
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease pathology
Gestational trophoblastic disease comprises a heterogeneous group of lesions arising from
abnormal proliferation of trophoblast of the placenta.
Classification of Gestational trophoblastic disease :
1. hydatidiform mole
a. Complete
b. partial
.
c. invasive .
2. choriocarcinoma
.
(Hydatidiform Mole )
•
Complete H. mole.
• This is an abnormal conceptus in which an embryo is absent and the placental villi are so
distended by fluid that they resemble a bunch of grapes
.
• women with a mole has a
2-3%
risk of eventually developing choriocarcinoma
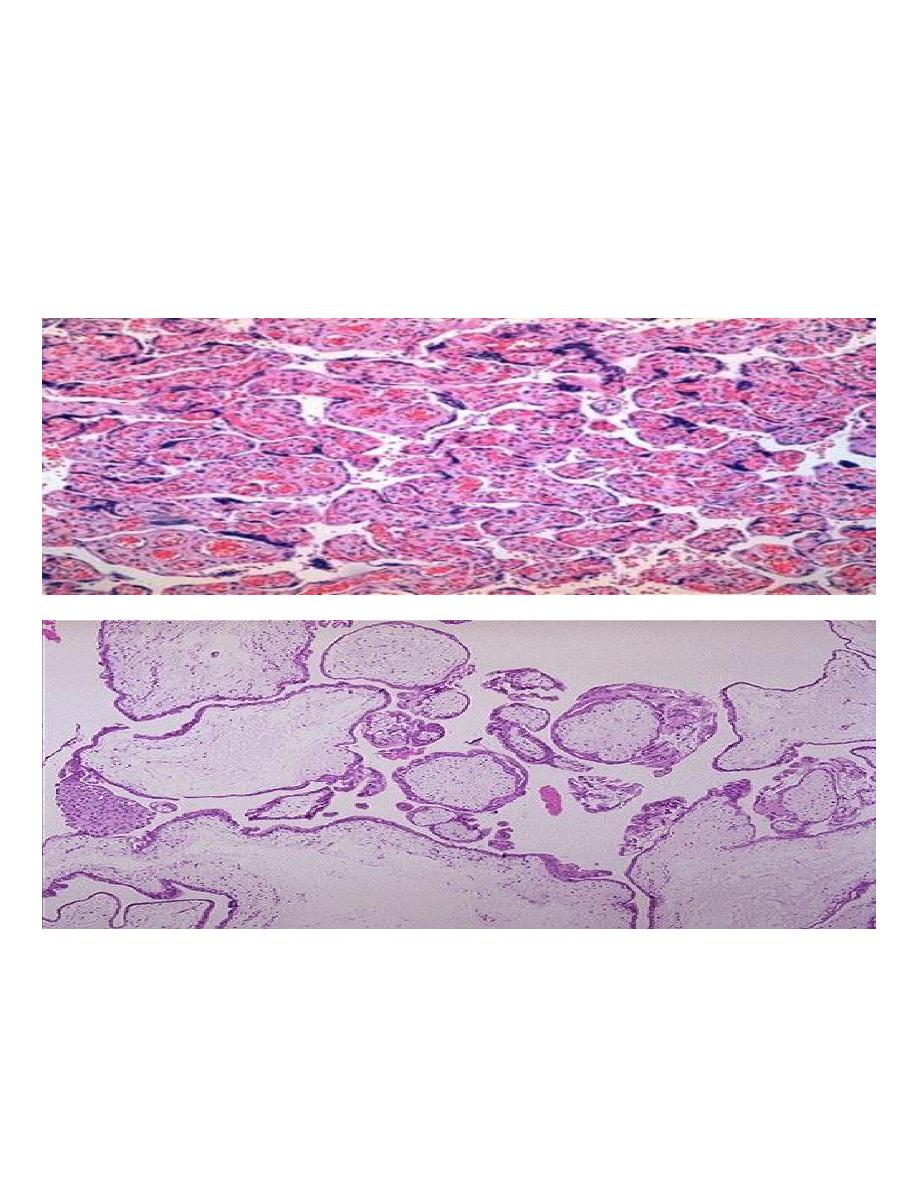
Microscopically
:
• The stroma of the villi is markedly edematous often with cistern formation .
• A constant feature is the presence o f a variable degree of atypical villous trophoblastic
hyperplasia
Placenta, normal villi :-These are normal third-trimester chorionic villi. Note the small size,
prominent vasculature, and lining of cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts.
Histologically, the hydatidiform mole has large avascular villi and areas of trophoblastic
proliferation. Of course, ultrasound confirms the diagnosis before currettage is done to evacuate
this tissue seen here.
• Complete H .Mole is caused by abnormal gametogenesis & fertilization .
• The nuclei of the trophoblastic cells in this disease contain only paternal chromosomes &
are therefore androgenetic in origin .
