
Basic Principles of Light Polarization

Polarization Photography
Reduce Sun Glare
Reduce Reflections
Darkens Sky
Increase Color Saturation
Reduce Haze
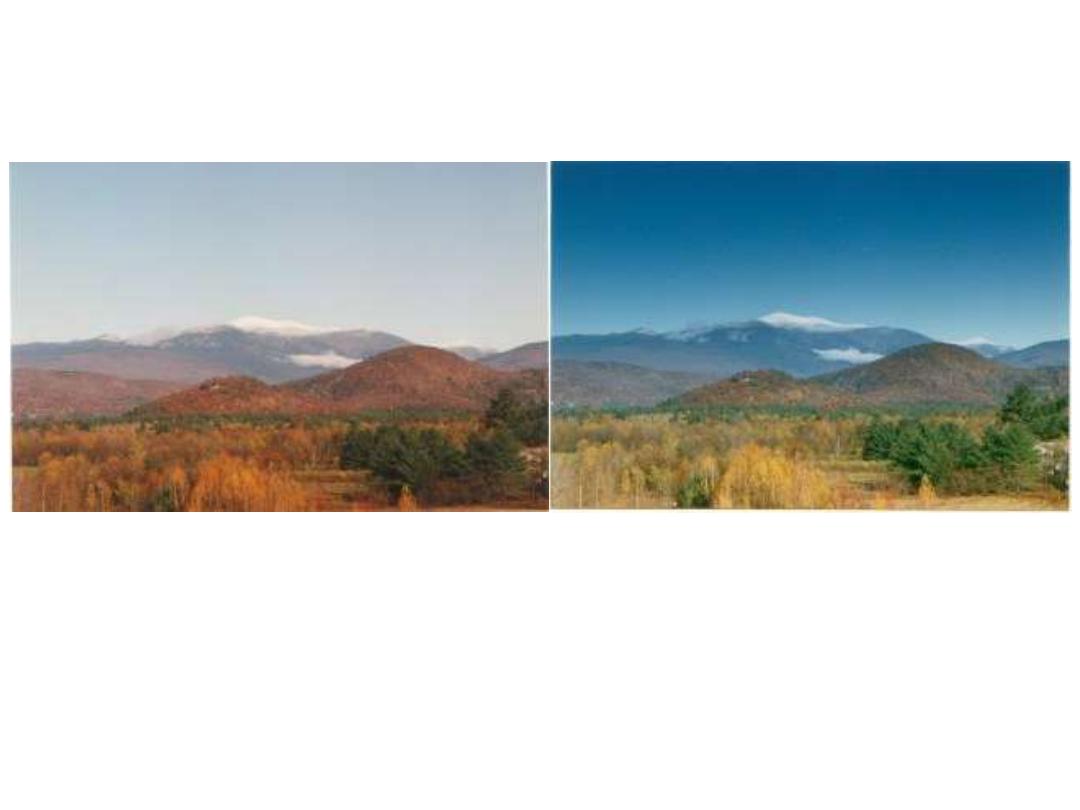

Polarization Photography
Without Polarizer
With Polarizer
• Provides better Color Saturation
• Darkens the sky
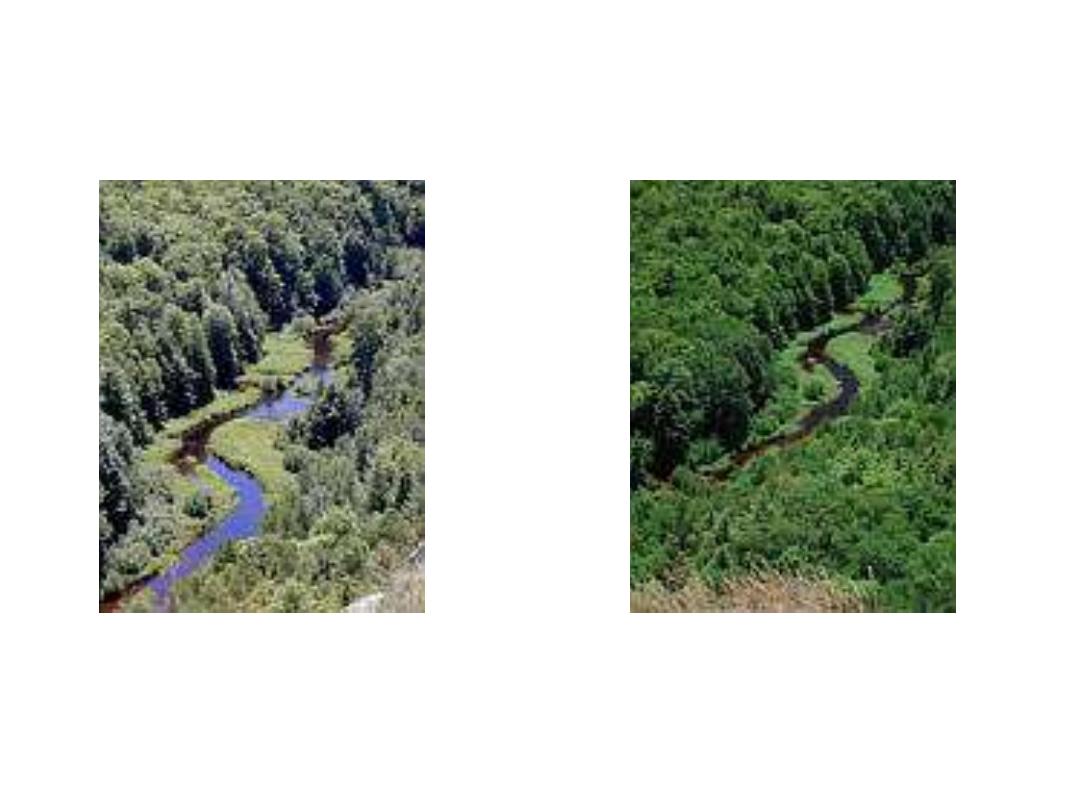

Polarization Photography
Without Polarizer
With Polarizer
