
Blood Physiology Lec. 1
Dr. Basim A. Al-Ka’abi
MBChB (Medicine)
MSc, PhD (Medical Physiology)

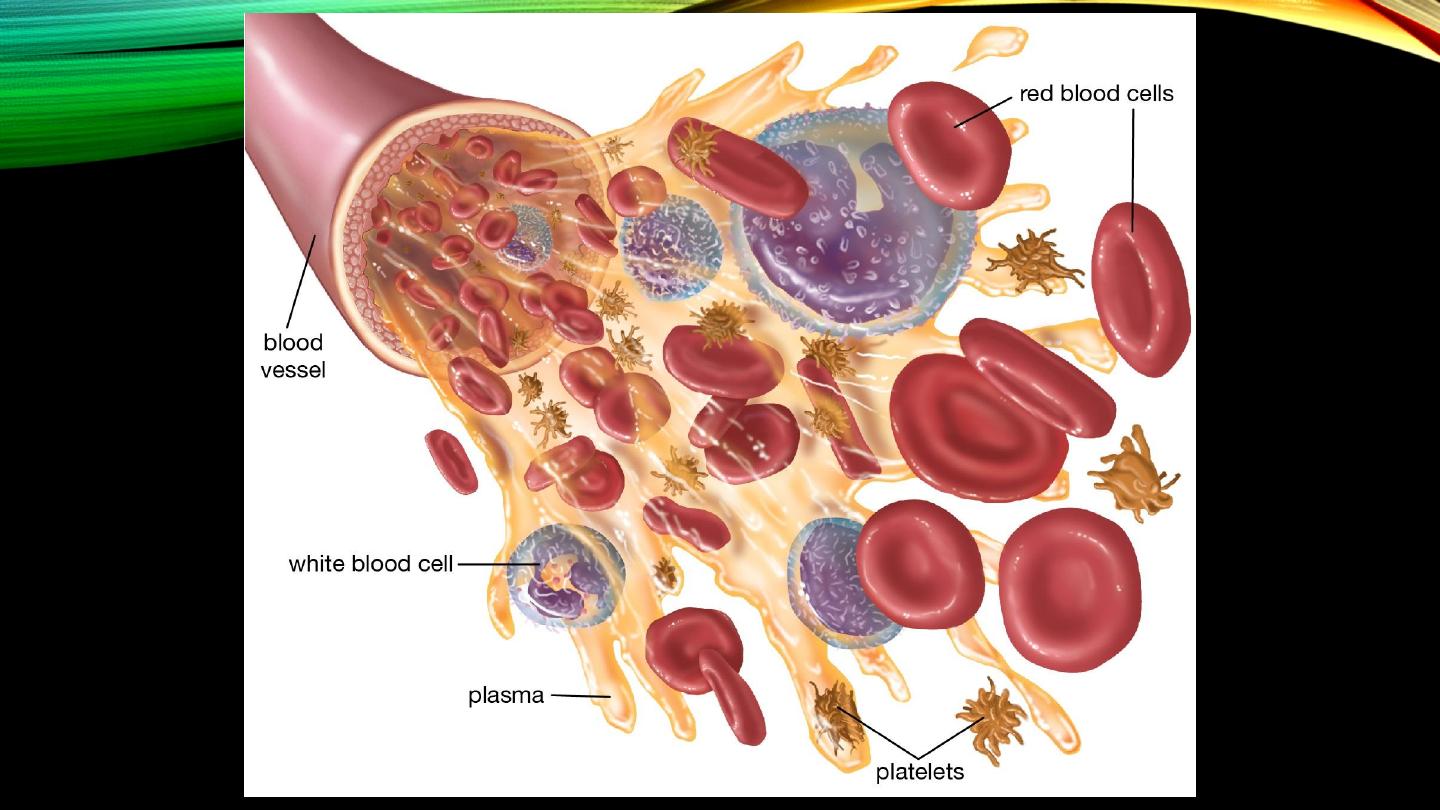
The blood:
• Definition
• Contents and their proportions
• Total blood volume

