
Blood Physiology Lec. 3
Dr. Basim A. Al-Ka’abi
MBChB (Medicine)
MSc, PhD (Medical Physiology)

The hemoglobin:
• Definition
• Function
• Normal values
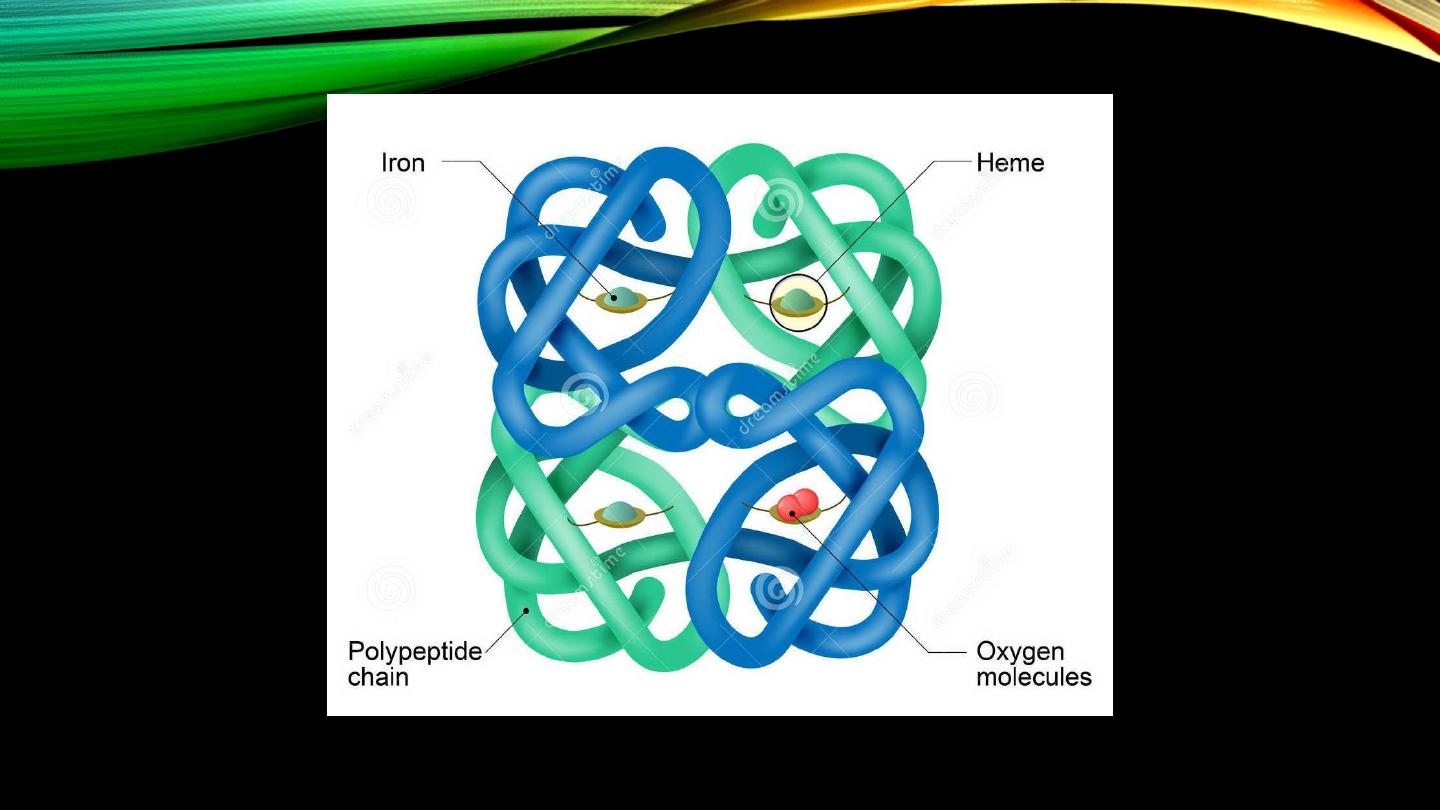

