
الدكتور
رافد رمثان حسين
التميمي
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
-Sympathetic nervous system
- Parasympathetic nervous system

INTRODUCTION
The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, consists of
the cranial nerves, spinal nerves and ganglia.
The peripheral nervous system subdivided into:
1.
Autonomic nervous system:
- sympathetic nervous system
- parasympathetic nervous system
2.
Somatic nervous system
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
2

T h e autonomic nervous system (ANS or visceral nervous system) is the part
of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning
largely below the level of consciousness, and controls function.
Responsible for control of “involuntary” or visceral bodily function:
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive functions
Key role in the bodies response to stress
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
3

The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activities of
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
General function of the autonomic nervous system.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
4

It is classically divided into two subsystems:
SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM:
Allow body to function under stress
Fight or flight
Primes body for intense skeletal muscle activity
PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Maintenance functions
Rest-and-digest
Counterbalances sympathetic function
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
5
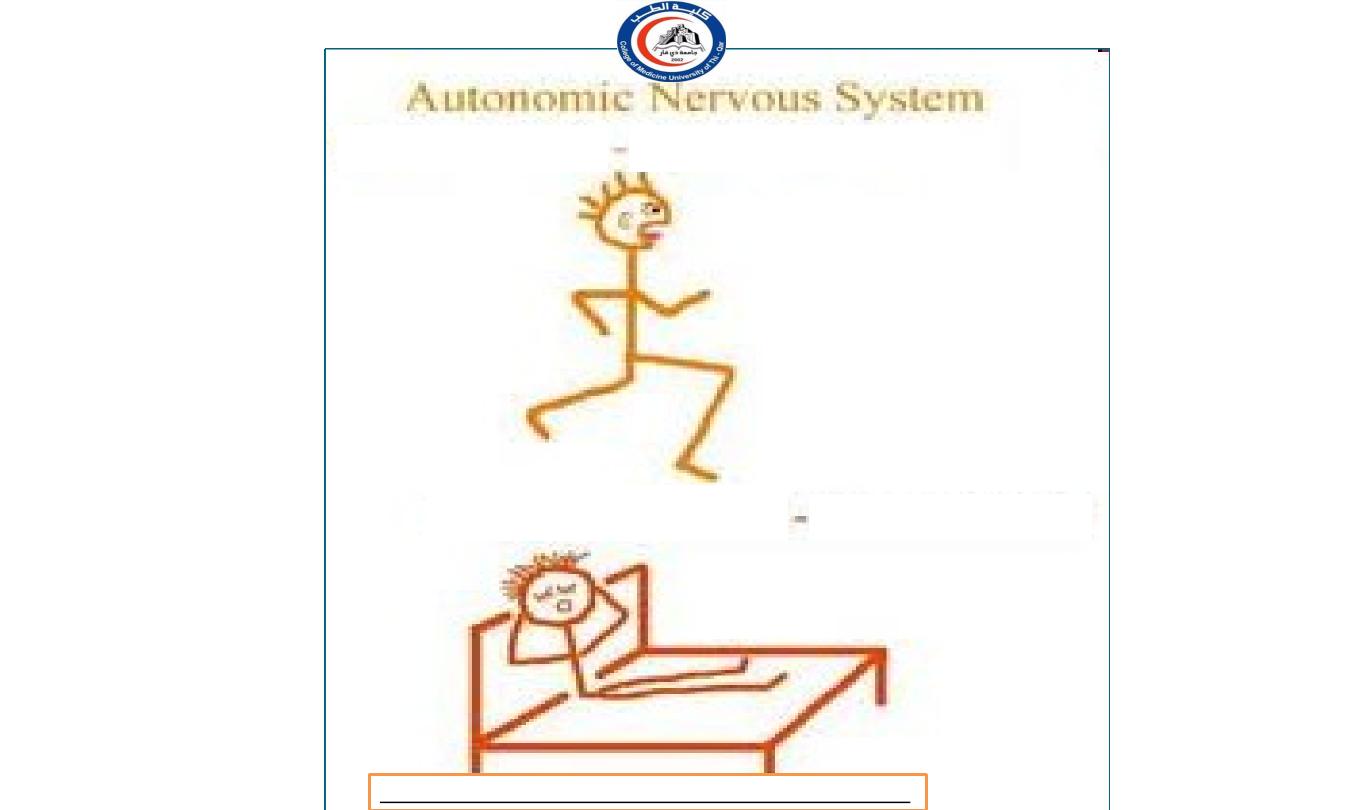
―Fight or flight‖
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
―Rest and Digest‖
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
6
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
7

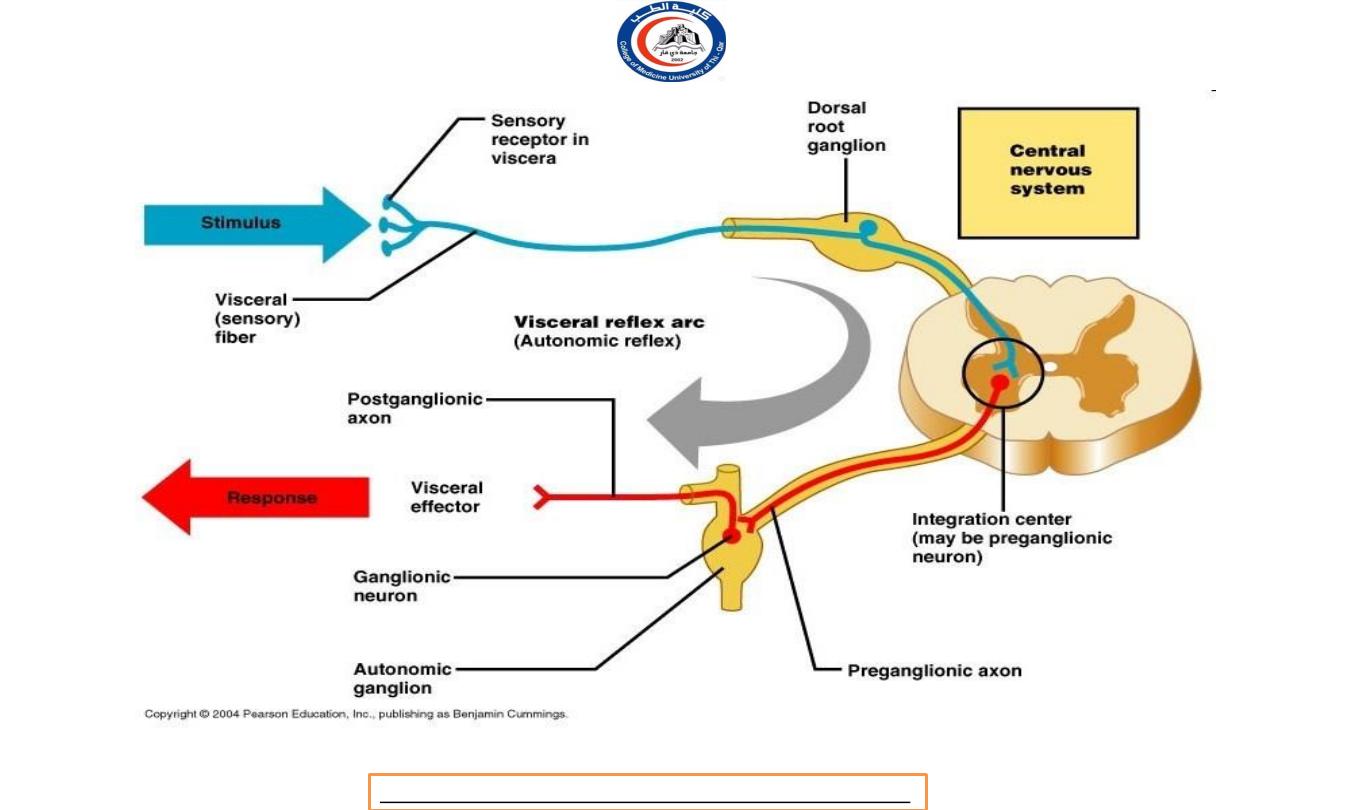
In general nerve impulses from one division of the ANS
stimulate the organ to increase its activity (excitation), and
another part inhibit the organs activity (inhibition).
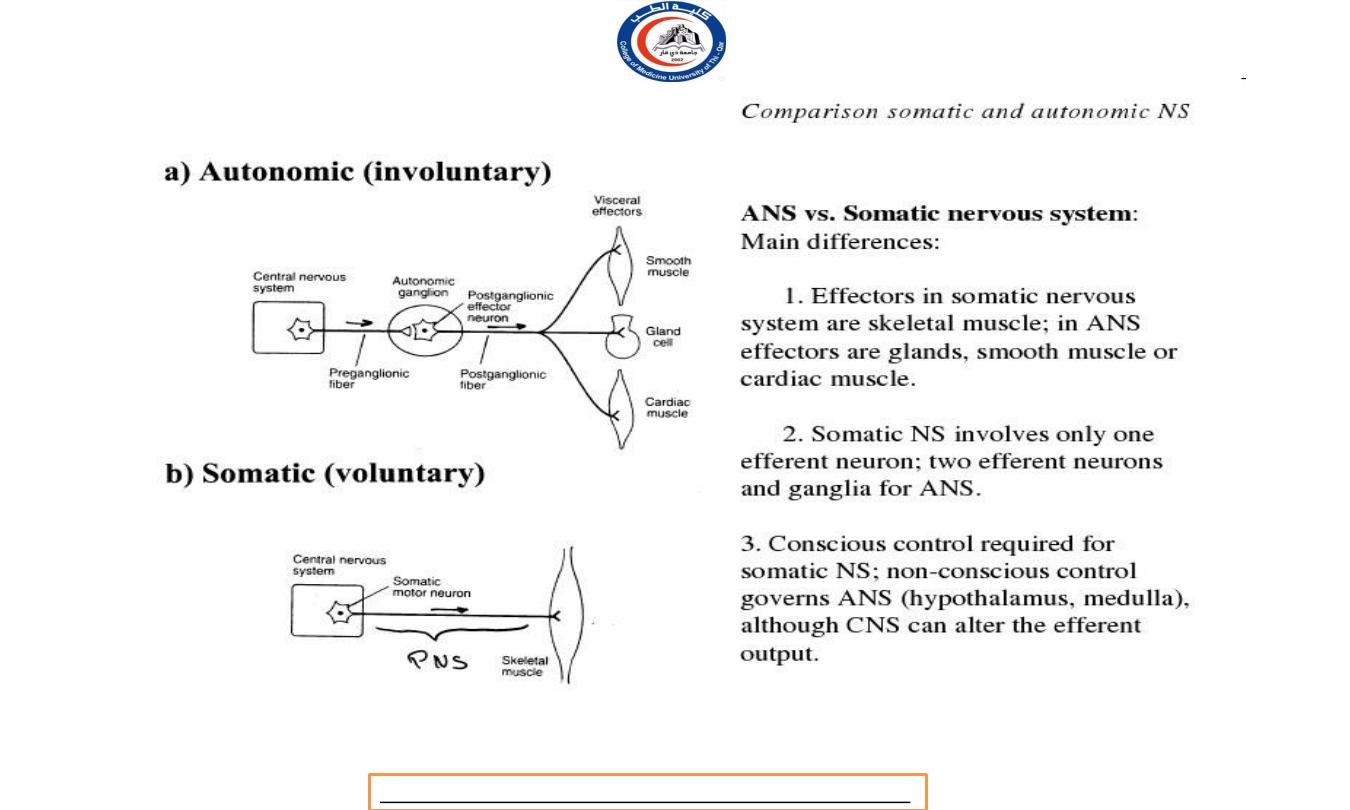
Structurally, ANS includes:
a.
autonomic sensory neurons (afferent)
b.
integrating centers in the CNS
c.
autonomic motor neurons (efferent)
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
8

