
Physiology of excitable tissue lecture 3 Asst. Prof. Dr. Zahid M. Kadhim
1
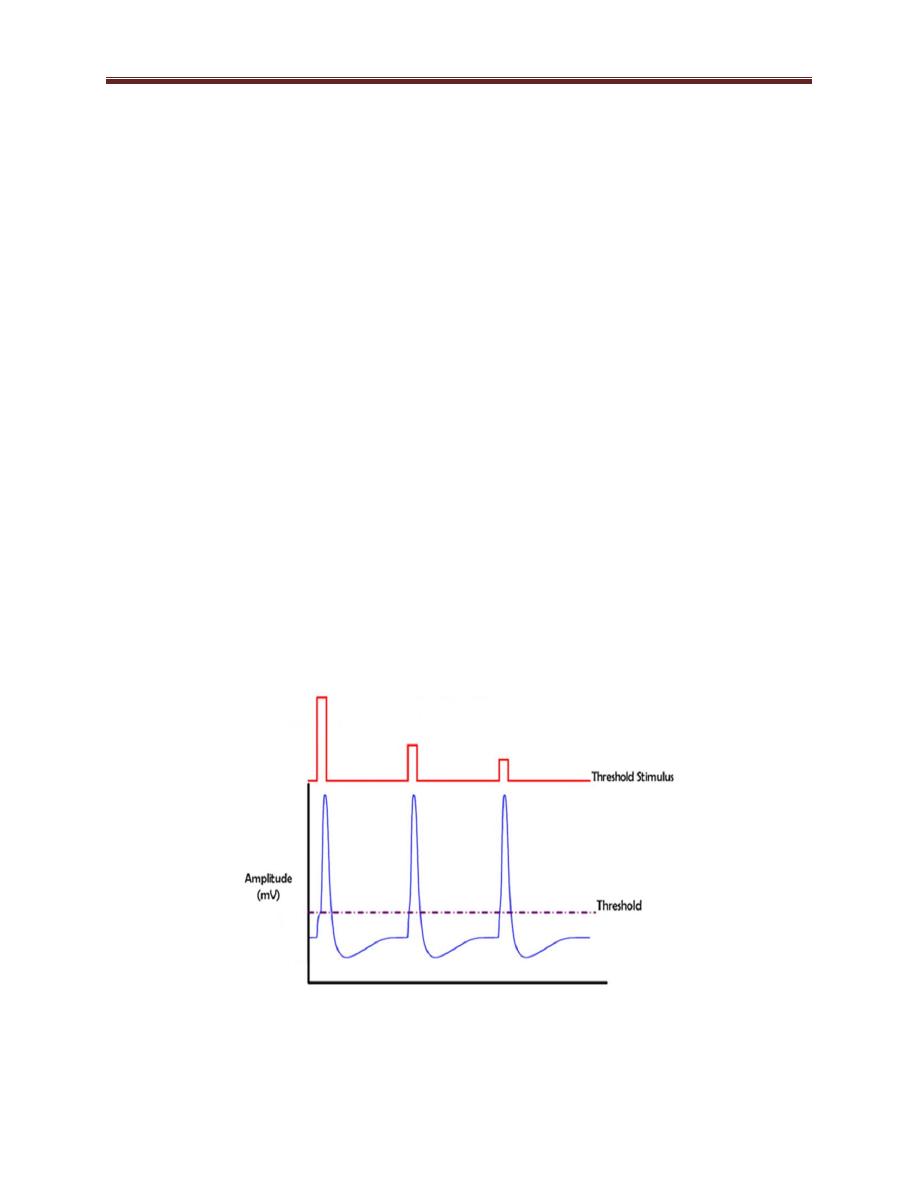
Threshold of action potential
Threshold intensity, It is the minimal intensity of stimulating current
capable of eliciting action potential, and then it is named threshold
potential (figure 3-1). To produce an action potential, it must have a
given strength & act for a given duration. The threshold intensity
varies with the duration; with weak stimuli it is long, and with strong
stimuli it is short.
Initiation of action potentials follows the all-or-none principle:
Whether a membrane is depolarized to threshold or greater, the
amplitude of the resulting action potential is the same; if the
membrane is not depolarized to the threshold, no action potential
occurs.
Our nervous system code various intensity of stimuli by increasing
the rate of firing of action potential by individual neuron, firing of
more than one neuron or adjacent neurons (figure 3-2).