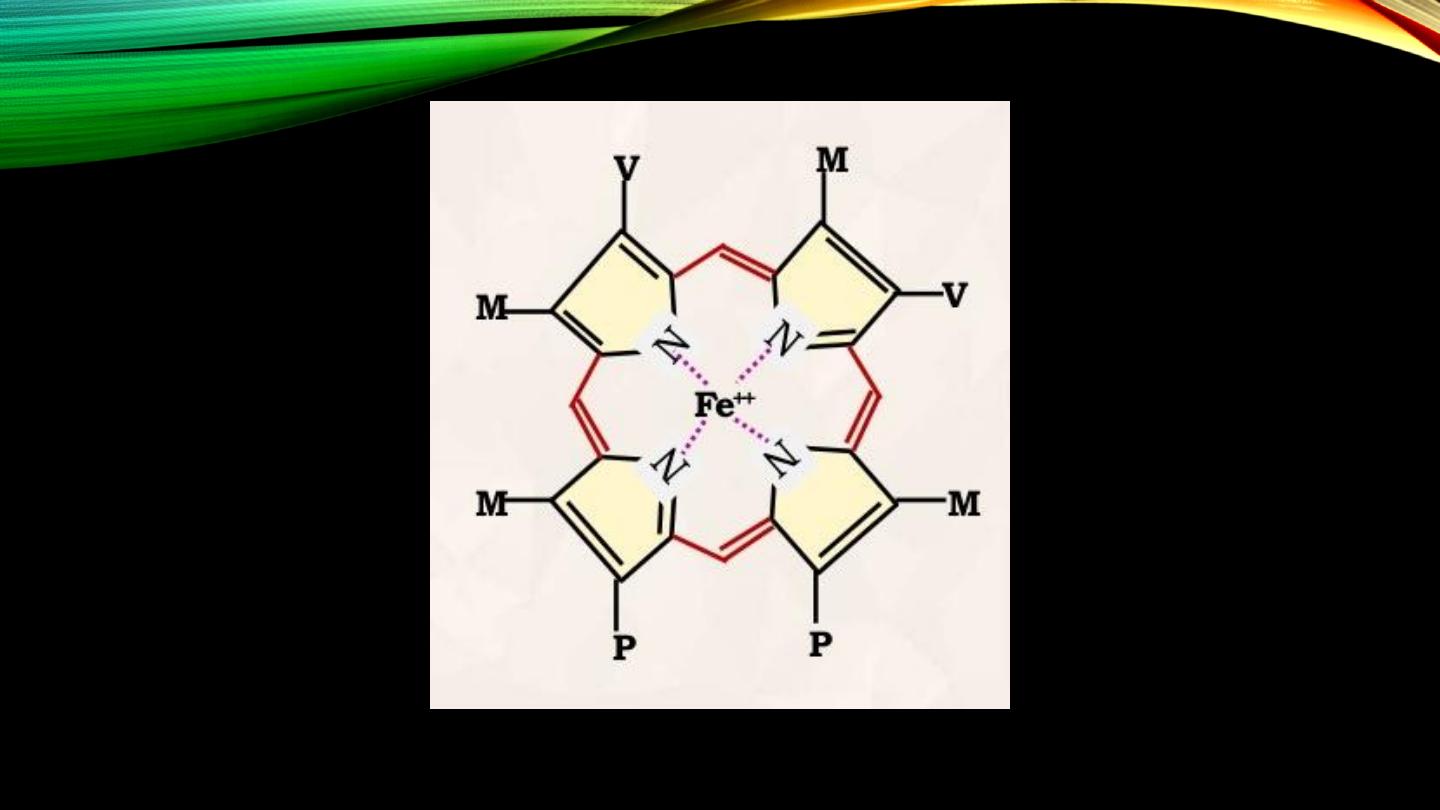
Hb structure: Heme structure
• “Ferroprotoporphyrin”

