INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS
1INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: DEFINITION
Microbial infection of the endothelial surface of the heartCharacteristic lesion: VEGETATION
2IE: DEFINITION:VEGETATIONS
Mass of platelets and fibrin, rich in bacteria, scanty inflammatory cellsSites: heart valves, septal defect, chordae tendineae or mural endocardium
3
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: DEFINITION
Infection of arteriovenous shunts or PDA or coarctation of the aorta is called infective endarteritis, but clinically resembles IE4
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: DEFINITION
Causative organism: bacteria, fungi, and rickettsiaeMost frequent organisms: streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci, and fastidious gram-negative coccobacilli
5
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS: PATHOGENESIS
6
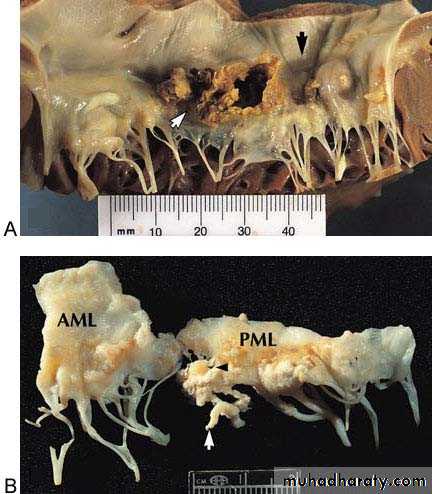
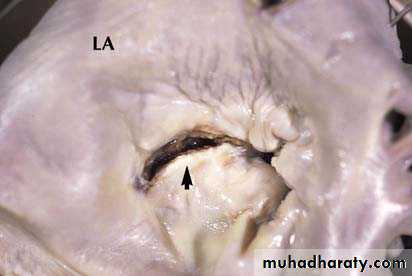
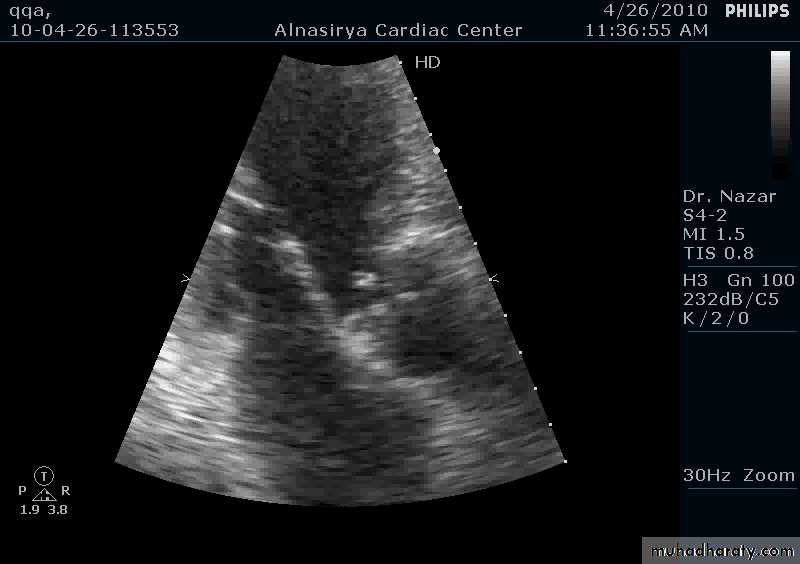
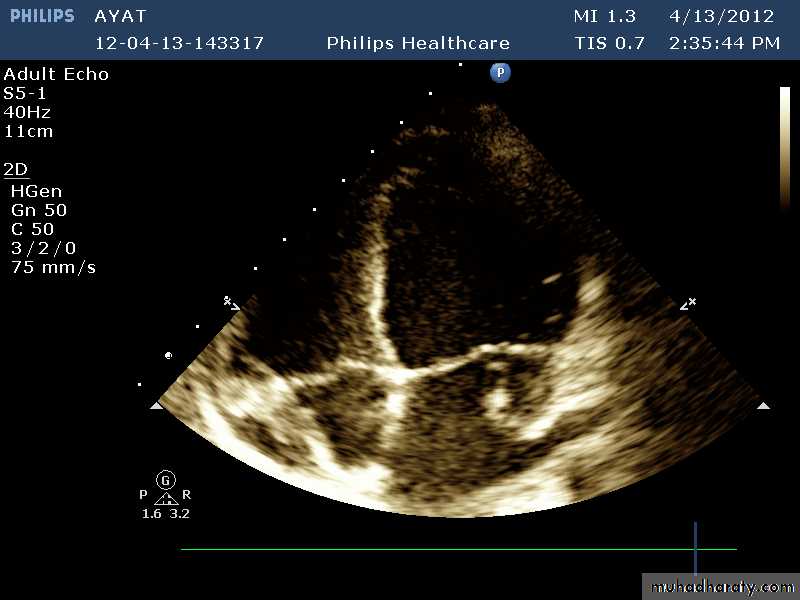
Vegatations on the mitral valve
7
Vegetations on top of mitral stenosis
8
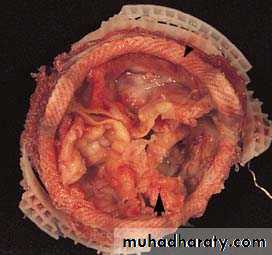
Vegetations on a biologic valve
9
IE: UNDERLYING HEART DISEASE
10IE: UNDERLYING HEART DISEASE
