Disorders of the urethra
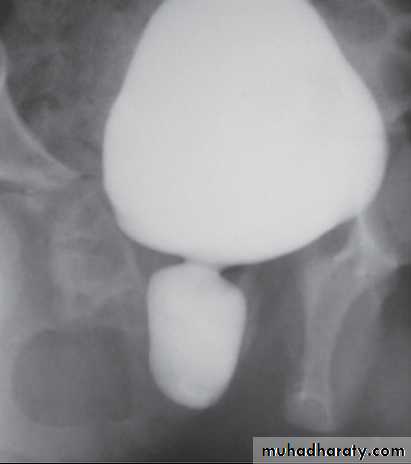
Posterior urethral valvesThe most common obstructive lesions in infants & newborns,
occur mainly in males & are found at the distal prostatic urethra.
The valves are mucosal folds that look like thin membranes; they may cause varying degrees of obstruction when the child attempts to void
Classification
Type 1 (90-95) valve extend from verumontanum to fuse anteriorly
Type 2 extending from verumontanum to bladder neck
Type 3 it ring like membrane found distal to verum.
Diagnosis :
Prenatal uls : bil. hydroureteronephrosis ,dilated bladder and posterior urethra ,oligohydromramnios renal dysplasia
Newborn and infants : Respiratory distress ,palpable abdominal mass ,ascites ,failure to thrive
Older children : recurrent UTI , weak stream ,incomplete empty , incontinence
.VUR
Investigation:
uls
Voiding cystourethrogram :dilated post. Urethra ,valve leaflet , thick Bladder neck
Isotope renal scan: assess renal function
Videourodynamics : to diagnose associated voiding dysfunction
Treatment:
Bladder drainageIf boy born with suspected PUV then treat by drainage and if possible immediate VCUG
Drainage either by
urethral catheterization
suprapubic catheter
Valve ablation
When medical fitness is acheif and creatinine is normal then removing of valve by resectoscop
Vesicostomy
High diversion : used if bladder drainage is insufficient to drain the upper urinary tract
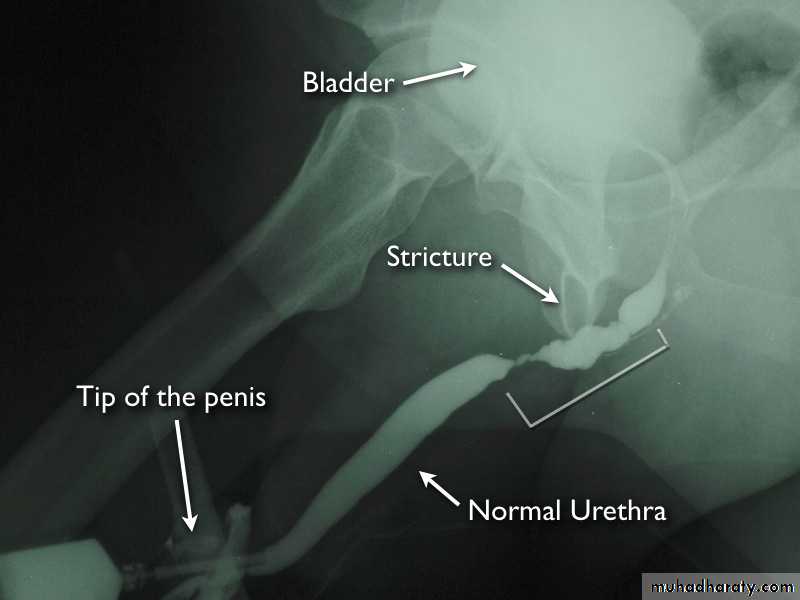
Urethral stricture
Is an area of narrowing in the urethral calibre due to scar formation in the tissue surrounding urethrait is either congenital or acquired,
most acquired strictures are due to:Inflammation
remains a major cause particularly infection from long term user of indwelling catheters.
External trauma
Straddle injury – blow to bulbar urethra
Iatrogenic – instrumentation
Urethral strictures are fibrotic narrowing compose of dens collagen & fibroblasts
These narrowing restrict urine flow
Complications.
Chronic prostatitis
cystitis, chronic UTI
diverticula
urethrocutaneous fistula,
periurethral abscess
Vesicle calculi
Clinical findings
Voiding symptoms – hesitancy, poor stream ,post voiding dribbling ,low flow rate
Urinary retention
UTI - prostatitis ,epdidymitis
Investigation
Urethrogram: show location and lengh of strictureReal-time uls
MRI
Endoscopic examination
Treatment.
1- dilatation of the urethra is not usually curative, it fracture the scar tissue as the healing occur, the scar tissue reform.2- endoscopic urethrotomy.
3- surgical reconstruction
Hypospadias
Hypo= below , spadon =orifice
The condition in which the urethral meatus opens on the ventral side of the penis proximal to the tip of the glans penis
Incidence 1/250
It consist of 3 anomalies
1- abnormal opening of the urethral meatus any where located from the ventral aspect of glans to perineum
2- abnormal ventral curvature o penis (chordee)
3- abnormal distribution of foreskin(hood)
Classification
According to location:
1- Anterior including: glandular, coronal and sub coronal
2- Middle include distal penile, midshaft and proximal penile3-Posterior include penosecrotal ,scrotal and perineal
Assessment
Patient with hypospdias should diagnosed at birthAssess the associated anomaly like undescended testis , ingunal hernia
Severe hypospedious or hypospedious with uni or bilateral cryptoricdism or penosecrotal hypospedious should have chromosomal study to exclude intersexuality
Treatment
For psychological reasons hypospadias should be repaired before the patient reach the school age;
in most cases this can be done before the age 2.
Epispadias
The urethra is displaced dorsally
Most females with epispadias are incontinent.
The pubic bone are separated as in exstrophy of the urinary bladder.
Treatment, by surgery.
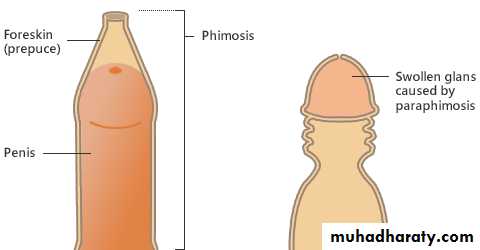
Phimosis
Is a condition in which contracted foreskin cannot retracted over the glans.Chronic infection from poor local hygiene is its most common cause.
Calculi & squamous cell ca may developed under the foreskin.
Edema, erythema, & tenderness of the prepuce & the presence of purulent discharge are usual presentation.
Treatment
The initial infection should be treated with broad spectrum antimicrobial drugs.
The dorsal foreskin can be slit if improved drainage is necessary.
Circumcision should be done after the infection is controlled
Paraphimosis
Is the condition in which the foreskin once retracted over the glans cannot replaced in its normal positionIt regard as urological emergnency
This is due to chronic inflammation under the redundant foreskin & formation of tight ring of skin when the foreskin retracted behind the glans.
the skin ring cause venous congestion
Treatment consists of
Manual compression of the oedematous tissue with subsequent attempt to retract the tightened foreskin over the glanis
Adorsal incision of constrictive ring may be required or circumcision
Circumcision
routinely performed in some countries for religious or cultural reasons.
There is higher incidence of penile carcinoma in uncircumcised males, but chronic infection & poor hygiene are usually underlying factors in such instances.
Circumcision is indicated in patients with
-infection,
-phimosis
-Paraphimosis.