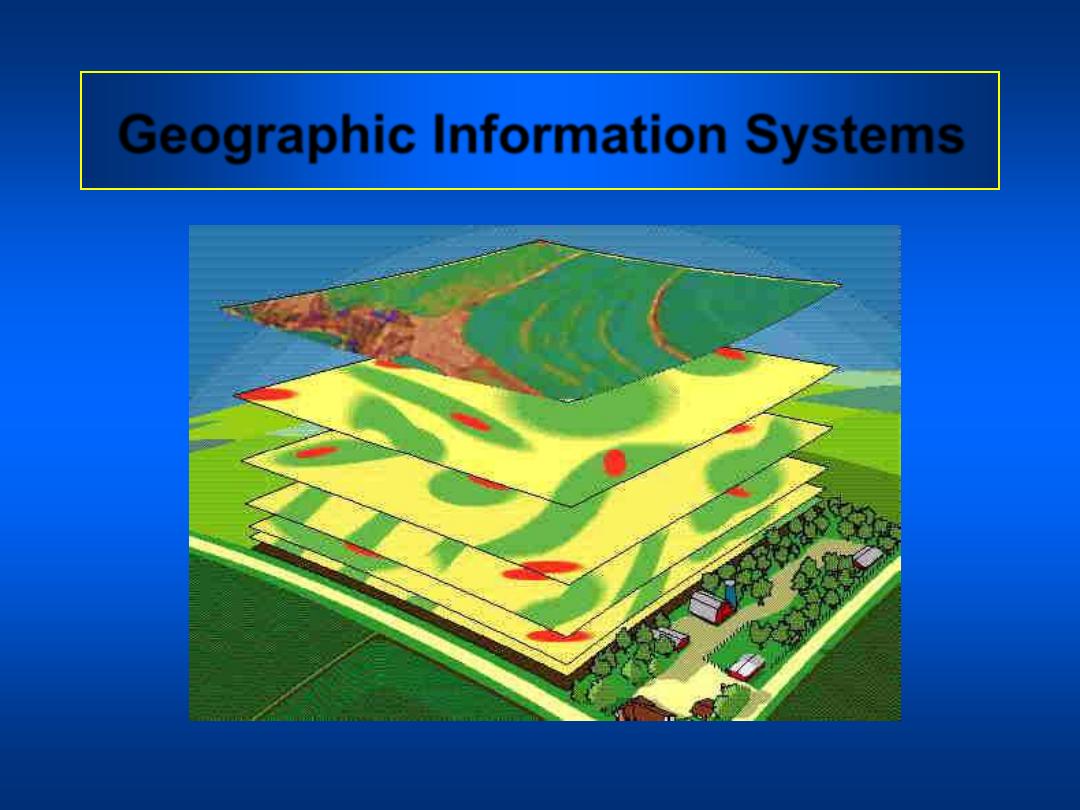
Geographic Information Systems

• In a geographic information system,
information is characterized spatially.
• In a GIS the common purpose is decision
making to manage:
– land
– resources
– transportation
– retailing
– OR any other spatially distributed activity

• A GIS is an organized collection of
computer hardware, software, geographic
data, and personnel to efficiently capture,
store, update, manipulate, analyze, and
display all forms of geographically
referenced information.
• A GIS
integrates
spatial and other kinds of
information within a single system to
provide a consistent framework for
analyzing geographic (spatial) data.