• Chromosomes are diploid
46,XX in 90% cases
46,XY in a small part
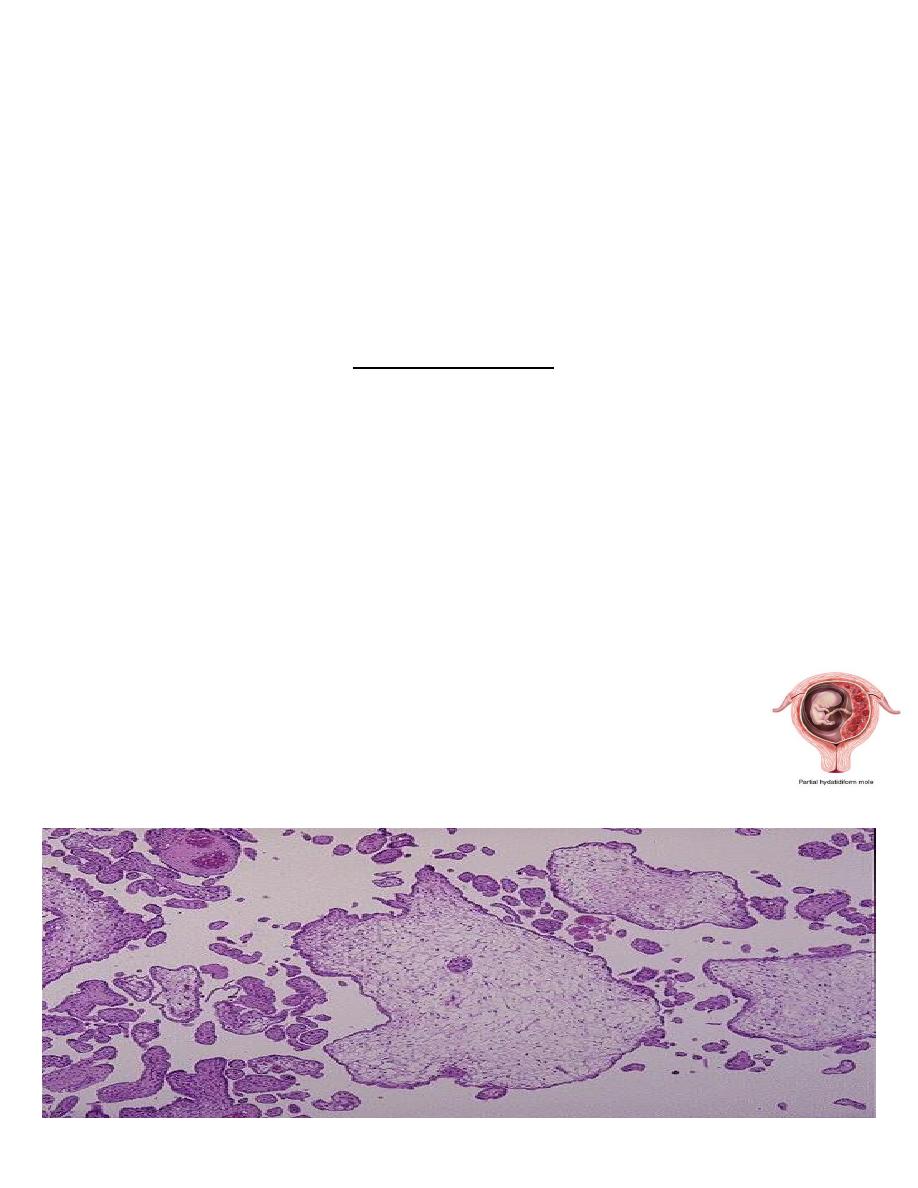
Partial H.Mole
• About 15 - 35% of all moles are of the partial type .
• It is often associated with the presence of an embryo although is usually abnormal.
• The risk for the development of choriocarcinoma following a partial mole is
very low .
• 5 -10 % of partial mole progress to invasive mole
Grossly :
• The placenta contain mixture of normal & vesicular villi .These villi show focal edema
leading to central “cisternal” formation .Many of the villi contain fetal (nucleated ) red
blood cells
.
• Trophoblastic proliferation is present but in lesser degree than in complete H. mole .
• Most partial moles are triploid (69xxx or 69xxy) & few show trisomy 16.
• This is a partial mole that occurs when two sperms fertilize a single ovum. The result is
triploidy (69 XXY). Only some of the villi are grape- like, and a fetus can be present, but
abnormal
• A partial mole is often accompanied by a fetus that is usually grossly
abnormal
.
