
Biochemistry lectures
First stage
By
Assistant professor Dr.Suhayr Aessa Hussein
phD. Clinical Biochemistry
College of Medicine University of Babylon

Lipid
L 3
Phospholipid and Eicosanoid

➢ Objectives
•
Know the types of phospholipidlipids
•
Know Eicosanoid lipids

Compound lipid
A)Phospholipids
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
consist
from
fatty
acids
+alcohol+nitrgen base+ phospharic acid •
There re two types
I GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS
: contain glycerol, saturated
and unsaturated fatty acid, phosphoric acid and a
nitrogenous base.
II SPHINGOPHOSPHOLIPIDS
: contains sphingosine
(instead of glycerol) fatty acid, phosphate and choline
Ex: sphingomyelin
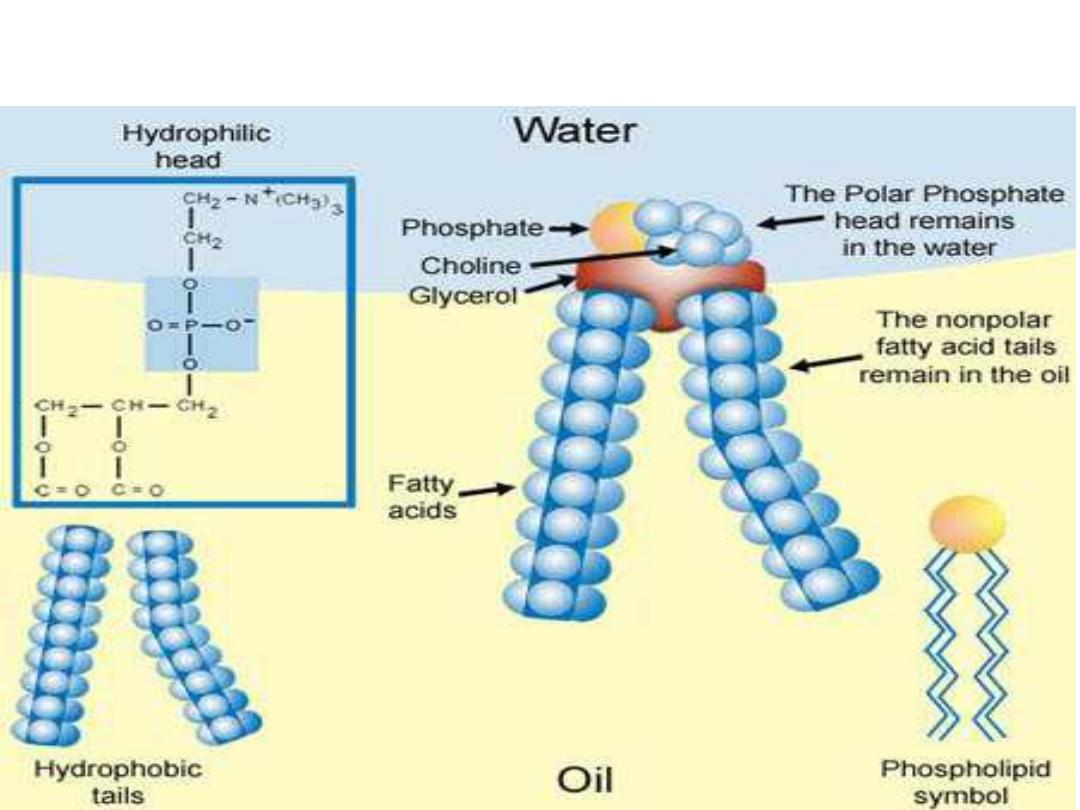
Phospholipids (Contd.)

Classification of Phospholipids
Based on nature of alcohol-
1)Glycerophospholipids- Glycerol is the alcohol group.