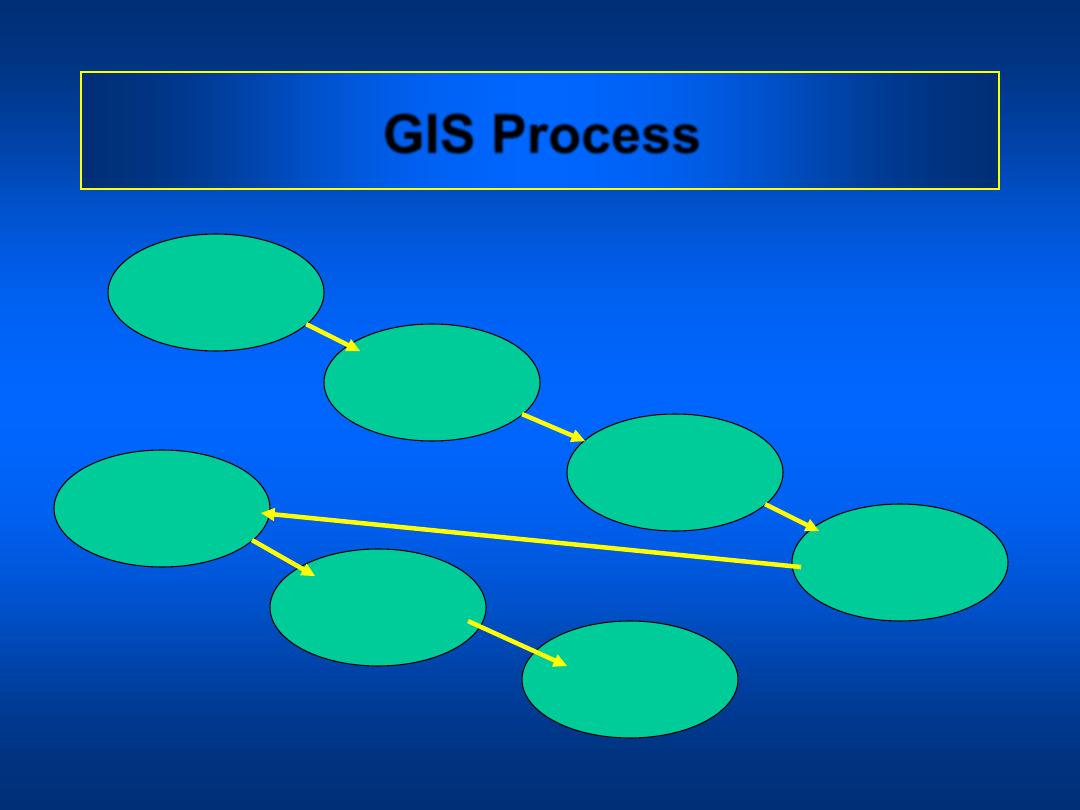
Capture
Data
GIS Process
Register
Map Base
Interpret
Data
Convert Data
to Digital
Format
Store Data
in Computer
Process
Data
Display
Results
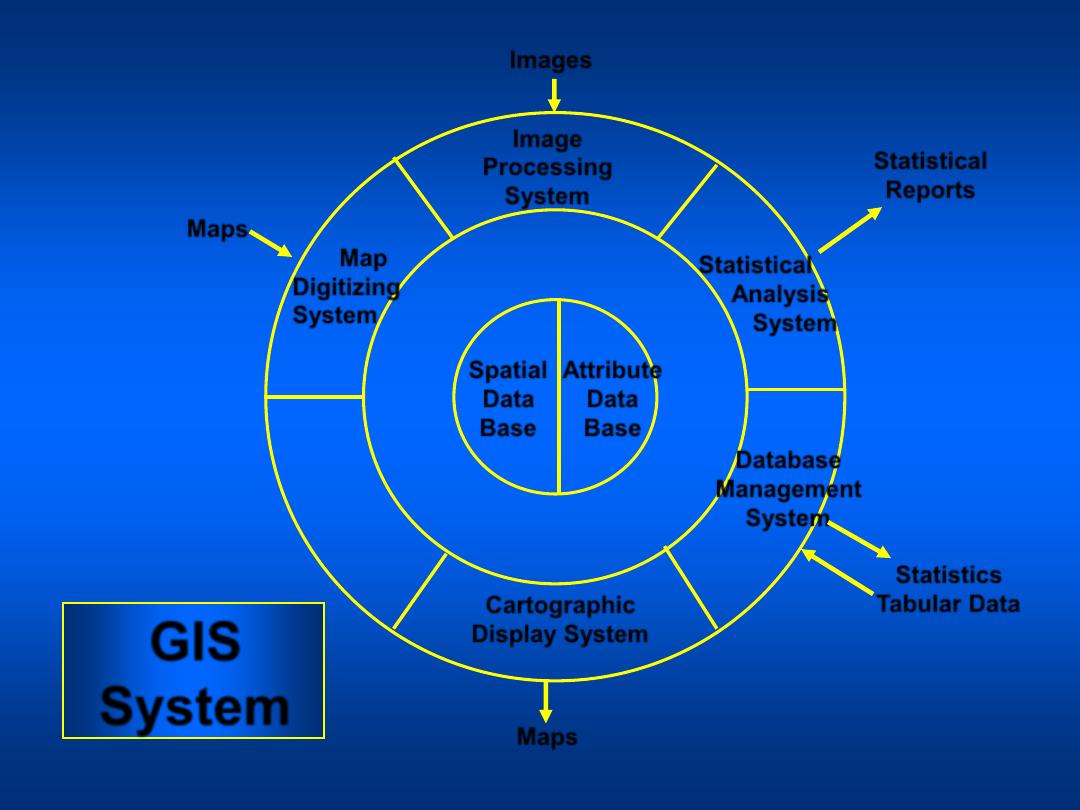
GIS
System
Spatial
Data
Base
Attribute
Data
Base
