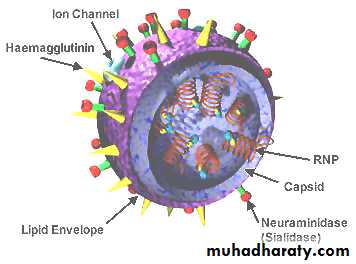
Antiviral Agents that Prevent Virus Uncoating or Release
Antiviral DNA Synthesis InhibitorsNucleotide and Nonnucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Protease Inhibitors
Antiviral DrugsDr, Jawad Al-Musawi(2020)
Antimicrobial Drugs > Antiviral Drugs
• View on Boundless.comAntimicrobial Drugs > Antiviral Drugs
Drugs such as acyclovir, are nucleoside analogues that lack a free 3' group that is needed for the addition of the next nucleotide. When added into a growing DNA chain they stop its synthesis.
Another drug, foscarnet, mimics pyrophosphates and inactivates the activity of the viral DNA polymerase.
Resistance can develop against both of these groups of drugs.
Antiviral DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Antimicrobial Drugs > Antiviral Drugs
Nucleoside and nucleotide inhibitors are competitive substrate inhibitors that mimic the structure of a normal nucleotide but lack the 3' hydroxyl group needed for the addition of the next nucleotide for DNA elongation.
Non-nucleotide inhibitors bind to a site different than the active one and cause rearrangements of the protein domains needed for DNA polymerization.
Mutations in the reverse transcriptase gene can cause resistance to both types of drugs.
Nucleotide and Nonnucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Antimicrobial Drugs > Antiviral Drugs
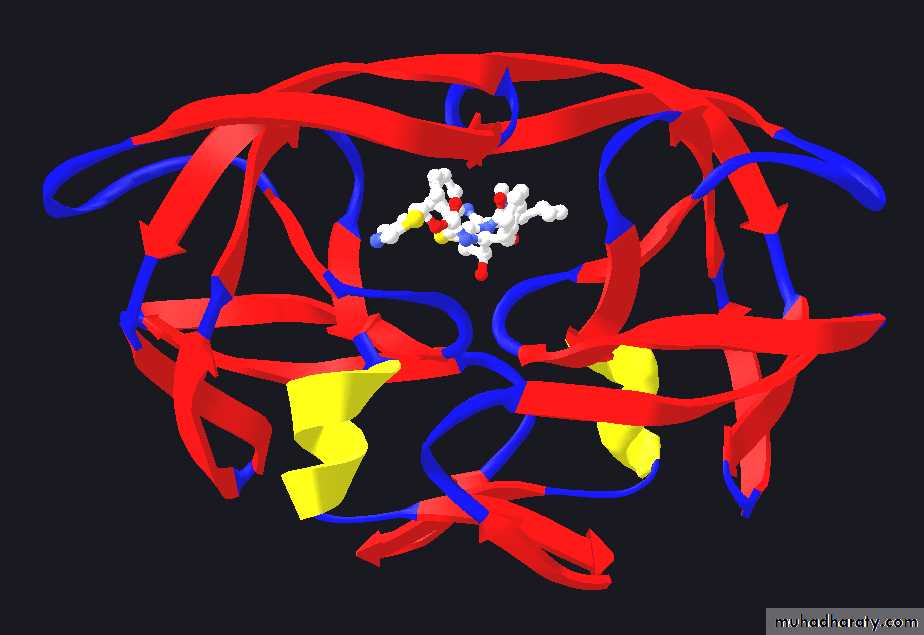
Protease inhibitors mimic peptides or are chemicals that can be inserted in the active site of a protease. They prevent it from binding the viral polyproteins.Such drugs were one of the first to be used against HIV. They are an inseparable part of the HIV/AIDS therapy.
Mutations in the enzyme active site and other sites, which cause conformational changes, can cause resistance.
Protease Inhibitors
HIV protease with bound protease inhibitor
Antimicrobial Drugs > Antiviral DrugsKey terms
CMV retinitis An inflammation of the eye's retina caused by CMV. It can lead to blindness.competitive substrate inhibitors Molecules that bind to the active site of an enzyme and prevent the real substrate from binding to it.
cross-resistance Bacterial or viral resistance to a chemical which causes resistance to other chemicals of the same group.
non-competitive inhibitors Molecules that bind to sites other than the active site of an enzyme while still being able to indirectly inhibit its function.
nucleotide the monomer comprising DNA or RNA biopolymer molecules, consisting of a nitrogenous heterocyclic base; a five-carbon pentose sugar; and a phosphate group
sialic acid A derivative of neuraminic acid (a nine-carbon monosaccharide) that is often the sugar part of glycoproteins.
Antimicrobial Drugs