LANDSAT OBSERVATİON
SATELITE SYSTEM
Landsat satellites have been collecting images
of the Earth's surface for more than thirty
years. NASA launched the first Landsat
satellite in 1972, and the most recent one,
Landsat 7, in 1999. Instruments onboard the
satellites have acquired millions of images of
the Earth. These images provide a unique
resource for people who work in agriculture,
geology, forestry, regional planning,
education, mapping, and global change
research

TIROS
The Television Infrared Observation Satellite Program
(TIROS)
The TIROS Program (Television Infrared Observation Satellite) was NASA's first
experimental step to determine if satellites could be useful in the study of the Earth.
At that time, the effectiveness of satellite observations was still unproven. Since
satellites were a new technology, the TIROS Program also tested various design
issues for spacecraft: instruments, data and operational parameters. The goal was to
improve satellite applications for Earth-bound decisions, such as "should we evacuate
the coast because of the hurricane?".
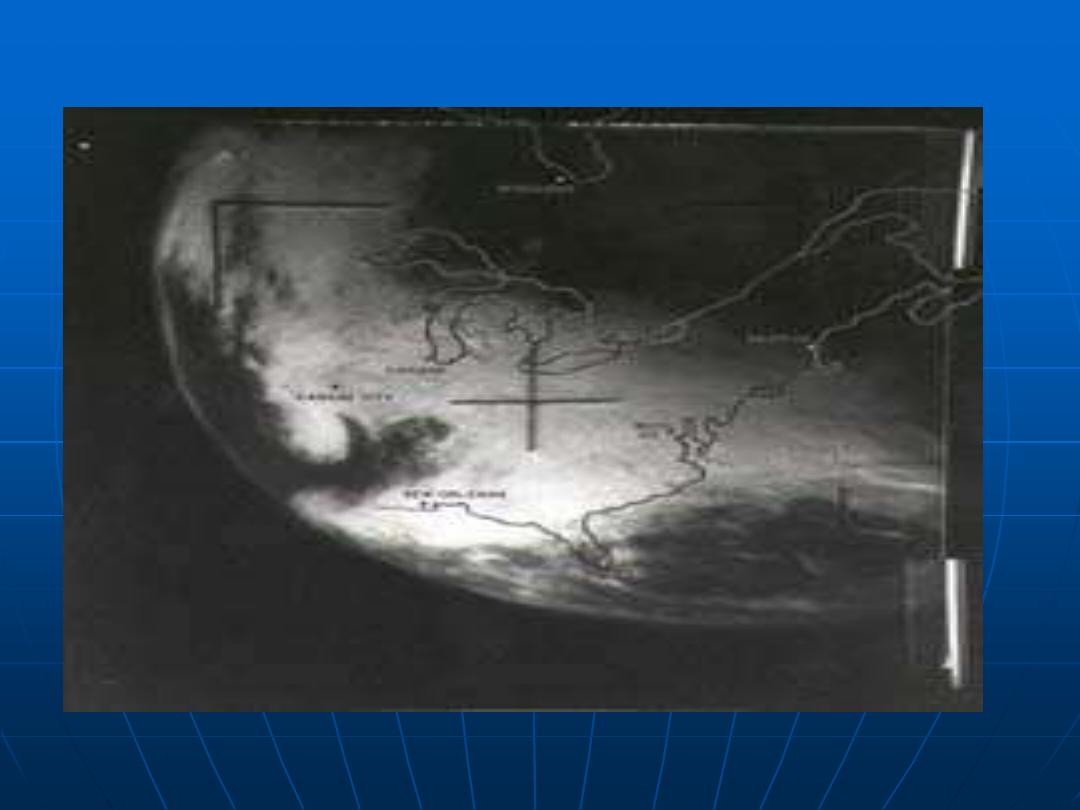
The TIROS Program's first priority was the development of a meteorological satellite
information system. Weather forecasting was deemed the most promising application
of space-based observations.
TIROS proved extremely successful, providing the first accurate weather forecasts
based on data gathered from space. TIROS began continuous coverage of the Earth's
weather in 1962, and was used by meteorologists worldwide. The program's success
with many instrument types and orbital configurations lead to the development of
more sophisticated meteorological observation satellites

AVHRR
ADVENCED VERY HIGH RESOLUTION
RADİOMETER
The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR)
provides four- to six-band multispectral data from the
NOAA polar-orbiting satellite series. There is fairly
continuous global coverage since June 1979, with morning
and afternoon acquisitions available. The resolution is 1.1
kilometer at nadir
.