Red blood cells:
• Total number
• Dimensions
• Life span

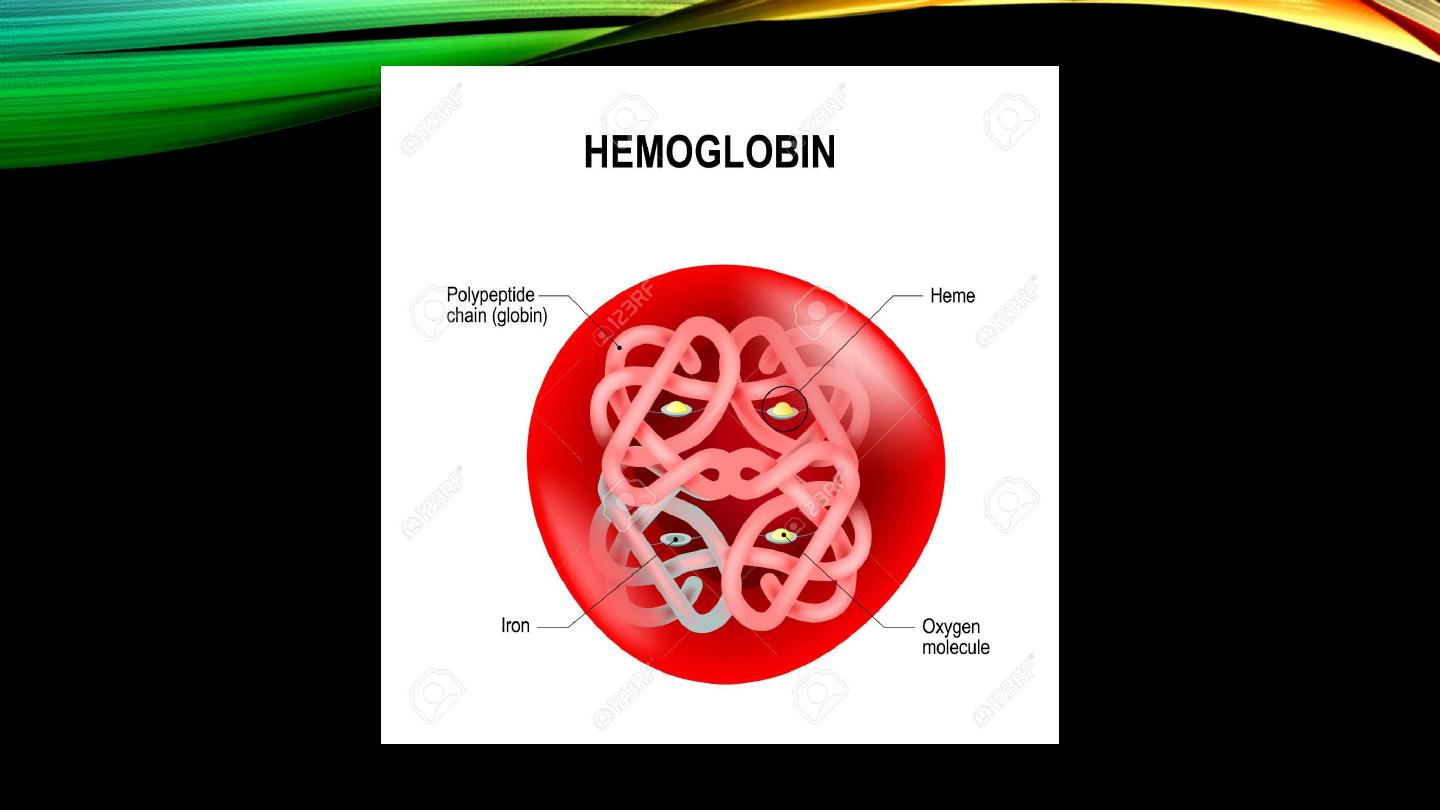
Red blood cells (cont’d):
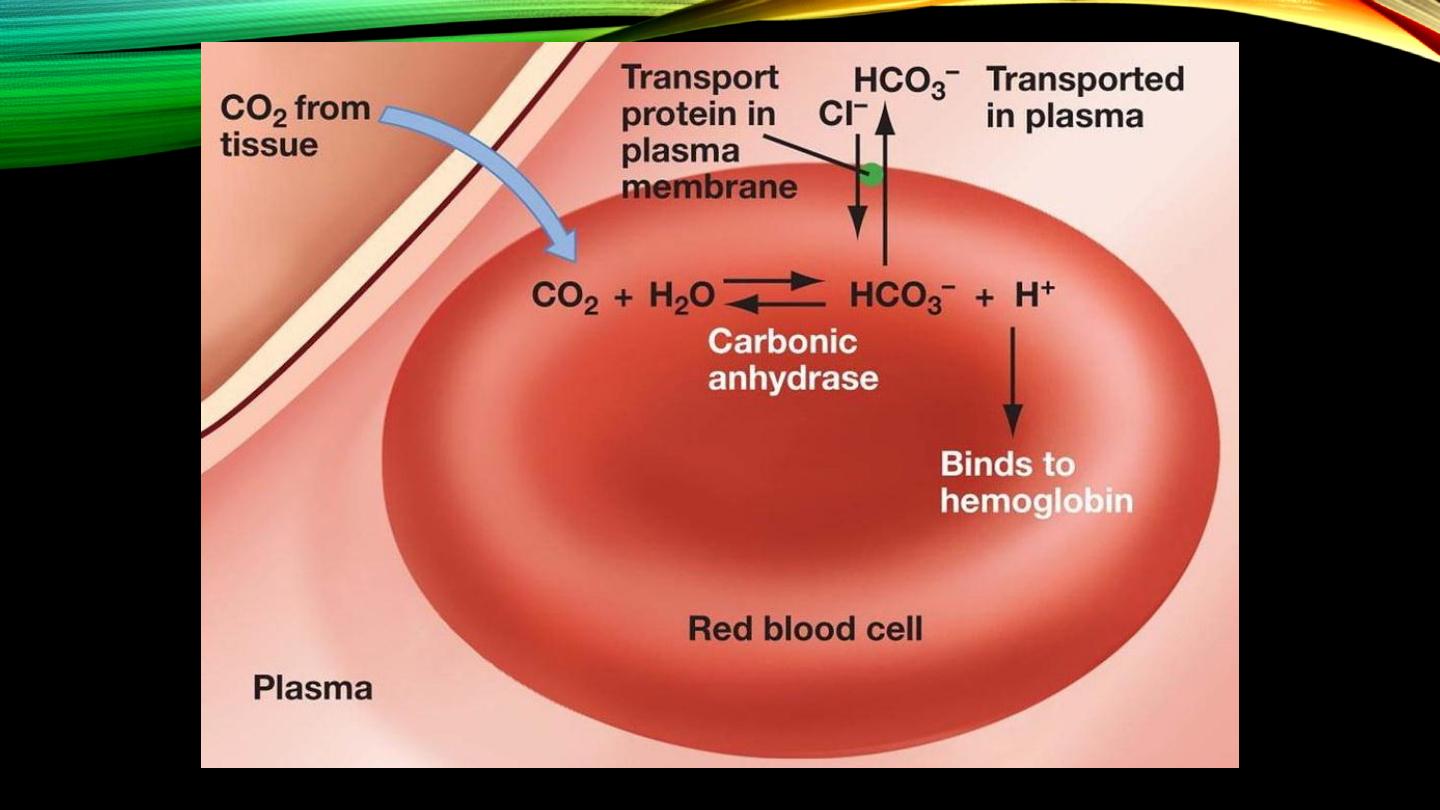
• Red cell membrane permeability
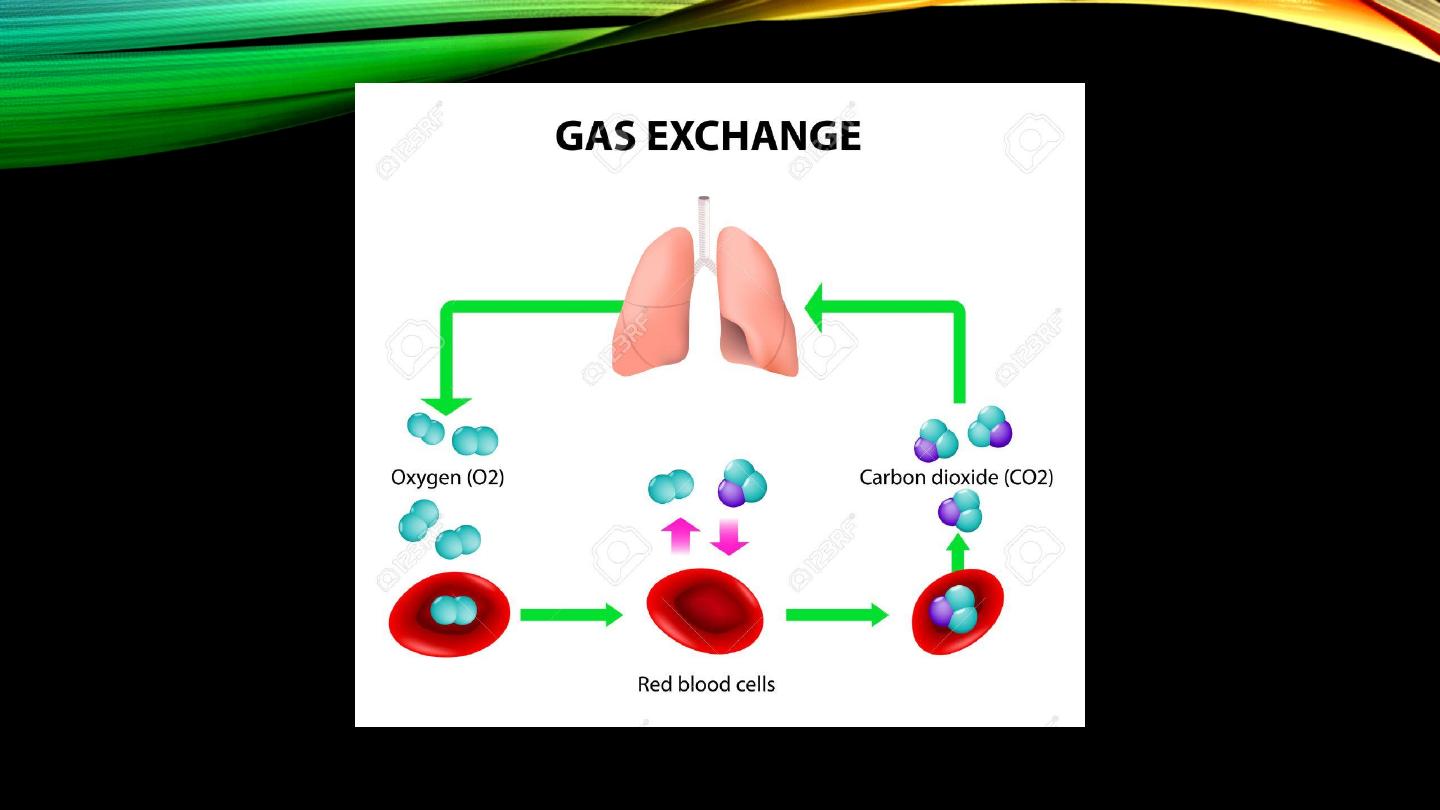
• Major function
• Carbonic anhydrase

