
Remote Sensing

What is remote sensing?
The International Society for Photogrammetry and
Remote Sensing (ISPRS) defined Remote Sensing
(RS) as:
“The art, science, and technology of obtaining reliable
information about physical objects and the
environment, through the process of recording,
measuring, and interpreting imagery and digital
representation of energy patterns derived from non
contact sensor system " . This definition considered
photogrammetry as sub-field of remote sensing
– via cameras recording on film, which may then be scanned (aerial photos)
– via sensors, which directly output digital data (satellite imagery)
Remote sensing
Aero-plane
Satellite

History of remote sensing
•
1783: The Marquis d’Arlandes and Pilatre made a voyage near Paris using a balloon.
•
Photography using balloon, pigeon
•
1860: Aerial photos in Russia and the USA
•
1914-19: The first World War and the second World War (1939-45) had seen
tremendous development in photography
•
1927: Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket.
•
1955: Work began on the Baikonur launch site in central Asia.
•
1957: Sputnik 1 launched from Baikonur (first satellite)
•
1961: Yuri Gagarin launched in the Vostok 1 capsule, becoming the first human
in space.
•
1969: Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the
Moon.
•
1971: The first Space Station in history, the Russian Salyut 1
•
1972: (US Landsat1) the concept of imaging from satellites is introduced
•
1986: France launched the first stereo-image satellite (SPOT1)
•
1992: The space year (the maturity of remote sensing - 20 years of operation)
•
1995 The Shuttle-Mir Program (1
st
phase of the International Space Station
(ISS).
•
2000 The first 3 astronauts (2 Russian and one American) start to live in the
ISS

Remote Sensing Organizations
• ISPRS-
International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote
Sensing
• IGARSS-
International Geosciences And Remote Sensing
Symposium
• NASA -
National Aeronautic and Space Administration (USA)
• ESA-
European Space Agency (Europe)
• NASDA-
National Space Development Agency (Japan)
• CNES-
Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (France )
• DARA
- German Space Agency
• CSA
- Canadian Space Agency
• NRSA
- National Remote Sensing Agency of India