Visible, NIR, Thermal
1.1 km Resolution - local area coverage (LAC)
4 km Resolution - global area coverage (GAC)
Used for meteorological studies
Vegetation pattern analy

LANDSAT (ERTS) - Earth
Resources Technology Satellite
.
The Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS) mock-up in a
space chamber test at General Electric's Space Division. The ERTS
program represented a concentrated effort to observe and
monitor the limited resources of the Earth, in order to best
conserve and utilize the resources in support of a burgeoning
world population. The first ERTS was launched in 1972 and was
later named Land Remote-Sensing Satellite (Landsat), to better
represent the civil satellite program's prime emphasis on remote
sensing of land resources. Multiple sensors survey and relay back
masses of data in various ways from the Landsat. NASA has built
7 Land Remote Sensing Satellites, which have helped agricultural
experts pick up underutilized land areas and new prospects for
land use through irrigation. It has also assisted in pinpointing the
spread of crop disease and in charting new uses of the sea for
oceanographers.
Visible, NIR spectral bands (Landsats 1,2,3), and MIR and
Thermal (Landsats 4
and 5)

Sensors
Multispectral scanner (MSS)
The MSS instrument has operated on the
first five Landsat spacecraft. Although the basics of scanning spectroradiometric
sensors were reviewed earlier in this Section, because of MSS's important role in
these missions which extended over 31 years some of this information is repeated
