
Buffer in solutions
Dr.Alaa J.Mahrath
Medical Chemistry
College of Medicine Babylon
University

Objective
LEARNING GOAL: Describe the role
of buffers in maintaining the pH of a
solution in body fluids.
AJM BioChem
2

The pH of water and most solutions
changes drastically when a small amount
of acid or base is added.
However, when an acid or base is added
to a
buffer solution
, there is little change in
pH.
A buffer solution
maintains pH by
neutralizing small amounts of added acid
or base.
AJM BioChem
3

For example, blood contains buffers that
maintain a consistent pH of
about 7.4 .
If the pH of the blood goes slightly above or
below
7.4,
changes in oxygen levels and
metabolic processes can be drastic enough
to cause death.
Even though we obtain
acids
and
bases
from
foods and cellular reactions
, the buffers in
the body absorb those compounds so
effectively that the pH of the blood remains
essentially unchanged (see Figure 1)
AJM BioChem
4
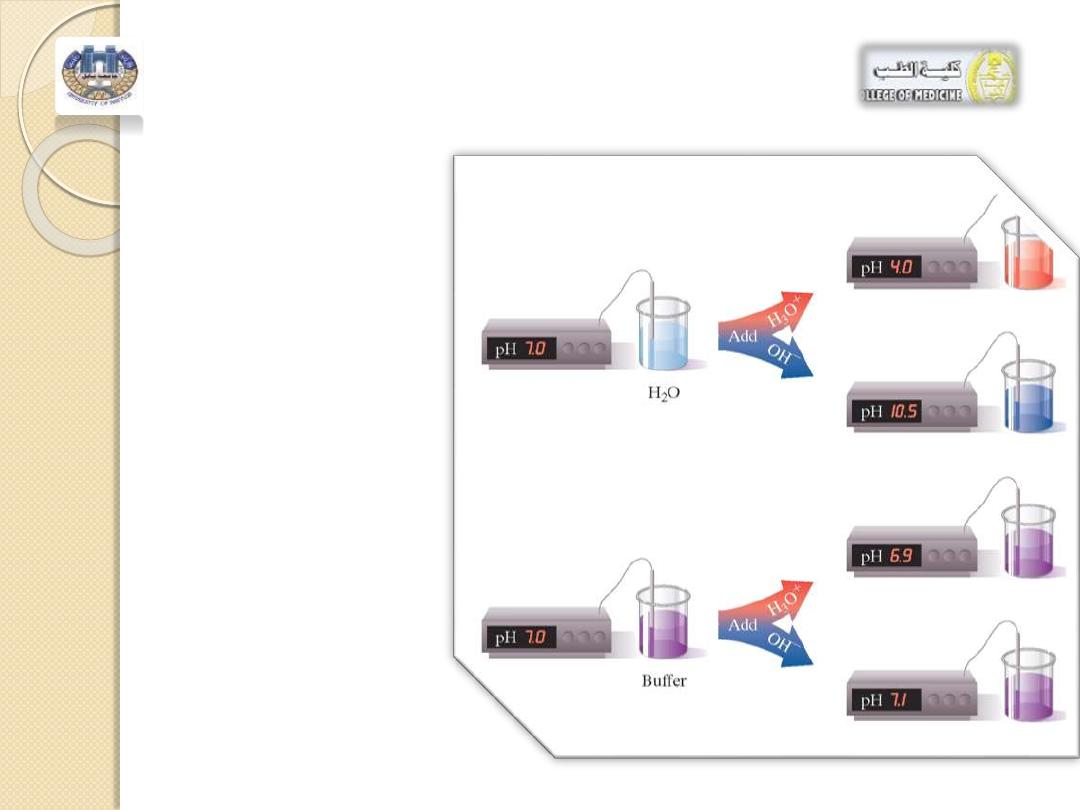
FIGURE 1
►
Adding
an acid or a base to
water
changes
the
pH drastically, but a
buffer
resists
pH
change when small
amounts of acid or
base
are
added.
AJM BioChem
5

In a buffer, an
acid
must be present to react
with any
OH
-
that is added, and a base must
be available to react with any added
H
3
O
+
.
However, that acid and base must not
neutralize each other,
Therefore, a combination of an acid-base
conjugate pair is used to prepare a buffer.