Cardiac lesions with low or no pressure gradients are unlikely to be complicated by IE e.g. ASD11
IE: MICRO-ORGANISMS
S. viridansEnterococcus fecalis
Staphylococcus aureus
Coagulase negative Staphylococci
Gram-negative bacilli
Brucella
Rickettsia
Fungi
12
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
13
IE: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
1415
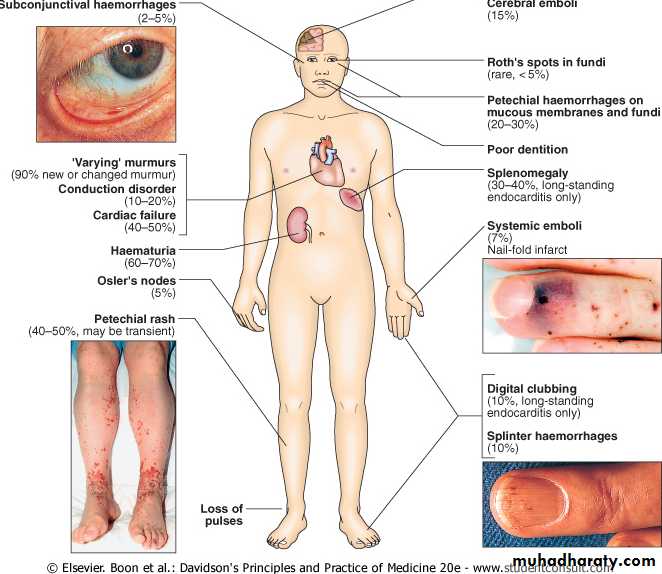
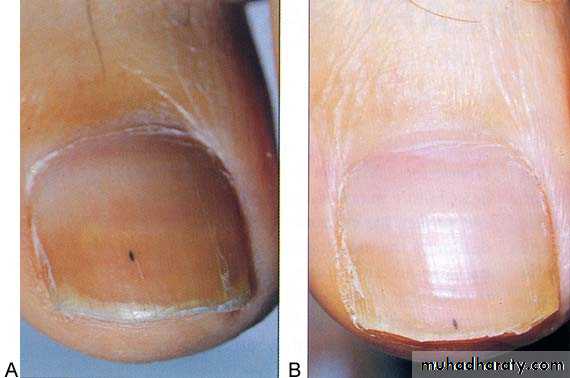
IE: PERIPHERAL MANIFESTATIONS
Splinter hemorrhageOsler’s nodes: subcutaneous nodules, tender
16
Osler’s nodes
17
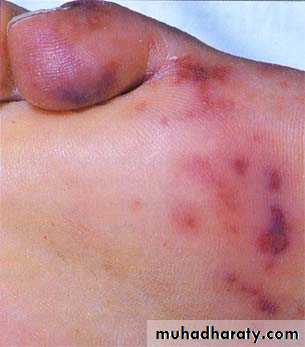
Dermal infarcts
18
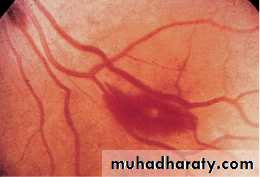
IE: EYE MANIFESTATIONS
Roth’s spots: on fundoscopy19
IE: EYE MANIFESTATIONS
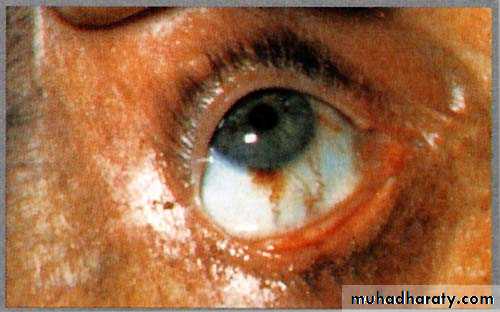
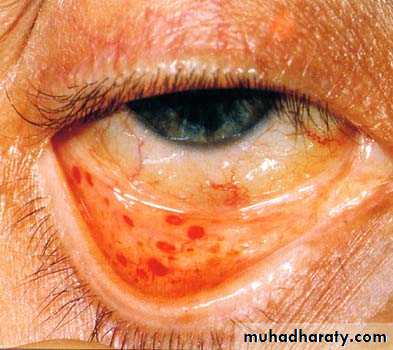
Subconjunctival hemorrhage20
IE: PERIPHERAL MANIFESTATIONS: THE EYE
Petechiae: conjunctiva, buccal mucosa, limbs21
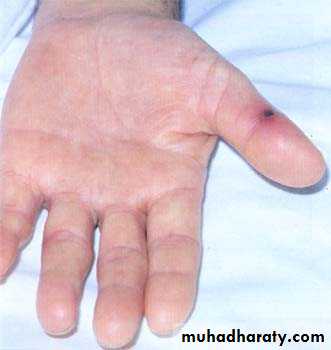
Janeway’s lesions: macular non-tender lesions on the palms and soles:
Evanesent: appear and disappear rapidly22
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
23LOCAL DESTRUCTIVE EFFECTS
24IE: SYSTEMIC EMBOLI
25
IE: NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATIONS
HeadacheConfusion
Convulsions
Long tract signs & focal neurological deficit
