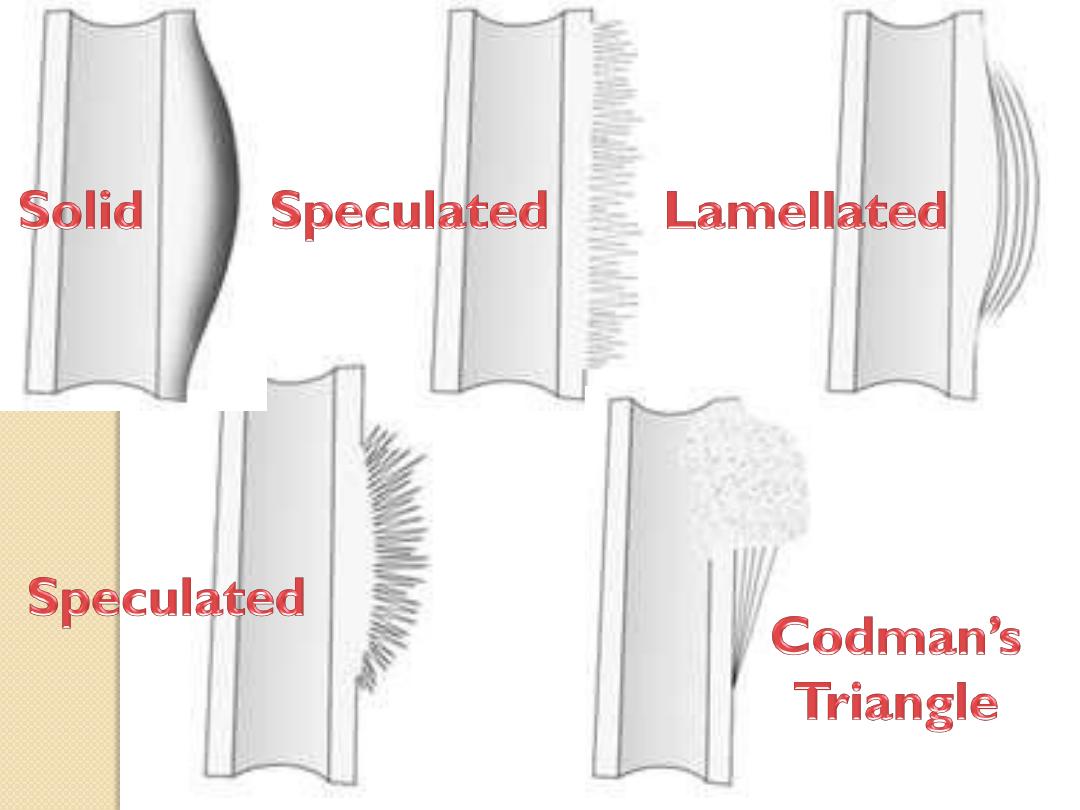
Periosteal Reactions
• Benign
– None
– Solid
• Aggressive/malignant
– onion-peel
– Sunburst
– Codman’s triangle
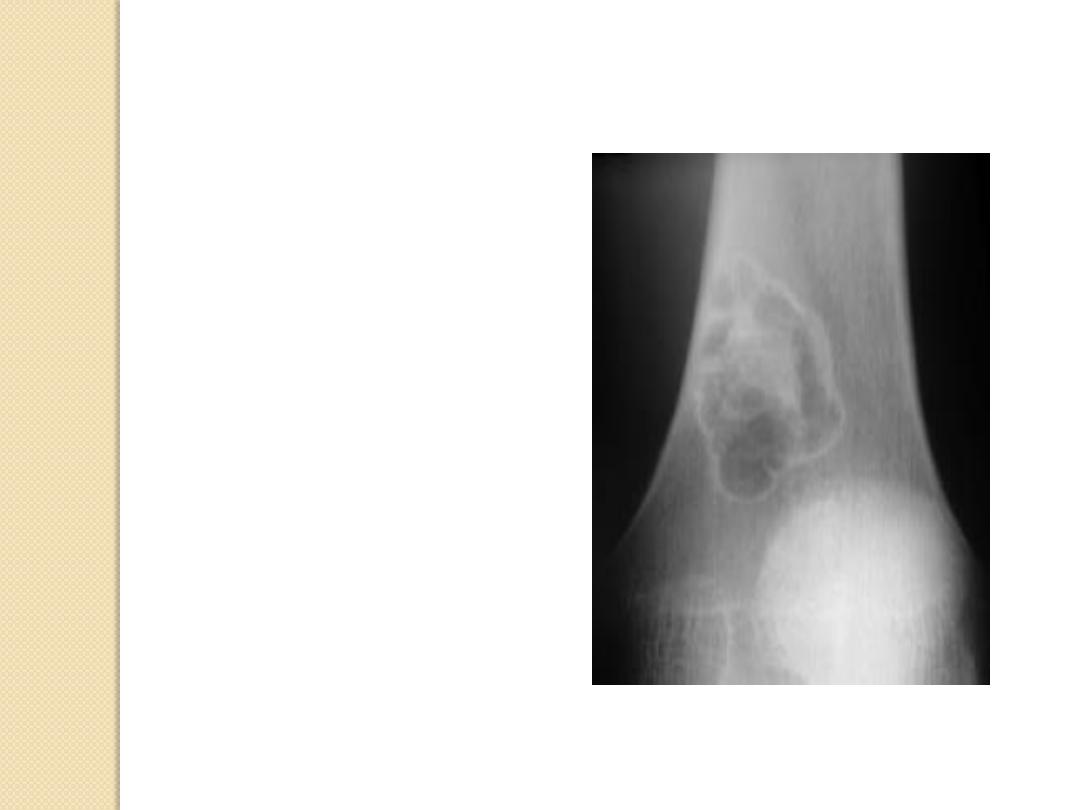
Non-ossifying fibroma
Periosteal Reactions
• Benign
– None
– Solid
• Aggressive/malignant
– onion-peel
– Sunburst
– Codman’s triangle
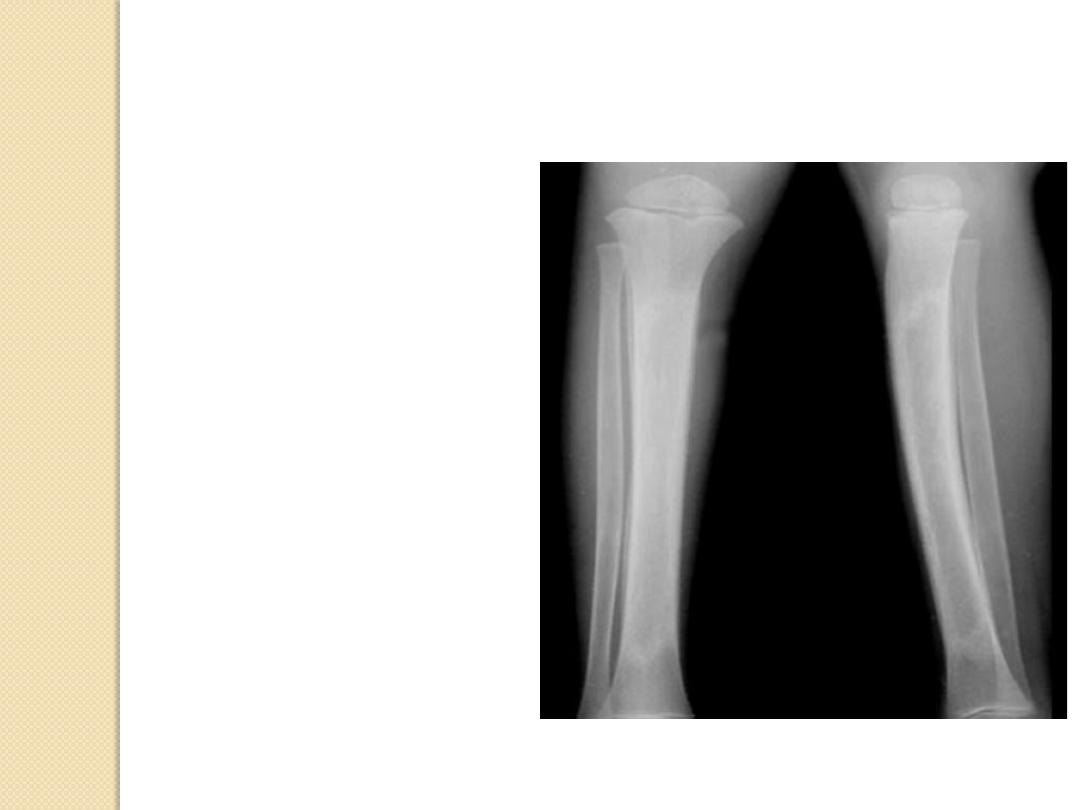
Chronic osteomyelitis
Periosteal Reactions
• Benign
– None
– Solid
• Aggressive/malignant
– onion-peel
– Sunburst
– Codman’s triangle
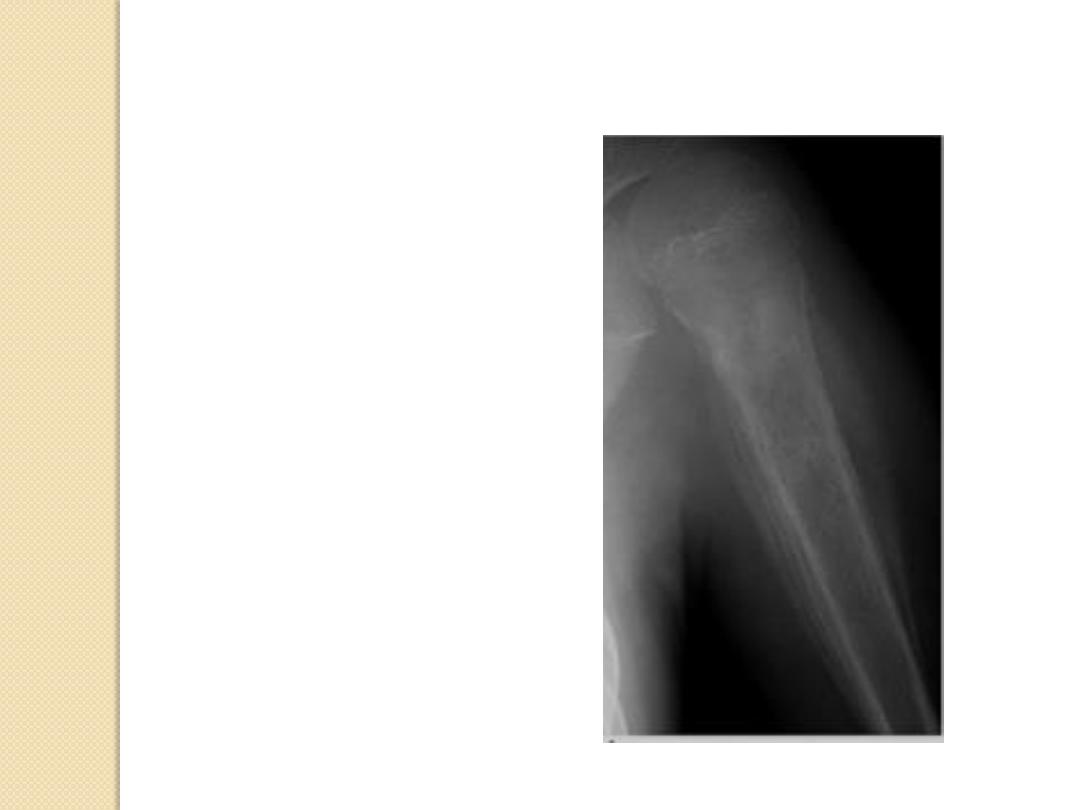
Ewing sarcoma
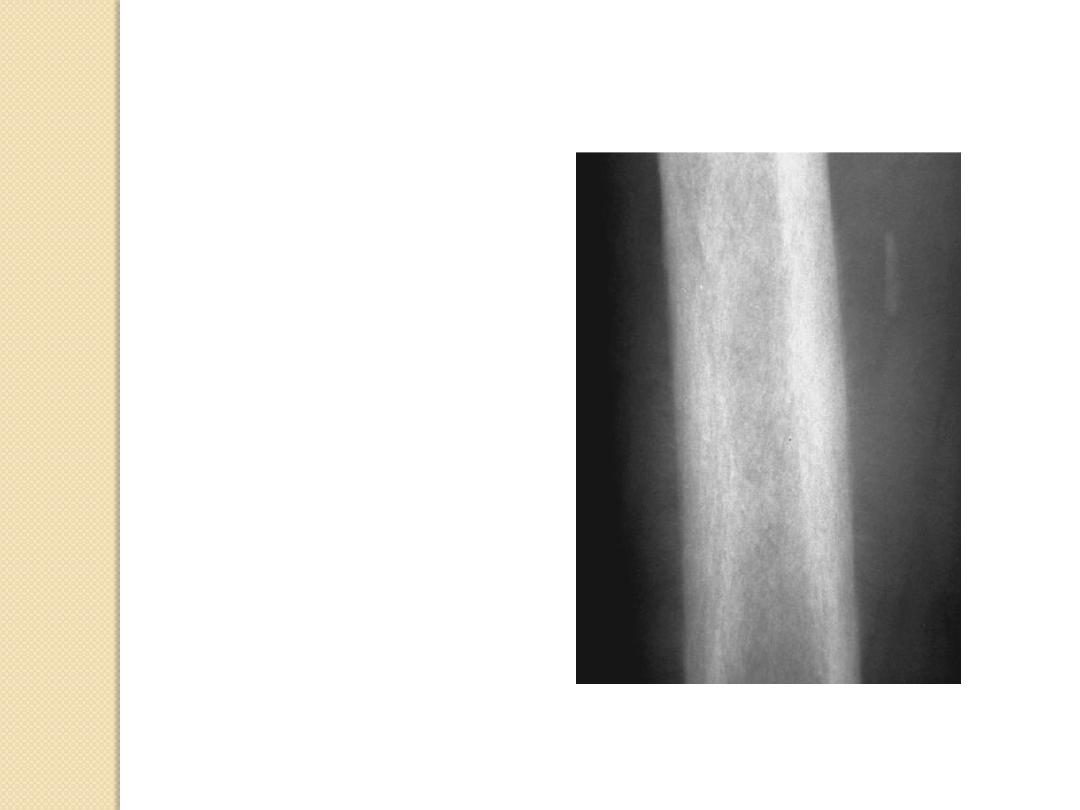
Periosteal Reactions
• Benign
– None
– Solid
• Aggressive/malignant
– onion-peel
– Sunburst
– Codman’s triangle
Osteo-sarcoma
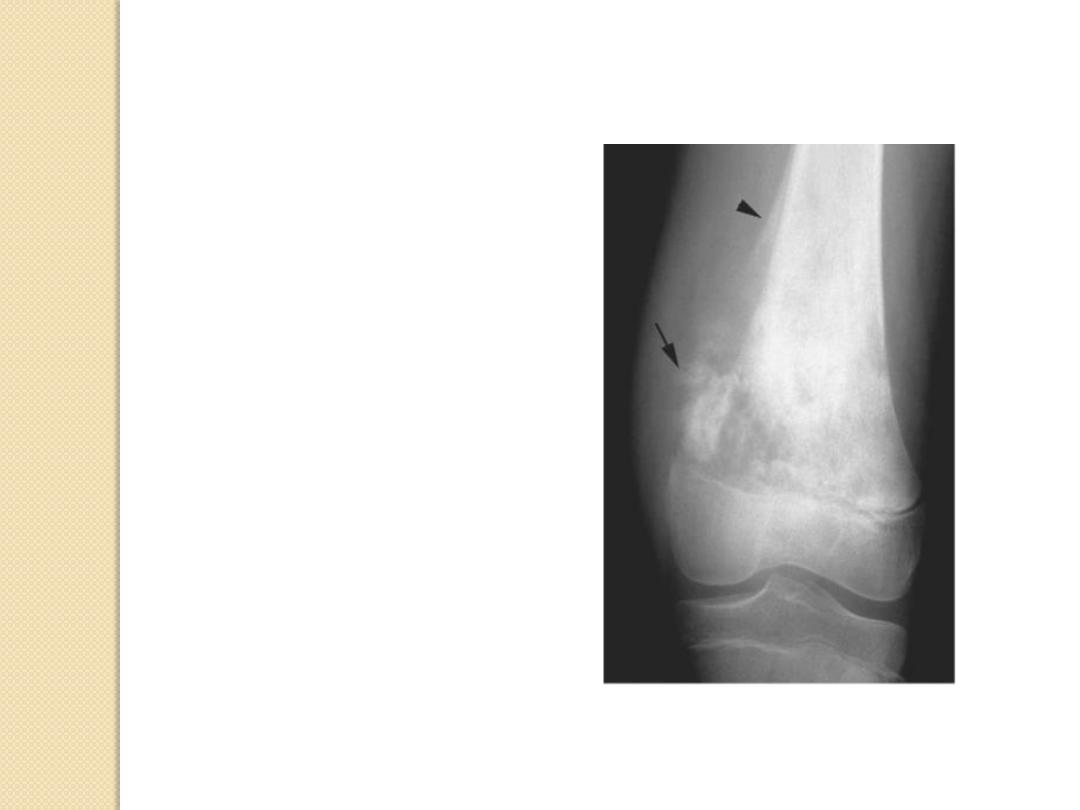
Periosteal Reactions
• Benign
– None
– Solid
• Aggressive/malignant
– onion-peel
– Sunburst
– Codman’s triangle
Osteo-sarcoma