Examples
-
❖ Phosphatidyl choline (lecithin ):
Choline is important in nervous transmission, as
acetylcholine, and as a store of labile methyl groups
❖ Dipalmitoyl lecithin is a very effective surface active agent and a major constituent of the
surfactant preventing adherence, due to surface tension, of the inner surfaces of the lungs.
Its absence from the lungs of premature infants causes respiratory distress syndrome.
➢
Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
➢
Phosphatidyl serine
➢
Phosphatidyl inositol
➢
Phosphatidic acid
➢
Cardiolipin
➢
Plasmalogen
➢
Platelet activating factor PAF
activates inflammatory cells and mediates
hypersensitivity, acute inflammatory and anaphylactic reactions
➢
Phosphatidyl Glycerol
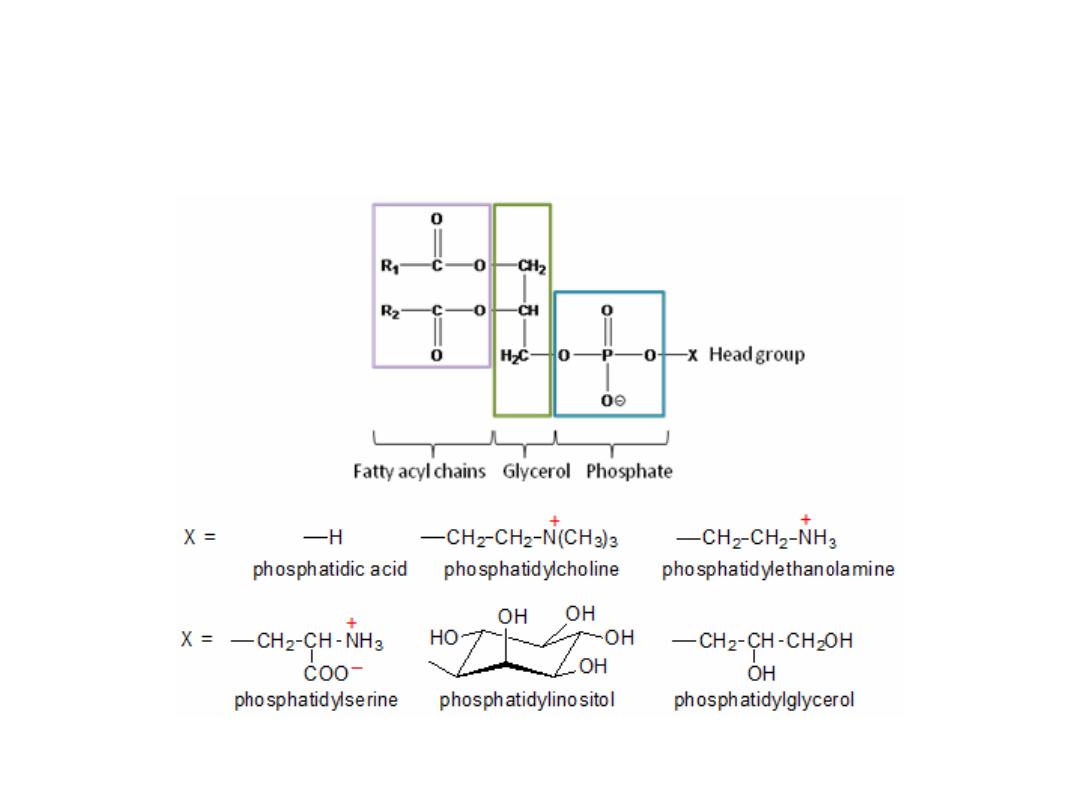
Glycerophospholipids
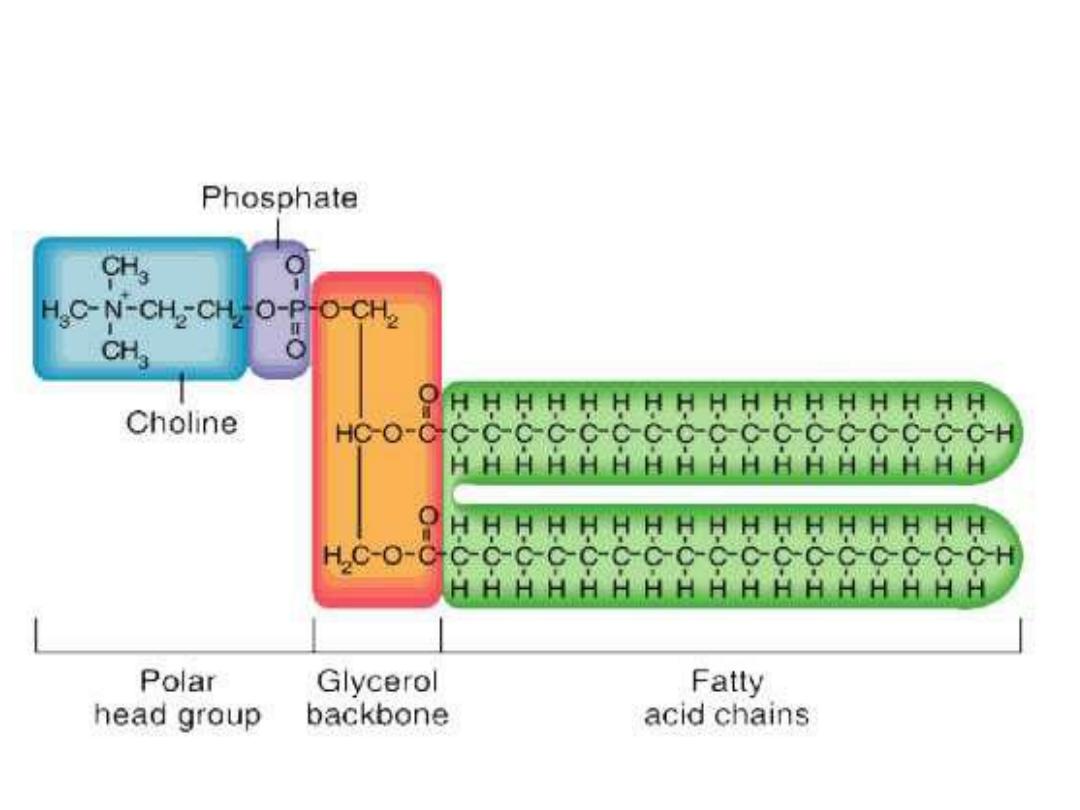