Red blood cells (cont’d):
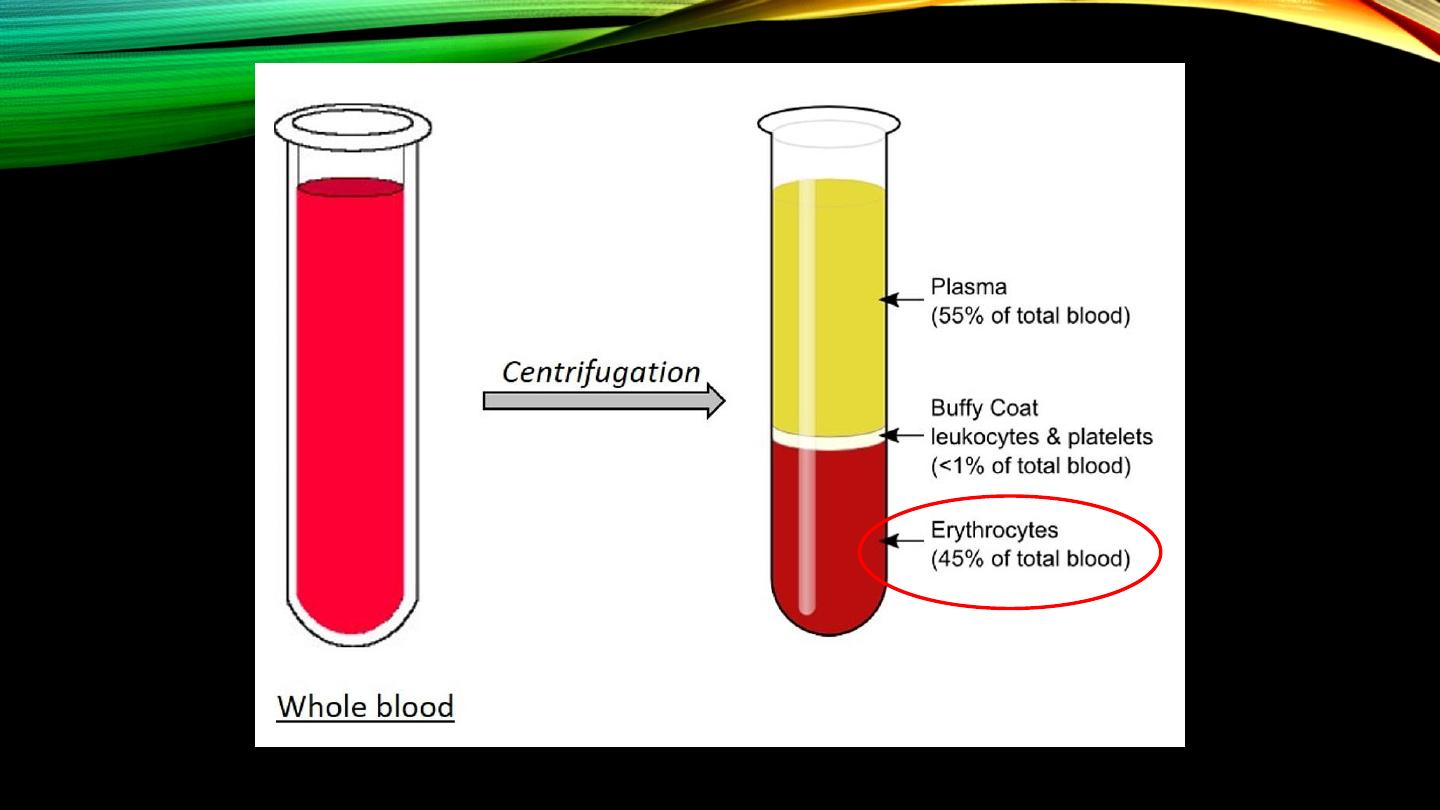
• Hematocrit?

