Basic
Chest Radiology
Tikrit University
College of Medicine
Department of Radiology
Chest Series

Conventional X-ray (Chest X-Ray)
Computed tomography (CT scan)
Radionuclide imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Angiography (conventional , CT ,MRI)
Interventional techniques

Simple
Low cost
Widely available
Sensitive
Good resolution

OPPIRA
▪
O
=
orientation (Name, Age, Sex, etc)
▪
P
= position (PA, AP, Lateral, Erect, etc)
▪
P
= penetration of x-ray beam
▪
I
= inspiration
▪
R
= rotation
▪
A
= angulation
O
PPIRA
Orientation
Including all information written on the film
that may orient you as:
Age
Sex
Date
O
P
PIRA
Position
Postero-anterior (PA)
Antero-posteriro (AP)
This is depend on the direction of x ray beam
(from - to)
Lateral (LT lateral & RT lateral)
Erect
Supine
O
P
PIRA
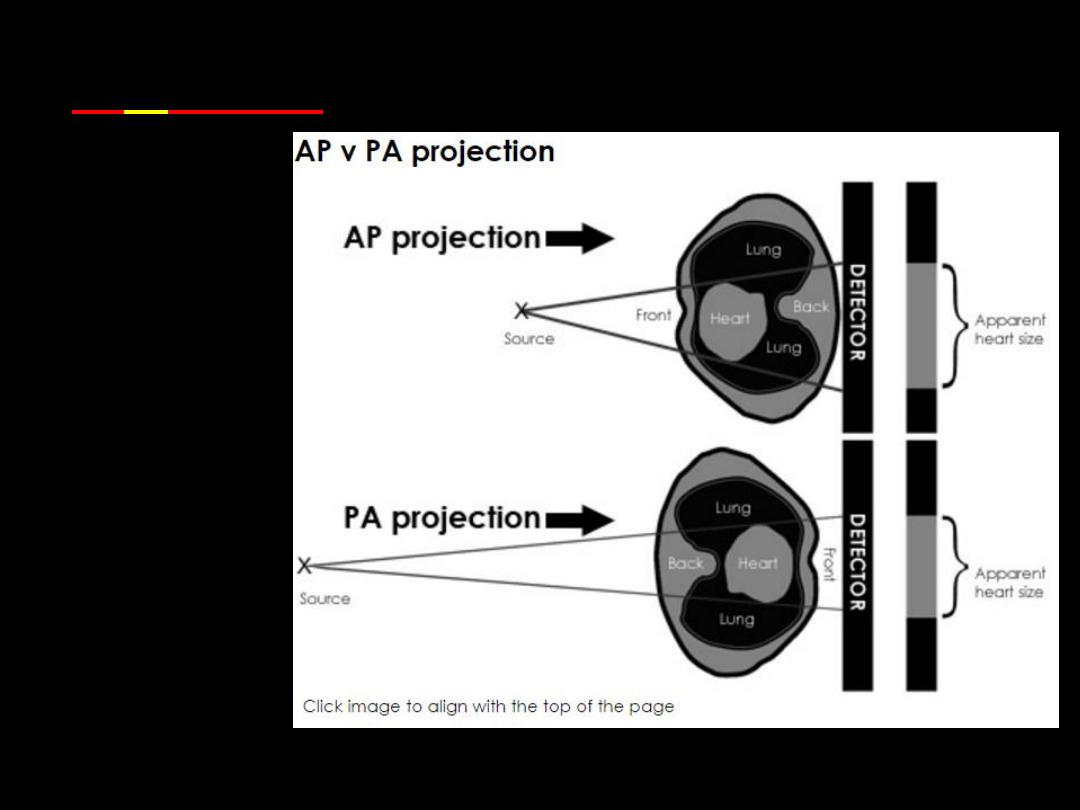
PA vs AP

•Posterior-Anterior (
PA
) is the standard
projection.
•PA
projection is not always possible.
•PA
views are of higher quality and more
accurately assess heart size than AP
images
•If an
AP
projection is performed, ask
yourself if the clinical question can still be
answered.