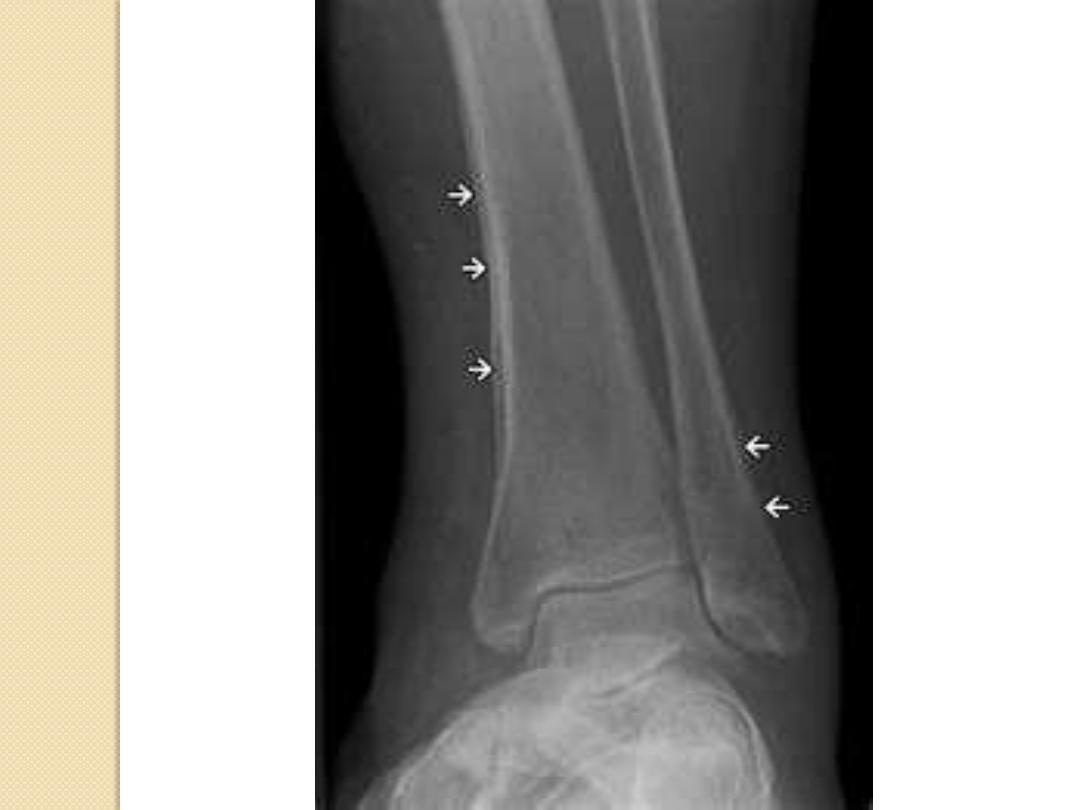
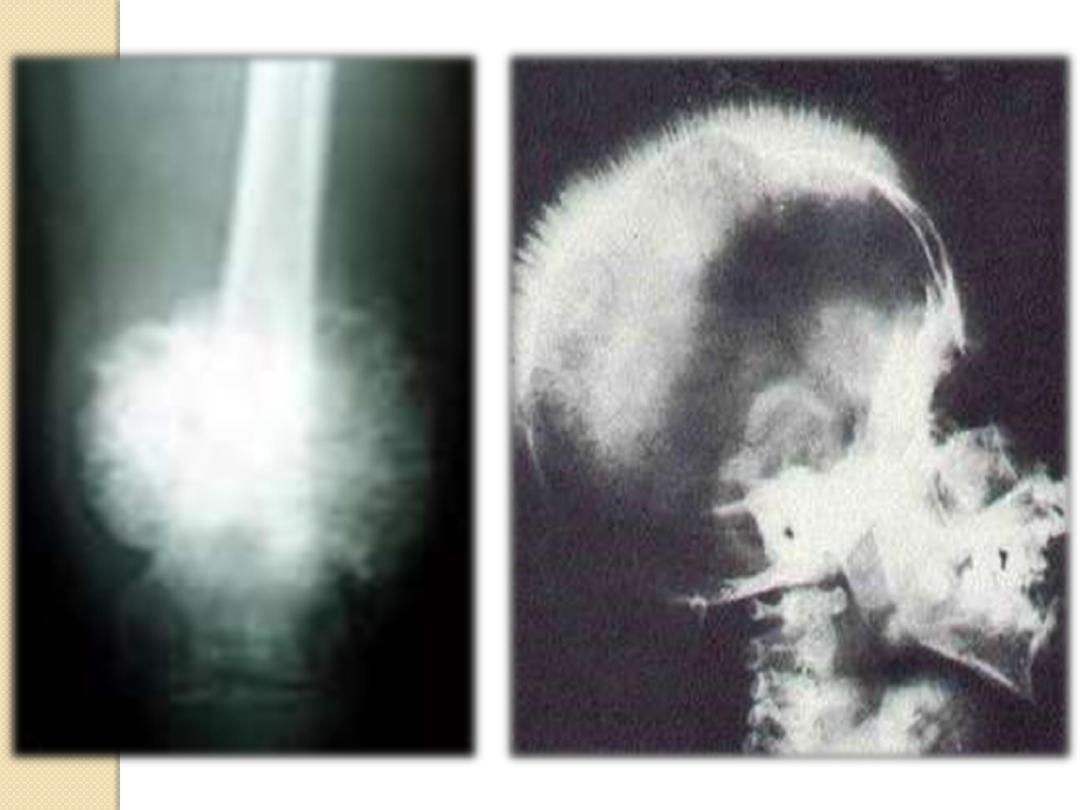
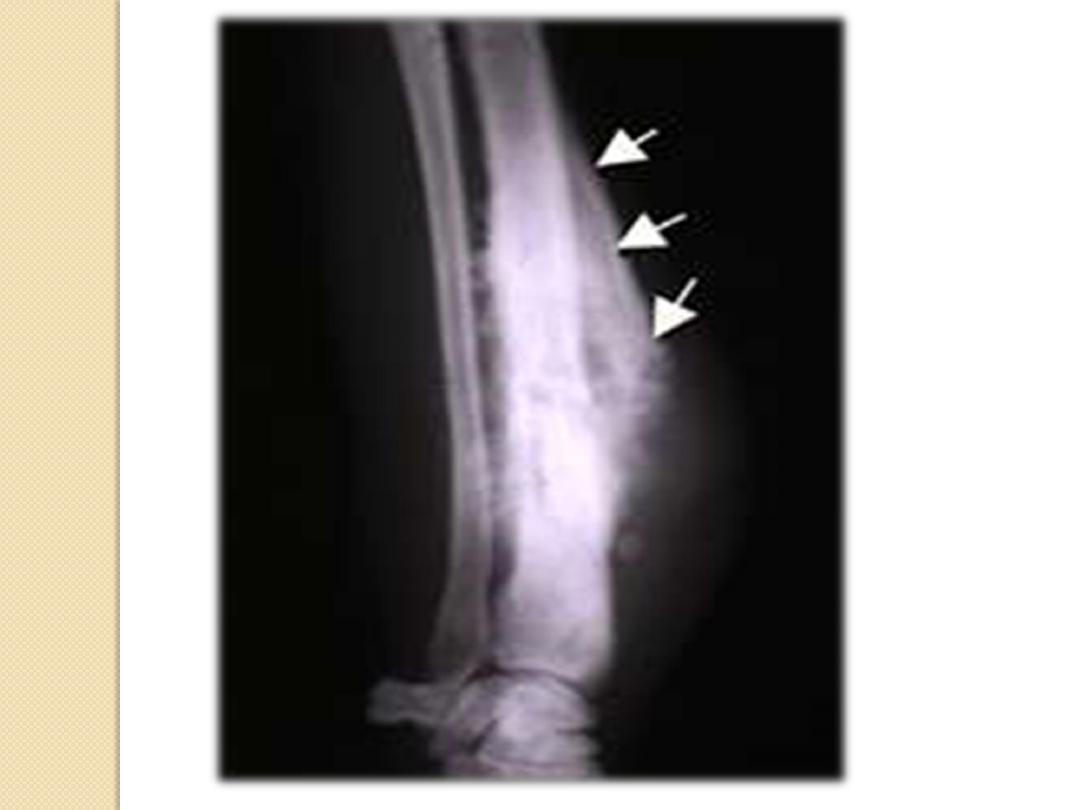
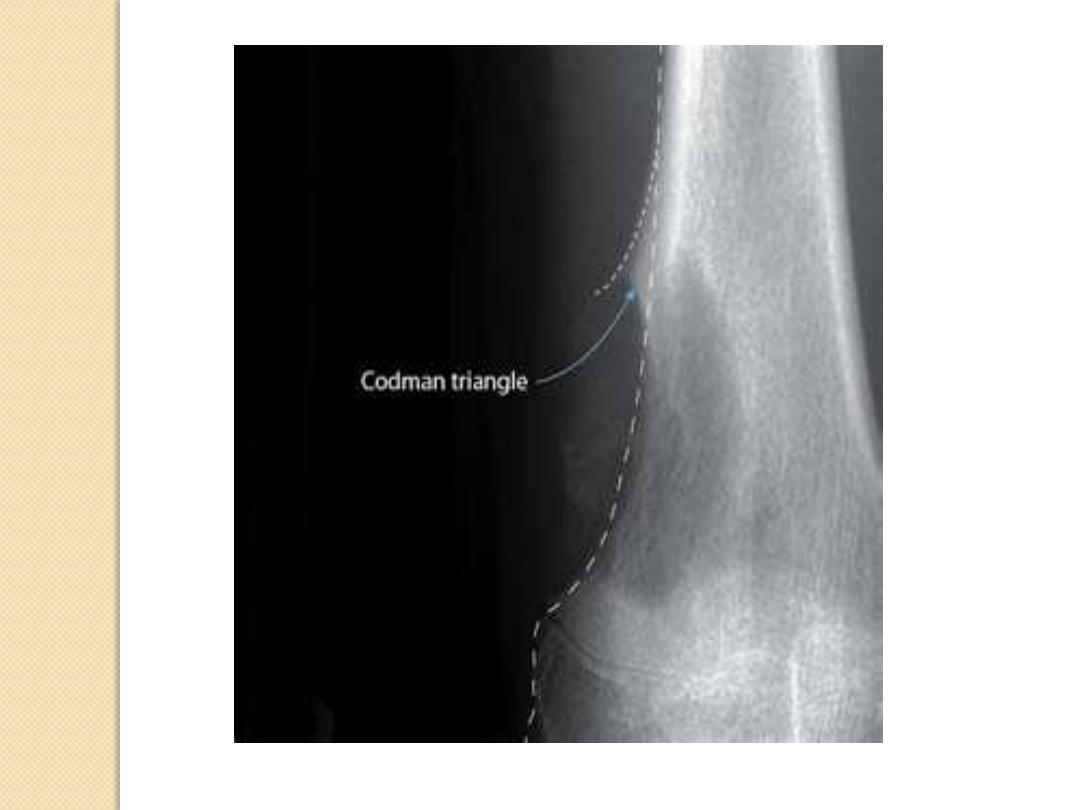
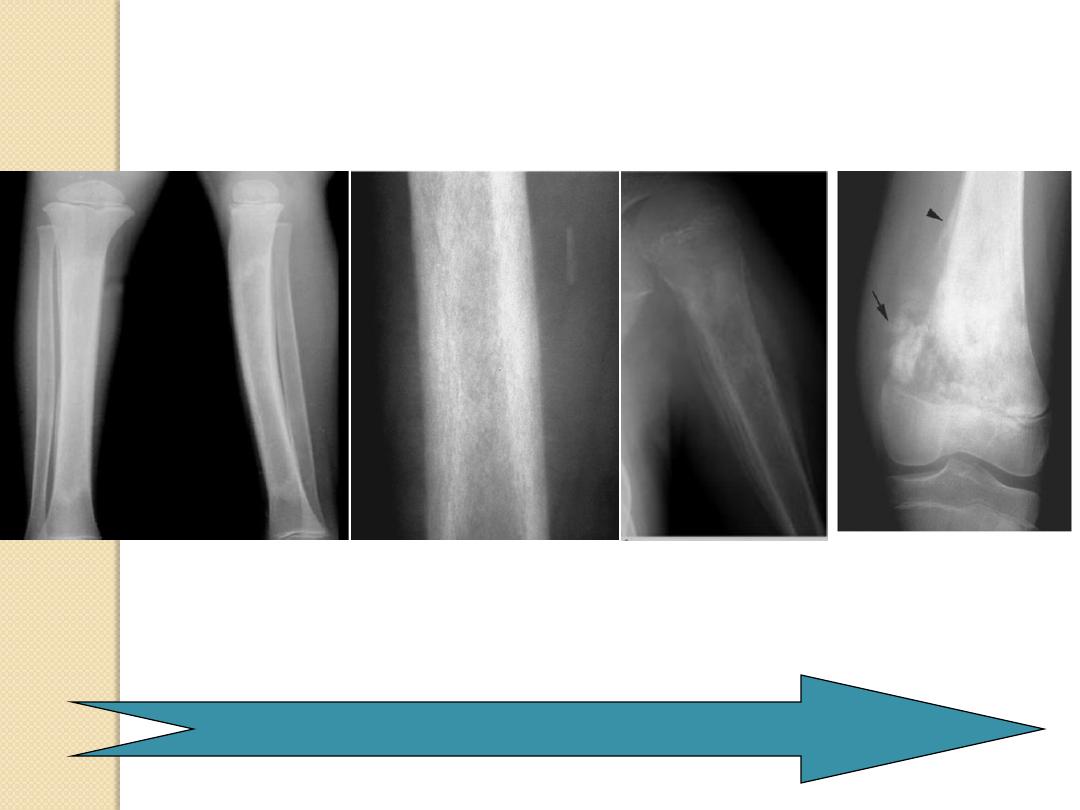
Periosteal Reactions
Solid
onion-peel
Sunburst
Codman
’s
triangle
Less malignant
More malignant

Soft Tissue Extension
Usually implies malignancy
More likely to form discrete soft tissue mass
Benign conditions with soft tissue
extension
Osteomyelitis
Usually infiltration of fat
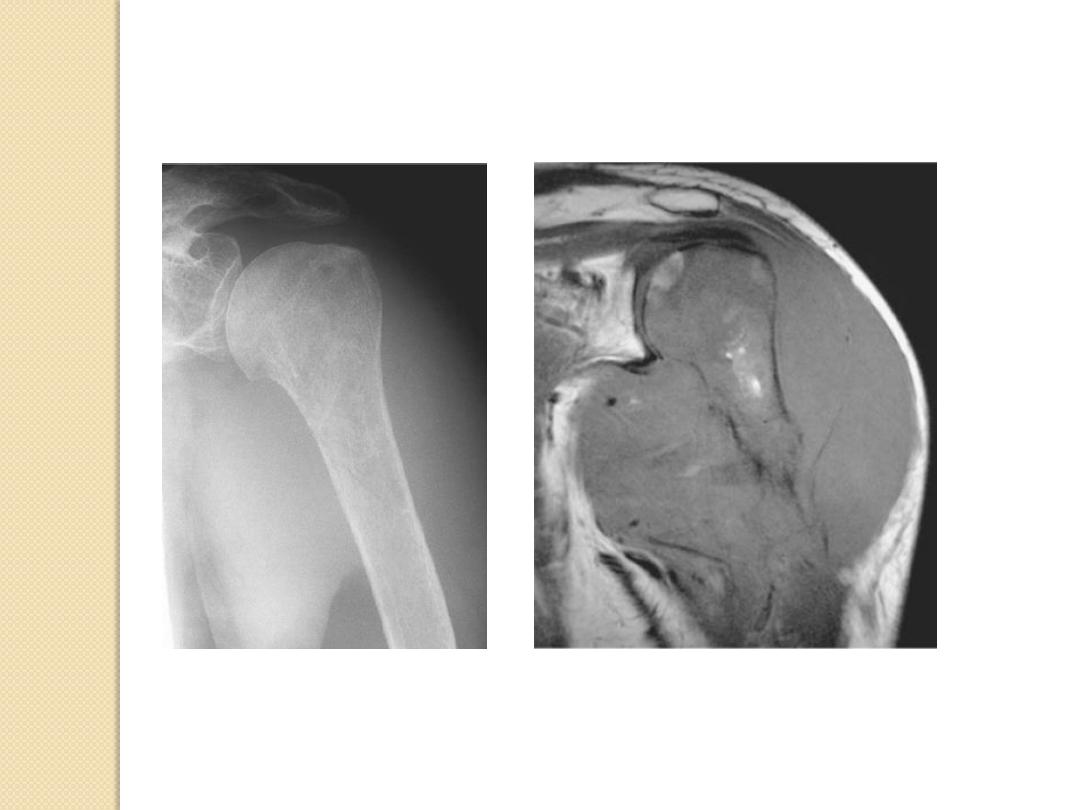
lymphoma
Soft Tissue Extension

Tumor Matrix
Osteoblastic
◦
Fluffy, cotton-like or cloud-like densities
◦
Osteosarcoma
Cartilaginous
◦
Comma-shaped, punctate, annular, popcorn-like
◦
Enchondroma, chondrosarcoma, chondromyxoid fibroma
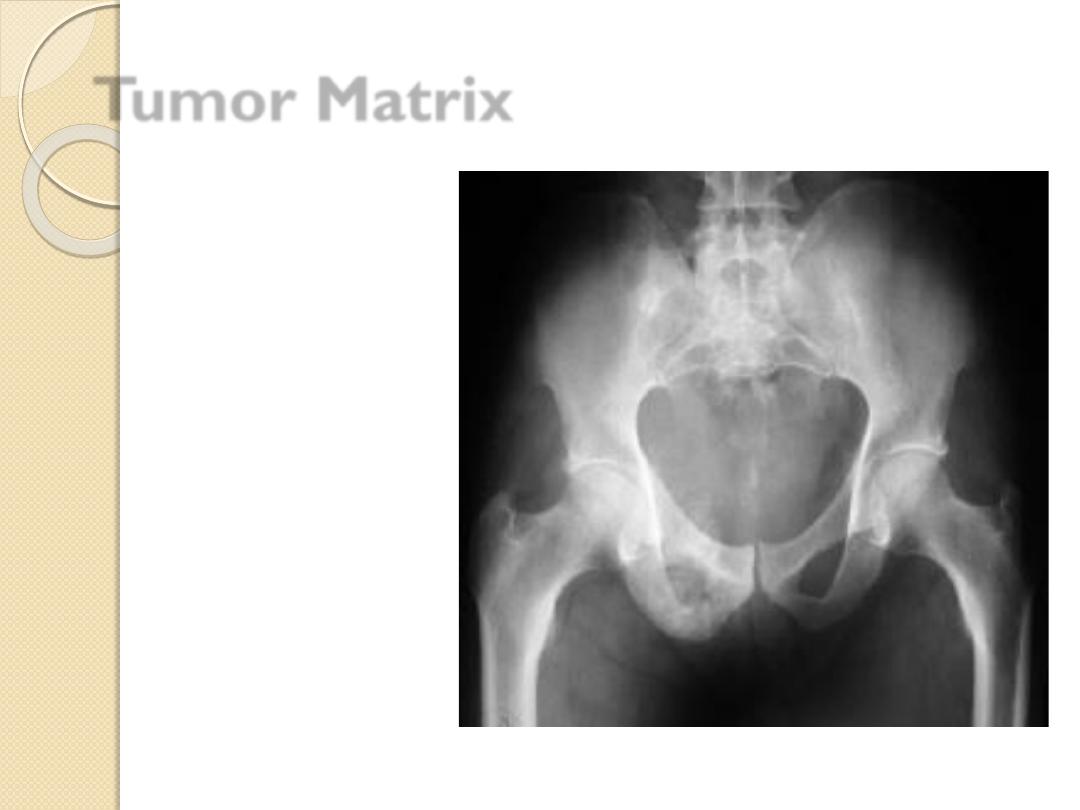
Tumor Matrix
Osteoblastic
Cartilaginous

Osteoblastic
◦
Fluffy, cotton-like or cloud-like densities