Cartographic
Display System
Geographic
Analysis
System
Map
Digitizing
System
Image
Processing
System
Statistical
Analysis
System
Database
Management
System
Images
Maps
Maps
Statistical
Reports
Statistics
Tabular Data
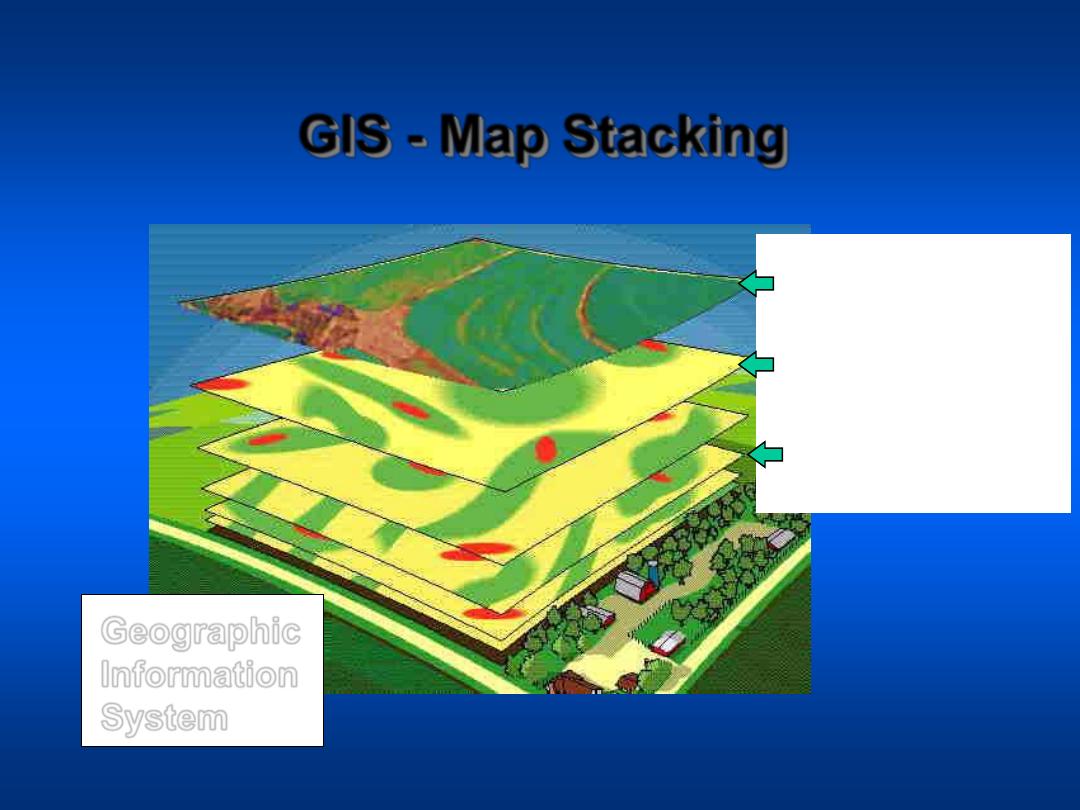
GIS - Map Stacking
