
Vulvar Cancer

Epidemiology & risk factor
⚫
4th common GYN
cancer
⚫
Postmenopause
⚫
65 y/o
⚫
Cigarette smoking
⚫
Vulvar dystrophy (eg,
lichen sclerosis)
⚫
VIN or CIN
⚫
HPV infection
⚫
Immunodeficiency
⚫
Cx. cancer Hx.
⚫
Northern European
ancestry

Clinical manifestations
⚫
Unifocal vulvar plaque, ulcer or mass
(most labia majora)
⚫
5% multifocal
(evaluate vulvar and
perianal skin, cervix, vagina)
⚫
Synchromous second neoplasm
(most
cervical neoplasm): 22%
⚫
Pruritus
(vulvar bleeding, discharge, dysuria, enlarged
groin LN…)
Diagnosis
⚫
Biopsy !!
-- Determine the
depth
and
nature
of stromal
invasion
-- Taken from the
center
of the lesion
-- If multiple abnormal areas: multiple
biopsies to map
-- Use acetic acid & colposcopy if not sure !
Squamous cell carcinoma
⚫
Keratizing,
differenrtiated or
simplex type
-- More common
-- Older
p’ts
-- No related to HPV
infection
-- Associated with
vulvar dystrophy
⚫
Classic, warty or
Bowenoid type
-- HPV 16, 18, 33
--
Younger p’ts
-- Most present with
early stage
>90% of vulvar malignancy, 2 subtypes
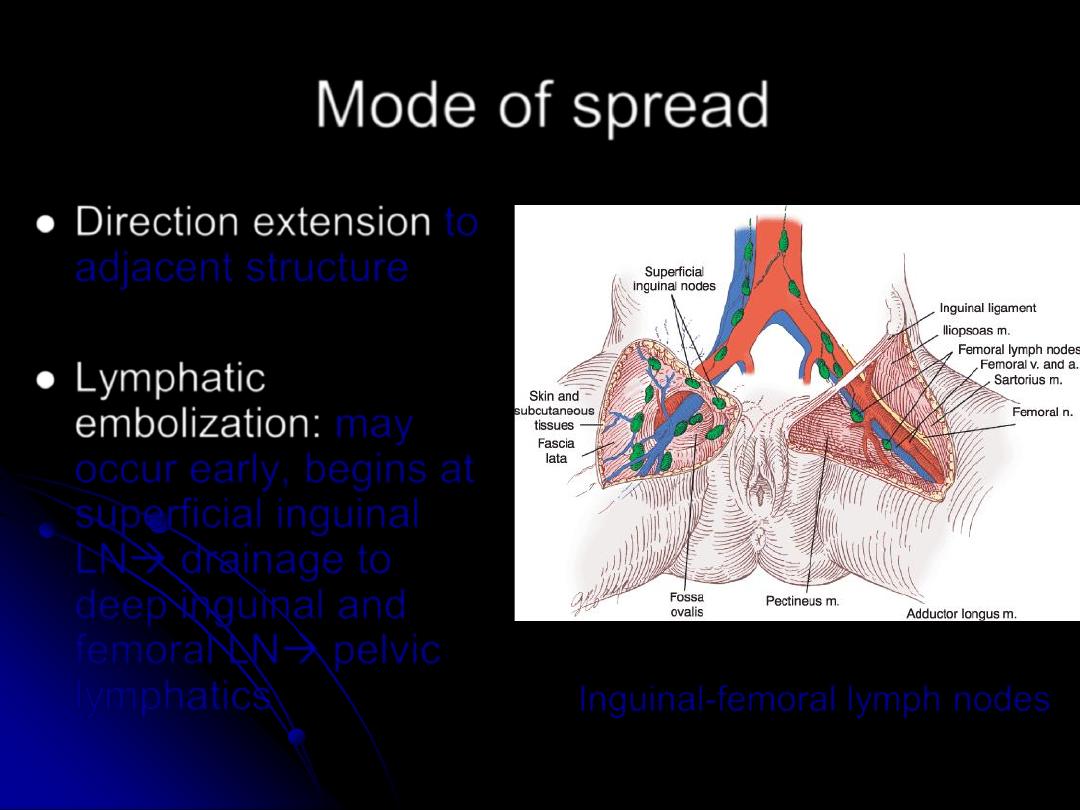
Mode of spread
⚫
Direction extension
to
adjacent structure
⚫
Lymphatic
embolization:
may
occur early, begins at
superficial inguinal
LN→ drainage to
deep inguinal and
femoral LN→ pelvic
lymphatics
Inguinal-femoral lymph nodes