as Osteosarcoma
Cartilaginous
◦
Comma-shaped, punctate, annular,
popcorn-like
as Enchondroma, chondrosarcoma,
chondromyxoid fibroma
Tumor Matrix
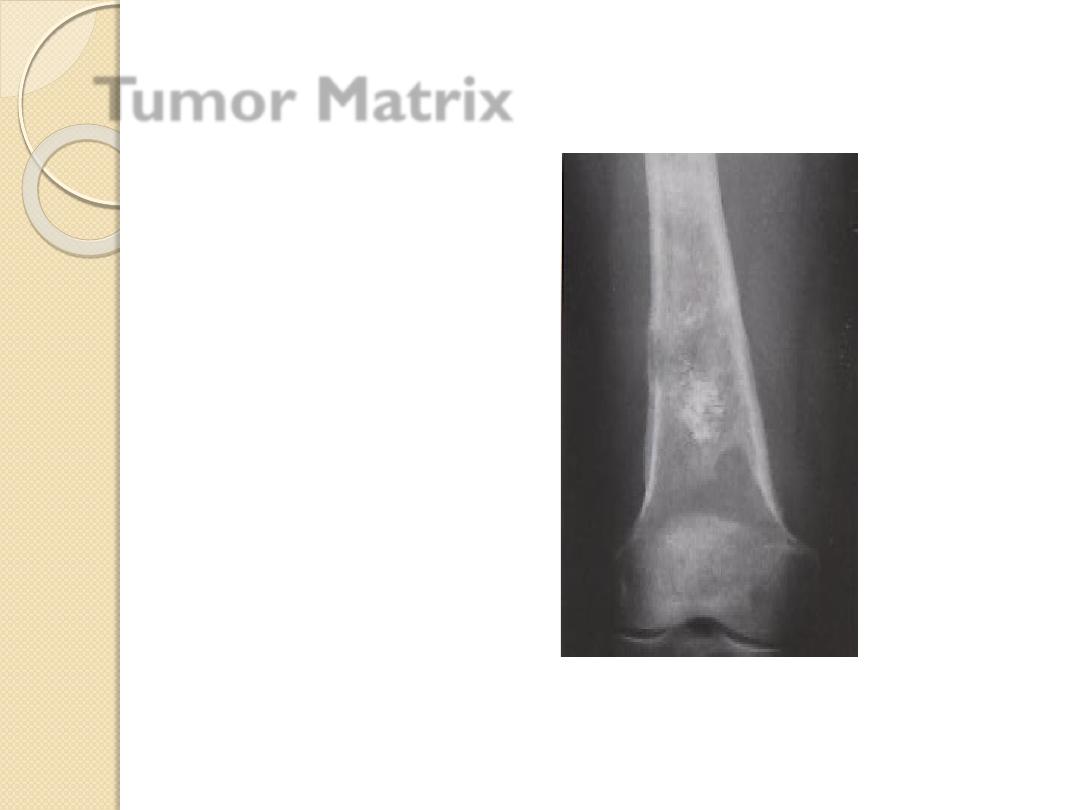
Osteoblastic
Cartilaginous
Tumor Matrix
Chondrosarcoma

•
Multiple myeloma
•
Mets
•
Brown tumor
•
Enchondroma
•
Aneurysmal bone cyst
•
Fibrous dysplasia
Expansile Lesions of Bone
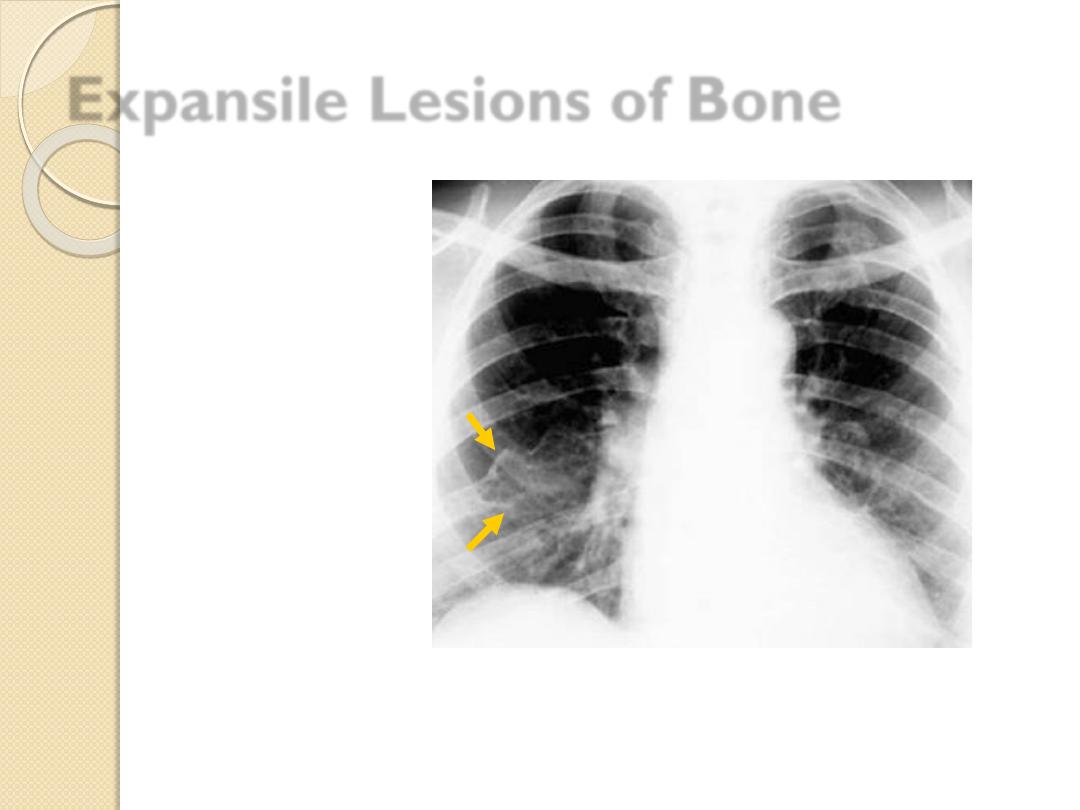
Expansile Lesions of Bone
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
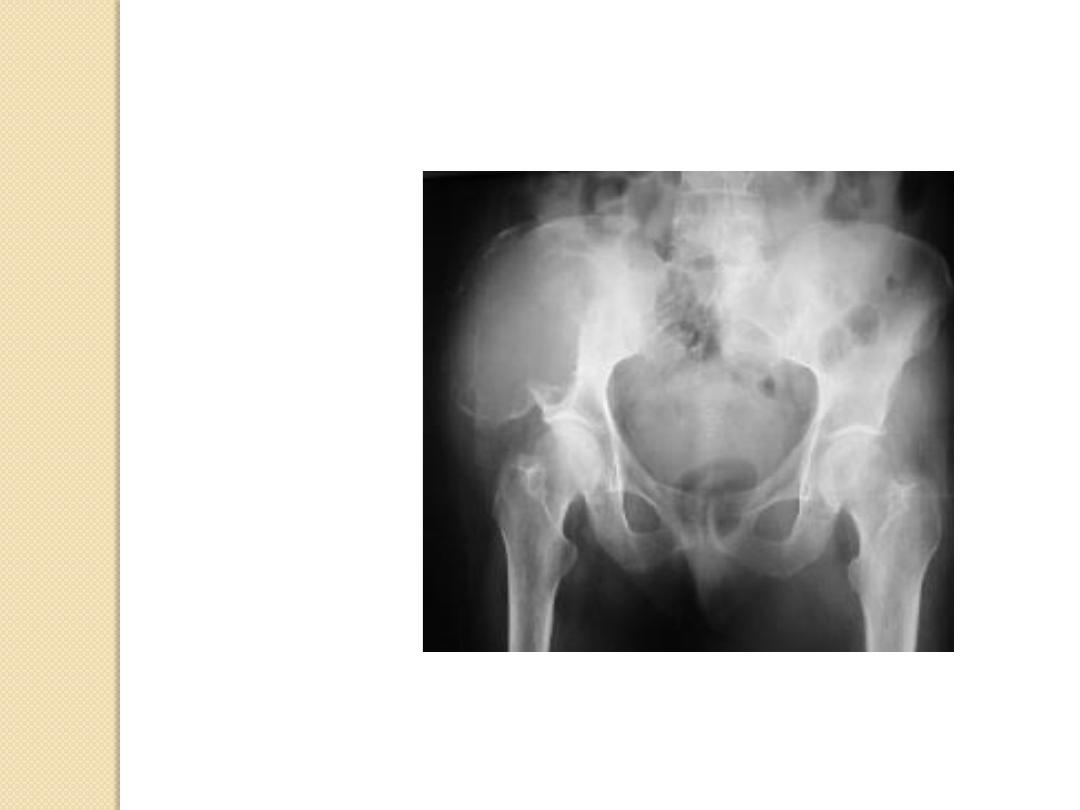
Expansile Lesions of Bone
Renal cell carcinoma
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
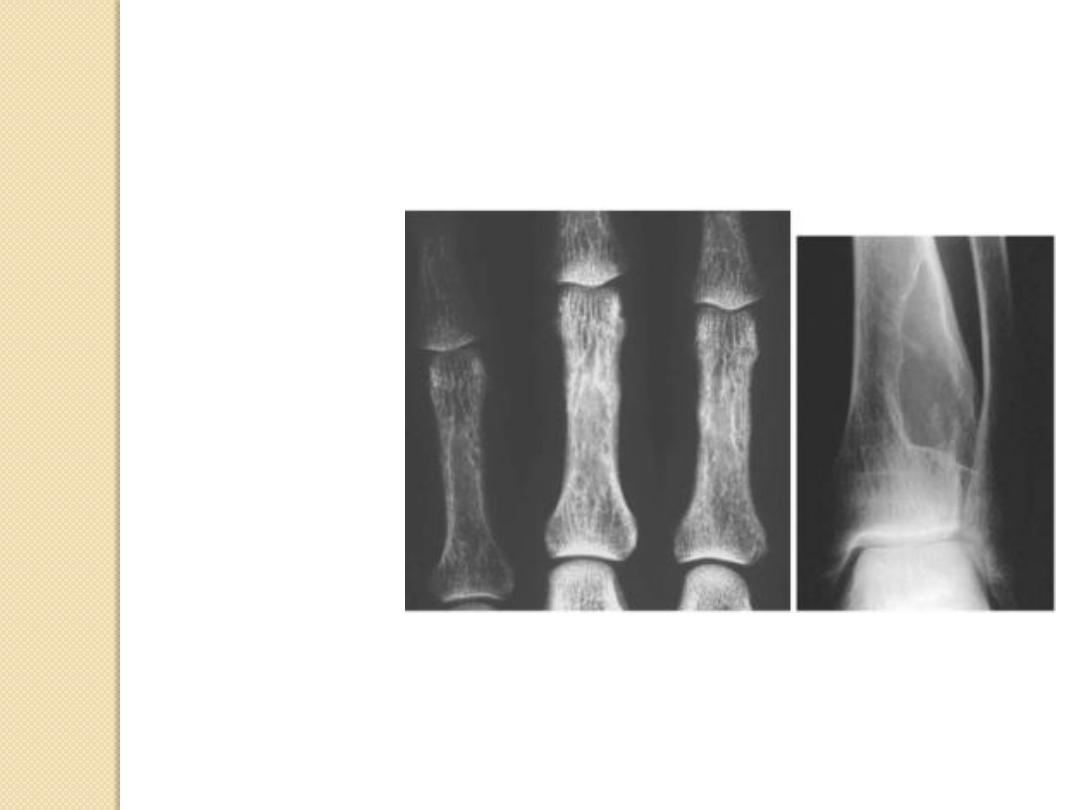
Expansile Lesions of Bone
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
Expansile Lesions of Bone
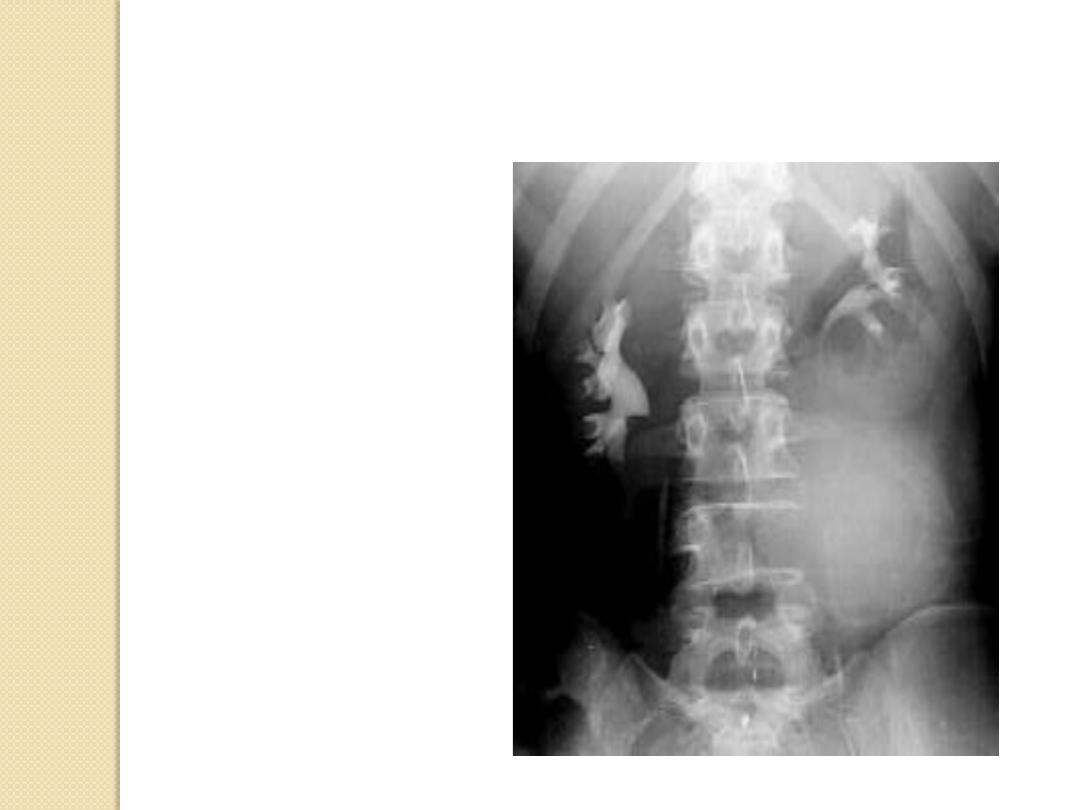
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone
cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
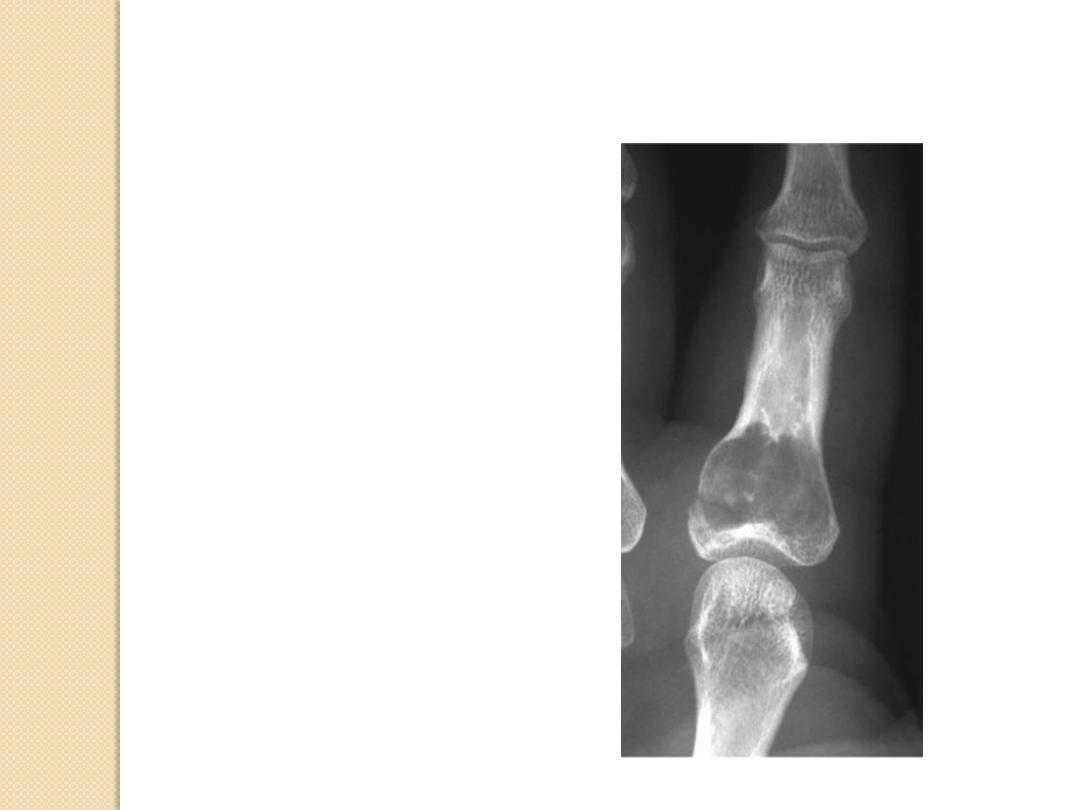
Expansile Lesions of Bone
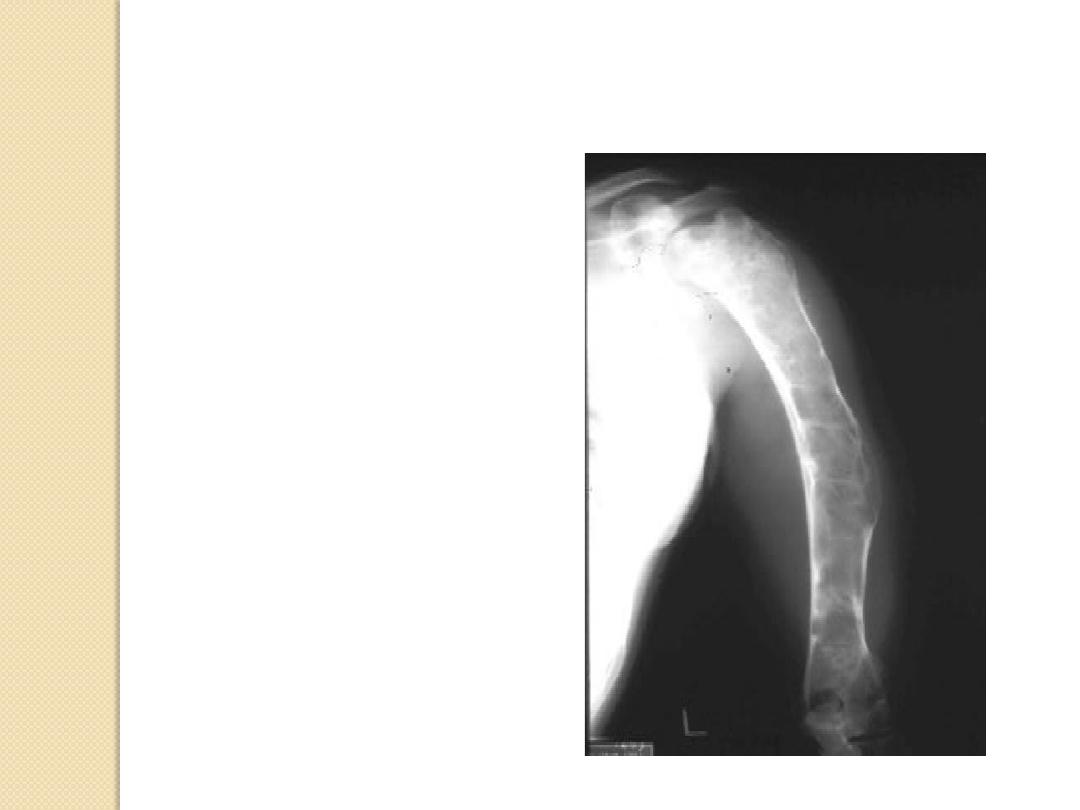
Multiple myeloma
Mets
Brown tumor
Enchondroma
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Fibrous dysplasia
Expansile Lesions of Bone

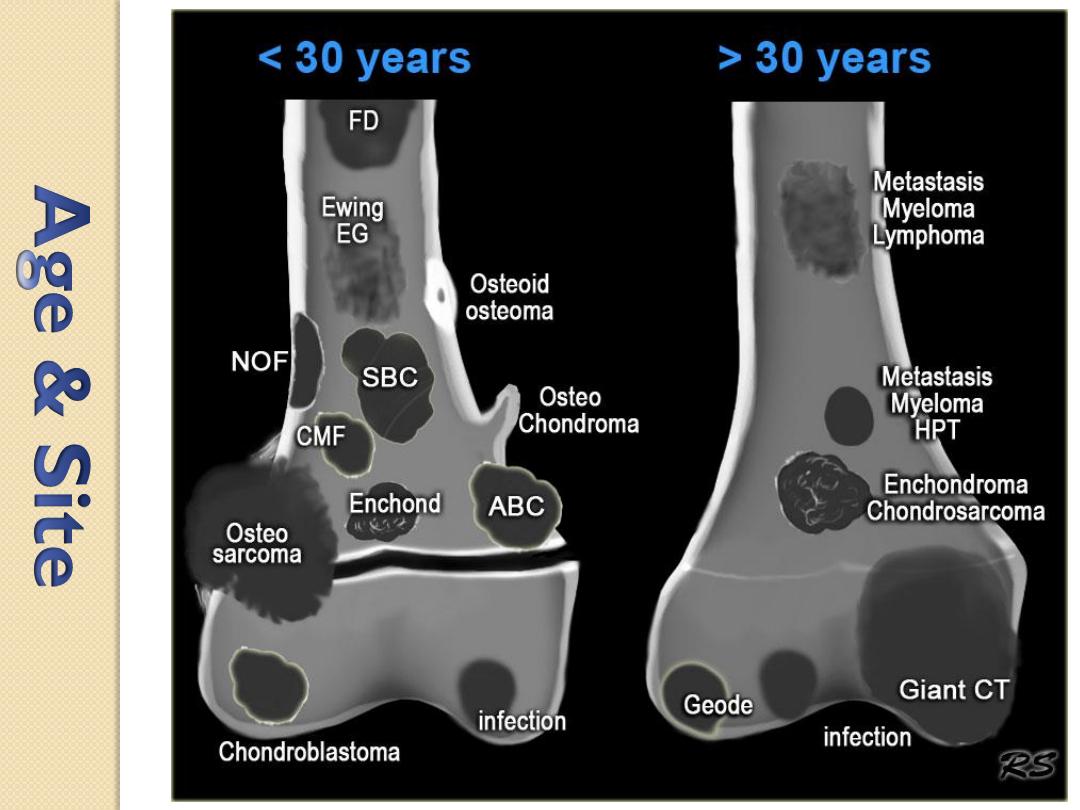
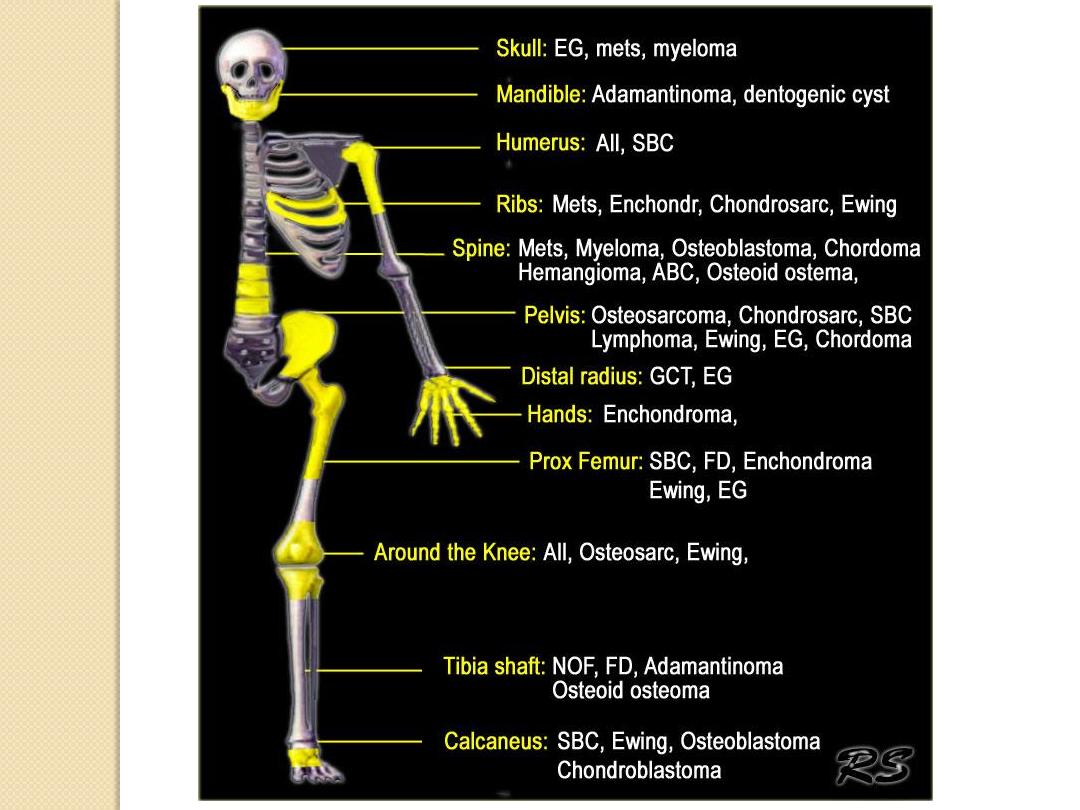
Clues by Location of Lesion
• In the Transverse Plane
• In the Longitudinal Plane
• Characteristic Locations by tumors
• Characteristic Tumors by Body Site
– Pelvic Lesions
– Expansile Rib Lesions
– Lesions of the Spine
In the Transverse Plane
.
.
.

Epiphyseal
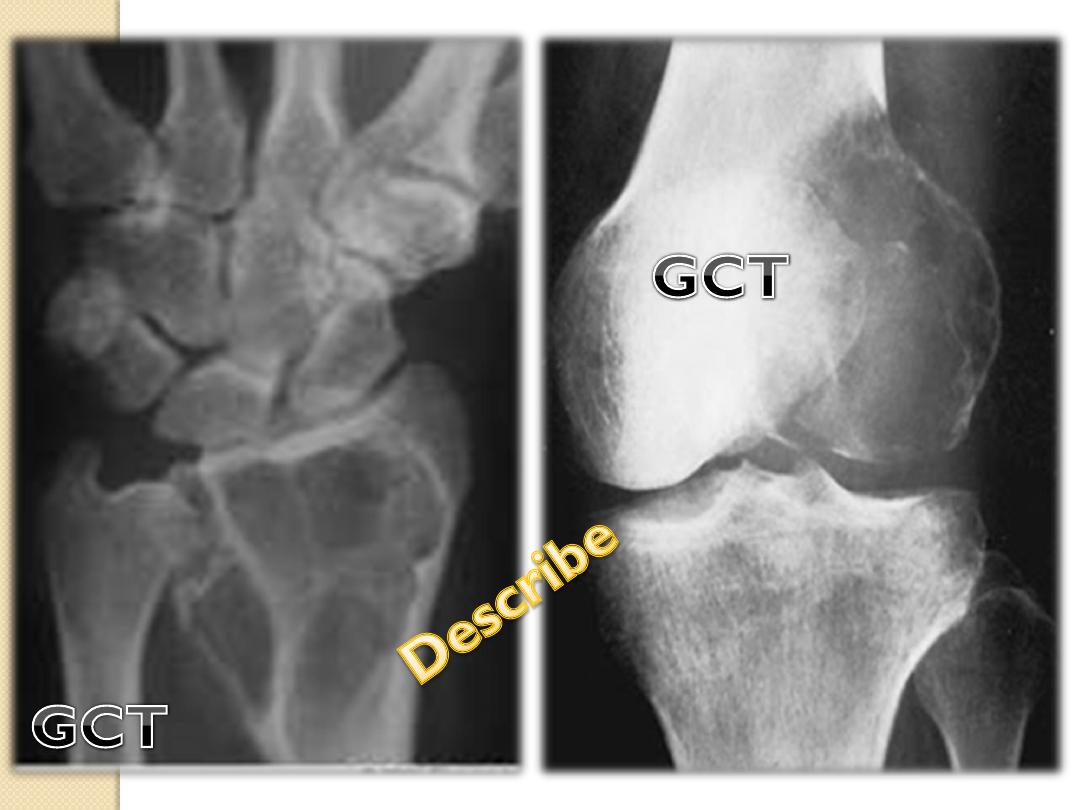
GCT, chondroblastoma
Metaphyseal
Osteomyelitis, osteo-and chondrosarcoma
Diaphyseal
Round cell lesions, ABC, enchondroma
In the longitudinal Plane
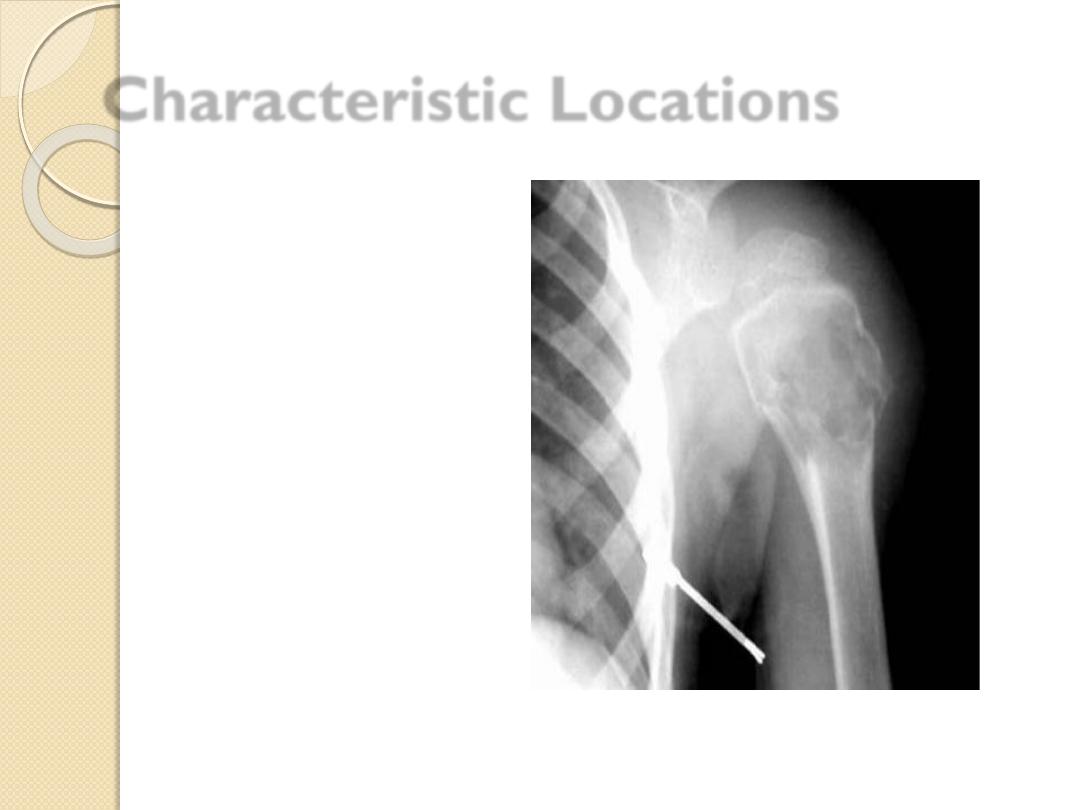
Characteristic Locations