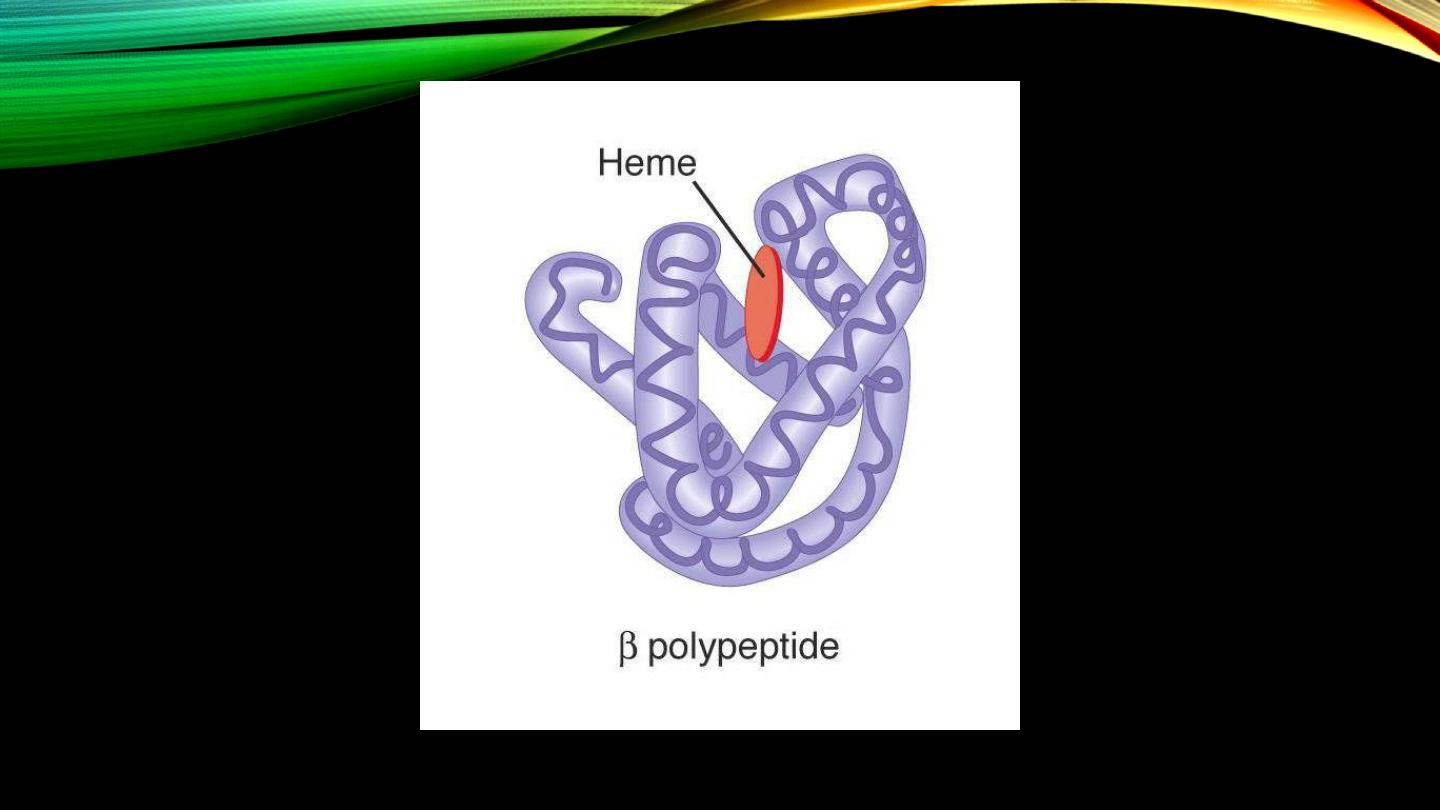
Hb structure (cont’d): Globin structure:
• Two pairs of pp
• HbA
• HbA
2
• HbF

Hb synthesis:
• Heme synthesis
• Globin synthesis

Catabolism of Hb:
• RBC destruction in RES
• Heme: pyrrole (bile), iron (reused)
• Globin: recycled, destroyed or metabolized (liver)