Meningeal irritation
26
IE: RENAL MANIFESTATIONS
GlomerulonephritisFocal renal infarcts: hematuria
Renal failure:
immune-complex deposition
Congestive heart failure
drug-induced
27
IE: CLINICAL SETUP
depending on the clinical presentation:Acute IE:
Subacute IE (SBE)
Postoperative IE: following cardiac surgery
28
ACUTE IE
Caused by virulent organisms on top of normal heart:Usually staphylococcus aureus
E.g. cannula infection, staphylococcal septicemia, drug abusers
29
ACUTE IE
30ACUTE IE: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Severe febrile illness
Petechiae
Embolic events common
Rapid progression of cardiac and renal failure
31
SUBACUTE IE
Caused by infection with low-virulence organisms on top of pre-existing cardiac diseasePersistent fever, tiredness, weight loss, night sweats
32
PROSTHETIC VALVE ENDOCARDITIS
IE following cardiac surgeryEarly postoperative IE:
infection is acquired at the time of surgery
High mortality: repeat surgery often required
Late postoperative IE:
Community-acquired infection
Complication rates lower than early form
33
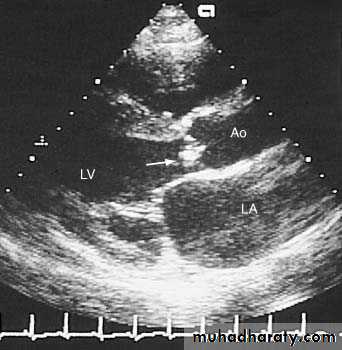
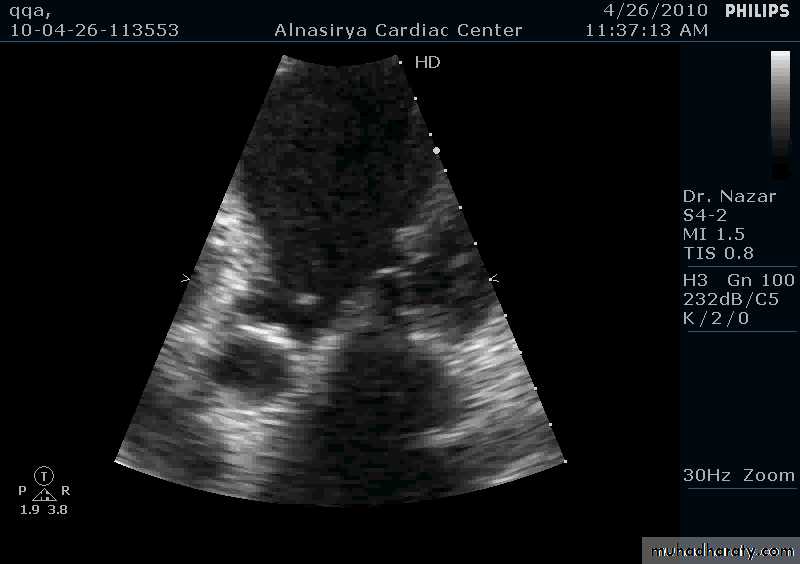
IE: INVESTIGATIONS
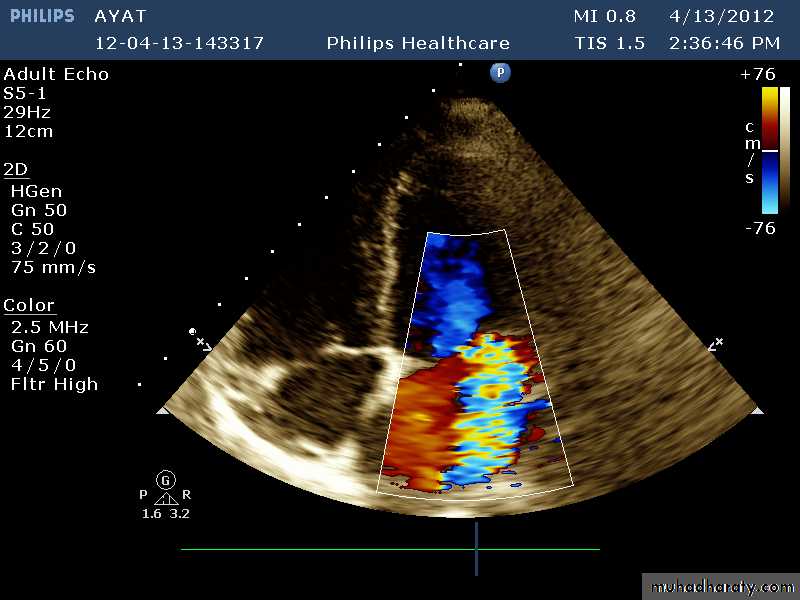
Blood culturesEchocardiography: transthoracic (TTE) and transesophageal (TEE)
Vegetations
Serial follow up