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
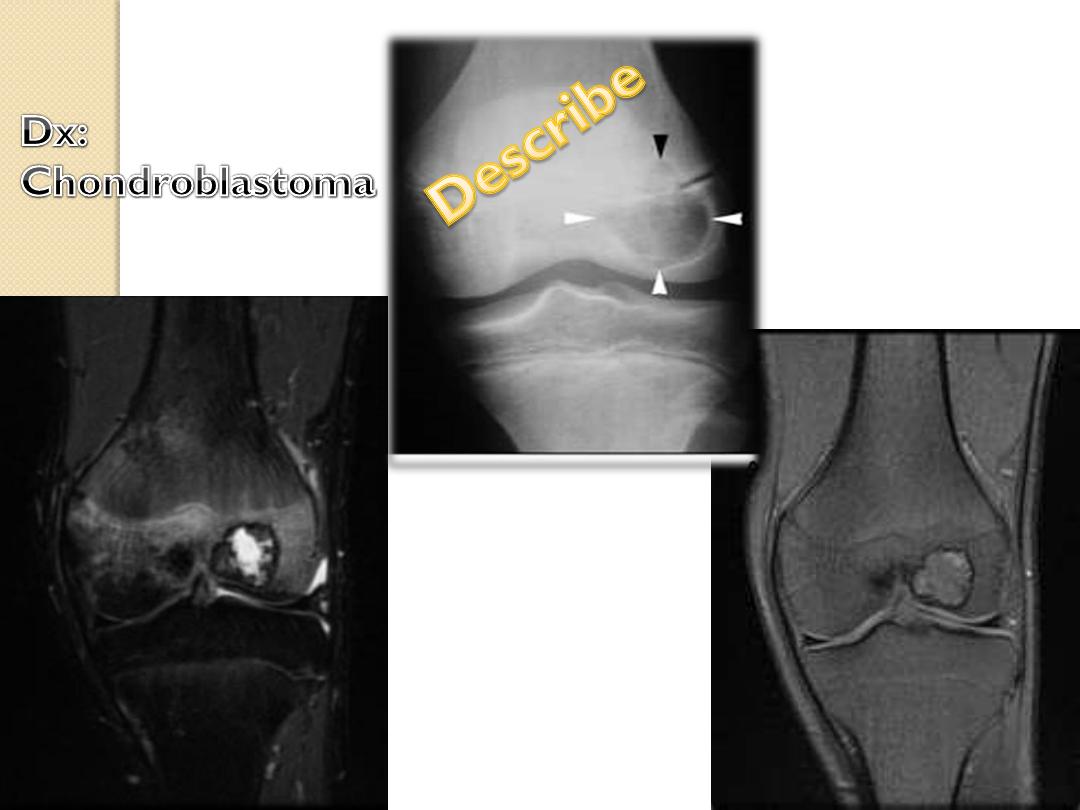
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
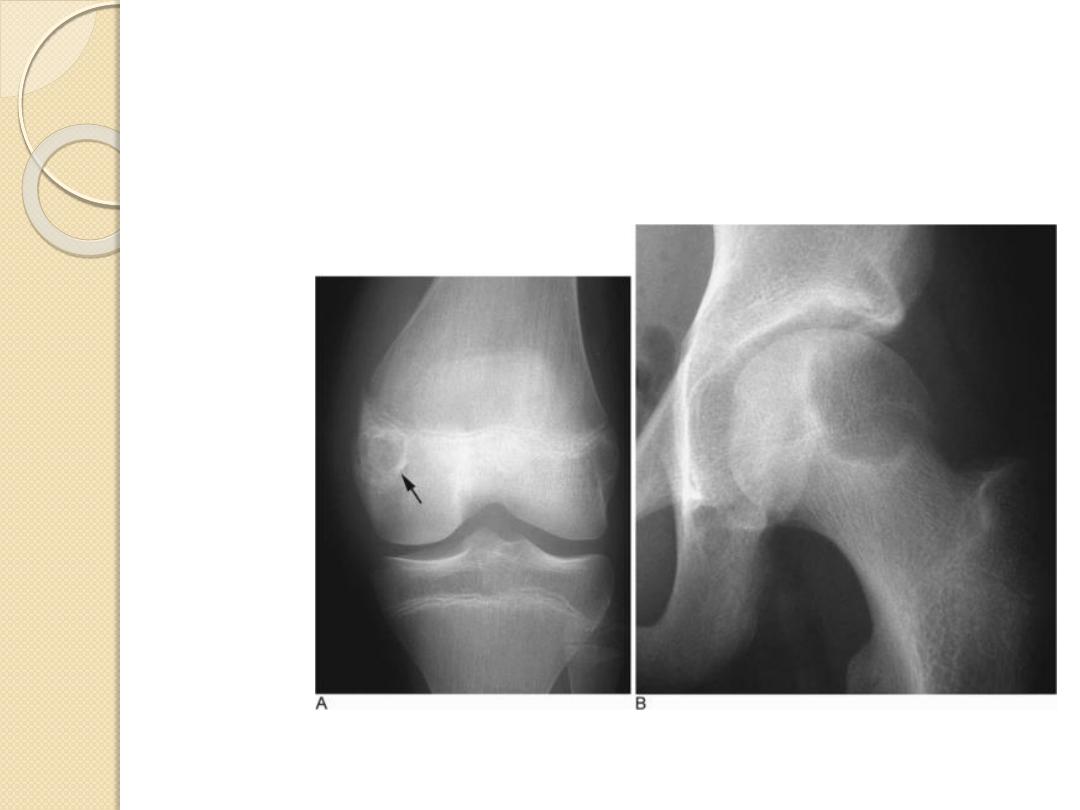
Characteristic Locations
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
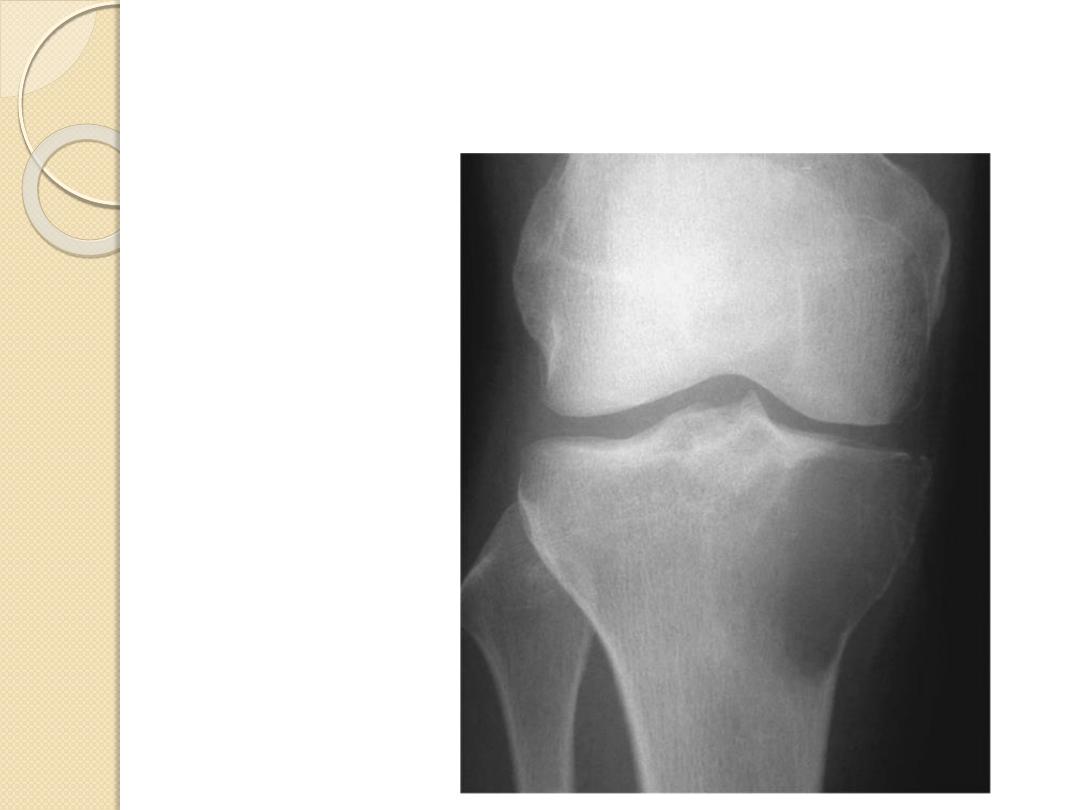
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
Characteristic Locations
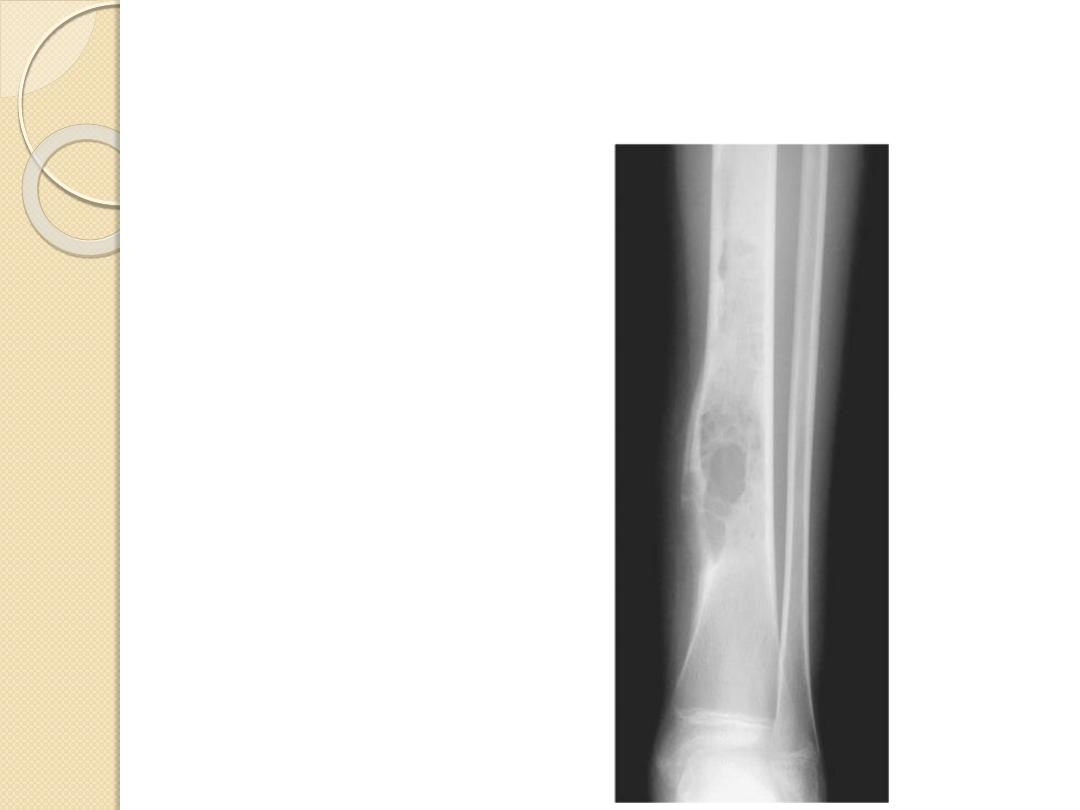
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
Characteristic Locations
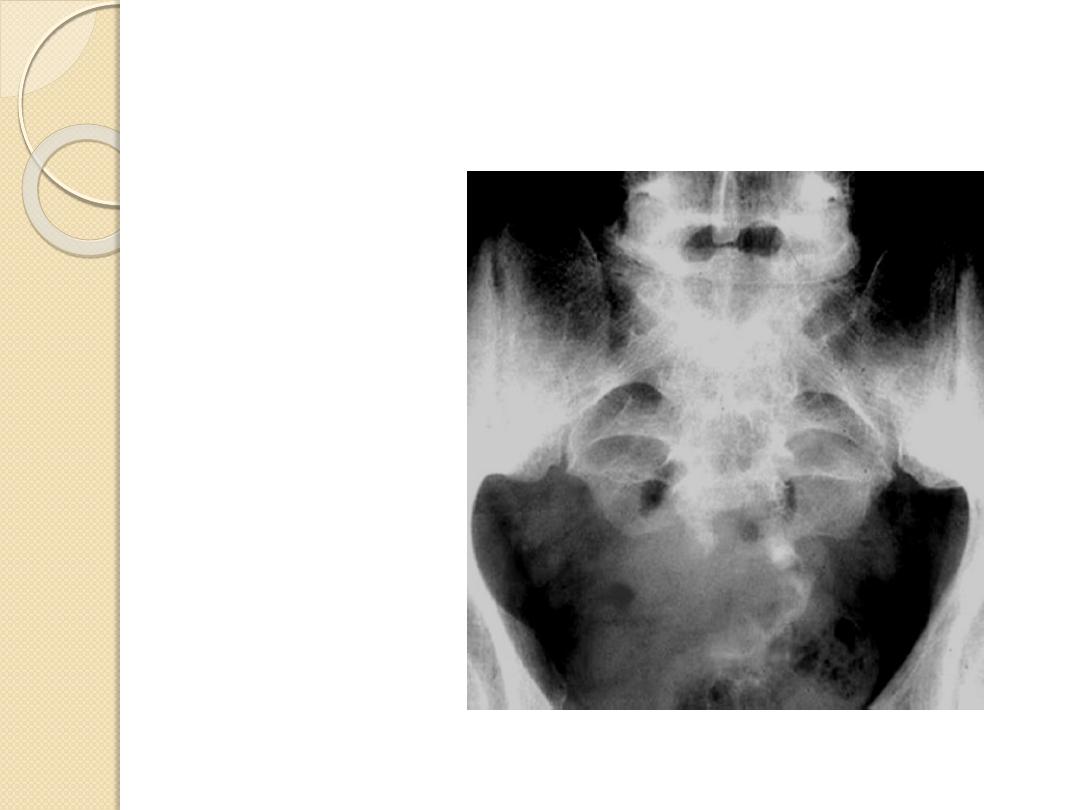
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
Characteristic Locations
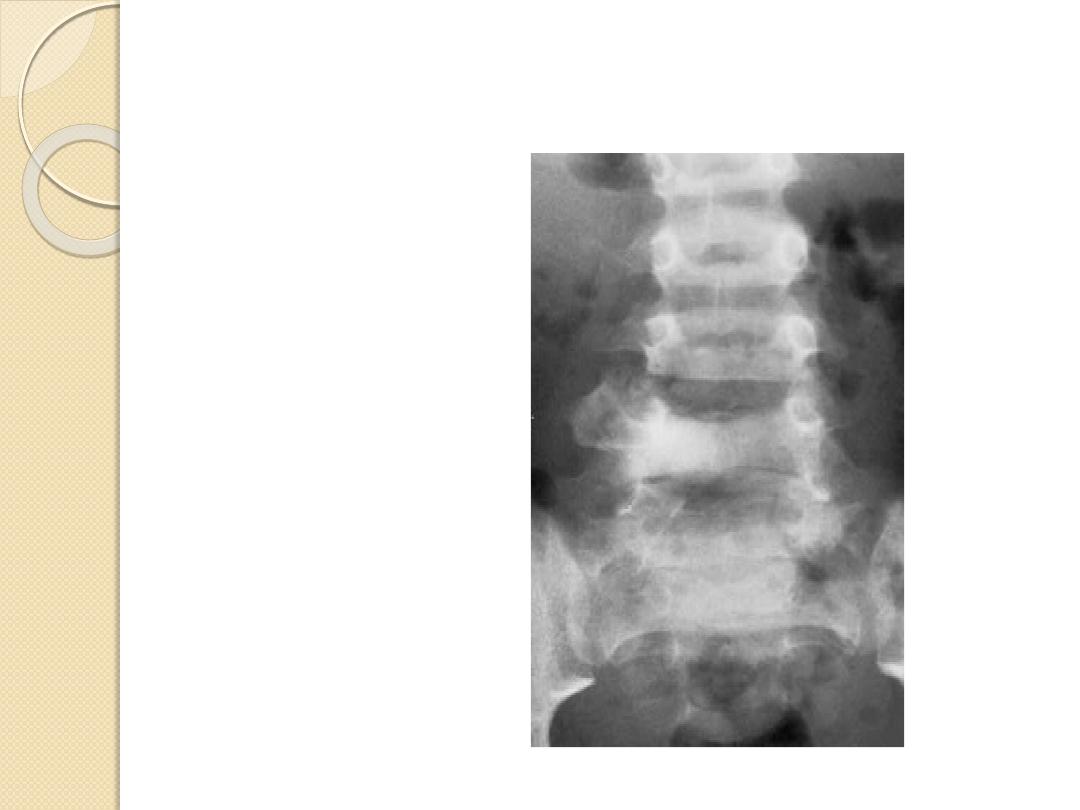
Simple bone cyst
Proximal humerus
Chondroblastoma
Epiphyses
Giant Cell tumor
Epiphyses
Adamantinoma
Tibia
Chordoma
Sacrum, clivus
Osteoblastoma
Spine, posterior
Characteristic Locations

Clues by Density of Lesion