Structure of Phosphatidyl Choline
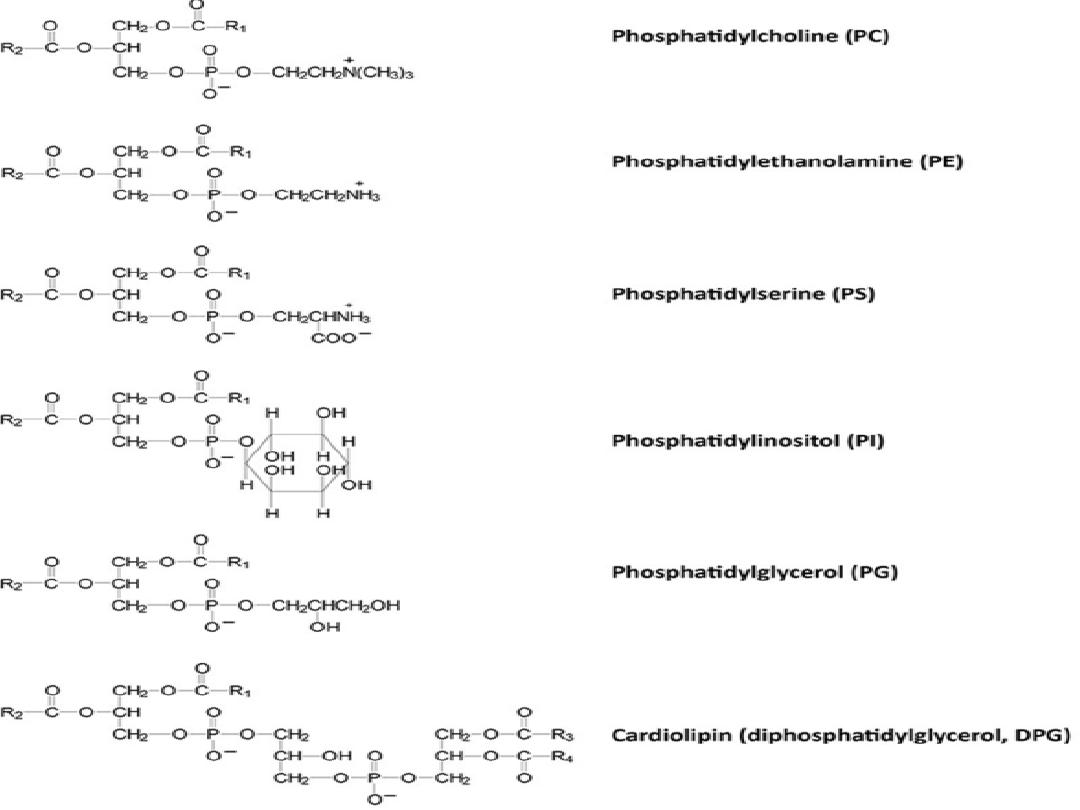

2)Sphingophospholipids- Sphingol is the alcohol group
Example-
Sphingomyelin
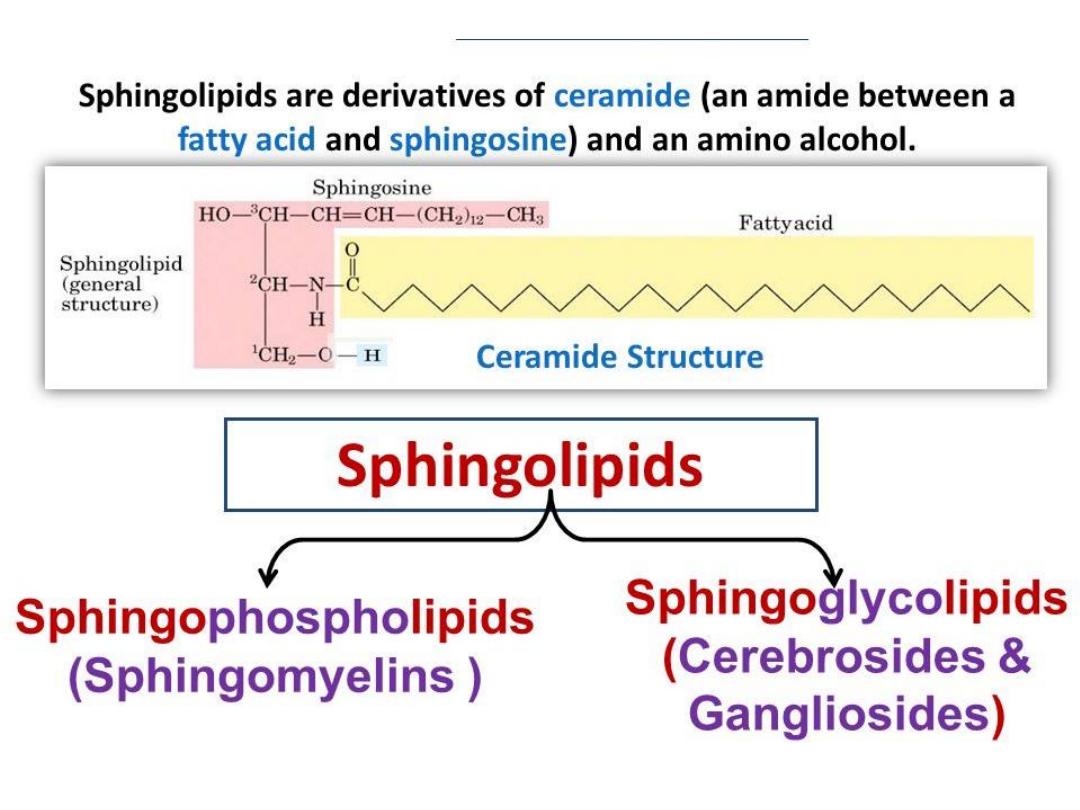
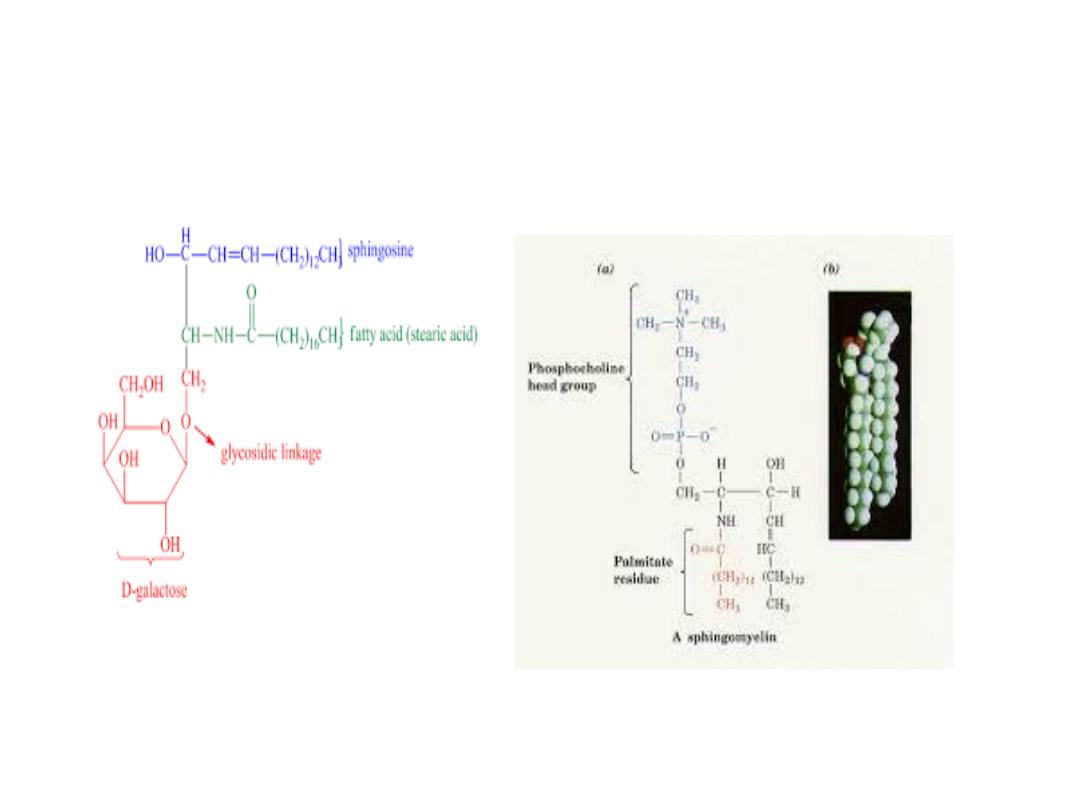
sphingoglycolipid

Sphingophospholipid
❖ Sphingomyelin-
❖ Backbone is sphingosine (amino alcohol)
❖ A long chain fatty acid is attached to amino group of
sphingosine to form Ceramide
❖ The alcohol group at carbon- 1of sphingosine is
esterified to phosphoryl choline, producing
sphingomyelin
❖ Sphingomyelin is an important component of myelin of
nerve fibers
97

Lecithin Sphingomyelin Ratio (L/S)
✓ L/S Ratio in amniotic fluid is used for the evaluation
of fetal lung maturity
✓ Prior to 34 weeks gestation, lecithin and sphingomyelin
concentrations are equal but afterwards there is marked
increase in Lecithin concentration.
