
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
Lecture 8:
Electricity Within the Body
Objectives: after the end of this lecture, the student must know:
1- The application of electricity within various body parts like brain (EEG) and
heart (ECG)
2- Current research of electricity in the body
A cross membrane of neuron an electrical potential (voltage) is present due to
presence of more negative ions in the inside of the membrane than outside.
Neuron to be polarized; the inside of the cell 60-90 mv more negative than
outside.
60-90 mv= resting potential
If stimulation (heat, cold, light, sound) causes change in the action potential
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
The action potential last few milliseconds, for most neuron and muscle. The
action potential last 150-300 msec for cardiac muscle.
The membrane of some axons is covered with fatty insulating layer called
myelin
, has small non-insulating gabs called nodes of Ranvier.
The action potential decreases in the amplitude as it travels through myelinated
segment just an electrical signal is attenuated when it passes through a cable.
The reduced signal then acts like stimulates at the next node of Ranvier (gab) to
restore the action so its original size and shape. This process repeat along the
axon. The action potential seems to jump from one node to the next, it travels by
salutatory conduction.
Electrical Signal From Muscle Electromyogram
The record of potentials from muscles during movement is called
Electromyogram
. The conduction velocity of sensory nerve was measured its
typical value are 40-60 m/sec.
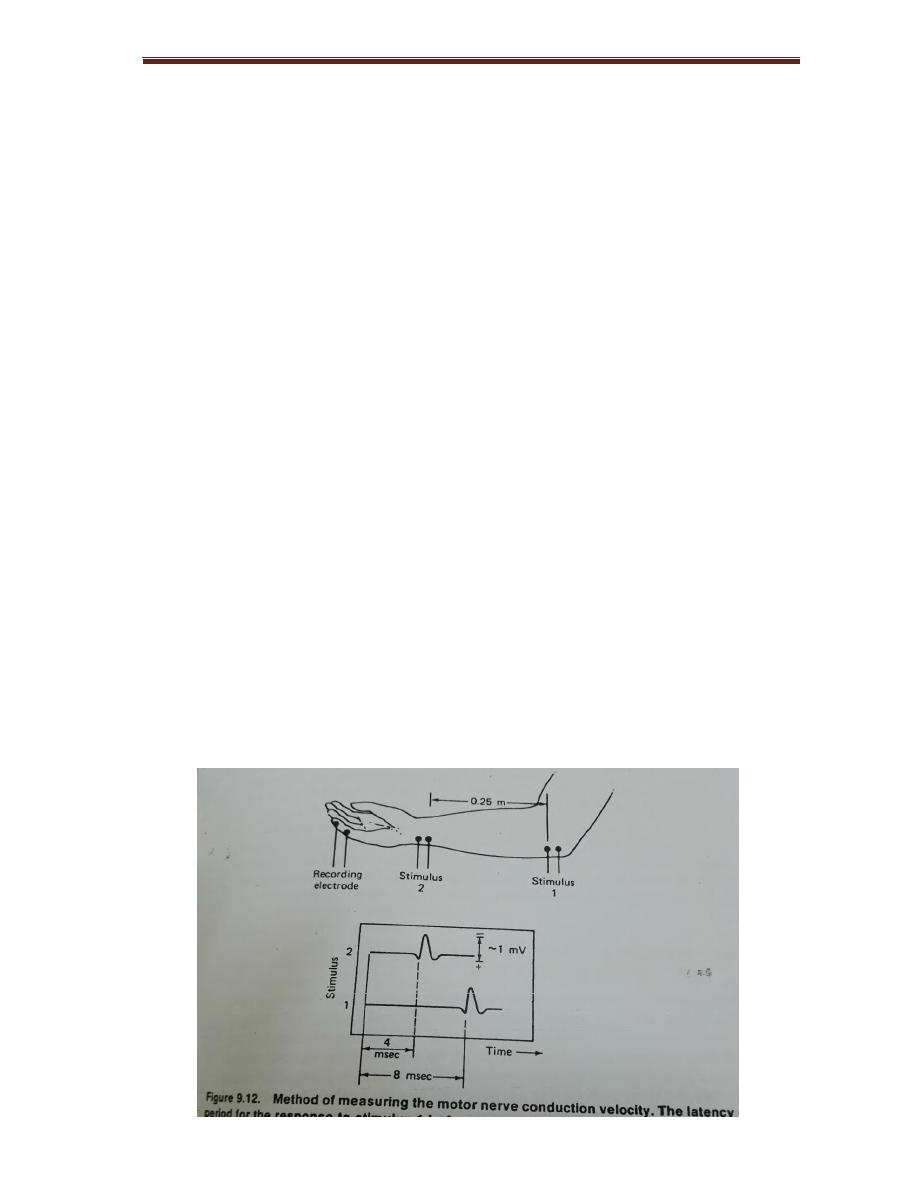
Fig is method of measuring the motor nerve conduction velocity. The latency
period for the response to stimulus 1 is 4sec longer than that for response
to stimulus 2

College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