Most buffer solutions consist of nearly equal
concentrations of a
weak acid and a salt
containing its conjugate base.
AJM BioChem
6

Buffers may also contain
a weak base and a
salt containing its conjugate acid.
FIGURE :2
►
The buffer described here consists of about equal concentrations of ace tic acid
(
HC
2
H
3
O
2
)
and its conjugate base, acetate ion
(
C
2
H
3
O
2
)
. Adding H
3
O
+
to the buffer reacts with C
2
H
3
O
2
, whereas adding
OH
"
neutralizes HC
2
H
3
O
2
. The pH of the solution is maintained as long as the added amounts of acid or base
are small compared to the concentrations of the buffer components
AJM BioChem
7

Question ?
How does this (acetic acid-acetate ion) buffer
maintain pH ?
For example
, a typical buffer can be made from
the weak acid, acetic acid
(HC
2
H
3
O
2
),
and its
salt, sodium acetate
(NaC
2
H
3
O
2
).
As a weak acid, acetic acid ionizes slightly in
water to form
H
3
O
+
and a small amount of
C
2
H
3
O
2
-
.
The addition of its salt provides a much larger
concentration of the acetate ion
(C
2
H
3
O
2
-
),
which is necessary for its buffering capability.
AJM BioChem
8
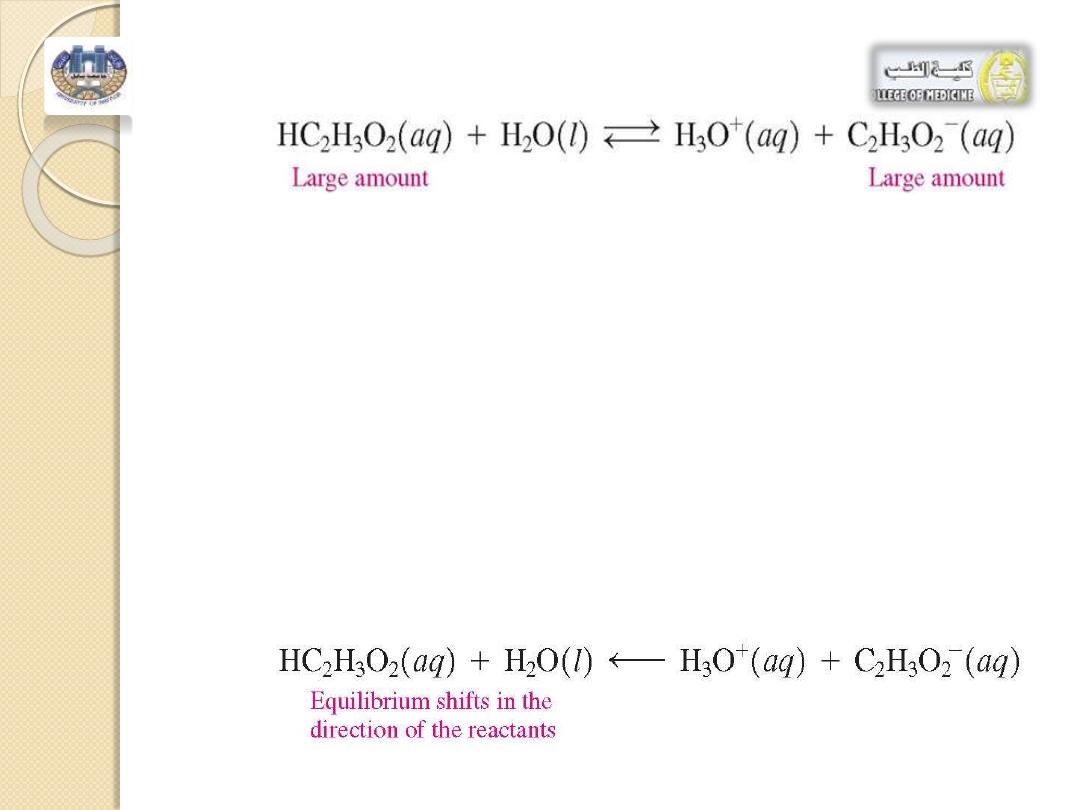
•
We can now describe how this buffer solution maintains the
[H
3
O
+
]. ?
