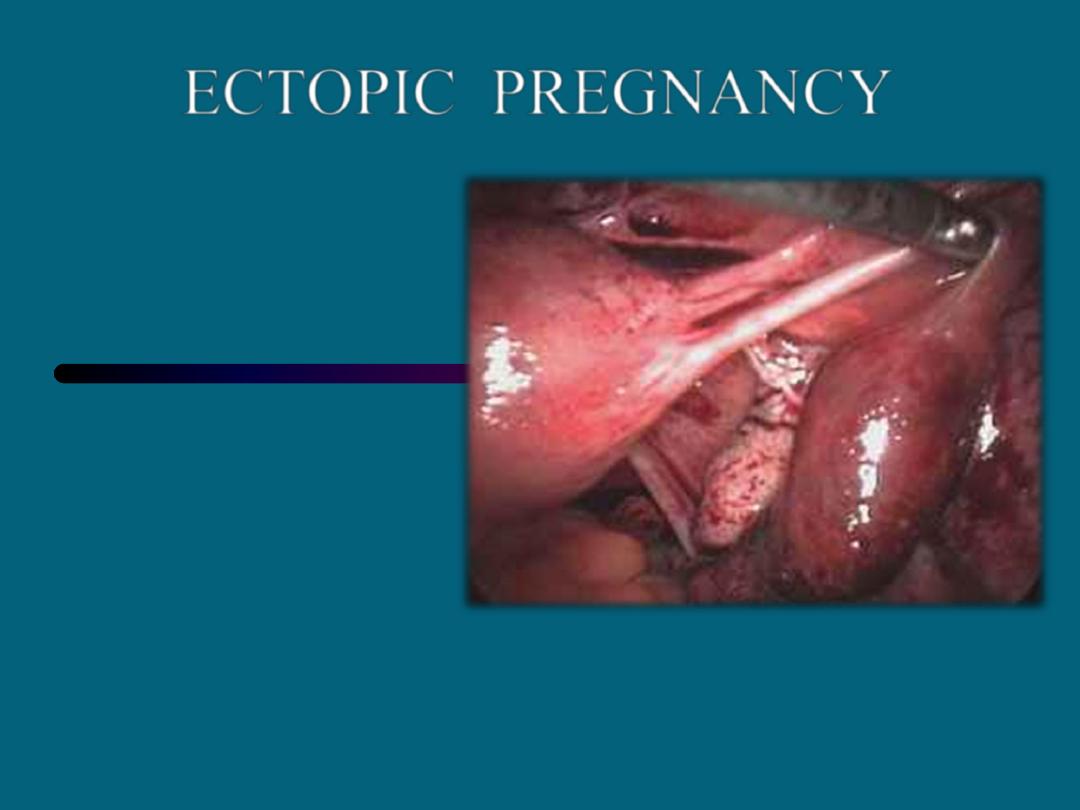
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Etemad Muthanna Yusif
Tikrit University, MD. PhD.
21-11-2018

2
Introduction
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which
the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms
classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
Fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these
symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or
crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding
into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result
in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare
exceptions the fetus is unable to survive.
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
Ectopic Pregnancy
3
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
DEFINITION
Any pregnancy where the fertilised ovum
gets implanted & develops in a site other
than uterine cavity.
ectopic / extrauterine
heterotopic