Mode of spread
⚫
Hematogenous dissemination
-- typically late in the course
--
rare in p’ts without inguinofemoral LN
involvement

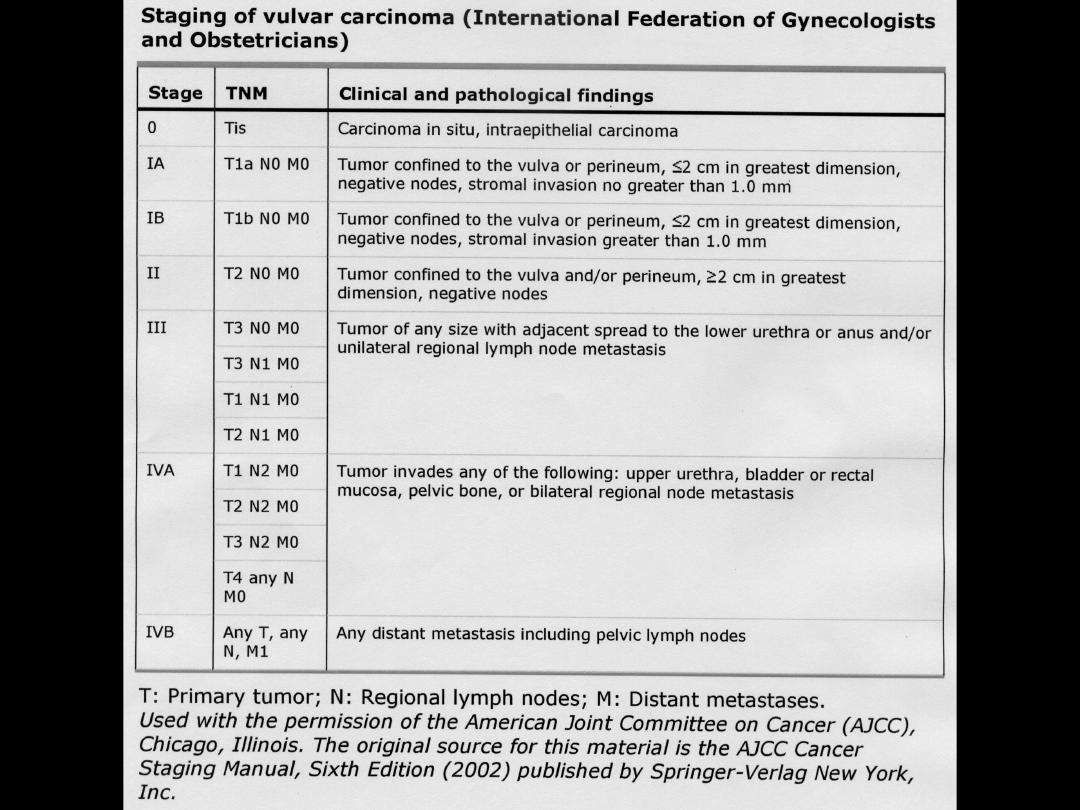
Staging
⚫
Clinical staging
-- PE (palpate LN: inguinal, axillary,
supraclavicular )
-- PV (Cx. Cytology, colposcopy of Cx,
vagina & vulva due to multifocal lesions)
-- Radiographic and endoscopic studied in
large tumor or suspected metastasis

Staging
⚫
Surgical staging
—FIGO
--
Inguinofemoral LN status
: the most important
predictor of overall prognosis (clinical
assessment of groin LN: false negative)
-- Inguinofemoral lymphadenctomy (except stage
IA)
# Unilateral: unilateral lesion, distant from the
midline
# Bilateral: midline or bilateral lesions or unilateral
lesion with positive ipsilateral LN

Staging
⚫
Less invasive means to assess LN status
→
Sentinel node biopsy
(unilateral)
→
Reduce acute and long-term complications
(1)Lymphoscintigraphy using radiolabeled
human albumin and an intraoperative
γ-
detecting probe
(2)Peritumor injection of isosulfan blue dye
→
Bilateral groin involvement is common in
midline vulvar cancers ➔ not suggest !!