•
When a small amount of acid is added, it combines with the
acetate ion, C
2
H
3
O
2
-, causing the equilibrium to shift in the
direction of HC
2
H
3
O
2
. There will be a slight decrease in
[C
2
H
3
O
2
-] and a slight increase in [HC
2
H
3
O
2
]; thus both
[H
3
O
+
] and pH are maintained.
AJM BioChem
9
CH
3
COOH CH
3
COO
-
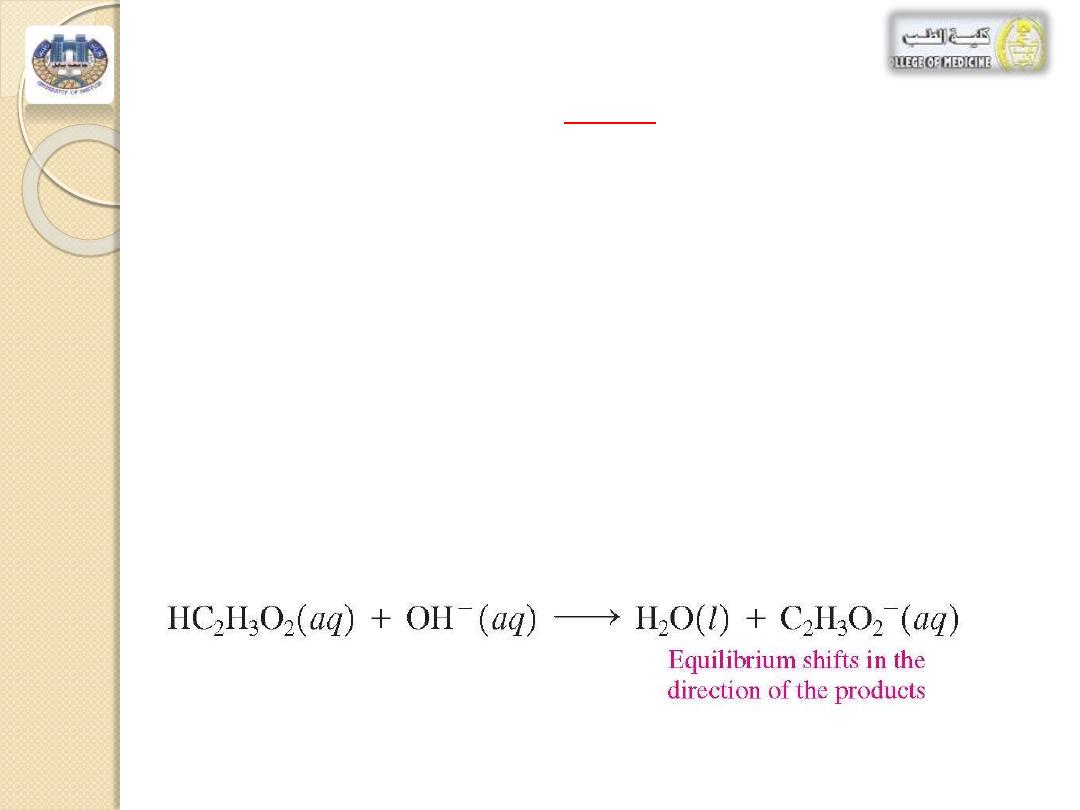
If a small amount of
base
is added to this buffer
solution, it is neutralized by the acetic acid,
HC
2
H
3
O
2
.
The equilibrium shifts in the direction of the
products, water
and [C
2
H
3
O
2
-
]
.
The
[HC
2
H
3
O
2
] decreases
slightly and the
[C
2
H
3
O
2
-
] increases
slightly, but again the
[H
3
O
+
]
and the pH of the solution are maintained (see
Figure 2).
AJM BioChem
10

Sample problem 1
: indicate whether each of the
following would make a buffer solution:
a. HCl, a strong acid, and NaCl
b. H3PO
4
, a weak acid
c. HF ,a weak acid ,and NaF
SOLUTION
a. No. A buffer requires a weak acid and a salt
containing its conjugate base.
b. No. A weak acid is part of a buffer, but the salt
containing the conjugate base of the weak acid is
also needed.
c. Yes. This mixture would be a buffer since it
contains a weak acid and a salt containing its
conjugate base.