Standard Chest Radiograph:
•Posterior-Anterior (PA) Erect.
•LT Lateral Erect.
AP film done in:
•Pediatric
age
group
(cardiac
size
assessment not needed in pediatrics).
•Severely ill – bedridden patient.
OP
P
IRA
Penetration
•
A well penetrated chest X-ray when the vertebrae are
just visible behind the heart & the LT hemi diaphragm is
reaching the spine.
OPP
I
RA
Inspiration
It should be full inspiratory film.
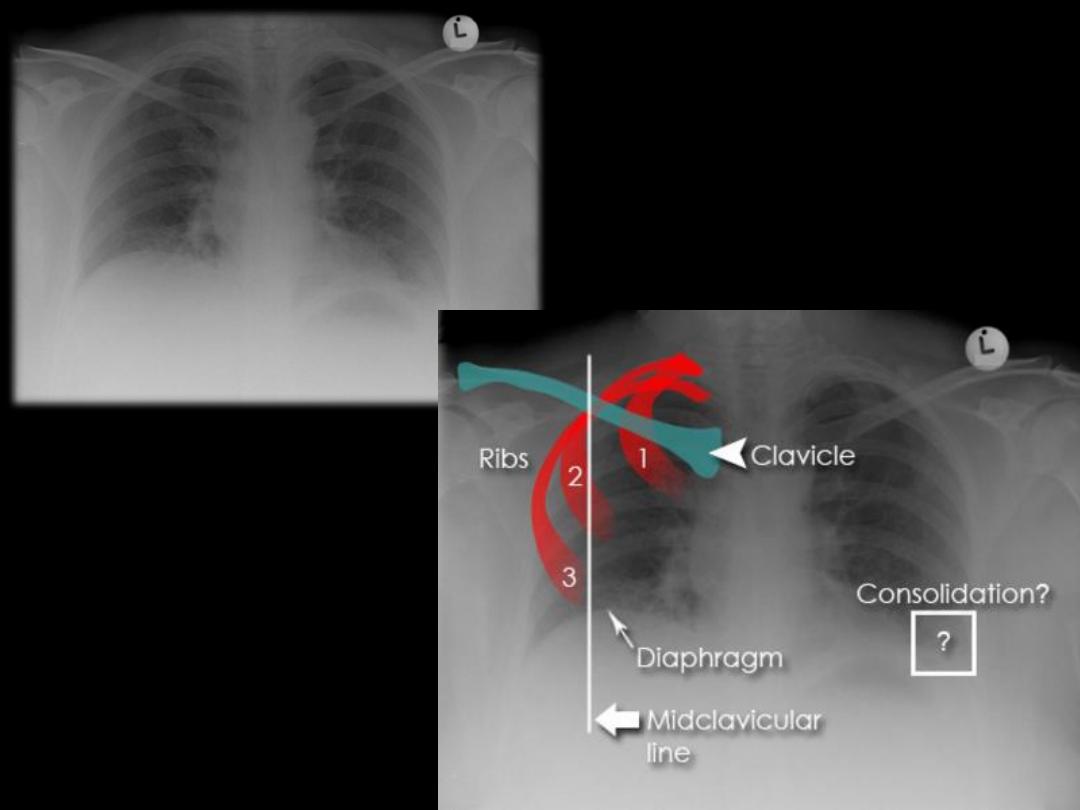
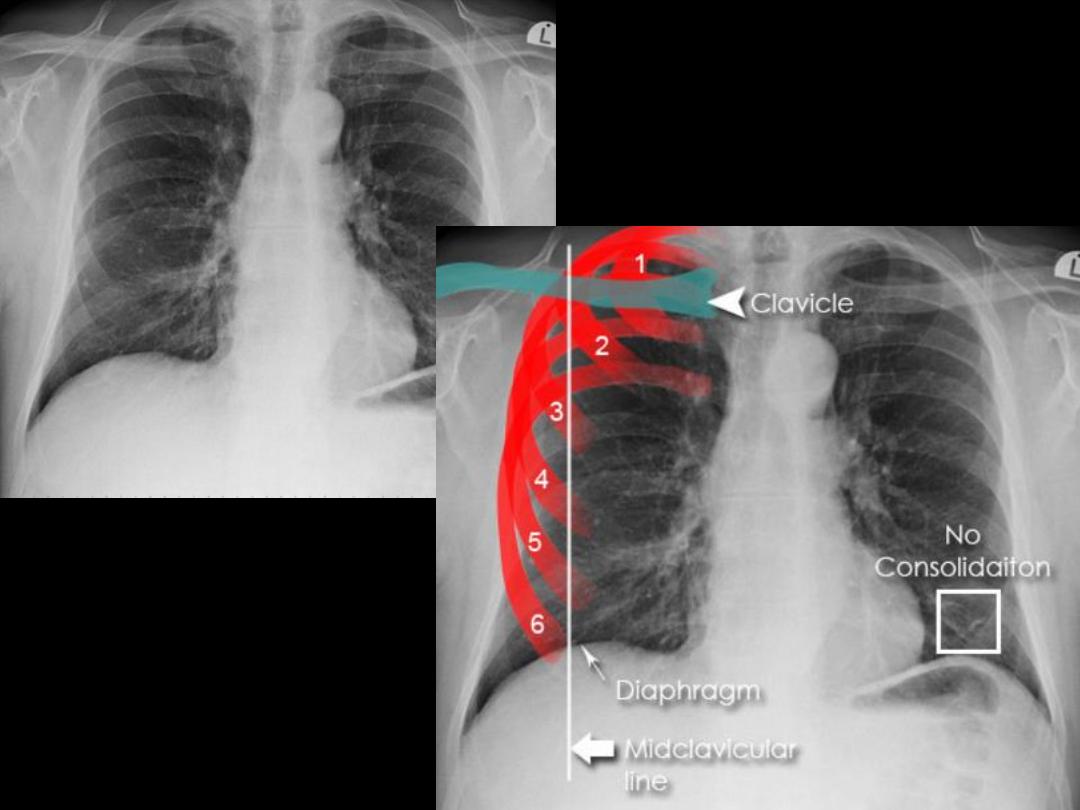
Assessing inspiration
•To assess the degree of inspiration it is conventional to count
ribs down to the diaphragm. The diaphragm should be
intersected by the:
5
th
to 7
th
anterior ribs in the mid-clavicular
line or
8
th
to 9
th
posterior rib. Less is a sign of incomplete
inspiration.

