
contraception

•
Definition
:
It’s a voluntary prevention of
pregnancy by methods other than abstinence
from coitus.
•
Characteristics
:
of ideal contraception:
1.
Highly effective.
2.
No side effects.
3.
Cheap.
4.
Independent of intercourse.
5.
Rapidly reversible.
6.
Wide spread availability.
7.
Easily distributed.
8.
Acceptable to all cultures and religions.
9.
Can be administered by non health care
personnel.

Indication for contraception
1.
Limitation of population.
2.
Temporary ill health.
3.
Chronic systemic disease.
4.
Previous obstetric complications.
5.
Diseases transmitted to the fetus.
6.
Birth spacing ,to maintain female health.
7.
Family limitation.

classification
1.Hormonal contraception :
a)combined; oral contraceptive pills(COC).
combined hormonal patches,combined injections and vaginal
rings.
b)progesterone only preparations: pills, inject able , implant.
2. Intrauterine contraception: copper IUCD , hormonal
releasing IUCD
3.Barrier methods: condoms, female barriers.
4.Coitus interrupts.
5.Natural family planning.
6.Emergency contraception.
7.Sterilization female sterilization , vasectomy.
❖
Failure rate
is the number of pregnancies(failure)per100
women-years(HWY)
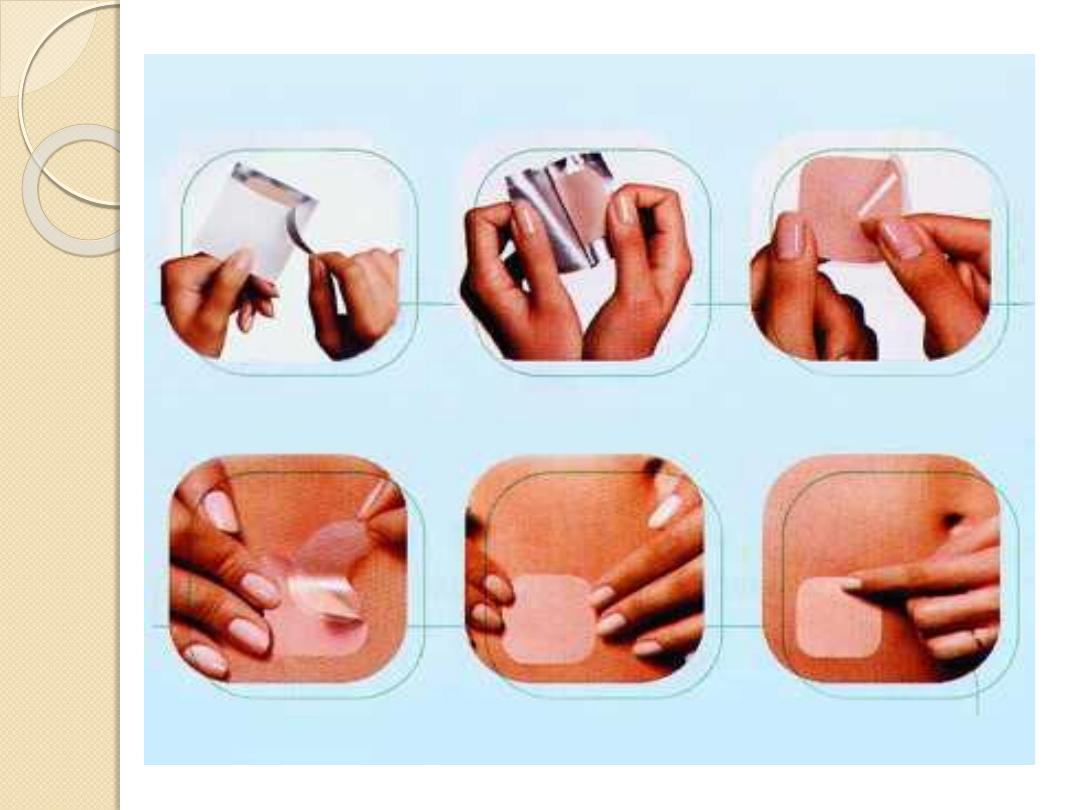
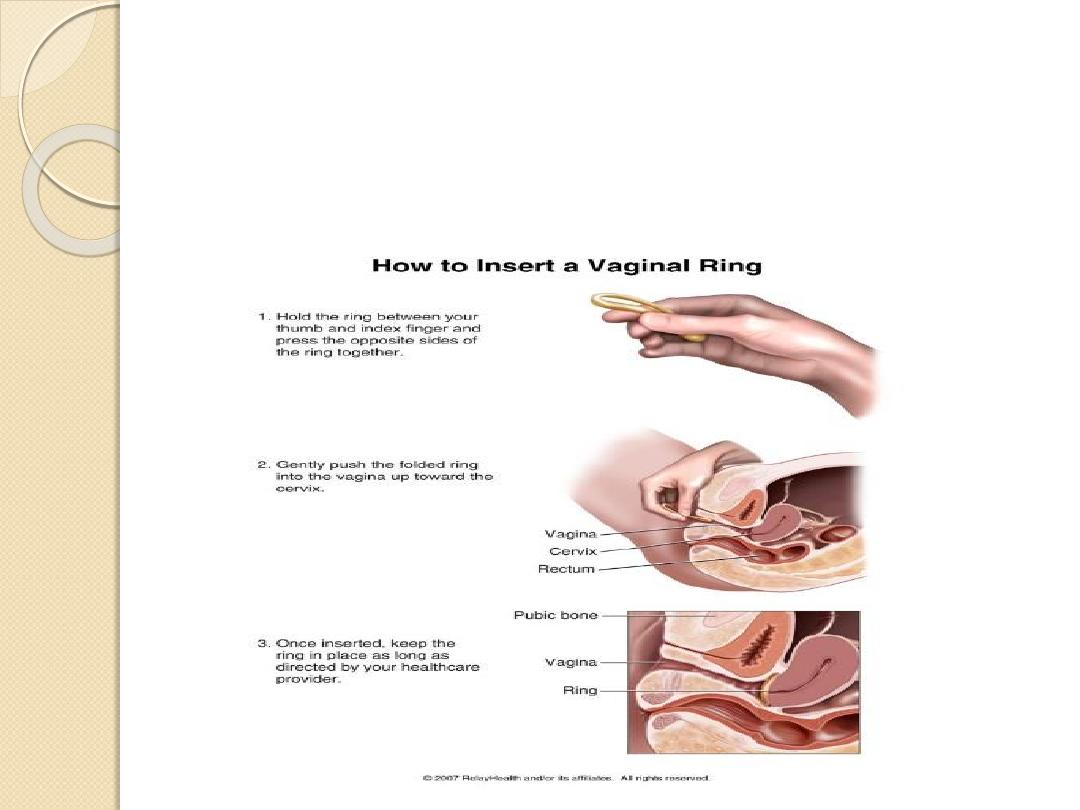