∆ t = 4 x 10̄³ sec
∆ x = 0. 25 m
V = ∆ x / ∆ t = 0. 25 m / 4 x 10̄ ³ sec = 62. 5 m / sec
This is the nerve conduction velocity
Electrical signal from the heart ( Electrocardiogram )
The electrical signals from SA nods or pacemaker initiates the depolarization
of the nerve and muscles of both atria , causing atria to contract and pump blood
into ventricles
The electrical signals then passes through atrioventricular (AV) node, which
initiate depolarization of right and left ventricles, causing them to contract and
force blood to pulmonary and general circulation. The ventricle nerves and
muscles then repolarized and the sequence begins again
The major electrical events of the normal heart cycle as
1- the atrial depolarization which produce ( P wave )
2- the atrial repolarization which rarely seen and is un labeled
3- the ventricular depolarization which produces ( QRS)
4- the ventricular repolarization which produces ( T wave )
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
Electrical signals from the brain (electroencephalogram)
The recording of signals from the brain is called EEG the frequencies of EEG
signals depends on mental activity
For example :
Relaxed person has EEG signals of 8-13 Hz or ( α wave )
More alerted person has EEG signals above 13Hz (ß wave)
Applications of EEG
1- in the diagnosis of epilepsy
2- in confirming brain tumor, since electrical activity is reduced in the region of
tumor.
3- EEG used as monitor in surgery in addition to ECG, also useful in surgery for
indicating anesthesia level of the patient
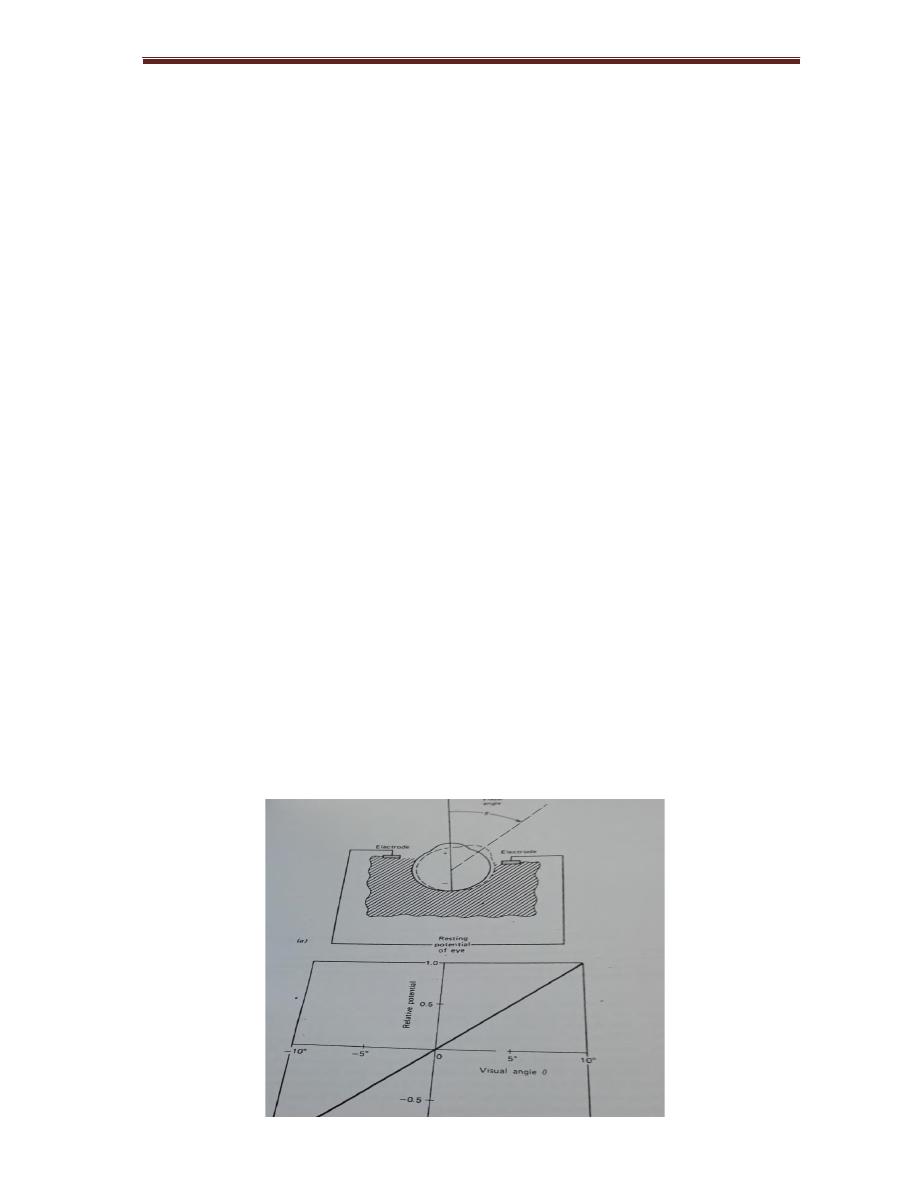
Electrical signal from the eye (electroretinogram and electrooculogram)
The recording of potential changes producing by the eyes when the retina is
exposed to flash of light is called ERG, the recording of potential changes due to
