
1
Polysaccharides
Assistant. Prof Dr. Ban Mahmood Shaker Al-joda

2
Polysaccharides :
are large molecules
containing 10 or more monosaccharide units.
Carbohydrate units are connected in one
continuous chain or the chain can be
branched.

3
POLYSACCHARIDES
These are polymerized products of many
monosaccharide units. They may be
1. Homoglycans
are composed of single
kind of monosaccharides, e.g.
starch,
glycogen and cellulose.
2. Heteroglycans
are composed of two or
more different monosaccharides, e.g.
hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulphate
.

4
•
Classification of polysaccharide
When polysaccharides are composed of a
single monosaccharide building block, they
are termed
homopolysaccharides
.
They are
Branched
or
unbranched
Storage or structural
Polysaccharides composed of more than one
type of monosaccharide are termed
heteropolysaccharides
5
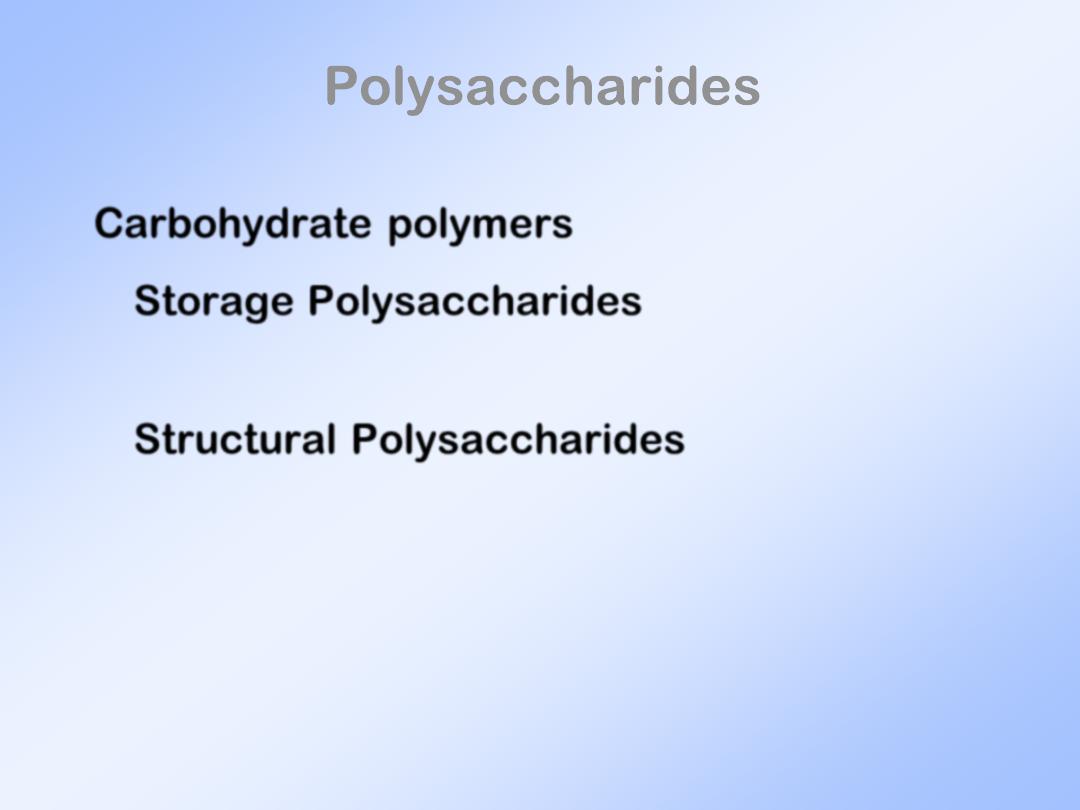
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrate polymers
Storage Polysaccharides
Energy storage - starch and glycogen
Structural Polysaccharides
Used to provide protective walls or
lubricative coating to cells - cellulose
and mucopolysaccharides.