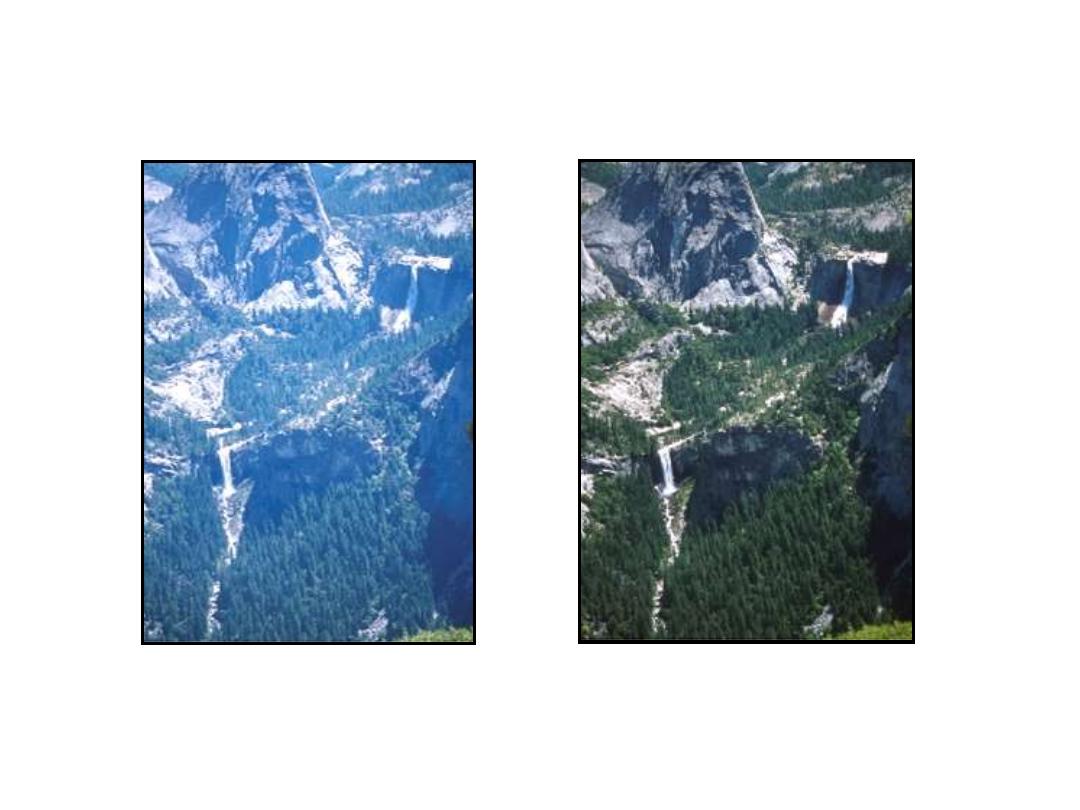

Polarization Photography : Scattering
De-hazed
Haze
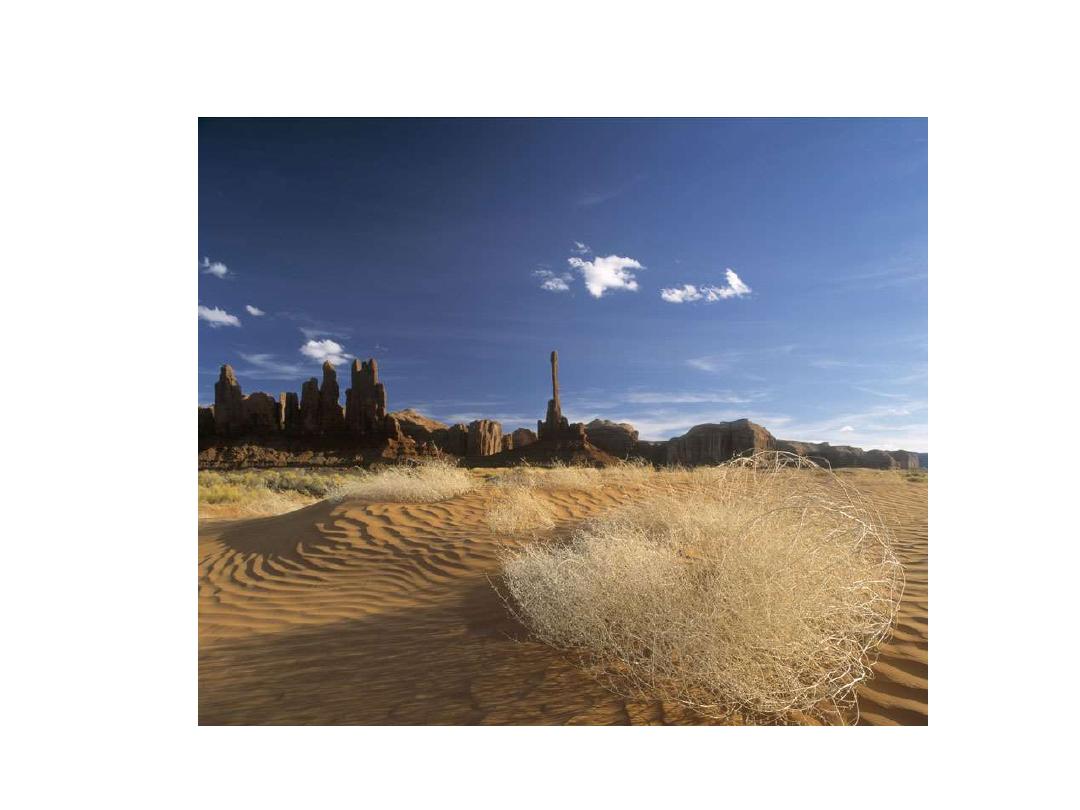

Polarization Photography : Wide Angle Lenses
Vignetting of the Sky
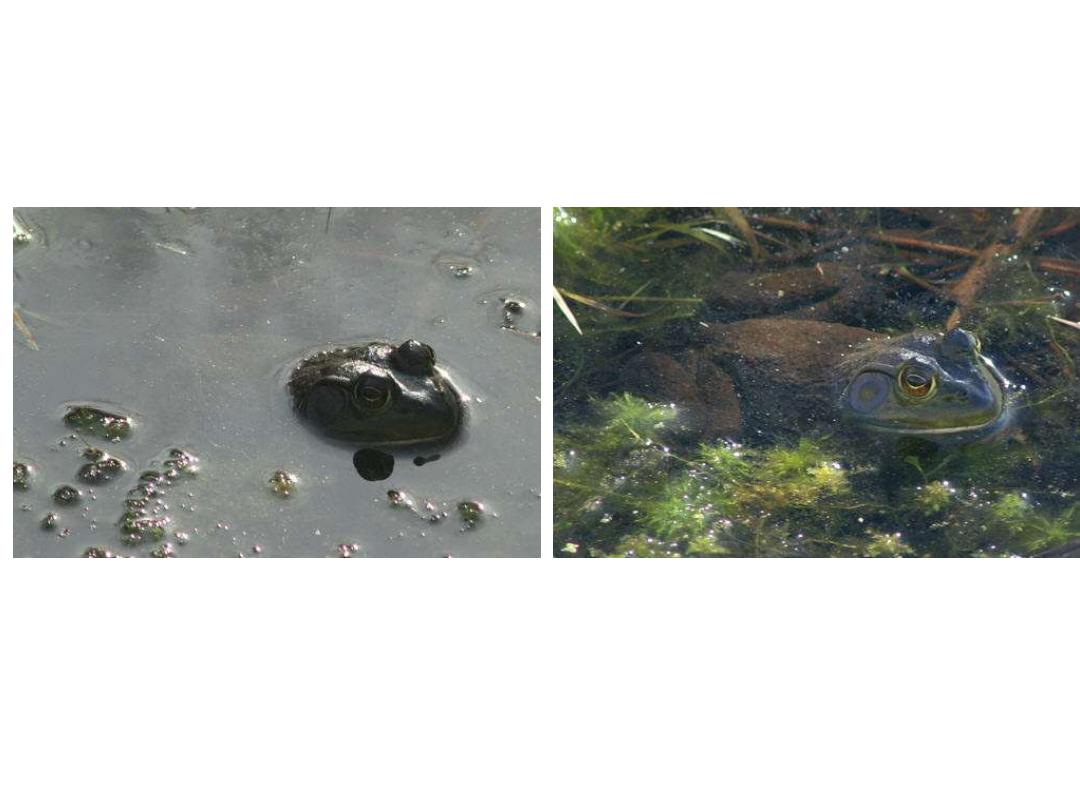

Polarization Photography : Reflections
Reduce Reflections
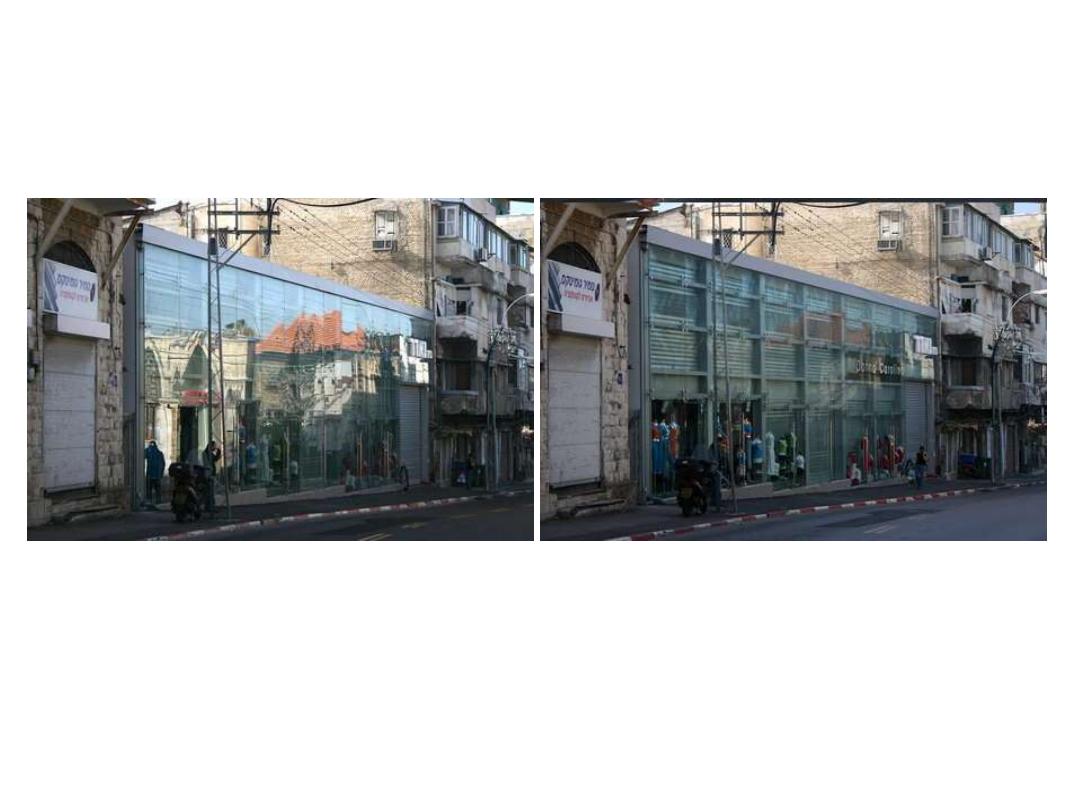

Polarization Photography : Reflections
Reduce Reflections

