
Medical biology
Lecture 2
Light Microscopy

Types of microscopes
Conventional bright-field microscopy
Fluorescence,
Phase-contrast,
Confocal,
Based on the interaction of light and
tissue components and can be used to
reveal and study tissue features
.
Bright-Field Microscopy
With the bright-field microscope (e.g. Compound
Microscope), widely used by students of histology,
stained preparations
are examined by means of
ordinary light
that
passes
through the specimen.
The microscope is composed of
mechanical
and
optical
parts
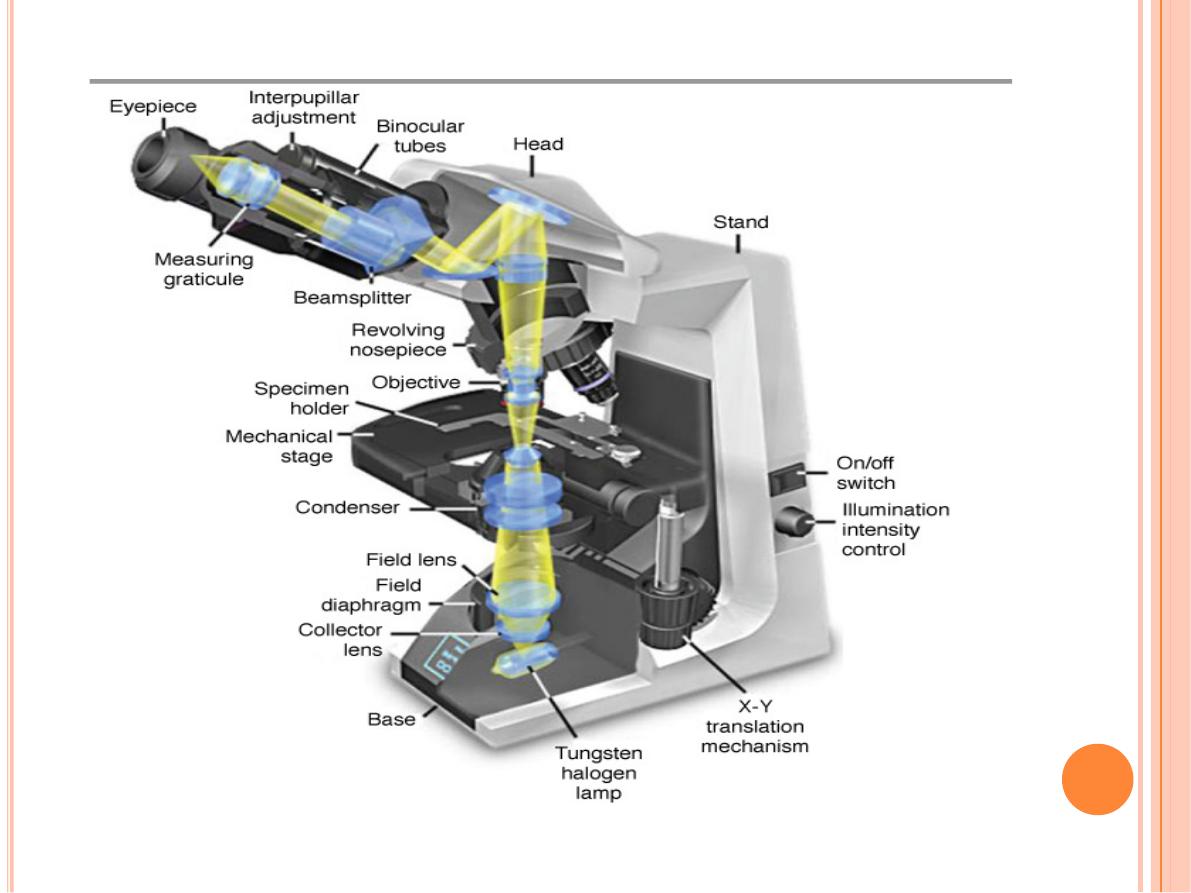

The optical components consist of three systems of
lenses
.
The
condenser
collects and focuses light, producing a
cone of light that illuminates the object to be observed.
The
objective
lenses enlarge and project the illuminated
image of the object in the direction of the eyepiece.
The
eyepiece
or ocular lens further magnifies this image
and projects it onto the viewer's
retina
,
photographic film
,
or (to obtain a digital image) a
detector
such as a
charge-
coupled device (CCD) camera
.
The total magnification =
magnifying power
of the
objective
x
magnifying power
of the
ocular
lenses.
**
The critical factor in obtaining a detailed image with a light
microscope is its
resolving power
(the smallest distance
between two particles at which they can be seen as separate
objects).
**
The maximal resolving power of the light microscope is
approximately 0.2um; this power permits good images
magnified 1000–1500 times.