6
Starch
Energy storage used by plants
Long repeating chain of
-D-glucose
Chains up to 4000 units
Amylose
straight chain
major form of starch
Amylopectin
branched structure
7
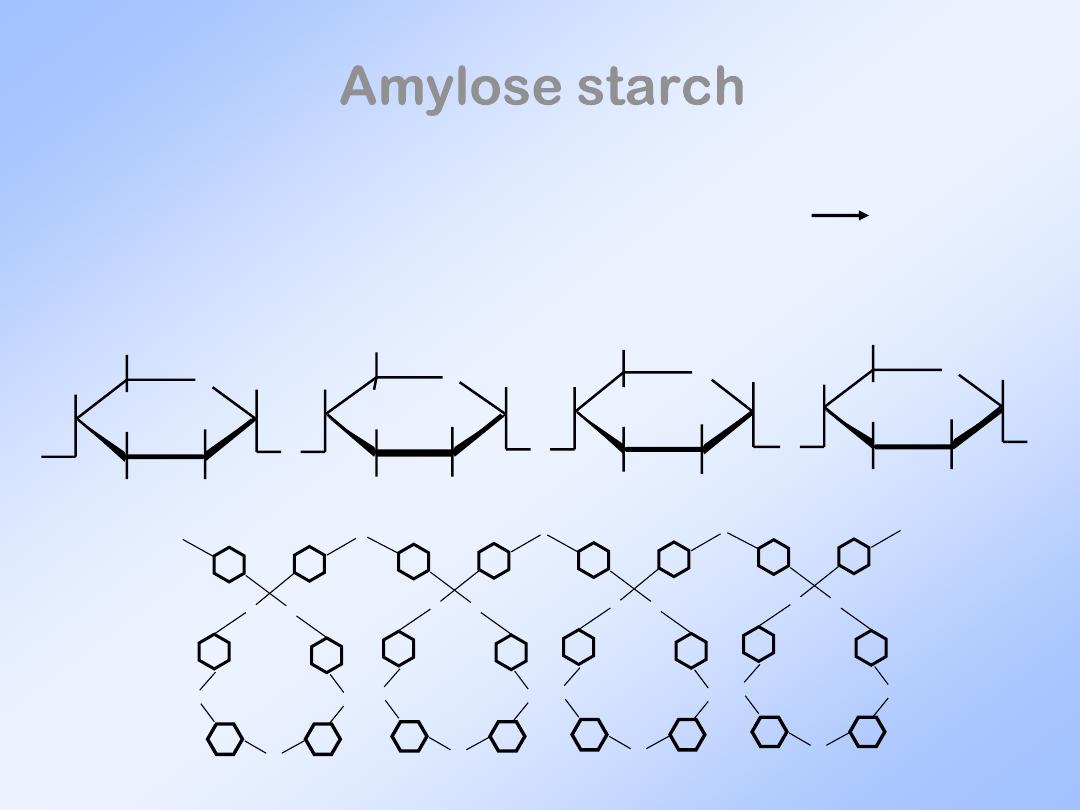
Amylose starch
Straight chain that forms coils
(1 4)
linkage. Most common type of starch.
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
8
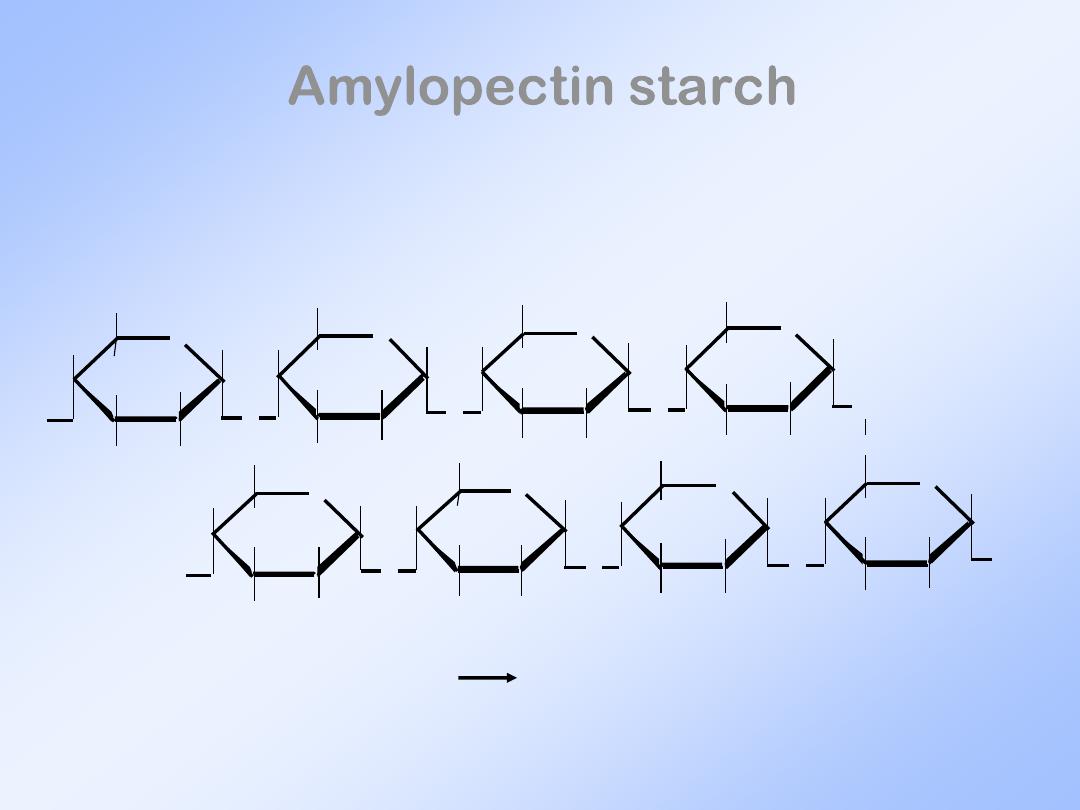
Amylopectin starch
Branched structure due to crosslinks.
(1 6) linkage
at crosslink
OH
H
OH
H
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
H
O
O
9
c
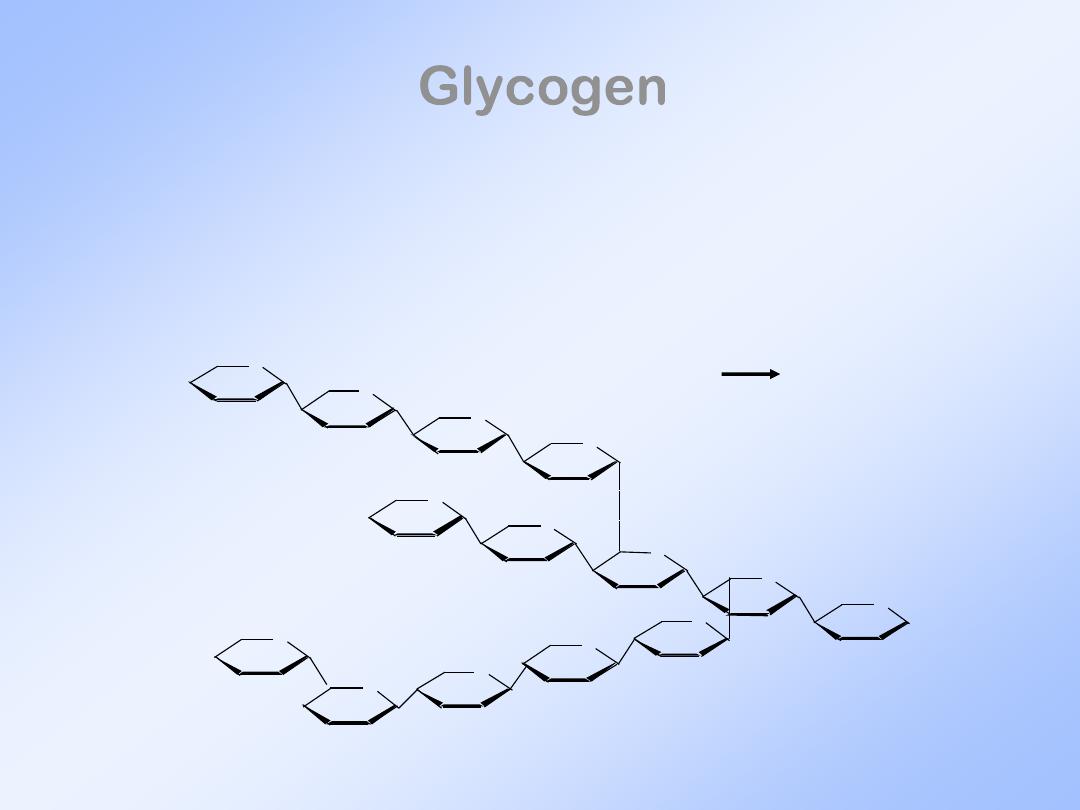
Glycogen
•
Energy storage of animals.
•
Stored in liver and muscles as granules.
•
