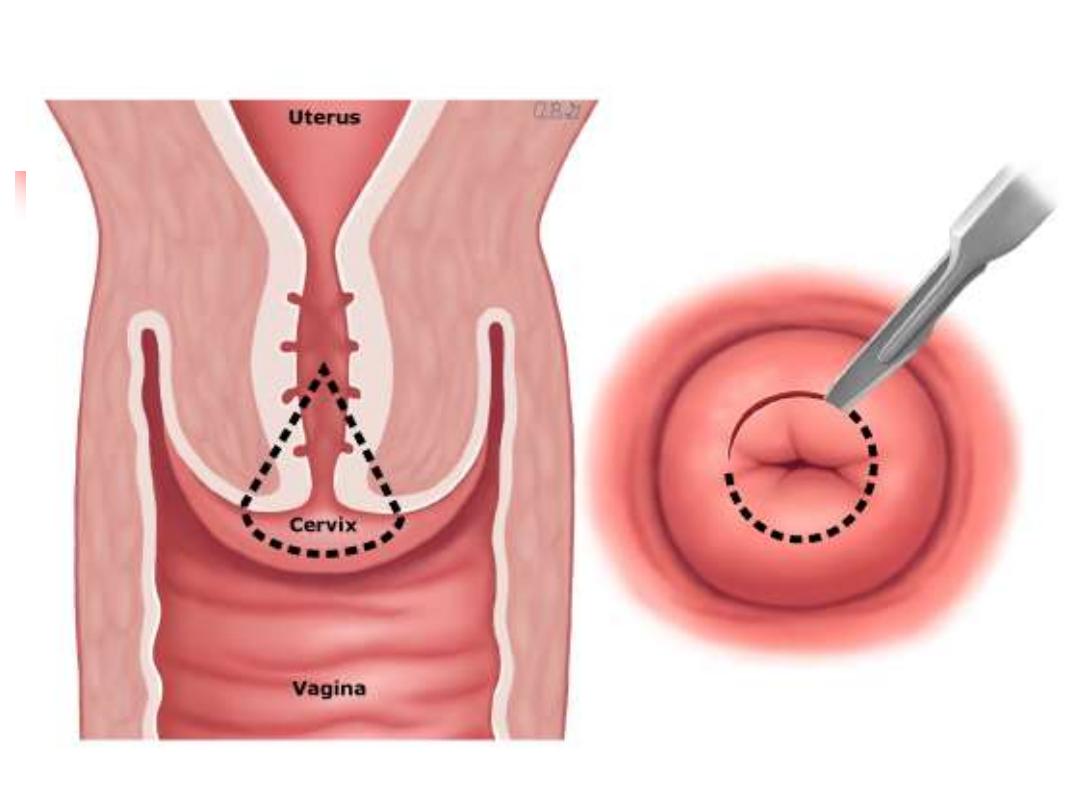
TREATMENT OF CIN
two main methods of treatment are:
1- ablative techniques
2- excisional techniques
The success of treatment is usually
defined as negative cytology six months
following intervention
the ablative and excisional methods
achieve cure (or success) rates of 90–
98%
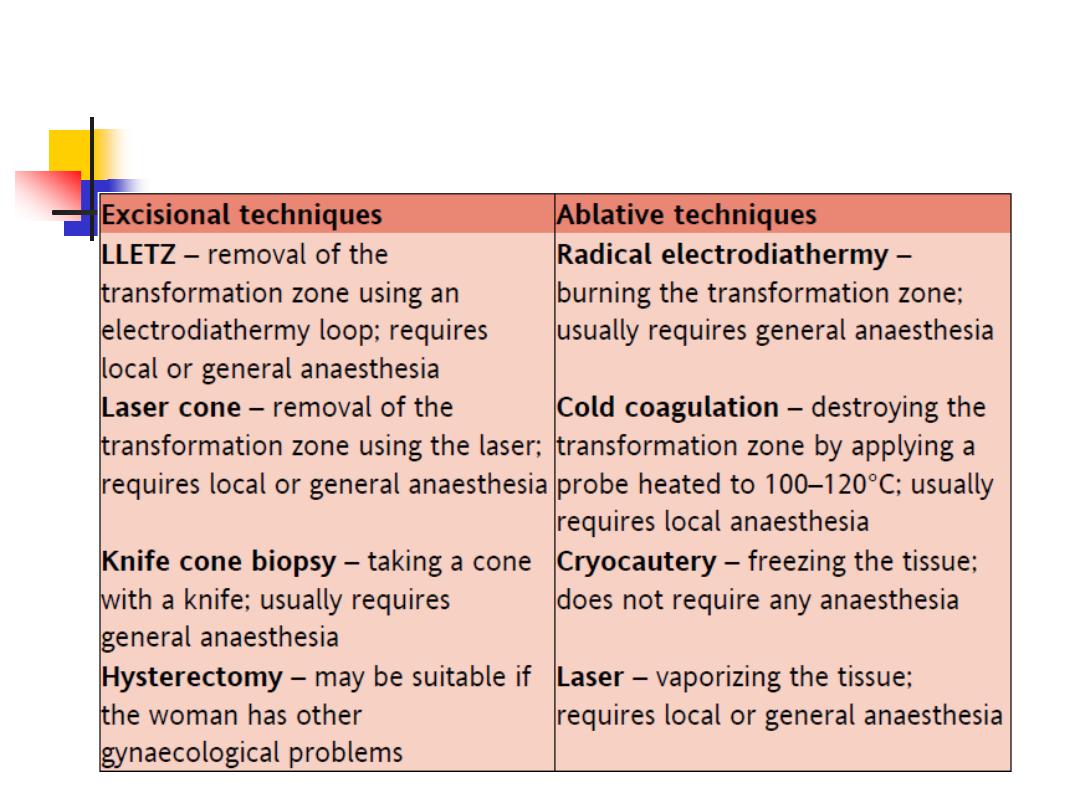
TREATMENT OF CIN