Polarization Photography : Reflections
Many titled planes
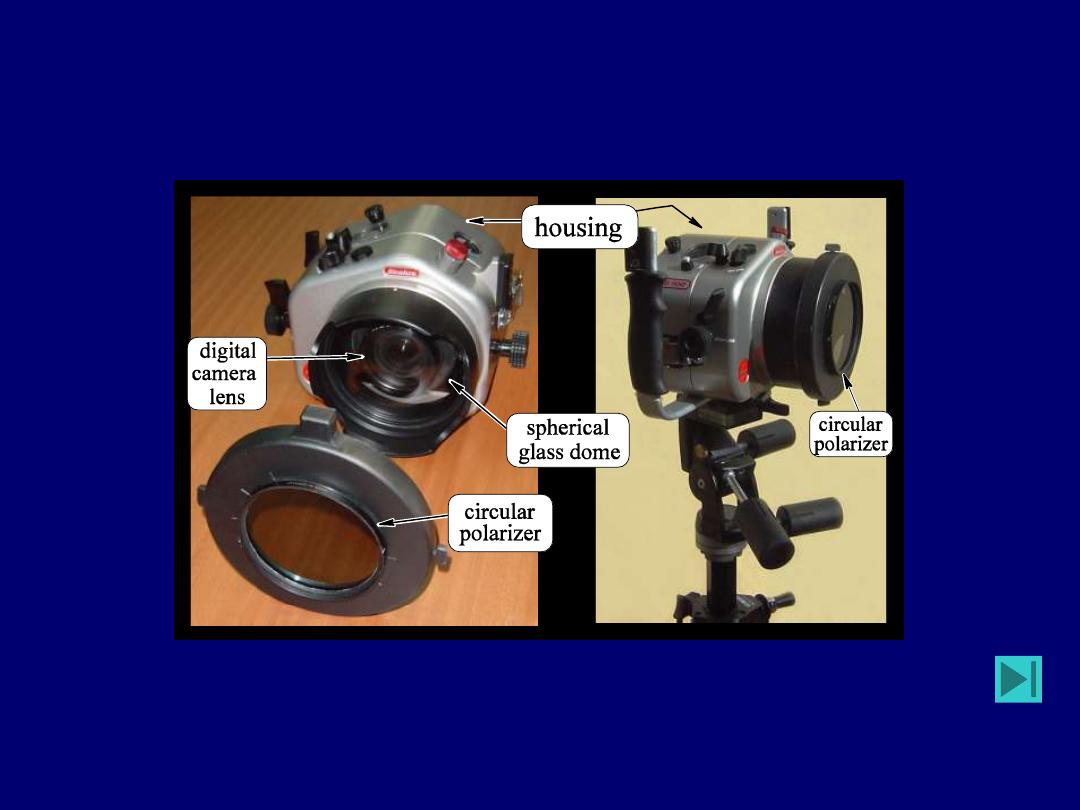

Aqua-polaricam
Y. Schechner & N. Karpel,
underwater imaging
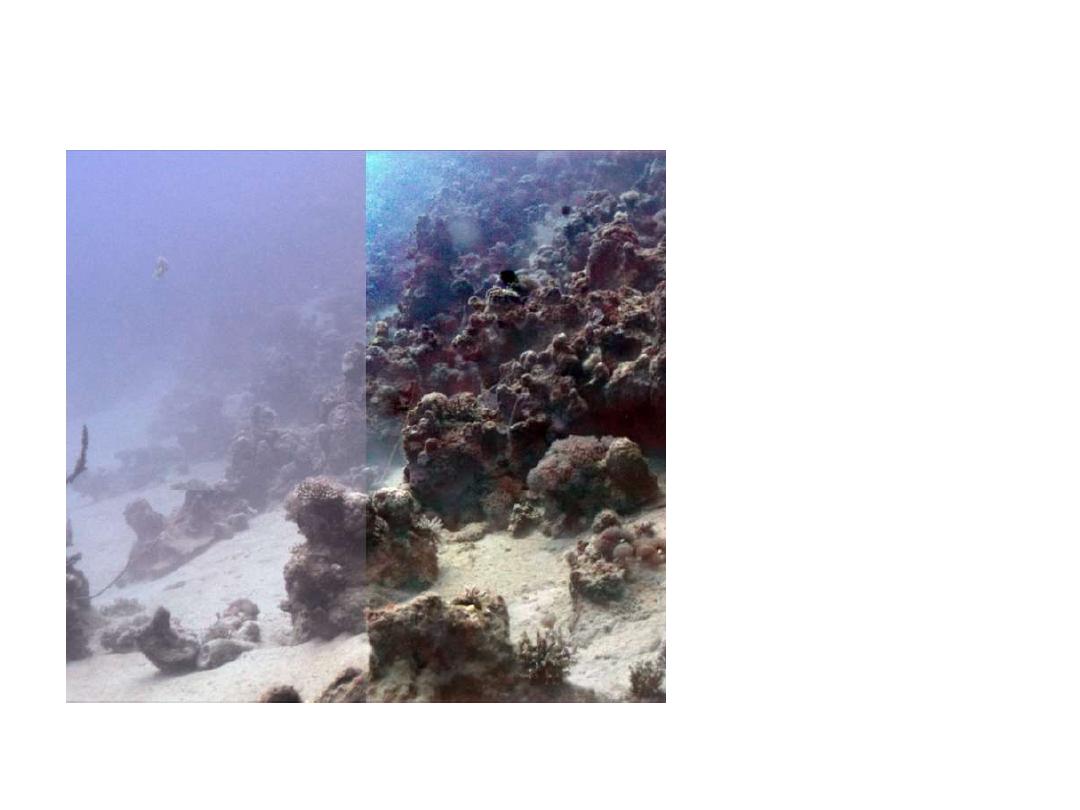

Polarization Photography : Underwater
•
Underwater pipelines
and communication
•
Offshore structures
•
Underwater ROV/AOV
•
Offshore drilling rigs
•
Vessel inspection
•
Recreational photography
•
Marine archaeology
•