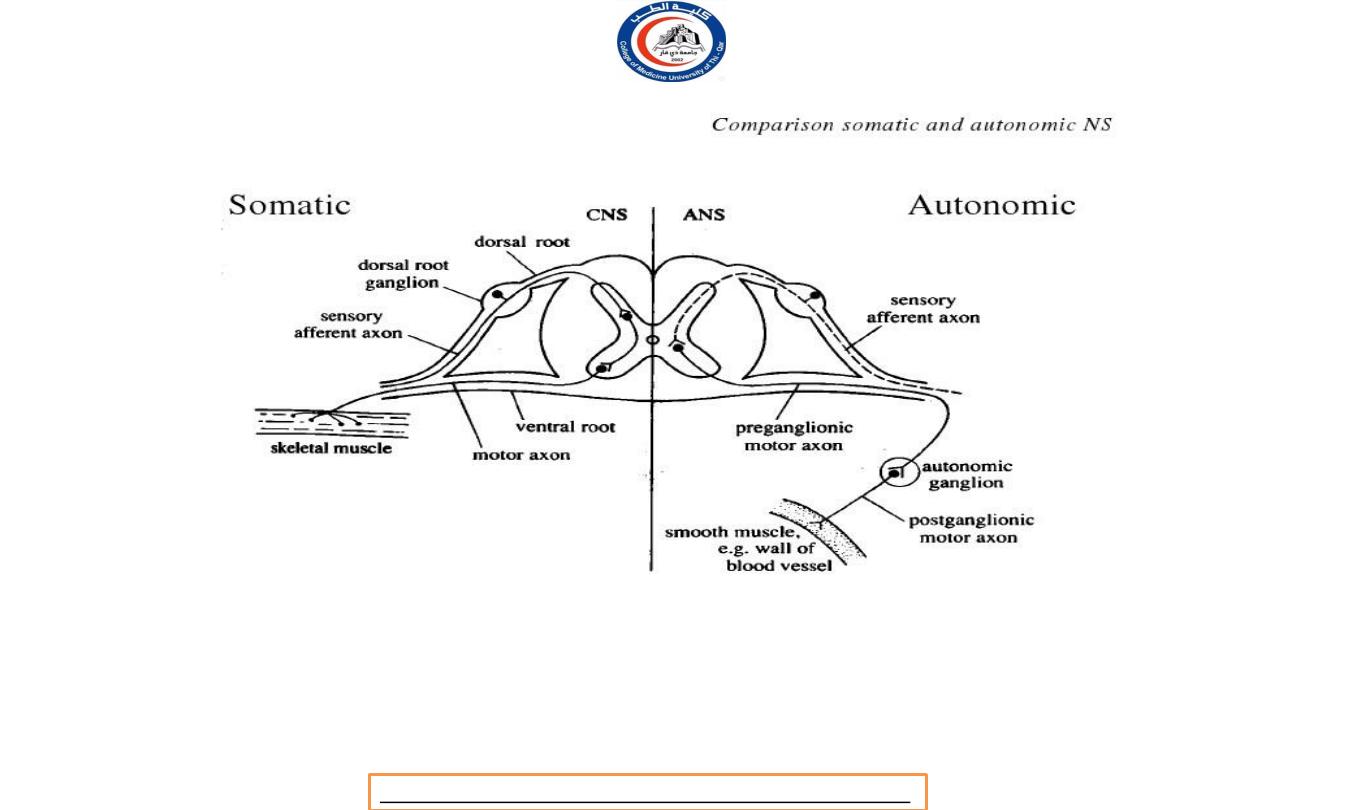
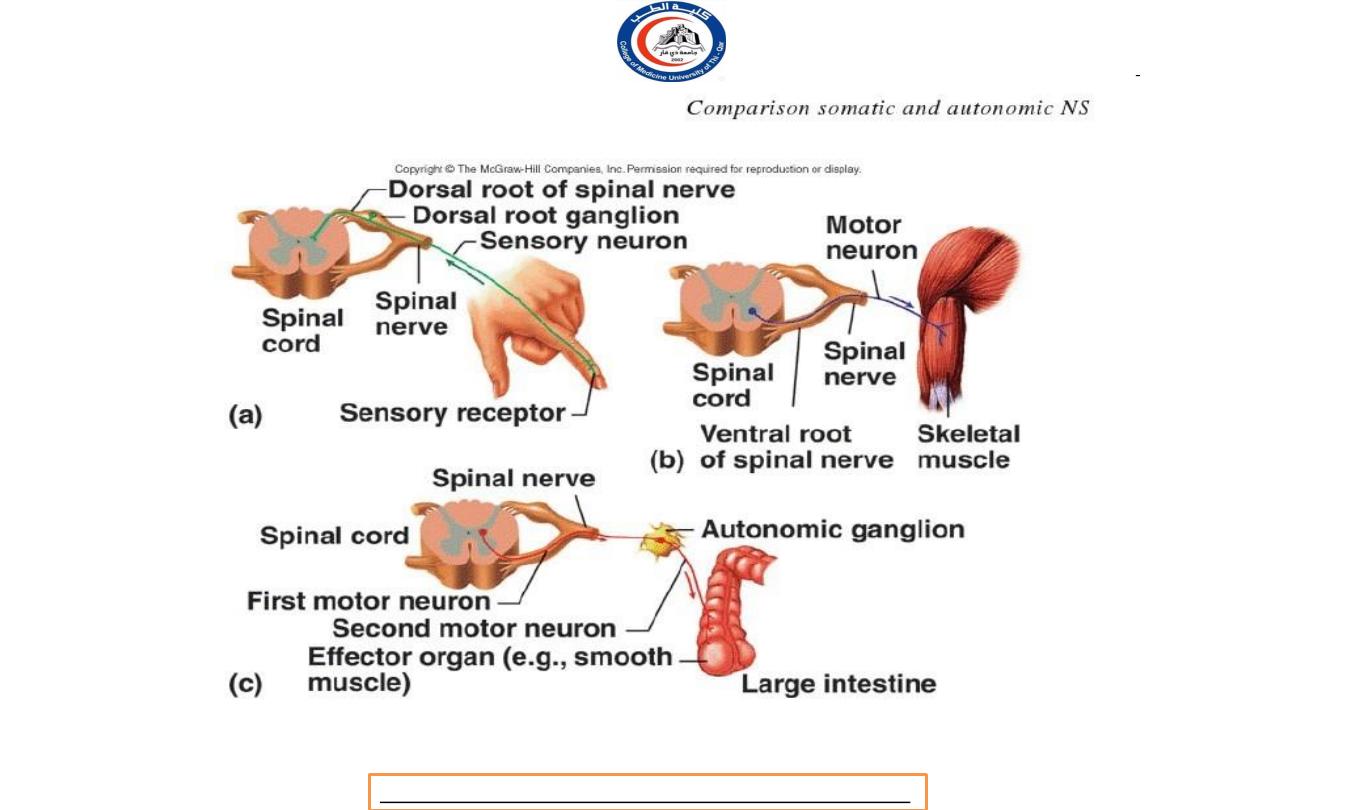
Comparison Somatic and
Autonomic Nervous System
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
9
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
10
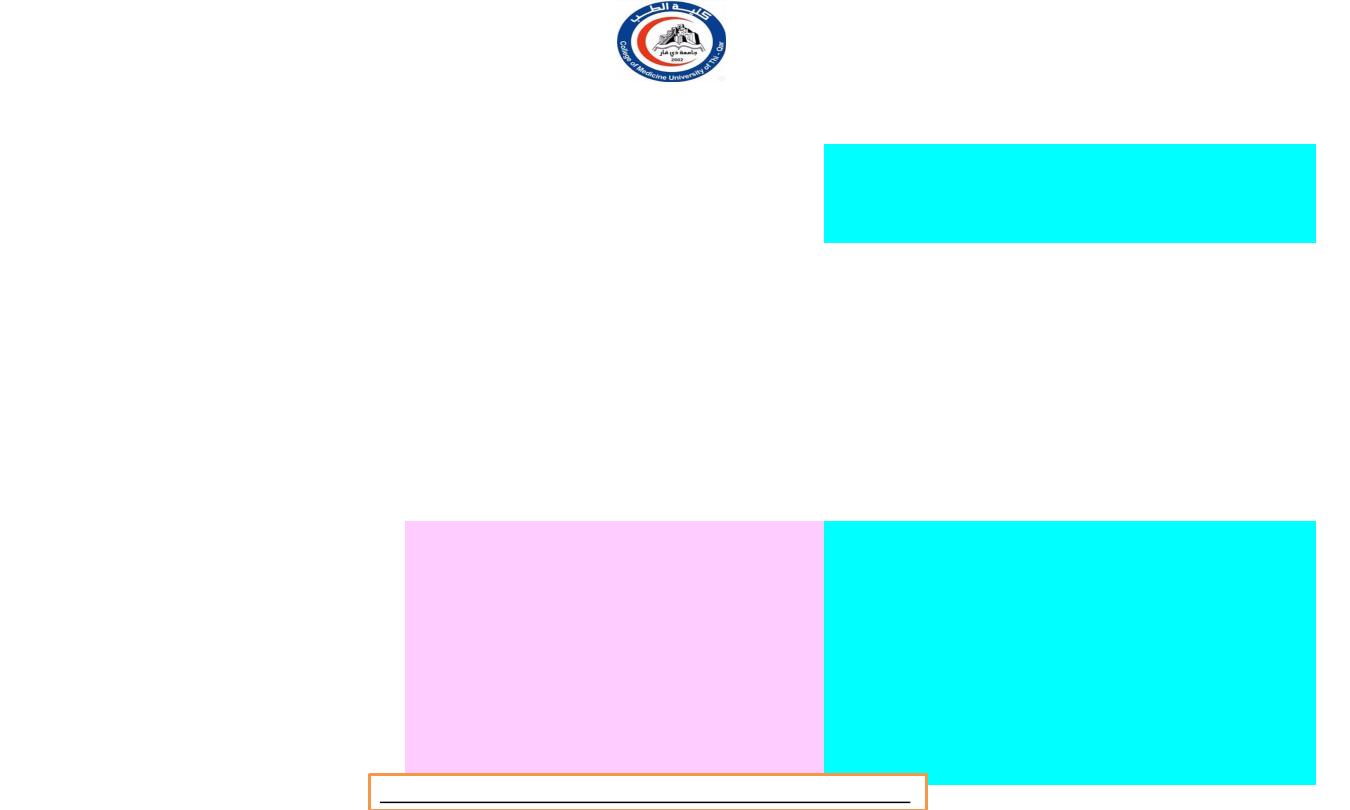
Characteristics
Sensory neuron
Somatic nervous
system
Somatic senses and
special senses
Effector
Skeletal muscle
Control of motor
neuron
Voluntary control from
cerebral cortex, with
contribution from basal
ganglia, cerebellum,
brainstem and spinal
cord.
Autonomic nervous
system
Mainly from interoceptors
9located in blood vessel,
visceral organ, nervous system
that monitor internal
environment)
Cardiac, smooth muscle and
glands
Involuntary control from
hypothalamus, lymbic
system, brain stem and spinal
cord;
limited control
from cerebral cortex.
Comparison Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
11
Characteristics
Motor neuron
(efferent) pathway
Somatic nervous
system
One motor axon from
CNS to effector
Autonomic nervous
system
Two neuron pathway:
One
motor axon from CNS to
autonomic ganglion
(preganglionic)
One motor axon from
autonomic ganglion to
effector (postganglionic)
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
12
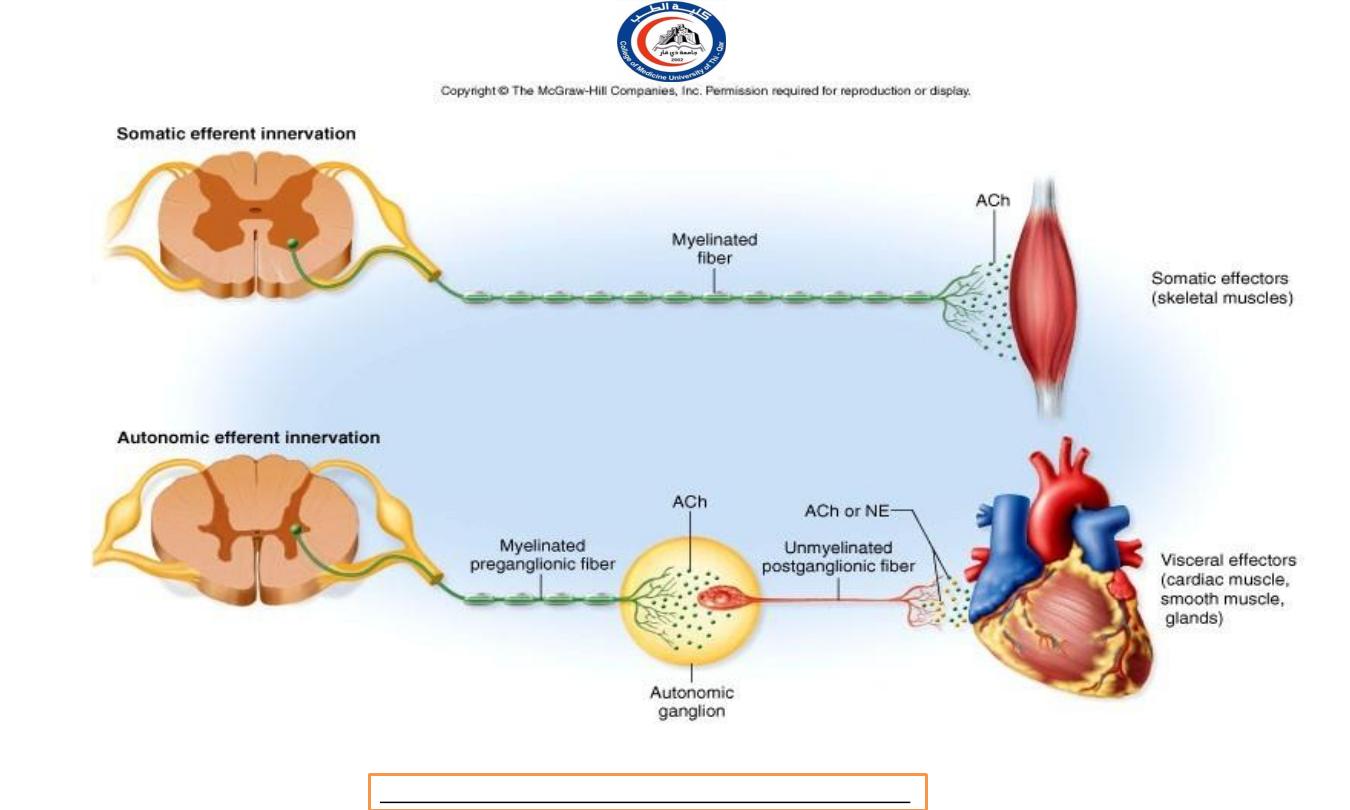
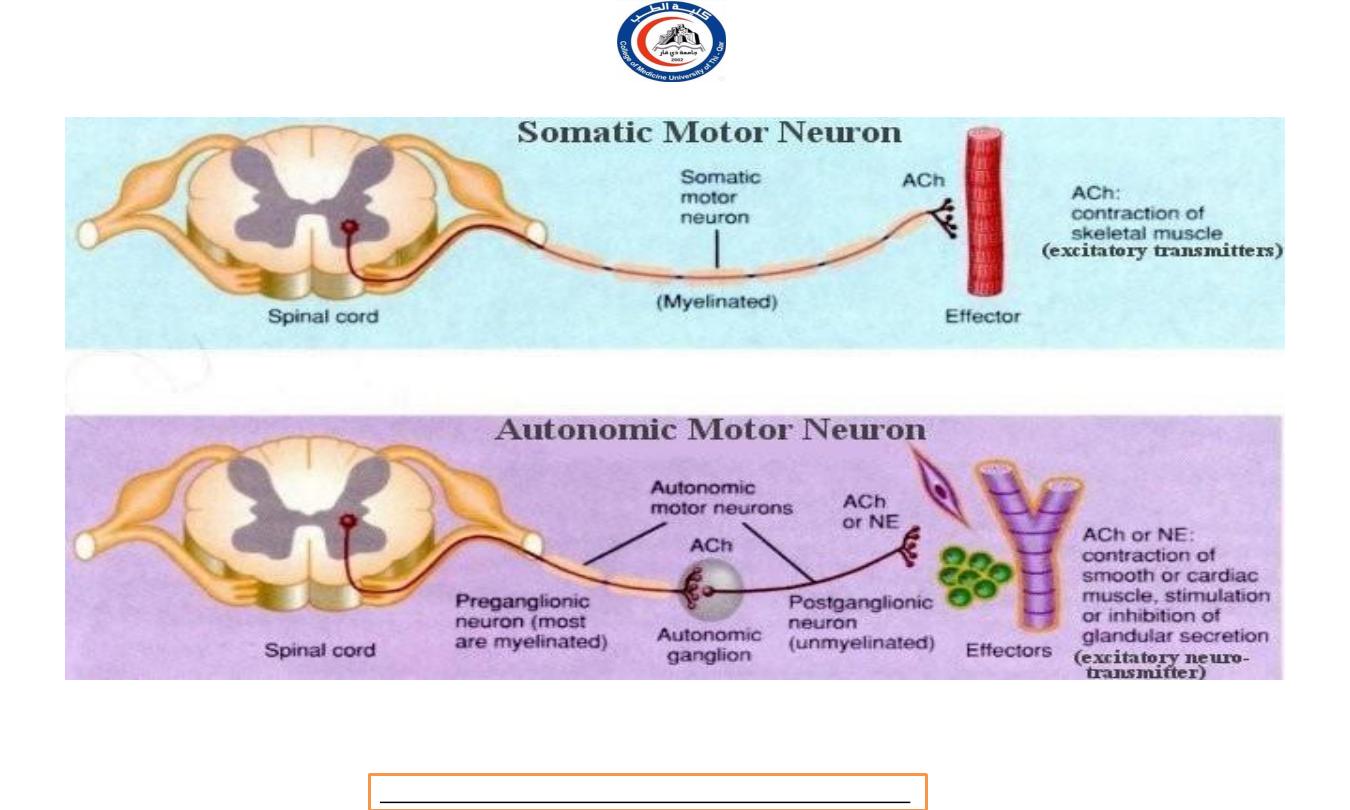
Characteristics
Somatic nervous
system
Autonomic nervous
system
Location of
ganglion
Motor in CNS.
Sensory in dorsal
root.
Autonomic ganglion
outside CNS.
Preganglionic and sensory
shared with somatic nervous
system.
Neurontransmitter
Acetylcholine (Ach):
always excitatory
Sympathetic postganglionic
neurons release
Norepinephrine (NE), to
sweat gland release ACH. All
parasympathetic
postganglionic neurons
release ACh.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
13
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
14
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
15
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
16
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
17
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
18