Hormonal contraception
Combined oral contraceptive pills(COC) .
contain both estrogen usually ethinyloestradiol
and progesterone
•
Mode of action:
1.
Suppression of ovulation.
2.
Changes in cervical mucus.
3.
Endometrial atrophy.
4.
Impaired uterine receptivity
•
The combined pills are available as:
➢
monophasic: the same dose of steroids in all pills.
➢
biphasic: the dose change once during the cycle.
➢
triphasic: the dose change twice during the cycle.

Other uses of Combined oral contraceptive
pills{ non contraceptive benefits}
1.
Menstrual period, shorter less painful….
2.
Decrease breast lump incidence.
3.
Decrease functional ovarian cysts.
4.
Decrease the incidence of endometriosis . acne and
possibly PID
5.
Protect against endometrial &ovarian cancer.
6.
Possible protection against Rh. arthritis , DU and thyroid
disease.
•
So they are the 1
st
line treatment in:
➢
Dysmenorrhea.
➢
Premenstrual syndrome.
➢
Menorrhagia and ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding .

Contraindication of COC
❖
Absolute:
A))) Past or present circulatory disease
1.
Proven past arterial or venous thrombosis.
2.
Ischemic heart disease.
3.
Sever or multiple risk factors for venous or arterial disease.
4.
Focal migraine.
5.
Transient ischemic attacks.
6.
Atherogenic lipid disorders.
7.
Inherited or acquired thrombophilias.
8.
Past cerebral hg.
9.
Vascular malformations of the brain.
10.
Significant structural heart disease.
11.
Pulmonary hypertension.

B))) Liver disease
1.
Active liver disease.
2.
Liver adenoma or carcinoma.
3.
Gallstone.
4.
Acute hepatic porphyria.
C))) Others
1.
Pregnancy.
2.
Undiagnosed genital tract bleeding.
3.
Estrogen dependent neoplasm i.e. breast cancer
D))) History of serious condition known to be
affected
by
sex
steroid
i.e.
pomphigoid
gestationis.

❖
Relative:
Undiagnosed oligomenorrhea.
Cigarette smoking over the age 35y.
D.M.
Non focal migraine.
sickle cell disease(not triat).
I.B.D.
Obesity.

Risk & Side Effects
➢
Minor S/E:
1.
Weight gain.
2.
Fluid retention.
3.
Headache.
4.
N&V.
5.
Chloasms.
6.
Mood change.
7.
Loss of libido.
8.
Mastalgia.
9.
Breast enlargement.
10.
Greasy skin. most of the above improve within
3-6months of starting the pills.