Similar to amylopectin.
(1 6) linkage
at crosslink
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
c
10
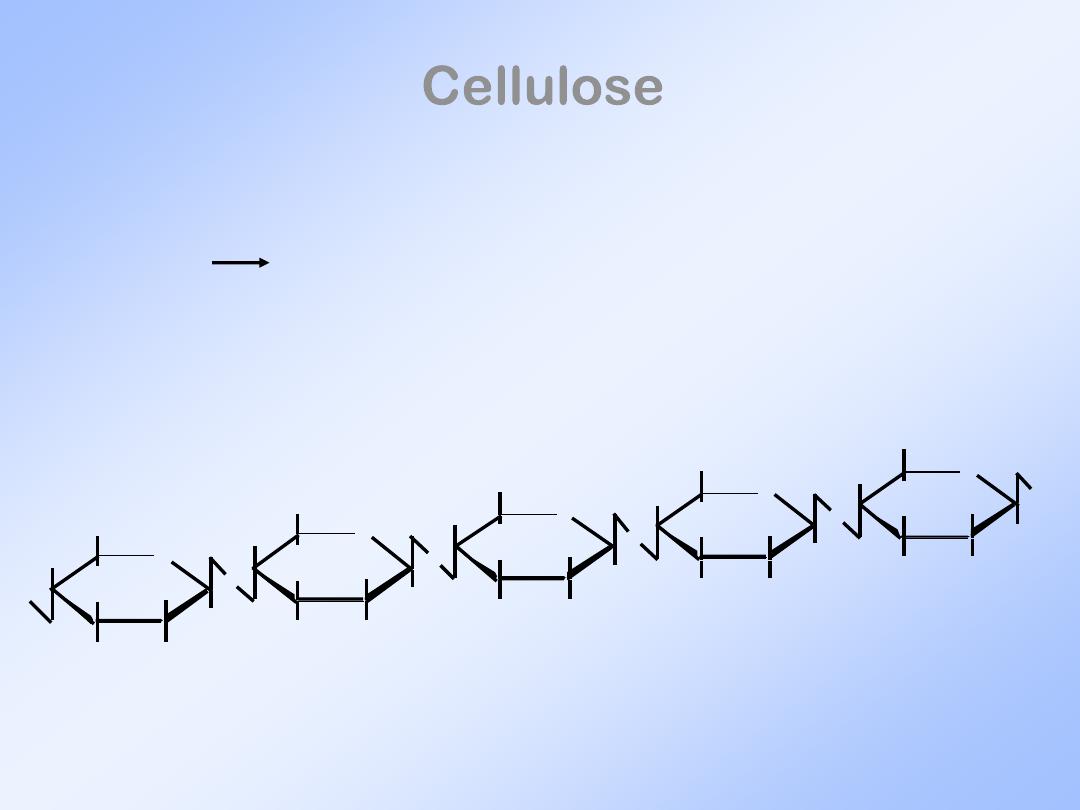
Cellulose
•
Most abundant polysaccharide.
•
(1 4) glycosidic linkages.
•
Result in long fibers - for plant structure.
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
O
O
H
H
H
OH
H
OH
CH
2
OH
H
O
11
▪
Cellulose
: is the chief insoluble constituent
of plants framework.
▪
It consists of β-D-glucopyranose units
linked by
β(1 → 4)
bonds to form long,
straight chains.
▪
Cellulose
cannot be
digested by human
because of the absence of an enzyme that
hydrolyzes the
β linkage.
▪
There is limited bacterial metabolism of
cellulose in the human colon