Sclerotic Cortical Lesions
Lytic Lesions in Children
Lytic Lesions in Adults
Blastic Lesions in Children
Blastic Lesions in Adults
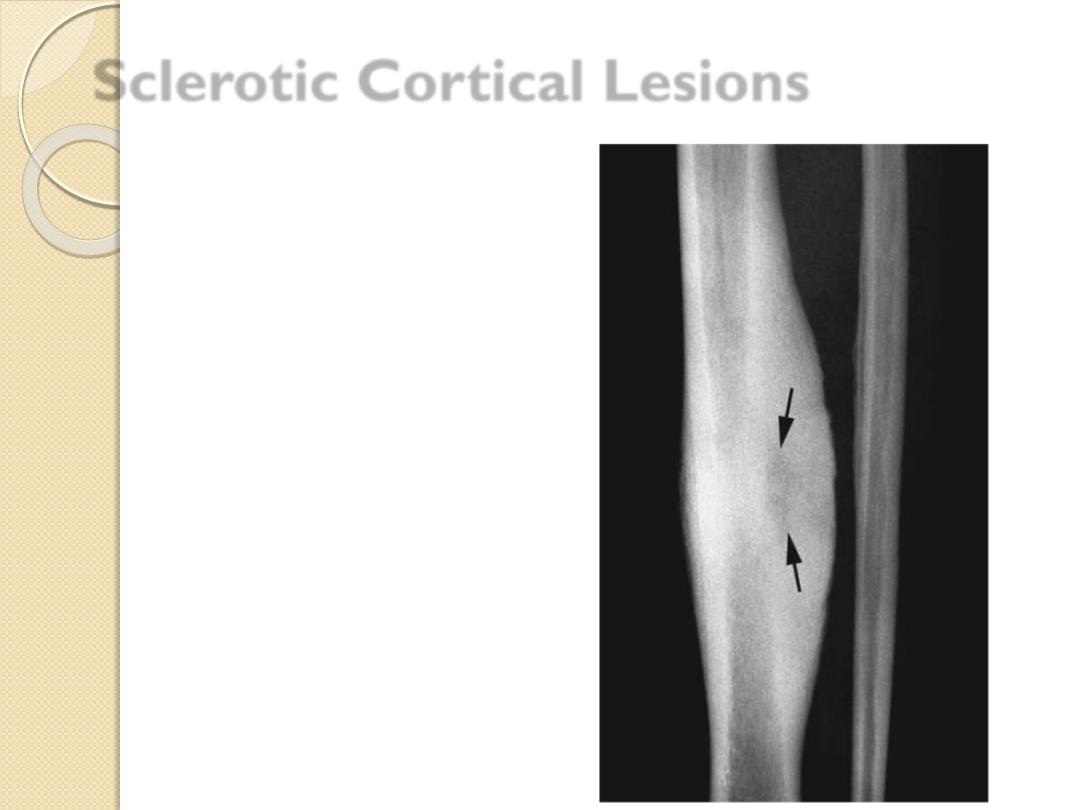
Sclerotic Cortical Lesions
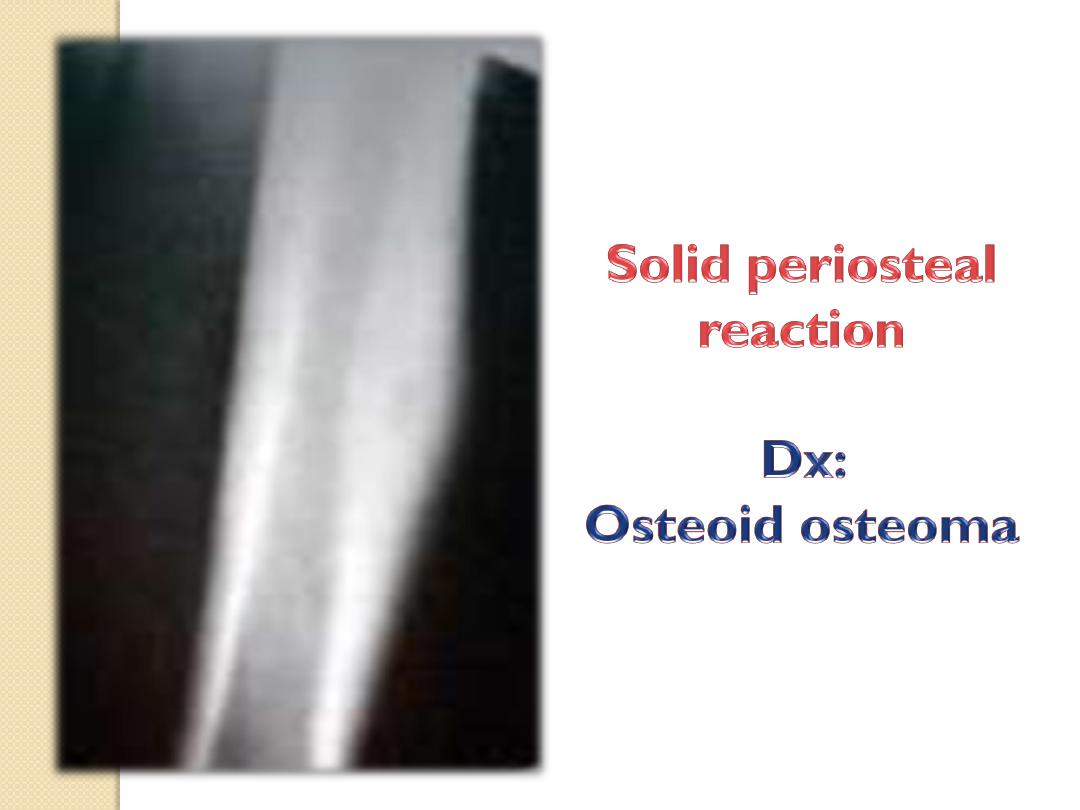
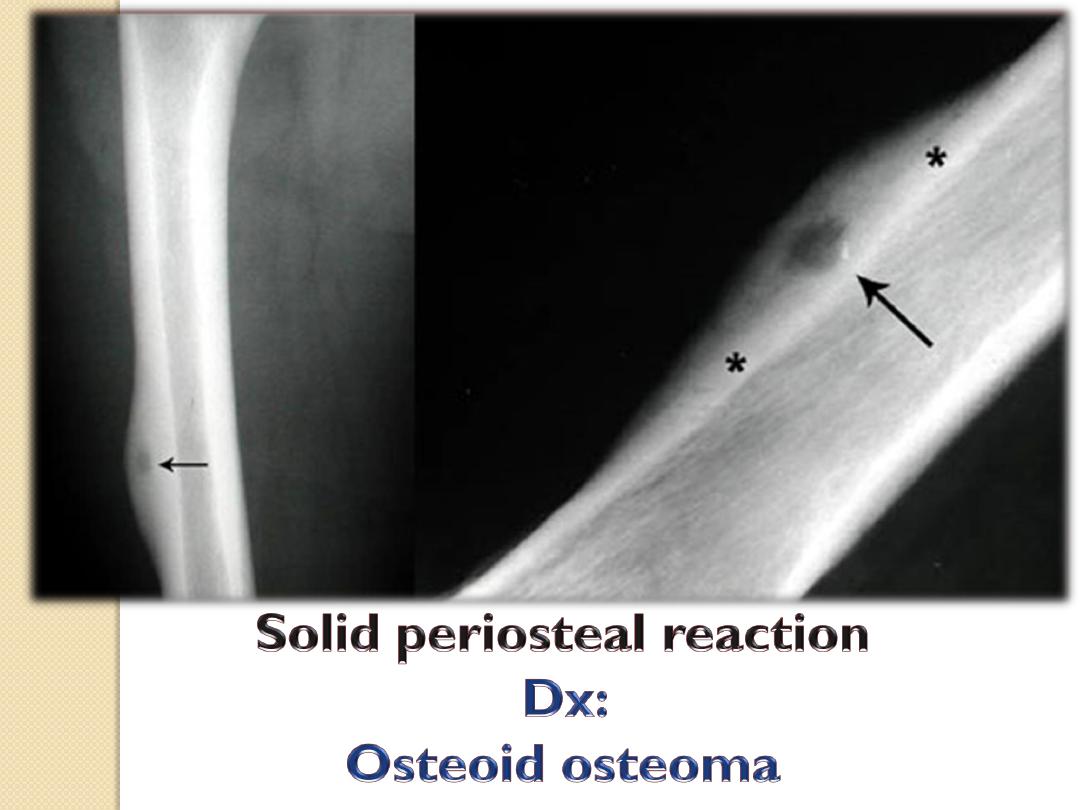
Osteoid
osteoma
Brodie’s abscess
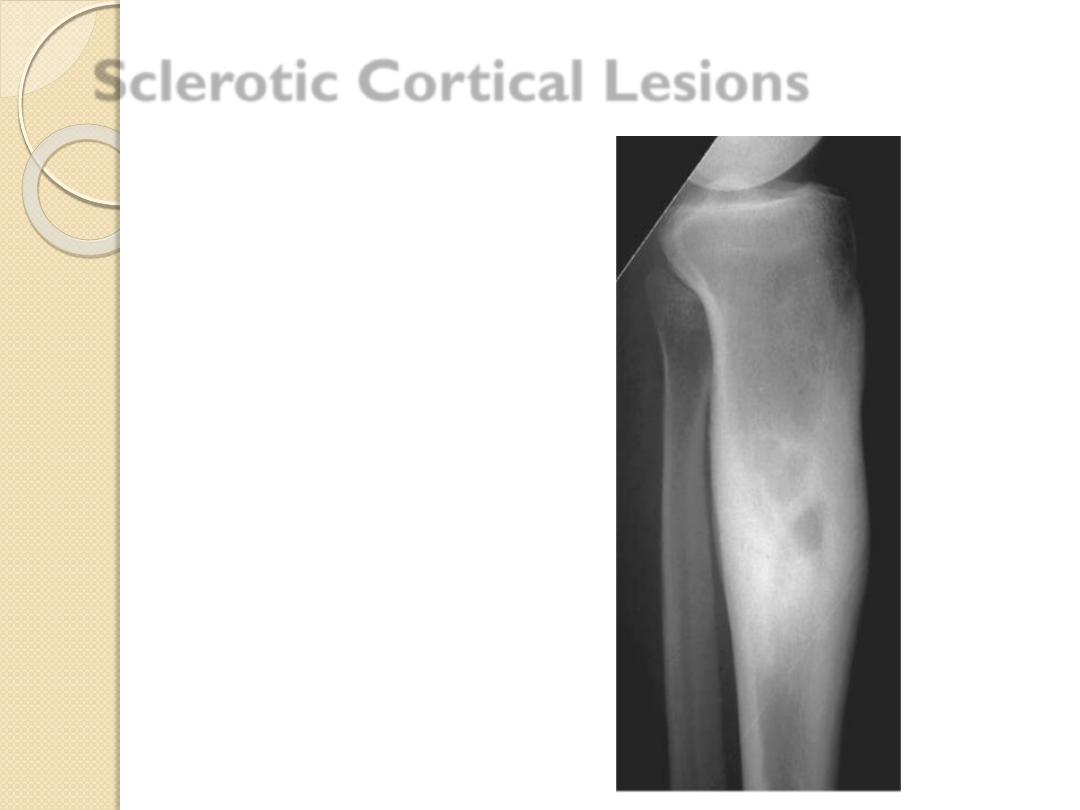
Osteoid osteoma
Brodie’s
abscess
Sclerotic Cortical Lesions
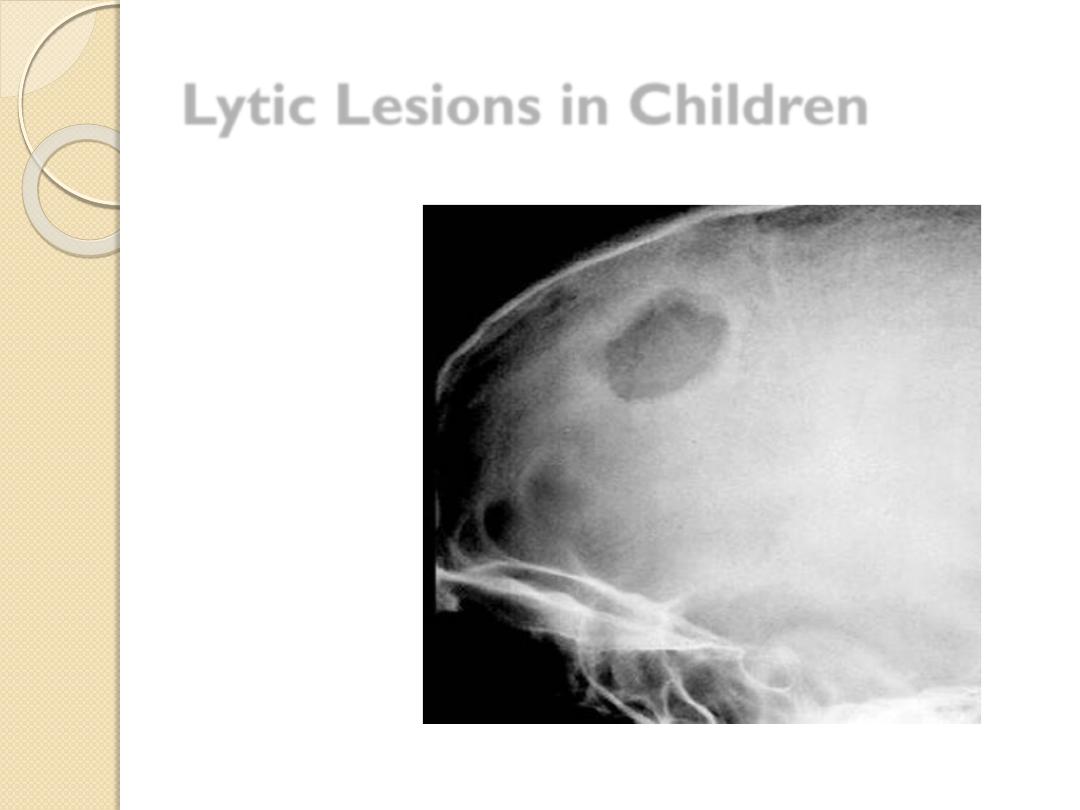
Lytic Lesions in Children
Eosinophilic
granuloma
Leukemia
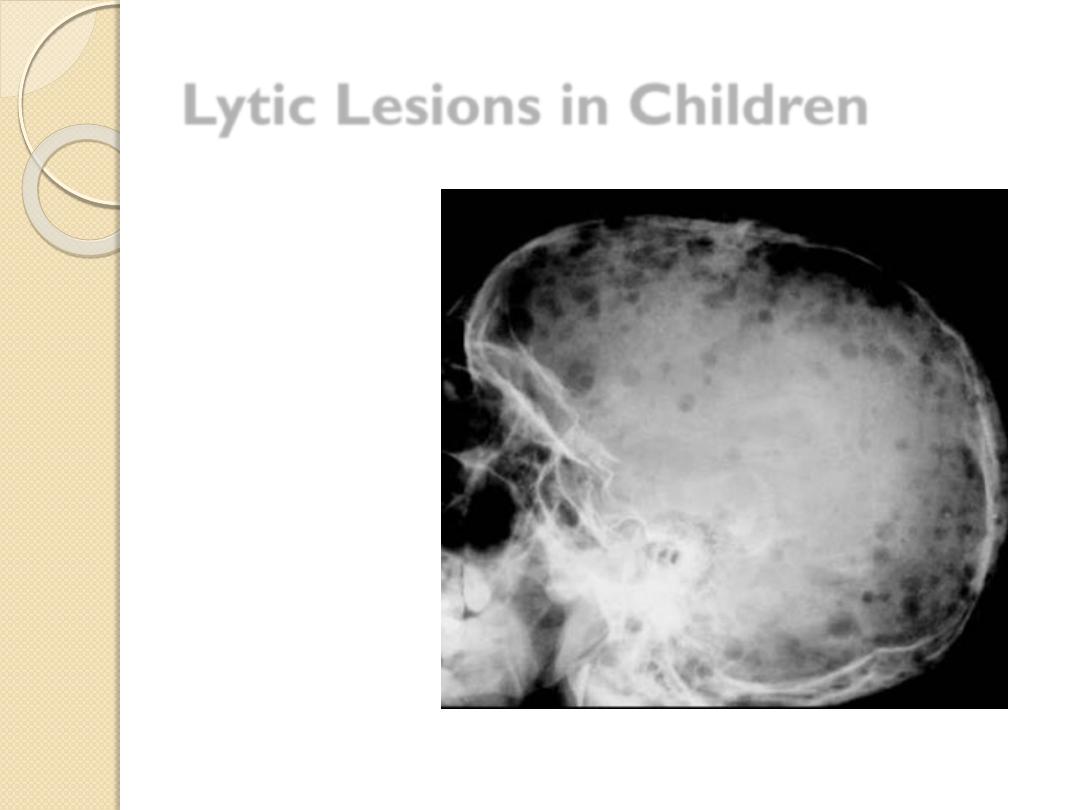
Lytic Lesions in Children
Eosinophilic granuloma
Leukemia
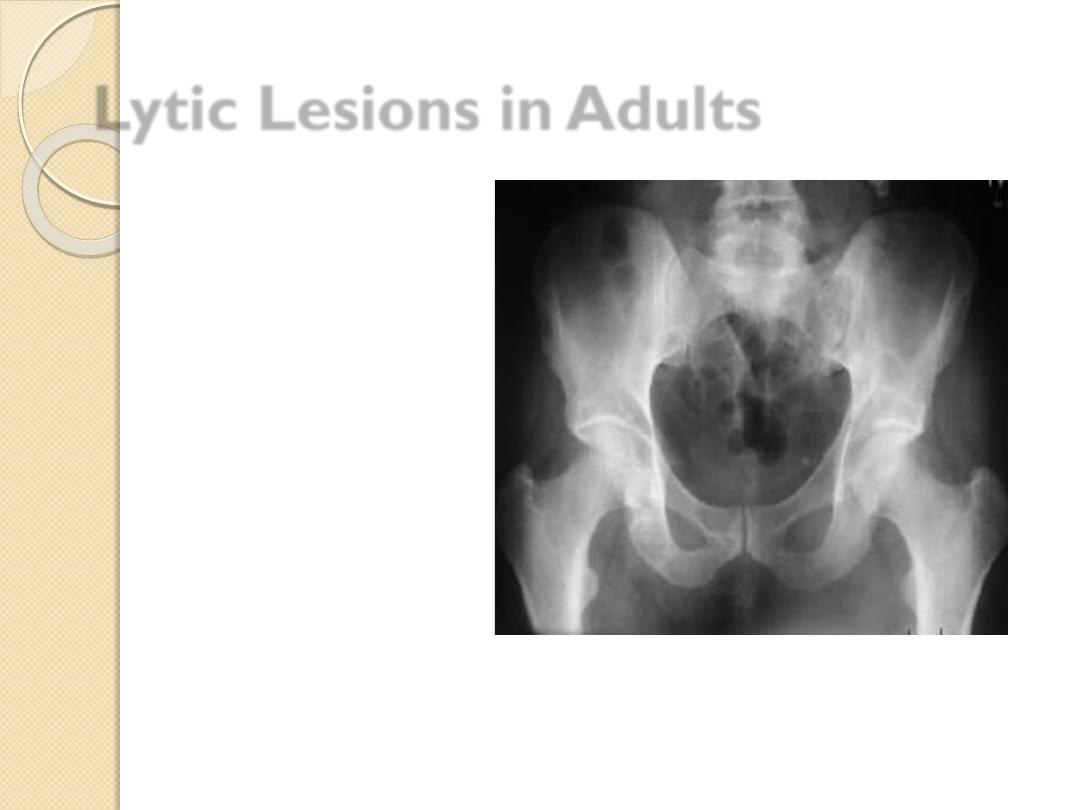
Lytic Lesions in Adults
Metastatic lesions
◦
Lung
◦
Renal
◦
Thyroid
Multiple myeloma
Primary bone tumor
Metastatic thyroid carcinoma
Metastatic lesions
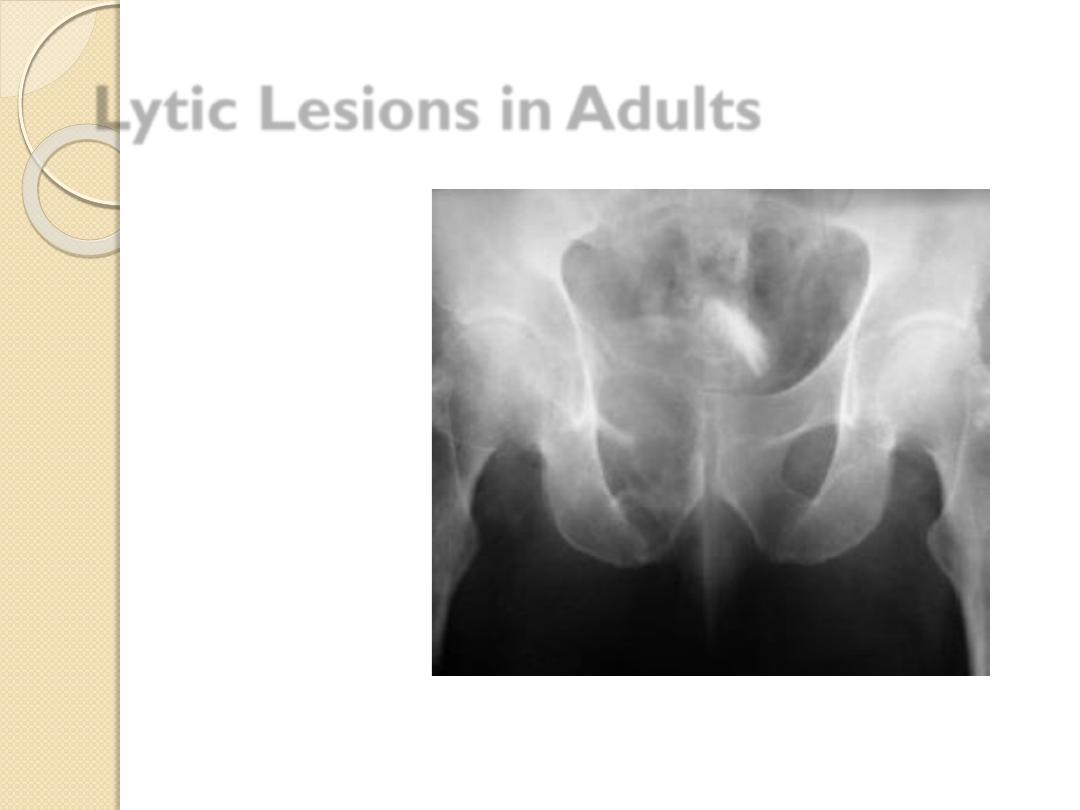
◦
Lung
◦
Renal
◦
Thyroid
Multiple myeloma