➢
Major S/E:
1.
Risk of thromboembolism ,unaffected by age,
smoking, duration of use, return to normal by
3months after stopping.
2.
Arterial diseases, related to age , strongly
influence by smoking.
3.
Malignant disease
❑
Ca breast ,risk persist 10 years after stopping.
❑
Cervical adenocarcinoma.
❑
Benign hepatic adenoma.
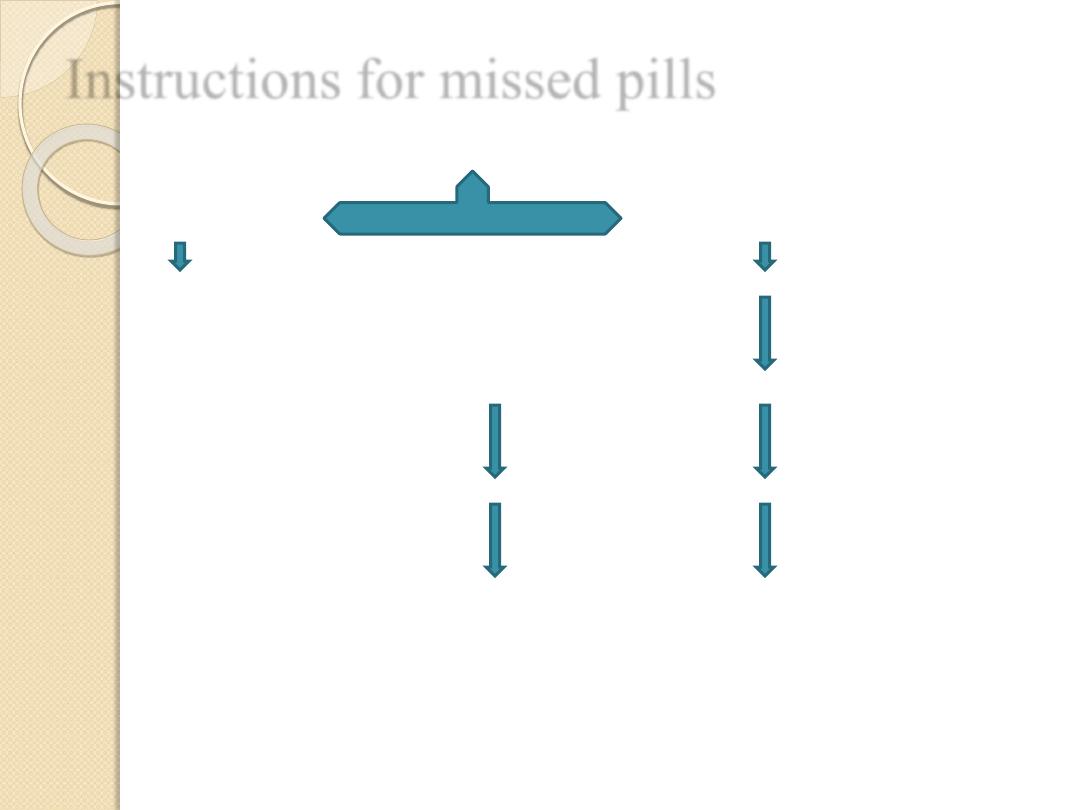
Instructions for missed pills
Ask the patient , how late you are?
<12hour late >12 hour late
Just take the delayed pill take the most recently delayed pill
how many pills are left in the back
7or more fewer than 7pills
After finishing the back,7day break After finishing the back , start
the next back without break

Progesterone only contraception:
(pills ,inject able ,implants)
Mode of action:
1.
High dose(injection) →inhibit ovulation . Low dose
→ovulation may be inhibited.
2.
By all route→ affect cervical mucus → decrease sperm
penetration and transport.
3.
All have effects on the endometrium → compromise
implantation.
4.
Local effects on the ovary.
5.
Inhibit FSH&LH.
S&E
1.
Irregular vaginal bleeding(low dose)
2.
Alter the vasculature of the endometrium → chance of
bleeding.

(I)Progesterone only pills(POP)
Indications(pop):
for female with absolute or relative C.I
to
estrogen
1.
Cardiovascular risk factor.
2.
Migraine
3.
D.M.
4.
Mild HT.
5.
Over35years
6.
lactating female.
S/E(pop):
➢
short term risk : irregular bleeding , functional ovarian cyst,
headache . nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, mood changes,
oily skin and acne.
➢
Long term risk : Depo-Provera → protect against endometrial
ca, and ovarian ca. and increase risk of breast cancer if for 5years.

Contraindications(pop)
Absolute:
1.
Known or suspected pregnancy.
2.
Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding.
3.
Current hx of sever cardiovascular disease.
4.
Any serious side effects with COC and not known to be due to estrogen or
associated with past progesterone use i.e. hepatic adenoma.
5.
Acute porphyria.
6.
Injectable methods →C.I. in patients with bleeding disorders or on
anticoagulants.
Relative:
1.
Multiple risk factors for arterial disease.
2.
Sever obesity.
3.
Untreated breast cancer.
4.
Trophoblastic disease.
5.
Current use of enzyme inducer.
6.
Hx of recurrent functional ovarian cysts(low dose may not inhibit ovulation
and may exacerbate those.
7.
Past hx of ectopic.

