Done by
Dr.Rafid Remthan Al-Temimi
Clinical Radiology
CAMB,DMRD,M.B.Ch.B.,.
المرحلة
:
الثانية
المادة
:
التشريح
ج
امعة ذي قار
/
كلية الطب
الدكتور
رافد
رمثان التميمي
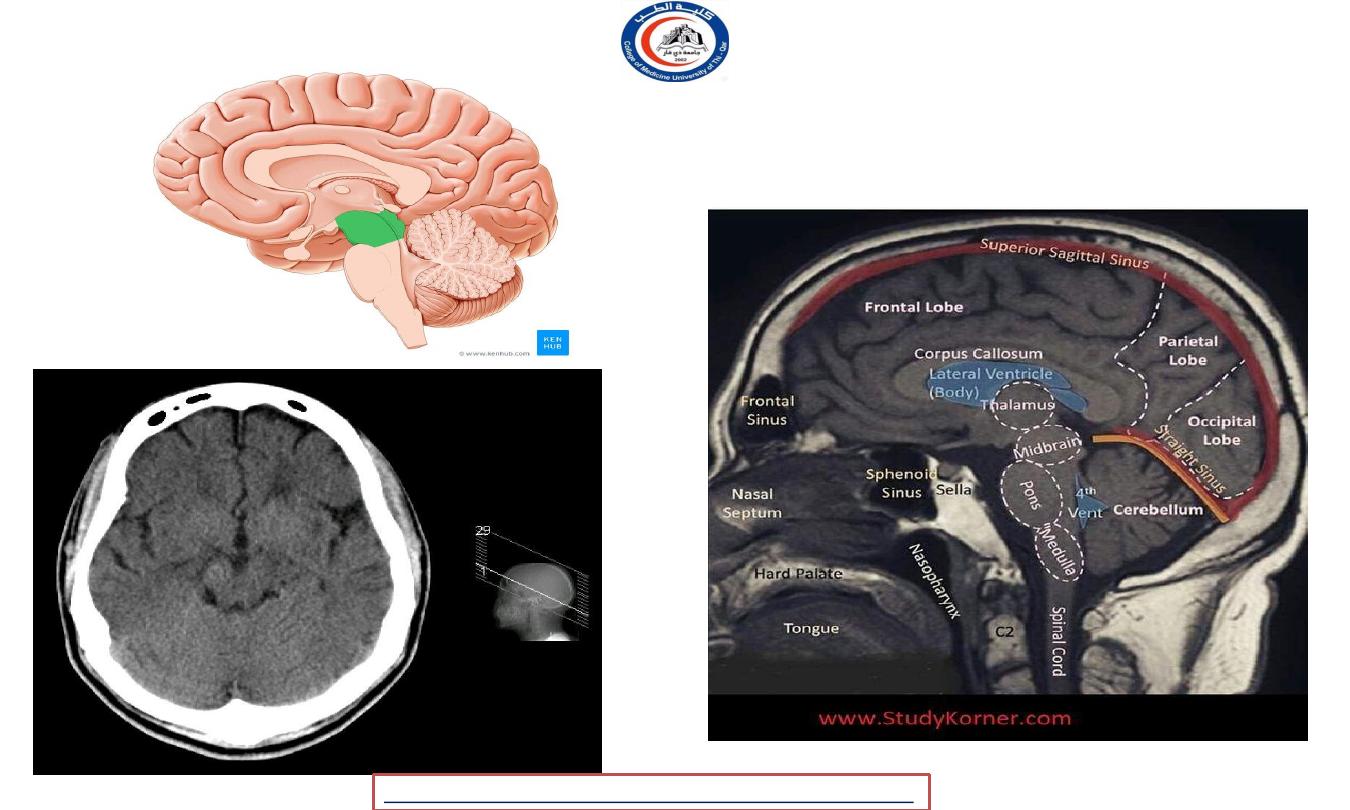
Brain stem, 1
st
part
Midbrain
• The midbrain or mesencephalon is a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision,
hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.
Forebrain
midbrain
hindbrain
2 Cerebral
hemisphere+ 2
lateral cavity
Deep
portion
(thalamus
&
hypothalamus
) with their cavity
( the 3
rd
ventricle )
Connect the
forebrain with
the hindbrain
Adequate
cerebellum
pons
Medulla
oblongata
Cerebellum
4
th
vemtricle
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
3
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
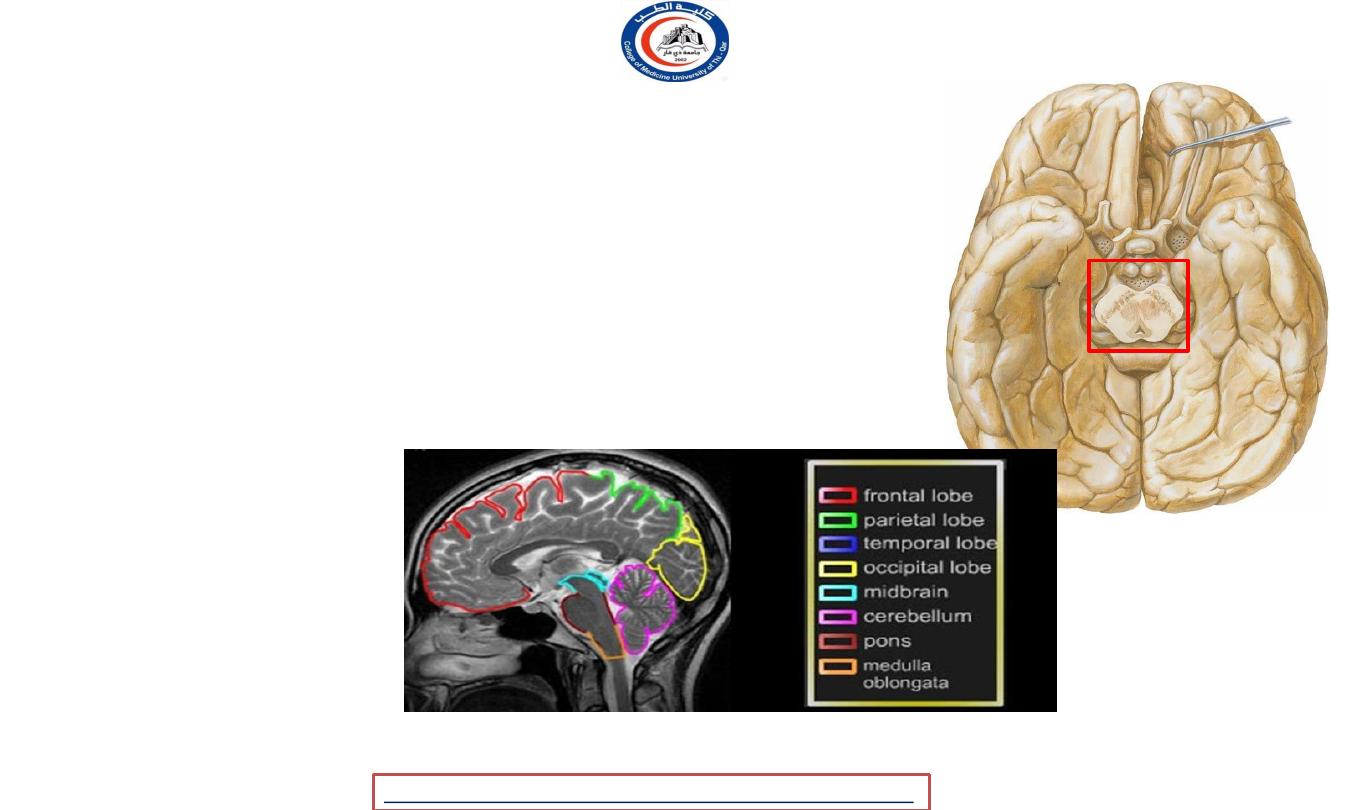
Midbrain
• connects
cerebellum
the pons
and
with
the
diencephalon ( structures lateral to the 3
rd
ventricle ).
• Specifically, the midbrain consists of :
Tectum“Corpora quadrigemina”
1.
inferior colliculi
2.
superior colliculi
cerebral peduncle
1.
midbrain tegmentum
2.
crus cerebri
3.