Treatment
⚫
Goal
-- Cure the cancer
-- Minimize perioperative morbidity
-- Maximize long-term psychosexual and
physical well-being

Treatment--SCC
✓
Stage IA
⚫
Radical local excision
without
LN
dissection
⚫
Inguinofemoral LN metastases :
<1 %
⚫
Wide, deep excision of the lesion down to
the inf. fascia of the urogenital diaphragm
⚫
Clear margin: 2 cm (at least 1 cm)

Treatment--SCC
✓
Stage IB
⚫
Inguinofemoral LN metastases :
>8 %
⚫
Radical local excision + ipslateral
inguinofemoral LN dissection ( lateralized
lesion) or bilateral inguinofemoral LN
dissection (central lesions)

Treatment--SCC
✓
Stage II
⚫
Modified radical vulvectomy + ipslateral /
bilateral inguinofemoral
lymphadenectomy
⚫
Clear margin: at least 1 cm
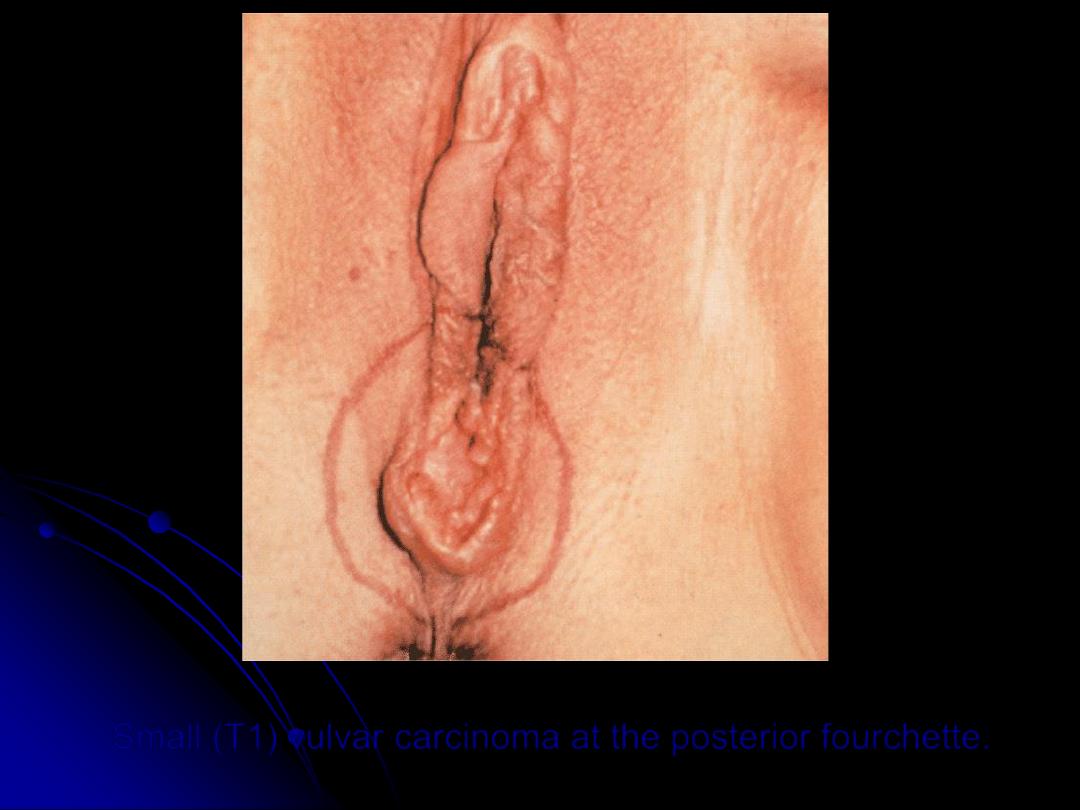
Small (T1) vulvar carcinoma at the posterior fourchette.

Treatment--SCC
⚫
Adjuvant R/T ?
-- appears benefit those with
two or more positive
inguinal LN or positive/closes surgical margin
-- The minimum number of nodes that should be
examined is unclear !!
-- GOG study: adjuvant R/T to
high risk p
’ts
(> 4.1
cm tumor, positive margins, lymphovascular
space invasion)
with negative LN➔ reasonable
to consider !!

Treatment--SCC
✓
Stage III and IV
⚫
Radical vulvectomy combined with pelvic
exenteration→ high morbidity !!
⚫
Preoperative radiation therapy
: downstage
the tumor, allow a more conservative
surgery
⚫
Chemoradiotherapy
: locally advanced
vulvar cancer (cisplatin + 5-FU, Mitomycin
+ 5-FU

Treatment--SCC
✓
Stage III and IV
⚫
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy
—for recurrent
or locally advanced disease
--Decreased tumor bulk and permit later
resection
--Result is inf. to chemoradiotherapy

Treatment
—Verrucous carcinoma
⚫
Radical local excision
⚫
Bx. suspicious LN, if positive→
inguinofemoral lymphadenectomy
⚫
RT: contraindication !!
(induce anaplastic
transformation and increase the likehood
of metastases)
⚫
Recurrence: surgical excision

Thank you for your attentions !!