Remote sensing basic processes
• Data acquisition (energy propagation, platforms)
• Processing (conversion of energy pattern to
images)
• Analysis (quantitative and qualitative analysis)
• Accuracy assessment (radiometric and geometric
correction)
• Information distribution to users (hard copy, CCT,
CD-ROM, X-BYTE)
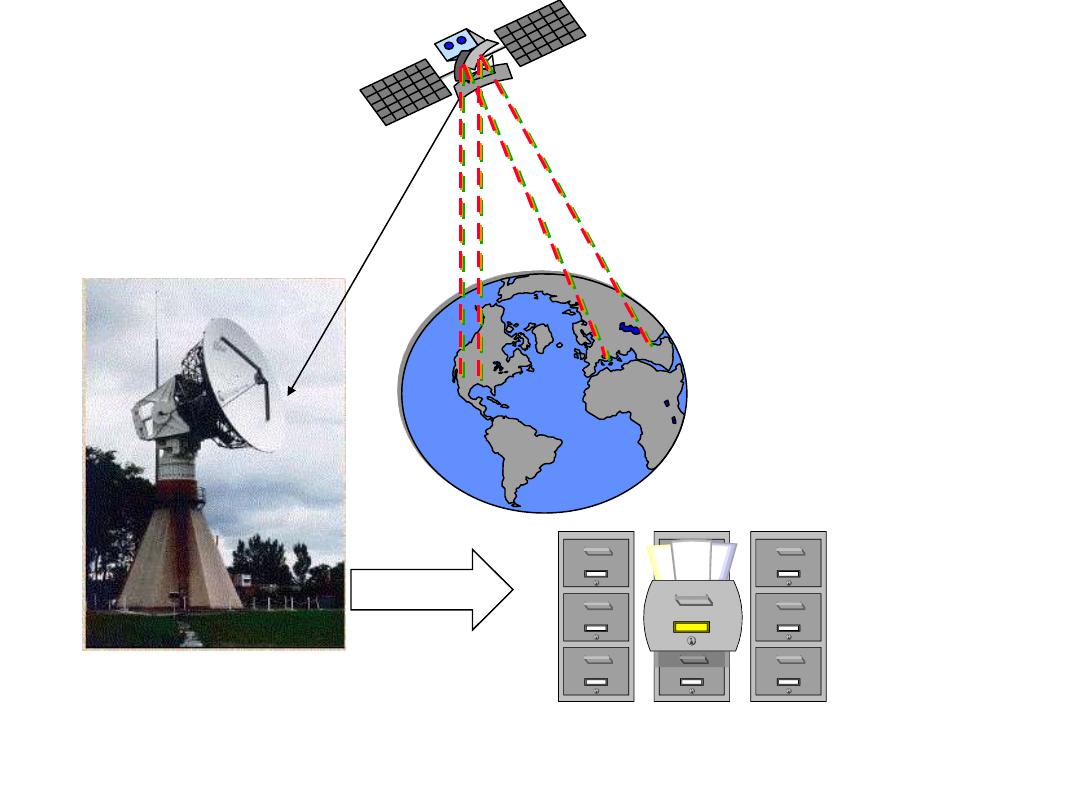
Receiving station
processing
Archiving
Distribution
7
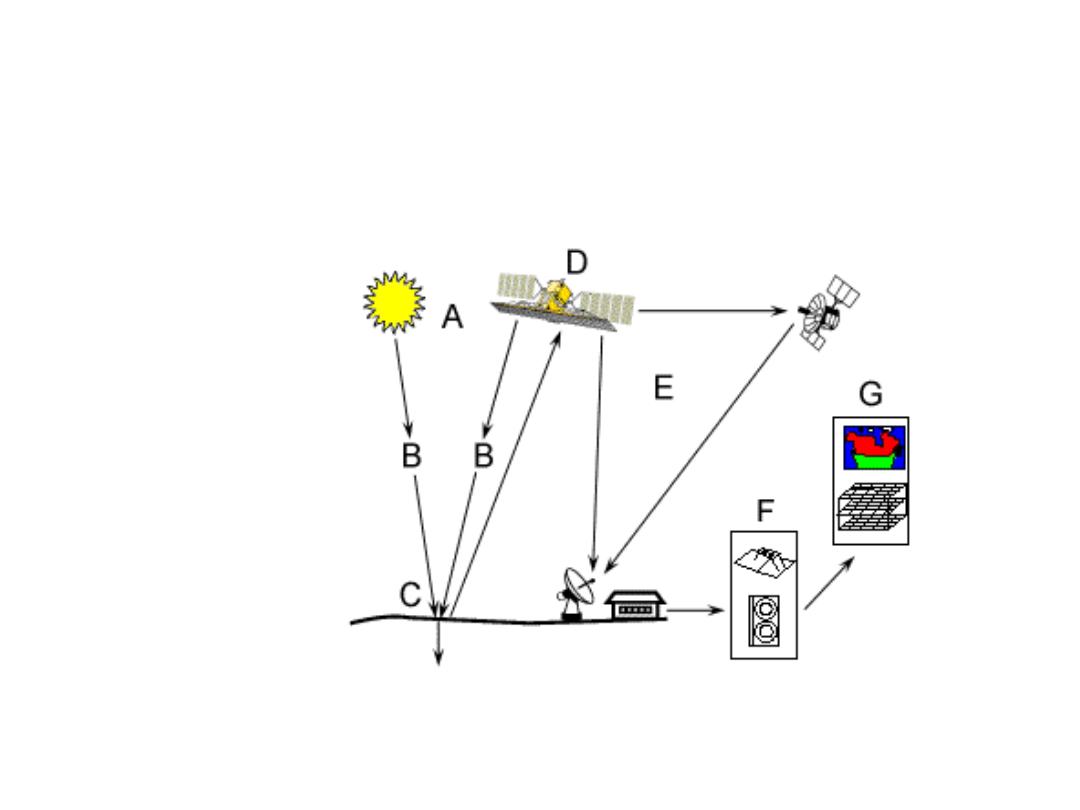
Remote sensing basic processes