substantia nigra
Cerebral aqueduct :
connect the 3
rd
and
4
th
ventricles
4
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
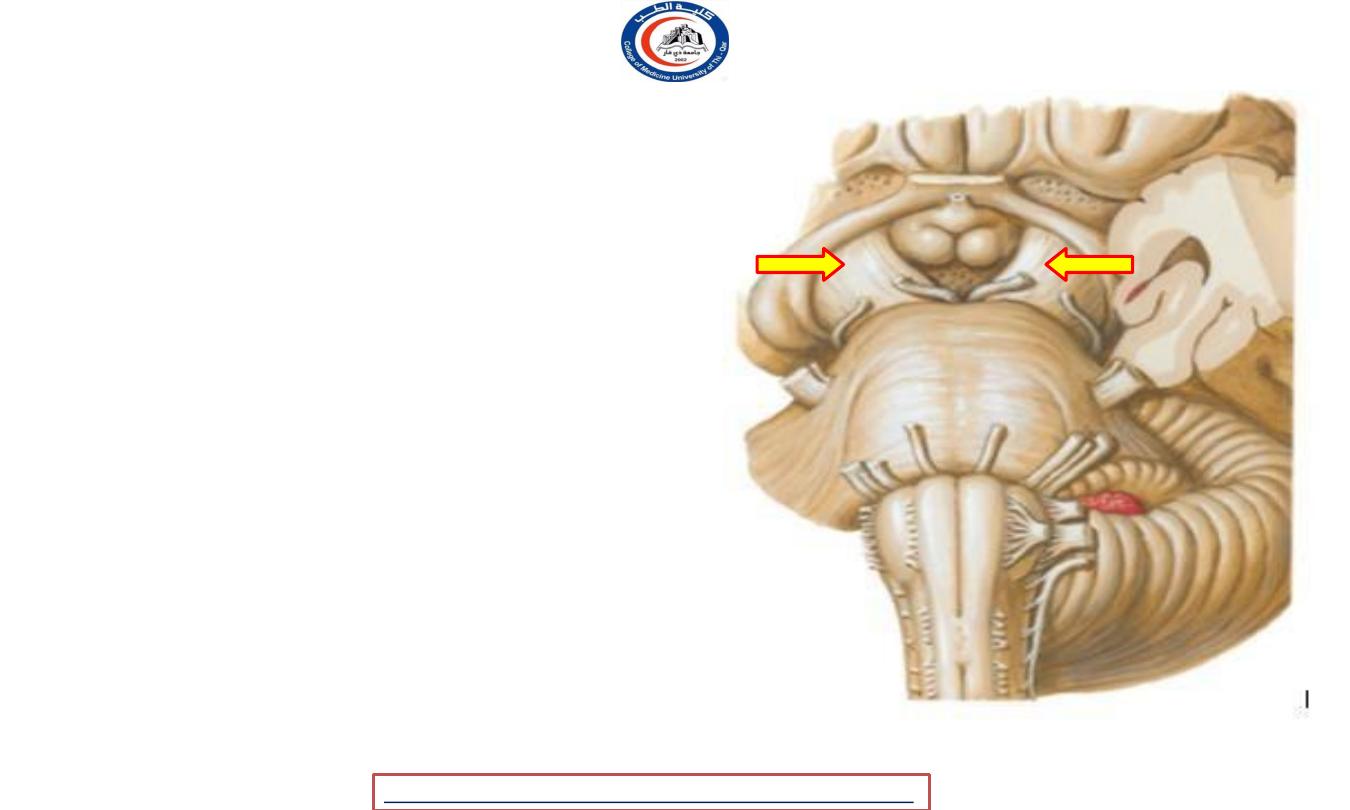
Cerebral peduncle
-
Two cylindrical masses situated at the base of
the brain largely hidden by the temporal
lobes
-
They emerge from the upper surface of the
pons & diverge as they pass upward to
disappear into the substance of the cerebral
hemispheres
-
The interpeduncular fossa between them is
occupied by the posterior perforated
substance
-
They are surrounded by the parahippocampal
gyrus & optic tracts
5
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
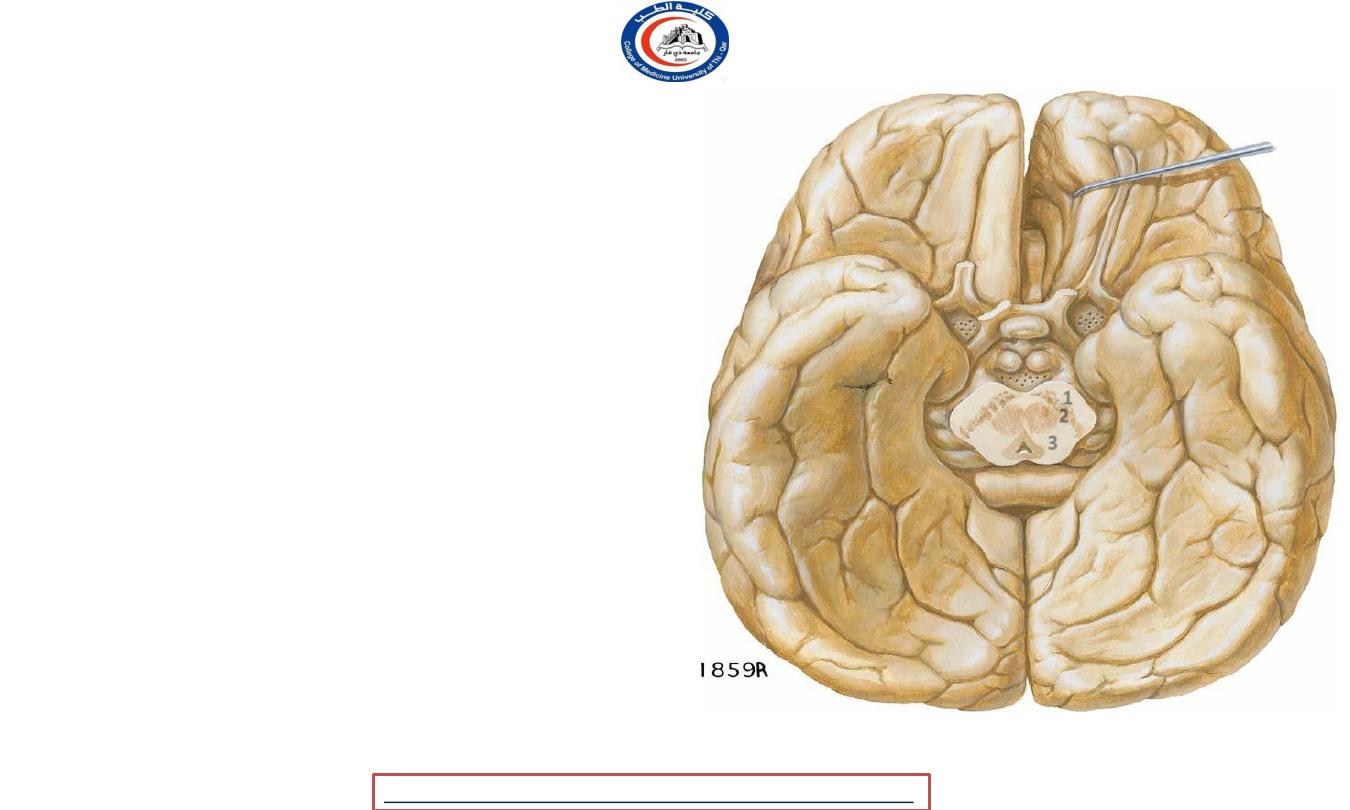
Cerebral peduncles
• The cerebral peduncles are structures at the
front of the midbrain which arise from the front
of the pons and contain the large ascending
(sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts
that run to and from the cerebrum from the
pons.
• Mainly,
the three common areas that give rise to
the cerebral peduncles are
the cerebral cortex,
the spinal cord and the cerebellum.
• The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is
everything in the midbrain except the tectum.
Cerebral peduncles include the
1.
Crus cerebri
2.
Substantia nigra
3.
Tegentum
1
2
3
6
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
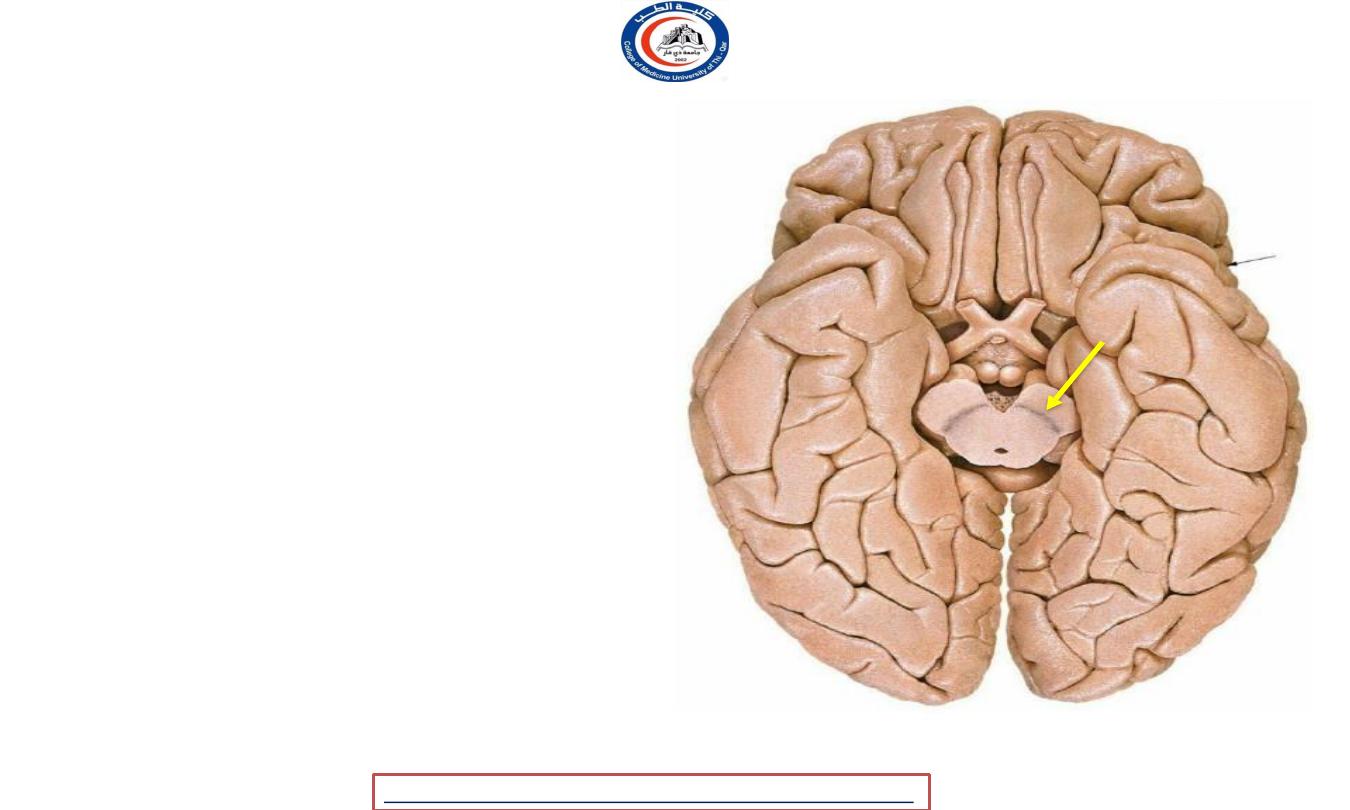
Crus cerebri
• The cerebral crus (crus cerebri) is the anterior
portion of the cerebral peduncle which contains
the motor tracts
• In some older texts this is called the cerebral
peduncle but presently it is usually limited to
just the anterior white matter portion of it.
• So, cerebral crus composed of nerve fibers ( It is
a white mater ) !
1.
Cortico-ponto-cerebellar fibers
2.
Corticonuclear fibers
3.
Corticospinal fibers
• PART OF THE MOTOR PATHWAY !!!