AJM BioChem
11

STUDY CHECK 2
In a buffer made from the weak acid
HCHO
2
and its salt, KCHO
2
, when H
3
O
+
is added, is neutralized by :
(1) the salt,
(2) H
2
O,
(3) OH-, or
(4) the acid?
AJM BioChem
12
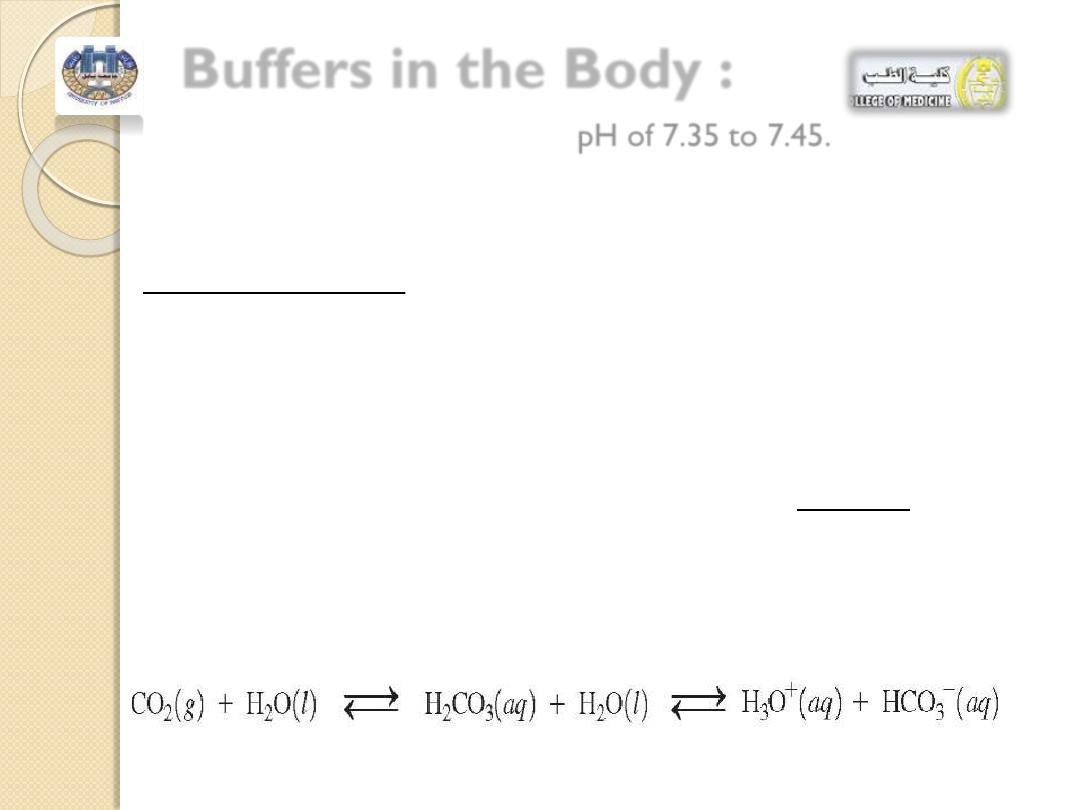
Buffers in the Body :
The arterial blood has a normal
pH of 7.35 to 7.45.
If changes in
H
3
O
+
lower the pH
below 6.8
or raise it
above 8.0
,
cells cannot function properly and death may result.
In our cells,
CO
2
is continually produced as an end product of
cellular metabolism.
Some
CO
2
is carried to the lungs for elimination, and the rest
dissolves in body fluids such as plasma and saliva, forming
carbonic
acid (H
2
CO
3
)
As a
weak acid, carbonic acid
ionizes to give bicarbonate,
HCO
3
-
and
H
3
O
+
.
More of the anion
HCO
3
-
is supplied by the kidneys to give an
important buffer system in the body fluid:
the
H
2
CO
3
/
HCO
3
-
buffer.
AJM BioChem
13

Excess
H
3
O
+
entering the body fluids reacts
with the
HCO
3
-
and excess
OH
-
reacts with
the
carbonic acid.