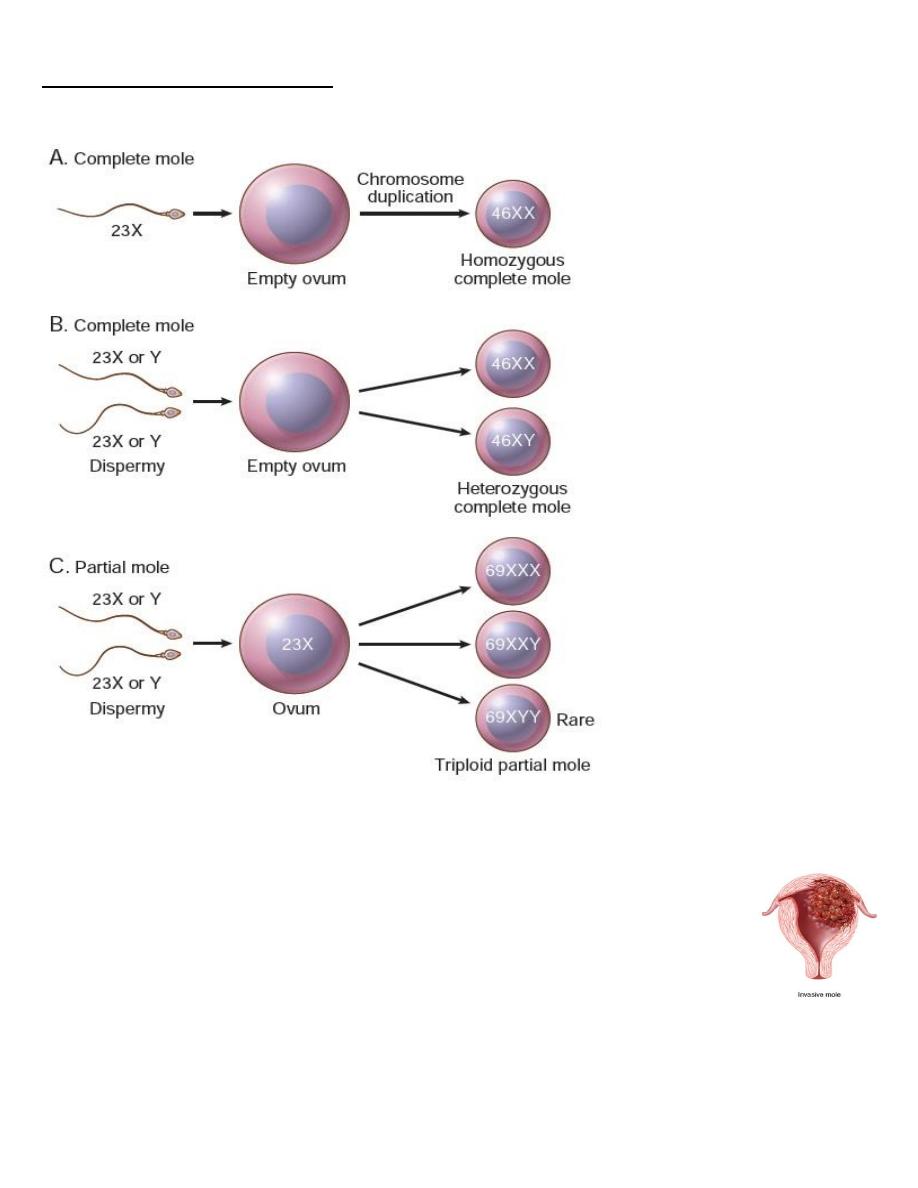
Pathogenesis of molar pregnancy
Invasive Mole
It refers to H.M. ( nearly always of the complete type but occasionally of the
partial type ) in which
the villi penetrate the myometrium &/or its blood vessels
.
This phenomenon which occur in 17% of all complete moles , it is an exaggerated
expression of the capacity of normal trophoblast for invasion
.
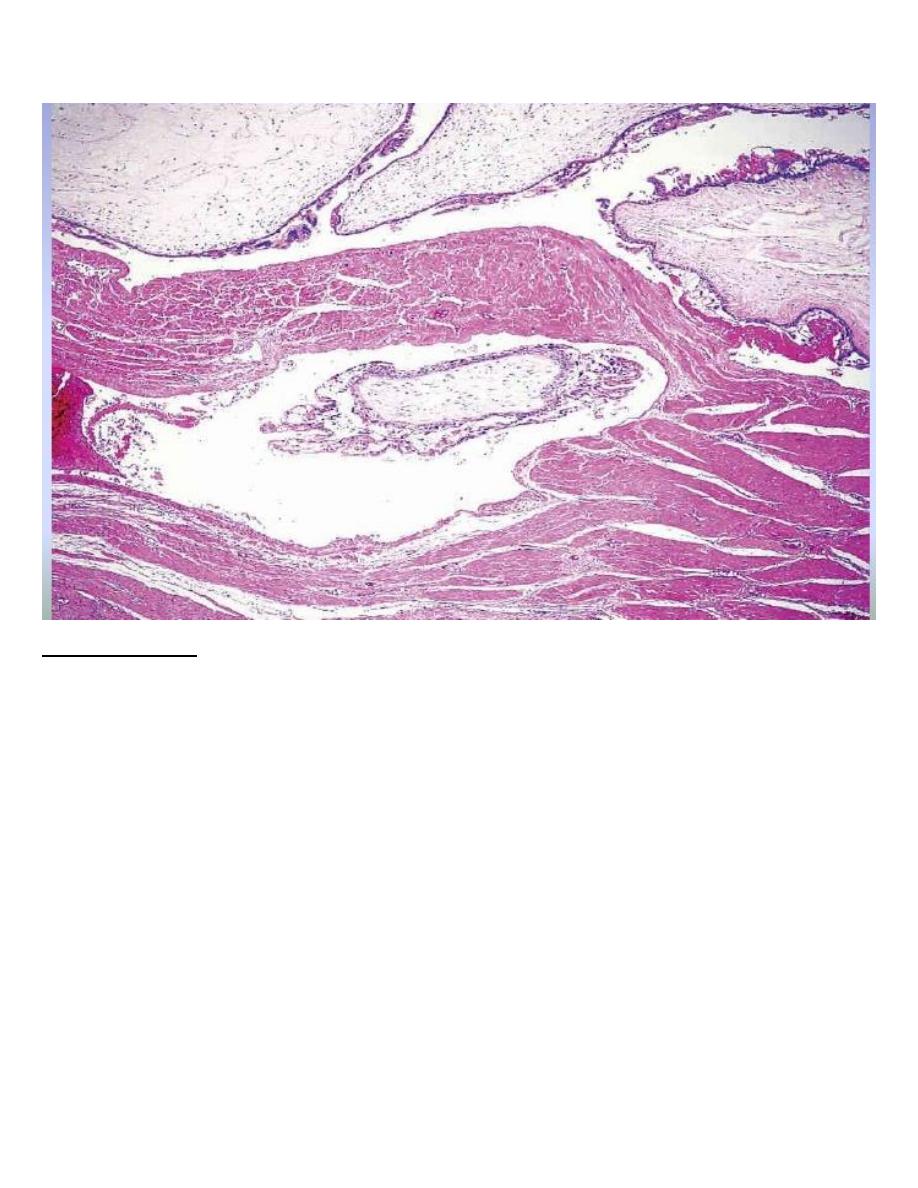
Invasive mole : hydropic villi within the myometrium
Choriocarcinoma
• It is a malignant tumor of trophoblast & is formed of both cytotrophoblast &
syncytiotrophoblast .
• It is a unique neoplasm in that being purely fetal origin .
• It is neoplastic allograft in the mother .
• The tumor follows H.mole in 50% of cases & unremarkable abortion in a further 25% ;the
remainder develop often after a period of months or years ,as
a sequel to an apparently