7
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
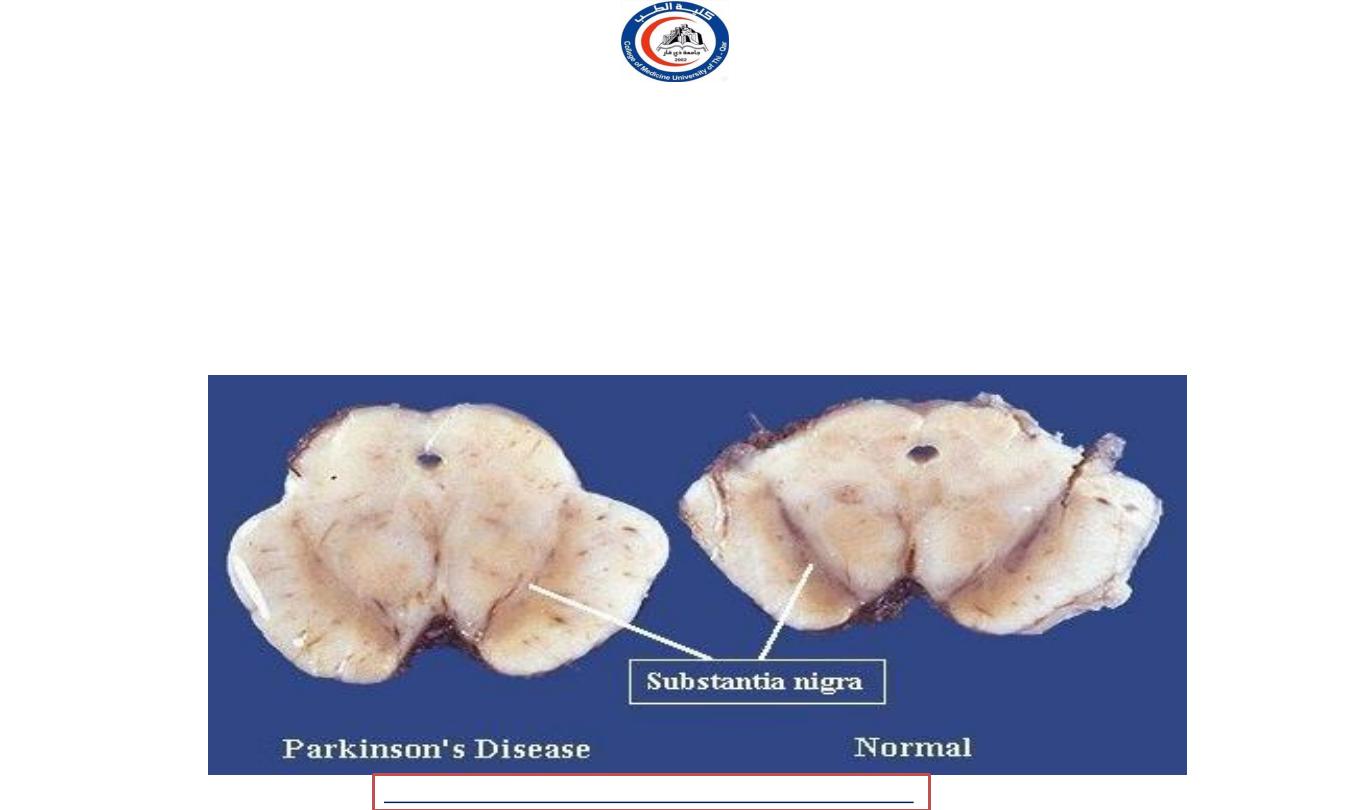
Substantia nigra
• Main afferent :
corpus striatum ( basal ganglia )
• Main efferent :
thalamus
• Functionally to the extrapyramidal system ..
• WILL BE STUDIED WITH THE EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM !!
8
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
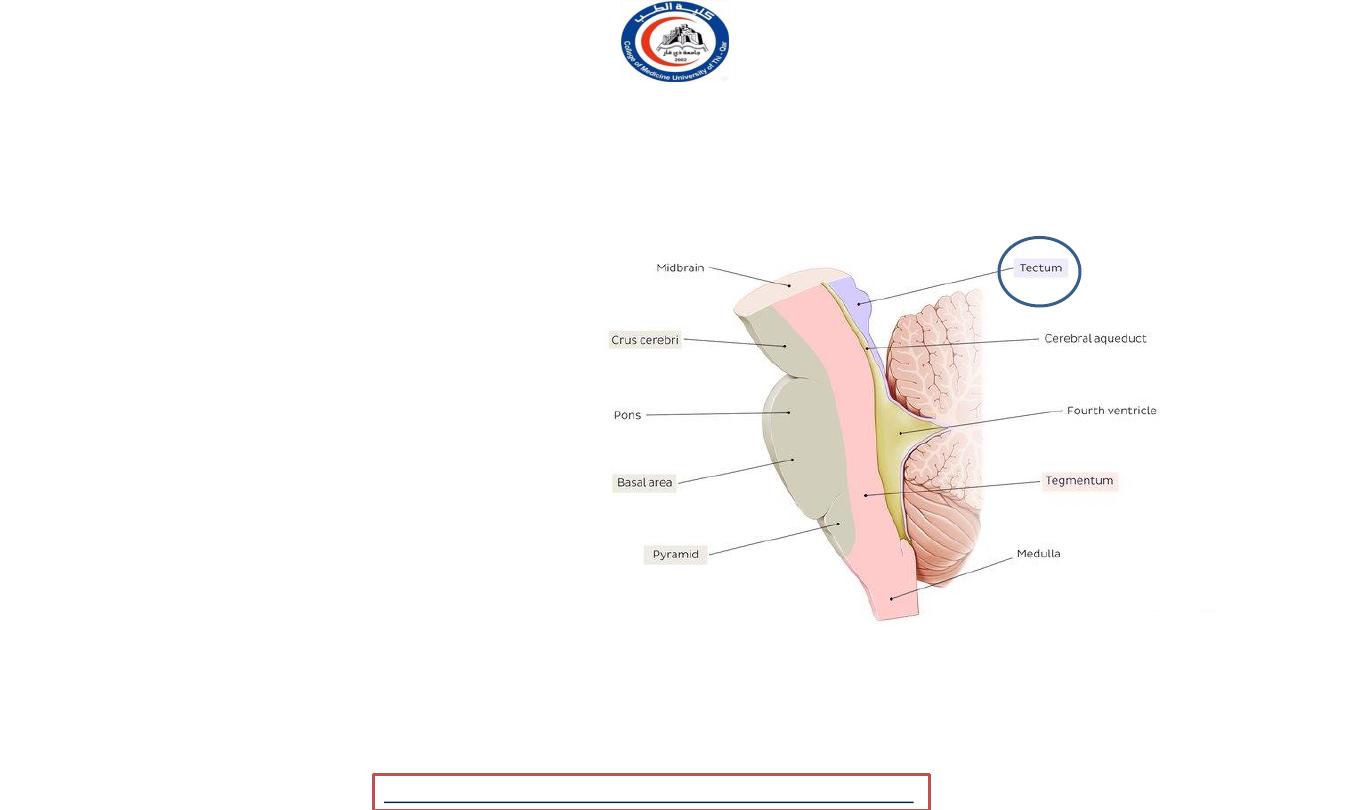
Tegmentum
1. Red nuclei
2. White mater
9
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
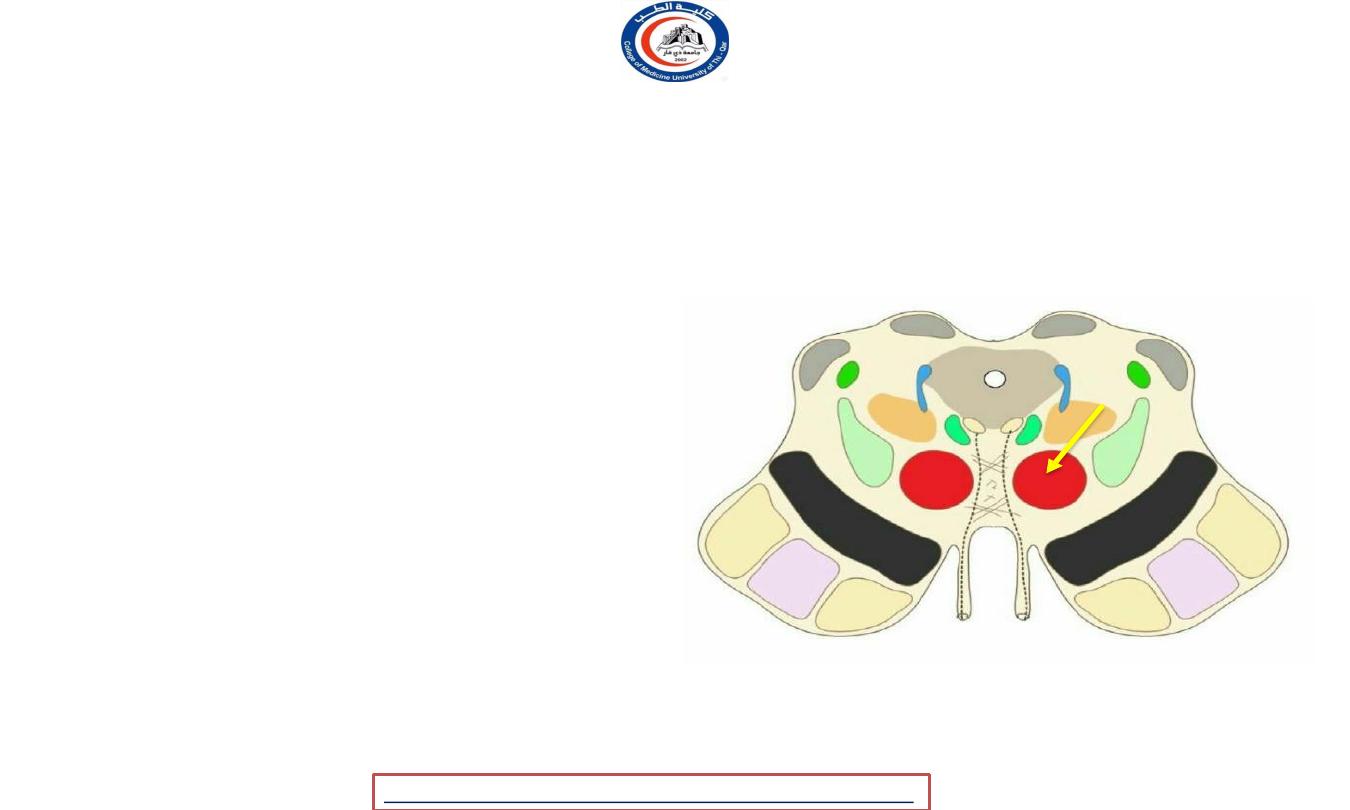
Red nucleus
• structure in the rostral midbrain
involved in
motor coordination
•
It is pale pink in color;
the color is believed to
be due to iron
, which is present in the red
nucleus in at least two different forms:
hemoglobin and ferritin
• It comprises a caudal
magnocellular
and a
rostral
parvocellular
part.
• It is located in the tegmentum of the midbrain
next to the substantia nigra.
•The red nucleus and substantia nigra are
subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor
system
.