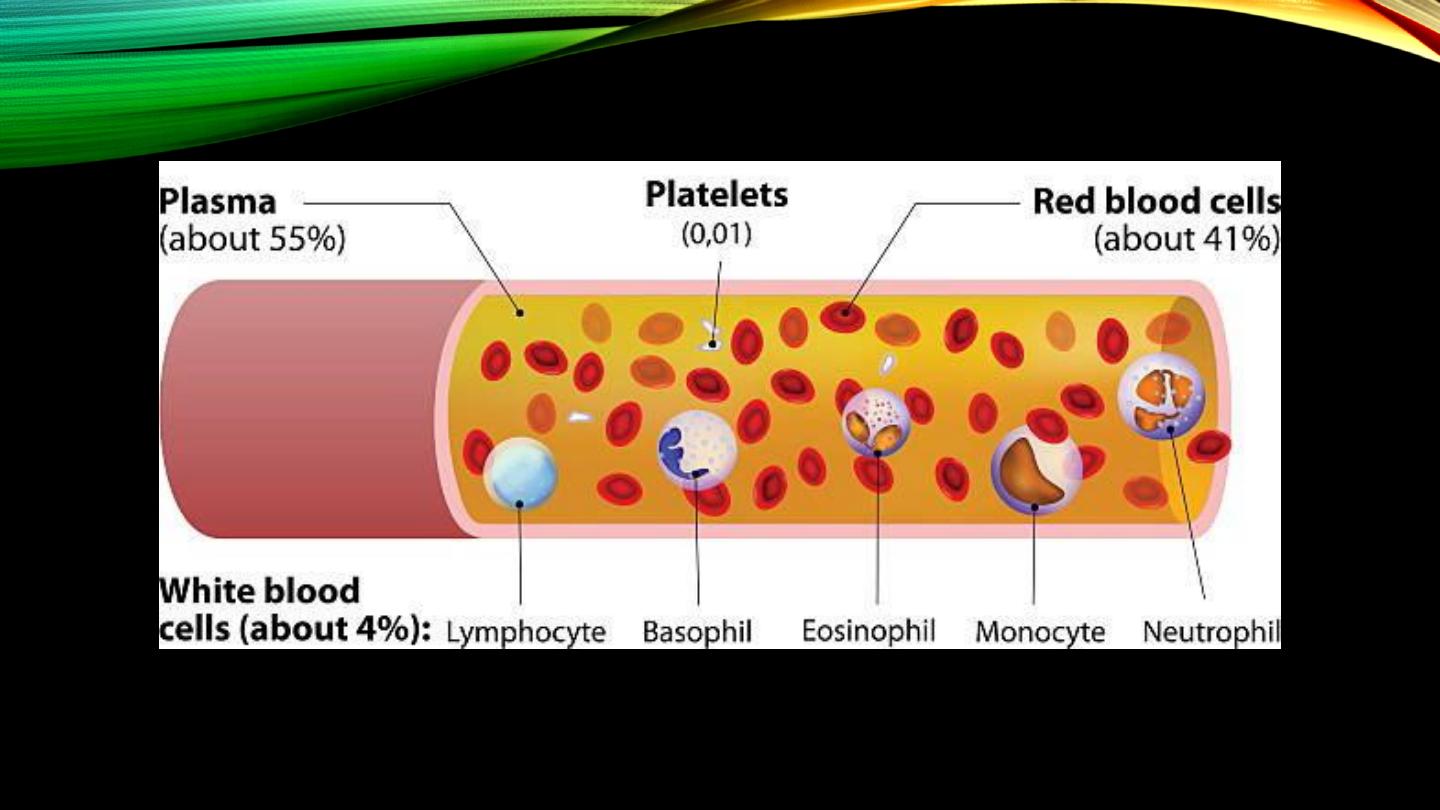
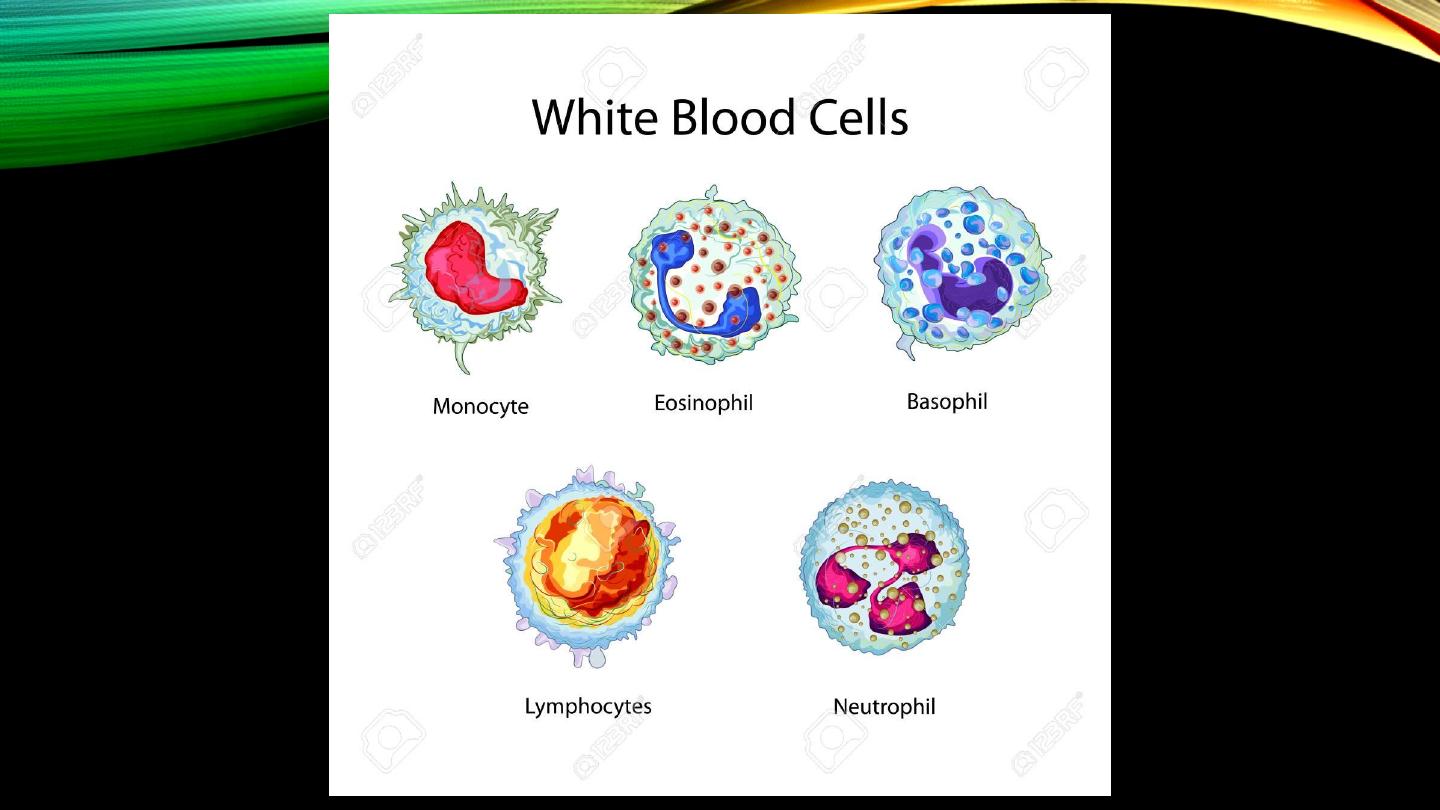
White blood cells:
• Definition
• Sites of formation
• Proportion in relation to RBCs
• Subtypes