Indicated in :
Small Pneumothorax
in expiratory film the volume of the thorax and lungs
is reduced ,Then the pneumothorax will occupy a
larger percentage of the area of the thorax and is
more easily visible.
Foreign body inhalation
to demonstrate air trapping. With expiration, the
normal lung is reduced in volume and becomes more
radiopaque. The obstructed portion of the lung
retains its air, thereby retaining its radiolucency and
forcing the mediastinum to shift toward the
contralateral side.
OPPI
R
A
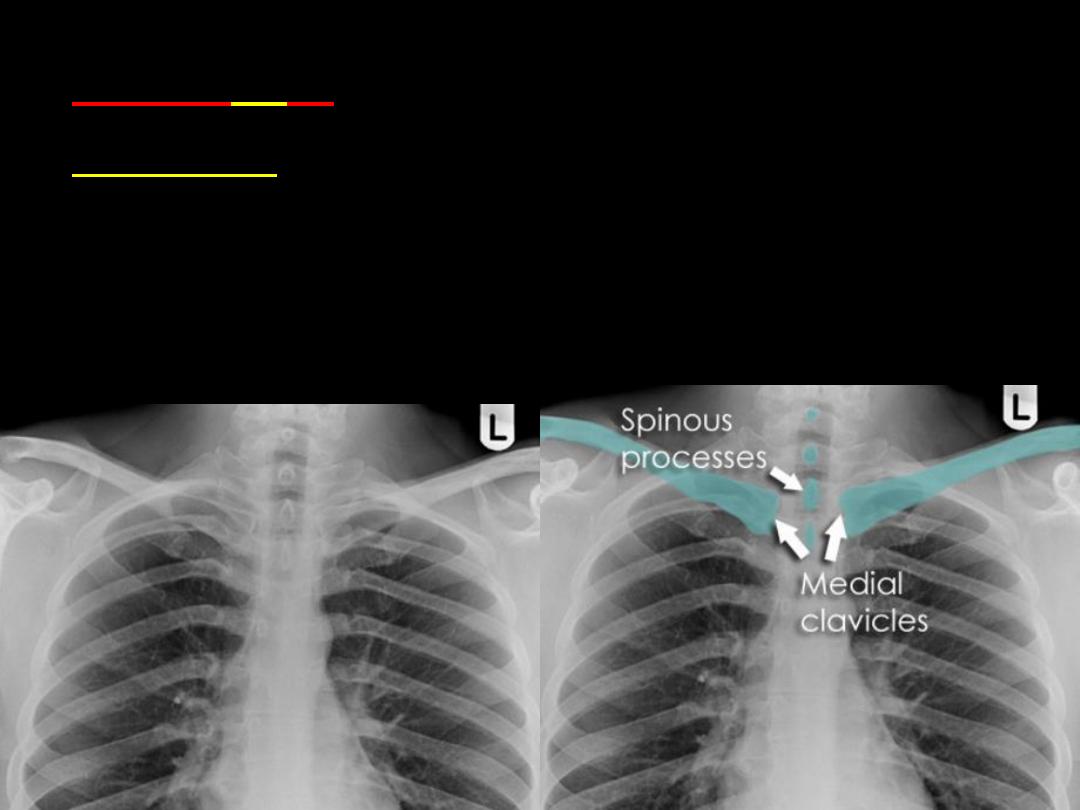
Rotation
•The spinous processes of the thoracic
vertebrae should form a vertical line equidistant
from the medial ends of the clavicles