10
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
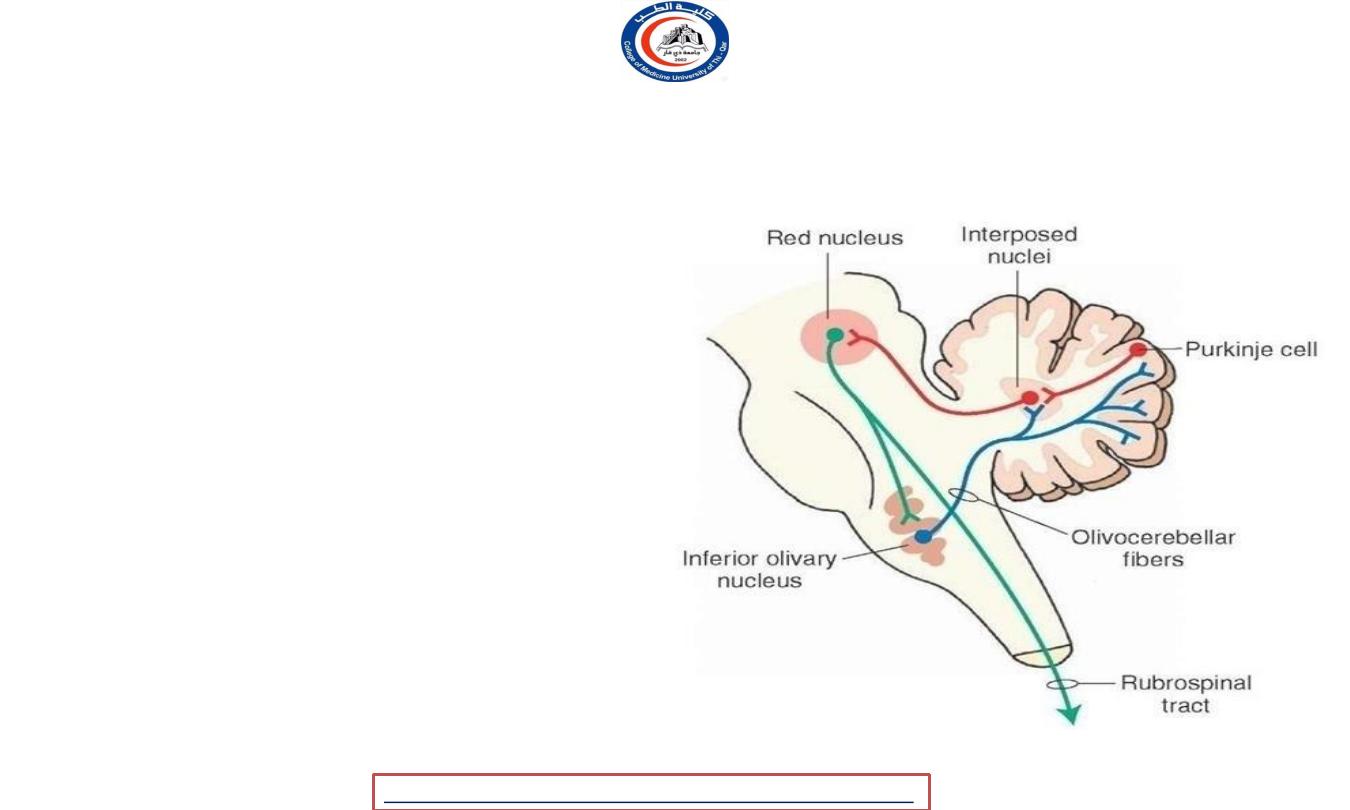
Red nucleus connections
• The red nucleus
receives
many inputs from the
cerebellum of the opposite side and an input from
the motor cortex of the same side.
• The red nucleus has two sets of efferents:-
1. In humans, the majority of the output goes to the
bundle of fibers continues through the medial
tegmental field toward the inferior olive of the
same side, to form part of a pathway that
ultimately influence the cerebellum.
2. The other
projection)
output (the rubrospinal
goes
to
the
rhombencephalic reticular formation and spinal
cord of the opposite side, making up the
rubrospinal tract
• because of the well-developed cerebral cortex, the
corticospinal tract has taken over the role of the
rubrospinal.
11
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

Red nucleus functions
• where the corticospinal tract is dominant (as in primates), the
rubrospinal tract may be considered to be vestigial
. Therefore,
here the red nucleus is less important in motor functions than
in many other mammals. However, the
crawling of babies
is
controlled by the red nucleus, as is arm swinging in typical
walking. The red nucleus may play an additional role in
controlling muscles of the shoulder and upper arm via
projections of its magnocellular part
. In humans, the red
nucleus also has sparse control over hands, as the rubrospinal
tract is more involved in large muscle movement such as that
for arms (but not the legs, as the tract terminates in the
superior thoracic region of the spinal cord).
Fine control of the
fingers is not modified by the functioning of the red nucleus
(rather it relies on the corticospinal tract)
12
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
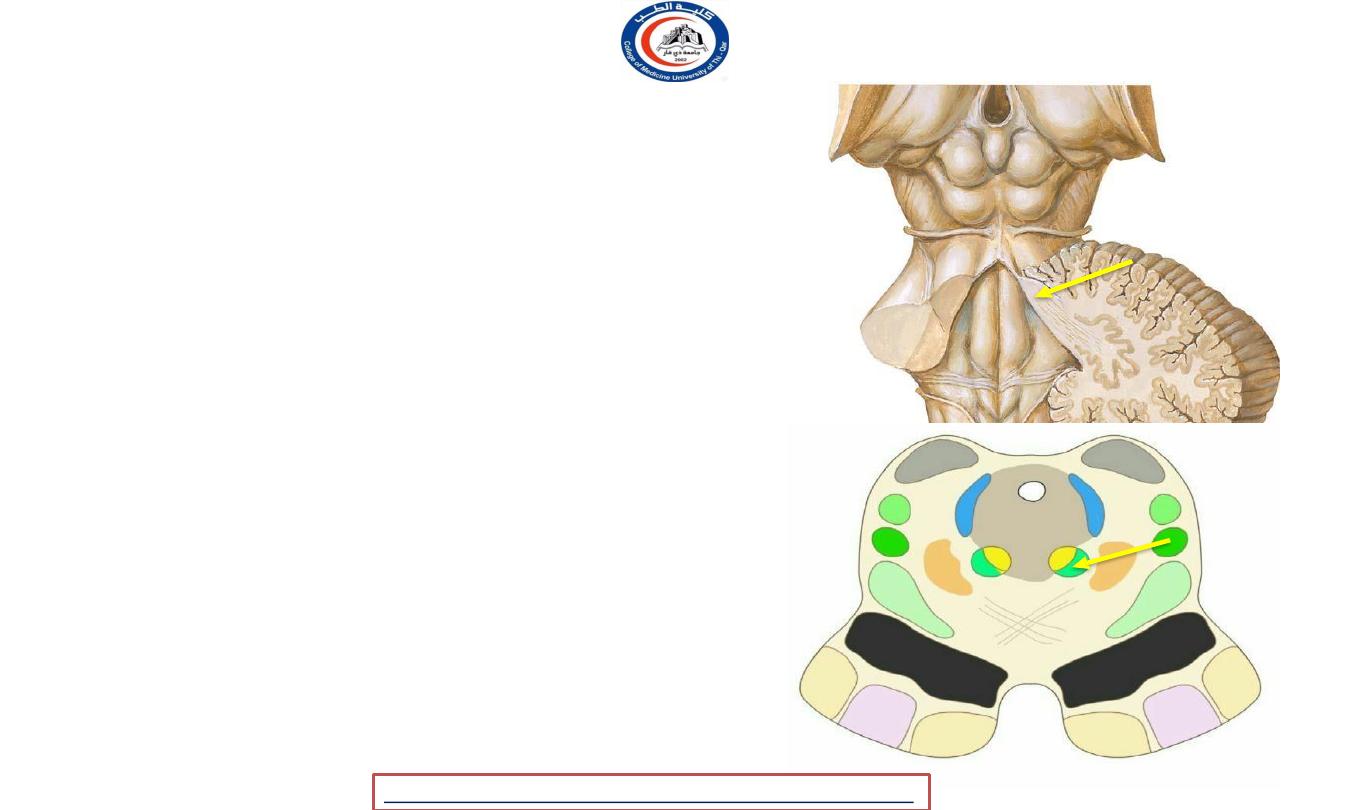
Tegmentum white mater
1. The superior cerebellar peduncle:
• Enter the midbrain tegmentum
• decussate at the level of the inferior colliculi on their
way to the red nuclei
2. The medial longitudinal
fasciculus:
• In the mid-brain it is situated on the ventral aspect
of the cerebral aqueduct
• It consists largely of fibers which connect the
nuclei of the hind- brain and mid-brain to each
other
• MLF is the main central connection for the
oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, and abducens
nerve.
13
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
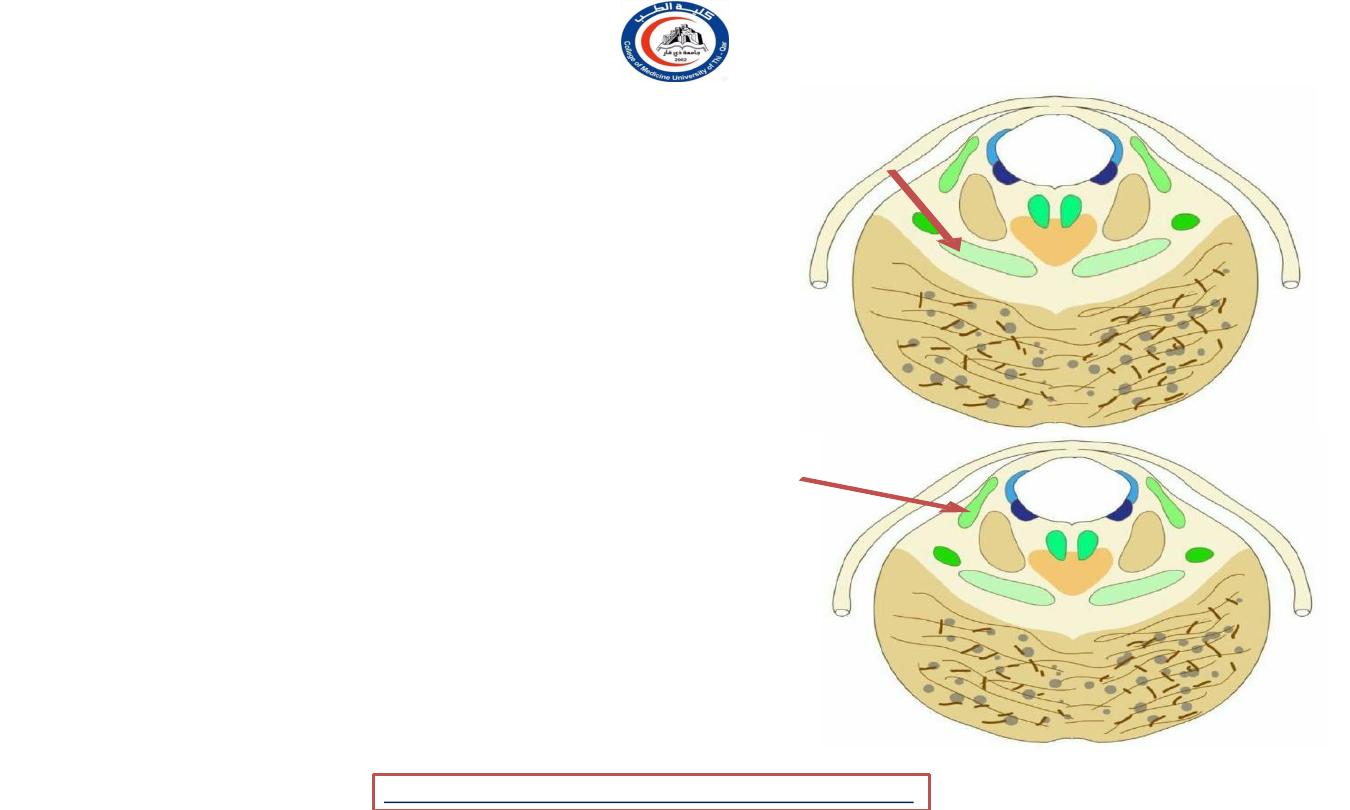
Tegmentum white mater
3. The medial lemniscus:
• -Arise in the gracile & cuneate nuclei of the
medulla ( of opposite site ) & decussate there as
internal arcuate fibres.