and expanded on this page. A simplified model of this optical-mechanical sensor
appears in the next figure
.
On Landsats 1,2,3,4,5
60 meter resolution
128 brighness values (radiometric resolution)
4 spectral bands
Green, Red, and 2 NIR
570 mile orbit (for Landsat 1,2,3)
Oscillating mirror design
One swath = 185 km x 474 meters
Each spectral band has 6 detectors
474 Meters / 6 Detectors = 79 Meter ground resolution

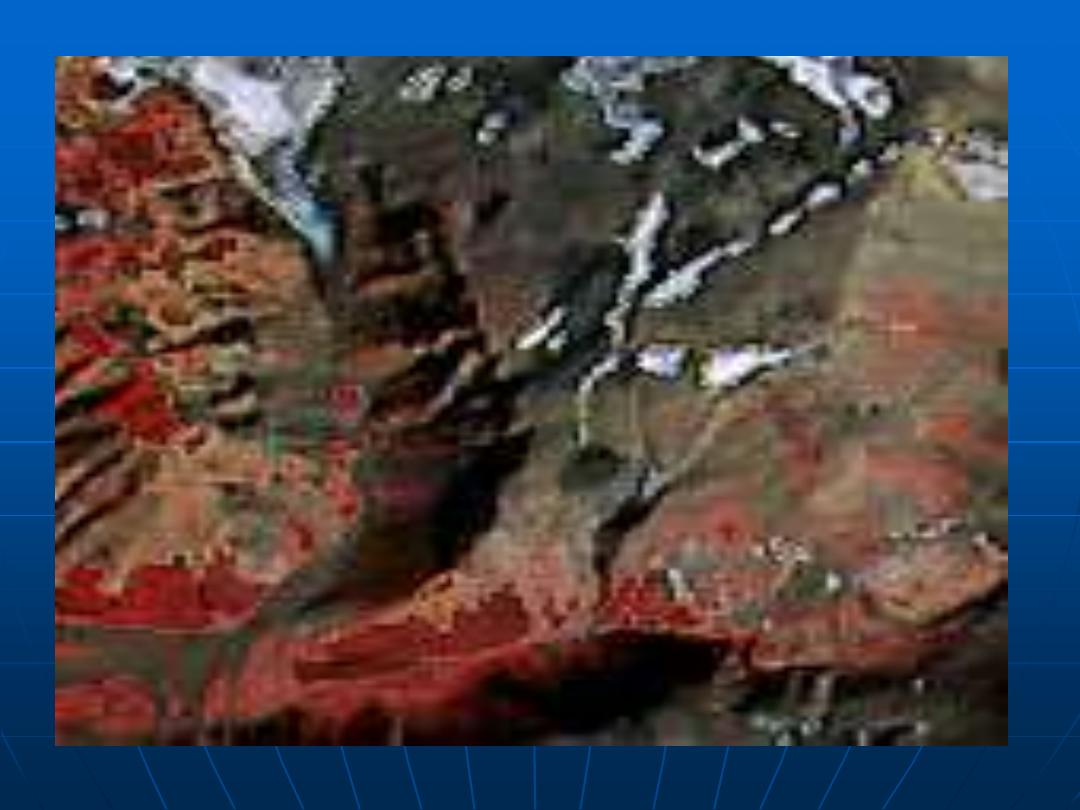