Primary bone tumor
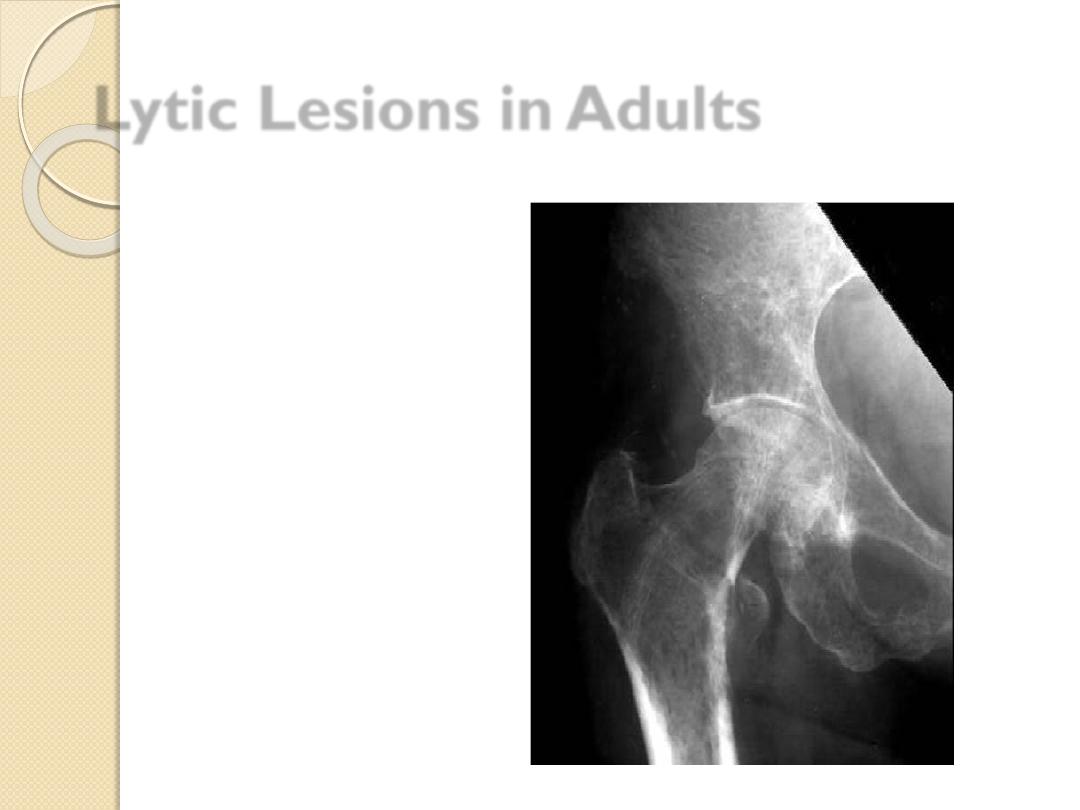
Lytic Lesions in Adults
Metastatic lesions
◦
Lung
◦
Renal
◦
Thyroid
Multiple myeloma
Primary bone
tumor
Chondrosarcoma
Lytic Lesions in Adults
Lymphoma
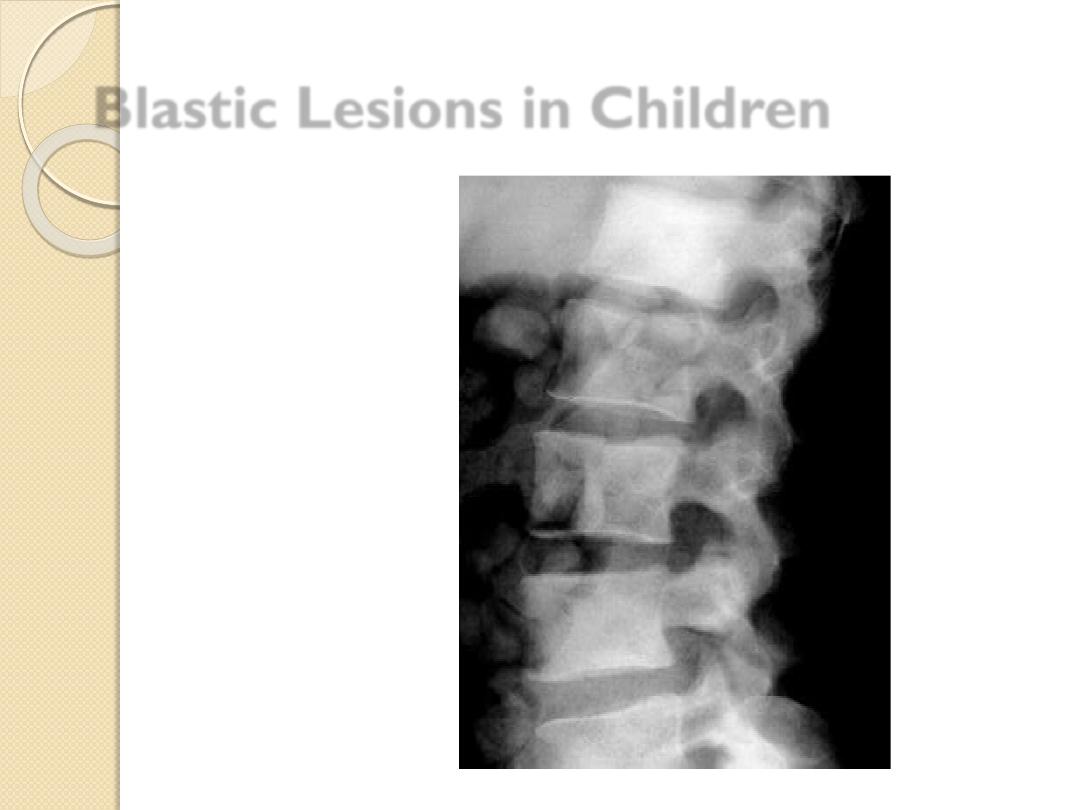
Blastic Lesions in Children
Metastatic
disease
Breast –
female
Prostate –
male
Lymphoma
Paget’s disease
Prostatic Ca.
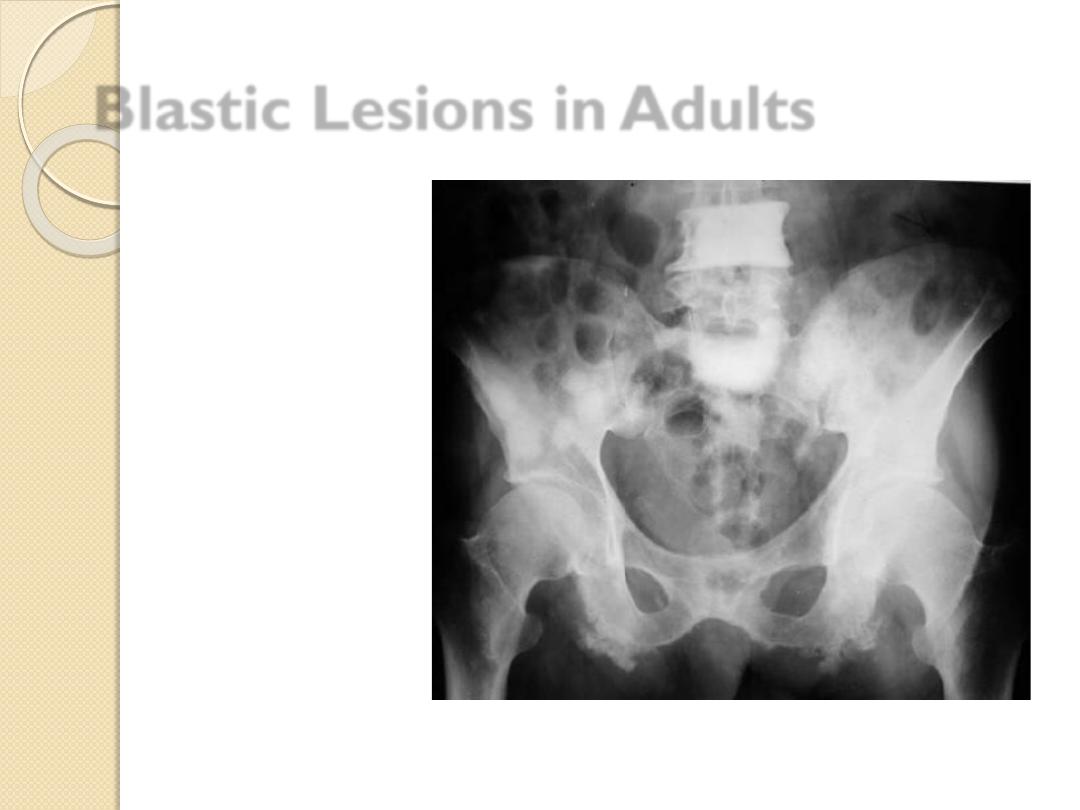
Blastic Lesions in Adults
Metastatic disease
Breast –female
Prostate –male
Lymphoma
Paget’s disease
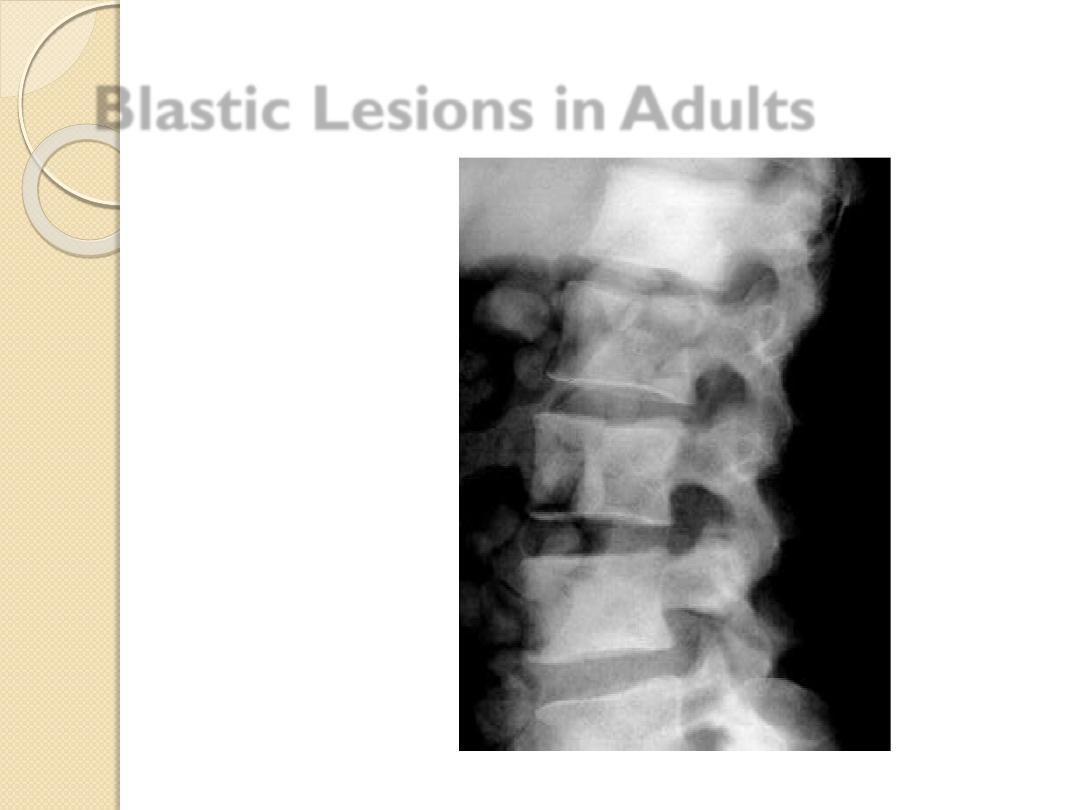
Blastic Lesions in Adults
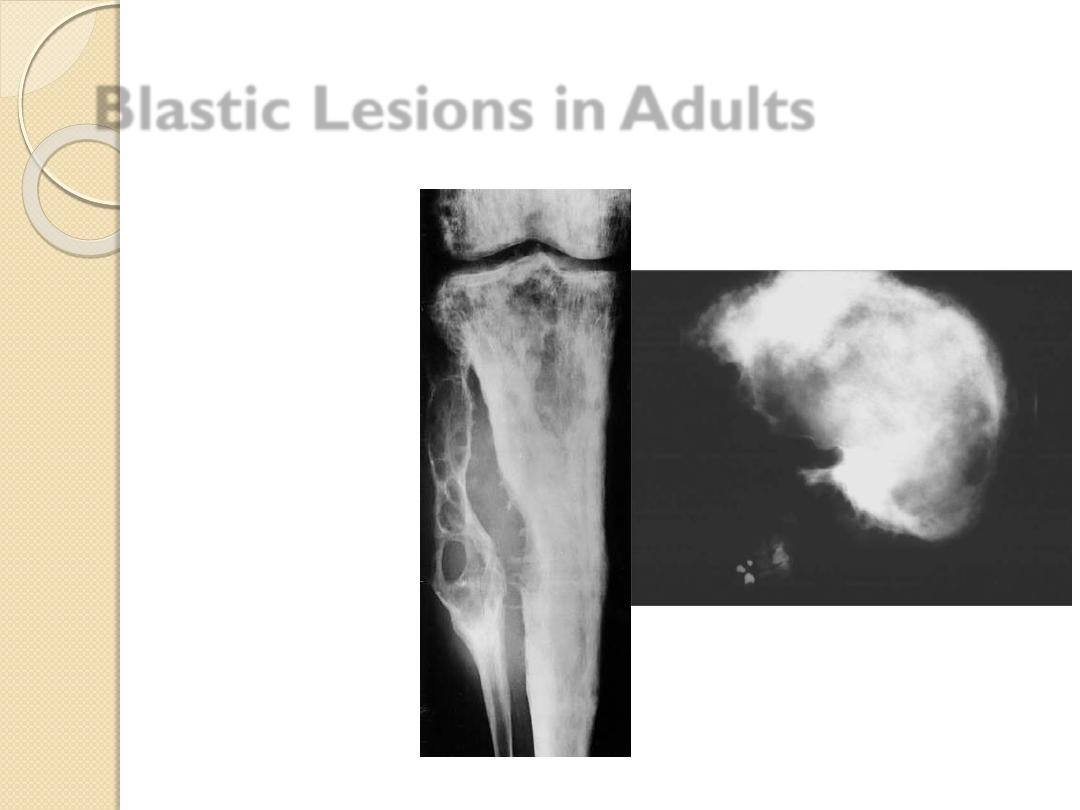
Metastatic disease
Breast –female
Prostate –male
Lymphoma
Paget’s disease
Blastic Lesions in Adults
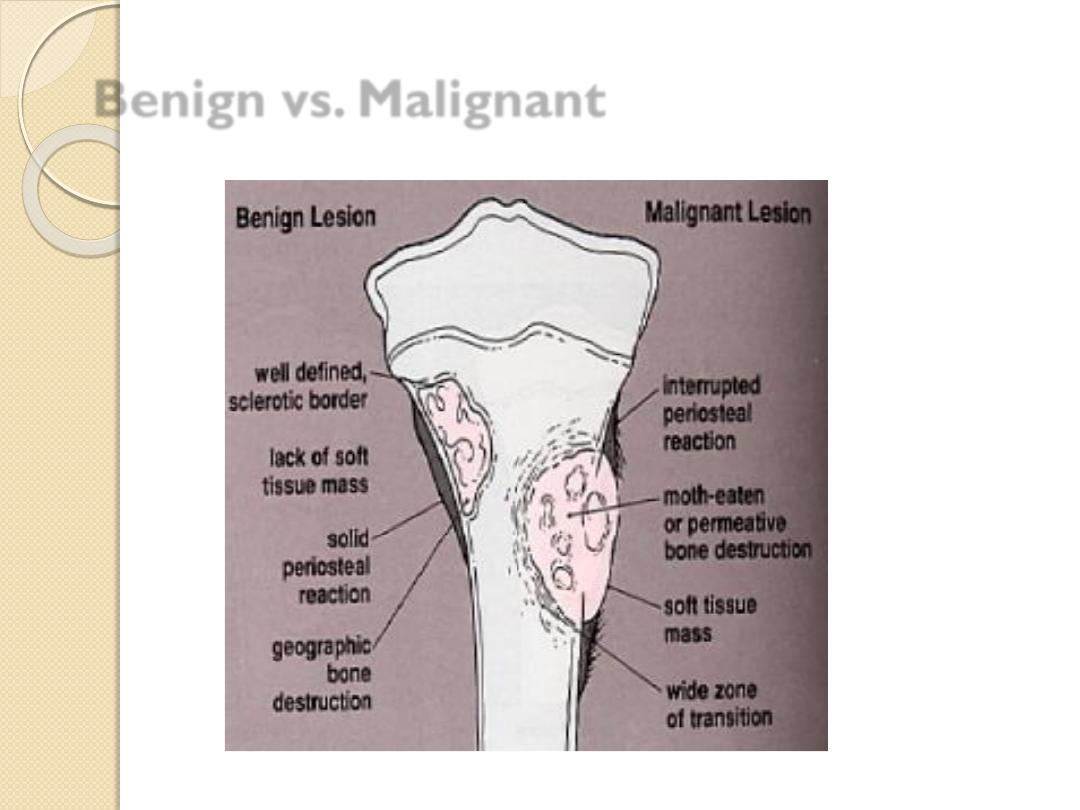
Benign vs. Malignant

Clinical presentation of bone pathology
Pain.
Limping.
Swelling.
Joint pain.
Pathological fracture.
