Foundation of Medicine
L6-medical terminology / onlineJune 15th , 2020
Family & Community medicine dept.
Dr. Muslim N. Saeed
The digestive system
objectives• 1. Identify and describe the major structures
• and functions of the digestive system.
• 2.Recognize, define, spell, and pronounce
• terms related to the pathology and the
• diagnostic and treatment procedures of
• the digestive system.
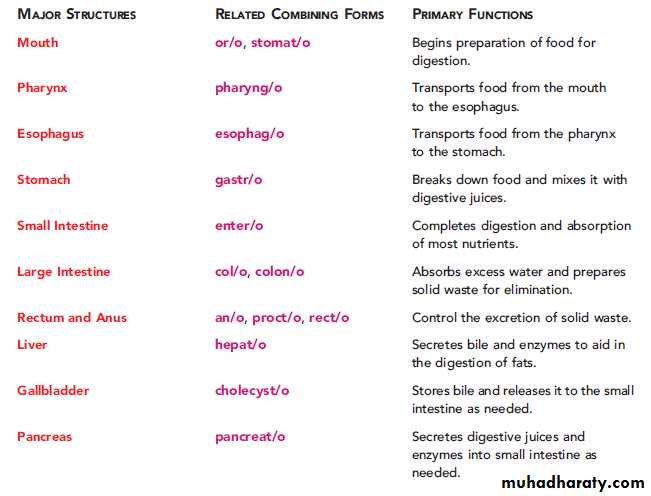
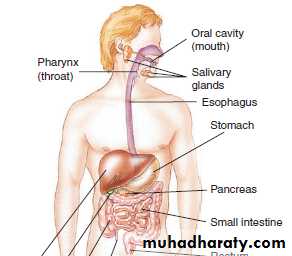
The major structures of the digestive system
• 1.Oral cavity (mouth)• 2.Pharynx (throat)
• 3.Esophagus (eh-SOF-ah-gus).
• 4.Stomach
• 5.Small intestine
• 6.Large intestine
• 7.Rectum
• 8.Anus.
• The accessory organs(aid with digestion, but not part of the digestive system).
• liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
The Gastrointestinal Tract
The structures of the digestive system are described asthe gastrointestinal tract or GI tract (gastr/o means stomach, intestine means intestine, and -al means pertaining to).
-The upper GI tract: the mouth, esophagus, and stomach.
-The lower GI tract: small and large intestines (the bowels), plus the rectum, and anus.
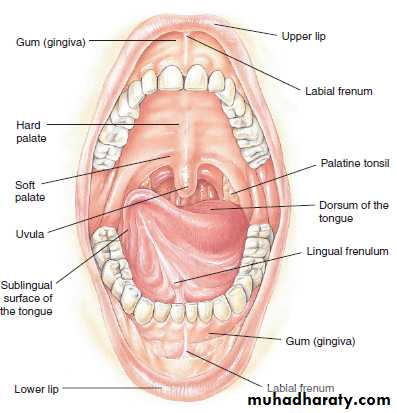
The Oral Cavity
-The major structures of the oral cavity (the mouth) are the lips, hard and soft palates, salivary glands, tongue, and teeth.-The palate (PAL-at) forms the roof of the mouth.
-The tongue is very strong, flexible, and muscular.
-The gingiva (JIN-jih-vah), commonly known as the
gums, is the mucous membrane that surrounds the teeth.
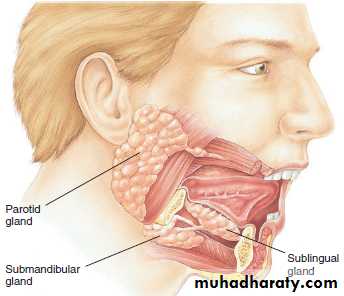
Salivary Glands
The three pairs of salivary glands (SALih-ver-ee) secrete saliva into the mouth.1.The parotid glands.
2.The sublingual glands.
3.The submandibular gland.
-The Pharynx (FAR-inks), which is the common passageway for both respiration and digestion.
-The epiglottis (ep-ih-GLOT-is) is a lid-like structure ….
The esophagus (eh-SOF-ah-gus) is the muscular tube through which ingested food passes from the pharynx to the stomach.
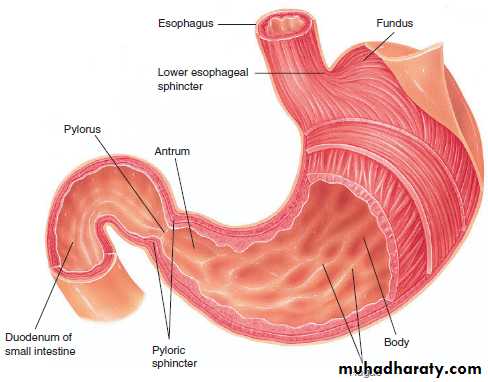
The Stomach
The stomach is a sac-like organ composed of the fundus (upper part), body (main portion), and antrum (lower part).The pylorus (pye-LOR-us)
connects the stomach with the small intestine.
The pyloric sphincter (pye-LOR-ick) muscle that controls the flow from the stomach to the
duodenum.
The Small Intestine
The small intestine extends from the pyloric sphincter to the first part of the large intestine. is up to 20 feet in length.consists of three sections where food is digested:
1.The duodenum (dew-oh-DEE-num) is the first portion of the small intestine.
2.The jejunum (jeh-JOO-num) is the middle portion of the small intestine.
3.The ileum (ILL-ee-um), which is the last and longest portion of the small intestine.
