
ﺑِ
ﺳْ
م
ﷲ
ا
ﻟ
ر
ﺣ
ﻣ
ن
ا
ﻟ
ر
ﺣ
ﯾ
م



•
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus commonly
target the nervous system (CNS & PNS)
•
In the CNS, diabetes may be associated with
cognitive decline, leukoencephalopathy, and an
increased risk of both stroke and dementia.
•
Hypoglycemia: headache, tremor sweating, anxiety,
seizures and loss of consciousness.

•
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) may lead to confusion
and decreased conscious level.
•
Cerebral edema complicates diabetic ketoacidosis
and may present with headache, papilloedema. it
may develop on presentation or during correction
of the metabolic disorder.

Diabetic neuropathy
•
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common cause
of peripheral neuropathy.
•
It affects 50-90% of patients, and 15- 30% will
have painful neuropathy.
•
Pathological features include axonal degeneration
of both myelinating and unmyelinating fibers.

classification of diabetic neuropathy
i-
polyneuropathy
1-symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy
2- asymmetric radiculoplexopathy
ii- mononeuropathy
1- cranial 2-peripheral
•
Cardiovascular
•
Gastrointestinal
•
Genitourinary
•
Pupillary
•
thermoregulatory

Diabetic distal symmetric sensory and sensorimotor
polyneuropathy (DSPN)
•
Is the most common form
•
Tingling, burning, deep aching pains may also be
apparent.
•
A variety of medications have been used with
variable success to treat painful symptoms
associated with DSPN, including antiepileptic
medications, antidepressants, and other analgesics
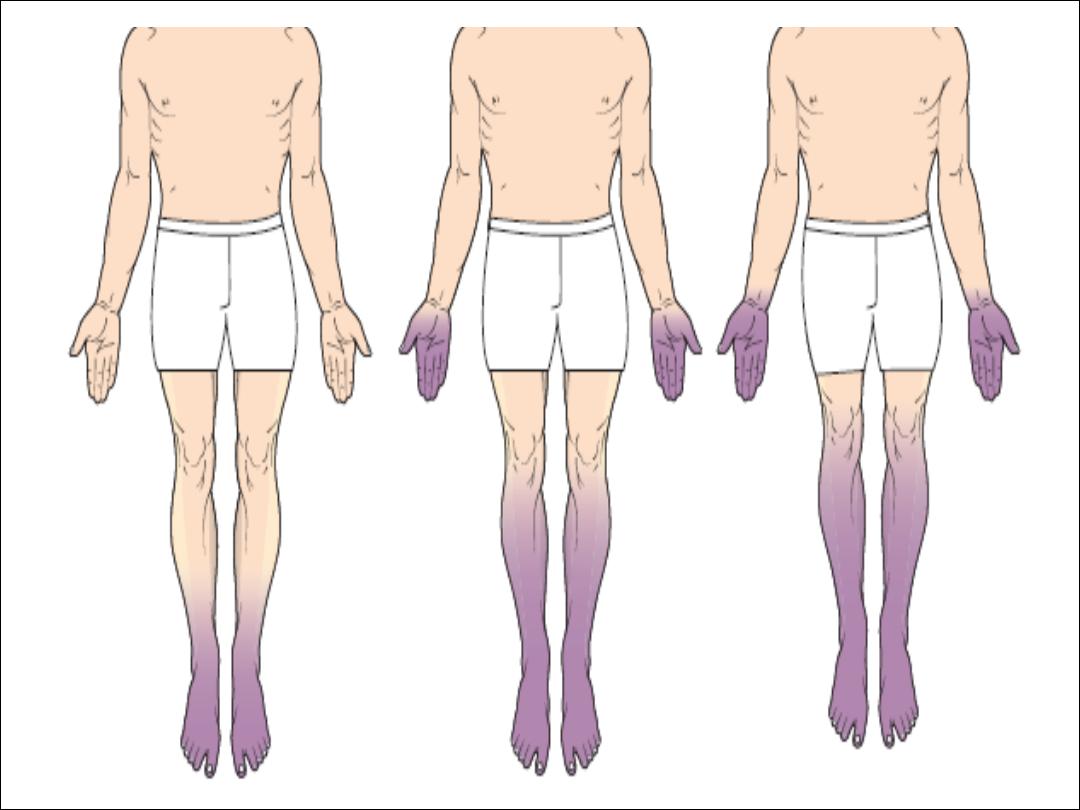

Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
•
is typically seen in combination with DSPN.
•
abnormal sweating, dysfunctional
thermoregulation, dry eyes and mouth,
arrhythmias, postural hypotension
•
gastrointestinal abnormalities (e.g., gastroparesis,
postprandial bloating, chronic diarrhea or
constipation)
•
genitourinary dysfunction (e.g., impotence,
retrograde ejaculation, incontinence).