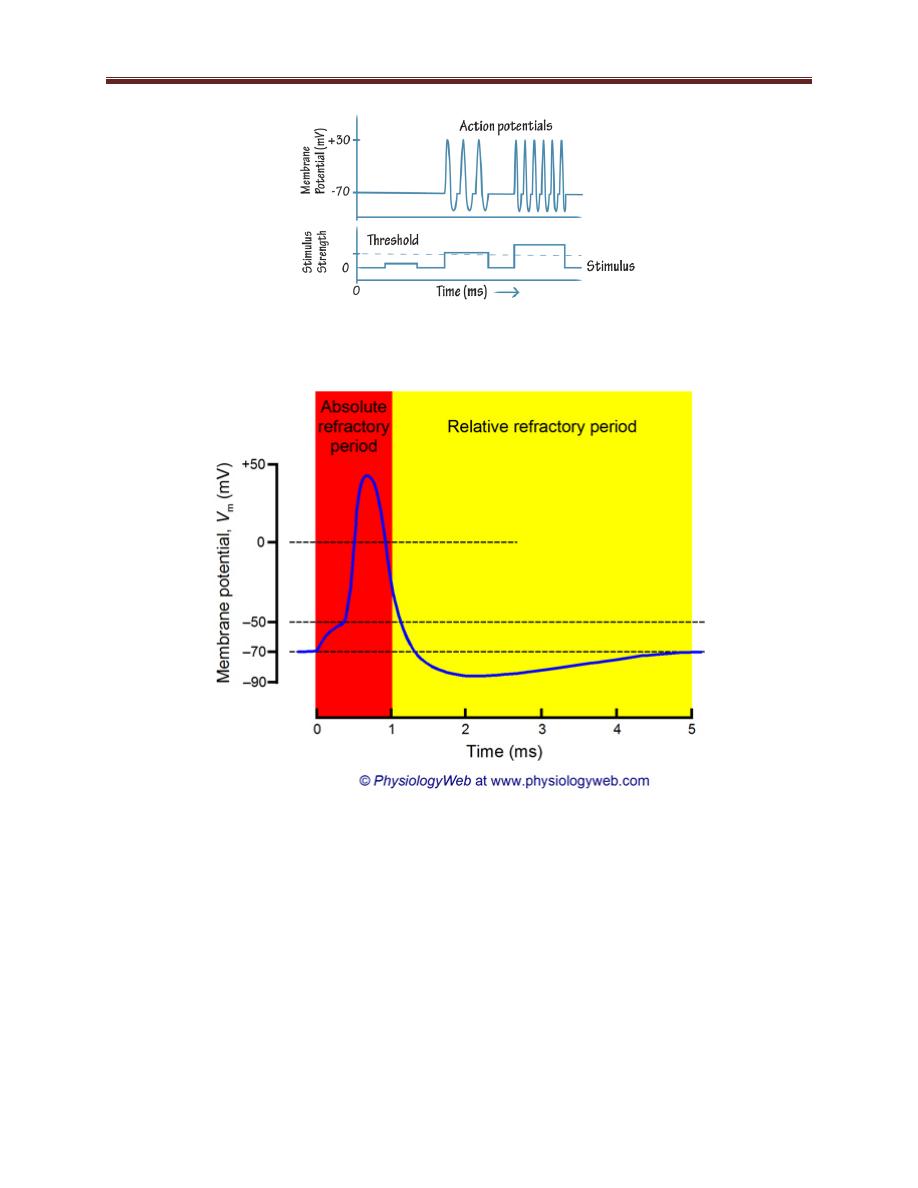
Refractory Periods (figure 3-3)
During and immediately after an action potential, the membrane is
less excitable than it is at rest. This period of reduced excitability is
called the refractory period. The refractory period can be divided
into two phases: the absolute refractory period and the relative
refractory period
The absolute refractory period spans all of the depolarization phase
plus most of the repolarization phase of an action potential (1–2
msec). During this time, a second action potential cannot be
generated in response to a second stimulus, regardless of the
Physiology of excitable tissue lecture 3 Asst. Prof. Dr. Zahid M. Kadhim
2
strength of that stimulus because sodium channels are in the
inactive state.
The relative refractory period occurs immediately after the absolute
refractory period and lasts approximately 5–15 msec. During this
period, it is possible to generate a second action potential, but only
in response to a stimulus stronger than that needed to reach
threshold under resting conditions because of increase potassium
conductance.