Advantages of remote sensing
• Provides a regional view (large areas)
• Provides repetitive looks at the same area
• Remote sensors "see" over a broader portion of the
spectrum than the human eye
• Sensors can focus in on a very specific bandwidth
in an image or a number of bandwidths
simultaneously
• Provides geo-referenced, digital, data
• Some remote sensors operate in all seasons, at
night, and in bad weather

Remote sensing applications
• Land-use mapping
• Forest and agriculture applications
• Telecommunication planning
• Environmental applications
• Hydrology and coastal mapping
• Urban planning
• Emergencies and Hazards
• Global change and Meteorology
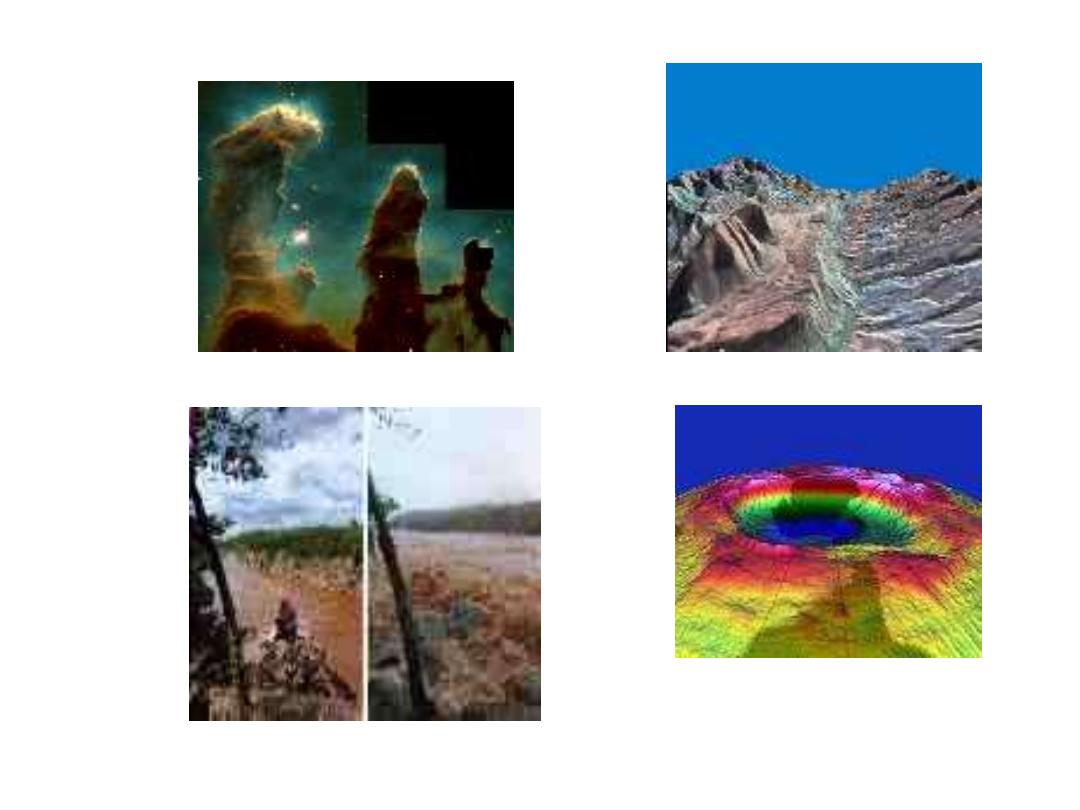

Applications