Ectopic Pregnancy
4
INCIDENCE
>1 in 100 pregnancies.
Ectopic Pregnancy
5
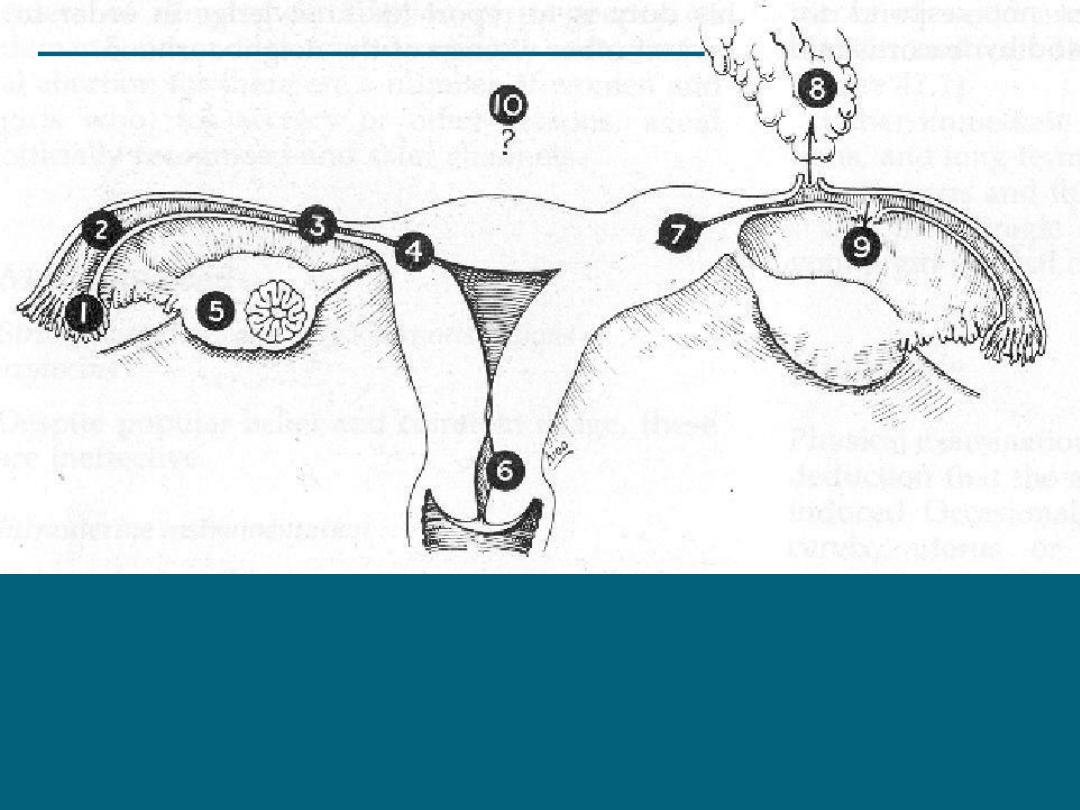
SITES OF ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
1)Fimbrial 2)Ampullary 3)Isthmic 4)Interstitial 5)Ovarian
6)Cervical 7)Cornual-Rudimentary horn 8)Secondary
abdominal 9)Broad ligament 10)Primary abdominal
Ampulla (>85%)
Isthmus (8%)
Cornual (< 2%)
Ovary (< 2%)
Abdomen (< 2%)
Cervix (< 2%)

Ectopic Pregnancy
6
ETIOLOGY
•
Any factor that causes delayed transport of
the fertilised ovum through the Fallopian
tube (tubal ectopic pregnancy).
•
These factors may be:
1.
congenital or acquired;
2.
mechanical or functional

Ectopic Pregnancy
7
ETIOLOGY
•
CONGENITAL -
tubal hypoplasia, tortuosity, congenital
diverticuli, accessory ostia, partial stenosis
•
ACQUIRED
–
Inflammatory
: PID, septic abortion, puerperal sepsis,
medical termination → intraluminal / peritubal adhesions
–
Surgical
: tubal reconstructive surgery, recanalisation of
tubes
–
Tumoral
: broad ligament myoma, ovarian tumour
–
Miscellaneous causes
: IUD, endometriosis, ART,
hormonal perturbations → tubal disfunctions
–
Previous ectopic pregnancy

Ectopic Pregnancy
8
EARLY MULTI-MODAL DIAGNOSIS
•
Vaginal ultrasound scanning (+ colour Doppler)
•
Serum beta HCG level
•
Serum progesterone levels < 5ng/mL
•
Uterine curettage
•
Culdocentesis
•
Laparoscopy / laparotomy