AJM BioChem
14
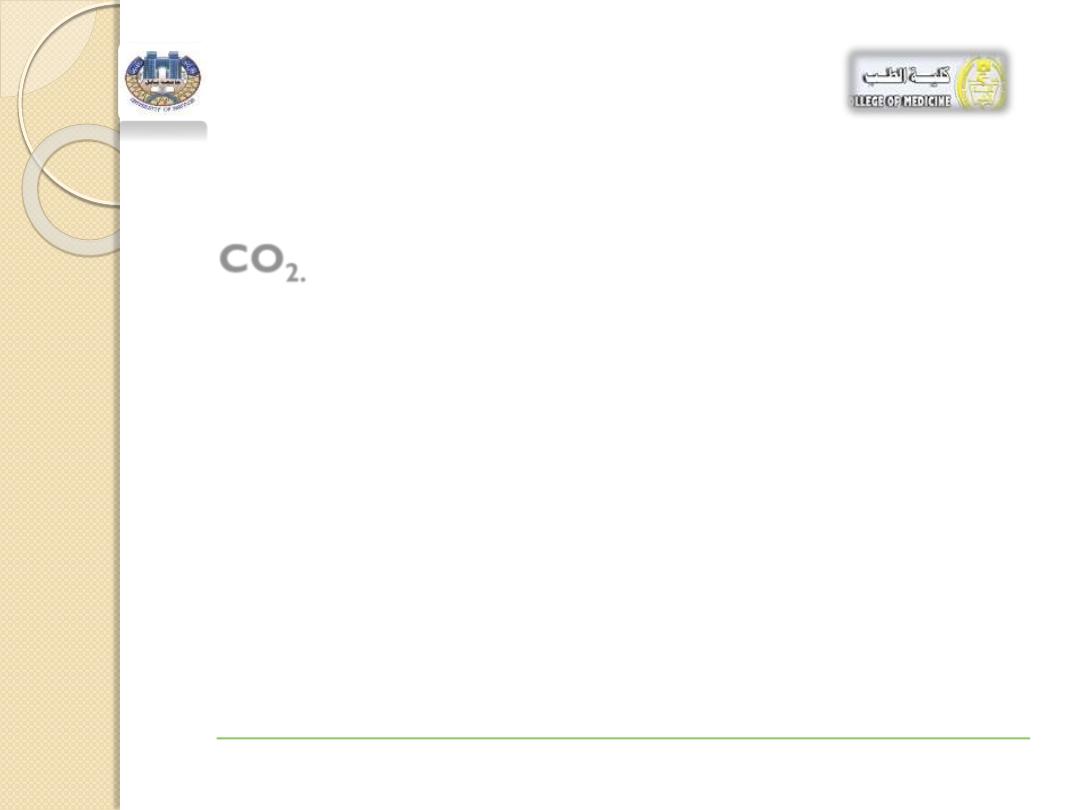
In the body,
the concentration of carbonic acid
is
closely associated with the partial pressure of
CO
2.
Table 1 : lists the normal values for arterial
blood.
If the
CO
2
level increases,
it produces more
H
2
CO
3
and more
H
3
O
+
, lowering the pH.
This condition is called
acidosis
. (Difficulty with
ventilation or gas diffusion can lead to respiratory
acidosis, which can happen in emphysema or
when the medulla of the brain is affected by an
accident or depressive drugs).You can see short