movement called EOG

54
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
Magnetic signal from heart and brain (magnetocardiogram and
magnetoencephalogram)
Since a flow of electrical charge produces magnetic field, a magnetic field
produced by the current in the heart during depolarization and repolarization,
the recording of heart magnetic field is MCG
MCG provide information in diagnosis of injury current exists in the heart
prior to heart attack, the recording of magnetic field surrounding the brain
called MEG
Current research involve electricity in the body
Bone contain collagen which is piezoelectric material, when force is
applied to collagen, small electrical potential is generated collagen behaves like
N-type semiconductor its current like negative charge.
Mineral crystal of bone (apatite) close to collagen behave like P-type
semiconductor its current by positive charge.
At junction current flows from P to N type, the forces on the bones produces
potential by piezoelectric and P N junction of collagen apatite produce currents
that induce and control bone growth.
Another small direct current arises in injured zone called injury current, the
electrical current at side of injury is higher than that in surrounding areas. This
high potential associated with limb regeneration in animals like salamander,
stimulation of fracture sites with direct current of 1—3 μA has been found to
promote healing of bone fractures.

55
College of Medicine/Babylon University
Medical Physics Module
Small group discussion
Qx/ Explain why cardiac muscle contraction need more time than other muscle
Qx/ Explain how the EEG can be used to measure anesthesia level?
Qx/ Discuss the total work done by the normal heart to pump the blood from left
ventricle to aorta?
Qx/ Discuss the effect of turbulent flow on pressure, velocity, viscosity, and heart
sound?
-