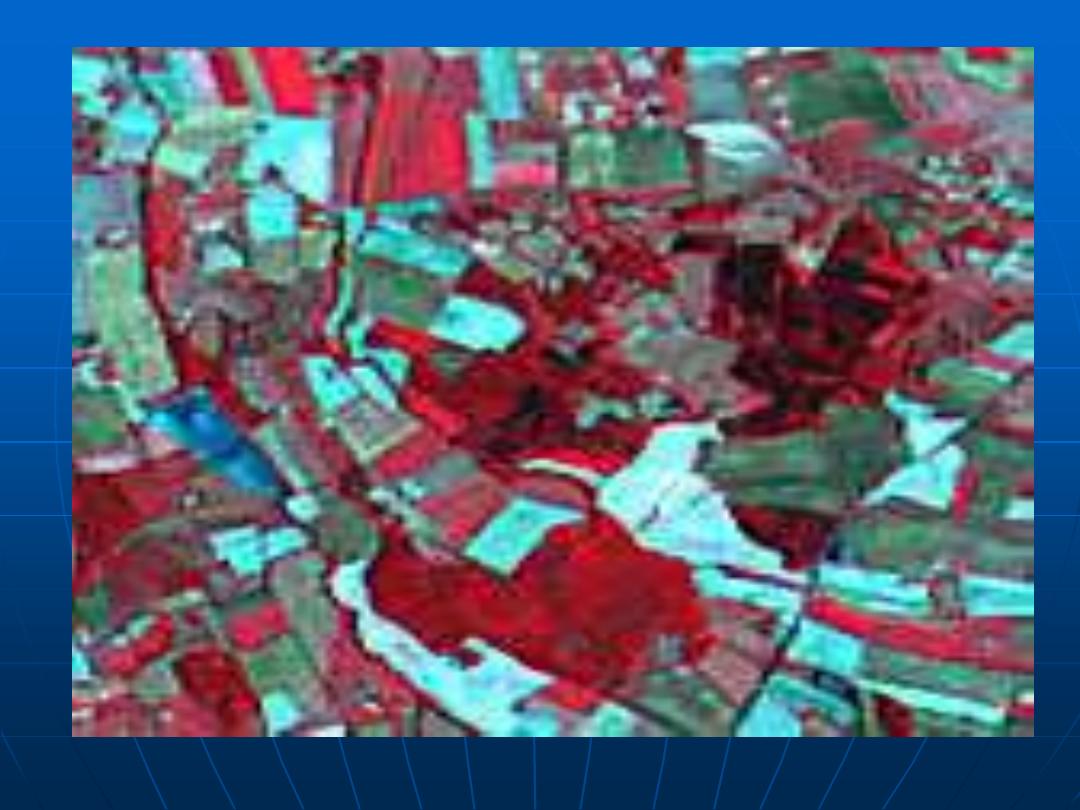
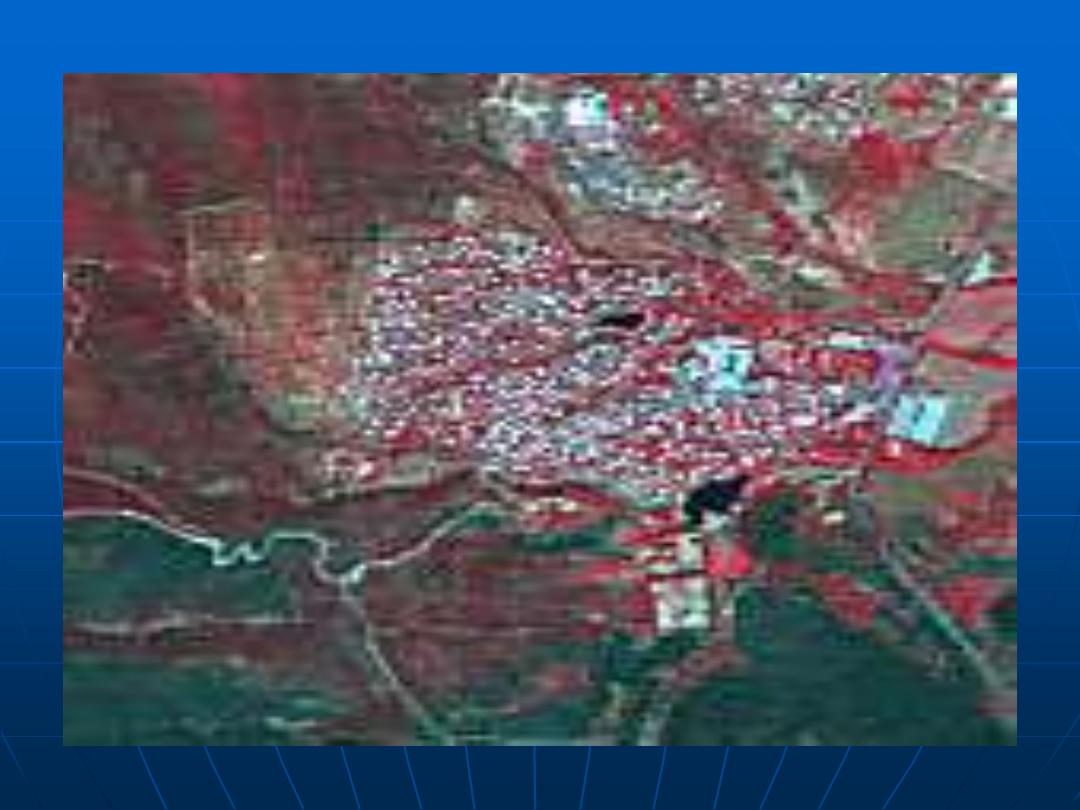
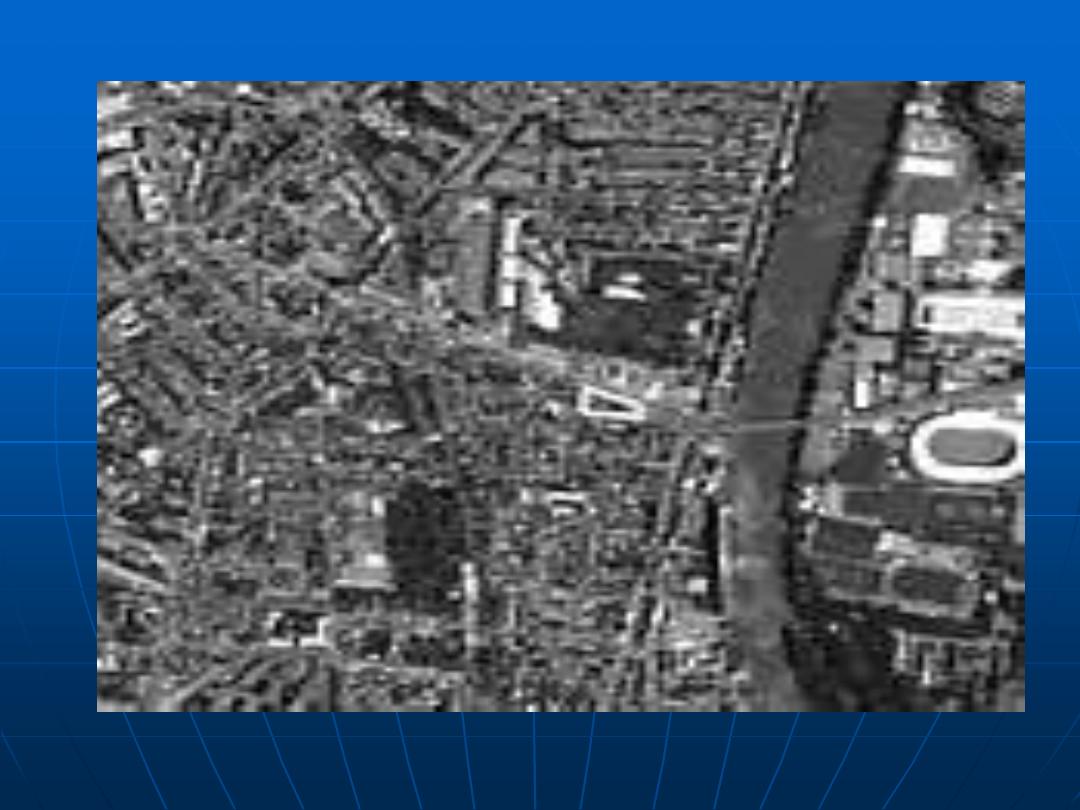
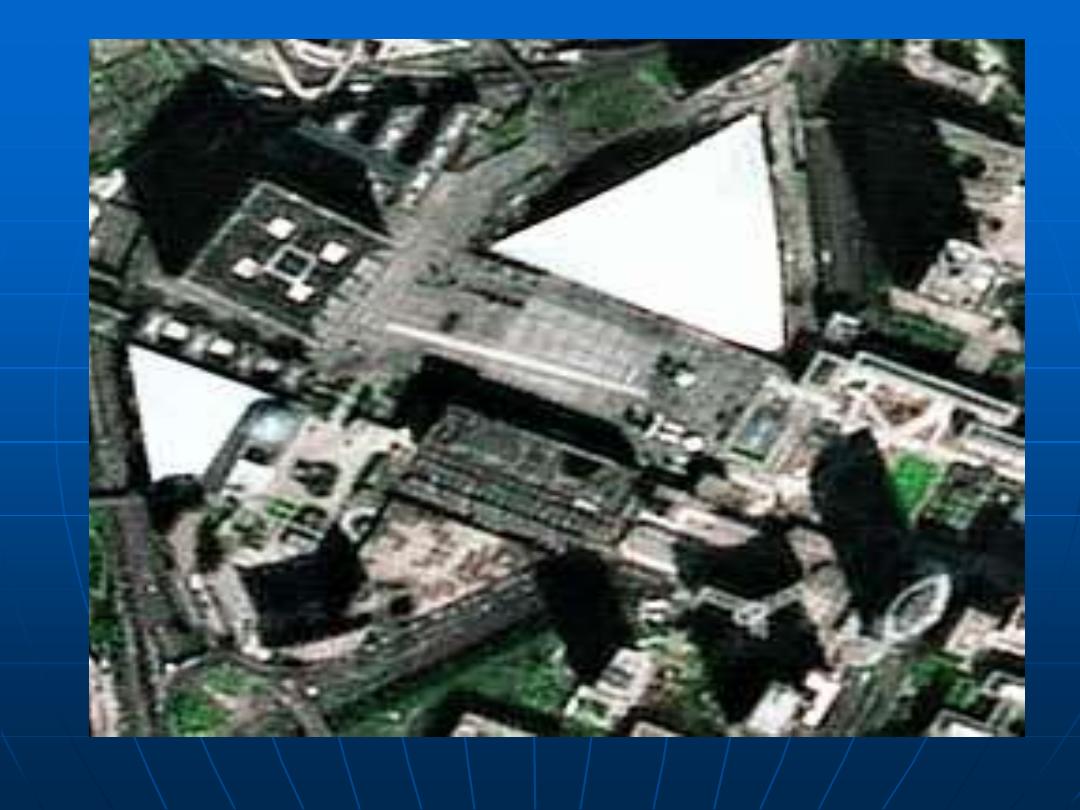
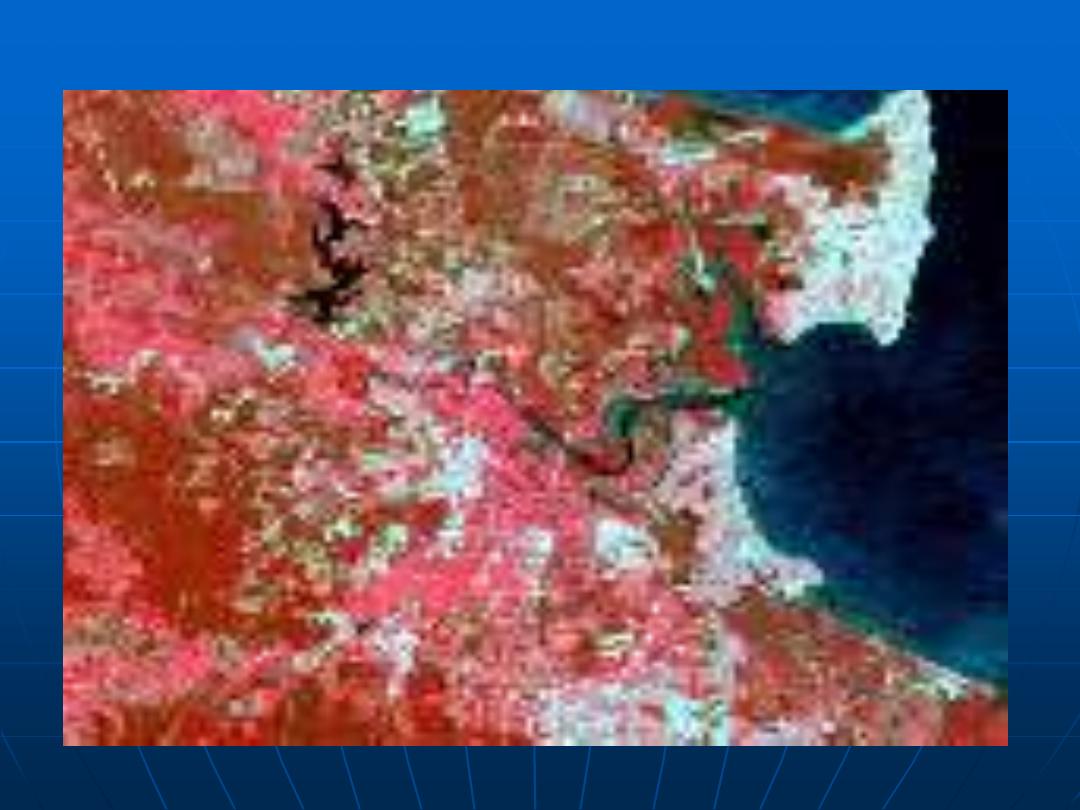
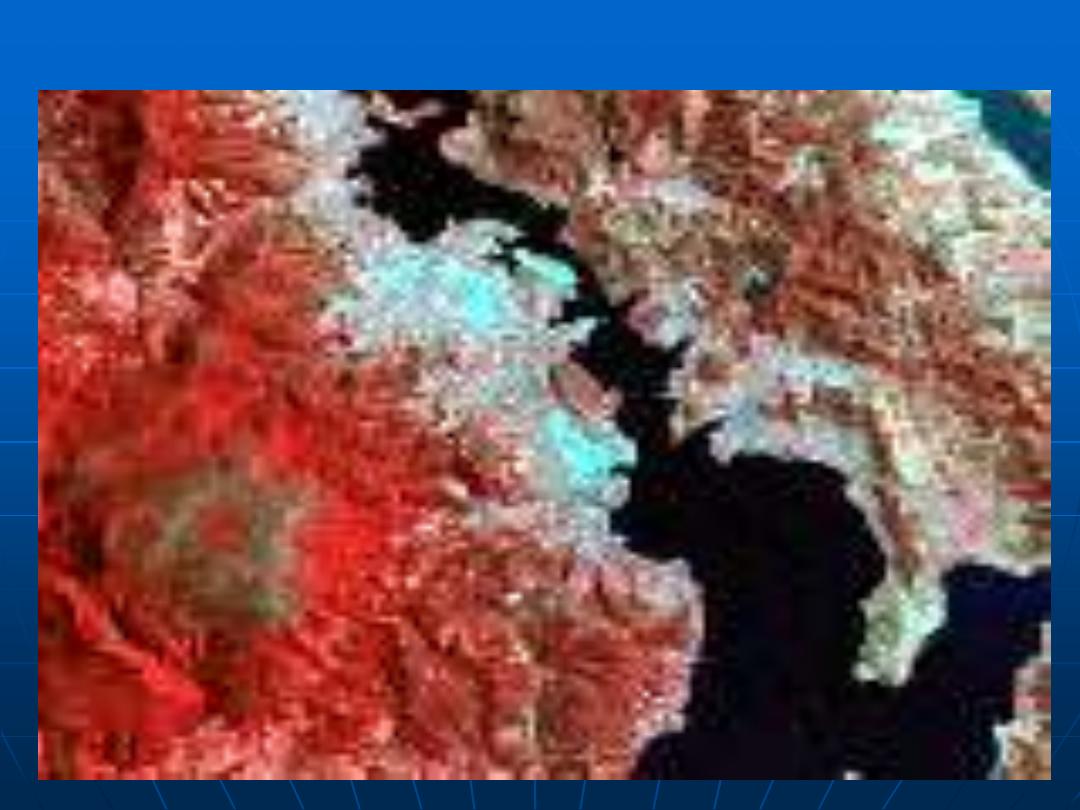
This data set consists of a series of Landsat Multispectral Scanner
scenes. Small regions have been selected from full scenes over the
capital cities in Australia





Thematic mapper (TM)
The Multispectral Scanners (MSSs) were the first Thematic Mapper (TM).