(II)Injectable progesterone:
A)Depo-provera(MPA)
B)norethisterone-enanthate
Given deep IM injection
=
Long term contraception
shorter
150mg
200mg
Every 12weeks
every 8 weeks.
S/E: Fertility may need >1yr to resume after stopping , wt
gain , bone mineral density , amenorrhea with long use.
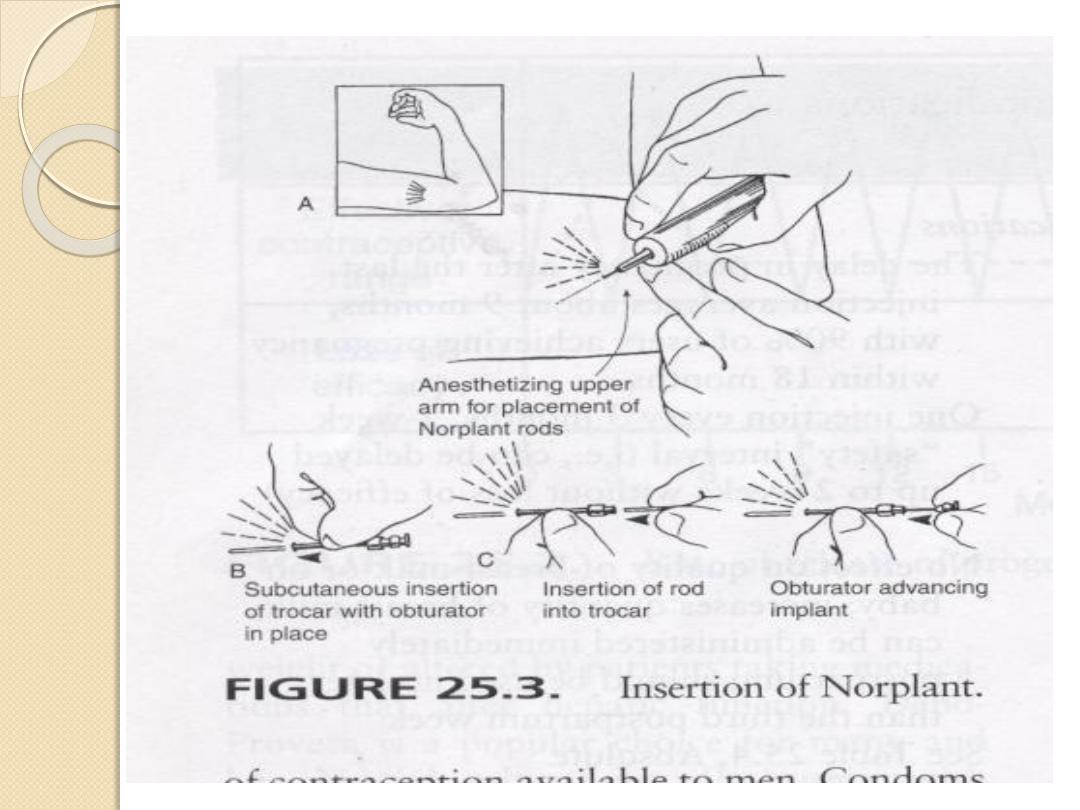
(III)Progesterone only implants:
a)Norplant
B)implanon
Long acting
=
Six flexible capsule
single
Low dose Levonorgestrel released
Etonorgestrel 68mg
Sub dermal under local anesthesia
same efficacy

I.Progesterone only pills (POP)
28 tablets