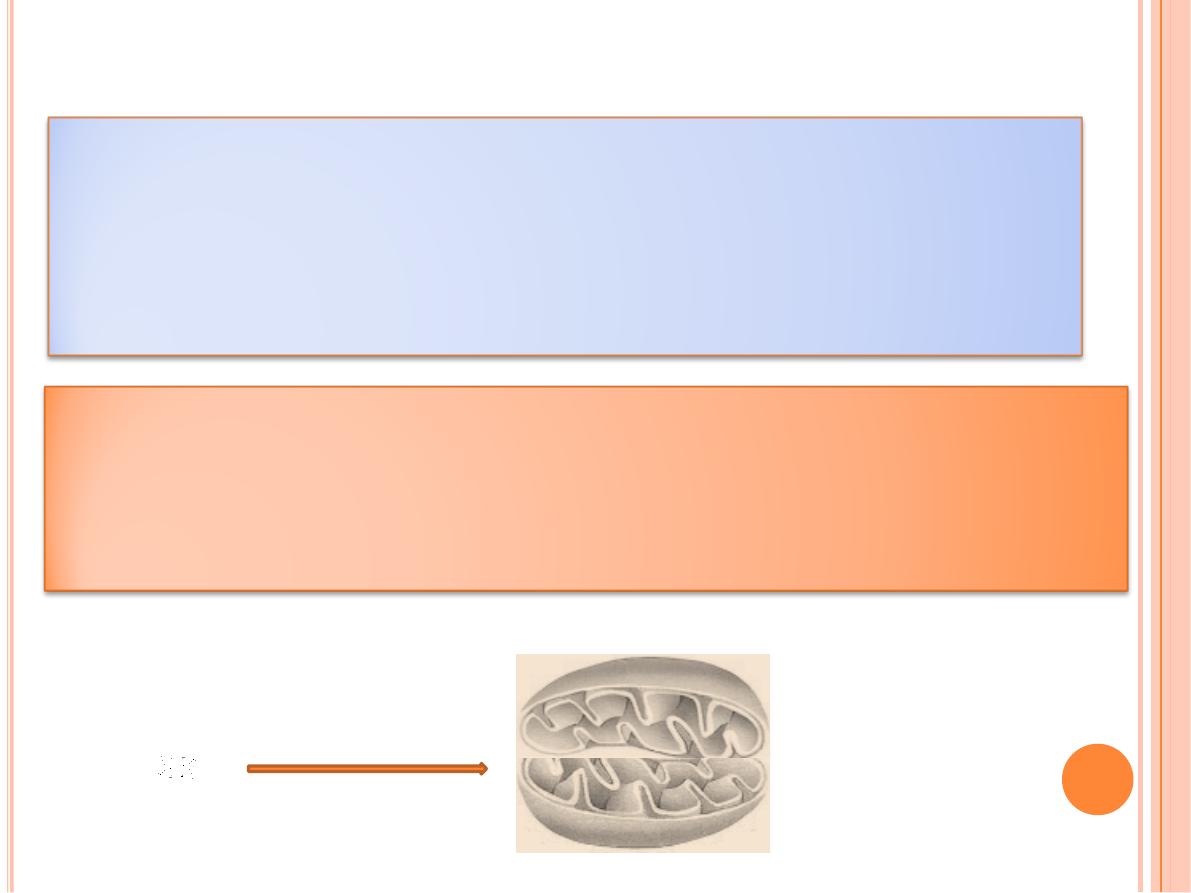
Objects smaller or
thinner
than
0.2um
(such as a
ribosome, a membrane, or a filament of actin)
cannot be distinguished with this instrument
Two objects such as mitochondria will be
seen as only one object if they are separated
by less than 0.2 um.
The
quality
of the image (its
clarity and richness
of detail)
depends on the microscope's resolving power.
The magnification is of value only when accompanied by
high resolution.
The resolving power of a microscope depends mainly on
the quality of its objective lens
.

The eyepiece lens enlarges only the image obtained by the
objective
it does not
improve resolution.
when comparing objectives of different magnifications,
those that provide higher magnification also have higher
resolving power
.
Video cameras highly sensitive to light
enhance
the power
of the bright-field and other light microscopes and allow
the capture of digitized images suitable for
computerized
image analysis and printing
.
With digital cameras and image-enhancement programs (to
enhance contrast, for example),
objects that may not be
visible when viewed directly through the ocular may be made
visible in the video screen.
video systems are useful for studying
living cells
for long
periods of time, because they use
low-intensity light
and thus
avoid the cellular damage from heat that can result from
intense illumination.