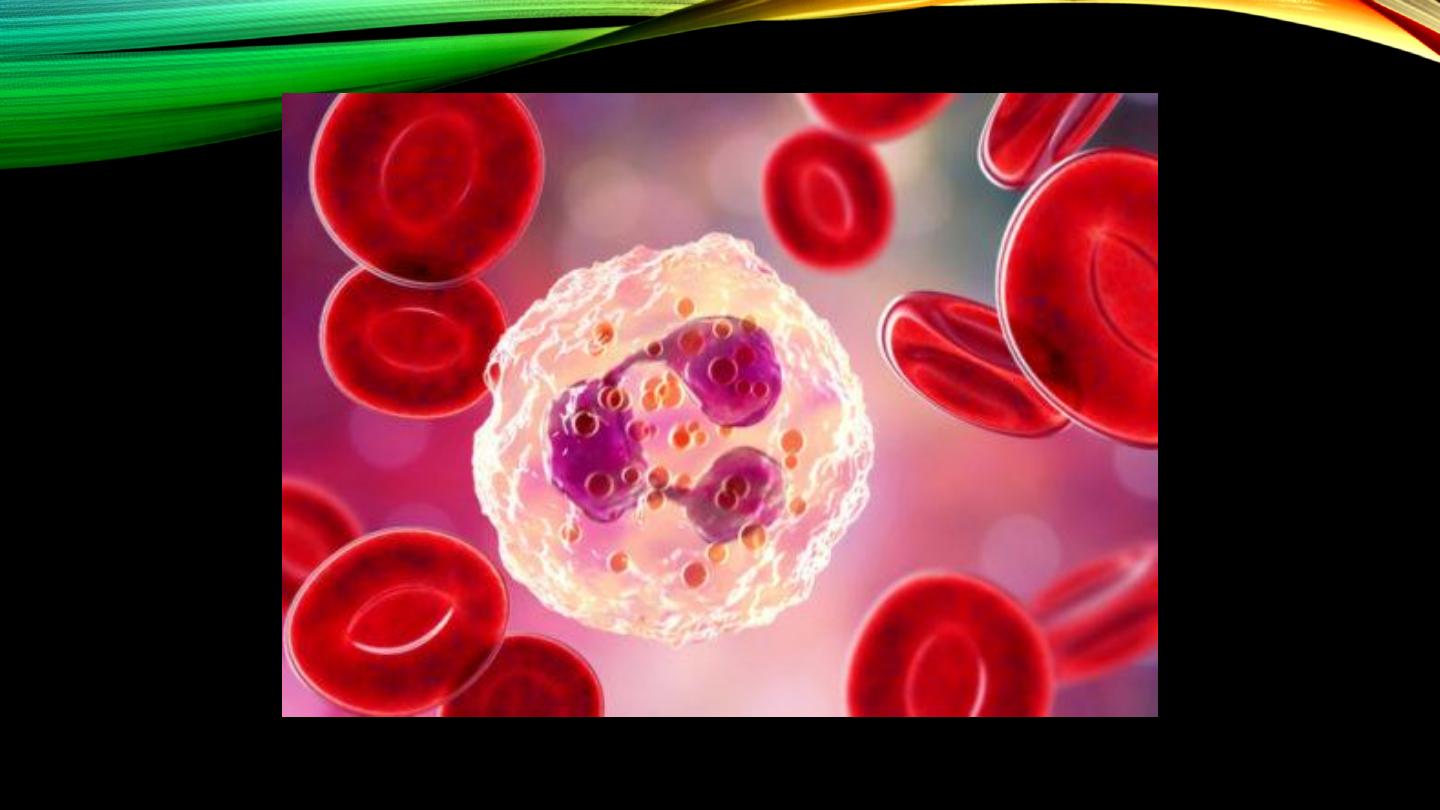
Neutrophils:
• Type and percentage
• Nucleus and cytoplasmic granules
• Main target microorganism

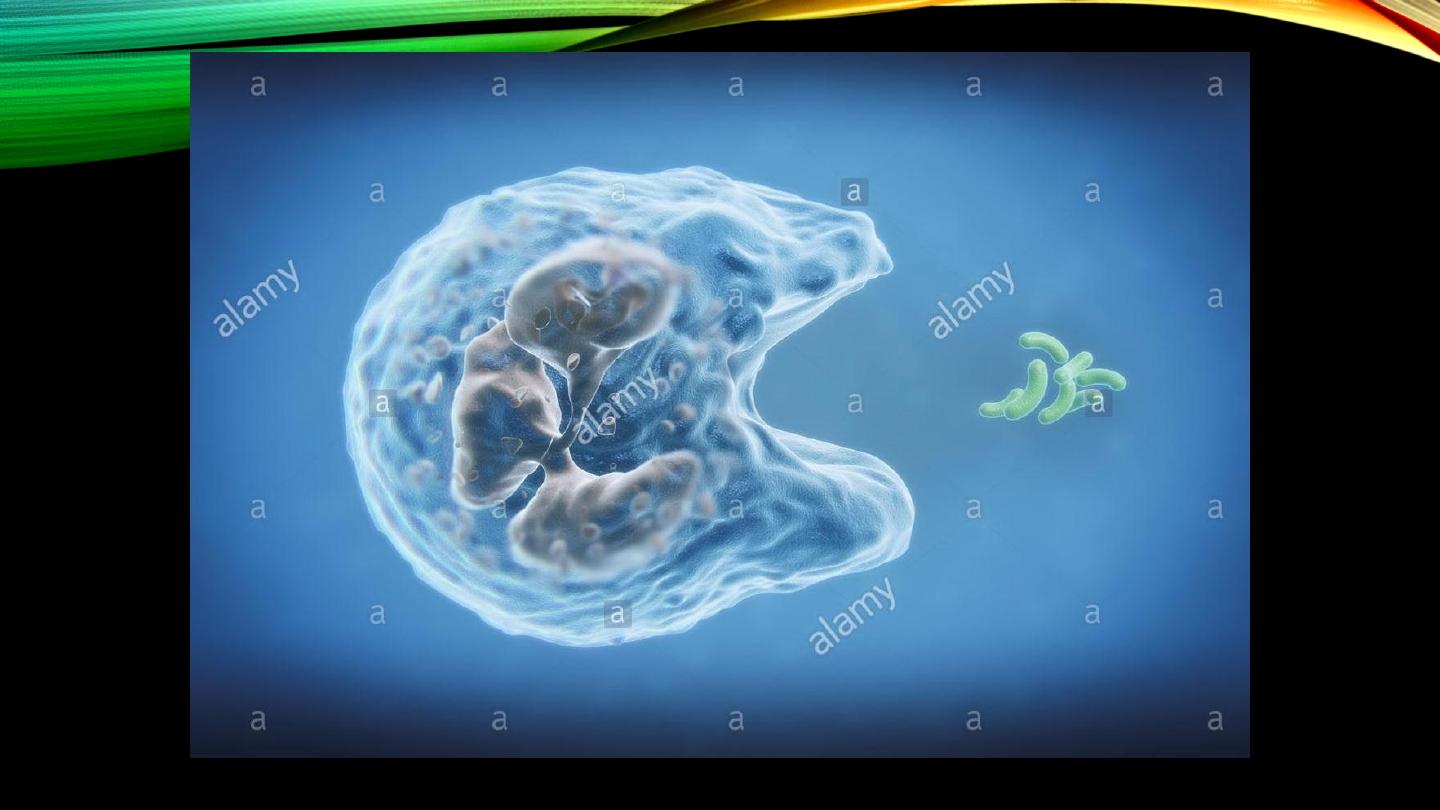
Neutrophils (cont’d):
• Phagocytosis
• Chemotaxis?

