
Laboratory Name
: Some Technical Aspects in Hematology
Lecturer Name
: Shrooq Majeed Al-Saleh
Department
: Medical Physiology
Stage
: First Stage Medical Students

The following steps should be taken in examining blood samples:
1) Select proper anticoagulants with the right proportion of ingredients.
2) Prevent clotting by proper mixing.
3) Drying pipettes before use is important to prevent dilution of the blood and lyses of red cells by water.
4) Label specimens correctly.
5) Always mix blood sample in sample bottle very well by rotation before drawing any quantity for anew
count.
6) After drawing blood from fingertip or sample bottle with any pipette wipe off any blood present on
outside of tip of the pipette to prevent error in case of hemoglobin and contaminating diluting fluid in cases
of RBC and WBC counts.
7) Prepare blood samples and run tests immediately (2-3 hours) after drawing blood because RBC may swell
and give erroneous measurement of hematocrit (PCV) and red cell indices if kept at room temperature for
more than 5-6 hours. However, anti-coagulated blood stored at 8 C˚ may stay for 24 hours without
significant changes in RBC & WBC.


.
Are substances or drugs that prevent coagulation or clotting of blood outside the body.
. Excess anticoagulant powder gives error in counts and morphology. Delaying the blood sample in anticoagulant is also
harmful
.
Types of anticoagulant
a- Disodium or dipotassium ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA).
It’s 1st choice in routine hematological work, trapping on calcium ions in the blood. When we add excess EDTA into blood, it
causes shrinkage and degenerative changes of both red blood cells (RBC) and white blood cells (WBC).
b- Ammonium and potassium oxalate mixture.
c- Tri-sodium citrate.
study coagulation capability of blood, estimation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
d- Heparin.
the best anticoagulant used for testing osmotic fragility of RBC.
e- Acid-Citrate-Dextrose Solution (A.C.D).
Acid citrate dextrose solution is preferred anticoagulant during blood transfusion.

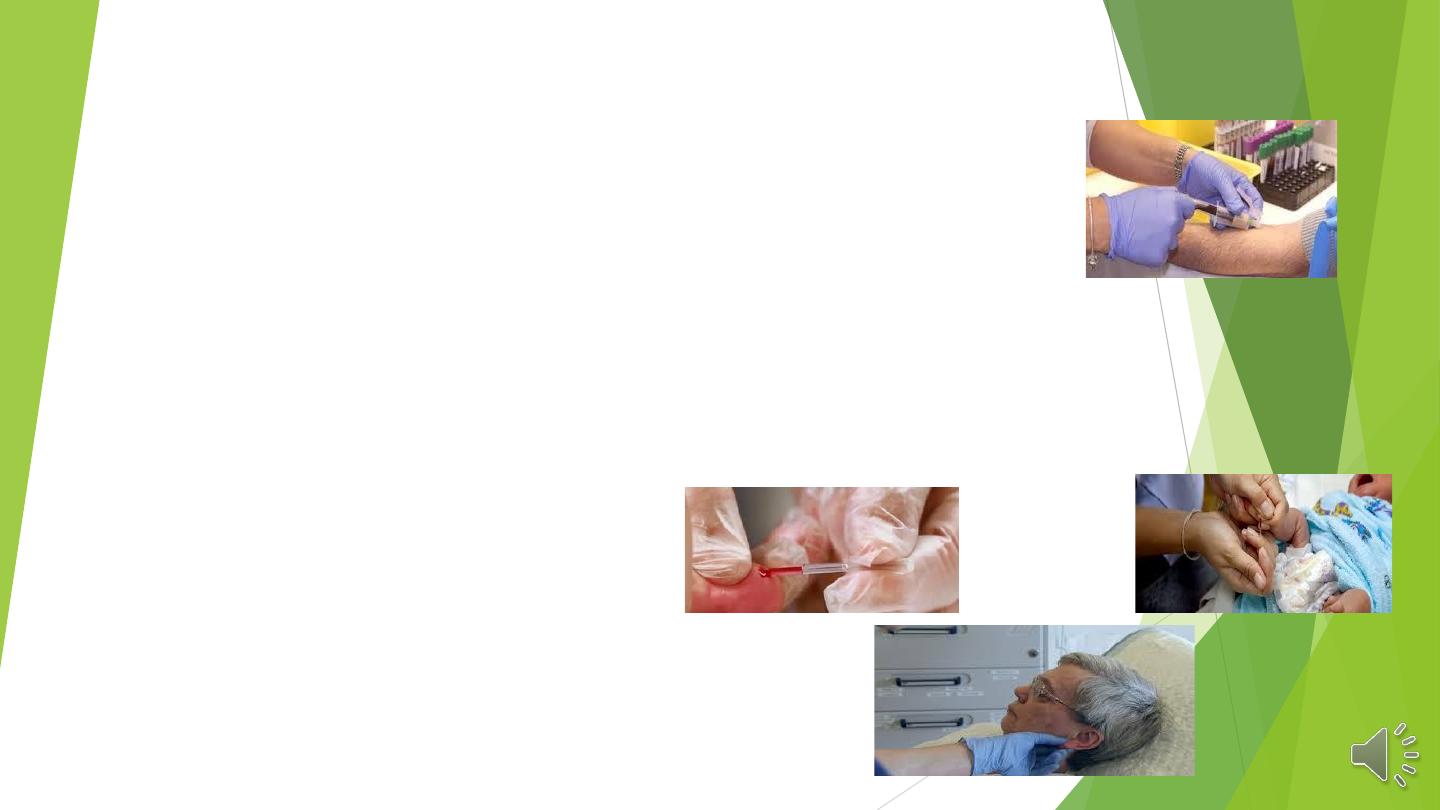
The objective of blood sample collection is to obtain representative sample of the circulating blood in a form
best suited to the investigations required.
two way of obtaining the samples:
1) From the vein. (few ml)
Q/ Venous blood sample is preferred? Why
Because larger amount of blood can be obtained than capillary blood sample and then a number of
investigations can be done and repeated on the same sample and because the examination can be done at
leisure.
In the adult, one of the veins in the antecubital fossa is chosen (median cubital vein).
2) From the capillary. (few drops) …. Pricking
1- The palmer surfaces of the tip of the finger.
2- The lobe of the ear.
3- In infants, from the plantar surface of the heel or the big toe.


.
Blood must be diluted to enable cells to be counted.
. This diluting fluid is that it should (Characteristics of diluting fluids)
1) Prevent lyses or gross changes in the cells to be counted
2) Destroy unwanted cells.
3) Contain an anticoagulant.
4) Be free from debris.

THANKS

Phlebotomy - Medical Assistant Skills Video #7