software for image analysis allows rapid measurements
and quantitative study of microscopic structures
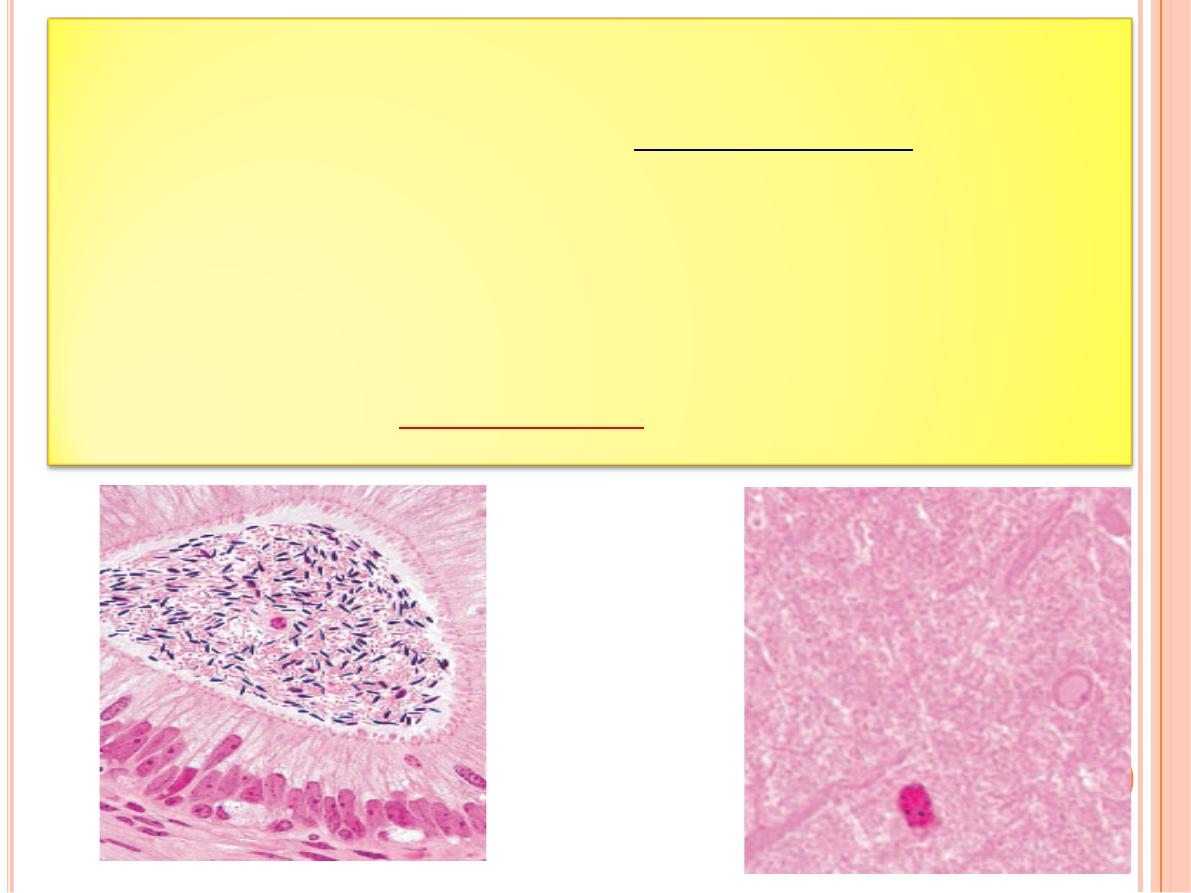
Fluorescence Microscopy
When certain substances are irradiated by light of a proper
wavelength, they emit light with a longer wavelength. This
phenomenon is called
fluorescence
.
In
fluorescence microscopy
, tissue sections are usually
irradiated with
ultraviolet (UV) light
and the emission is in