Depth of destruction:
The depth of destruction of any local
treatment modality is important.
Ablation to a depth of 7 mm has been
recommended for eradication of the
disease.
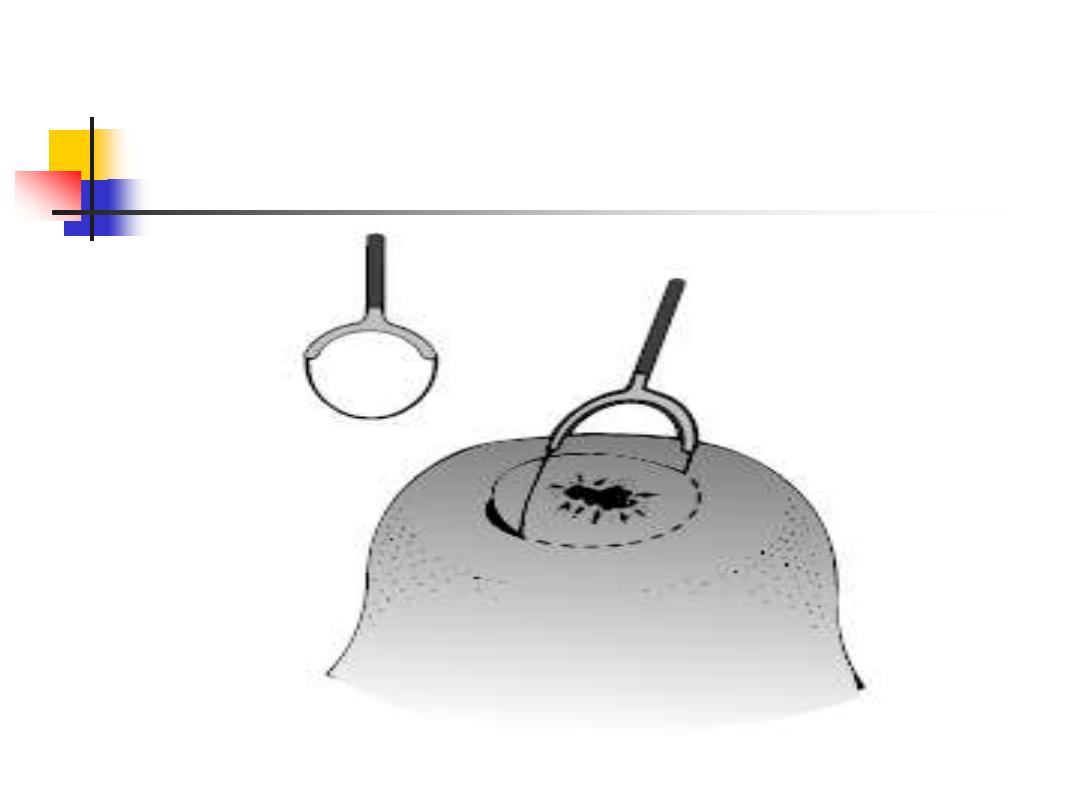
LLETZ