Geographic
Information
System
Courtesy of PPI
NDVI From Aerial
Image
pH Layer
Nitrogen Availability
Estimate from
Aerial Photo
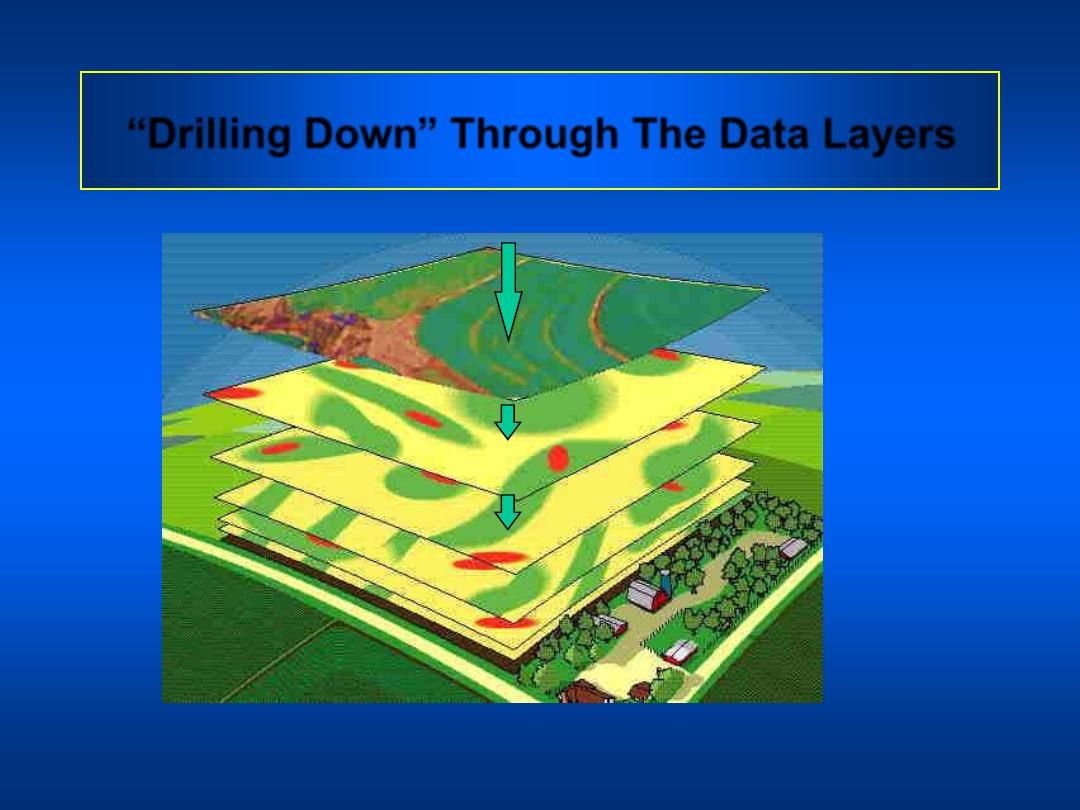
“Drilling Down” Through The Data Layers
Courtesy of PPI
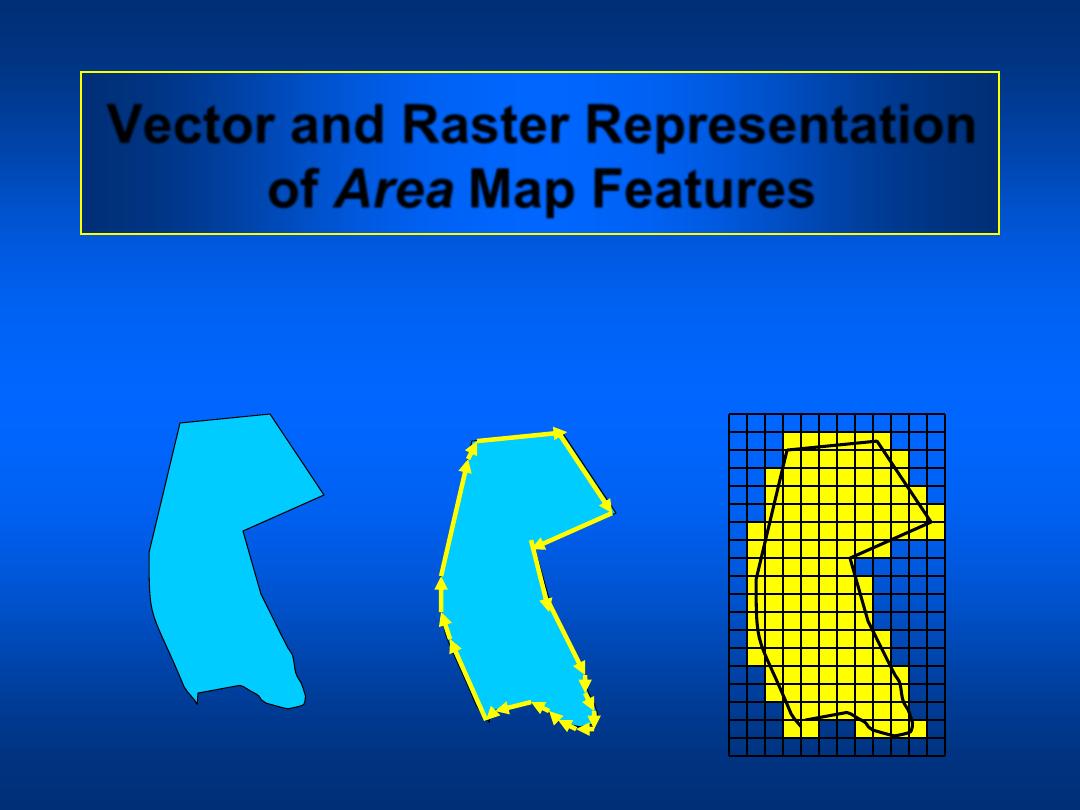