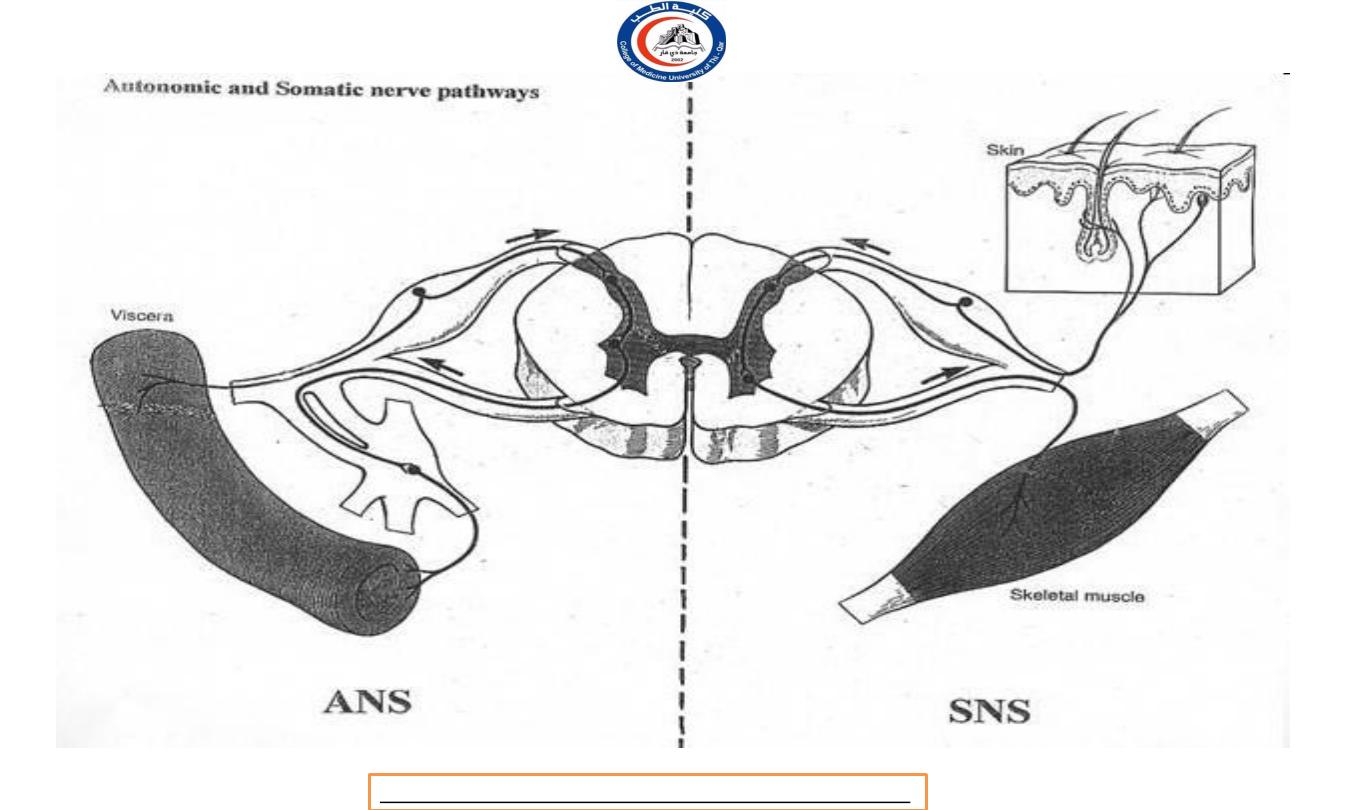
ANATOMY OF
AUTONOMIC MOTOR PATHWAYS
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
19
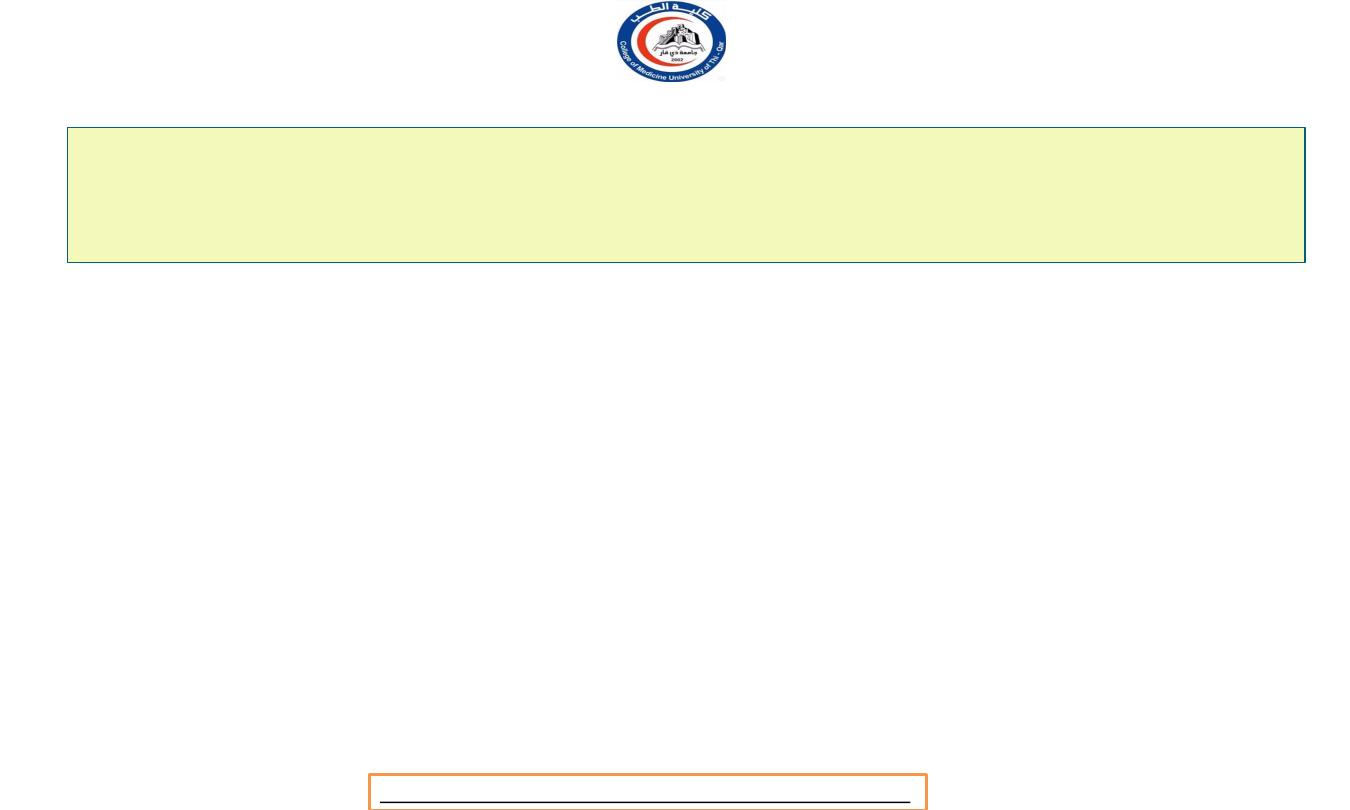
OVERVIEW
a. PREGANGLIONIC NEURONS (type B)
b. AUTONOMIC GANGLIA
c. POSTGANGLIONIC NEURONS (type C)
ANATOMY OF AUTONOMIC MOTOR PATHWAYS
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
20

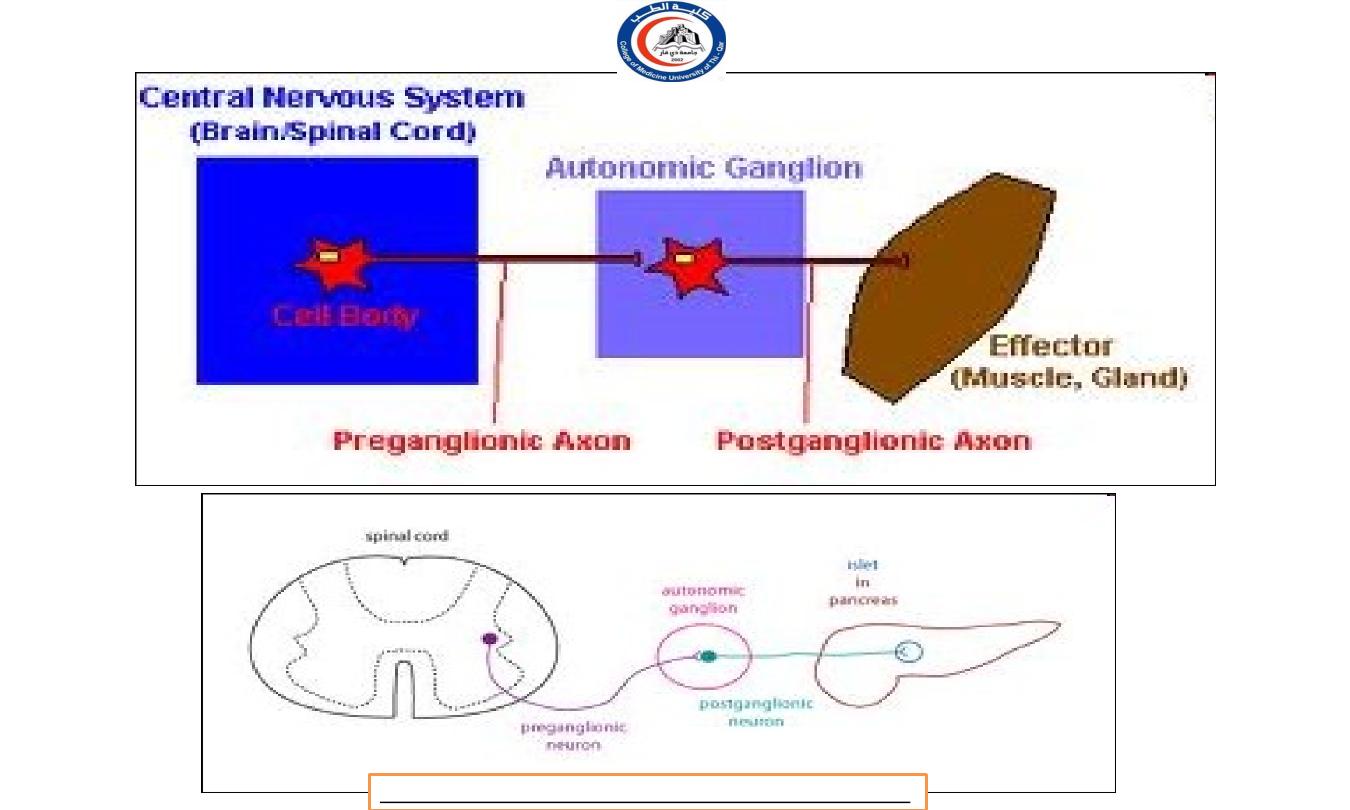
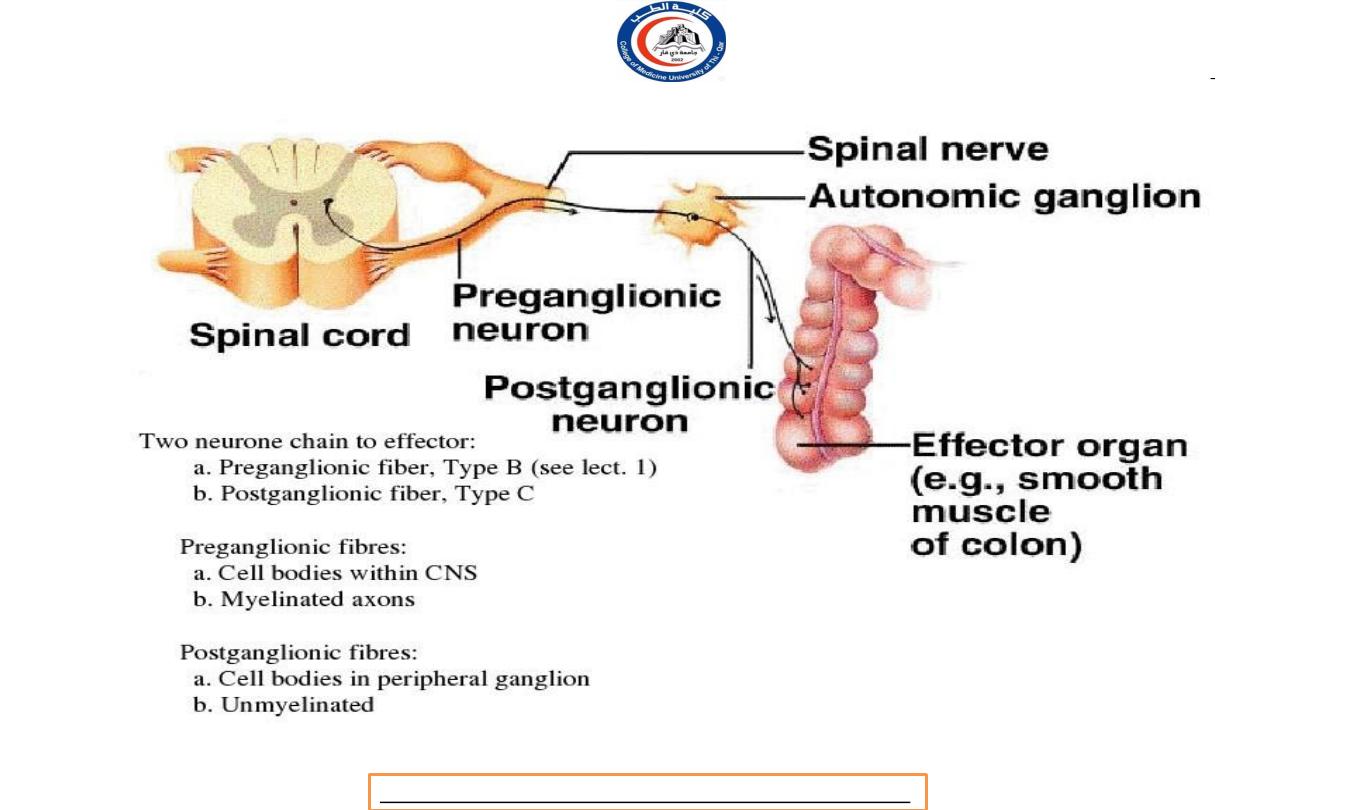
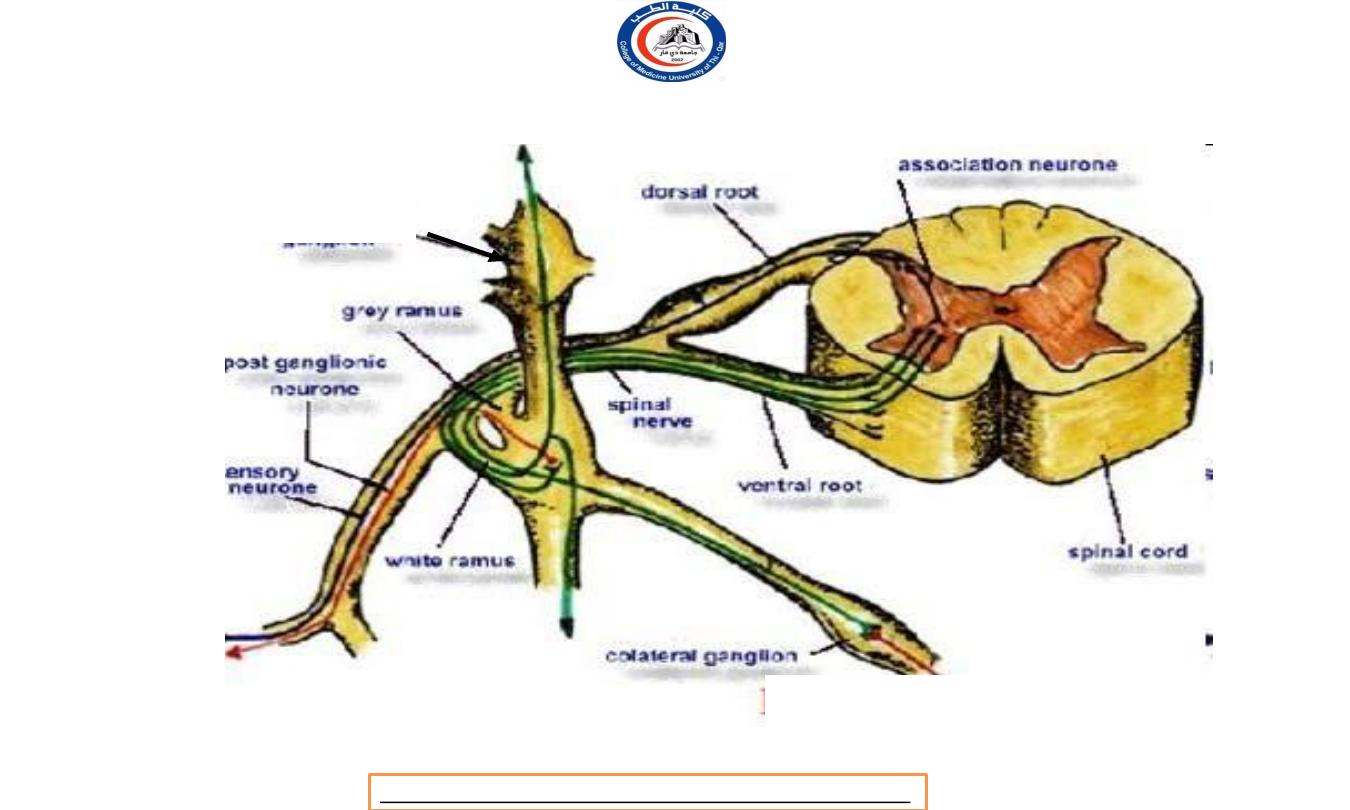
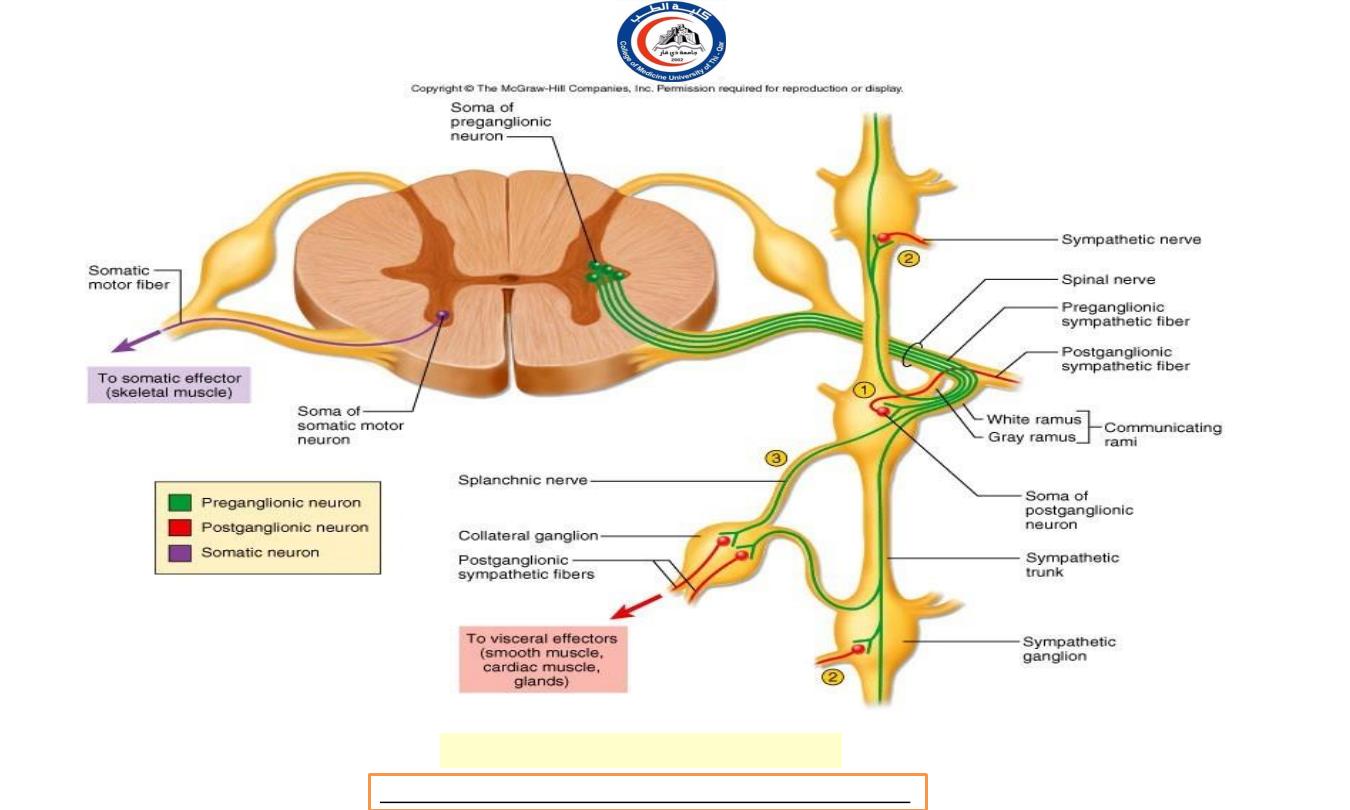
a. Preganglionic neurons:
Its cell body located within gray matter of the CNS (brain or
spinal cord)
Its myelinated axon exits the CNS.
The preganglionic axon passes from the CNS in a spinal or a cranial
nerve.
The preganglionic axon terminates in a ganglion.
b. Autonomic ganglion.
A ganglion is a collection of nerve cell bodies located in a specific site
within the body, but outside the CNS.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
21