• -In the midbrain it attains dorsolateral position
4. The lateral lemniscus:
• From trapezoid body
• terminates, on cells of the inferior colliculus and
medial geniculate body for auditory reflexes
• Both the trapezoid body and lateral lemniscus
contain cell stations which make connexions
with the extraocular nuclei via the medial
longitudinal bundle.
14
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

Tegmentum white mater
5.
The vestibulospinal tract:
-Arise in the vestibular nuclei
-Some of them descend in the spinal cord & some
ascend in the tegmentum of the midbrain
6.
The tectospinal tract:
-Arise in the superior colliculi
-Decussate
& descend
near
the midline
7.
The rubrospinal tract:
-Arise in the red nucleus
-Cross the midline & descends into the
lateral funiculus of the spinal cord
15
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
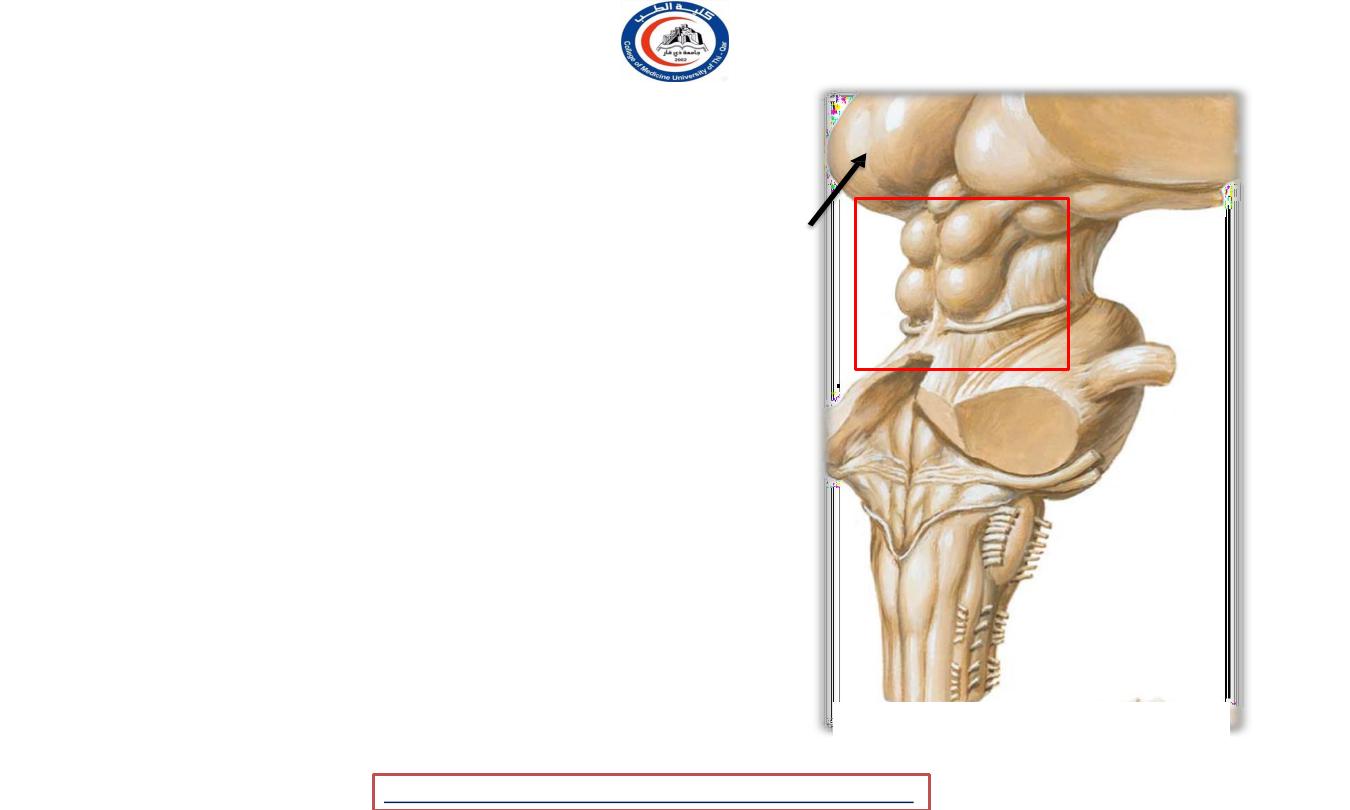
Corpora quadrigemina ( tectum )
• Tecum is region of the brain, specifically the
dorsal
part of the midbrain
• Corpora quadrigemina are the
four colliculi—
two
inferior, two superior—located on the tectum of
the dorsal aspect of the midbrain.
• The corpora quadrigemina are
reflex centers
involving vision and hearing
Pulvinir
16
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
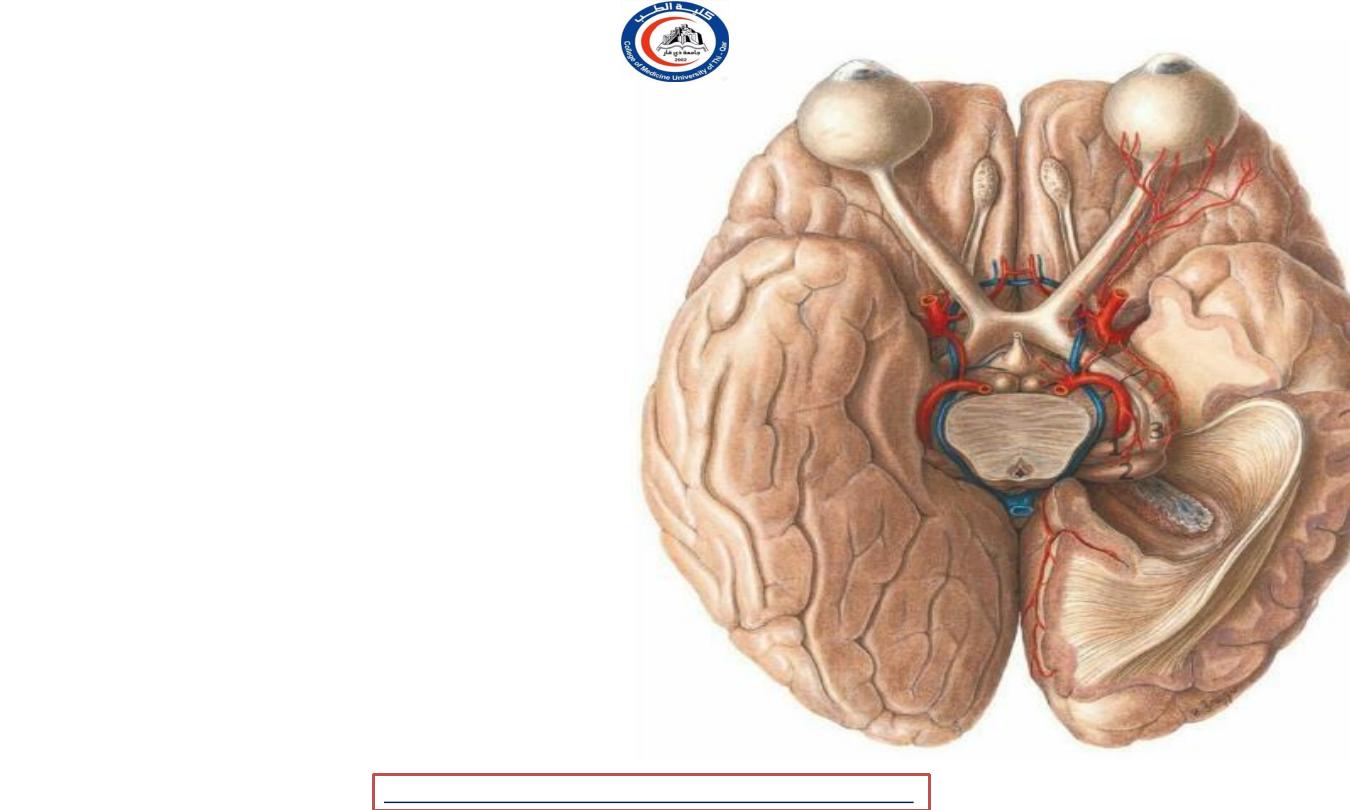
Superior colliculi
• The brachium of superior
colliculus
(or
superior
brachium)
extends
from
colliculus,
the
and,
laterally
superior
passing
between
the
pulvinar ( not shown )
and
medial geniculate
body
continued
into
eminence
called
(1)
, is partly
an the
lateral geniculate body
(2)
, and partly into the
optic
tract (3) .
1
2
3
17
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
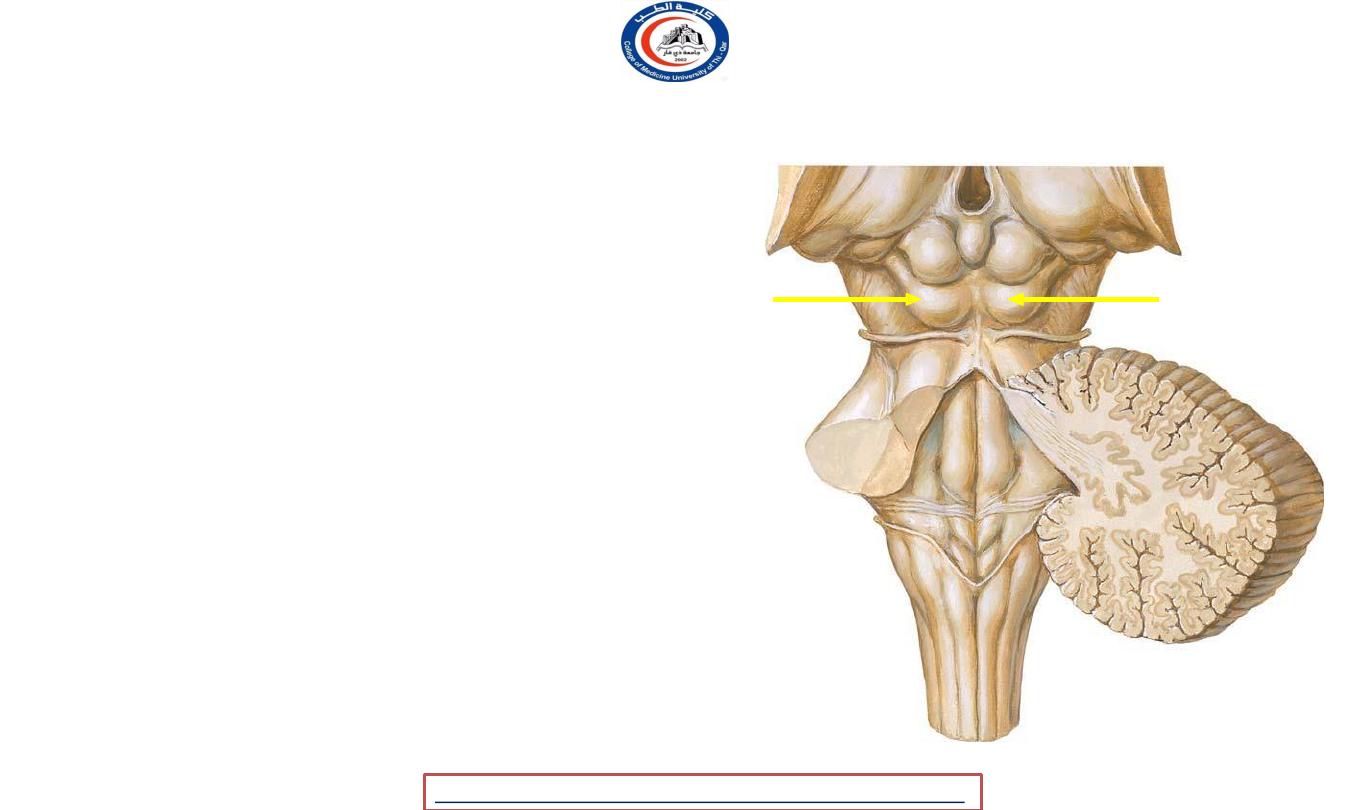
Inferior colliculi
• principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory
pathway
and receives input from several
peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory
pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory
cortex.