TREATMENT follow up
The primary objective of treating
women with CIN is to prevent invasive
cervical cancer.
women who have been treated for CIN
need long-term follow-up and she has
increased life time risk of recurrent CIN
and cancer.

Follow up
Patients treated for CIN should undergo a
‘test of cure’ 6 months later
.
This includes a:
high-risk HPV test and cytological
assessment.
If negative, the woman is returned to routine
recall; that is cervical screening in 3 years
time.
If positive, repeat colposcopy is indicated to
identify any residual untreated CIN.
Carcinoma of the cervix
By
Dr Suhaila Al-Shaikh

Carcinoma of the cervix is the
second commonest cancer
among women worldwide, with
only breast cancer occurring
more commonly.

HISTOLOGY
70% SCC
30% GCC and other types
Clinical presentation
*In early disease: asymptomatic discovered
accidentally after excisional treatment of CIN
*In more advanced disease vascular friable mass:
1- post-coital bleeding,
2- intermenstrual or postmenopausal bleeding.
3- offensive blood- stained vaginal discharge.
4- during pregnancy one of DDX of abnormal vag
bleeding
5- dysuria and urinary symptoms not uncommon
Clinical presentation:
In some women presenting with late disease:
there may be
1- backache,
2- leg pain, neurological invasion
3- leg oedema,
4- haematuria, and incontinence(vesico-vag
fistulae)
5- bowel changes,
6- malaise,
7- weight loss.
8- renal failure due to ureteric involvement.

Diagnosis
A pelvic and speculum examination
cervical mass that bleeds on contact
if advanced disease, a hardness and fixity of the
tissues
A biopsy should be taken in the outpatient setting.
To prove the diagnosis and histologic type
Combined recto-vaginal exam under anesthesia
MRI is the most important and useful for cervical
tissue involvement, parametria and LN
CXR, cystoscopy, sigmoidoscopy
IVU for ureteric involvement

Suspicious features at colposcopy:
1- intense acetowhiteness,
2- atypical vessels,

Spread
Carcinoma of the cervix may spread by:
1- direct infiltration
2- lymphatic vessels to pelvic LN
iliac, obturator, para-aortic
The direct spread:
a- downwards into the vaginal wall,
b- forward into the bladder,
c- laterally into the parametrium
d- or posteriorly into the rectum.
Blood spread occurs late in the disease.