Marine biology
•
Underwater mapping
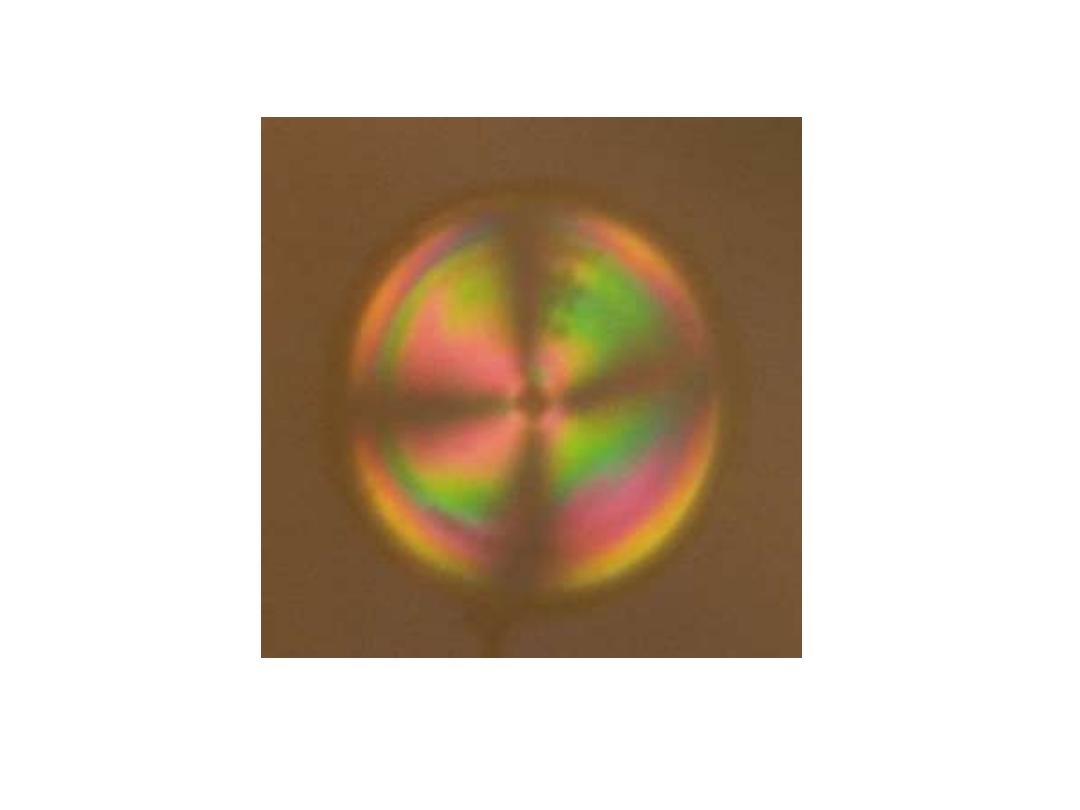
Birefrengence
Interference pattern due to different refractive indices
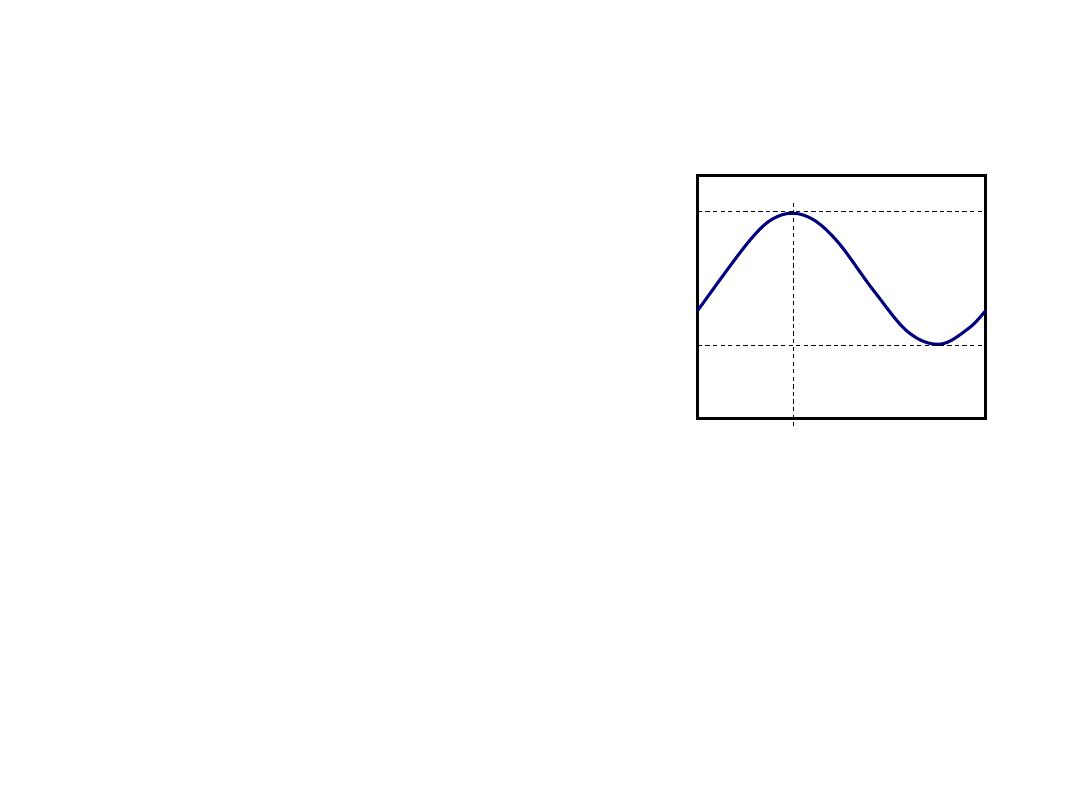
Light as Plane Waves
•Sinusoidal plane waves very
good approximation.
•Very useful for characterizing
polarization.
•Polarized Wave: Has only one preferred orientation.
•Un-polarized Wave: Has no preferred orientation.
or has all orientations.
•Partially polarized wave: Has preferred orientation but
has energy in other orientations as well.
180
o
min
I
max
I
max

Classification of Polarization
Linear : Two orthogonal plane waves with same phase but
possibly different amplitudes.
Circular: Two orthogonal plane waves with 90 deg phase
shift but same amplitudes.
Elliptical: Possibly any degree phase shift with
different amplitudes.