normal pregnancy
.
• Choriocarcinoma
& H.mole secrete placental HCG & assay of serum & urinary levels of
this tumor marker are used in patient management
.
• There is increased risk of choriocarcinoma for women of group A married to men of the
same group
.
Microscopically
:
• The tumor is composed of cluster of cytotrophoblast separated by streaming masses of
syncytiotrophoblast ,resulting in a characteristic dimorphic plexiform pattern .
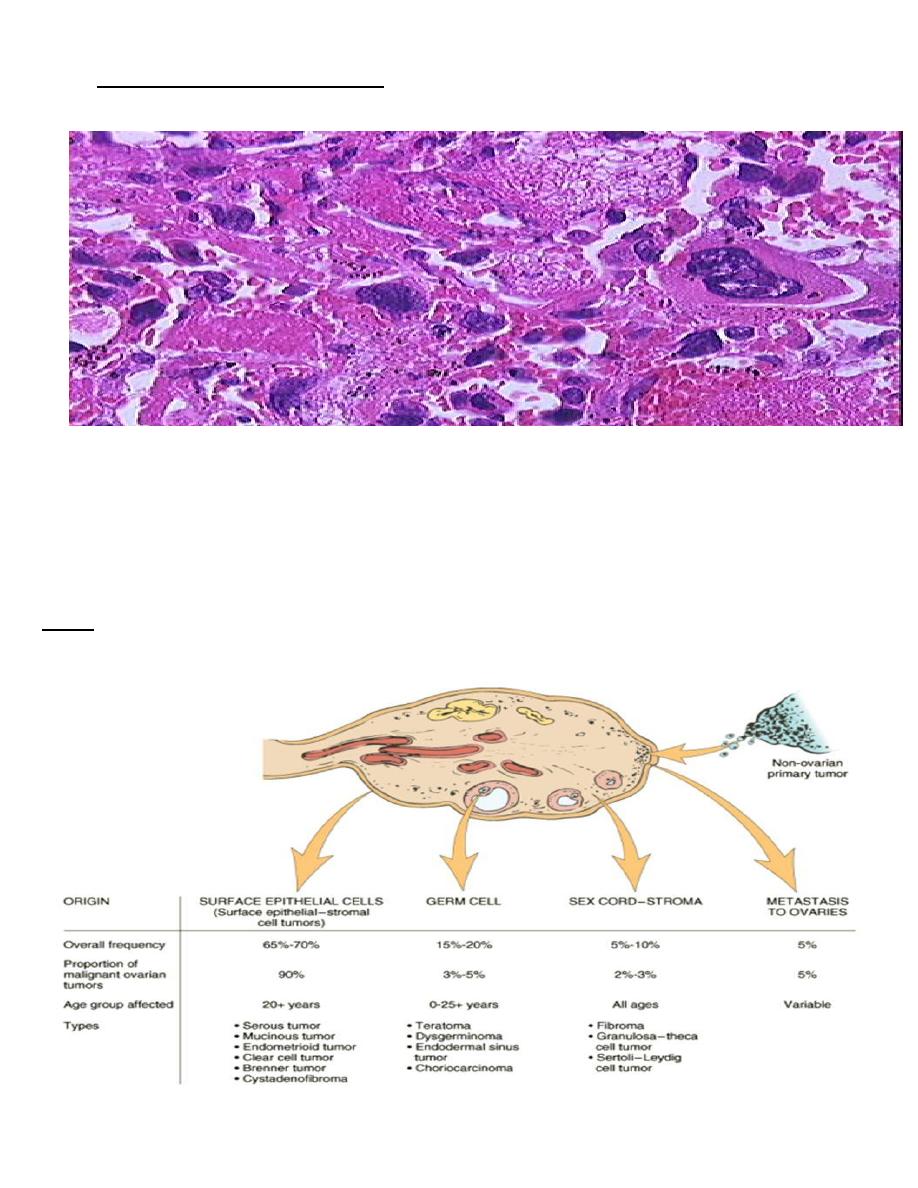
• Villi are characteristically absent as a matter of fact ,their presence is said to rule out the
diagnosis of choriocarcinoma .No matter how atypical the trophoblastic cells may be
The natural history of untreated choriocarcinoma is characterized by the development of
early
hematogenous metastasis
,the most common sites being the lung, vagina, brain, liver,
kidney &bowel & often present with massive hemorrhage
.