Staging:
Staging is
clinical
process including
assessment of disease extent and sites of
spread.
early cancers are staged according to the
surgical specimen.
Why the disease is staged?
1) the treatment can be planned appropriately.
2) give an idea of prognosis.
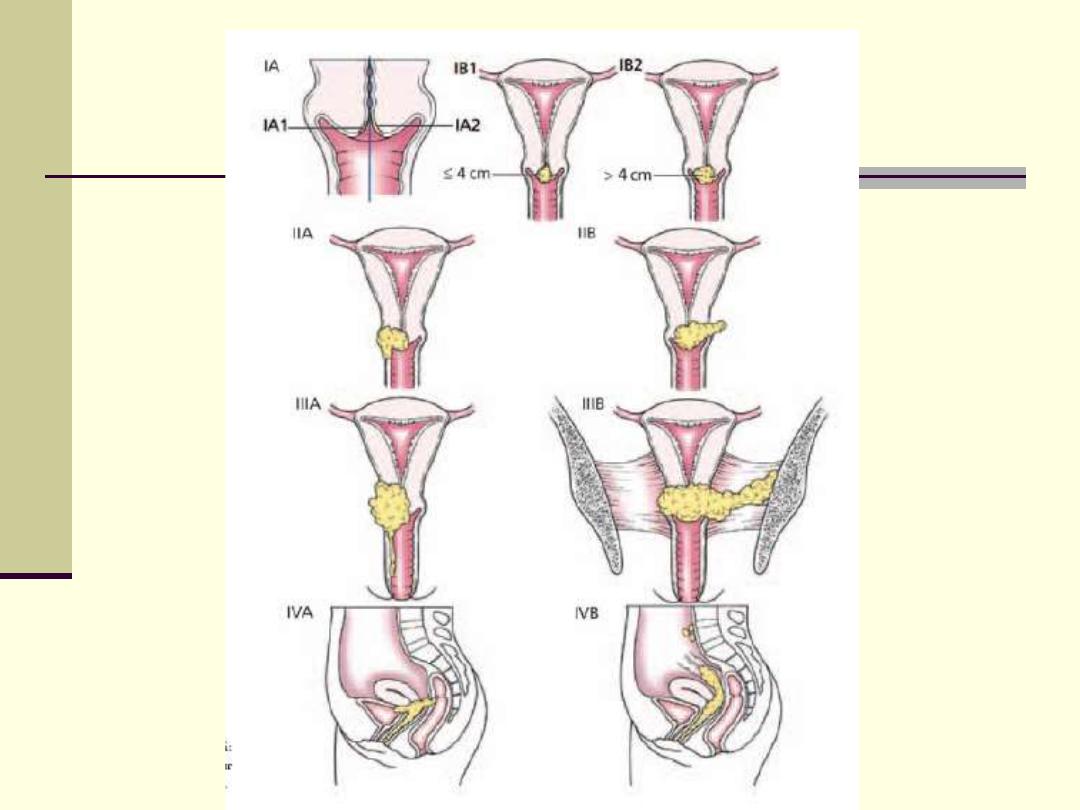
stages

stages
Page 328
in gynecology by ten teachers 20 Ed 2017
Table 16.1 for more details
Stage 1 confined to cervix
A) preclinical ( microscopical )
B) clinical
Stage 2 spread beyond cervix
A) to upper 2 third of vagina
B) parametrium but not reach pelvic side walls
Stage 3 A) to lower third of vagina
B) pelvic side walls
Stage 4 A) mucosa of bladder and rectum
B) distant
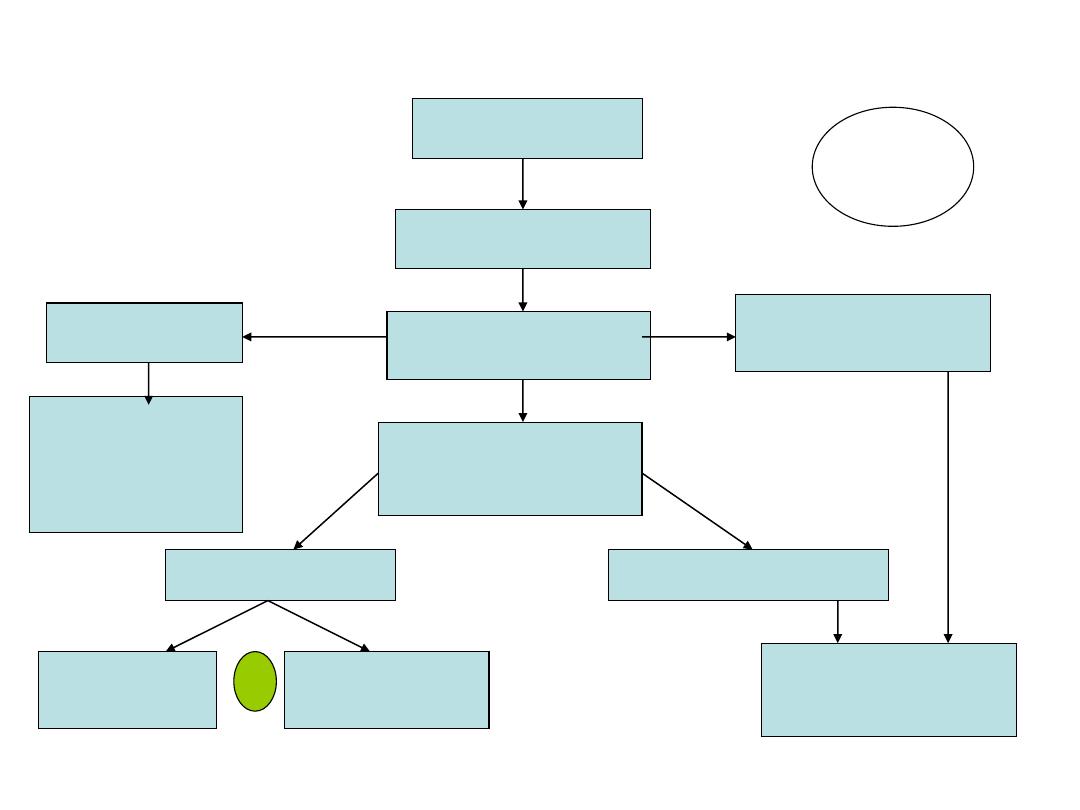
Flow chart showing management of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer
Clinical staging
Stage Ia
Stage Ib 1
Stage Ib2, IIa-IV
Assess L.N
laparoscopically
L.N -ve
L.N +ve
Conservative
Surgery
(cone or simple
hysterectomy
Radical
hysterectomy
Radical
trachelectomy
chemoradiation
or
مهم