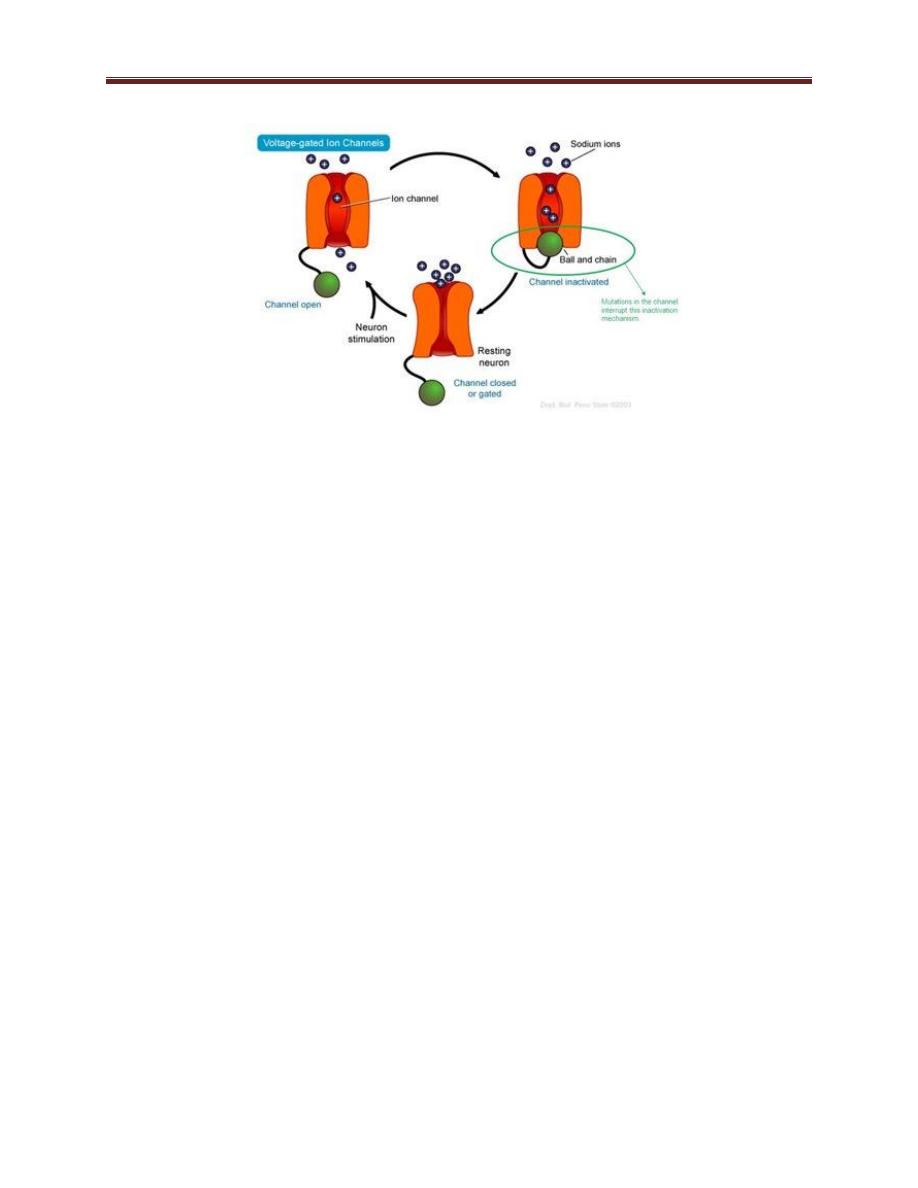
Na channel is a voltage gated channel that has three states: 1- closed
state which when stimulated by change in voltage inside the cell will
pass to next state, 2- open state during action potential which is very
short period allowing large amount of Na ion to enter the cell making
the inside positive in regard to outside, and after short period of
time, the channel will go to state 3- inactive state, during which the
channel want open again unless it return back to closed state as
shown in figure 3-4
Figure 3-1: threshold intensity
Physiology of excitable tissue lecture 3 Asst. Prof. Dr. Zahid M. Kadhim
3
Figure 3-2: coding of information
Figure 3-3: refractory periods
Physiology of excitable tissue lecture 3 Asst. Prof. Dr. Zahid M. Kadhim
4
Figure 3-4: sodium channel