• Its bimodal neurons are implied in
auditory-
somatosensory interaction
, receiving projections
from somatosensory nuclei. This
underlie a filtering of
effected
sounds
vocalization,
chewing,
multisensory integration may
self- from
or
respiration activities
• Inferior brachium
pass to the
medial geniculate body
18
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
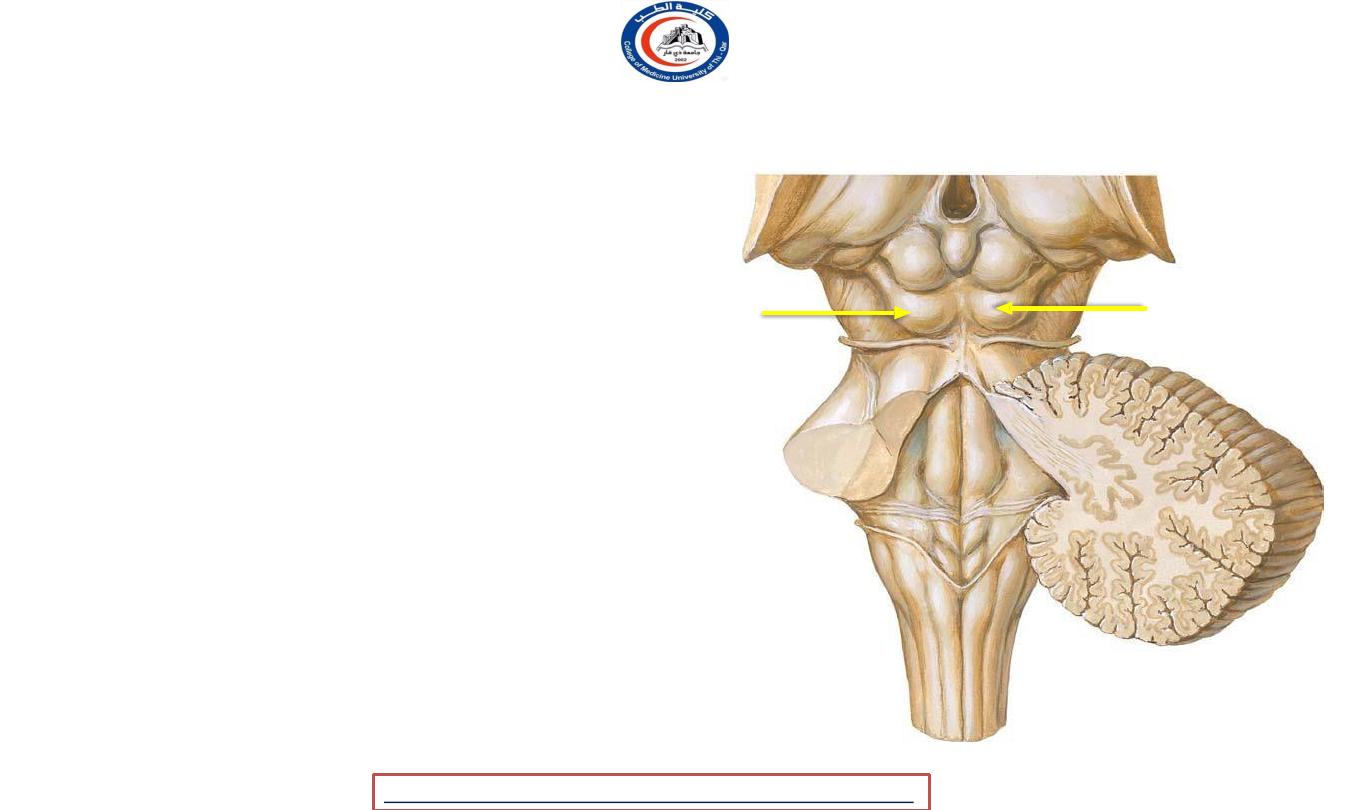
Note
• Lateral geniculate and medial geniculate
bodies are part of the diencephalon (
Forebrain ) !!
19
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
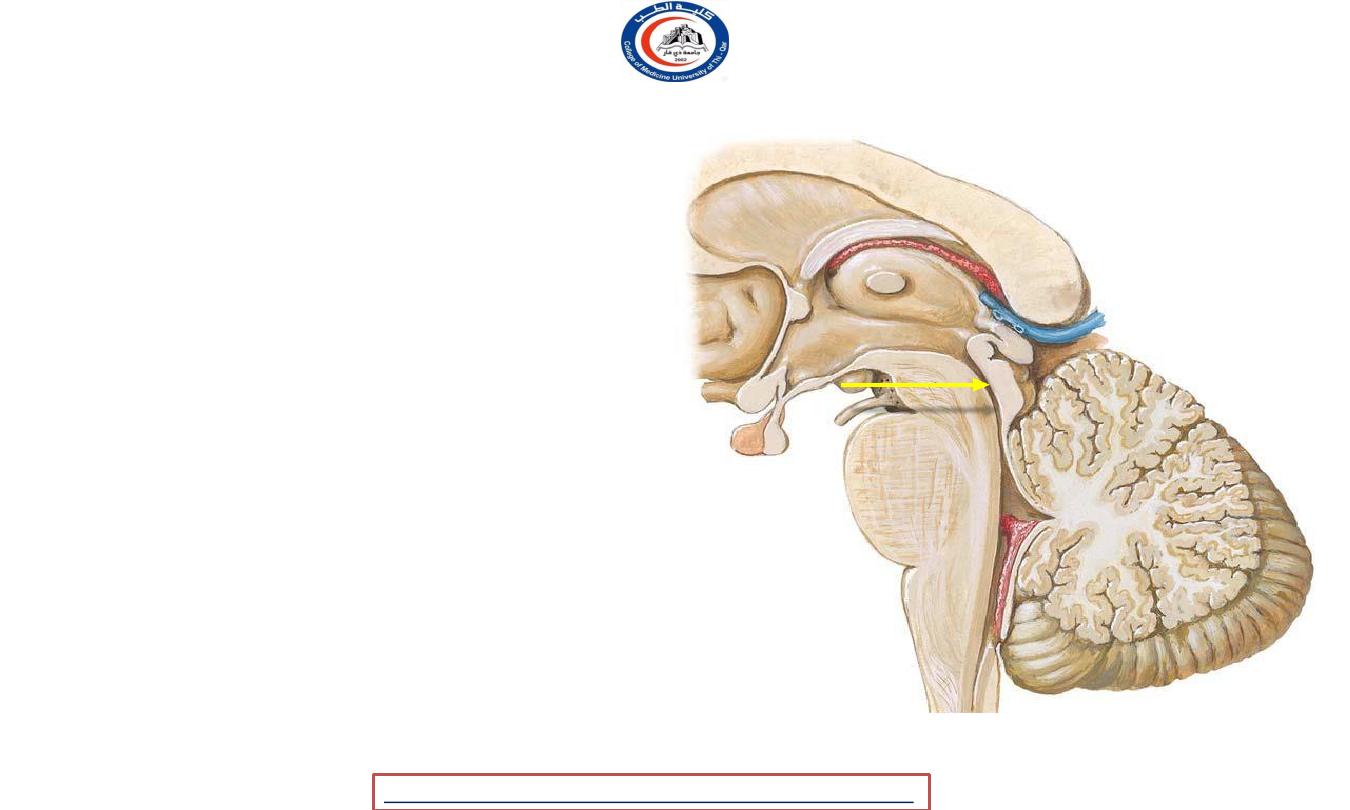
Cerebral aqueduct
• 1.8 cm long
• Traverses the midbrain
• Surrounded by a layer of gray
matter called the
(periaqueductal)
no
choroid
central
gray
• Contains
plexus
• Transmits
CSF from the
third
to
the
fourth
ventricle
20
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
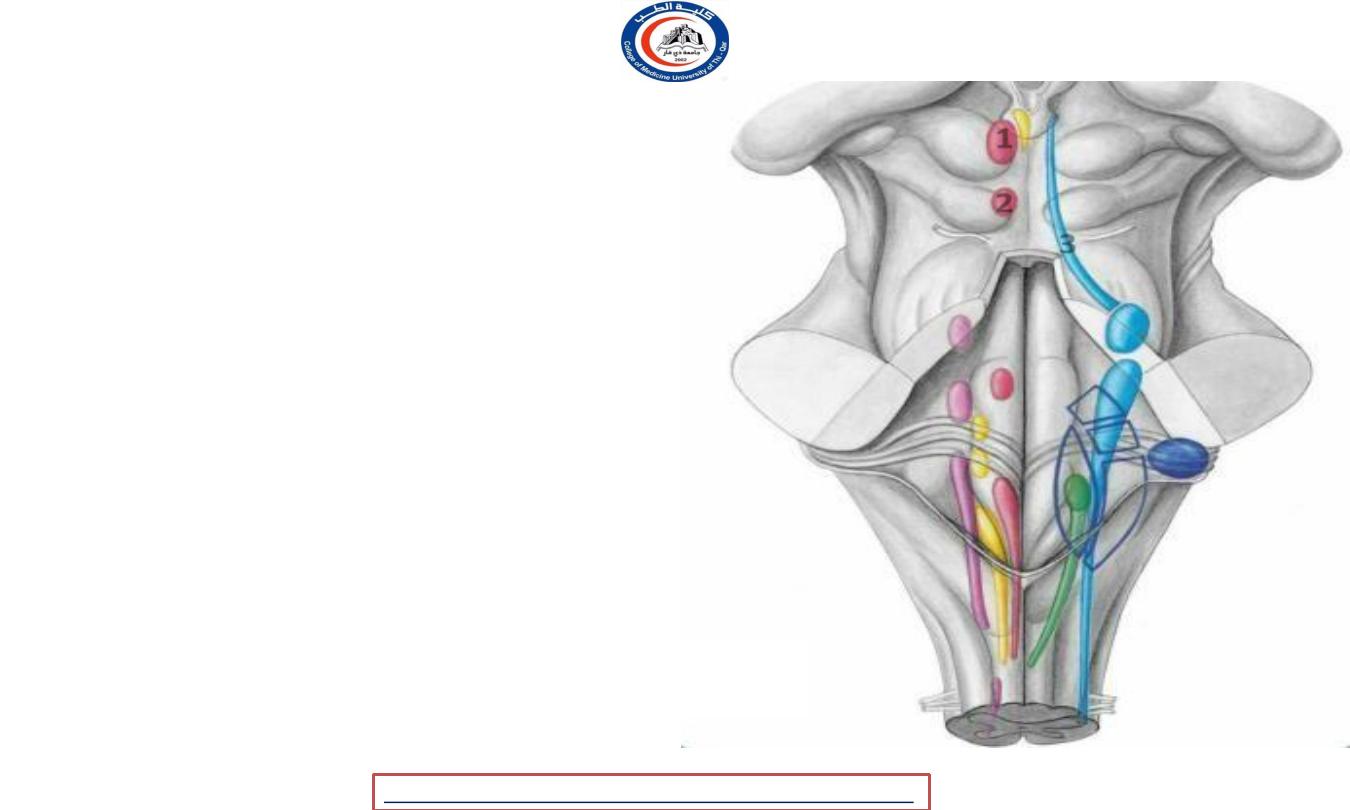
Nuclei in periaqueductal grey mater
• 1) The nuclei of oculomotor nerve
(level with the superior colliculi)
• 2) The nucleus of the trochlear nerve
(level
with the inferior colliculi
the
• ( 1 & 2 lie in the ventral part of the gray )