✓ A L/S ratio of> 2 or > 5 indicates adequate fetal lung
maturity
✓ Delivery of a premature, low birth weight baby with low
L/S ratio (1 or<1) predisposes the child to respiratory
distress syndrome

Functions of Phospholipids
❖ Components of cell membrane, mitochondrial membrane and
lipoproteins
❖ Participate in lipid absorption and transportation from intestine
❖ Play important role in blood coagulation
❖ Required for enzyme action- especially in mitochondrial electron
transport chain
❖ Choline acts as a lipotropic agent
❖ Membrane phospholipids acts as source of Arachidonic acid
❖ Act as reservoir of second messenger- Phosphatidyl Inositol
❖ Act as cofactor for the activity of Lipoprotein lipase
❖ Phospholipids of myelin sheath provide insulation around the nerve
fibers
❖ Dipalmitoyl lecithin acts as a surfactant
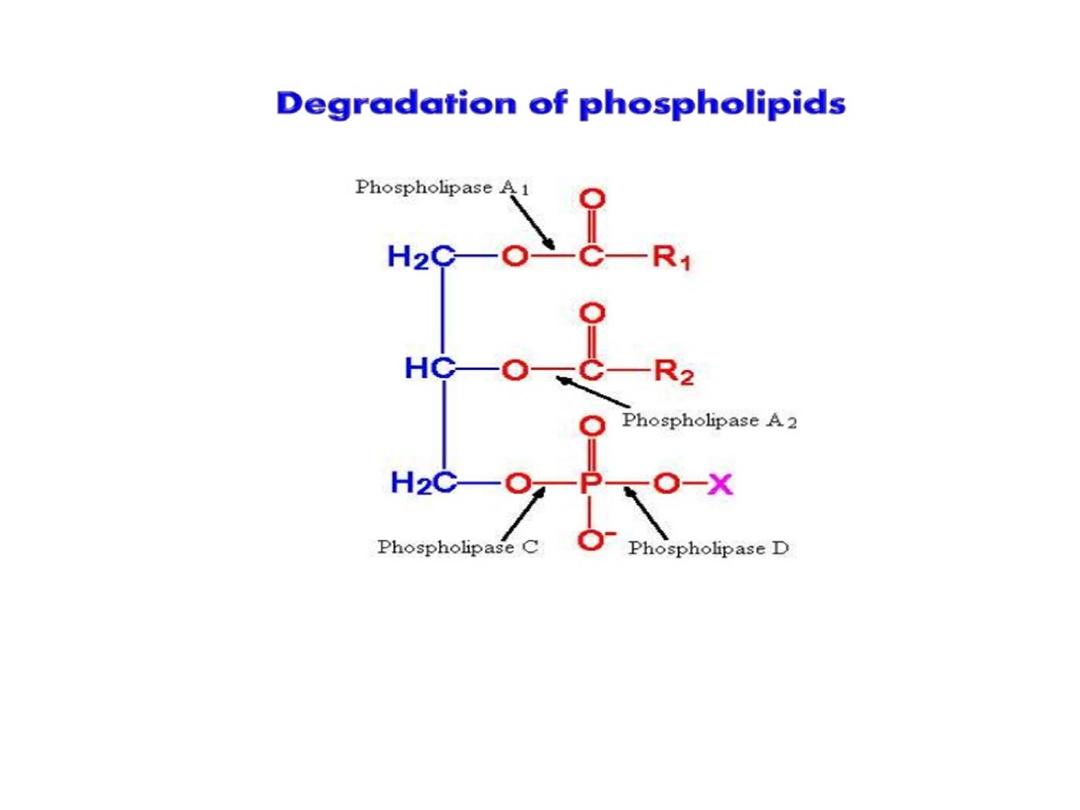
Sites of action of the phospholipases A1, A2, C and D.