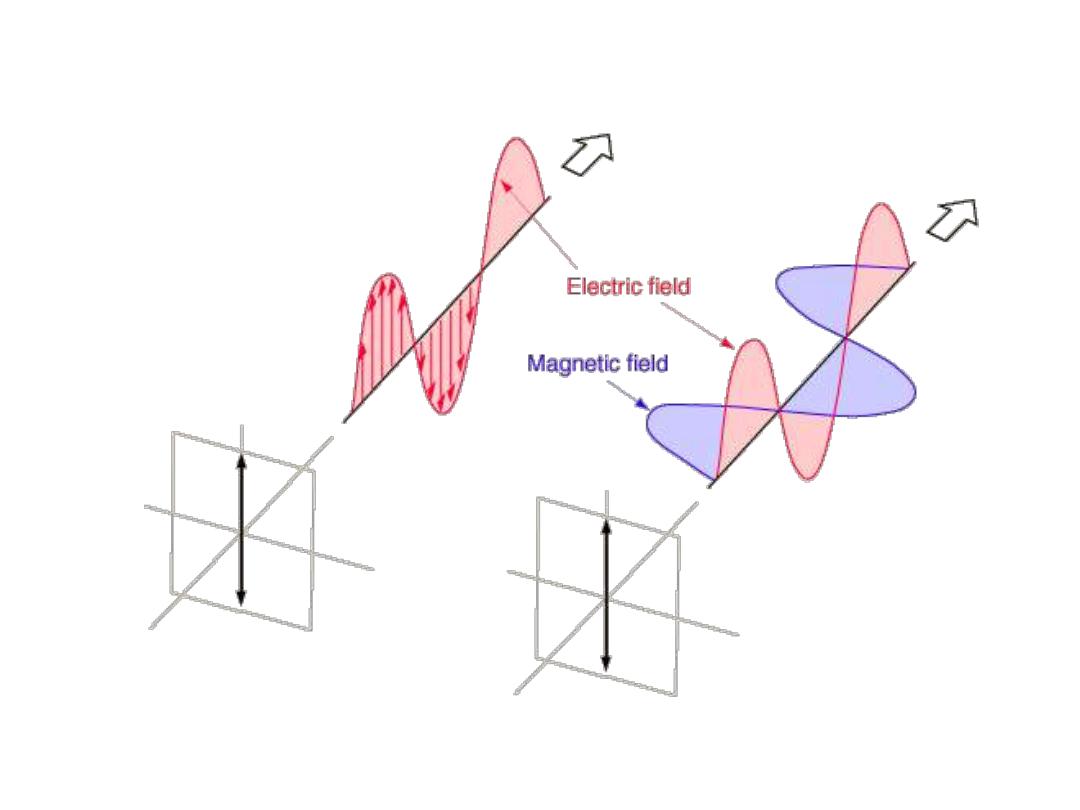
Linear Polarization
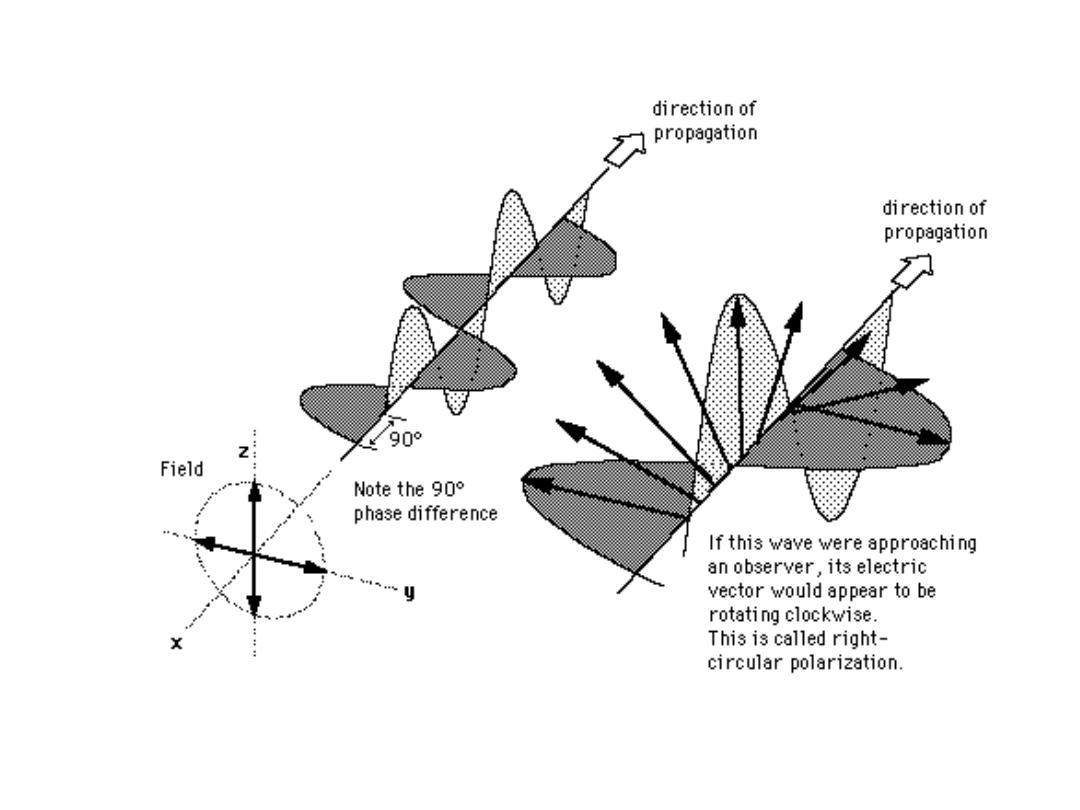
Circular Polarization
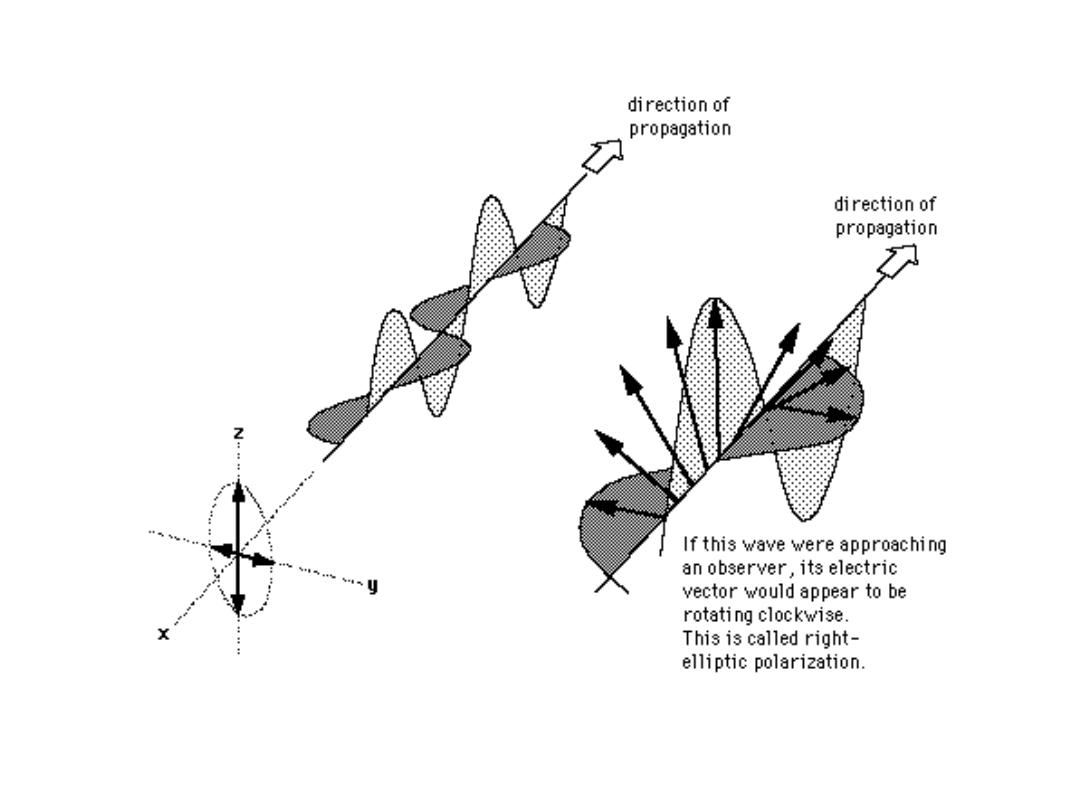
Elliptical Polarization
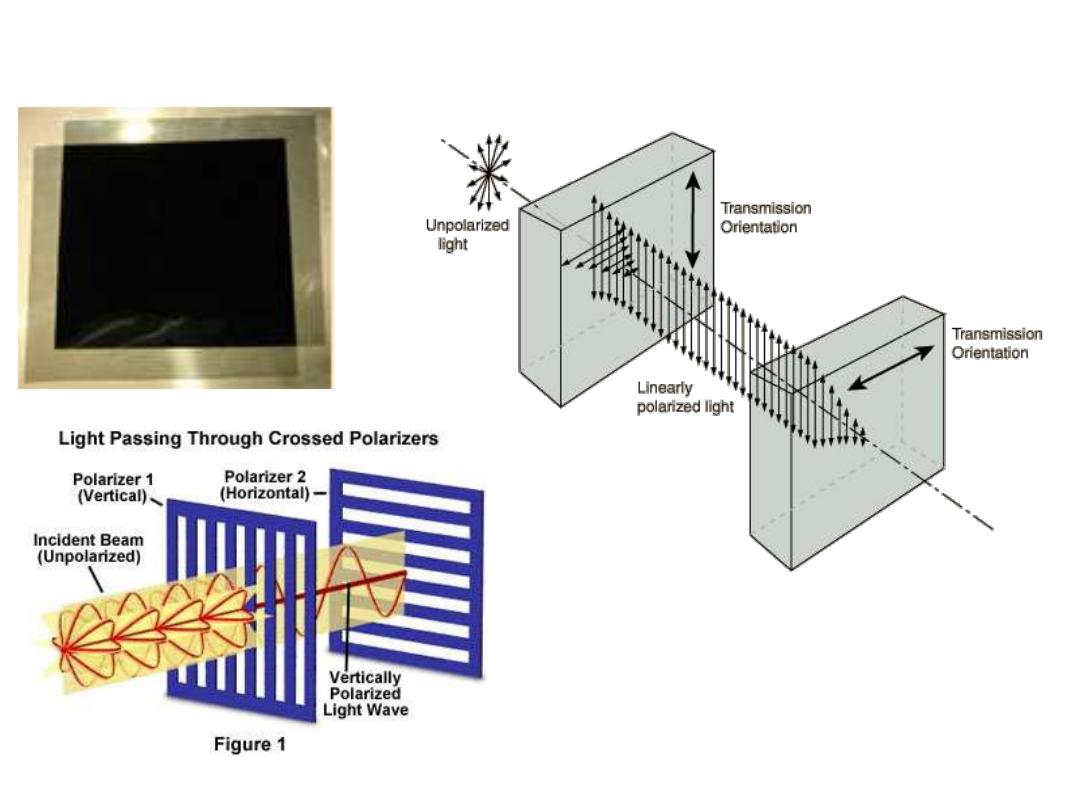