Ectopic Pregnancy
9
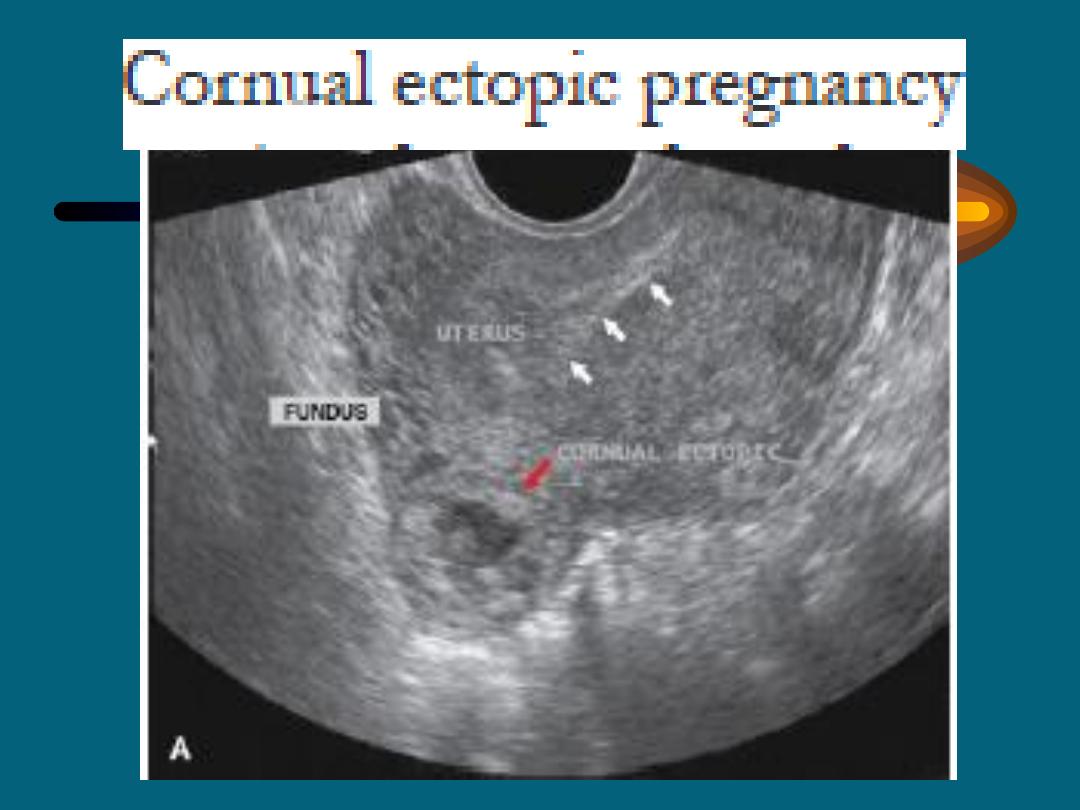
METHODS OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS
Multi-modality diagnosis results
1.
TV – US
- Demonstration of the gestational sac
with or without an alive embryo outside the uterus .
- Ruptured ectopic with fluid in the cul-de-
sac and an empty uterus.
2. Culdocentesis