Eosinophils:
• Type and percentage
• Nucleus and cytoplasmic granules
• Main target microorganism
• Role in allergic reactions
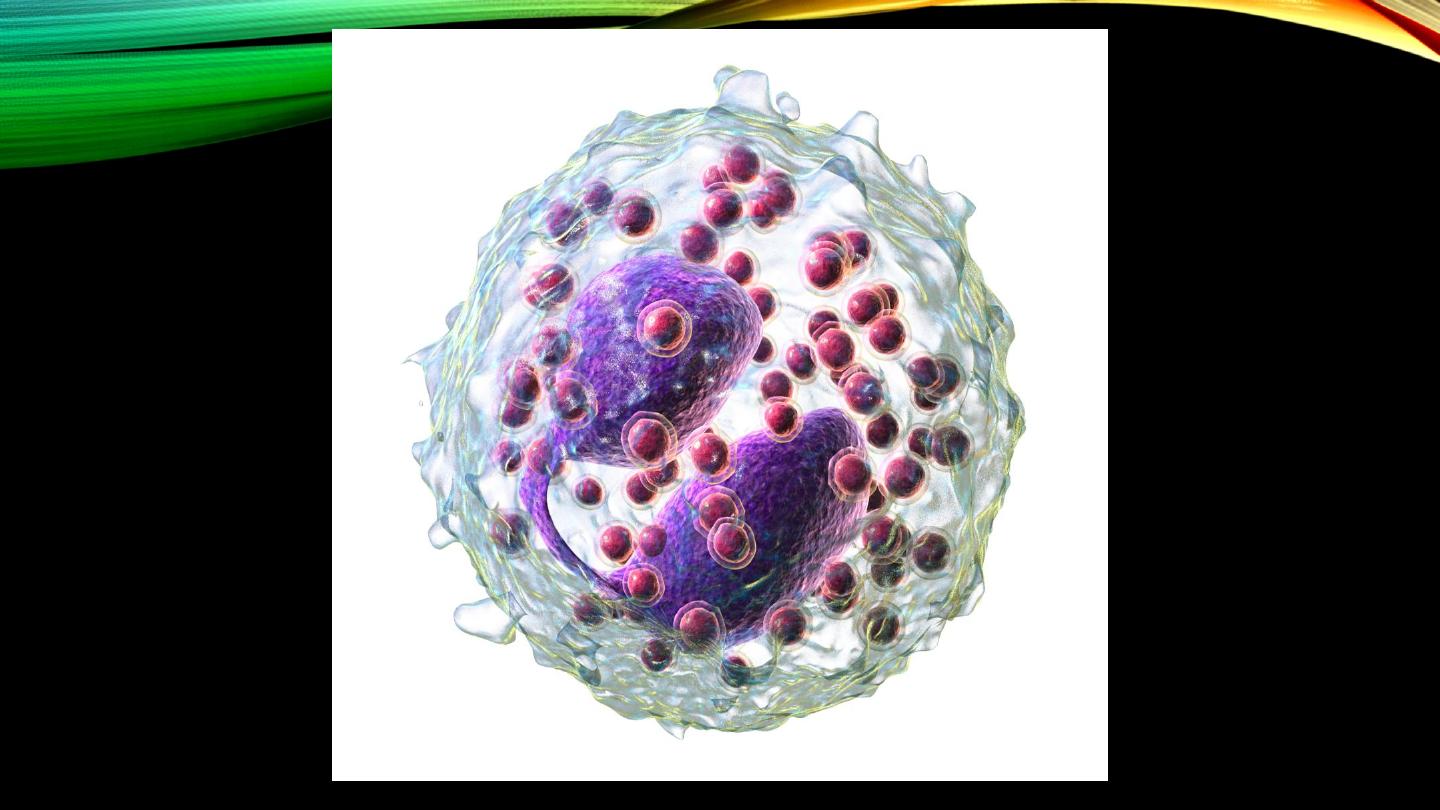

Basophils:
• Type and percentage
• Nucleus and cytoplasmic granules
• Similarity to mast cells
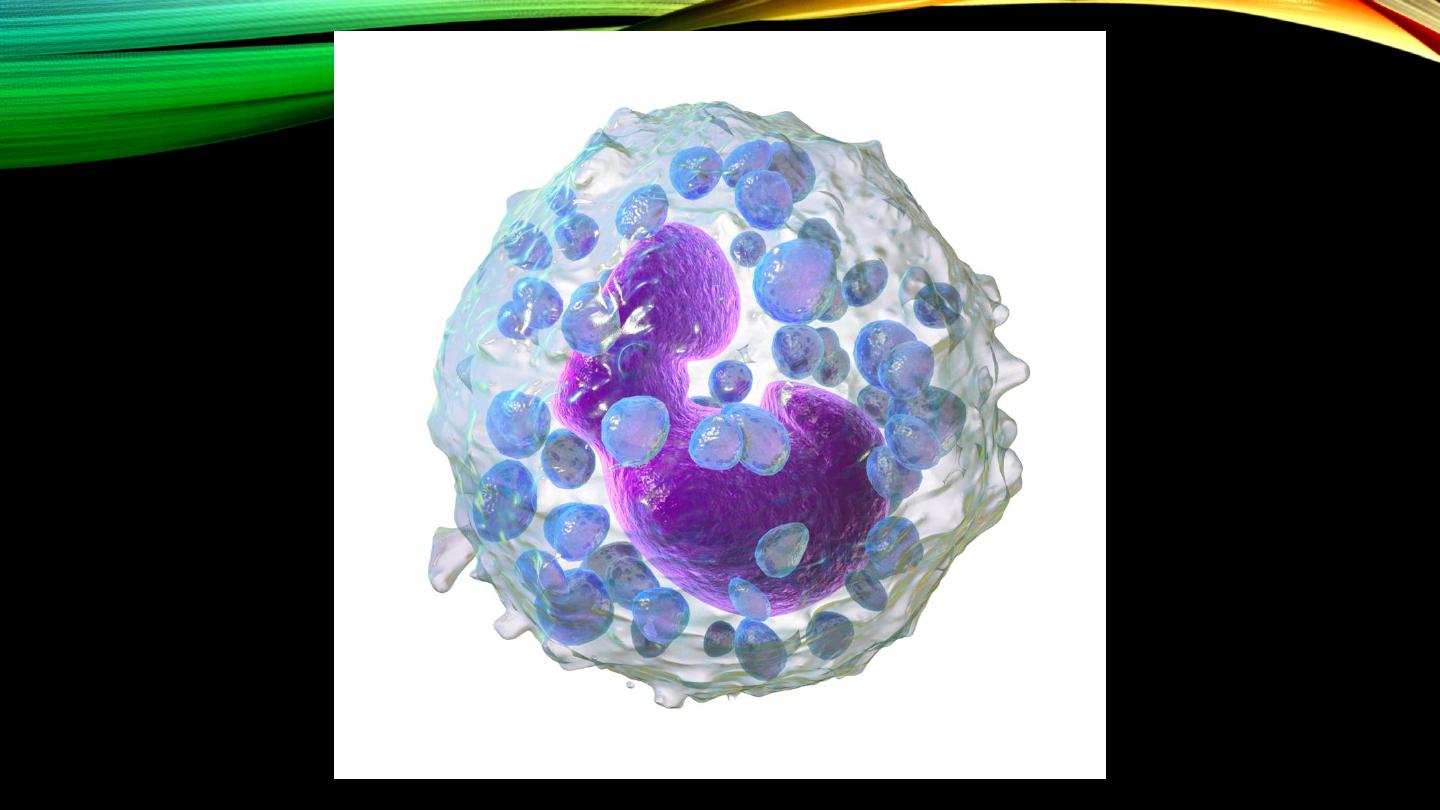