Diabetic mononeuropathies
•
Unlike the gradual progression of distal symmetric and
autonomic neuropathy, mononeuropathies are severe and
of rapid onset.
•
The most common mononeuropathies are median
neuropathy at the wrist (CTS) and ulnar neuropathy at the
elbow.
•
In regard to cranial mononeuropathies; 3
rd
, 6
th
and 7
th
are
commonly involved.
•
Diabetic third nerve palsies are characteristically pupil-
sparing.
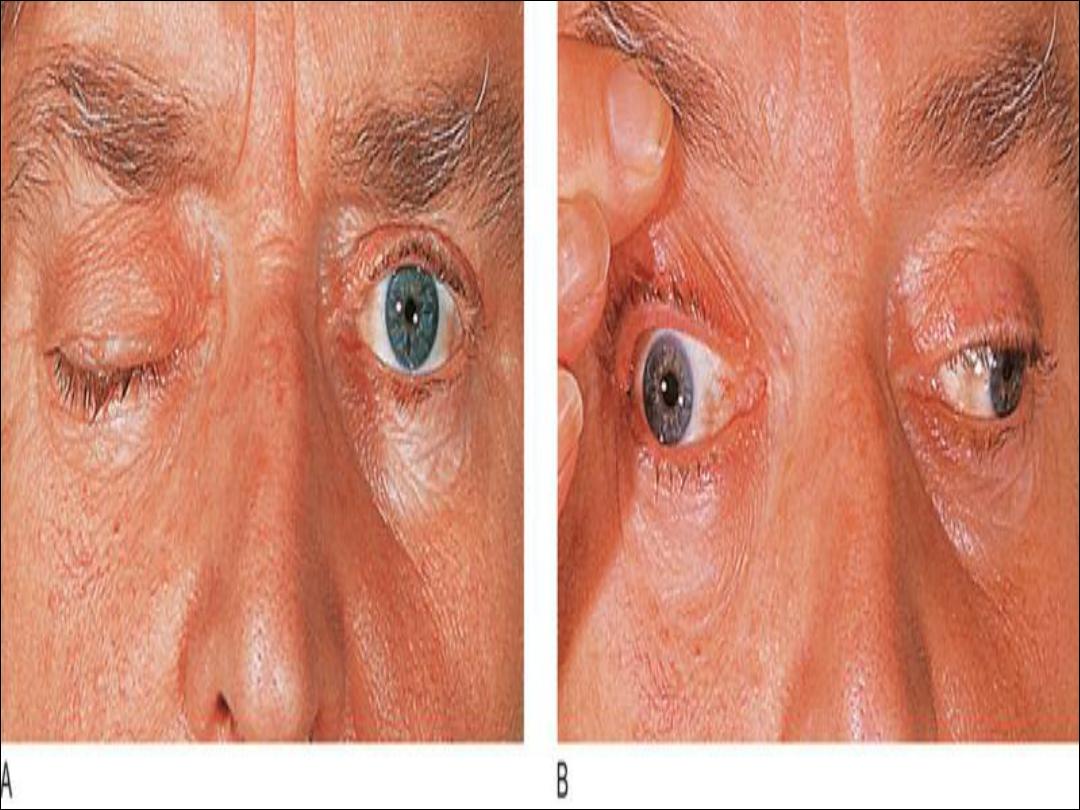