video about buffer in body by this link :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lDmn8zeJbQs
AJM BioChem
15
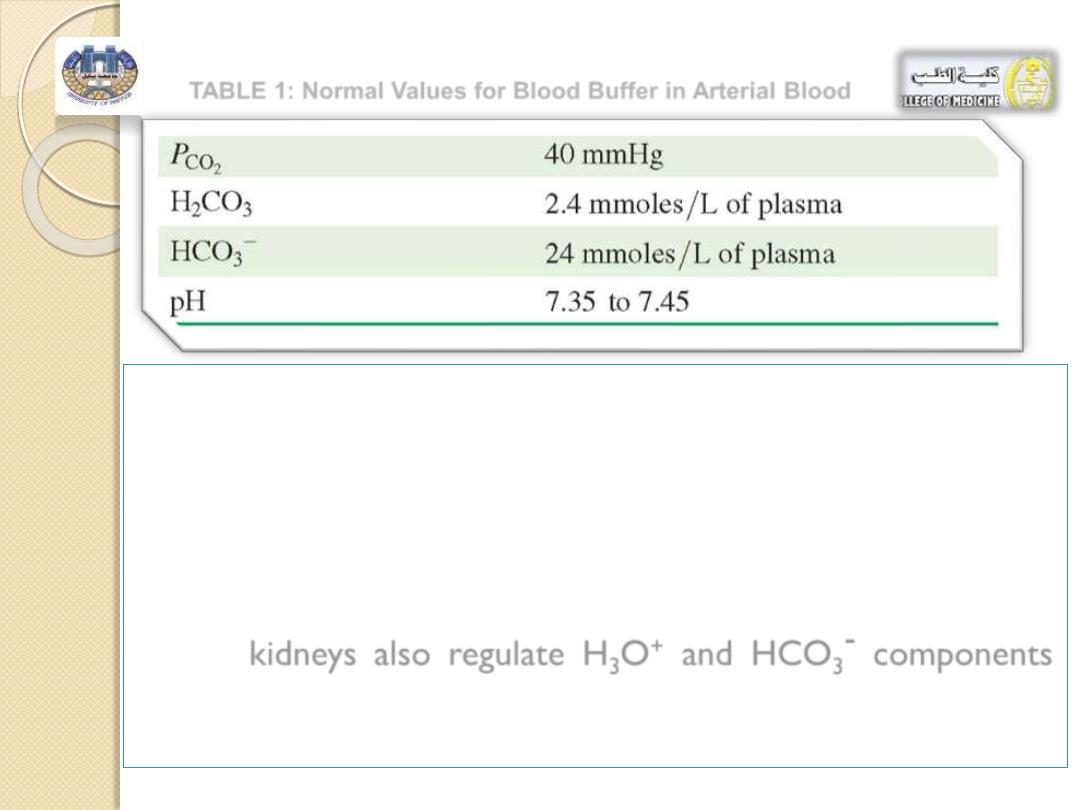
TABLE 1: Normal Values for Blood Buffer in Arterial Blood
•
A decrease in the
CO
2
level leads to a
high blood pH,
a
condition called
alkalosis.
Excitement, trauma, or a high
temperature may cause a person to hyperventilate, which
expels large amounts of
CO
2
. As the partial pressure of
CO
2
in the blood falls below normal
, H
2
CO
3
forms CO
2
and H
2
O,
decreasing the [H
3
O
+
] and raising the pH.
•
The
kidneys also regulate H