Should be taken daily without break
Less effective than combined pills
Suitable for lactating women

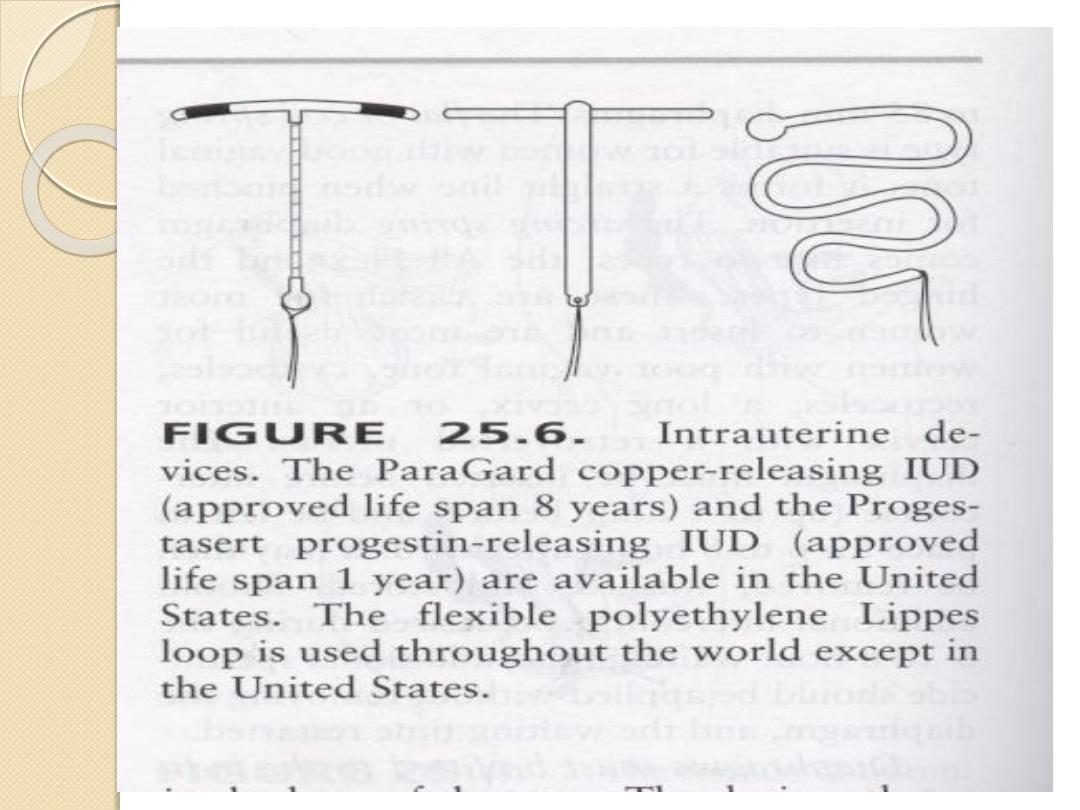
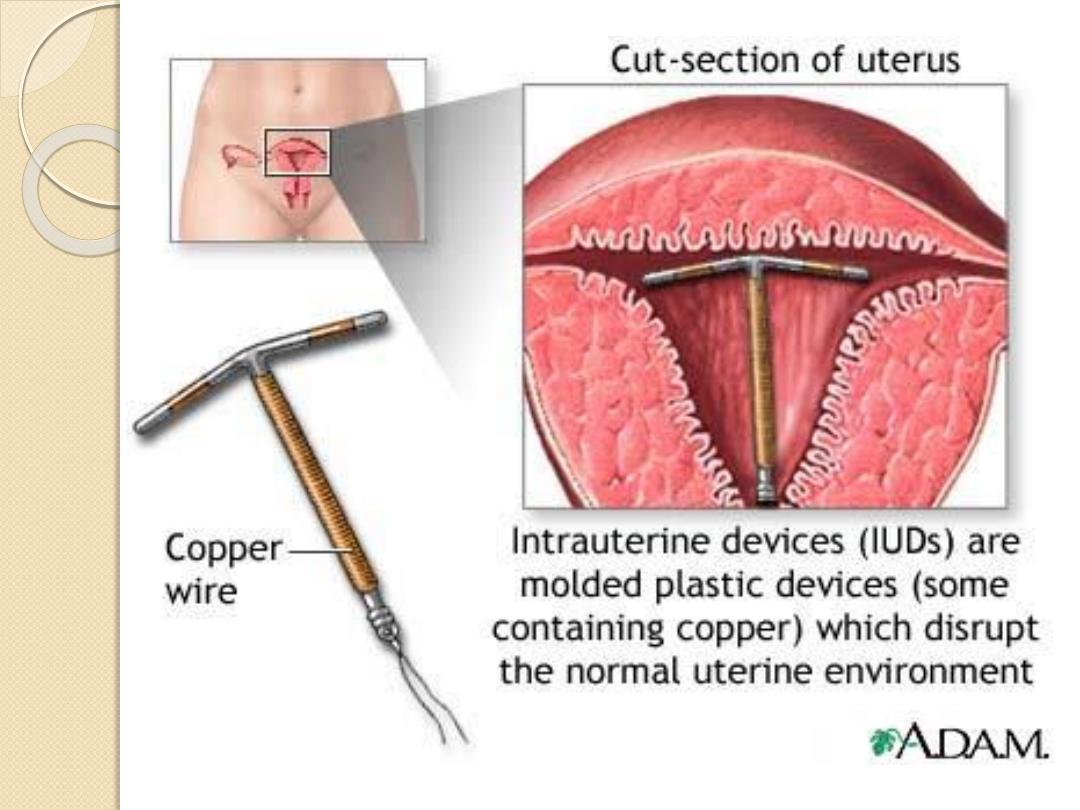
IUCD(Intrauterine Contraceptive Device)
1.
Inert polyethylene.
2.
Copper IUCD.
3.
Hormone releasing IUCD(mirina).
4.
New development(CU-safe,gynaefix ,tailless)
Mechanism of action:
1.
Prevention of implantation.
2.
Affect both egg and sperm and interfere with sperm
transport.
Side Effects:
1.
Menstrual disturbance.
2.
Perforation.
3.
Expulsion.
4.
Ectopic pregnancy.
5.
Pelvic infection.
WWW.SMSO.NET