OPPIR
A
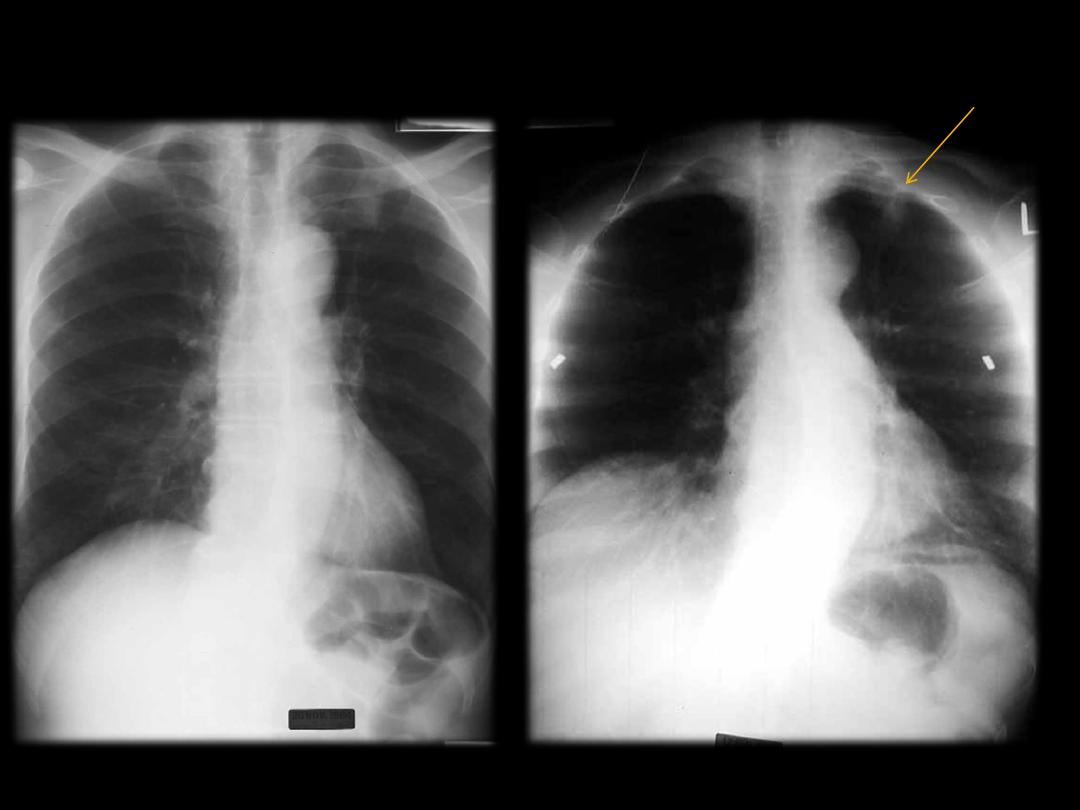
Angulation
Normally , the clavicle seen over 3
rd
rib posteriorly.
With the patient in a more lordotic projection the clavicles will
project superiorly relative to the upper thorax again causing
some distortion of the normal mediastinal anatomy.
With the lordotic projection, the ribs assume a more
horizontal orientation.
Occasionally a lordotic x-ray can be obtained intentionally to
better visualize structures in the thoracic apex obscured by
overlying boney structures.
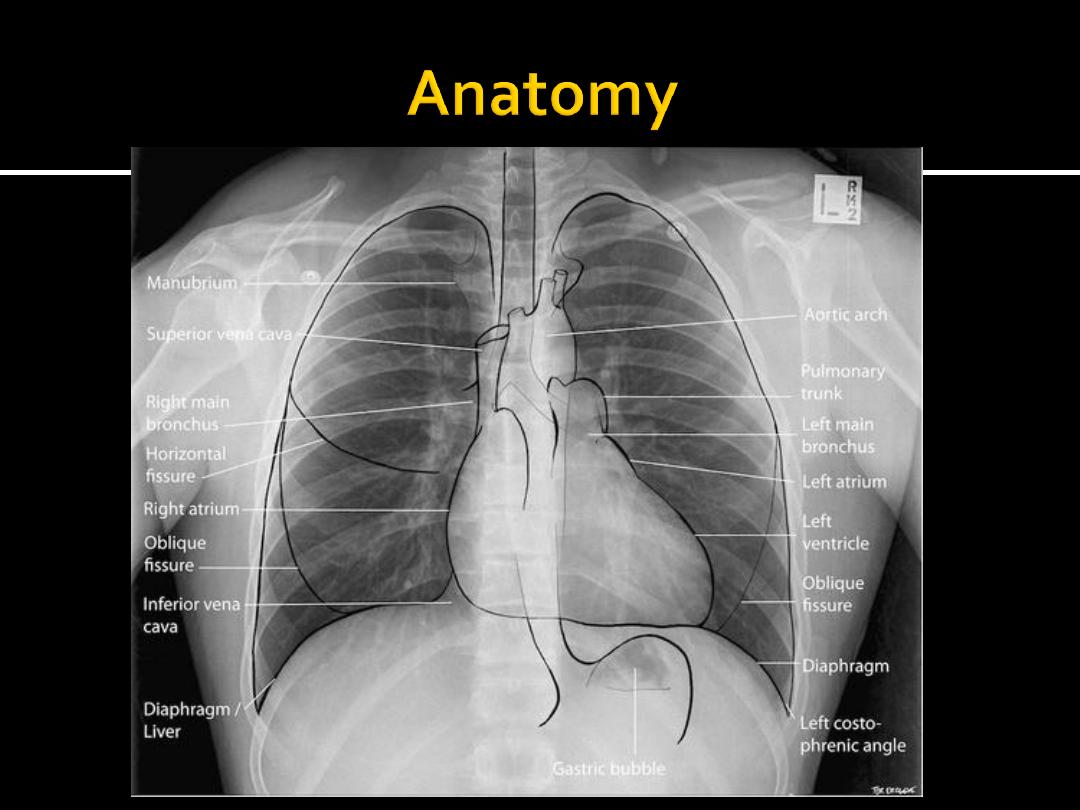