3
O
+
and HCO
3
- components
,
but more slowly than the adjustment made by the lungs
through ventilation.
AJM BioChem
16
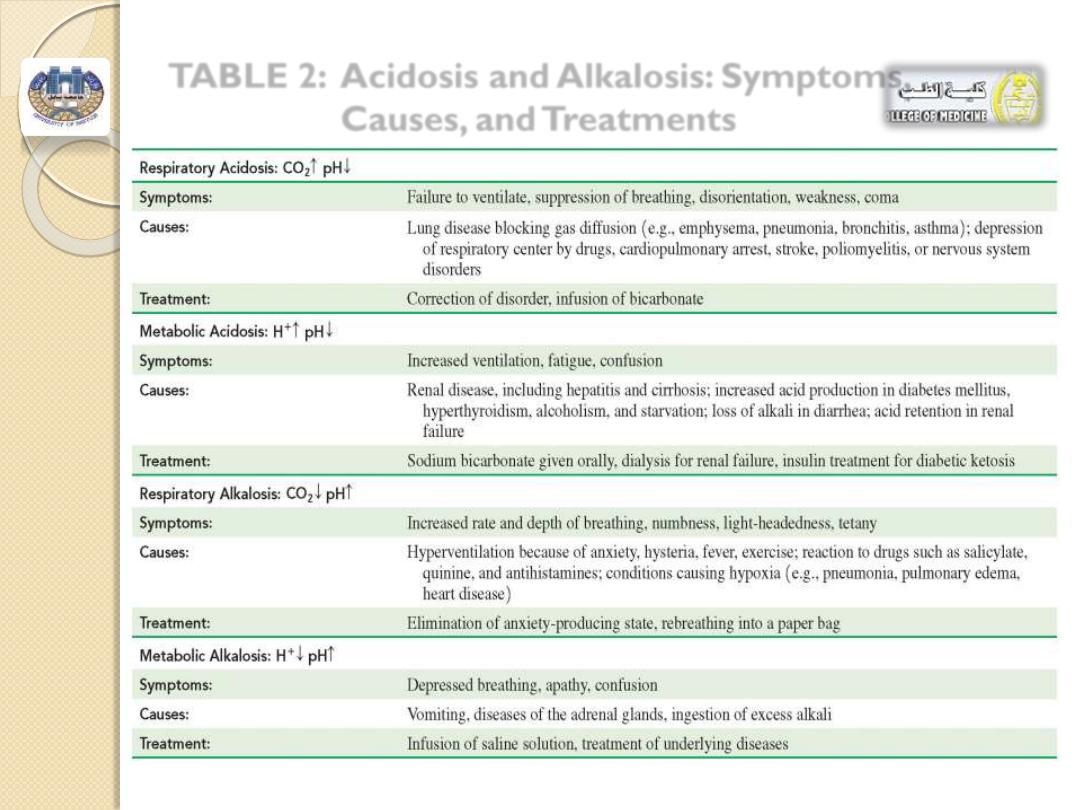
TABLE 2: Acidosis and Alkalosis: Symptoms,
Causes, and Treatments
AJM BioChem
17
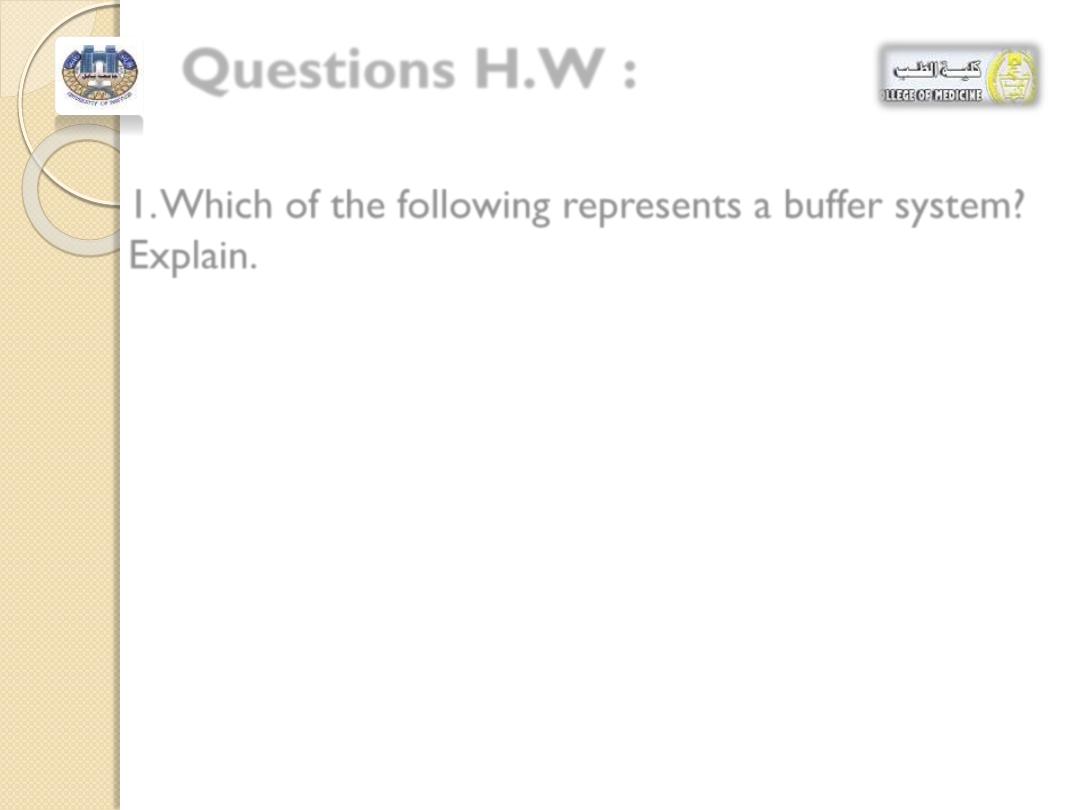
Questions H.W :
1. Which of the following represents a buffer system?
Explain.
a. NaOH and NaCl
b. H
2
CO
3
and NaHCO
3
c. HF and KF
d. KC1 and NaCl
2. Which of the following represents a buffer system?
Explain.
a. H
3
PO
3
b. NaNO
3
c. HC
2
H
3
O
2
and NaC
2
H
3
O
2
d. HC1 and NaOH.