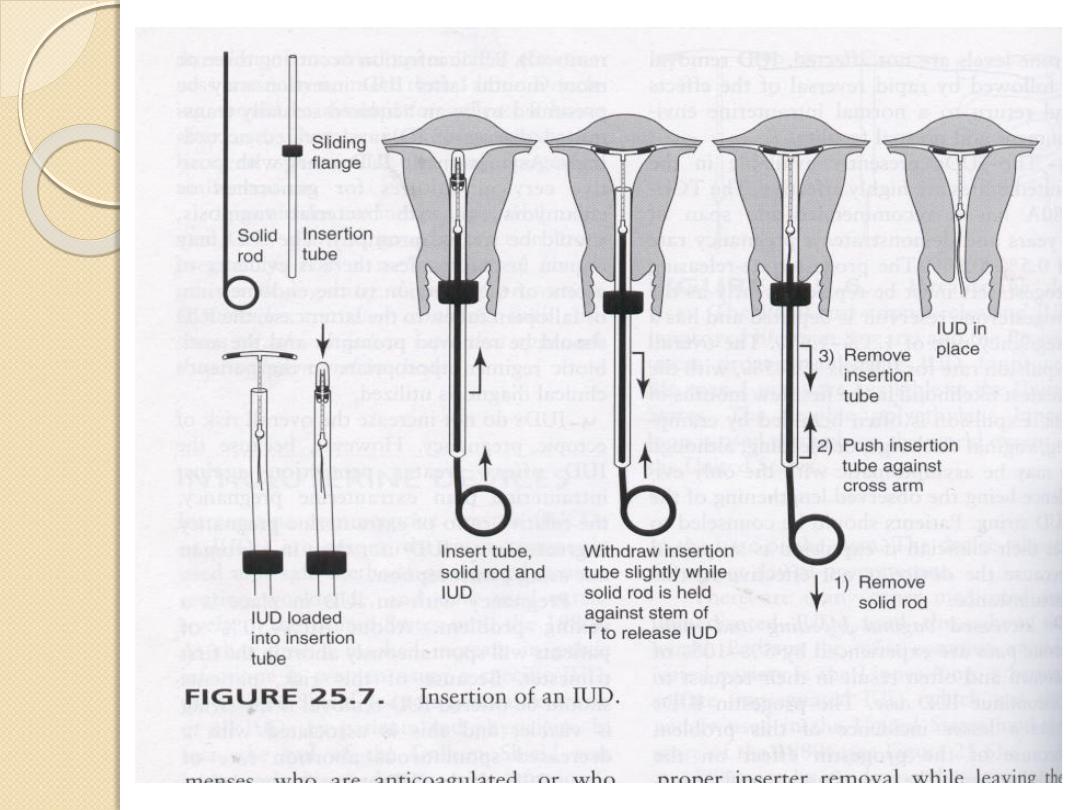
Insertion :
If the female already on effective contraceptive methods → IUCD can be inserted
at any time of the cycle .If not , should be within the 1
st
7days of the cycle → bec.
natural cervical dilatation decrease discomfort.
Post partum insertion : should be delayed until 8weeks to(1)decrease risk of
expulsion.(2)the risk of perforation have returned to normal.
After abortion , the IUCD can be inserted immediately after spontaneous or induced
abortion .but expulsion is more after 2
nd
trimester abortion.
Removal :
Unless pregnancy is desired , removal should only done in the luteal phase of the
cycle or in the 1
st
7days.
In menopausal female the IUCD should be left for 1year after the last menstrual
period.
If IUCD +actinomycosis by smear , if asymptomatic → left in and repeat smear 6-
12months later . If symptomatic → IUCD removed with avoidance of contamination
from the vagina and the tail which is contaminated should removed before sending
the device for culture.