• 3- The mesencephalic nucleus of the
trigeminal
nerve
extends along
the entire
length of the
aqueduct in the lateral part of gray
1
2
3
21
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Oculomotor nerve
Nerve
Modality
Nuclei
Location
Distribution
Parasympathetic
innervation to
Edinger-
sphincter pupillae and
SVE
wesphal
Midbrain
ciliary
nucleus
muscles that constrict
Oculomotor
pupil and
nerve
accommodate lens of
eye
To eye muscles except
Nucleus of
lateral rectus (
GSE
oculomotor
Midbrain
abducens ) and
nerve
superior oblique (
trochlear
22
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
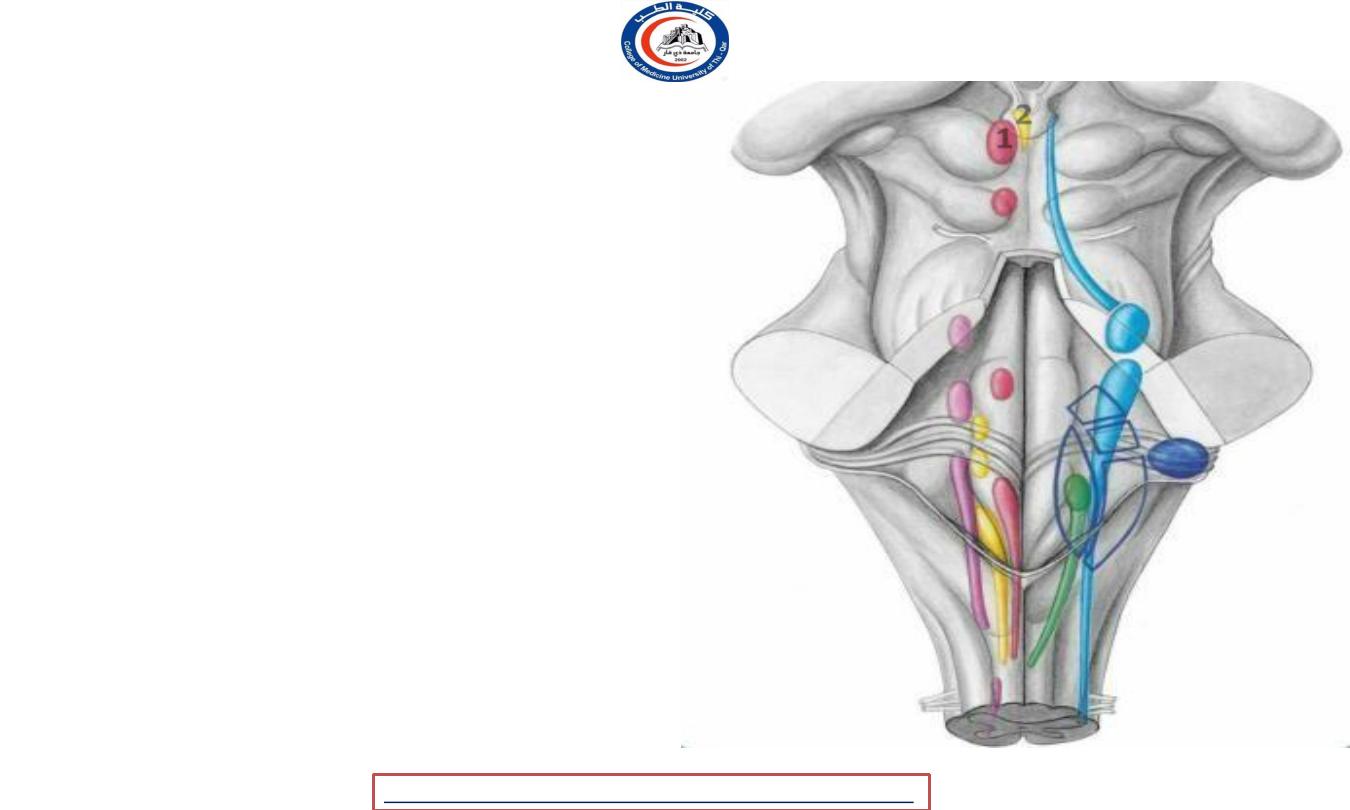
Oculomotor nerve
nuclei
1 E-W nuclei
2 motor nucleus
2
1
23
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
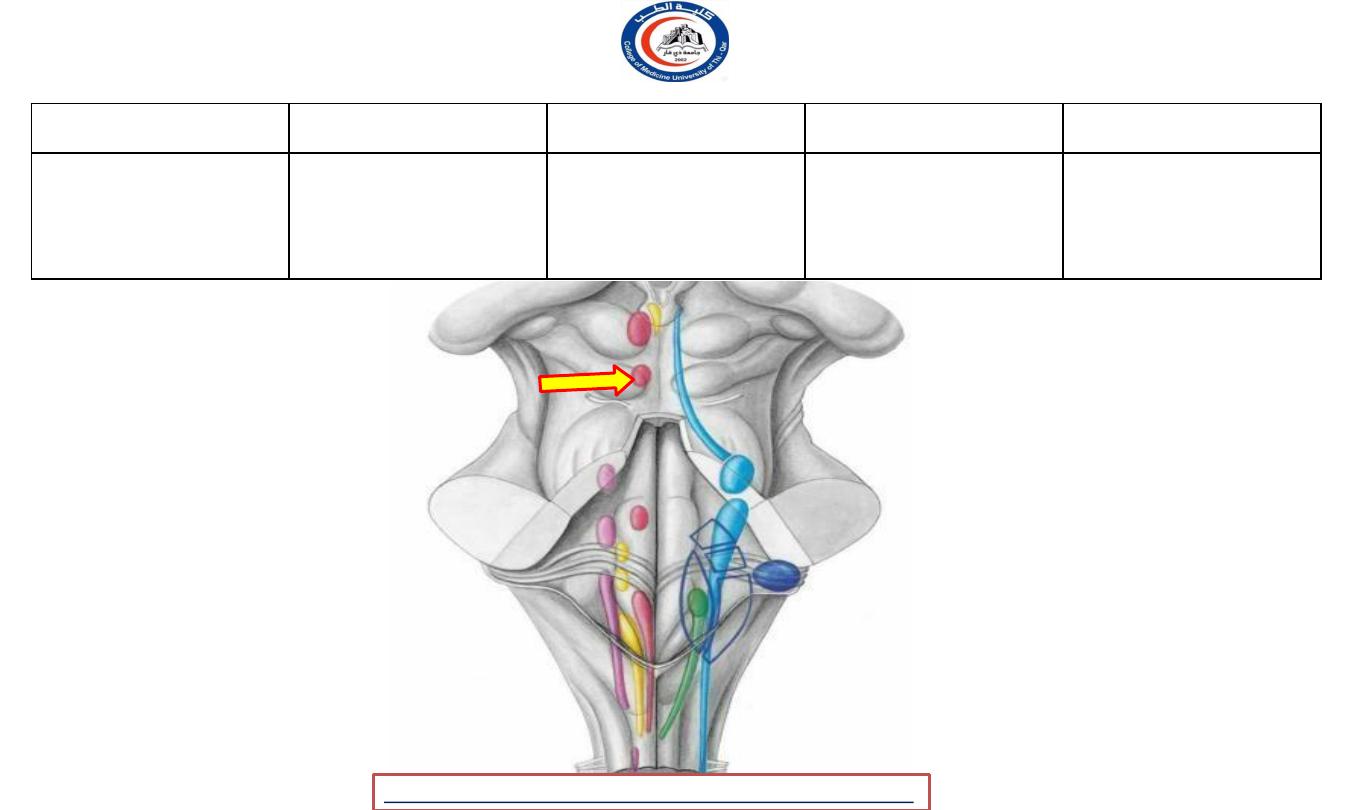
Trochlear nerve
Nerve
Modality
Nucleus
Lcation
Distribution
Trochlear
nerve
GSE
Nucleus of
trochlear
nerve
Midbrain
To superior
oblique
muscle
24
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
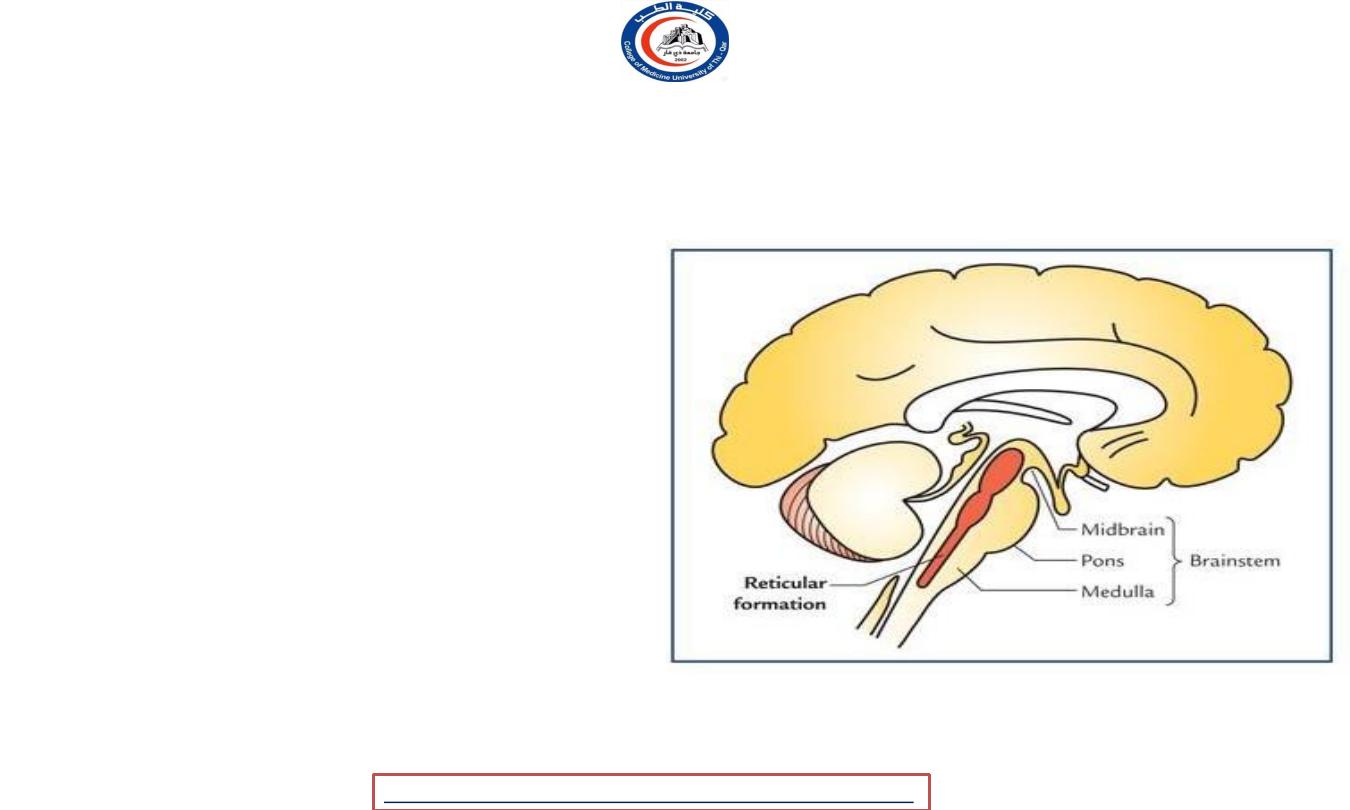
Reticular formation
• Gray and white mater
• More in the tegmentum ( midbrain )
• Upward connection thalamus and
cortex.