c. Postganglionic neurons:
The cell body located in an autonomic ganglion.
The location of the ganglion is dependent upon the division of the
ANS to which the neuron belongs and which organ it will
innervate.
The axons of a postganglionic unmylinated fiber.
The postganglionic axon passes from the ganglion to the effector
(cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or gland) is either stimulated or
inhibited.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
22
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
23
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
24
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
25

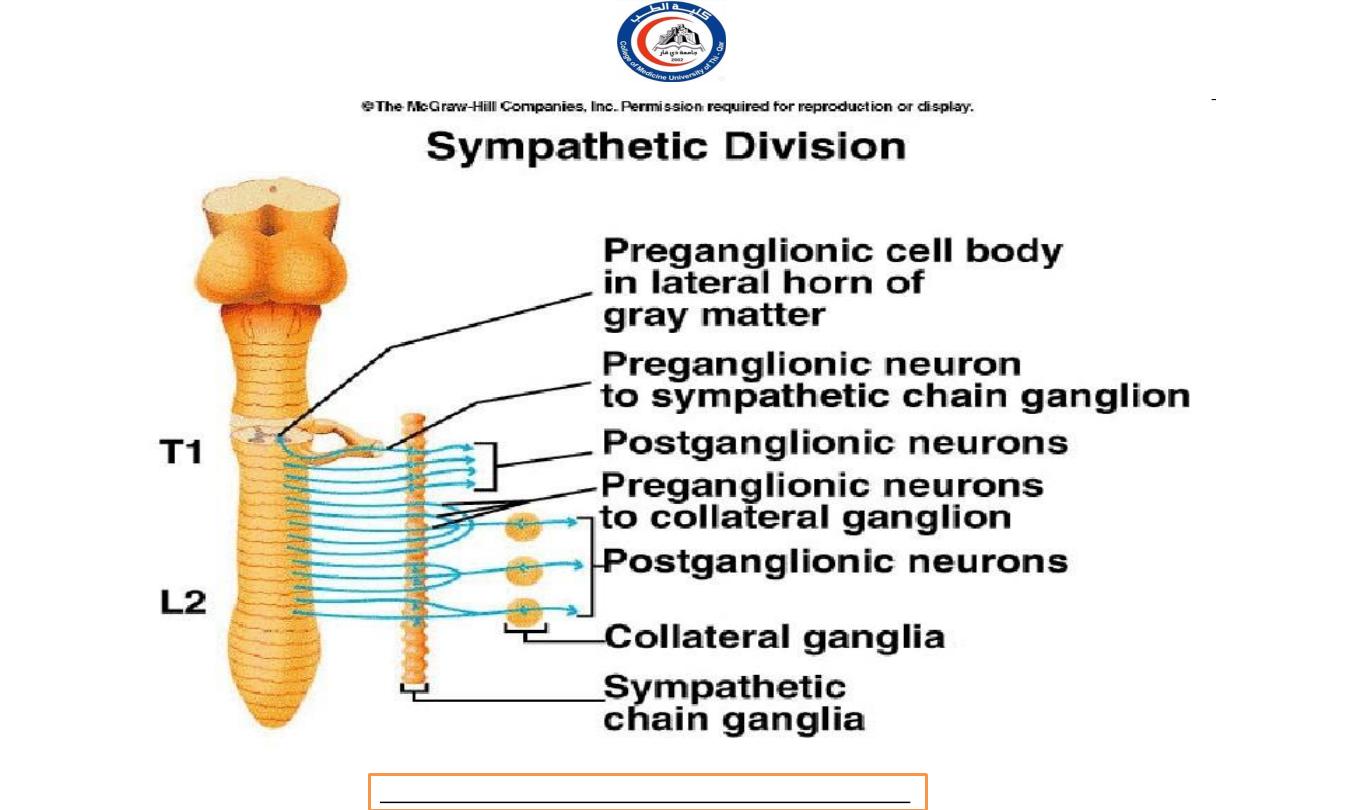
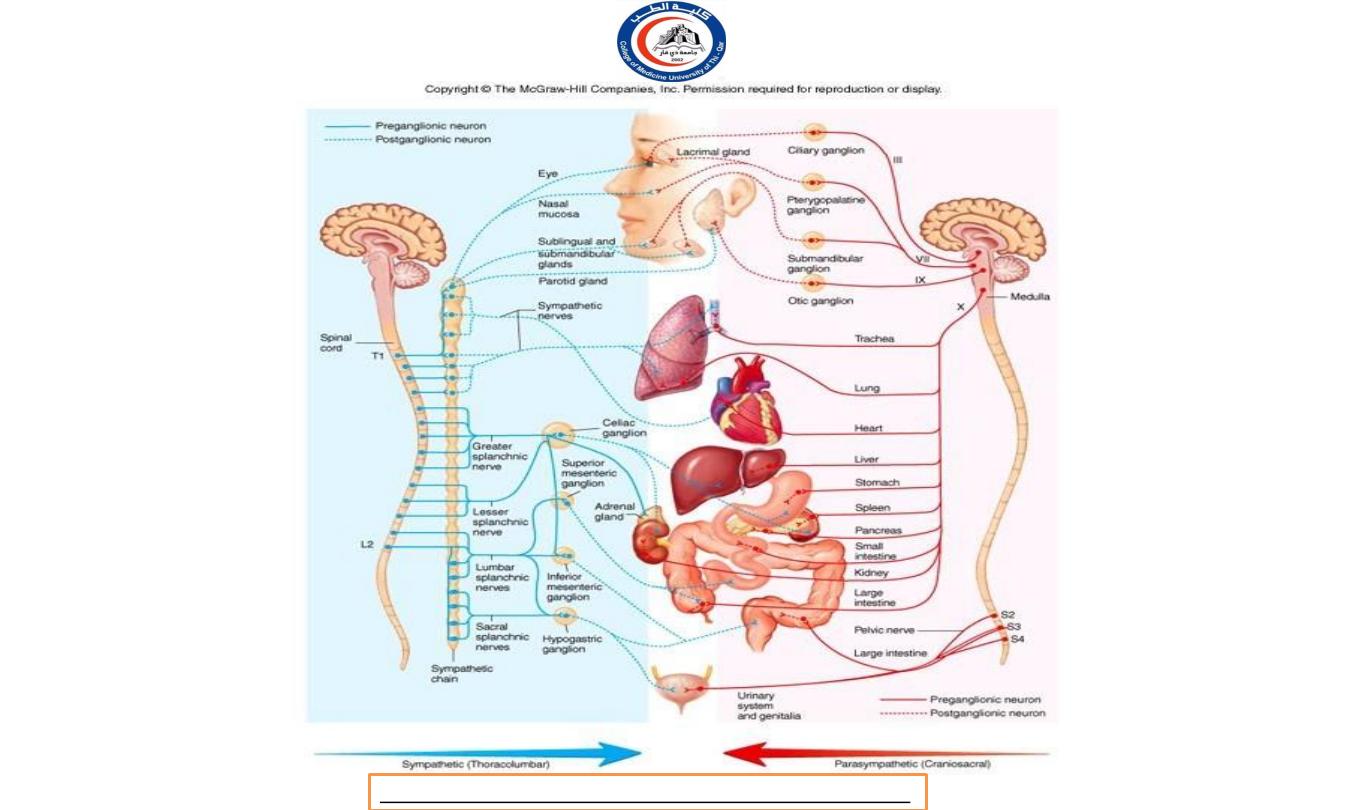
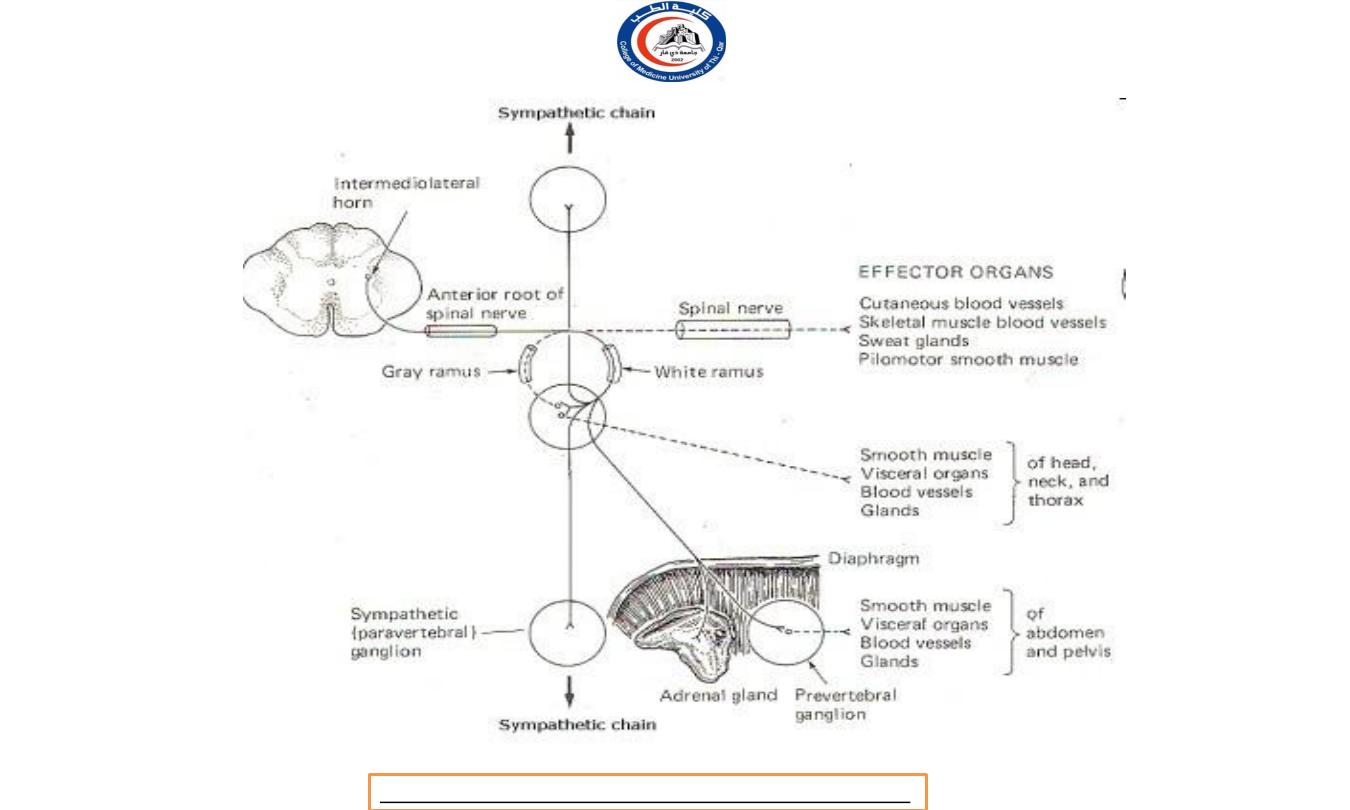
Sympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
In the Sympathetic Division (thoracolumbar division):
The cell bodies in the lateral horns of the gray matter in the
12 thoracic segments (T1-T12) and the first two (L1-L2) lumbar
segments of the spinal cord.
Therefore, the sympathetic division
is called the thoracolumbar division.
Their axons travel in the spinal nerves of these segments,
known as the thoracolumbar outflow.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
26
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
27
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
28