Basophils (cont’d):
• IgE-related allergic reaction
• Secretion of heparin, histamine and bradykinin
• Role in reducing inflammation
• Phagocytic?

Lymphocytes:
• Type and percentage
• Nucleus and cytoplasm
• Site of formation
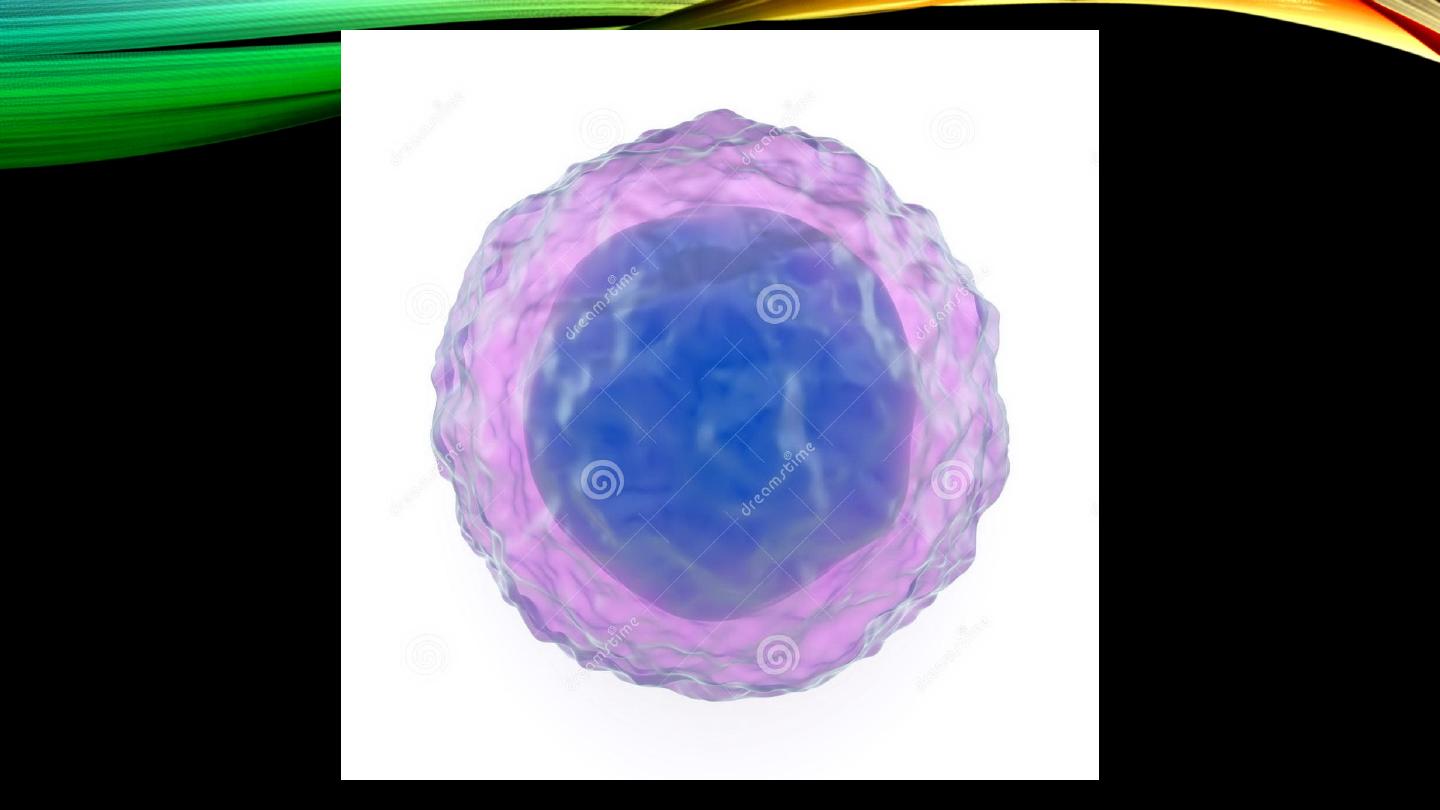