Crossed Polarizers
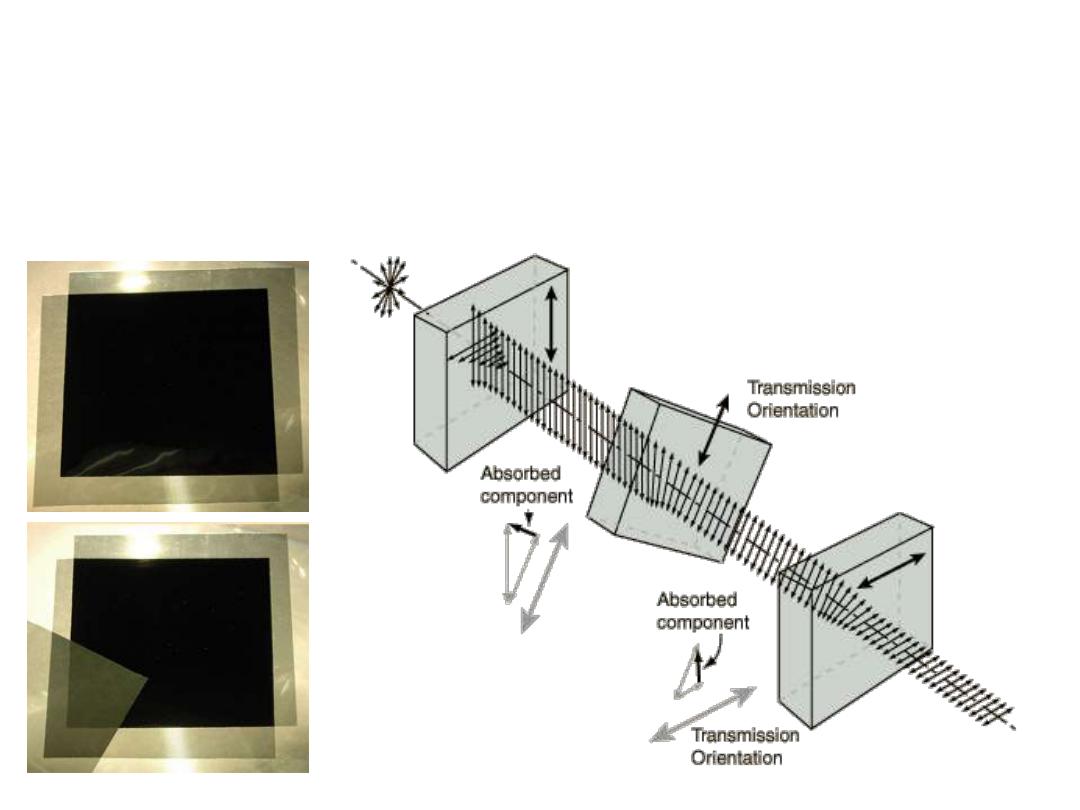
Polarizer Puzzle
If crossed polarizers block all light, why does putting a third polarizer at
45° between them result in some transmission of light?