the
visible
portion of the spectrum.
The fluorescent
substances appear brilliant on a dark background
.
For this
method, the microscope has a strong UV light source and
special filters that select rays of different wavelengths
emitted by the substances.
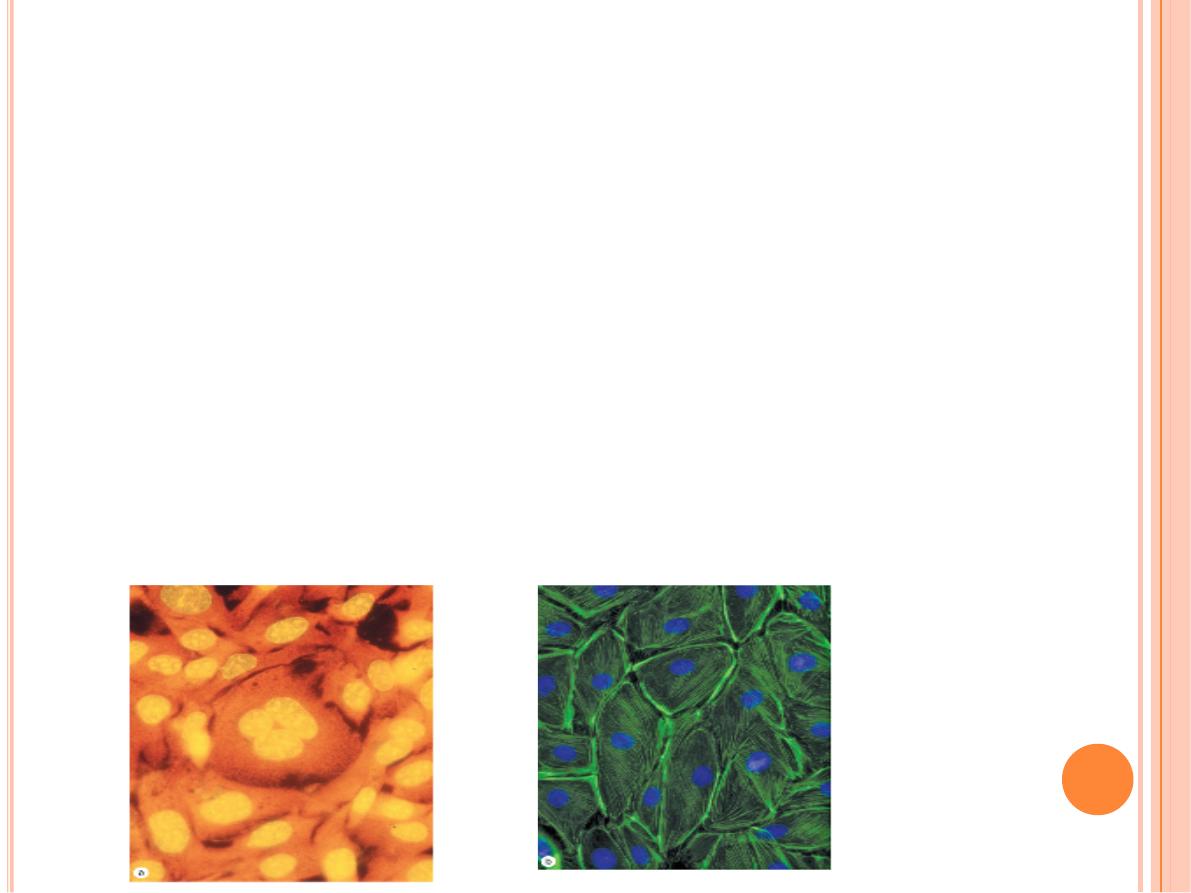
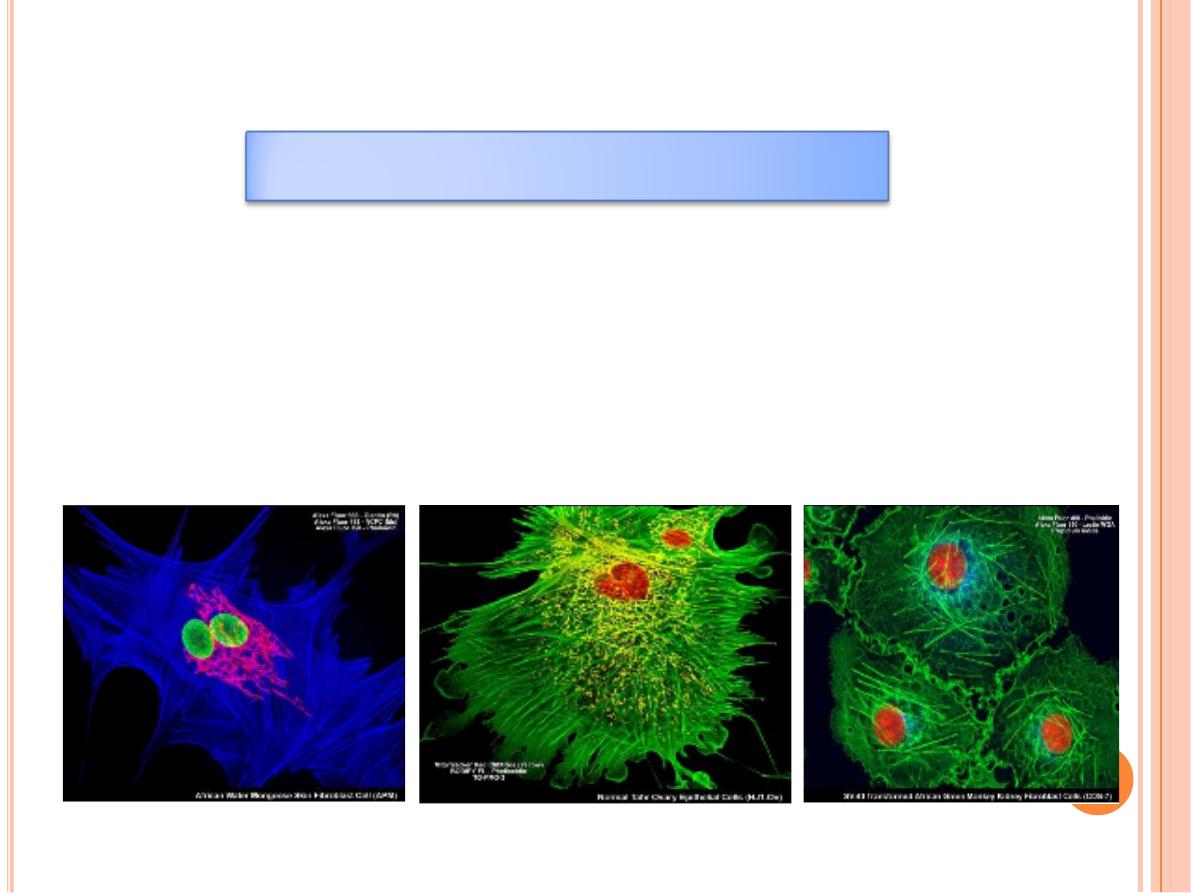
Fluorescent compounds with affinity for specific cell macromolecules
may be used as
fluorescent stains
.