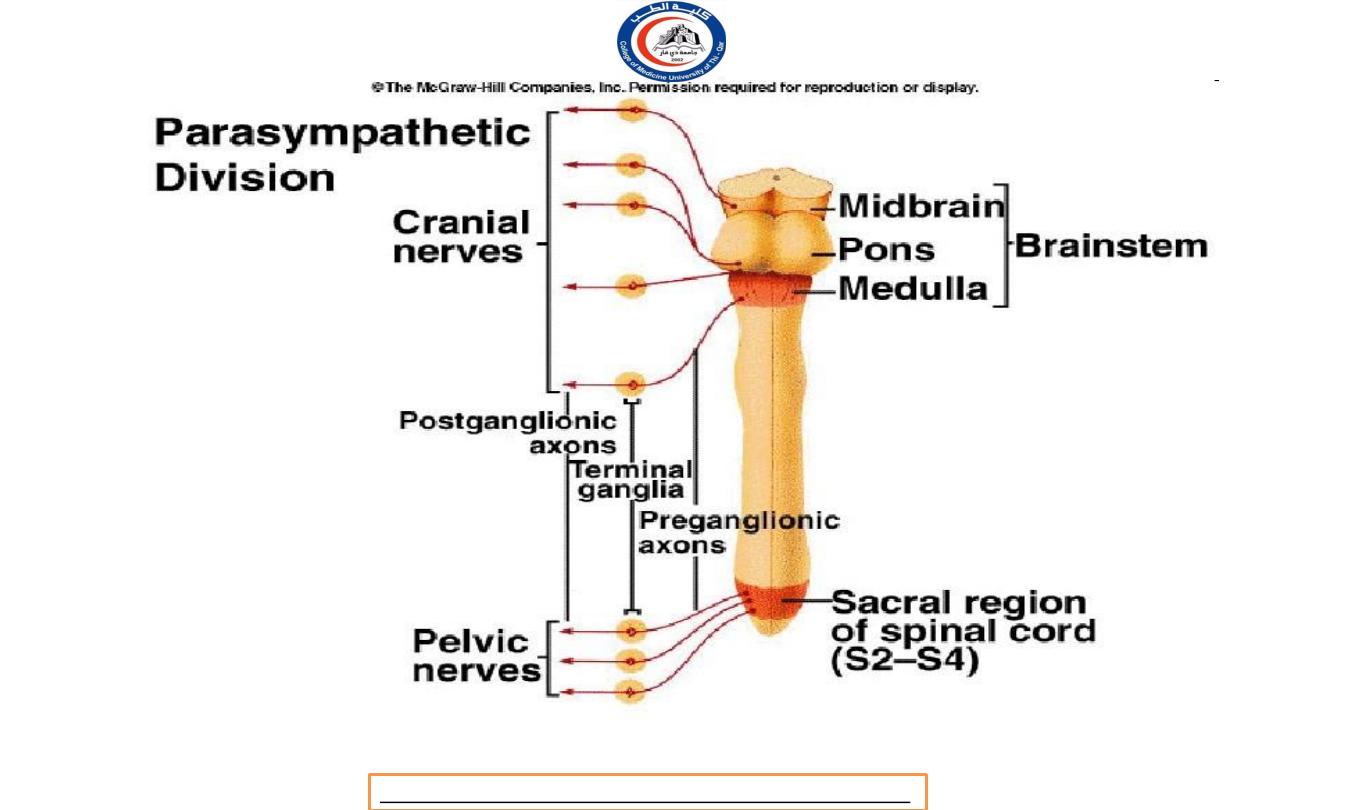
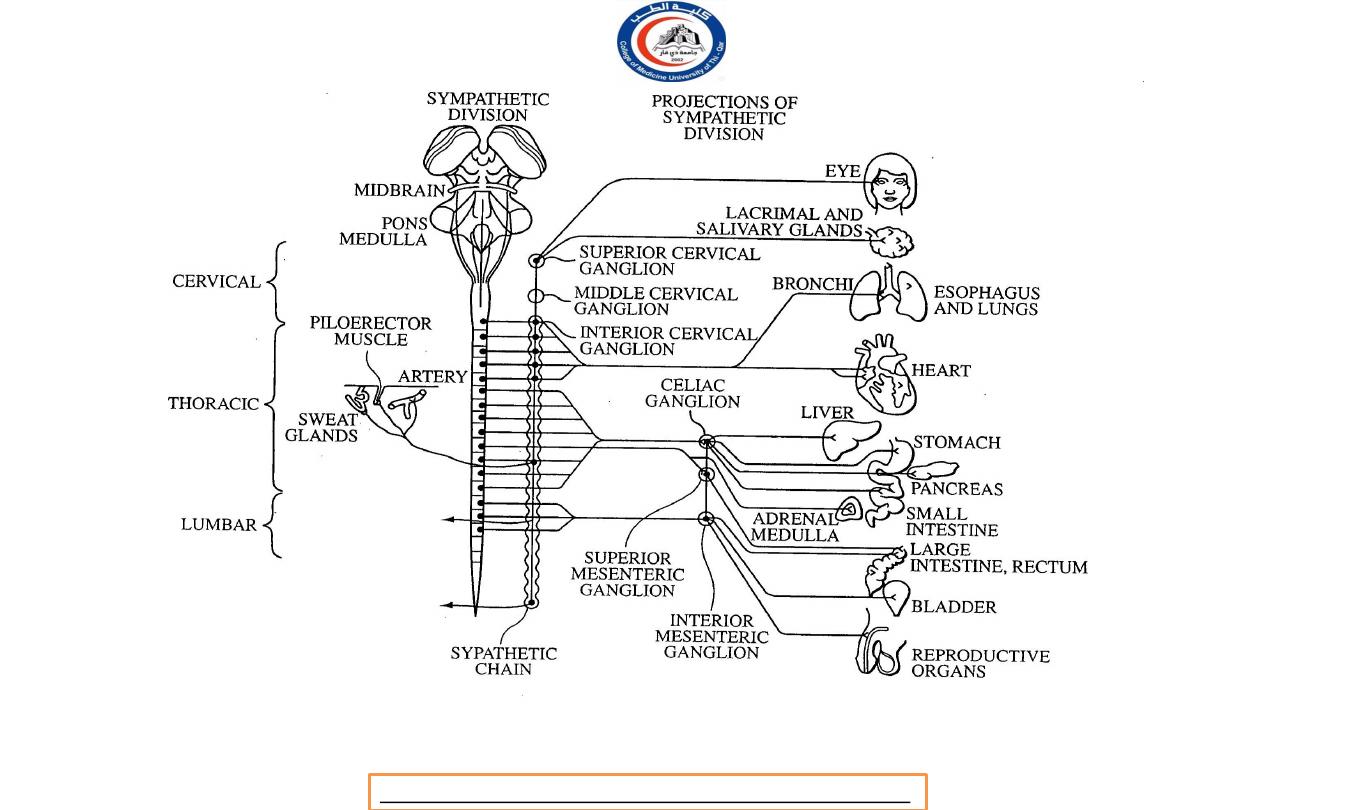
Parasympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
In the Parasympathetic Division (craniosacral division)
cell bodies arise from the nuclei of cranial nerves in the
brainstem III, VII, IX, and X and in the lateral gray matter of the
second through fourth sacral segments (S2-S4) of the spinal
cord, called the craniosacral division.
The axons of the preganglionic neurons are referred to as
the craniosacral outflow.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
29
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
30
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
31
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
32

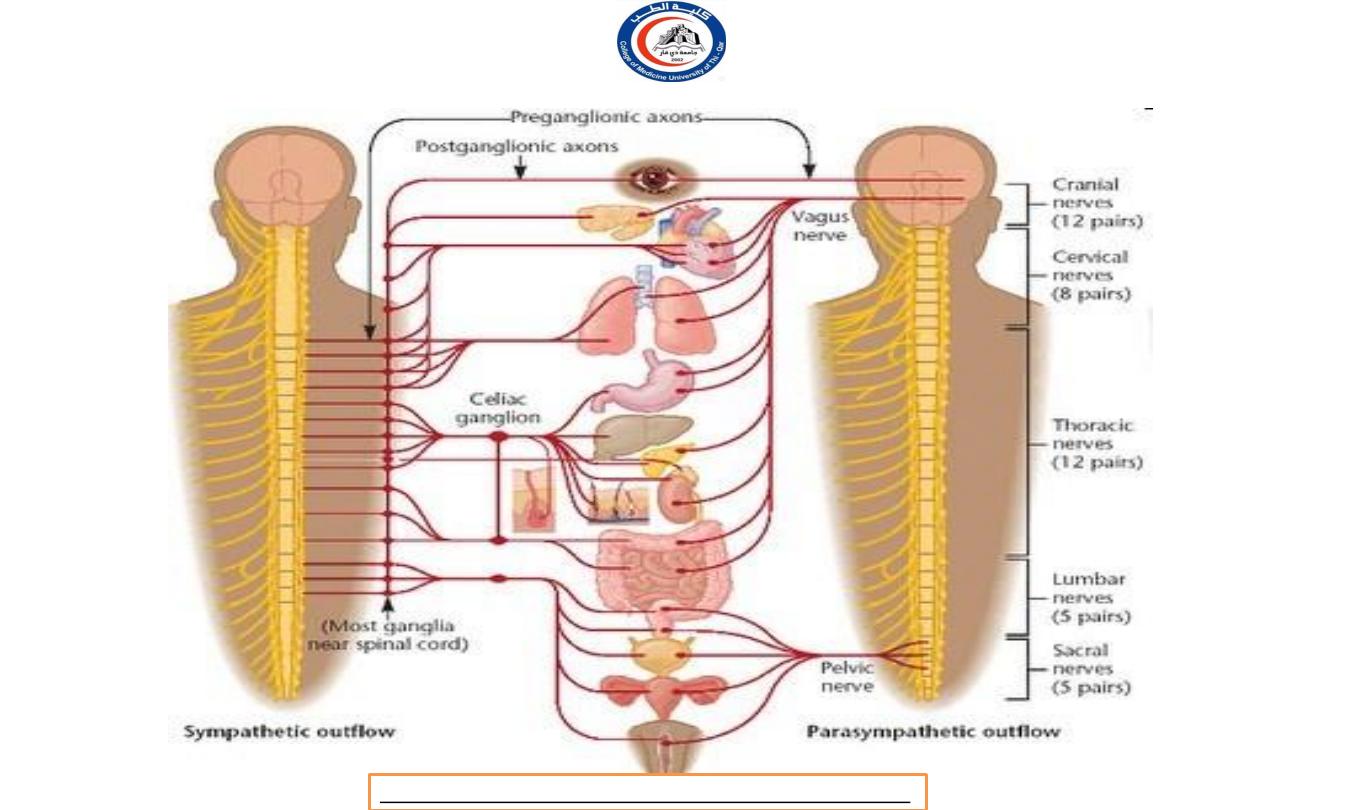
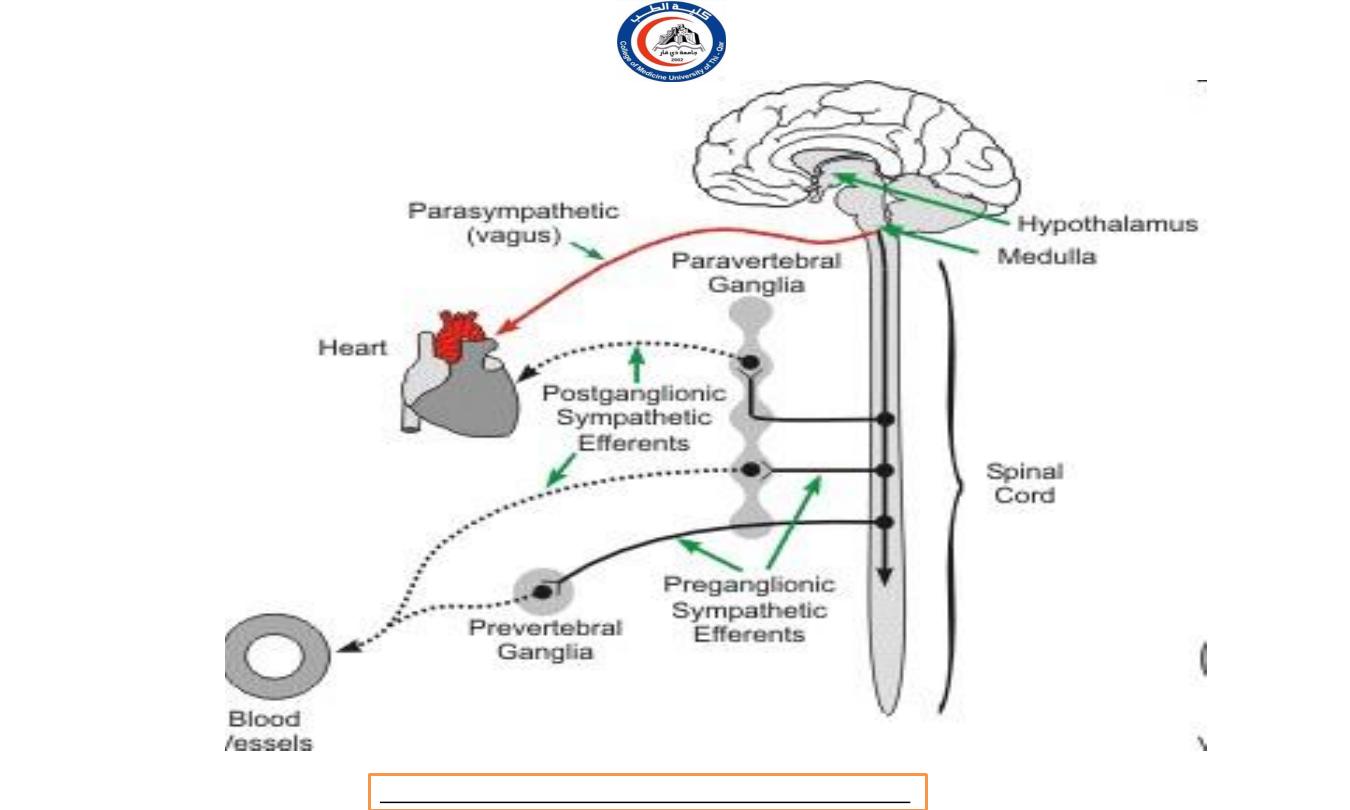
Two major groups of autonomic ganglia:
1.
Sympathetic ganglia (sympathetic division)
i.
Sympathetic trunk ganglia (vertebral chain ganglia or
paravertebral ganglia)
ii.
Prevertebral ganglia
2.
Parasympathetic ganglia (pasympathetic division)
i.
Terminal ganglia (ciliary ganglion, pterygopalatine
ganglion, submandibular ganglion, otic ganglion)
AUTONOMIC GANGLIA
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
33
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
34
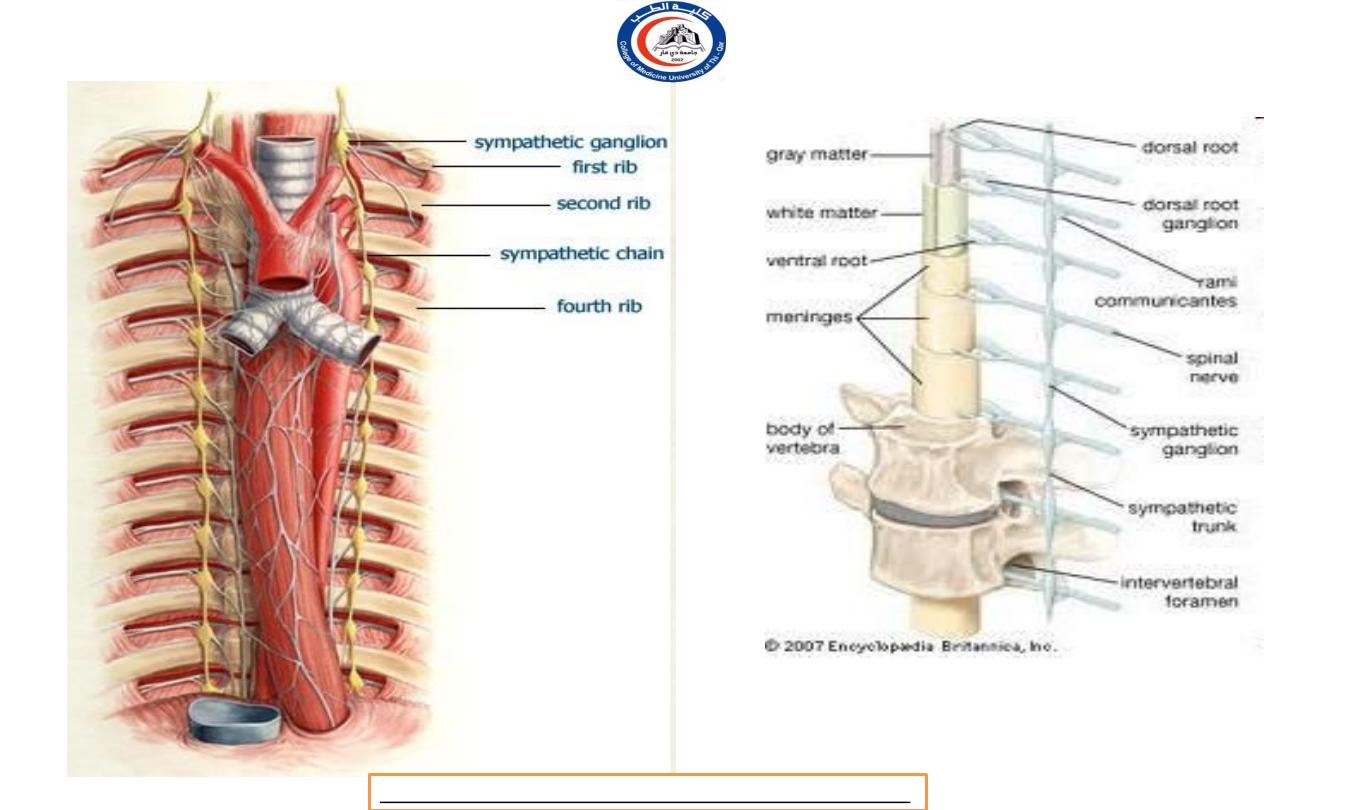
i.
Sympathetic trunk ganglia (Vertebral chain
ganglia
or paravertebral ganglia
)
Lie in a vertical row on either side of the vertebrae column.
Extend from the base of the skull to the coccyx.
Postganglionic axons from sympathetic trunk ganglia
primarily innervate organs above the diaphragm.
In the neck (specific names) called superior cervical ganglion,
middle cervical ganglion, and inferior cervical ganglia.
Most sympathetic preganglionic axons are shorter than
sympathetic postganglionic axons because sympathetic trunk
ganglia near to the spinal cord.
Sympathetic ganglia
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
35
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
36
ii.
Prevertebral ganglia in the sympathetic division:
Lie anterior to the vertebral column and close to the large
abdominal arteries.
In general, postganglionic axons from prevertebral ganglia
innervate organs below to the diaphragm.
5 major prevertebral ganglia:
i) Celiac ganglion
ii) Superior mesenteric ganglion
iii) Inferior mesenteric ganglion
iv) Aorticorenal ganglion
v) Renal ganglion
Sympathetic ganglia
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
37