Benign vs. Malignant bone lesion
Features
Benign
Malignent
Marrow
infiltration
No
Yes
Cortical
destruction
No
or
Geographic
Moth-eaten or
Permeative
Periosteal reaction No
or
Solid
Lamellated –
onion peel
Sunburst
Codman’s
triangle
Soft tissue
component
No
yes
USE THE FOLLOWING APPROACH TO DESCRIBE
THE LESION
A well
define
/
ill define
Expansile
/
non expansile
Osteolytic / Sclerotic
Lesion is seen at the
Epiphysis
/
metaphysis
/
diaphysis
Of the RT/LT (bone name)
Associated with
Type of periosteal reaction.
NEW
Pattern of cortical bone destruction/thinning.
NEW
Large / small Soft tissue component / internal septation or not.
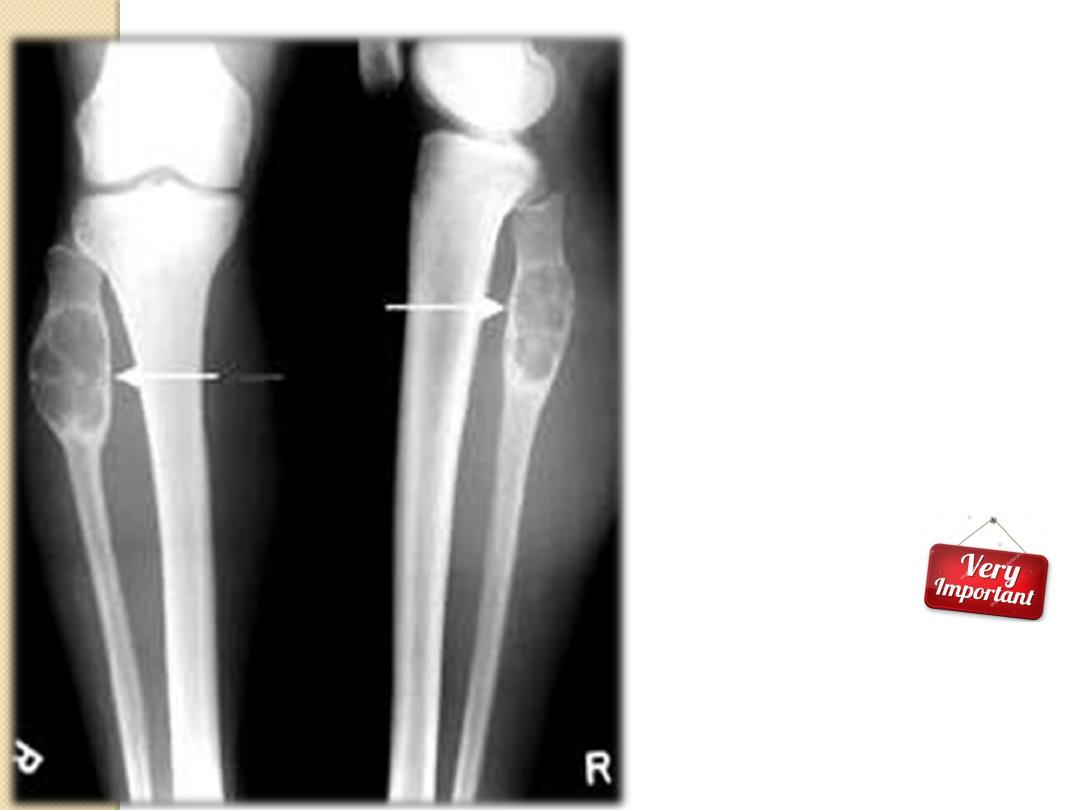
•
A well define
•
Osteolytic
Expansile lesion is seen at
the
Proximal Meta-diaphysis
Of the LT fibula
Associated with internal
septation and cortical
thinning.
No cortical destruction
No extra osseous soft
tissue component
Dx:
Bone cyst.
Simple
Aneurysmal
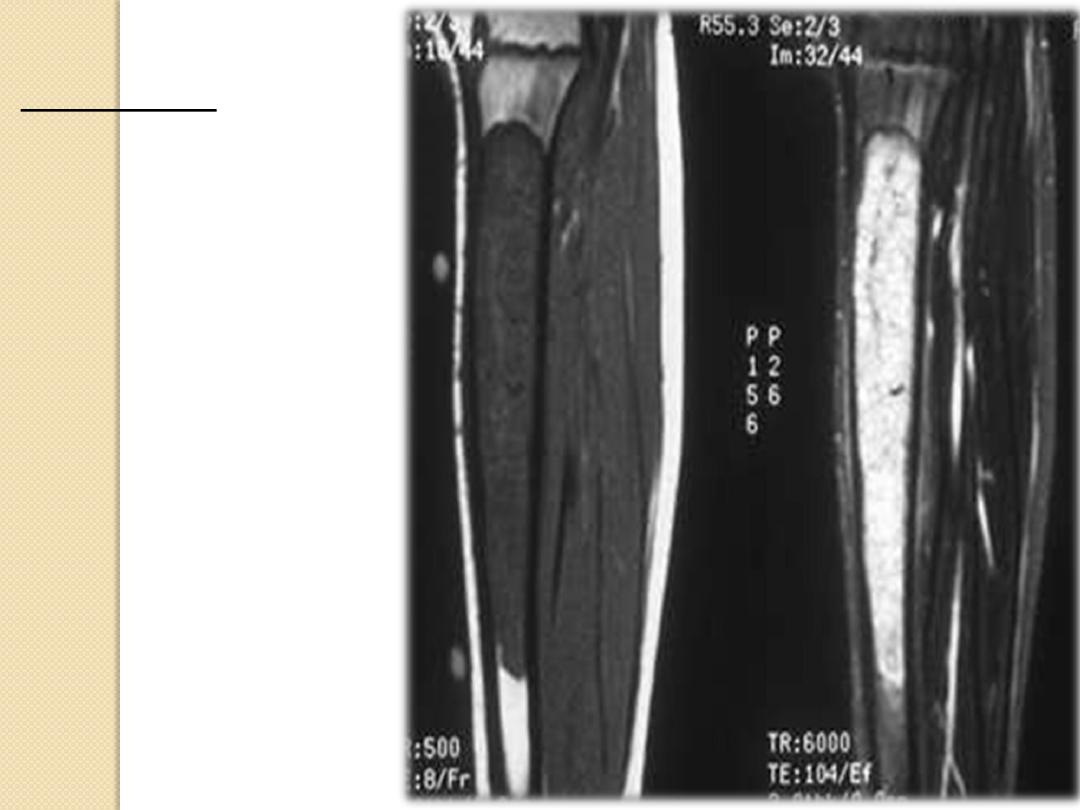
MRI study
Infiltrative
Marrow based
Diaphysis
Dx:
Ewing Sarcoma
FACTS
Benign bone tumors are much more
common than malignant bone tumors.
The most common malignant bone
tumors are secondaries (mets).
Most bone tumors induce variable
degrees of periosteal reaction.

Types of bone tumors
Benign (osteoid osteoma- Enchondroma..)
Malignant (osteosarcoma- fibrosarcoma..)
Benign locally aggressive (osteoclastoma-
bone cysts).

Common signs of malignant bone tumors
Extensive bizarre shaped periosteal reaction.
Bone destruction (cortical destruction).
Soft tissue mass.
Calcific matrix within the soft tissue mass.
◦
Pathological fracture (complication) & can be seen
in benign also.
DD: infections.
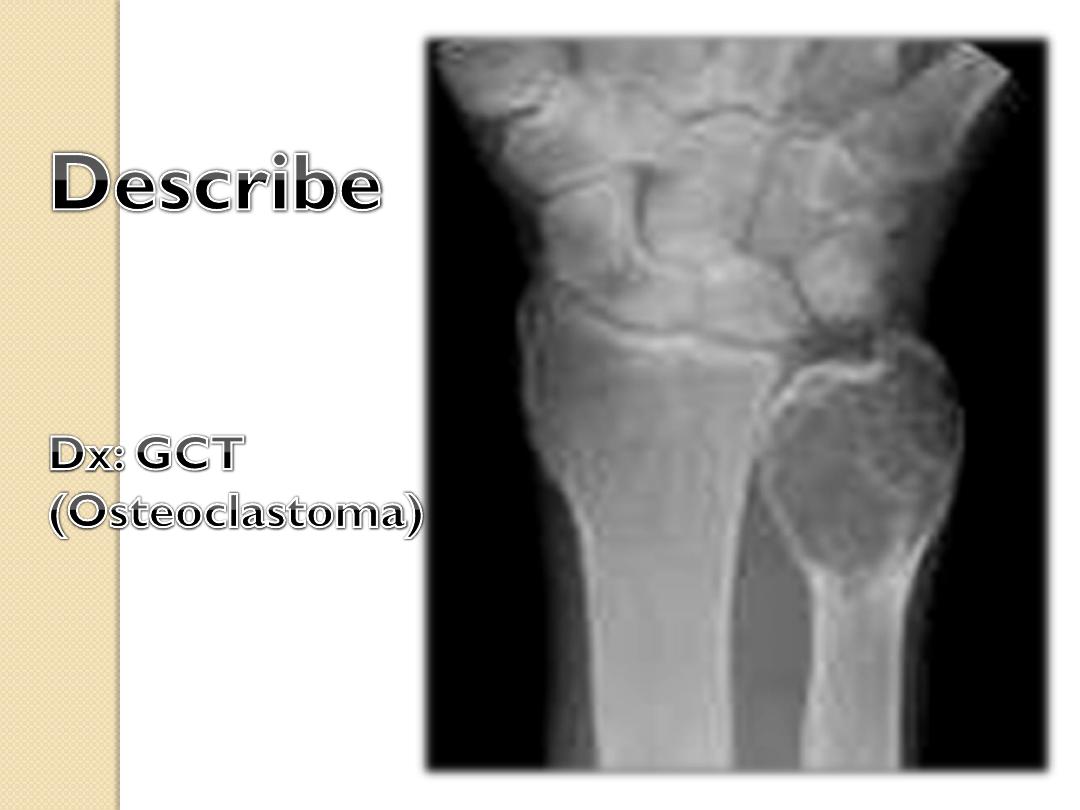
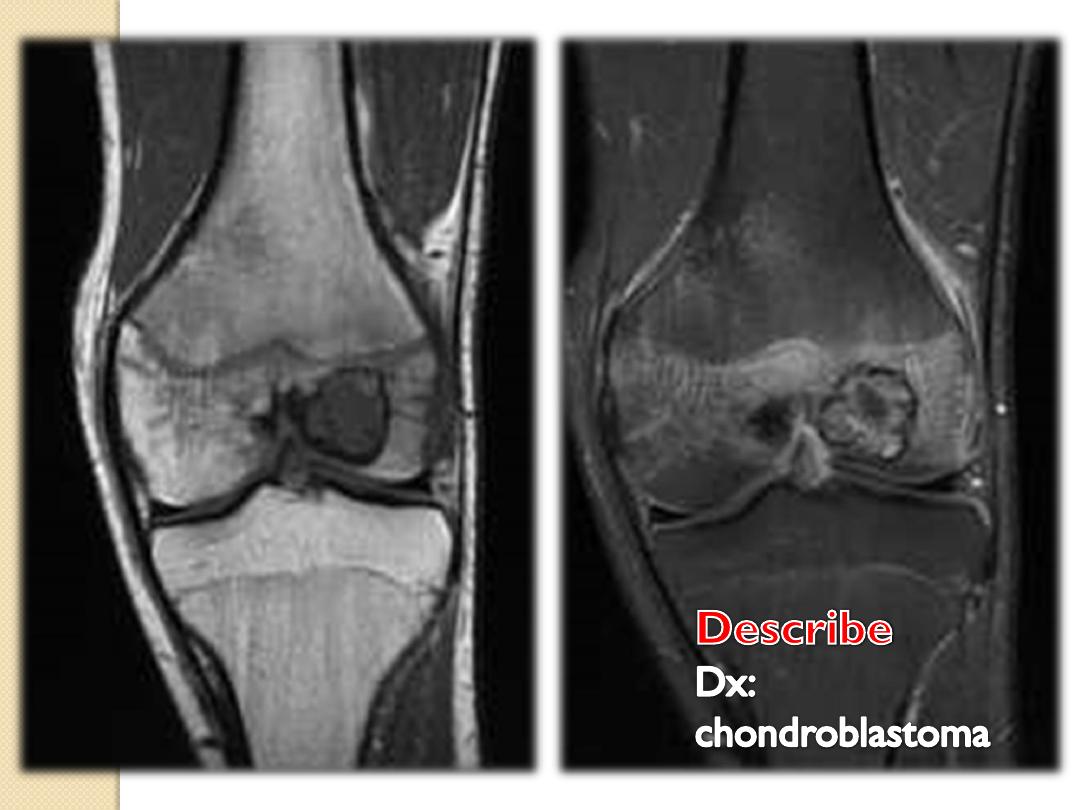
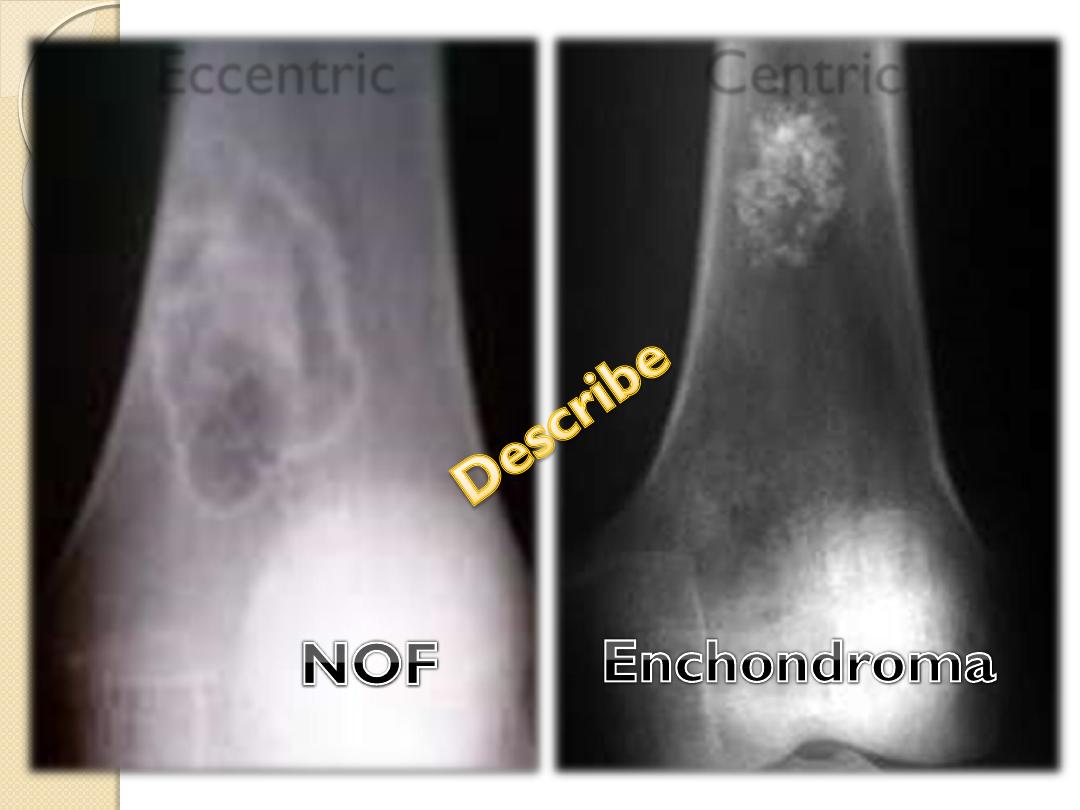
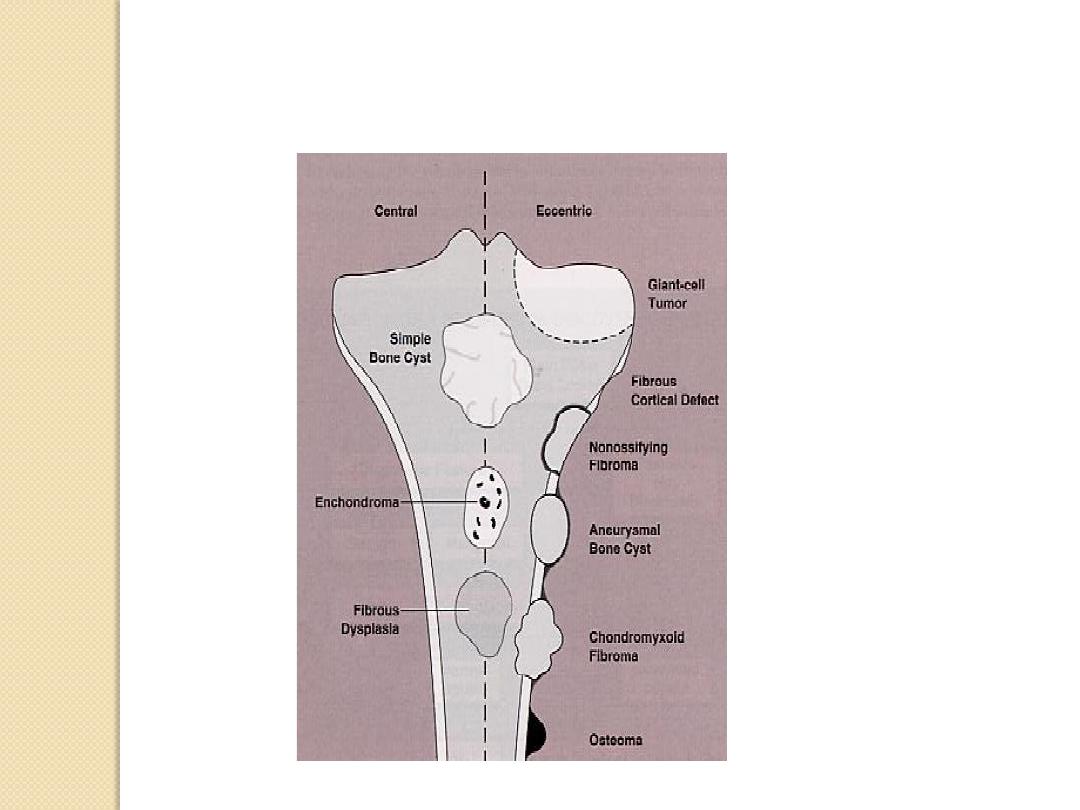
Eccentric Centric

thank you