Acridine orange
, which binds both
DNA and RNA, is an example. When observed in the fluorescence
microscope, these nucleic acids emit slightly different fluorescence,
allowing them to be localized separately in cells. Other compounds such
as
Hoechst stain
and
DAPI
specifically bind DNA and are used to stain
cell nuclei, emitting a characteristic blue fluorescence under UV.
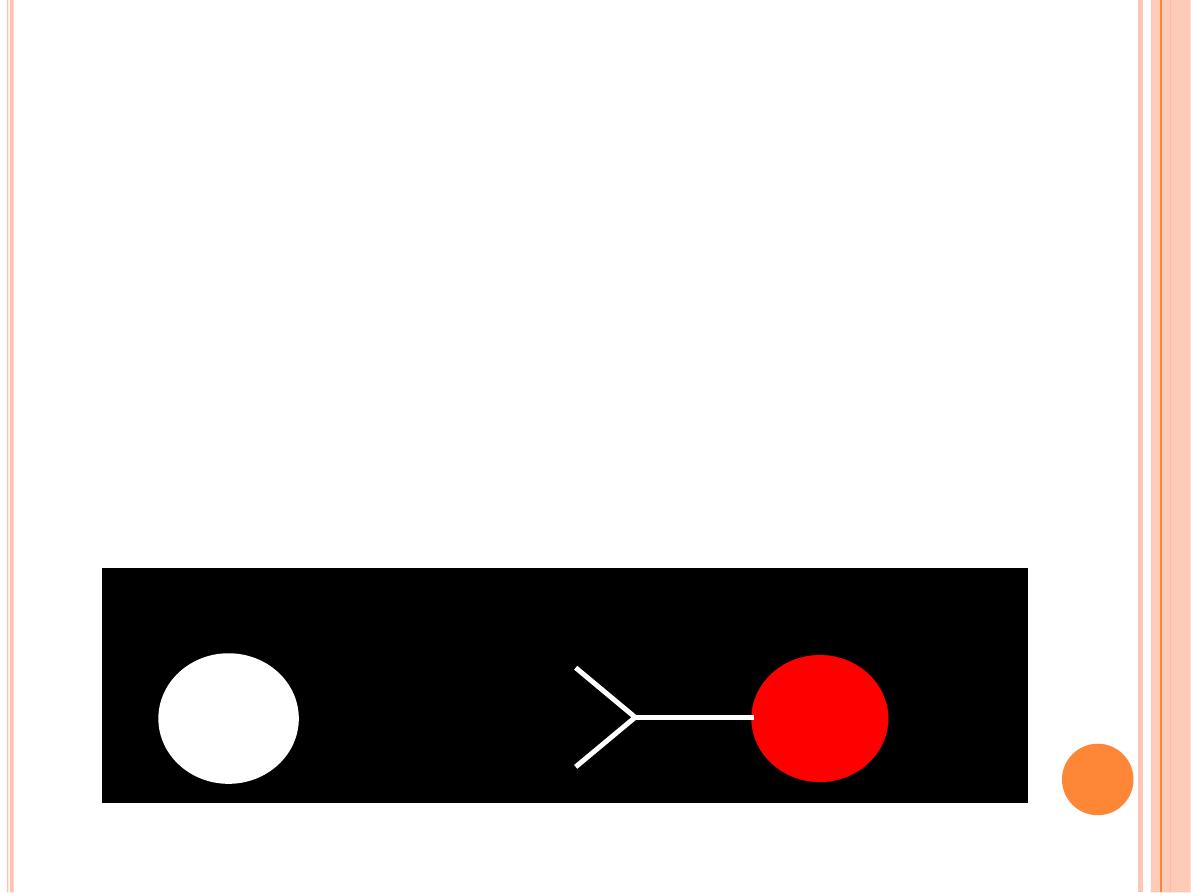
Antibodies labeled with fluorescent compounds are extremely
important in immunohistological staining.