Ovary

Classification of ovarian tumors
A simplified form of the classification of ovarian tumors in to 5 groups
:
I- Tumors derived from the surface epithelium(60% of all ovarian tumors):
1-Serous tumors ( benign ,border line ,malignant ).
2-Mucinous tumors (= , = , = ).
3-Endometriod tumors (= ,= , = ).
4-Clear cell tumors ( = , = , = ) .
5-Transitional cell tumors ( Brenner tumor of benign border line & malignant Brenner tumor).
• II-Tumors of sex cord & stromal origins
1-Granulosa –stromal cell tumors, leading to granulosa cell tumors ,tumors of the
thecoma –fibroma group .
2-Sertoli-stromal cell tumors ; androblastoma.
3-Sex cord tumor with annular tubules .
4-Gynandroblastoma .
5-Steroid (lipid) cell tumors .
• III-Tumors derived from the germ cells
1-Teratoma
2-Dysgerminoma identical to seminoma of testis .
3-Yolk sac tumor ( endodermal sinus tumor).
4-choriocarcinoma
• IV-Miscellaneous tumors
Primary lymphoma of the ovary .

V-Metastatic tumors
The ovary is a common site of secondary tumors especially from the uterus ,breast & GIT .
Krukenberg tumor :
it is secondary tumor in the ovaries which is due to transcoelomic spread of a gastric or
colonic adenocarcinoma & is characterized by the presence of mucin –containing signet ring
cells scattered in a fibrous stroma which is extremely cellular
.
The surface epithelial – stromal cells
• Surface epithelial origin cells are the most common which's constitute over than 90% of
ovarian neoplasms.
• studies have shown that many of the tumors thought to arise from the coelomic
epithelium that covers the surface of the ovary are now thought to arise from the
fimbriated end of the fallopian tube
• Important risk factors for ovarian cancer include nulliparity, family history, and germline
mutations in certain tumor suppressor genes most of these are associated with mutations
in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes which are also associated with hereditary
breast cancer .
Serous tumor:
• These are most frequent of the ovarian tumors, it's usually cystic so known as
cystadenoma for benign tumor and cystadenocarcinoma for malignant one and borderline
or recently named as tumor of low malignant potential for borderline tumor between
benign and malignant.