Celiac ganglion
– on either side of the celiac trunk, an
artery that just inferior to the diaphragm.
Superior mesenteric ganglion
– near the beginning of the
superior mesenteric artery in the upper abdomen.
Inferior mesenteric ganglion
– near to the inferior
mesenteric artery in the middle of the abdomen.
Aorticorenal ganglion and renal ganglion
– near to the
renal artery of each kidney.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
38
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
39
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
40
Sympathetic trunk
ganglia /
paravertebral ganglion
Prevertebral ganglion
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
41
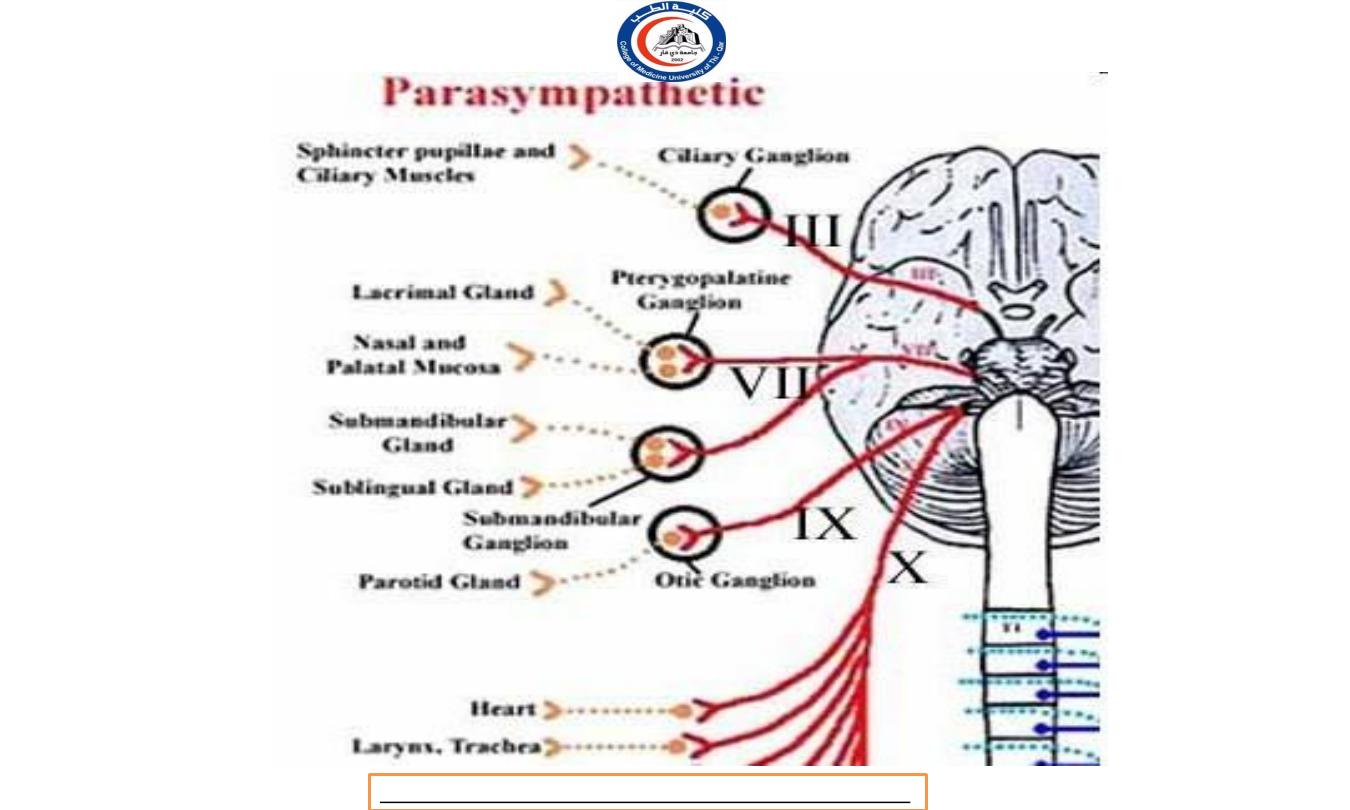
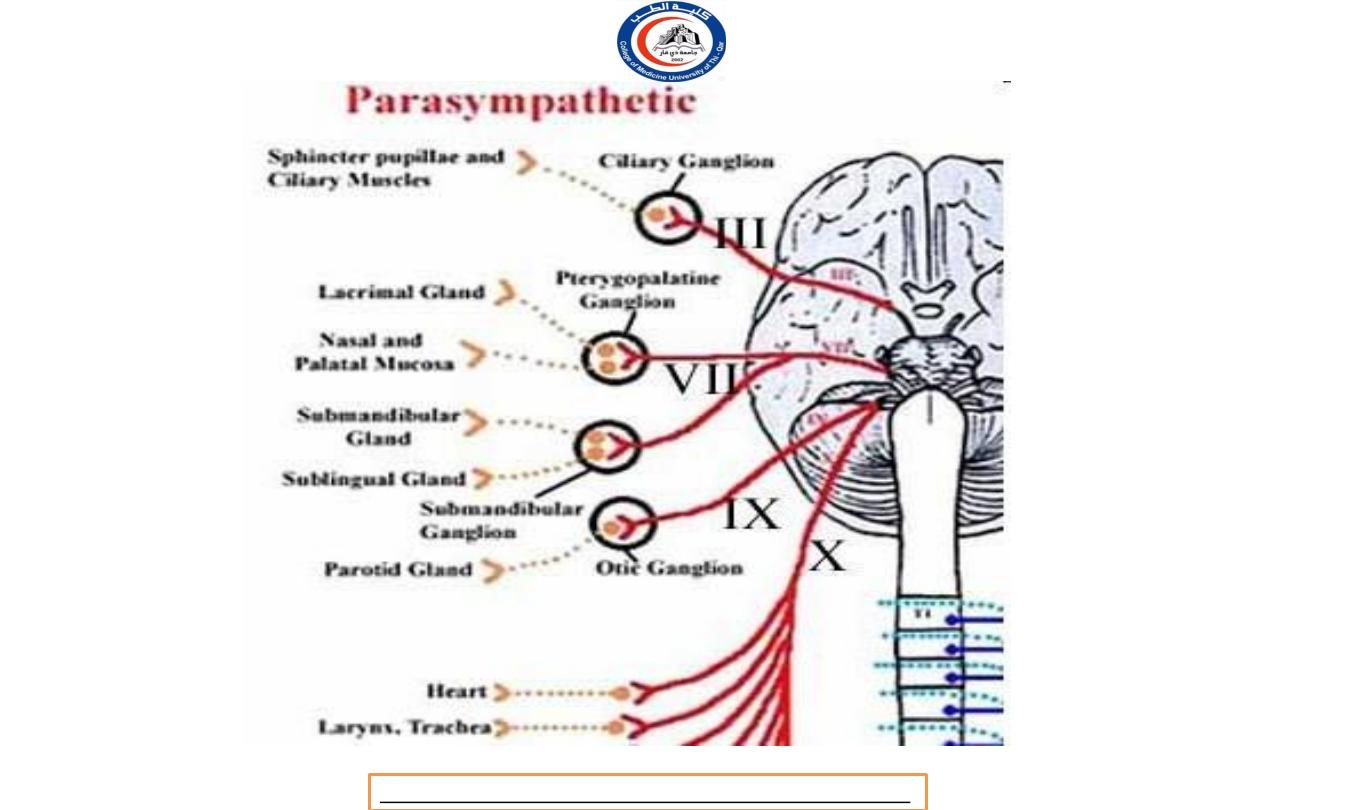
Parasympathetic Ganglia
Terminal ganglia -
The parasympathetic division uses terminal
(intramural) ganglia located very close to or within the walls of a
viscera organ to be innervated.
Terminal ganglia in the head are the ciliary ganglion,
pterygopalatine ganglion, submandibular ganglion
and otic ganglion.
Parasympathetic preganglionic axons are longer than
parasymapthetic postganglionic axons because terminal
ganglia are close to the visceral organ.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
42
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
43
Postganglionic Neurons
Because of the locations of ganglia, sympathetic postganglionic fibers
are relatively long while parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are
relatively short.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

IN THE SYMPATHETIC DIVISION
Once axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons pass to
sympathetic trunk ganglia, they may connect with postganglionic
neurons in one of the following ways:
1.
An axons may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion
it first reaches.
2.
An axons may ascend or descend to a higher or lower ganglion
before synapsing with postganglionic neurons. The network of
incoming axons collectively called sympathetic chains.
Sympathetic Postganglionic Neurons
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
45

3.
Without synapsing, an axons continue through the
sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at prevertebral ganglion
and synapse with postganglionic neurons there.
4.
Without synapsing, an axons may pass through
sympathetic trunk ganglion and prevertebral ganglion and
extend to the chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla.
Sympathetic
Postganglionic Neurons
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
46

Sympathetic
Postganglionic Neurons
•
A single sympathetic preganglionic fiber has many axon
collateral.
•
T h i s explain why many sympathetic responses affect
almost the entire body simultaneously.
•
A f t e r exiting to their ganglia, the postganglionic axons
typically terminate in several visceral effector.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
47
SYMPATHETIC DIVISION
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
48
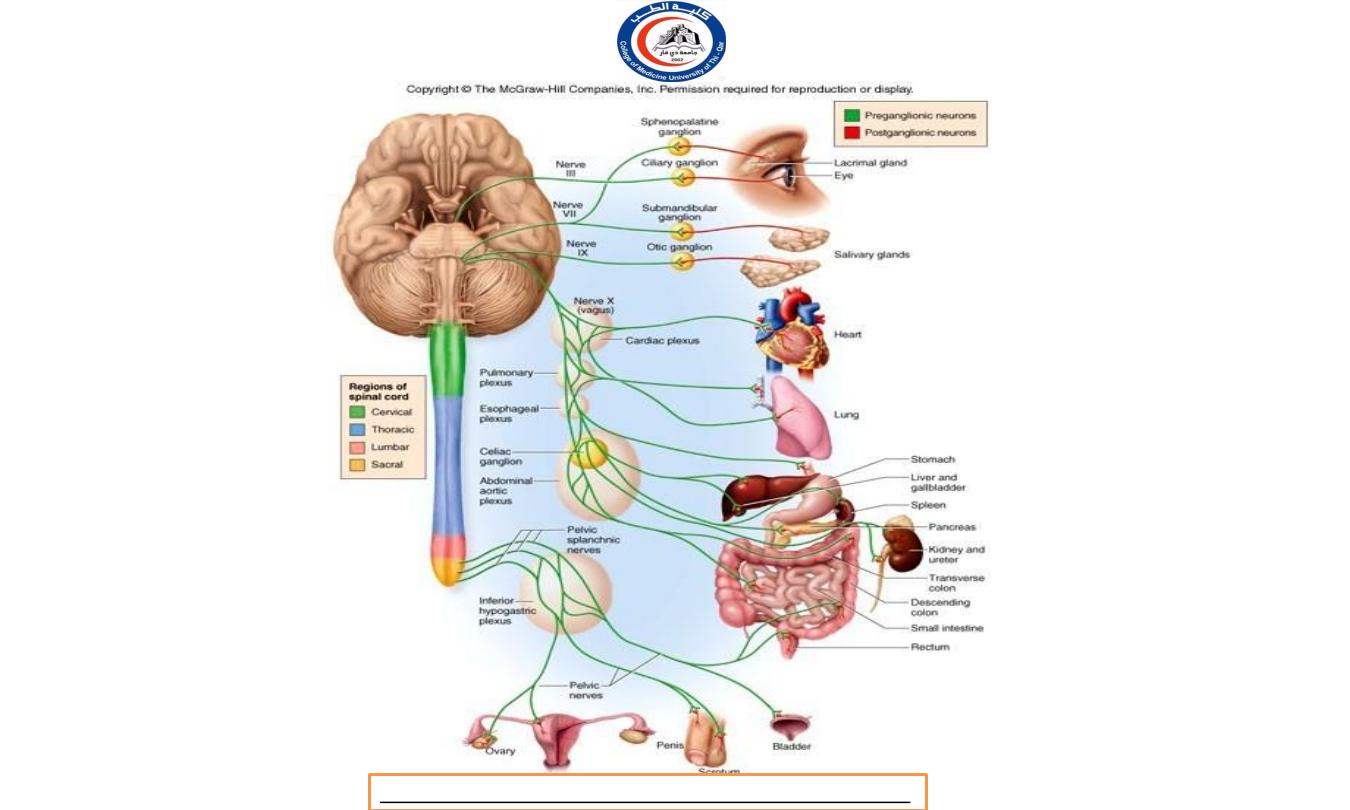
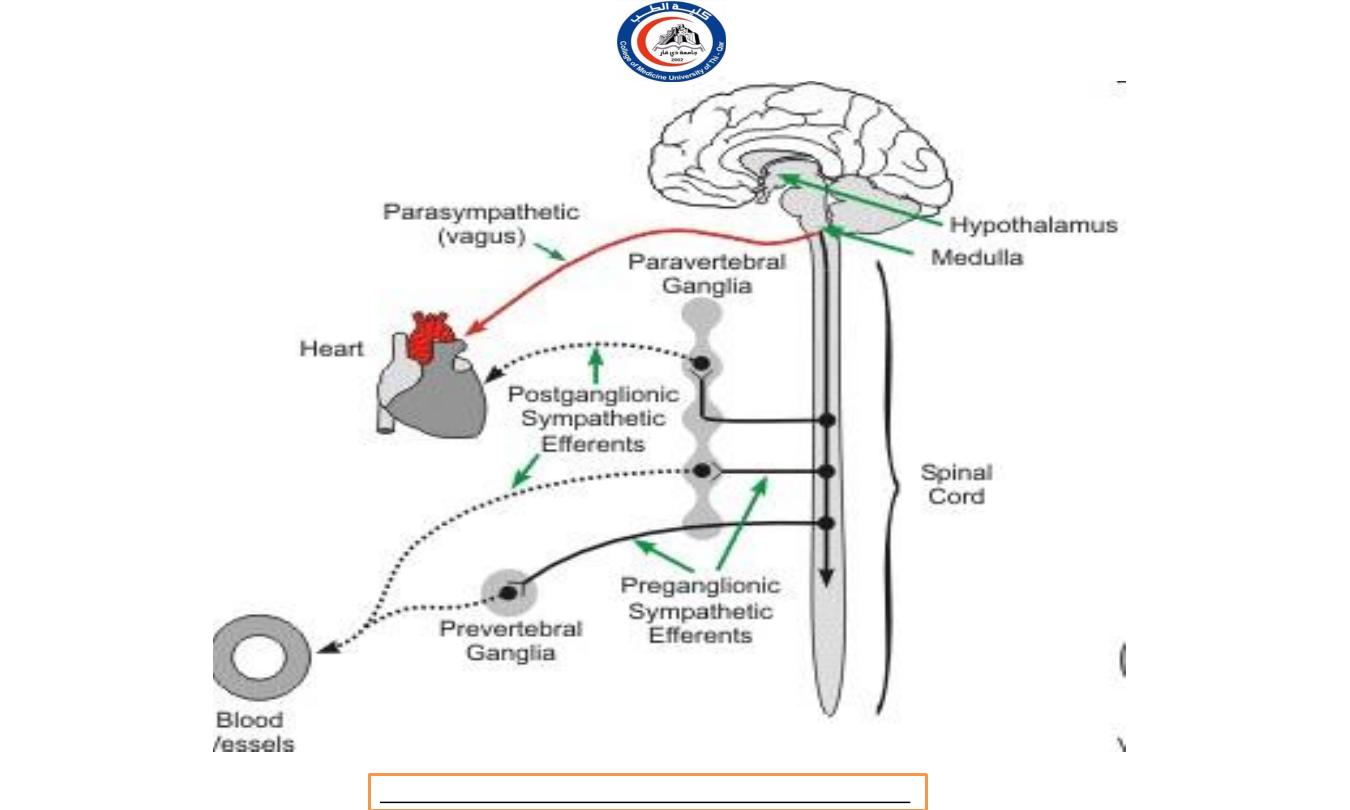
IN THE PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION
A xo n s of preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic
division pass to the terminal ganglia near or within a
visceral
effector.
I n the ganglion, the presynaptic neuron usually synapse
with 4 or 5 postsynaptic neurons, all of which supply a
single visceral effector, allowing parasympathetic response
to be localized to a single effector.
Postganglionic Neurons
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
49
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
50