ANTIGEN
ANTIBODY
FLUOROCHROME
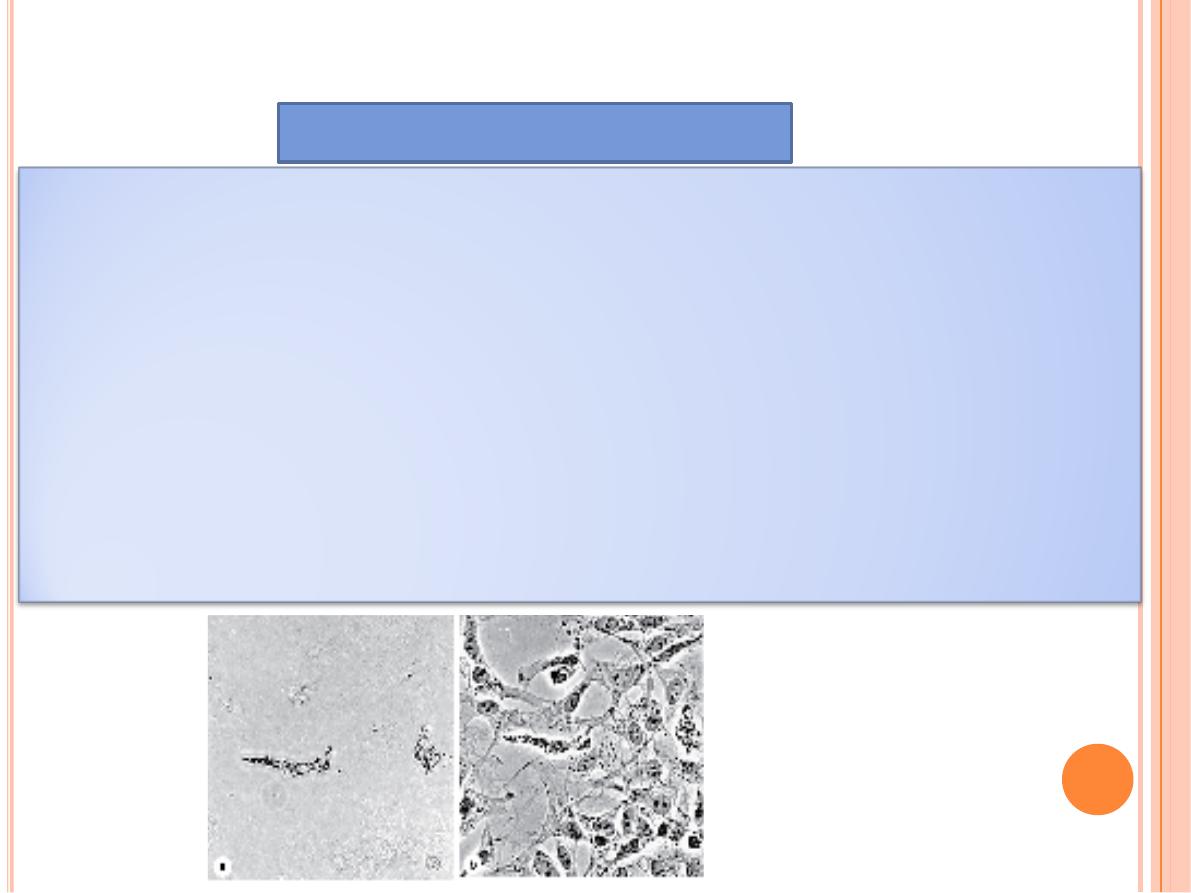
Phase-Contrast Microscopy
Some optical arrangements allow the observation of unstained cells
and tissue sections.
Unstained biological specimens are usually transparent and difficult to
view in detail, because all parts of the specimen have almost the same
optical density.
Phase-contrast microscopy, however, uses a lens system that produces
visible images from transparent objects

Phase-contrast microscopy is based on the principle that
light
changes its speed when passing through cellular and extracellular
structures with different refractive indices
.
These changes are used by the phase-contrast system to cause the
structures to appear lighter or darker in relation to each other.
Because it does not require fixation or staining, phase-contrast
microscopy allows observation of living cells and tissue cultures, and