Vector and Raster Representation
of Area Map Features
Map Feature
GIS Vector
Format
GIS Raster
Format
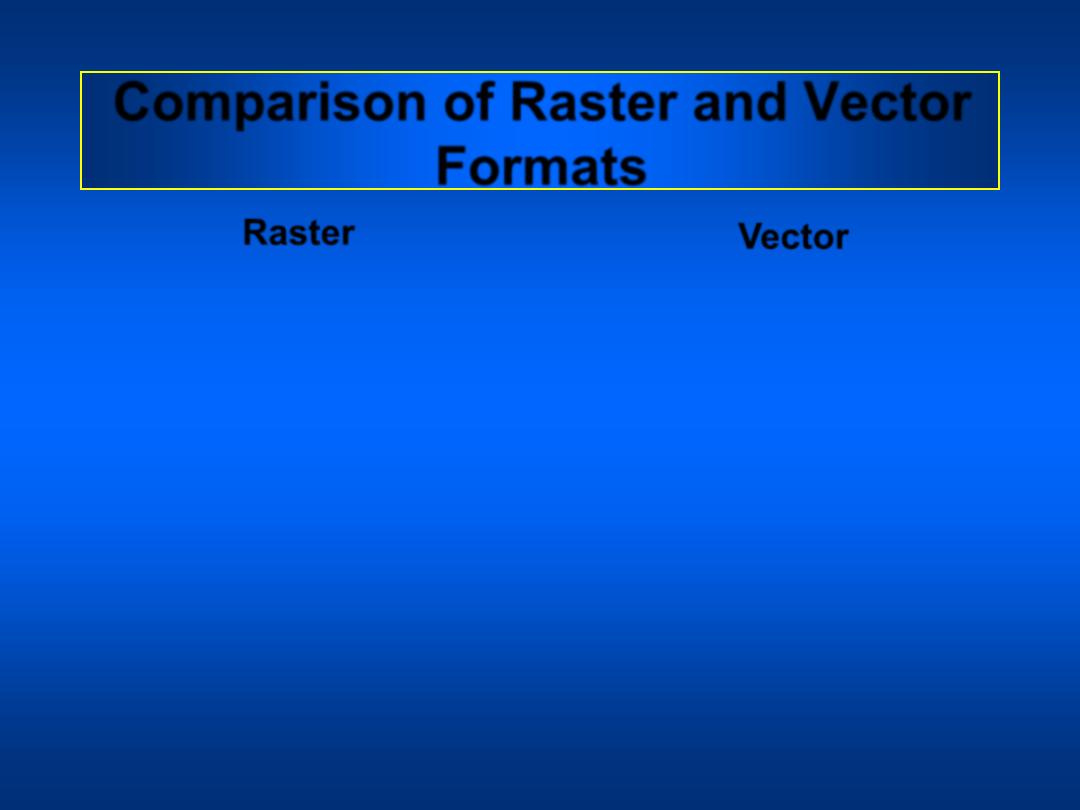
Comparison of Raster and Vector
Formats
• Raster formats are efficient
when comparing
information among arrays
with the same cell size.