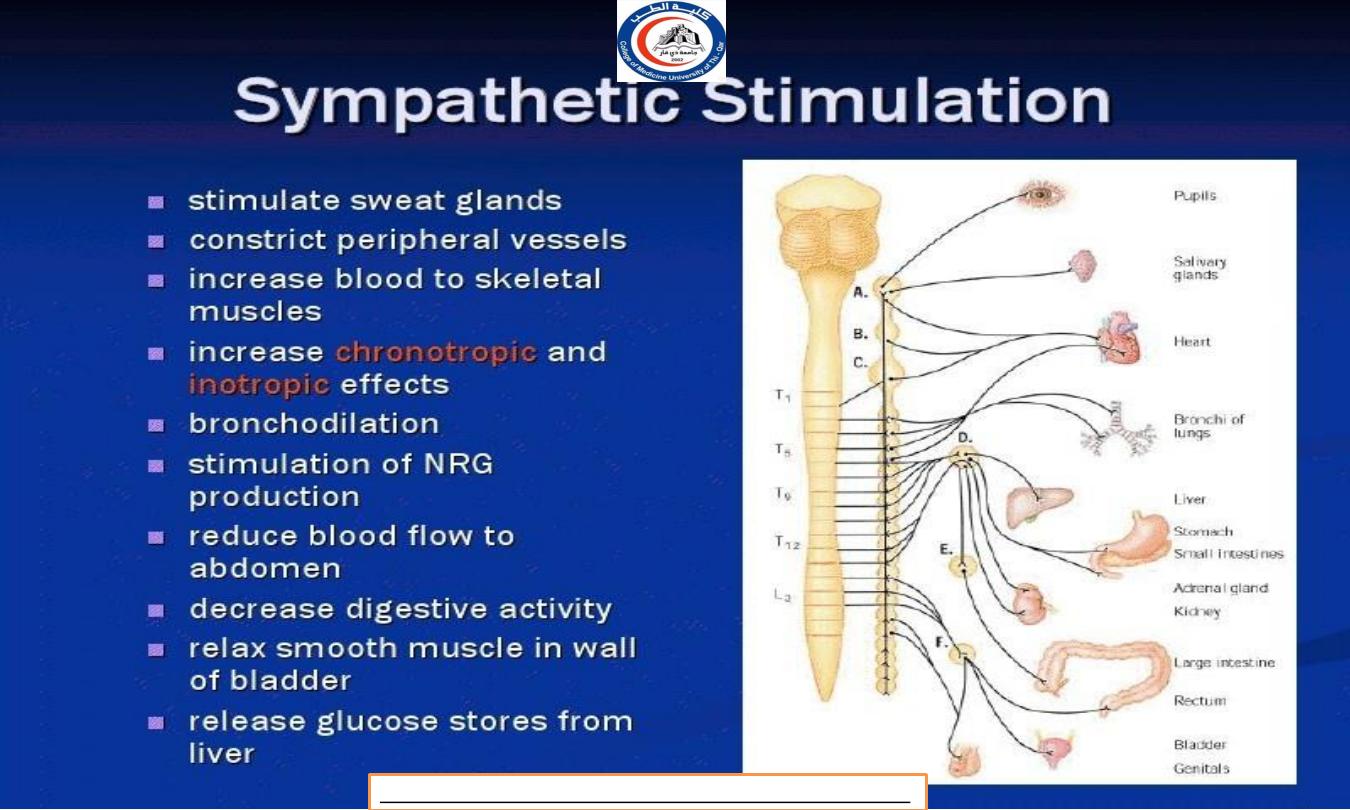
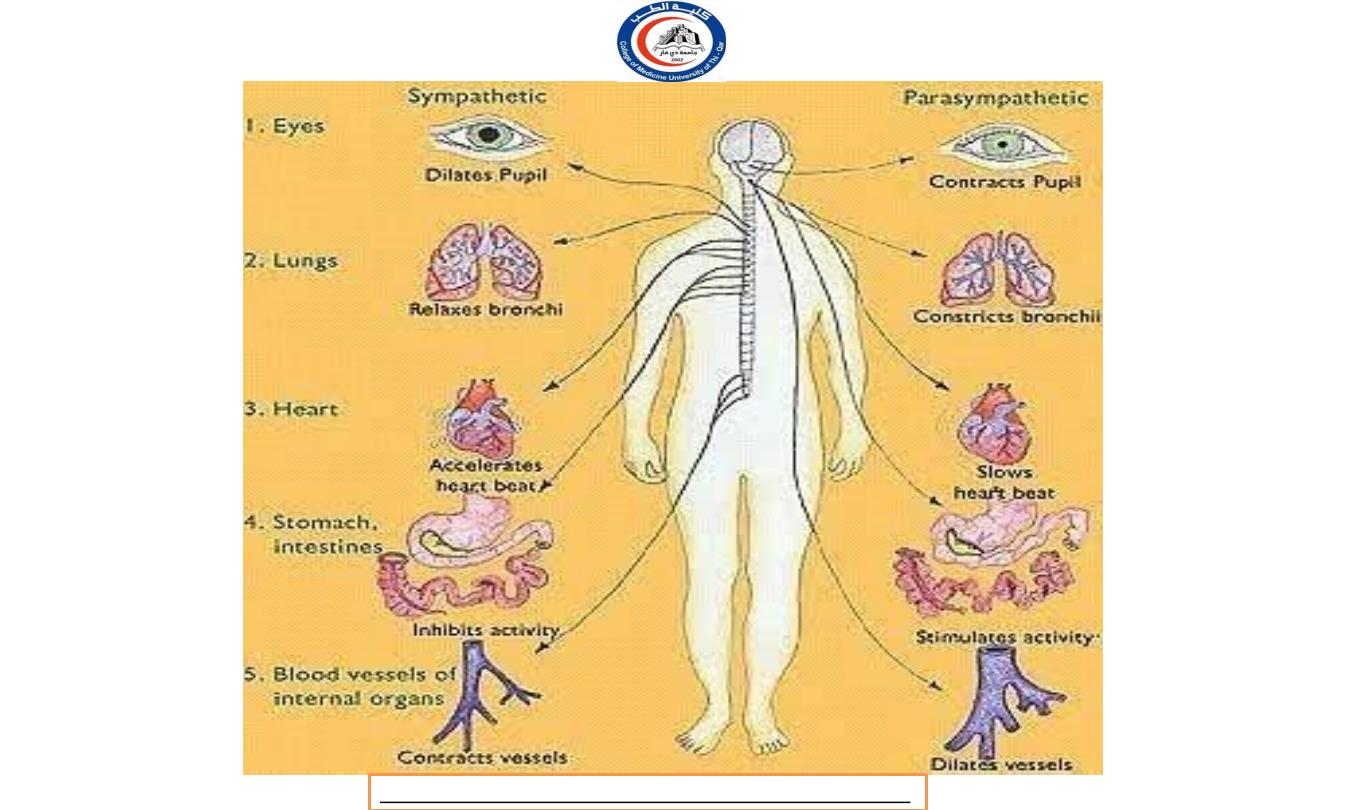
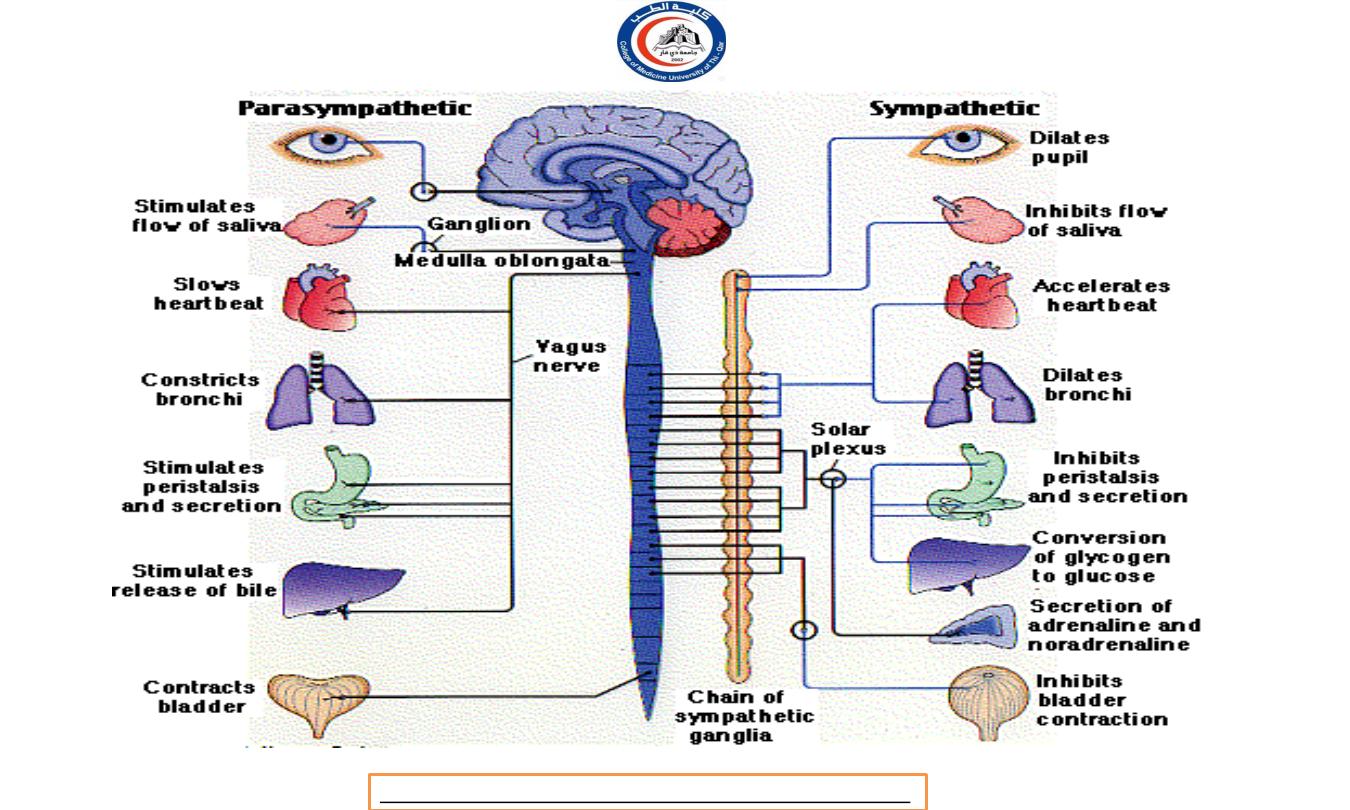
EFFECTS OF SYMPATHETIC
NERVOUS SYSTEM
T h e sympathetic system prepares the body to meet emergency
demands and is primarily involved with processes that expend
energy.
During physical or emotional
stress, the sympathetic division dominates the parasympathetic
system, initiating a series of activities known as the fight-or-flight
response.
I n addition, there is activation of the adrenal medulla, causing
secretion of norepinephrine and epinephrine as hormones to greatly
heighten the response.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
51

Cardiovascular System
Increasing heart beat
Increase blood supply to cardiac muscle (dilate the coronary
artery)
Raised peripheral resistance and blood pressure by
constricting the small artery the skin. In this way increase
blood supply is available for highly active tissue, such as
skeletal muscle, heart and brain.
Constrict the blood vessel in secretory glands of digestive
system
Accelerates blood coagulation because of
vasoconstriction.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
52

Respiratory system
Causes smooth muscle relaxation and therefore dilatation of
the airways, especially bronchioles.
Allowing a greater amount of air to enter the lungs at each
inspiration, and increase the respiratory rate.
D e a l
with ’fight and flight’ situation.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
53

Digestive and urinary system
Li ver increase conversion of glycogen to glucose
Stomach and small intestine; smooth muscle contraction
(peristalsis) and secretion of digestive juices are inhibited,
delaying digestion and the tone of sphinxter muscle is
increased.
Adrenal gland; stimulated to secrete adrenaline and noradrenaline
which potentiate and sustain the effect of sympathetic stimulation
Urethral and anal sphincter; muscle tone increase, inhibit
micturition and defecation.
Bladder walls relaxes
Metabolic rate increase
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
54

E y e
Dilating the pupil
Opening the eyes open wide and giving the appearance of
alertness and excitement
S k i n
Increase sweat secretion, leading to increased heat loss
from the body
Contract the arrector pili muscle on the skin
Constrict the peripheral blood vessel increasing blood supply
available to active organs, e.g heart and skeletal muscle.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
55
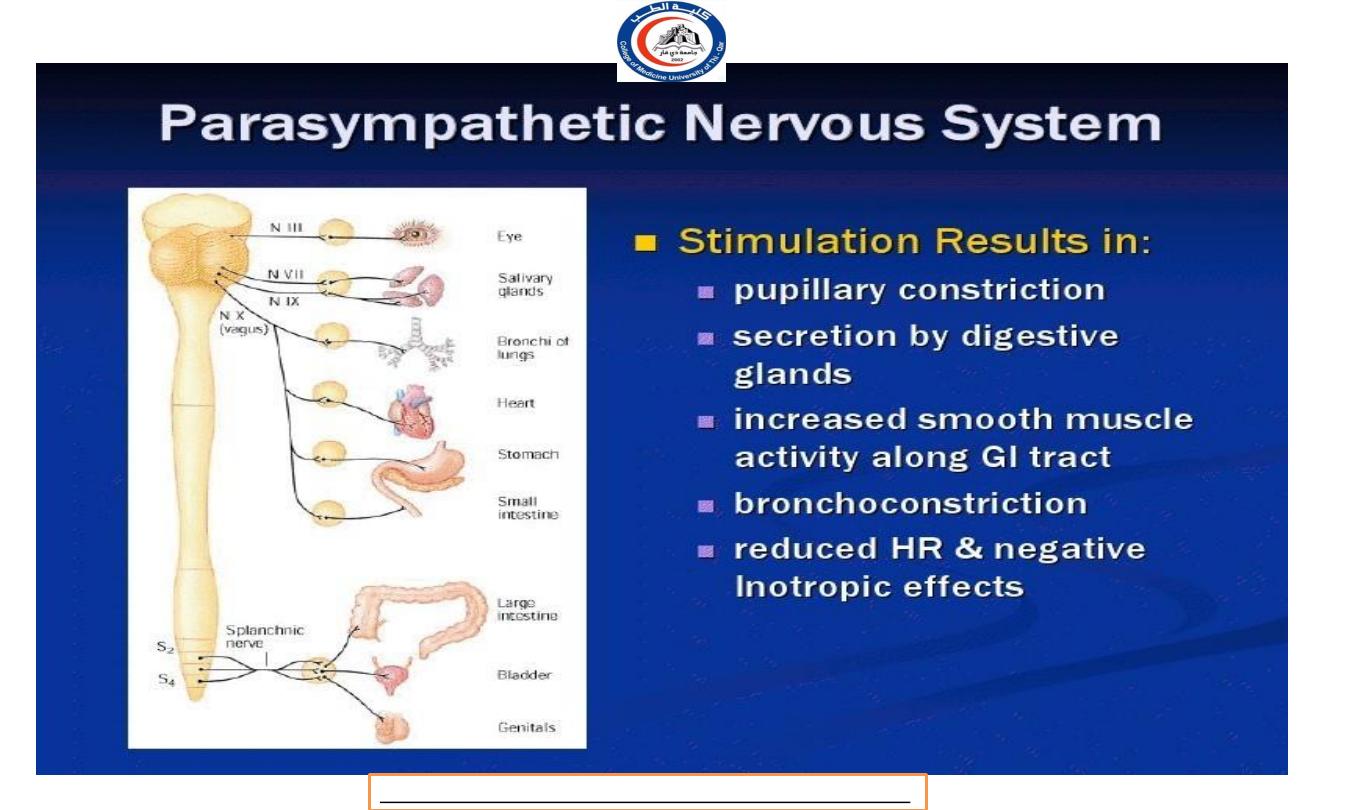
T h e parasympathetic nervous system is an energy conservation-
restorative system.
It regulates those activities
that conserve and restore body energy during times of rest and
digest.
T h e parasympathetic nervous system dominates over sympathetic
activity in the glands and smooth muscle of the gut, stimulating
glandular secretion and the gut movements necessary for food to
be digested and absorbed.
Salivation, lacrimation, urination, and defecation, all controlled by
the parasympathetic nervous system.
EFFECTS OF PARASYMPATHETIC
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
56