Emergency contraception
Any drug or device used after intercourse to prevent
pregnancy.
1.Hormonal methods:
Combined(CEP regimen), the pills should be taken
within 72hour of unprotected intercourse or condom
accidents. Failure rate 20-26%,
progesterone only(Levonelle-2), more effective and
better tolerated than combined if taken as soon as
possible after intercourse.
EllaOne;Progesterone receptor modulator-120 hours
2.IUCD: highly effective. Failure rate <1%.

sterilization
In female
Involve blockage of both tubes by laparoscopy (commonest),mini
lapratomy (more in postpartum period), lapratomy.
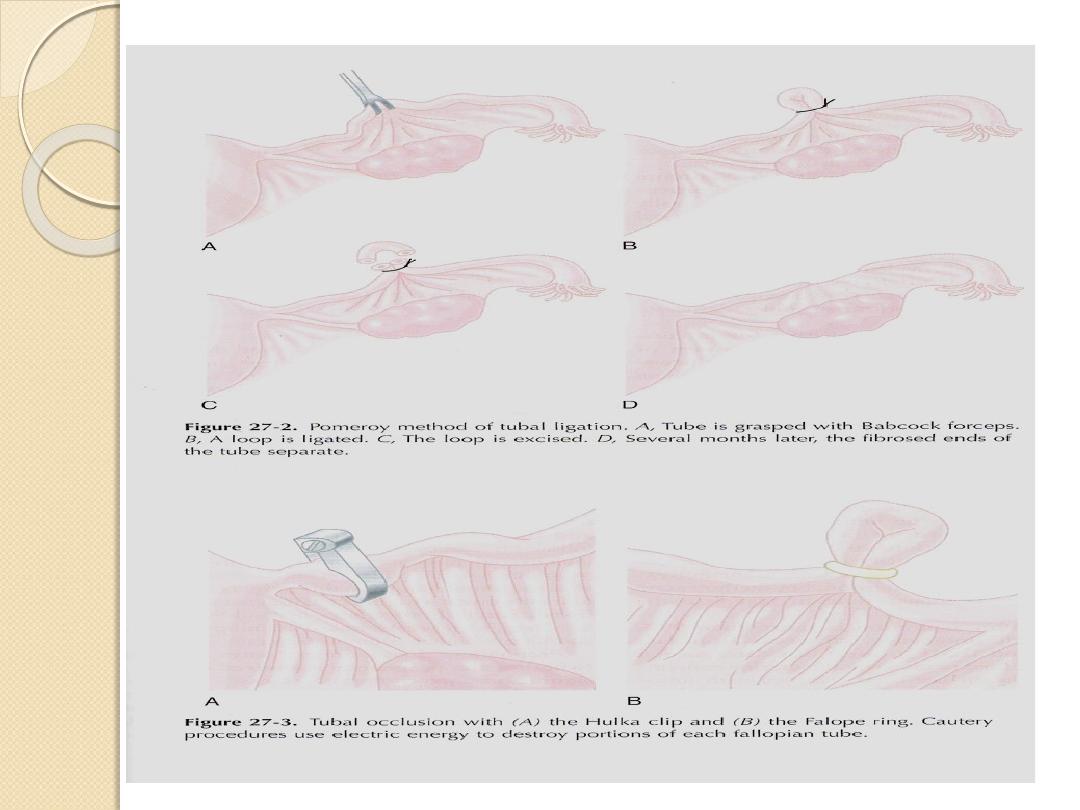
Methods:
1.
Commonest→
pomeroy
technique.
2.
Other→ electrocautary ,falope ring, clips ,laser ,chemical
gents(directly or transcervically)
3.
New methd;Essure.
➢
Immediate Complications: long term complication:
1.Mortality 1. Menstrual disorders.
2.Vascular or organ damage 2.Abdominal pain , dyspareunia.
3.Gas embolism. 3.Psychsexual problems→rare.
4.Thromboembolism. 4.Intestinal obstruction→very rare.
5.Wound infection.
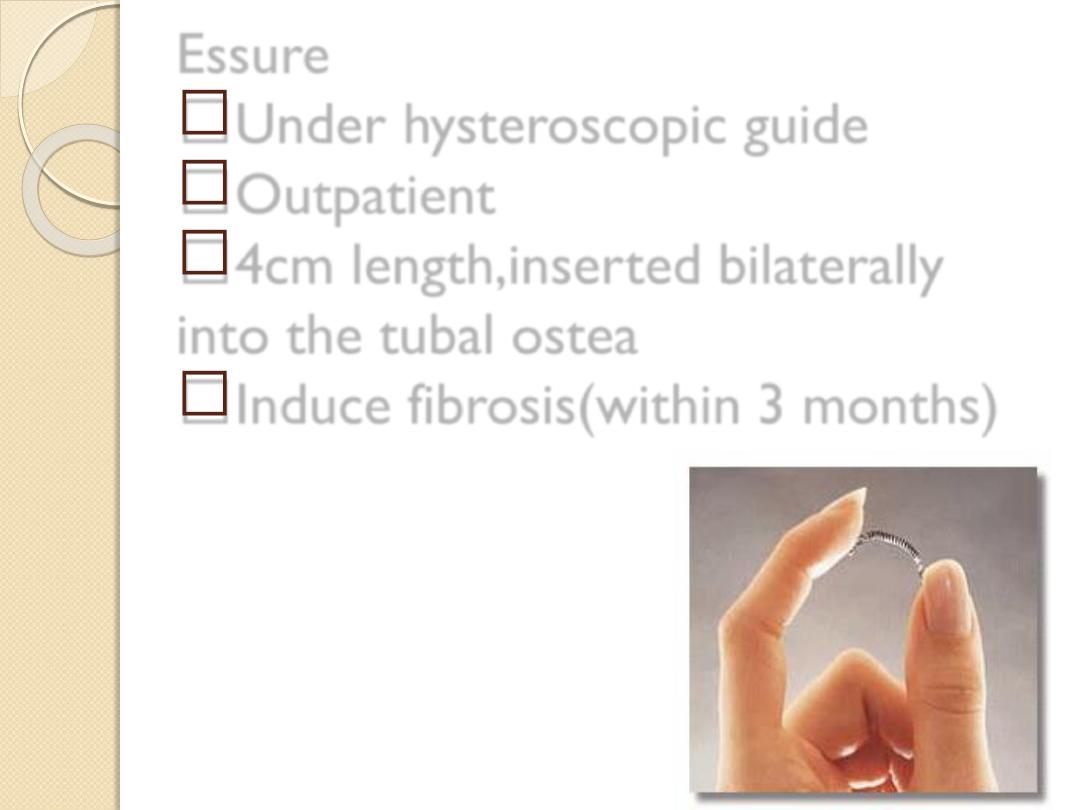
Essure
Under hysteroscopic guide
Outpatient
4cm length,inserted bilaterally
into the tubal ostea
Induce fibrosis(within 3 months)