12
▪
Inulin
is a homopolysaccharide
of
fructose
, linked by
β
(1-2)
glycosidic bond.
▪
found in tubers and roots of
artichoke
( used for assessment
of glomerular filtration rates .

13
Dextrans
These are highly branched homopolymers
of glucose units with 1-6, 1-4 and 1-3
linkages.
Dextrin
is the partially digested product of
starch. Dextran is high molecular weight
carbohydrate, synthesized by bacteria.
D-glucose is otherwise called Dextrose, a
term often used in bed-side medicine, e.g.
dextrose
drip.

14
Agar
i. It is prepared from sea weeds. It contains galactose,
glucose and other sugars.
ii. It is dissolved in water at 100
°C, which upon cooling sets
into a gel.
iii.Agar cannot be digested by bacteria and hence used widely
as a supporting agent to culture bacterial colonies. Agar is
used as a supporting medium for immuno-diffusion and
immuno-electrophoresis.
Agarose is made up of galactose combined with 3,6-
anhydrogalactose units; it is used as matrix for
electrophoresis

15
Homoglycans
Inulin D-fructose, beta-1,2 linkages
Dextran Glucose, 1-6, 1-4, 1-3 linkages
Heteroglycans
Agar Galactose, glucose
Agarose
Galactose, anhydrogalactose

16
Reference
TEXTBOOK OF BIOCHEMISTRY For Medical Students (Sixth
Edition) .
DM VASUDEVAN MBBS MD FAMS FRCPath Distinguished Professor of
Biochemistry College of Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences,
Cochin, Kerala (Formerly Principal, College of Medicine, Amrita, Kerala)
(Formerly, Dean, Sikkim Manipal Institute of Medical Sciences, Gangtok,
Sikkim) E-mail: dmvasudevan@yahoo.co.in