such microscopes are prominent tools in all cell culture labs.
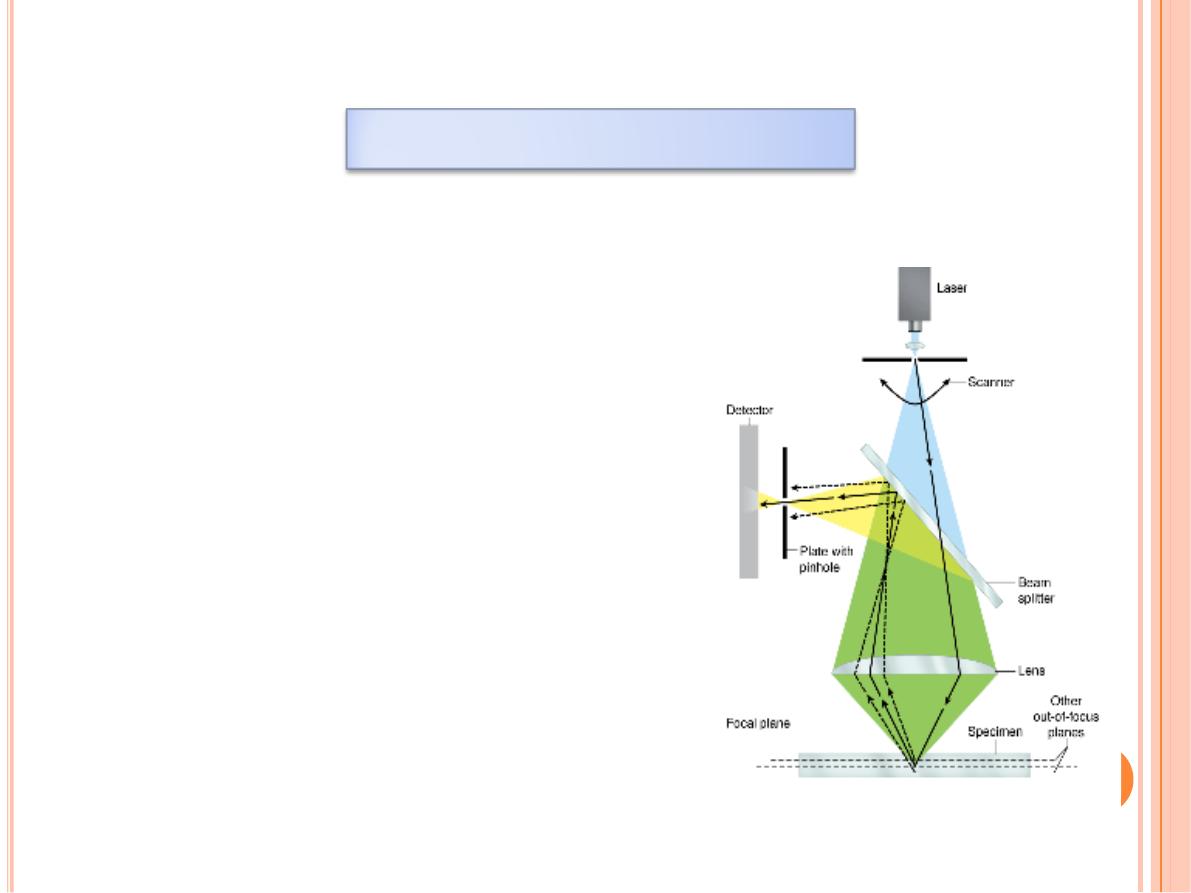
Confocal Microscopy
With a regular bright-field microscope
the beam of light is relatively large
and fills the specimen. Stray light
reduces contrast within the image and
compromises the resolving power of
the objective lens
Figure 1–6: Confocal microscope

Confocal microscopy avoids stray light and achieves greater
resolution by using:
(1) A small point of high-intensity light provided by a laser and
(2) A plate with a pinhole aperture in front of the image detector
.
The point
light source
, the
focal point
of the lens, and the detector's
pinpoint
aperture
are all optically conjugated or aligned to each other
in the focal plane (confocal) and
unfocused light does not pass
through the pinhole
.
This greatly improves resolution of the object in focus and allows the