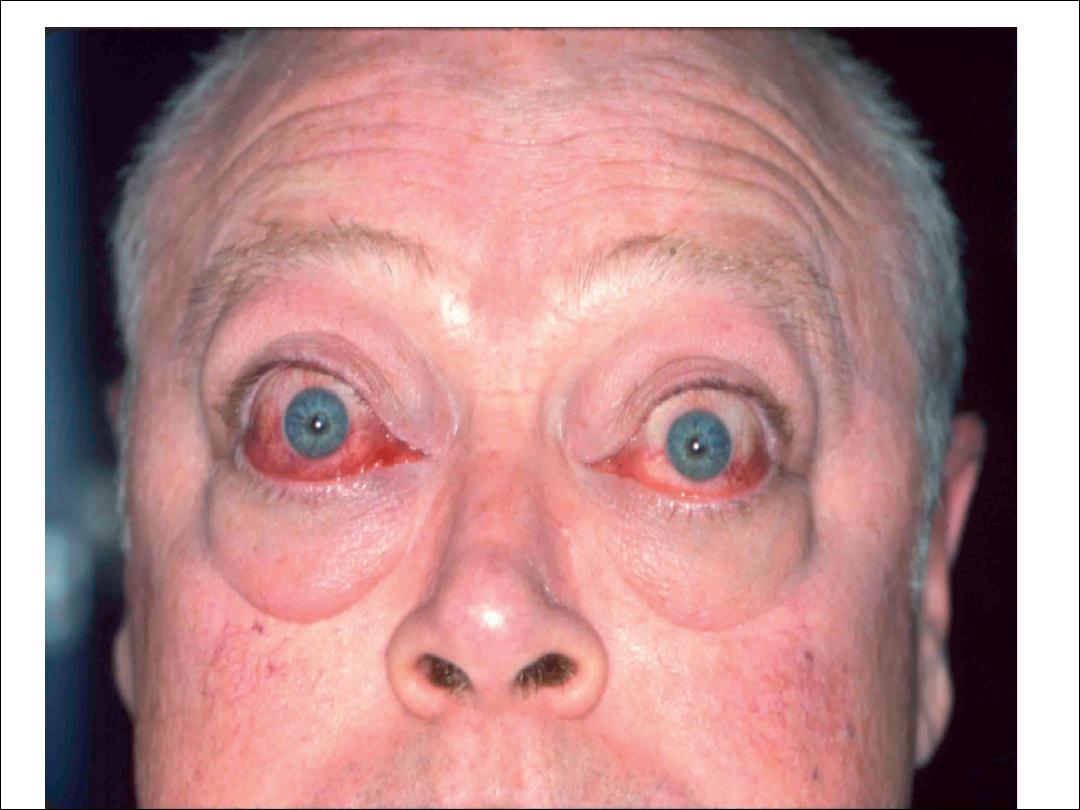
Hyperthyroidism
•
Muscle weakness and wasting
•
Muscle pain and stiffness
•
The tendon reflexes are normal or hyperactive
•
There may be non-sustained clonus
•
Periodic paralysis
•
Rarely bulbar myopathy
•
Tremor and chorea
•
Thyroid ophthalmoplegia

hypothyroidism
•
Hoarseness of voice
•
Carpal tunnel syndrome
•
Muscle stiffness and myopathy
•
Myxeodema coma
•
Delayed ankle jerk



1-Stroke
•
hypertension is associated with three- to fivefold increase
in stroke risk.
•
Even small reductions in blood pressure result in large
reductions in stroke risk.
2-cerebral aneurysm:
•
Hypertension is associated with cerebral aneurysm
formation and with subarachnoid hemorrhage.
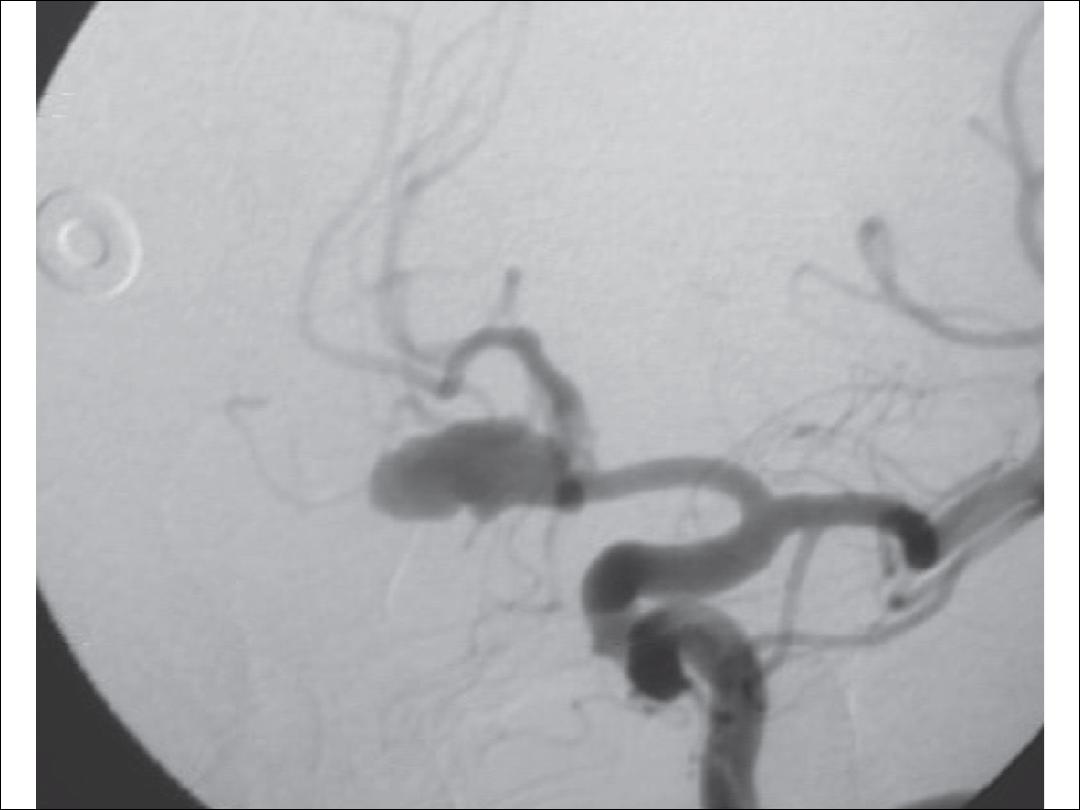