Cardiovascular System
Decrease the rate and force of the heartbeat
Constrict the coronary artery reducing the blood supply
to cardiac muscle
Respiratory
Produces contraction of smooth muscle in airway walls
causing their constriction, e.g. bronchioles and bronchi
E y e
Constricting the pupil
T h e eyelids tend to closed, giving the appearance
of sleepiness.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
57

Digestive and urinary system
Liver: conversion of glucose to glycogen and secretion of
bile are increased.
Stomach and small intestine: Motility and secretion are
increased together with the rate of digestion and absorption
of food.
Pancreas: secretion of pancreatic juice and the hormone
insulin are increase.
Urethral and anal sphincter: relaxation in urethral and
anal sphincter, micturition and defecation occurs.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
58
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
59
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
60
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
61
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
62

•
Neurotransmitters are chemicals which transmit signals from a
neuron to a target cell across the synapes.
•
T h e postganglionic neurons use different neurotransmitters and
the effectors bear different receptors.
•
T h e hypothalamus regulates the balance of sympathetic versus
parasympathetic activity or tone.
•
In general, we are in parasympathetic tone, except during states of
emergency when we immediately switch to sympathetic tone.
Neurotransmitter (Autonomic Nervous system)
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
63

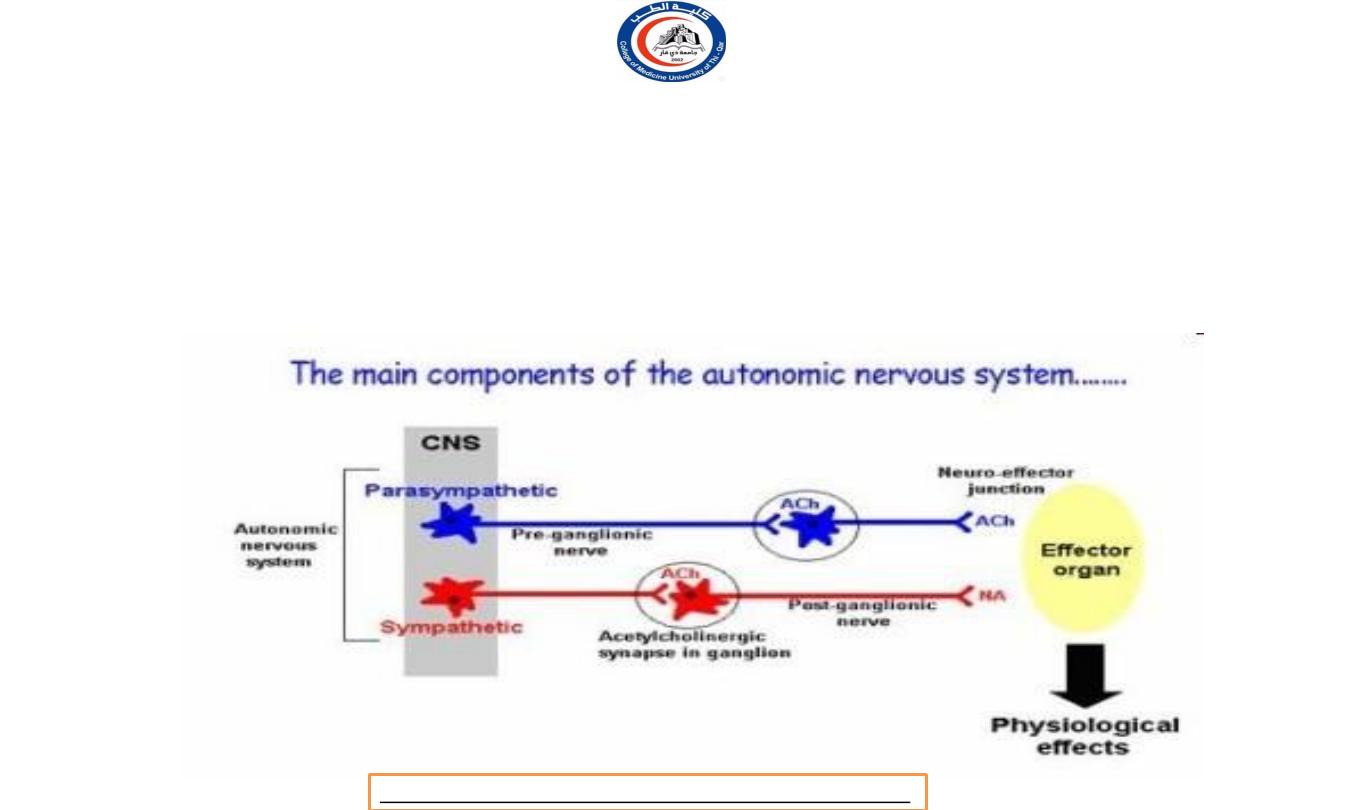
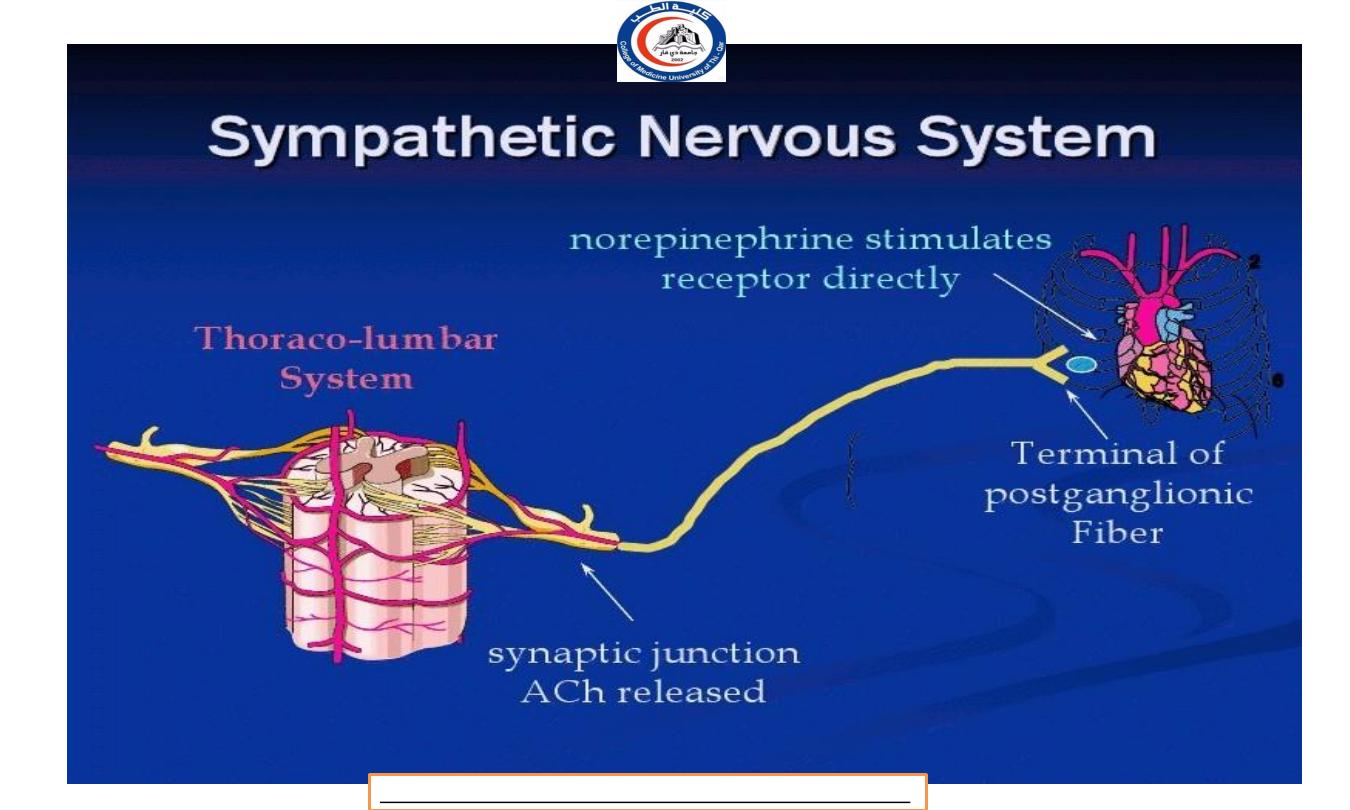
At a sympathetic nervous system:
Preganglionic neurons use Acetylcholine
(ACh)
as a neurotransmitter.
M o s t postganglionic neurons utilize noradrenaline
(norepinephrine)
—with the major exception that
postganglionic neurons innervating sweat glands use
acetylcholine.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
64
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
65

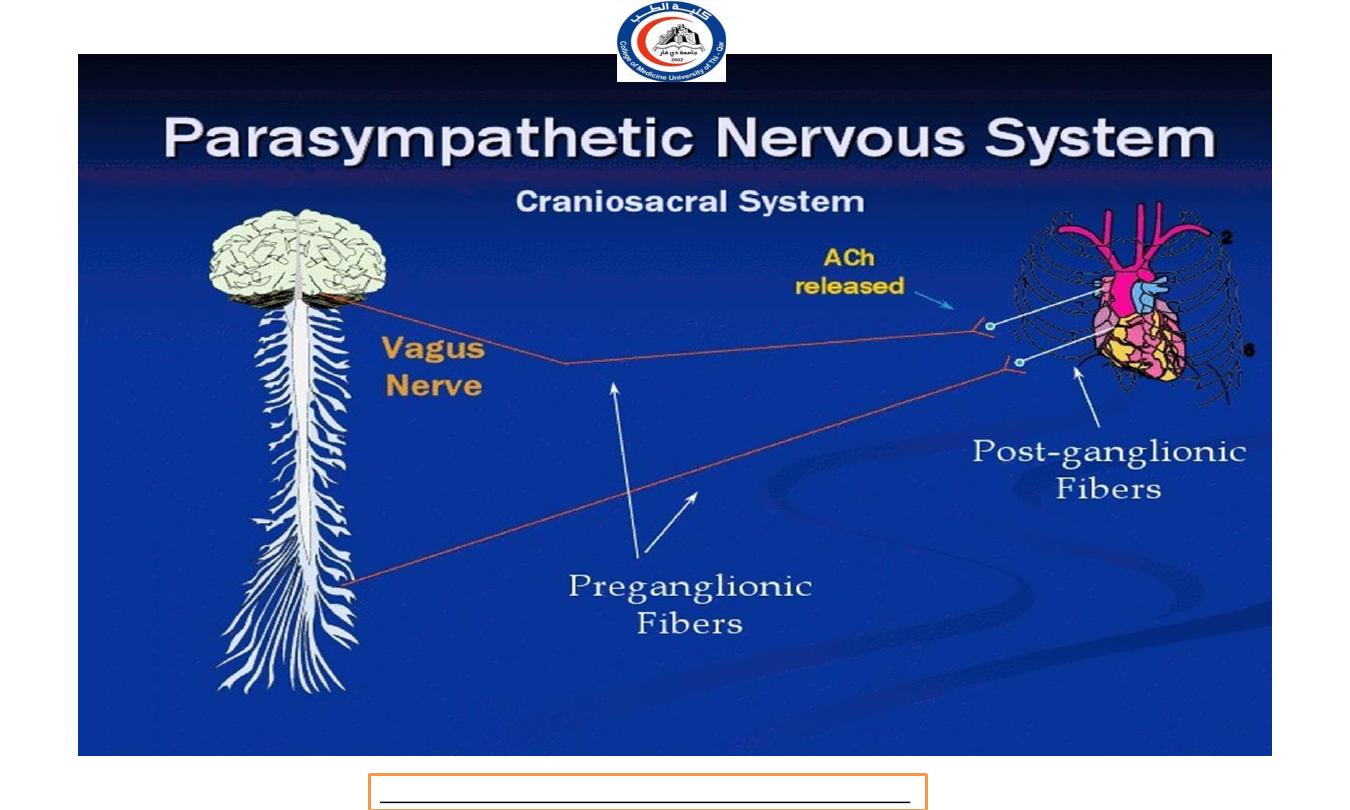
At the parasympathetic nervous system:
a l l preganglionic neurons and all postganglionic
parasympathetic neurons uses Acetylcholine (ACh) as its
neurotransmitter
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
66
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
67
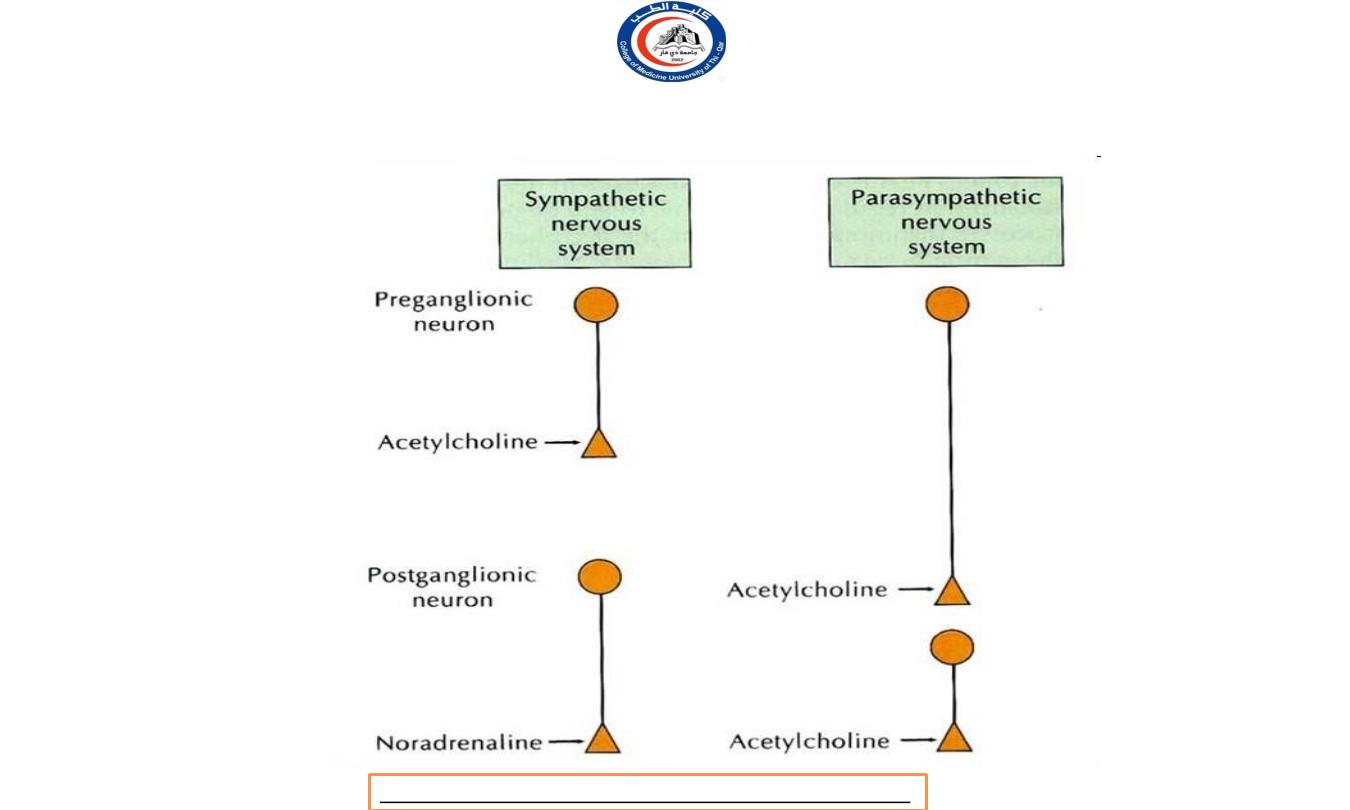
NEUROTRANSMITTER
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
68

University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Thank you
69