• Downward connection to spinal cord.
• RF is filter for stimuli !!
-
Prevent repetitive stimuli
-
Enhance infrequent stimuli
-
Allow important repetitive stimuli for example
the pain stimuli
• Sleep RF
• RF diseases Grades of coma !?
• GA ( general anesthesia ) drugs act on RF !
• Analgesic drugs have one of its
mechanism action through the RF
25
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
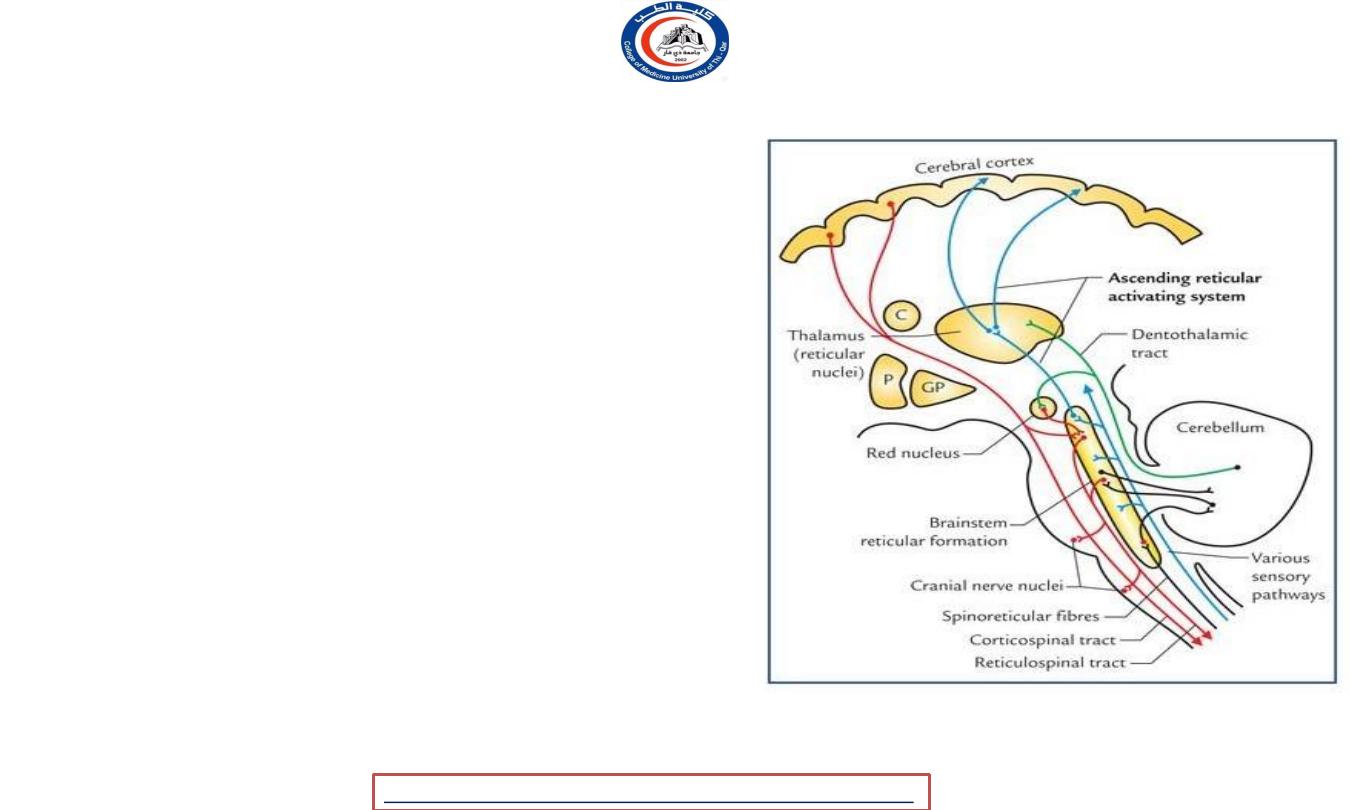
Reticular formation connections
• Afferent from :-
1.
Various
sensory pathways
and systems
2.
Other parts of CNS
3.
Factors infleucing the activity of RF (
e.g. drugs and hormones )
• Efferent to :-
1. Autonomic and locomotor control centres of
brainstem and spinal cord.
2. Cranial nerve nuclei, e.g. dorsal
nucleus of vagus.
3. Cerebral cortex—indirectly through
diencephalic nuclei.
4. Red nucleus, substantia nigra and
tectum of midbrain
.
26
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
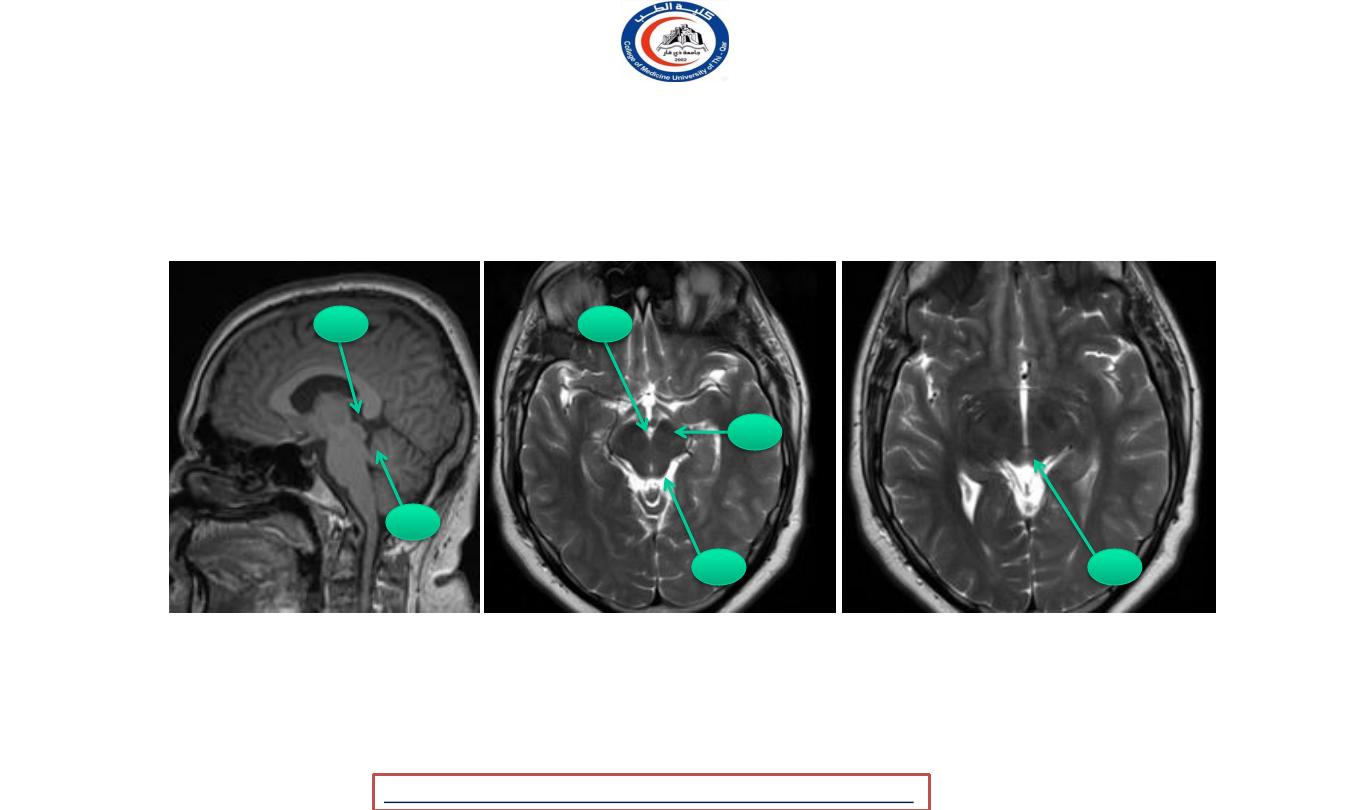
27
1
1
2
2
3
4
1 Superior colliculus
2 Inferior colliculus
3 Cerebral peduncle
4 Interpeduncular cistern
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

28
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Thank you with best wishes