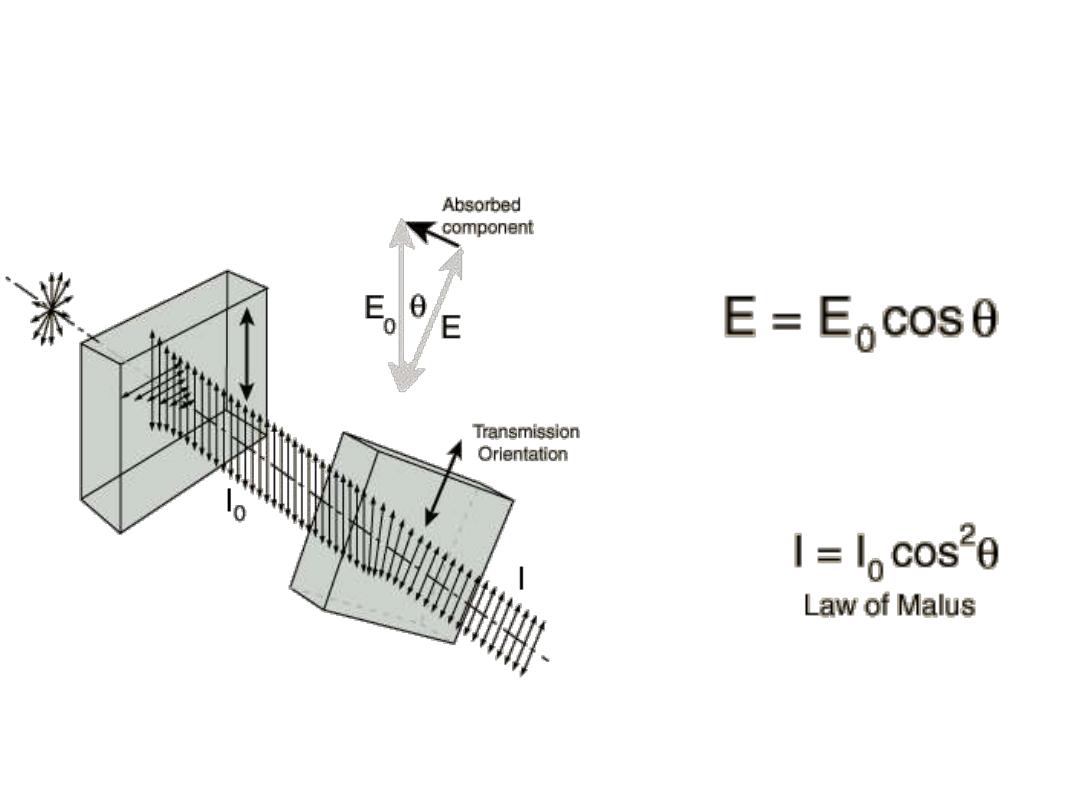
Law of Malus
Amplitude:
Intensity = Const . (Amplitude)^2
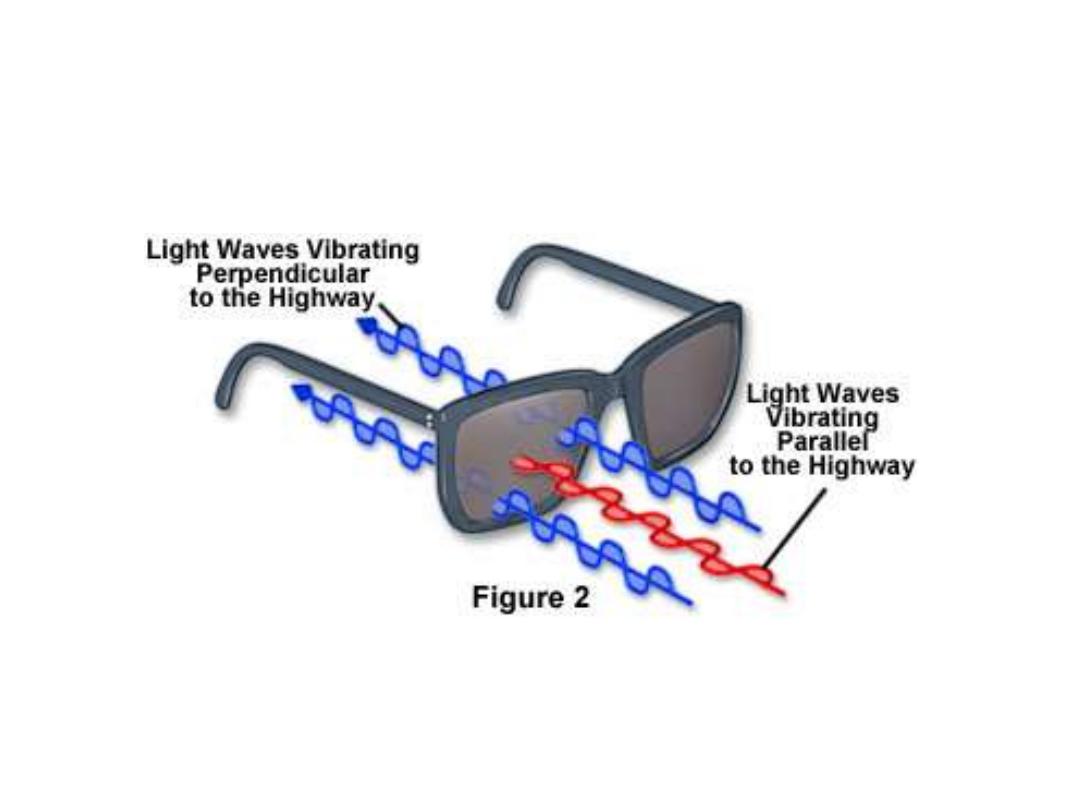
Polarized Sunglasses
Reduce glare off the roads while driving