Valve damage
Abscess fromation
34
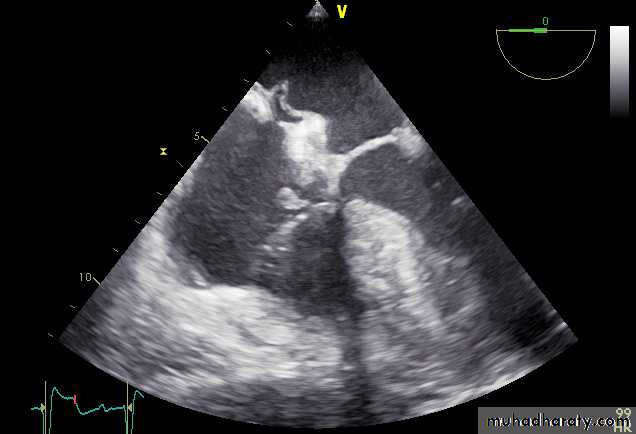
Vegatations on the aortic valve
35
VEGETATIONS
36
37
38
39
40
IE: INVESTIGATIONS
High ESRAnemia of chronic disease
Neutrophil leucocytosis
CRP
Hematuria
Proteinuria
Low serum complement
Rheumatoid factor
41
IE: INVESTIGATIONS
ECG:Heart block
Bundle branch block
arrhythmia
42
IE: TREATMENT
Combination antibiotic therapy according to culture & sensitivityEmpirical regimes pending the results of blood culture
43
IE: TREATMENT
Large dosesGiven intravenously
Protracted duration of therapy:
usually 4 weeks
6 weeks in PVE
44
Combination AB therapy
Benzyl penicillin or ampicillin i.vPlus gentamycin
For penicillin resistant or allergic: vancomycin infusion plus gentamycin
Oral rifampicin when staphylococcal infection suspected or confirmed45
CARIAC SURGERY: INDICATIONS
Failure to respond to medical treatmentHeart failure due to valve insufficiency
Large vegetations
Abscess formation
46
PREVENTION OF IE
Susceptible patients: those with valvular or congenital heart diseaseGood dental hygiene
47
PREVENTION OF IE
Avoidance of bacteremiaAntibiotic prophylaxis:
Dental manipulation
Genito-urinary tract catheterization or surgery
48
PROPHYLAXIS
For dental procedures:Oral amoxicillin given 30 min before and 6 hours after the procedure
49