Based upon the success of the Multispectral Scanner, the Thematic
Mapper, a second-generation sensor for monitoring Earth's resources, was
developed for Landsats 4 and 5. The MSS was also carried on these
spacecraft to provide data continuity. The TMs on Landsats 4 and 5 have
better spatial, spectral, and radiometric resolution and extend spectral
coverage into the blue, the short-wavelength infrared, and the thermal
infrared. These instruments have continued to operate for years beyond
their design-life goals. The Landsat 4 TM operated for more than 11 years,
while the Landsat 5 instrument has more than 13 years of successful
operation, as of this writing. The Enhanced Thematic Mapper was launched
as the sole instrument on Landsat 6 on October 5, 1993. The ETM,
developed for Landsat 6, had the same bands as the other TMs and also a
panchromatic band with 15-meter resolution. Increased redundancy was
incorporated into the instrument configuration to increase its lifetime, and
the redesigned monolithic prime focal plane offered improved band-to-
band registration. The data acquired by the Landsat 4 and 5 Thematic
Mappers have enhanced knowledge of Earth in the fields of agriculture,
geology, forestry, cartography, hydrology, oceanography, and bathymetry
and have been used for environmental monitoring, disaster assessment,
land-use and regional planning, range management

On Landsat 4,5
30 meter resolution reflected / 120 meter
emitted.
256 brightness values
7 spectral bands
Blue/Green, Green, Red, NIR, MIR, MIR, Thermal
423 mile orbit
Oscillating mirror design acquires data with each
sweep in both directions
One swath = 185 km x 474 meters
Each spectral band has 16 detectors except for
the thermal band which has 4 detectors.

SPOT
SPOT is the French government sponsored civil Earth observation
program, with support from Belgium and Sweden. A single SPOT
satellite provides complete coverage of the Earth every 26 days.
Image products from SPOT are handled by a commercial entity,
SPOT-Image Corp. Spacecraft: 3-Axis stabilised to 0.1 deg using
momentum wheels. Single solar arrays generates 1000 W (BOL)
power. Downlink at 8 GHz and 2 x 25 Mbps. Hydrazine propulsion
system provides orbit maintenance. Payload: The HRV (High
Resolution Visible) imaging payload provides 20 meter resolution
multispectral imagery and 10 meter panchromatic imagery using
push-broom sensors. HRV covers the following spectral bands: 0.5
- 0.59 µ m, 0.61 - 0.68 µ m, 0.79 - 0.89 µm; in addition to the
panchromatic band: 0.51 - 0.73 µ m. The field of view is 4.13 deg
in both modes (multispectral and panchromatic) with 3000 pixels
per multispectral line and 6000 pixels per panchromatic line. The
observed strip is 60 km wide (swath width). On-board recorder
capacity is 22 minutes for both modes. The HRV mass is 250 kg.
The spacecraft carries two identical HRVs to provide a total of 117
km swath (with 3 km overlap).

22 February 1986 SPOT 1 Spacecraft: SPOT-1-2-3. Mass: 1,830
kg. Launch Site: Kourou . Launch Vehicle: Ariane 1.
22 January 1990 SPOT 2 Spacecraft: SPOT-1-2-3. Mass: 1,870
kg. Launch Site: Kourou . Launch Vehicle: Ariane 4.
26 September 1993 SPOT 3 Spacecraft: SPOT-1-2-3. Mass:
1,907 kg. Launch Site: Kourou . Launch Vehicle: Ariane 4.
24 March 1998 SPOT 4 Spacecraft: SPOT-4. Mass: 2,755 kg.
Launch Site: Kourou . Launch Vehicle: Ariane 4
04 May 2002 SPOT 5 Spacecraft: SPOT-5A-5B. Mass:
