3-
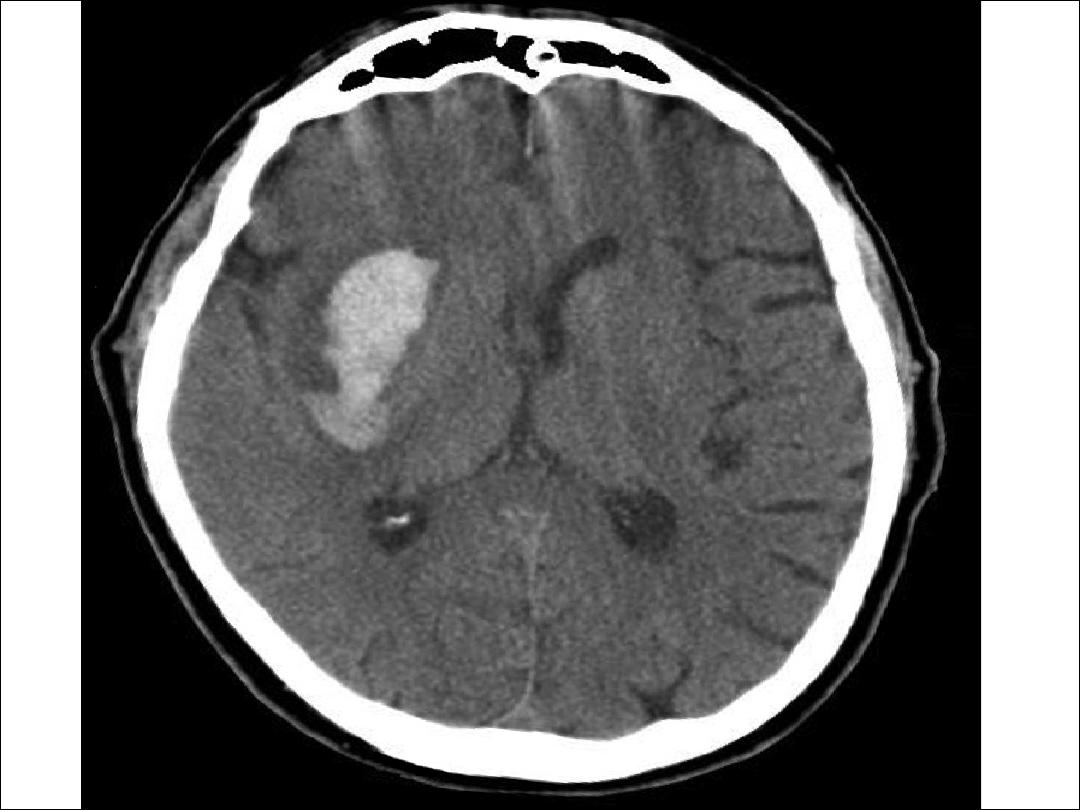
intracerebral hemorrhage
:
•
Hypertension is the most important identified risk factor
for intracerebral hemorrhage.
•
Fibrinoid necrosis of small arteries has been proposed as
the initial step in intracerebral hemorrhage.
4- Periventricular white matter disease:
•
Head CT shows a periventricular hypodensity, often most
profound at the frontal and occipital horns, which is
hyperintense on T2-weighted MRI.
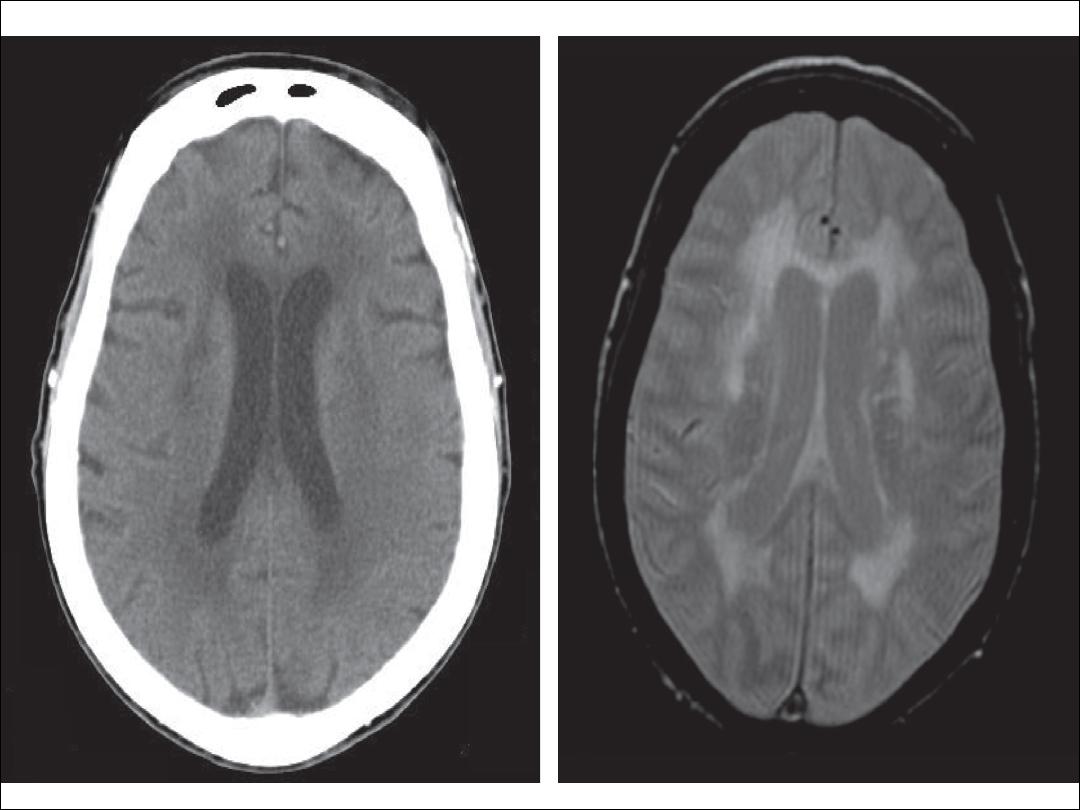