AJM BioChem
18
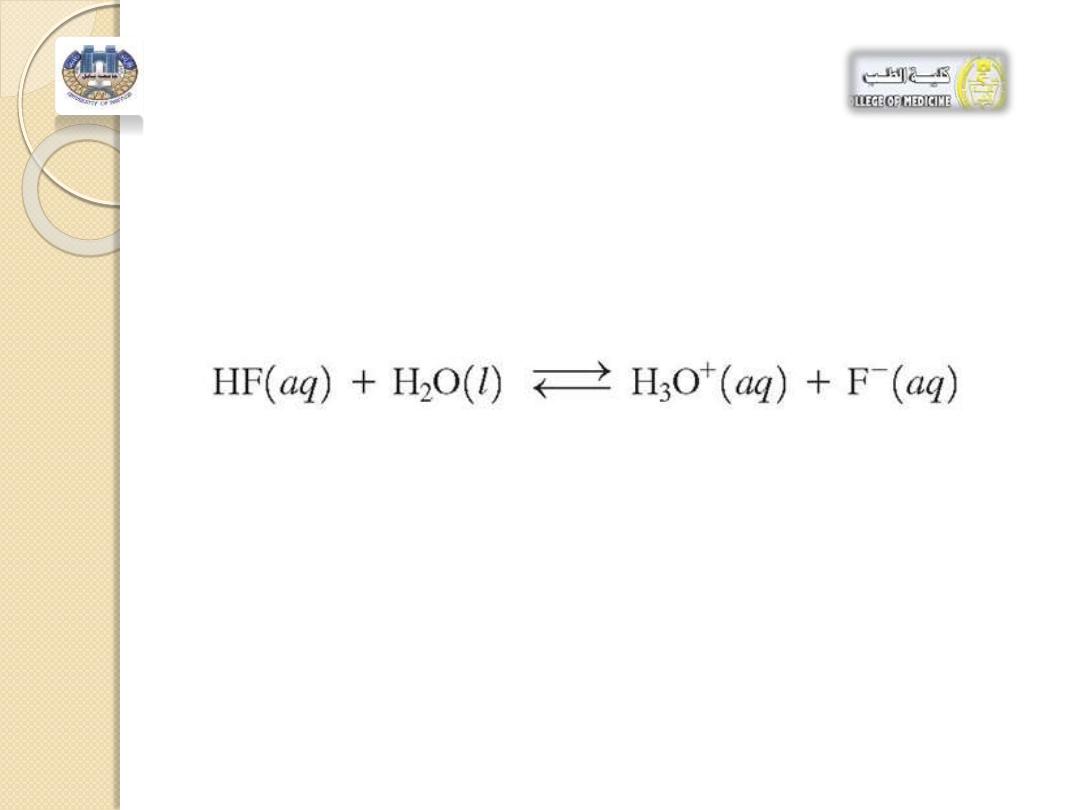
3. Consider the buffer system of
hydrofluoric acid, HF, and its salt, NaF.
a. The purpose of this buffer system is to:
1. maintain [HF] 2. maintain [F
-
]
3. maintain pH
AJM BioChem
19

b. The salt of the weak acid is needed to:
1.
provide the conjugate base
2.
neutralize added H
3
O
+
3.
provide the conjugate acid
c. If OH" is added, it is neutralized by:
1. the salt 2. H
2
O 3. H
3
O
+
d. When H
3
O
+
is added, the equilibrium
shifts in the direction of the:
1. Reactants 2. Products 3. does not
change
AJM BioChem
20

4.Consider the buffer system of nitrous
acid, HNO
2
, and its salt, NaNO
2
-
a
.The purpose of this buffer system is to:
1. maintain [HNO
2
] 2. maintain [NO
2
-
] 3. maintain pH
b
.The weak acid is needed to:
1. provide the conjugate base
2. neutralize added OH"
3. provide the conjugate acid
c.
If H
3
O
+
is added, it is neutralized by:
1. the salt
2. H
2
O 3. OH
-
d.When OH" is added, the equilibrium shifts in the direction
of the:
1. reactants
2. Products 3. does not change
AJM BioChem
21

THANK YOU
AJM BioChem
22