- in emergent situations to confirm
diagnosis, highly specific if performed and interpreted
correctly → presence of free-flowing, NON-clotting
blood
Ectopic Pregnancy
10
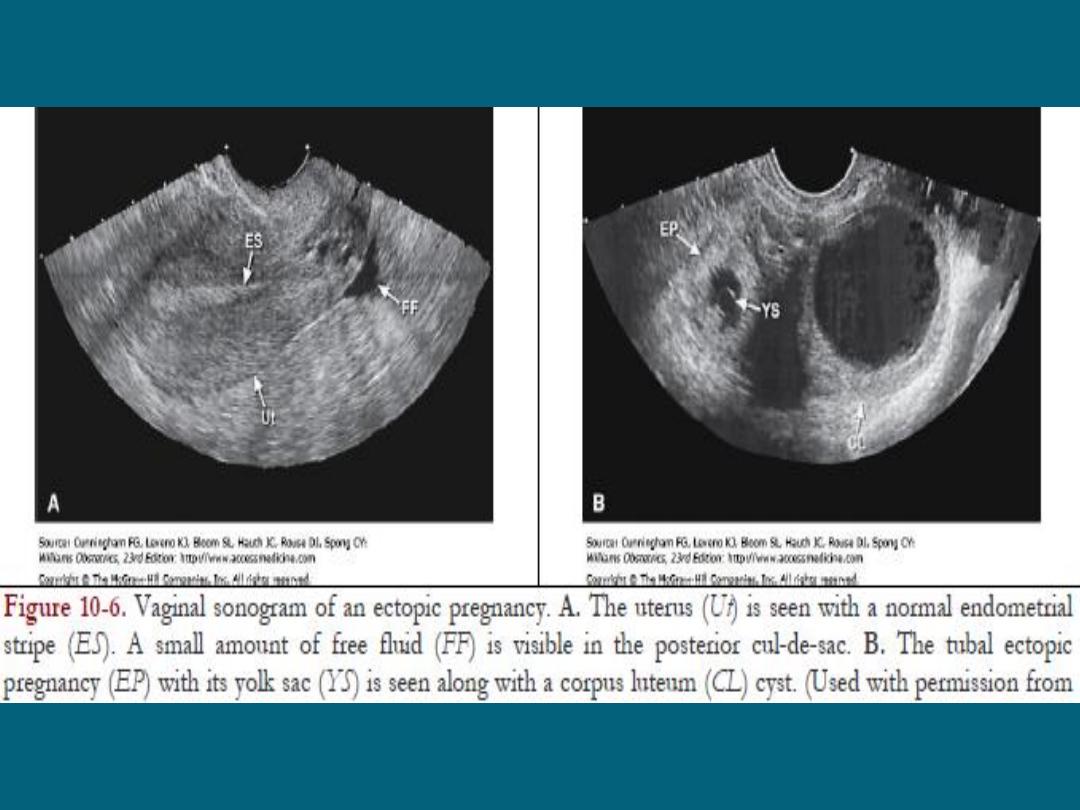
Ectopic Pregnancy
11
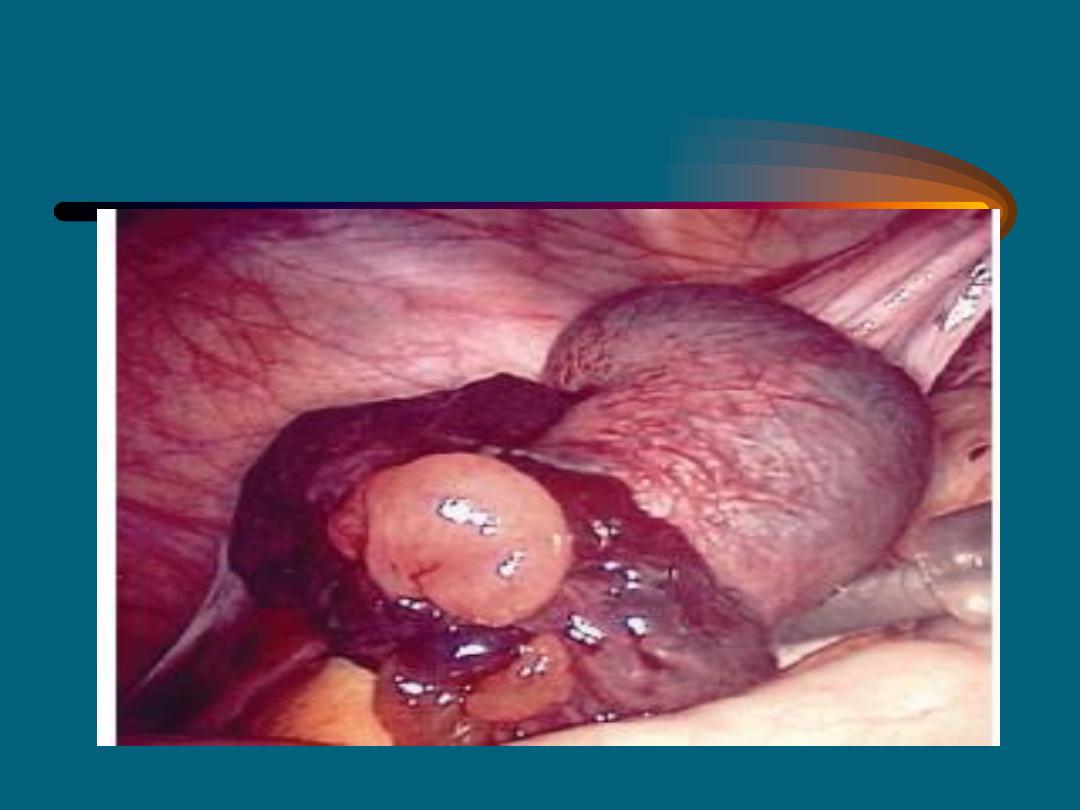
Ruptured tubal (ampullary) early pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
12