5- hypertensive encephalopathy
•
It tends to occur with a sudden elevation in blood pressure
rather than with chronic hypertension.
•
Precipitants include:
A- pheochromocytoma
B-abrupt antihypertensive discontinuation
C- Acute or chronic renal failure
D-renal artery stenosis.
•
Hypertensive encephalopathy is associated with cerebral
edema, particularly severe in the posterior regions of the
cerebral hemispheres,

•
Headache, Confusion and Visual disturbance.
•
Focal or generalized seizures may complicate the course.
•
Once a structural etiology has been excluded, treatment
of hypertension must be initiated.
•
Target blood pressures are tailored to individual patients,
with the goal of returning patients to their recent
baseline.
•
Close observation and intravenous antihypertensive are
generally indicated.


•
accurately called osmotic demyelination syndrome.
•
It is classically associated with the rapid correction of
Hyponatremia.
•
predisposing condition such as chronic alcoholism, recent
liver transplantation, burns.
•
Pseudobulbar palsy has been well described as dysartheria,
dysphagia, nystagmus, ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and a
flaccid then spastic quadriparesis.

•
Treatment is mainly supportive and includes correction of
all other underlying electrolyte and metabolic disorders
and management of all secondary complications such as
aspiration pneumonia.
•
patients with CPM who survive after aggressive supportive
therapy may be left with considerable neurologic deficits.

Paraneoplastic Neurological
Disorders

• are cancer-related syndromes that can affect any part of the
nervous system, caused by mechanisms other than metastasis.
• In 60% of patients, the neurologic symptoms precede the
cancer diagnosis.
• Common underlying tumors include neuroblastoma, small-cell
lung cancer (SCLC), thymoma, lymphoma, myeloma.
• In the majority of these cases, antigen production in the
body of the tumor leads to development of antibodies to
parts of the Nervous system.
• Autoantibodies are found in the serum and/or CSF,

•
PND of CNS
I. Limbic encephalitis
II. Myelopathy
III. Cerebellar
degeneration
IV. Stiff person syndrome
V. Opsiclonus-myoclonus
•
PND of PNS
I. Myasthenia
II. Lambert Eaton
III. Neuromyotonia
IV. Polyneuropathy
V. Polymyositis or
dermatomyositis

THANKS