Lymphocytes (cont’d):
• Subtypes
• T-cell, function
• B-cell, function
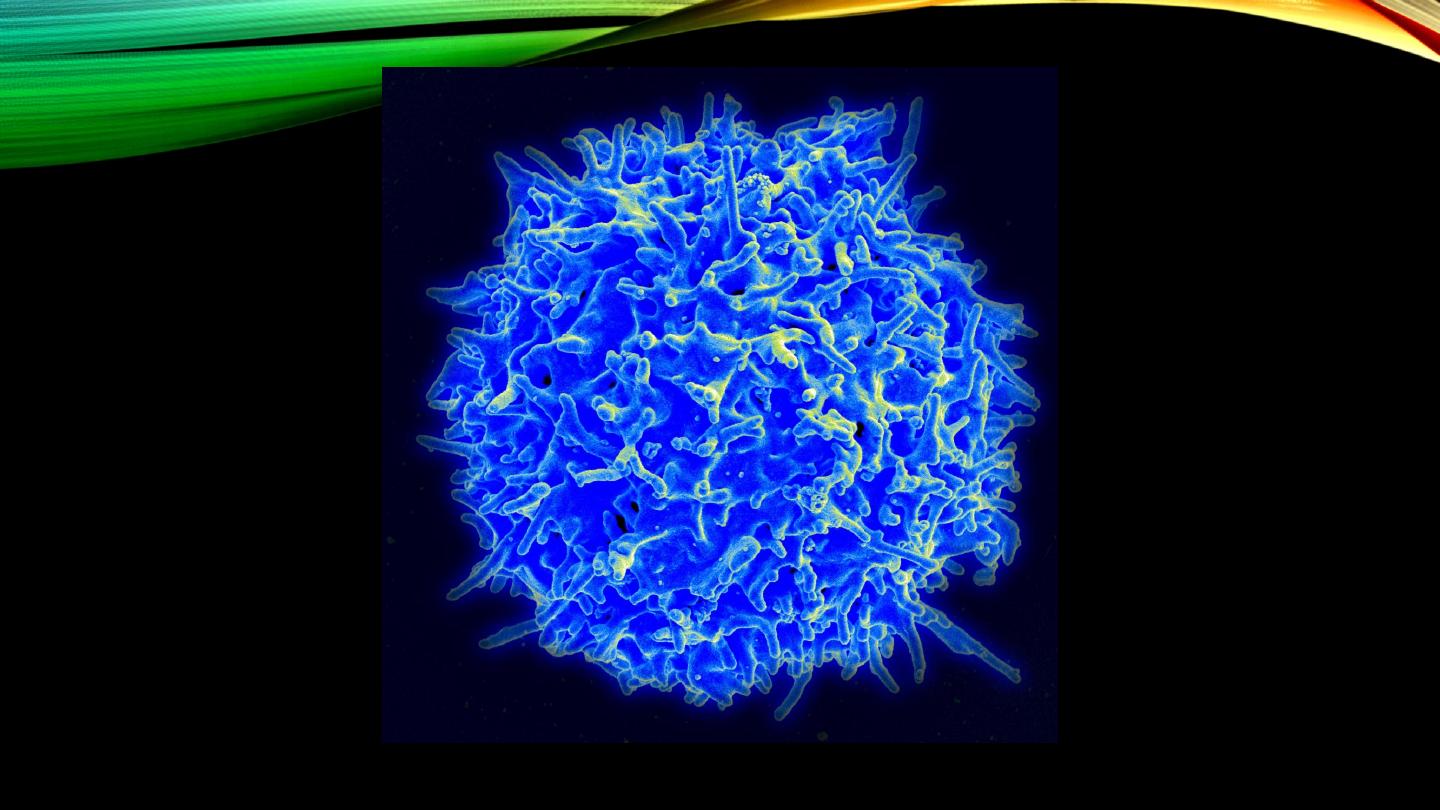
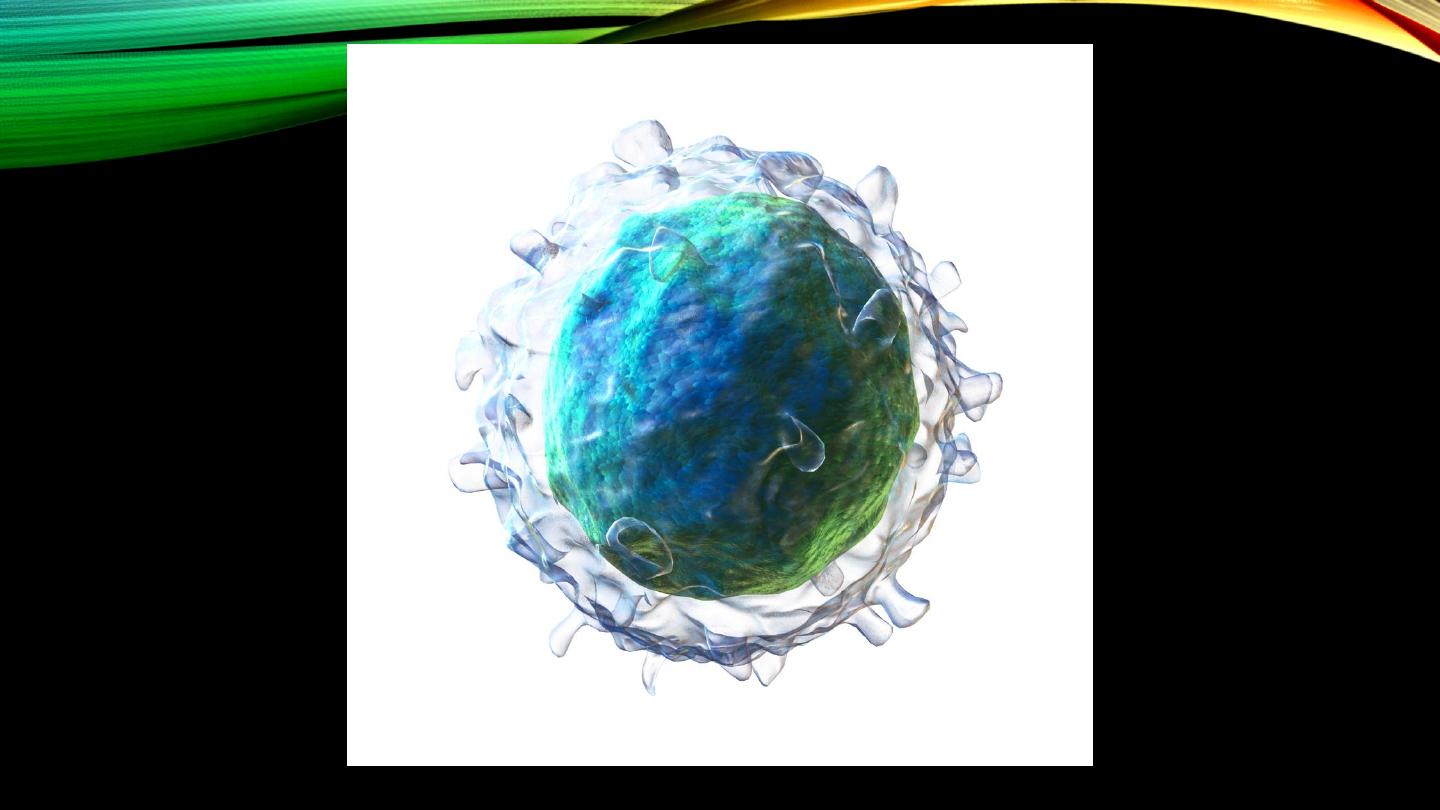

Monocytes:
• Type and percentage
• Size, nucleus and cytoplasm
• Phagocytosis, macrophages?

Life span of WBCs:
• Granulocytes, infection?
• Monocytes, in circulation and tissues
• Lymphocytes, continual circulation and body’s need

Good Luck