Ectopic Pregnancy
13
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
•
Threatened or incomplete abortion
•
Salpingo-ooforitis
•
Appendicitis
•
Twisted ovarian cyst
•
Rupture of a corpus luteum / follicular cyst
•
Other abdominal conditions

Ectopic Pregnancy
14
MANAGEMENT
•
Depends on the stage of the
disease and the condition of
the patient at diagnosis.
1.
COMPLICATED ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
2.
NON-COMPLICATED ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
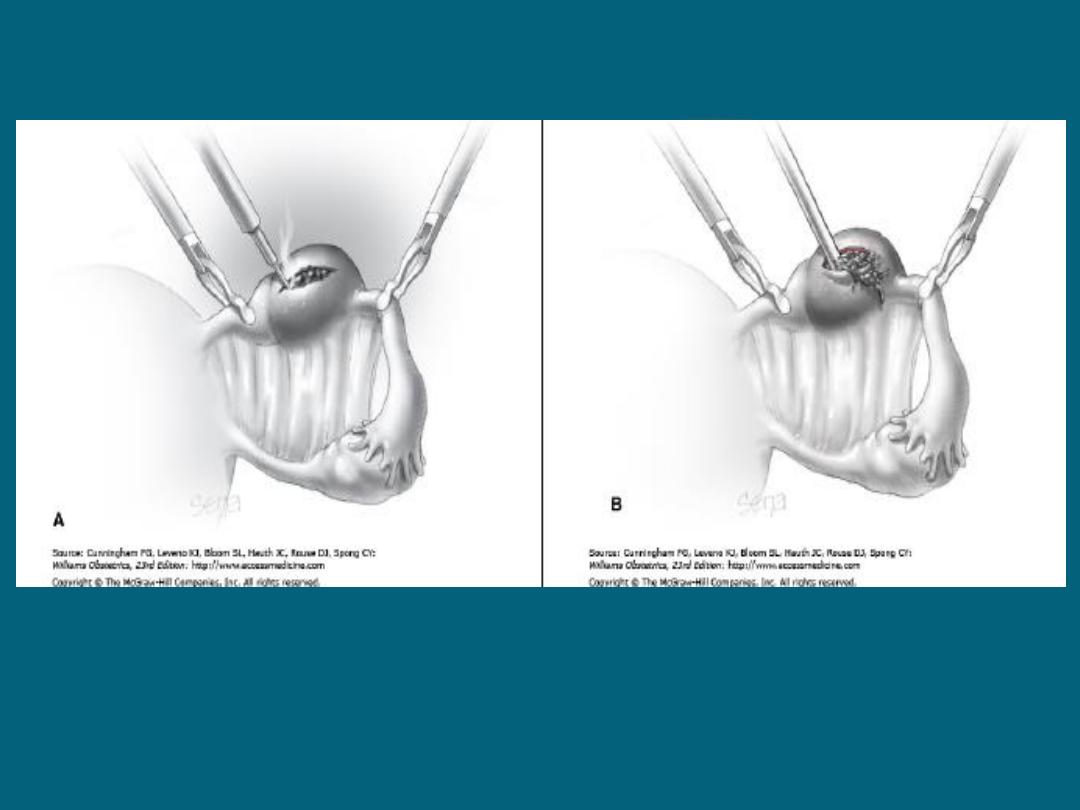
Ectopic Pregnancy
15

Ectopic Pregnancy
16
MANAGEMENT OF
COMPLICATED ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
TREATMENT – ALWAYS SURGICAL
•
Salpingectomy
of the offending tube
•
Posterior colpotomy -
if pelvic
haematocele is infected → to drain
the pelvic abscess
•
Salpingo-oophorectomy

Ectopic Pregnancy
17
MANAGEMENT OF NON-COMPLICATED
=
UNRUPTURED ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
•
SURGICAL
•
MEDICAL TREATMENT
•
EXPECTANT MANAGEMENT
OPTIONS

Ectopic Pregnancy
18
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF
UNRUPTURED
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
•
Carried out by Laparoscopy /
Laparotomy.
•
The procedures are:
–
Salpingectomy / Cornual resection /
Excision
–
Conservative surgery (in cases of
Infertility & desire for pregnancy)

Ectopic Pregnancy
19
MEDICAL TREATMENT
•
Trophotoxic substance:
– Methtrexate
- resolution of tubal / abdominal
pregnancy by systemic administration
–
Interferes with the DNA synthesis
•
Ectopic pregnancy size should be < 3.5 cm.
•
IV/IM/Oral, usually along with Folinic acid.
•
Injection into the ectopic pregnancy sac or affected tube

20

21
Thank you