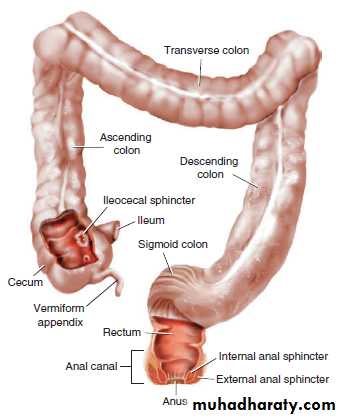
The Large Intestine
The large intestine extends from the end of the small intestine to the anus.The major parts of the large intestine are the cecum, colon, rectum, and anus
The cecum (SEE-kum) is a pouch that lies on the right side of the abdomen.
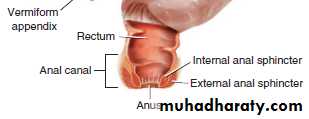
The vermiform appendix, commonly called the
appendix, hangs from the lower portion of the cecum.
The term vermiform refers to a worm-like shape.
The Colon
The colon, which is the longest part of the large intestine, is divided into 4 parts1.The ascending colon. Ascending means upward.
2.The transverse colon. Transverse means across.
3.The descending colon Descending means downward.
4.The sigmoid colon (SIG-moid) is S-shaped structure. Sigmoid means curved like the letter S.
-The rectum, which is the widest division of the large intestine, and ends at the anus.
-The anus is the lower opening of the digestive tract.-The term anorectal refers to the anus and rectum as a single unit (an/o means anus, rect means rectum, and -al means pertaining to).
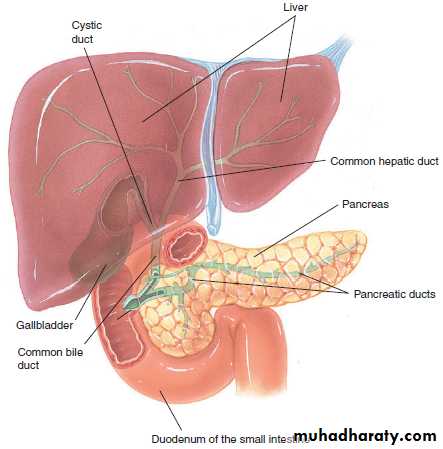
The Liver
The liver is a large organ located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.The term hepatic means pertaining to the
liver (hepat means liver, and -ic means pertaining to).
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ located under the liver.
The term cholecystic means pertaining to the gallbladder (cholecyst means gallbladder, and -ic means pertaining to).
-cholecystectomy (koh-lee-sis-TECK-toh-mee) .. ??
-cholecystitis (koh-lee-sis-TYE-tis) .. ??
The pancreas (PAN-kree-as) is a soft gland that is located behind the stomach.
Pancreatic means pertaining to the pancreas (pancreat means pancreas, and -tic means pertaining to.)Diseases of GIT
The mouth:-Aphthous ulcers (AF-thus UL-serz), also known as
canker sores or mouth ulcers.
-Oral thrush is the fungus growing in the mouth.
-Xerostomia (zeer-oh-STOH-mee-ah), also known as dry mouth, due to lack of saliva.
- Gingivitis (jin-jih-VYE-tis) is the inflammation of the gums (gingiv means gums, and -itis means
inflammation).
The Esophagus
-Dysphagia (dis-FAY-jee-ah) is difficulty in swallowing
(dys- means difficult, and -phagia means swallowing).
-Gastroesophageal reflux disease (gas-troh-eh-sof-ah-JEE-al REE-flucks), also known as GERD, is the upward flow of acid from the stomach into the esophagus (gastr/o means stomach, esophag means esophagus, and -eal means pertaining to). Reflux means a backward or return flow.
-Esophageal varices (eh-sof-ah-JEE-al VAYR-ih-seez)
are enlarged and swollen veins at the lower end of the
esophagus (singular, varix).
The Stomach
-Gastritis (gas-TRY-tis) is a common inflammation ofthe stomach lining(gastr means stomach, and -itis
means inflammation).
-Gastroenteritis (gas-troh-en-ter-EYE-tis) is an inflammation of the lining the stomach
and intestines (gastr/o means stomach, enter means small intestine, and -itis means inflammation).
Ulcers
-An ulcer is an erosion of the skin or mucous membrane.-Peptic ulcers (UL-serz) affect the mucous membranes of the digestive system (pept means digestion,
and -ic means pertaining to).
-Gastric ulcers are peptic ulcers that occur in the
stomach.
-Duodenal ulcers are peptic ulcers that occur in the duodenum.
-Anorexia (an-oh-RECK-see-ah) is the loss of appetite
for food, especially when caused by disease.
-Cachexia (kah-KEKS-eeh-ah) is a condition of loss of weight and muscle mass.
-Pica (PYE-kah) is an abnormal craving or appetite for nonfood substances, such as dirt, paint, or clay.
-Dehydration is a condition in which fluid loss exceeds fluid intake.
-Malabsorption (mal-ab-SORP-shun) is a condition in which the small intestine cannot absorb nutrients from food that passes through it.
-Dyspepsia (dis-PEP-see-ah), also known as indigestion, is pain or discomfort in digestion (dys- means painful, and -pepsia means digestion).
-Emesis (EM-eh-sis), also known as vomiting, is the
reflex ejection of the stomach contents through the
mouth.
-Hematemesis (hee-mah-TEM-eh-sis) is the vomiting of blood (hemat means blood, and -emesis means vomiting).
-Nausea (NAW-see-ah) is the urge to vomit.
-Regurgitation (ree-gur-jih-TAY-shun) is the return of
swallowed food into the mouth.