Treatment:
the treatment is conservative by local excision
(colposcopic directed)
1-For stage 0 local excision or ablation.
2-stage 1 preclinical (micro-invasive)
radical surgery or radical radiotherapy
If deep infiltration in > than stage 1 a
for premenopausal women, surgery (conserving
the ovaries) less morbidity & sexual dysfunction.
The optimal treatment is to obtain the highest
cure rate and the least associated morbidity

Surgery (conservative)
Cone surgery
Simple hysterectomy
Fertility sparing surgery (Radical
trachelectomy) in those with L.N
–ve :
removal of the cervix, parametrium, upper
1/3 of the vagina

:Surgery (radical)
Wertheim hysterectomy
(radical
hysterectomy):
For LN +ve
Complications include: urine retention and
sometimes lymphedema of the legs and
mons pubis

Radiotherapy
involves the use of:
1-
external beam therapy (teletherapy)
to
shrink the central carcinoma and also to
treat the possible sites of regional
metastasis.
2-
Internal sources (brachytherapy)
are
then placed in the upper vagina and within
the canal of the cervix to provide a very
high dose to the central tumour.
Most patients tolerate this treatment well.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
( Platinum based ) used as adjuvant therapy
with other modalities in more advanced
disease.

Carcinoma of the cervix and pregnancy
In early stage disease conservative surgery,
While in more advanced disease as below:
1- In early pregnancy
, external irradiation may be given;
abortion of a dead fetus will follow and then local
irradiation with caesium can be given.
2-
Later in pregnancy
, the uterus must be emptied by
hysterotomy or Caesarean section followed by
radiotherapy or radical surgery at the time of
Caesarean section
Survival
Survival is stage dependent and the advanced
stages are associated with a poor prognosis.
The relative survival rate for all women
treated for invasive cervical cancer is 64%.
*The 5-year relative survival rates is:
L.N +ve has 46% while L.V
–ve has 90%
83% for stage I,
65% for stage II,
36% for stage III
and 10% for stage IV.

Important points:
• Cervical cancer affects young women who
may not have completed their families.
• Many cervical tumours are picked up when
they are microscopic or very small volume,
making
fertility-sparing treatment is a possibility.
Cone biopsy
or
radical trachelectomy
with
bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy allows
preservation of the ovaries and uterus,
permitting pregnancy in the future.