Ensure optimal quality radiograph
Patient Data and previous films should be available
Then evaluate the followings:
Trachea & Lung parenchyma
Mediastinum
Pleura and chest wall
Cardiac shadow
Chest tubes

6 radiographic terminology are commonly used
Silhouette sign
Air bronchogram
Nodule
Mass
Patchy opacity
Cavitary lesion
Infiltrations

When there is an opacity in the lung adjacent to the
cardiac border:
If the cardiac border is masked by the opacity =
silhouette +ve, which means that the opacity is
located anteriorly because the heart is an anterior
structure.
If the opacity did not affect the definition of the
cardiac border = silhouette –ve, which means
that the opacity is posteriorly located
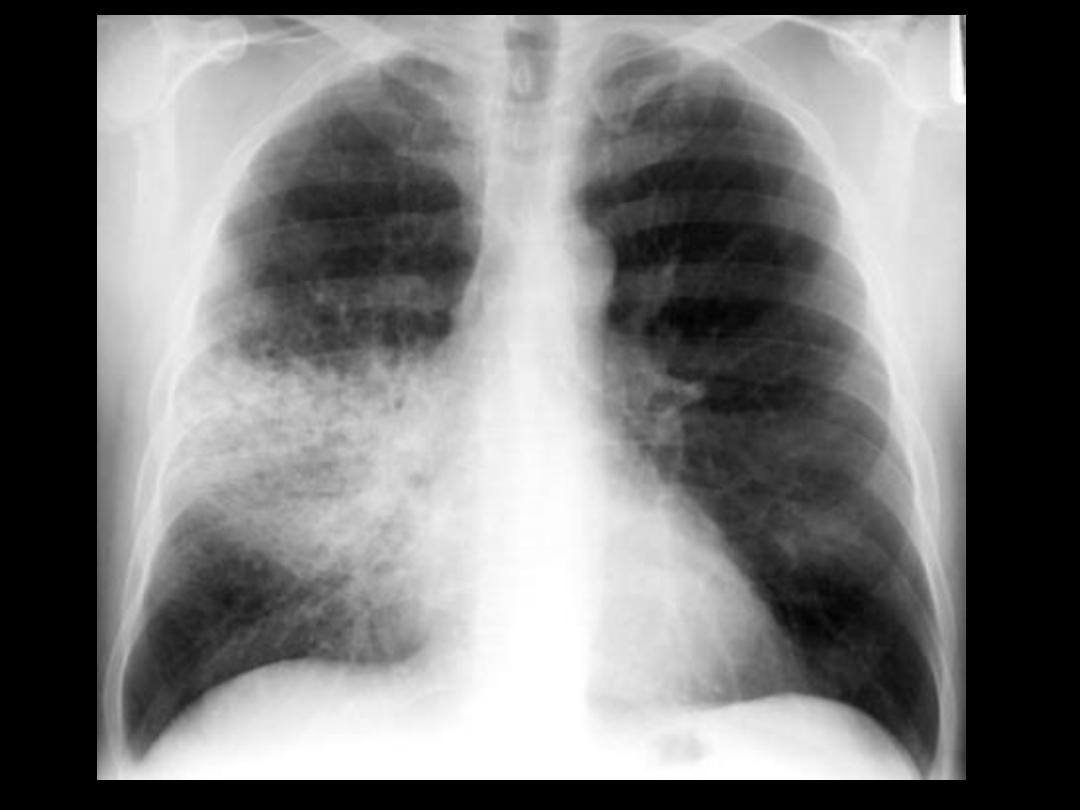

Patent bronchi containing air on the back
ground of opacified lung = consolidation =
replacement of air in the alveoli by one of
the following materials:
Fluid in cases of pulmonary edema
Exudates in cases of pneumonia
Blood in cases of hemorrhagic pulmonary diseases
Tumor cells in cases of alveolar cell carcinoma
Proteins in cases of alveolar protienosis

Nodule:
well defined lesion less than 3 cm in diameter
Mass :
well defined lesion more than 3cm in diameter
Patch :
ill- defined lesion showing air bronchogram
Cavity :
well defined lesion containing air either totally or
partially

Less than 3cm in size
Most common DDx are:
Tuberculoma
Hamartoma
Bronchogenic carcinoma.
Metastases
AVM [arteriovenous malformation]
Hydatid cyst

More than 3cm in size
Most common DDx are:
Bronchogenic carcinoma.
Metastasis.
Hydatid cys