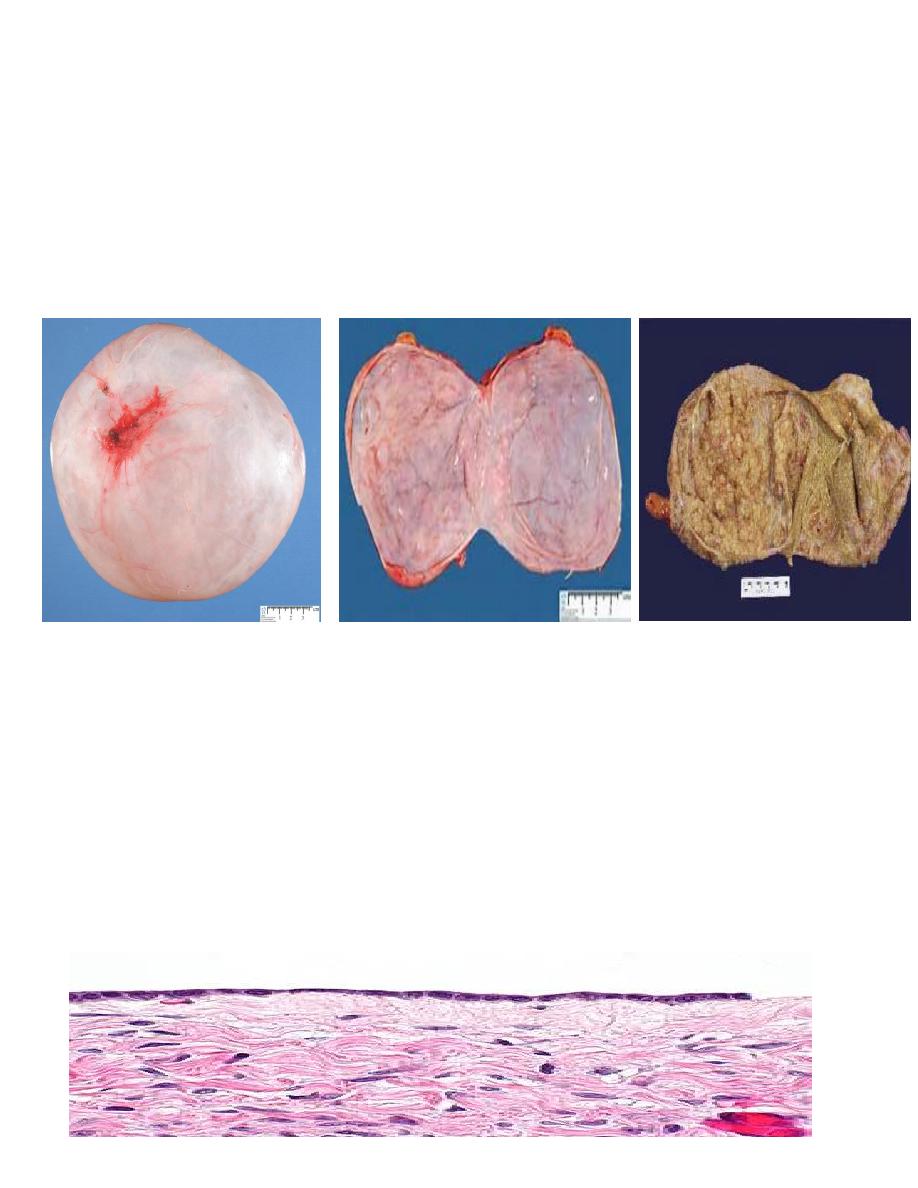
Morphology:-
• Grossly: serous tumor may be small 5 to 10 cm or may reached even 40 cm in diameter,
the surface in benign one is smooth and glistening while in malignant one is irregular, cut
section reveal unilocular or more multilocular cysts filled by serous fluid and smooth inner
surface in benign one while in malignant tumor the inner surface usually contain polypoid
and papillary growth.
Microscopically: in benign one usually consist of thin wall lined by single layer of tall columnar
serous epithelial cells.