• Raster files are generally
very large because each
cell occupies a separate
line of data, only one
attribute can be assigned
to each cell, and cell sizes
are relatively small
.
• Vector formats are efficient
when comparing
information whose
geographical shapes and
sizes are different.
• Vector files are much
smaller because a
relatively small number of
vectors can precisely
describe large areas and a
many attributes can be
ascribed to these areas.
Raster
Vector
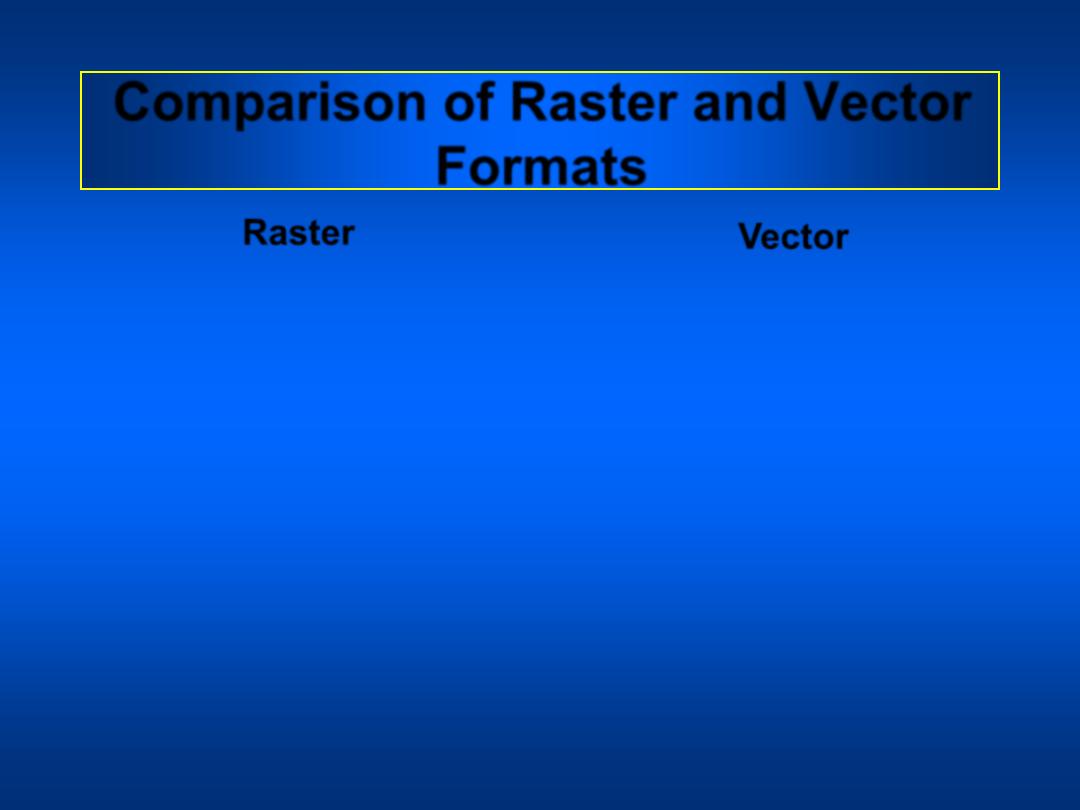
Comparison of Raster and Vector
Formats
• Raster representations are
relatively coarse and
imprecise
• Vector representations of
shapes can be very
precise.
Raster
Vector
Most GIS software can display both raster and
vector data. Only a limited number of programs
can analyze both types of data or make raster type
analyses in vector formats.

Coordinate Systems
• UTM, the preferred system, distance unit
is the meter.
• The unit of the state plane system is the
foot.
• There is generally a different coordinate
system for each state in the state plane
system.
• In the UTM system projections are made in
zones of approximately 6 degrees of
longitude.

Coordinate Systems
• There are two datums (reference planes)
commonly used to make projections:
North American Datum of 1927 (NAD27)
and the World Geographic Reference
System of 1984 (WGS84). The WGS84
datum can be used world wide. The
default datum of many GPS receivers is
the WGS84 datum.