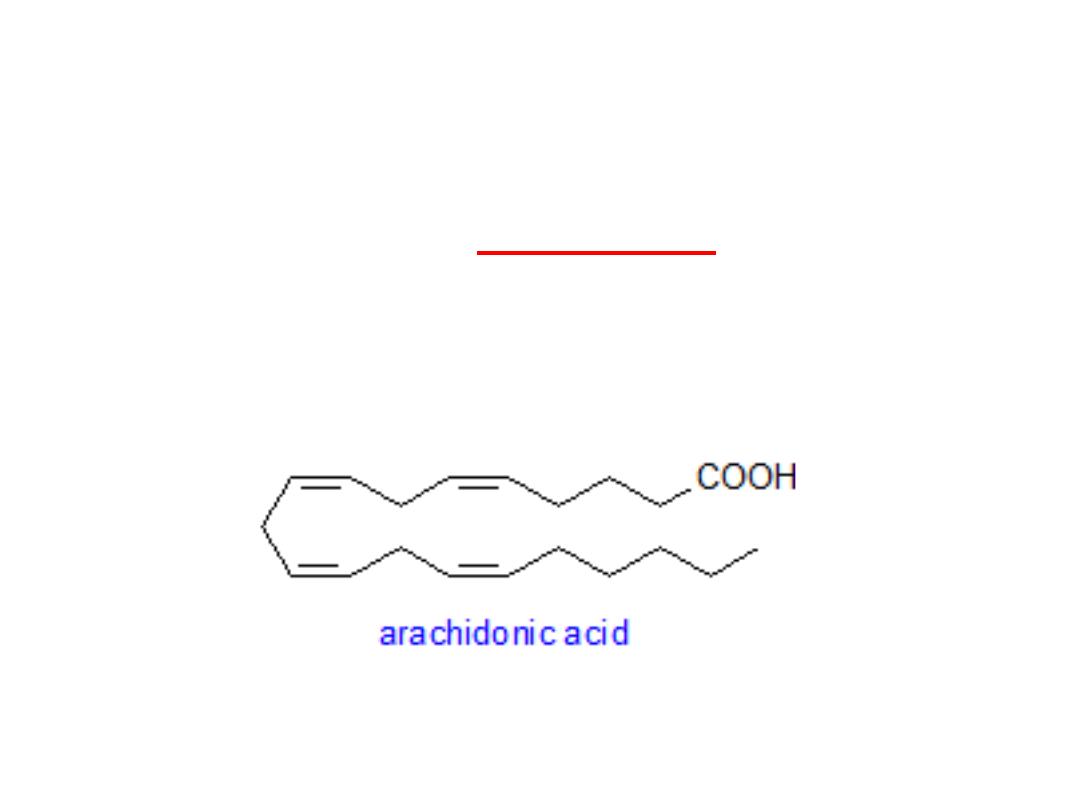
Eicosanoids
Prostaglandins and related compounds are
collectively known as
Eicosanoids
. Most are
produced from Arachidonic acid, (a20 –carbon
polyunsaturated fatty aid).

Major Classes of Eicosanoids
➢ Prostaglandins:
They play vital role in the regulation of endocrine,
nervous, digestive, Haemostatic functions If there is alteration in
prostaglandin production or metabolism this result in hypertension,
bronchial asthma, pain fever, inflammation and ulcer
➢ Thromboxanes
They are synthesized by platelets.
- Induce platelets aggregation,
- promote vasoconstriction,
- Lymphocyte proliferation,
- Broncho constriction,
-and Clot formation
➢ Prostacyclins
➢ Leukotrienes:
Leukotrienes have roles in inflammation. They are
produced in areas of inflammation in blood vessel walls as part of
the pathology of atherosclerosis.