localization of specimen components with much greater precision
than with the bright-field microscope.

Most confocal microscopes include a computer-driven mirror system
(the
beam splitter
) to move the point of illumination across the
specimen automatically and rapidly.
Digital images captured at many individual spots in a very thin
plane-
of-focus
are used to produce an "
optical section
" of that plane.
Moreover, creating optical sections at a series of focal planes through
the specimen allows them to be digitally reconstructed into a
three-
dimensional image

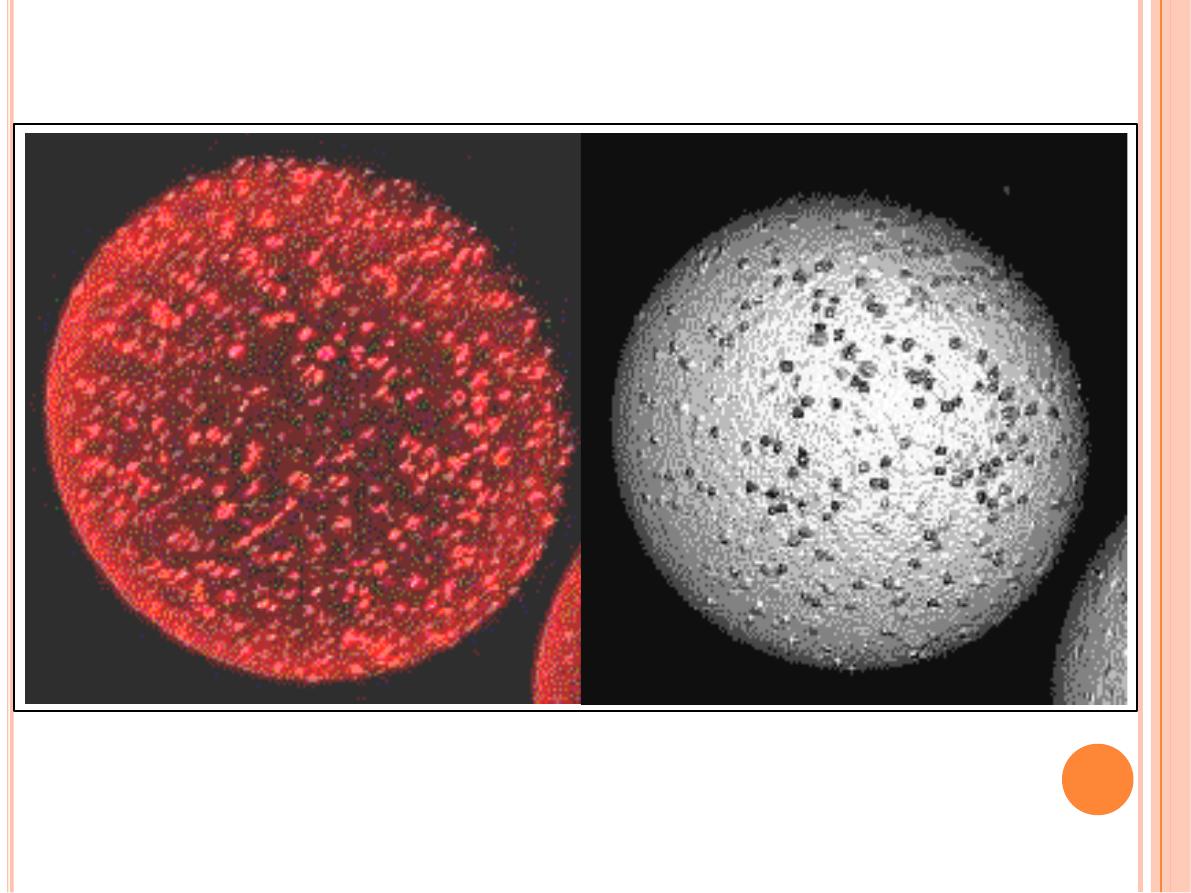
Animated 3-Dimensional Reconstruction
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
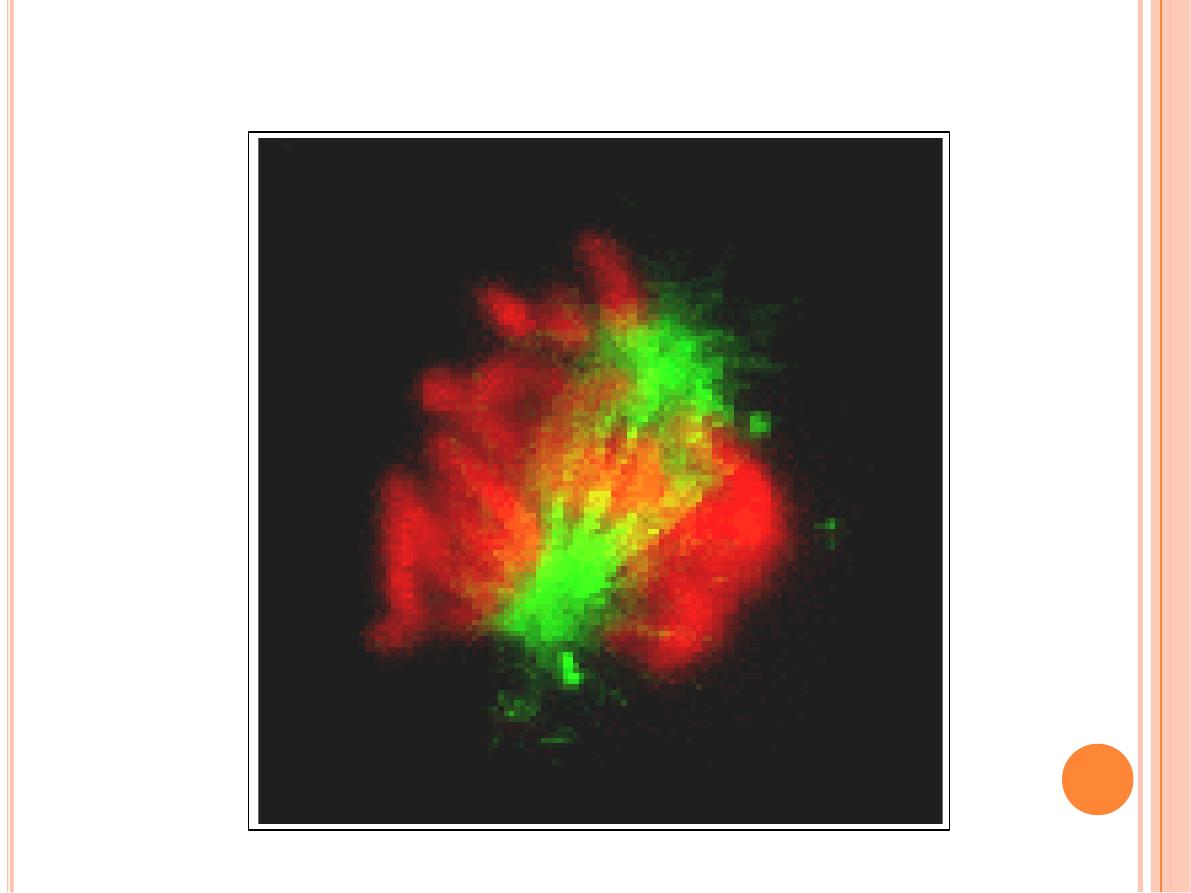
Animated 3-Dimensional Reconstruction
Mitosis
www.Zeiss.com

Q/
1- Define: resolving power
2- which type microscope not need stain?