While in malignant one usually composed of complex papillae lined by multilayring atypical
malignant cells with invasion of stroma, in borderline the atypia of lining papillae are present
but no stromal invasion seen.
The metastasis of this tumor is usually by local invasion of wall and implant itself in peritoneal
cavity so associated with ascetis.
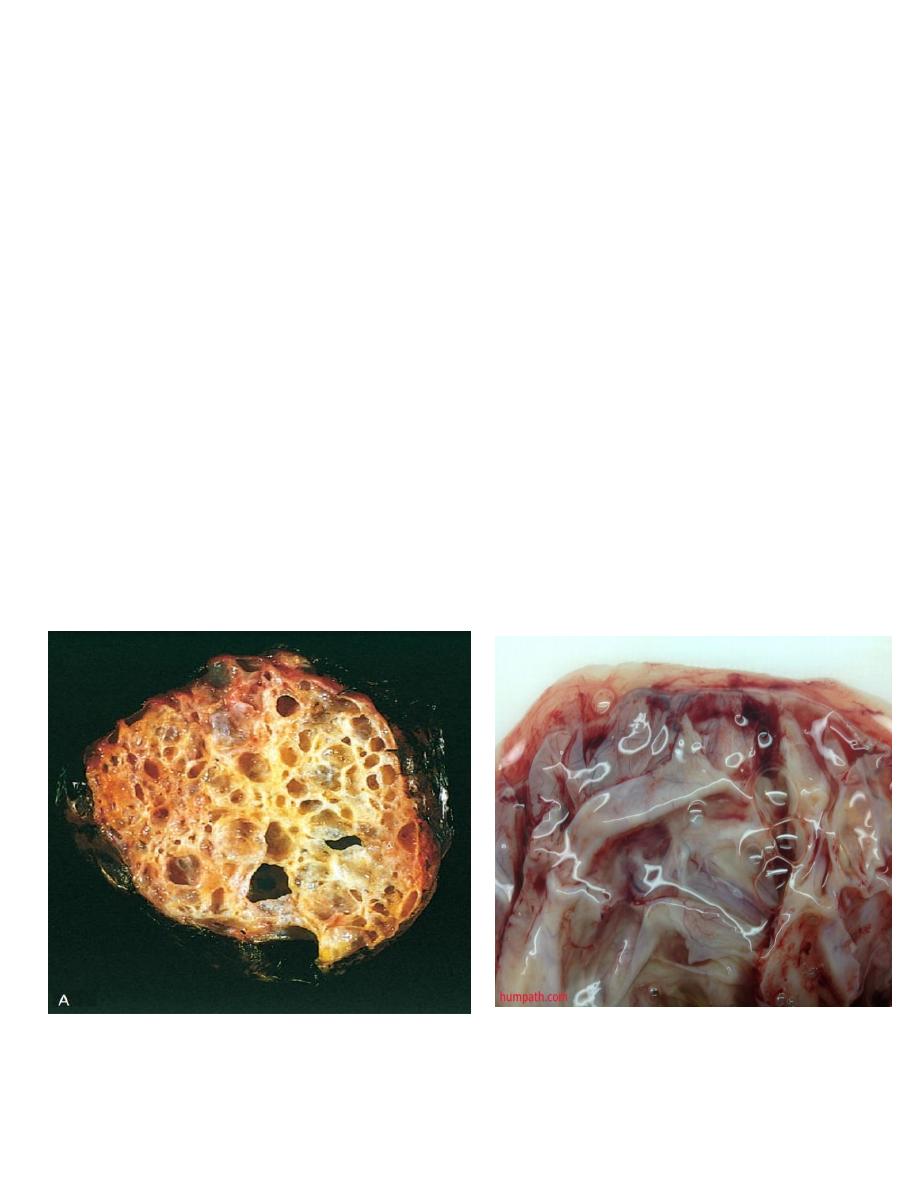
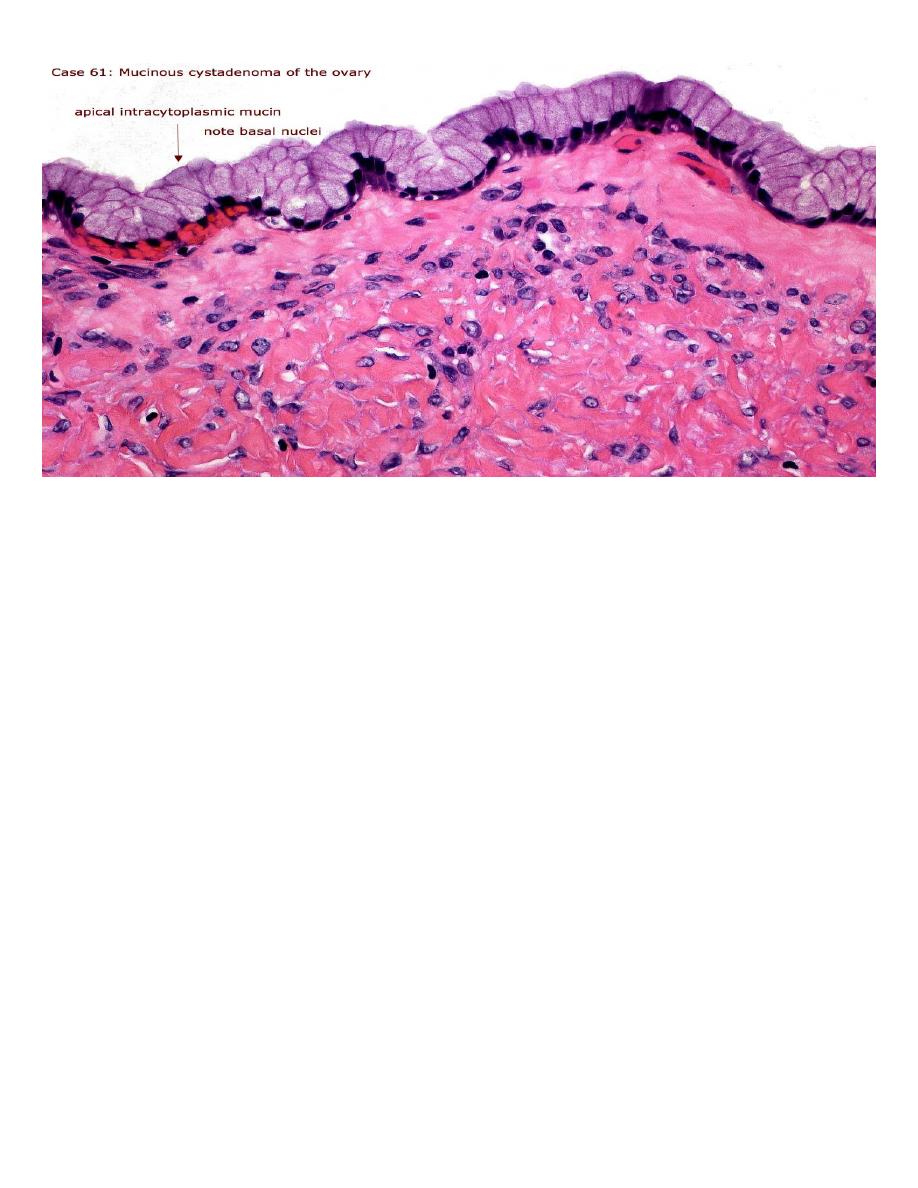
Mucinous tumor:
• This usually analogous to serous tumor but it's usually larger than serous cyst and
multilocular, it's lined by mucous secreting cells as endocervical cells.