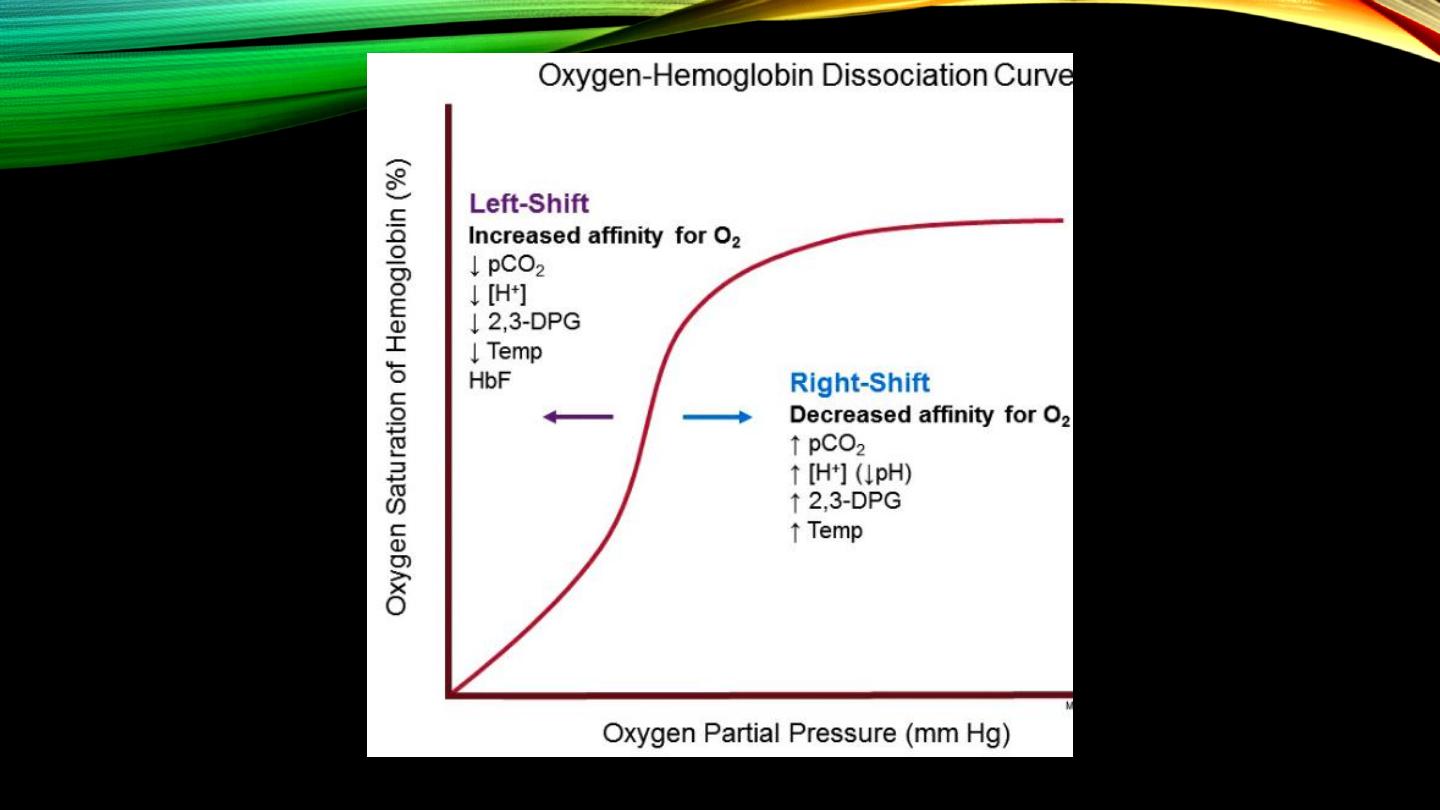
Reaction of Hb:
• Hb+O
2
=oxyHb
• Factos determining Hb affinity for O
2
• “Met-Hb and sulf-Hb”
• Hb+CO=carboxyHb

Iron metabolism (absorption):
• Mainly in the duodenum
• Low pH=good iron absorption
• Neutral or high pH=the reverse

Iron metabolism (transport):
• “Ferroxidase”
• “Transferrin”
• In erythroblasts and reticulocytes, reduction again

Iron metabolism (utilization):
• “mitochondria”

Iron metabolism (storage):
• Ferritin, 70%
• Hemosiderin, 30%

Iron metabolism (requirement):
• 1-2 mg are lost daily and the same amount only is absorbed
• Additional absorption: Pregnancy and MC

Good Luck