In male
→ vasectomy.
By division or occlusion by clips, diathermy, or percutaneous
injection of sclerosing or occlusive agents.
Success is checked by absence of sperm from two consecutive
samples of ejaculate at least 4weeks apart.
Immediate complications late complications
1.
Scrotal bruising. 1.antisperm AB
development development.
2.
Haematoma. 2.small inflam granuloma
.
3.
Infection. 3.ch. Testicular pain.
Reversal of sterilization:
1.
Female , lapratomy(70% success),(5% risk of ectopic).
2.
Male,(90% success).

Barrier methods
Work by prevent the passage of sperms into the
female genital tract.
Male condom:
One of the most popular methods.
Cheap, widely available , free from S/E except
occasional allergic reaction.
Advantages:
1.
Protect against STD.
2.
Decrease cervical diseases including cancer.
Most condoms are lubricated with
spermicides, the commonest of which is
nonoxenol-9.

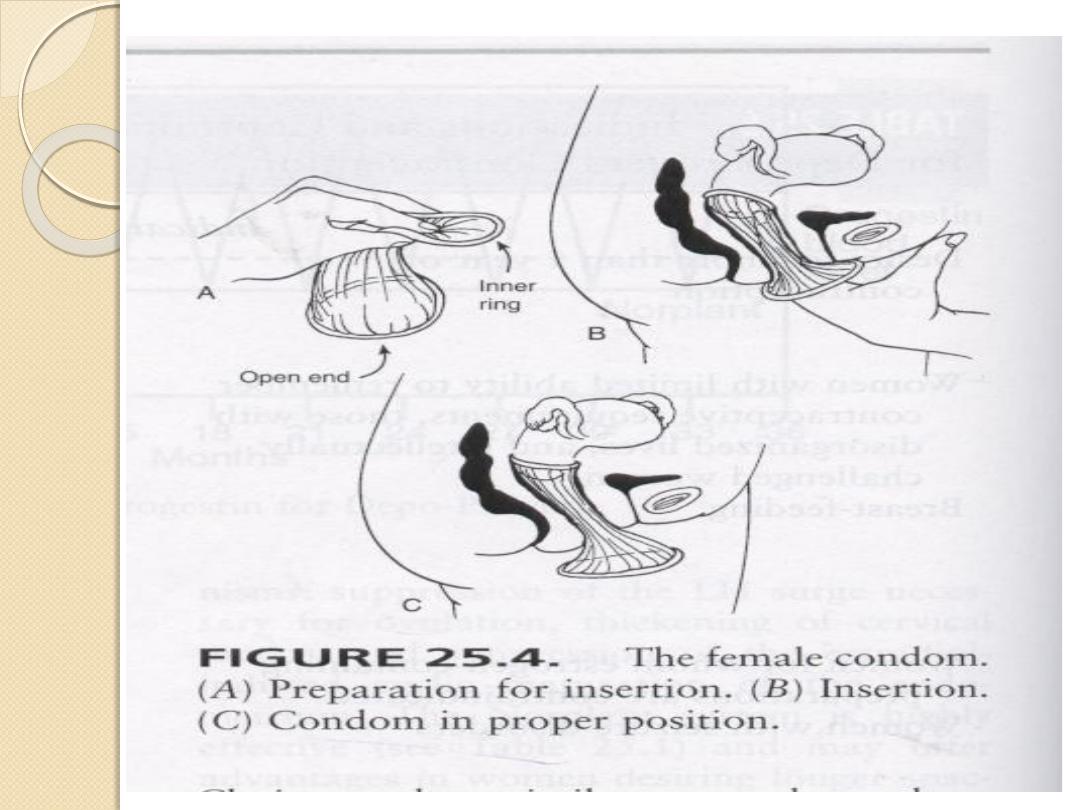
Female condom:
Polyurethane sheath, available in one size ,
single use , inexpensive, same failure rate as
male condom.
main aim is protection against STD.
Diaphragm and cervical cap:
Less popular than male condom.
Need doctor or nurse to insert.
Less protection against HIV.
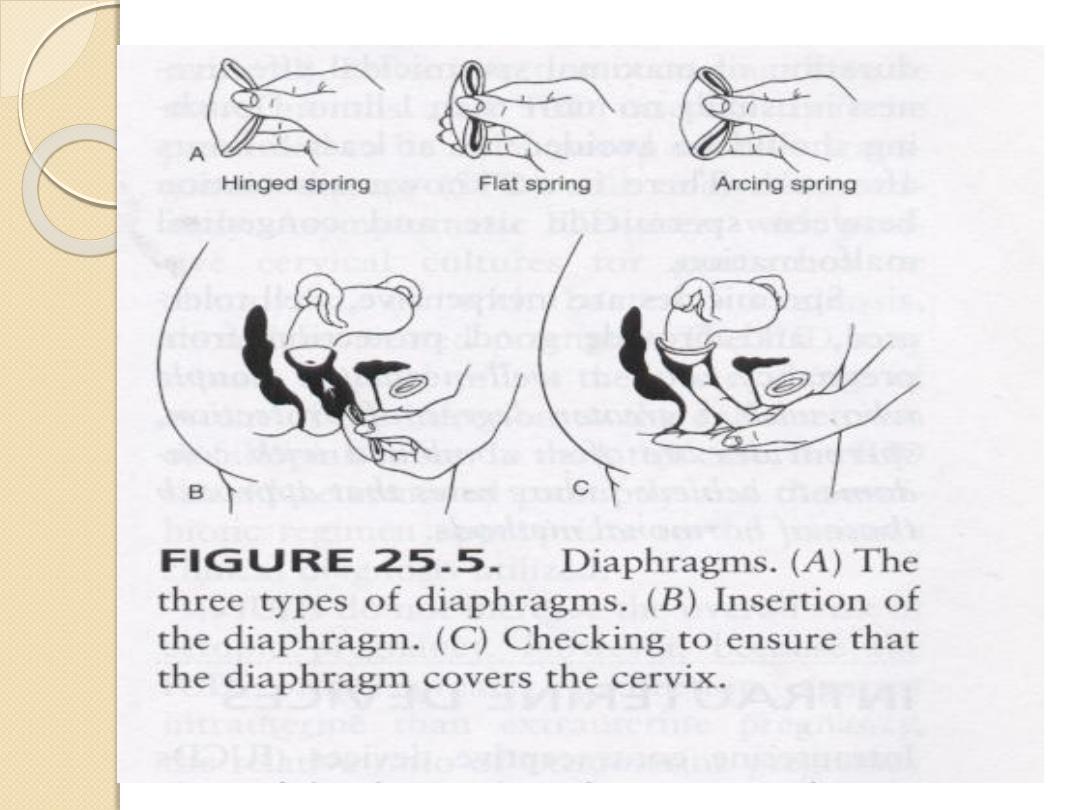

cervical cap:

Natural family planning
Periodic abstinence
; Involve avoidance of intercourse
during the fertile period of the cycle,methods differ in
recognition of the fertile period.
1)))Calender
;(rhythm method) calculation of the fertile
period according to the length of the cycle
Womans shortest cycle-20=first day of the fertile
period
Womans longest cycle-11=last day of the fertile
period.e.g.if the cycle length varies from 25 to 31 days.
25-20=5, 31-11=20 days(so the intercourse should be
avoided from day 5 to day 20).

2)))Symptoms:
which reflects fluctuating
concentration of estrogen and progesterone.
a)
Billing method: mucas method
b)
BBT:
c)
Hand held monitor (persona)
Lactational amenorrhea method:
Breast feeding delays resumption of fertility and the
length of delay is related to frequency and duration
of breast feeding and time of introduction of food.
In this method;
1.
Pure breast feeding for 6 months.
2.
Two breasts used for 5-10 minutes each feed.
Not useful after 6 months and failure rate is 2 %.