• Grossly: it can't be differentiated from serous cysts but on cut section reveal mucinous
thick material.
• Microscopically: in benign tumor, it consist of thin wall lined by single layer of mucous
secreting cells which consist of apical vacuoles and basal located nuclei, in malignant one
also consist of complex papillae lined by multilayering malignant cells with stromal invasion
which's not seen in borderline tumor.
The metastasis or rupture of mucinous cystadenocarcinoma may give rise to pseudomyxoma
peritonii, that the peritoneal cavity becomes filled with mucinous material with multiple
implants on serosal surface so abdominal viscera become matted together.
Many other types of tumors of germ cell and sex cord– stromal origin also arise in the ovary,
the most common are:
Teratomas:-
It's divided into
1- Mature (benign teratoma).
2- Immature (malignant teratoma).
•
Benign (Mature teratoma)
these tumors arise from totipotential germ cells to give origin of
3 embryonal layers:
1- Ectodermal 2- Mesodermal 3- Endodermal
• The more common take the differentiation of ectodermal totipotential germ cells, which
also this teratoma can contain teeth, bone, cartilage, nests of bronchial or gastrointestinal
epithelium even brain tissue.
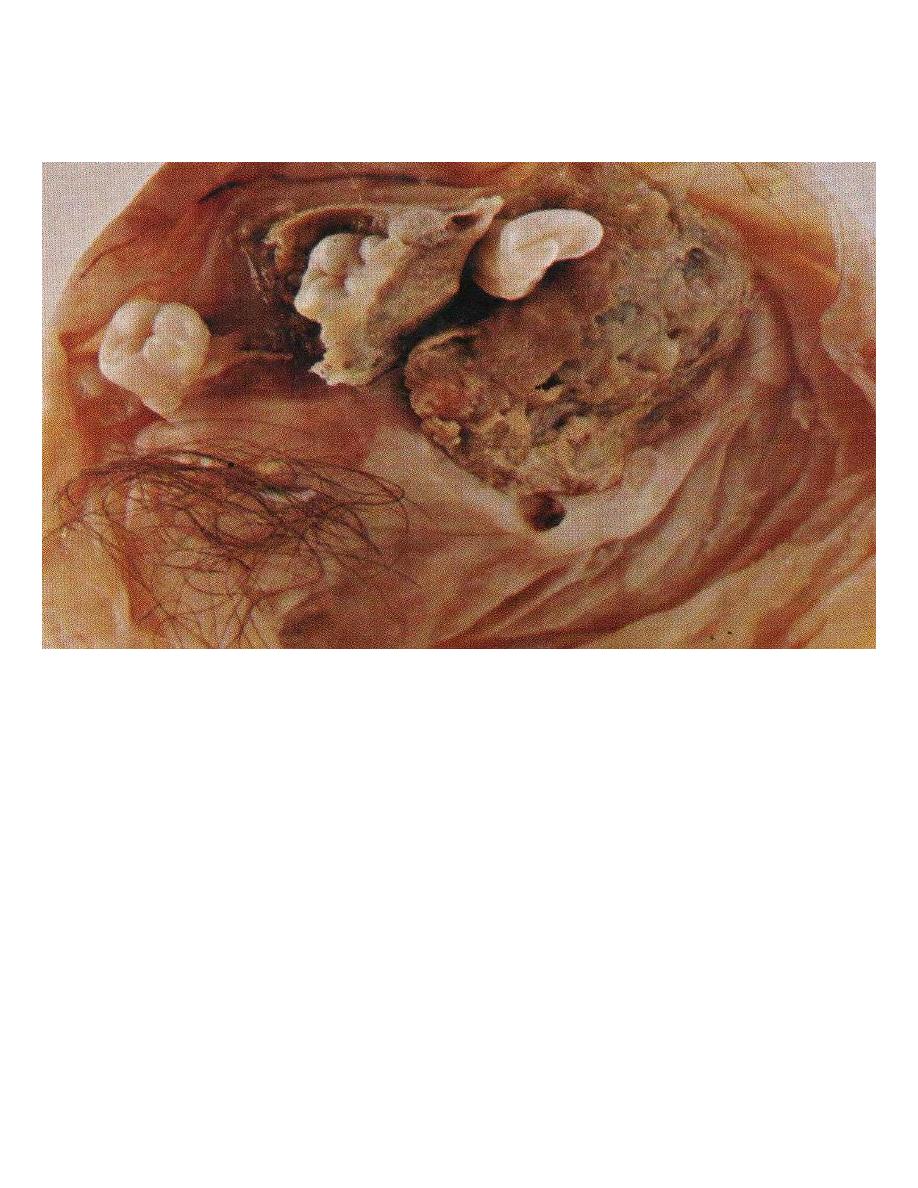
Teratoma containing tooth, cartilage & hair
Immature teratoma:-
• It usually occur in younger age group than mature, it's bulky and solid.
• Micrscopically consist of different tissues as undifferentiated and immature may be in one
element only especially in neuroepithelial cells.
