
1
Puberty
Definition :
• Age of transition from Childhood to adulthood physically ending in
full sexual & reproductive development .
• Puberty is a period of time ( 8 – 13 yr ) , menarche is an event
( 12yr )
Before puberty :
• There is no / very little ' E ' secreted due to :
- GnRH suppression ( unknown , mostly controlled by a gene in
GnRH nucleus ) .
- Very Sensitive HPO axis to – ve feedback of steroids .
• Variation of age of start of puberty is due to several factors : e.g.
- Constitutional , genetic pre disposition .
- Psychological factors .
- Nutrition , activity ( athletes have later puberty ) .
- Melatonin release from pineal glands .
-
Normal puberty :
- It takes a period of time 2 – 5 yr .
- Girls reach puberty + years < boys
* Somatic Changes :
- Growth spurt ( peaks at 11 yr ) … followed by closure of epiphysis
- Deposition of fat feminine round contour .
- Persistence of high pitched voice .
* Secondary sexual characters
- Conadarche : The initial release of LH & FSH
- Thelarche : First appearance of breast buds …… the 1
st
event
- Adrenache : Activation of adrenal androgens .
Pubarche (full appearance of axillary & public hair )
- Menarche : occurs 2 yr after onset of breast ….. the last event .
initial cycles are usually anovulatory .
* Genial changes
( d.t. E ) ….. development of the reproductive organs .
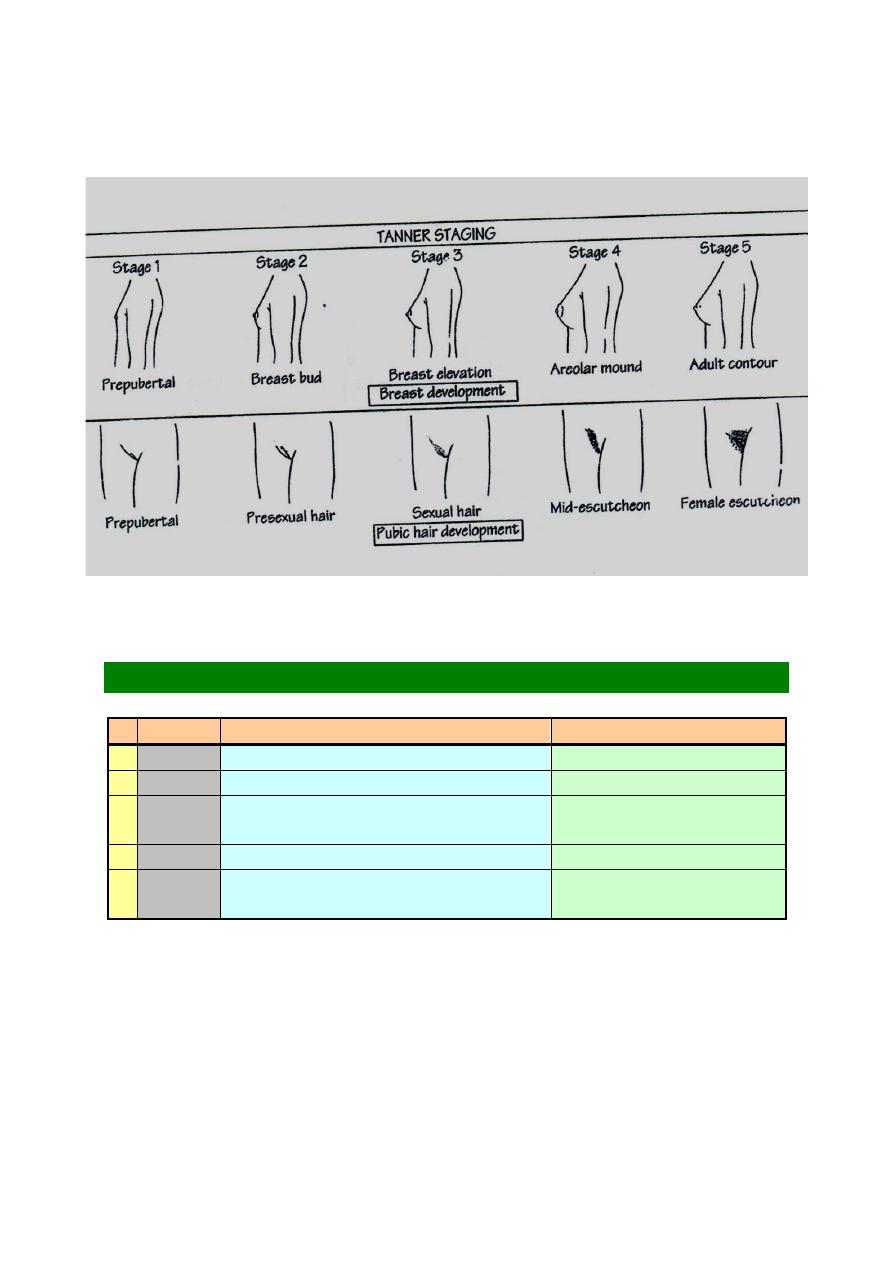
2
Tanner Classification
Breast
Public hair
1 Pre-pub Elevated breast papillae
Not present
2 10 yrs
Breast bud small mound
Sparse on labia majora
3 11 yrs
Further enlargement ( round &
small )
Darker , coarser , curled
4 12 yrs
2ry mound ( areola project out )
Also on mons pubis
5 14 yrs
Adult contour (2ry mound
disappear )
Also on medial thigh
3
4
Abnormal puberty / Adolescence / child-hood
• Congenital : ambiguous genitalia ( intersex )
• Traumatic : circumcision … sexual abuse … accidental trauma ( FB ) .
• Inflammatory : prepubertal vulvovaginitis
• Neoplastic : ovary ( germ cell tumor ) , vagina ( sarcoma botryoids )
• Miscellaneous :
- Early ( precocious ) / Delayed Puberty .
- Menorrhagia ( 1
st
/ exclude coagulopathy ) .
- Dysmenorrhea .
Q. The commonest pre-pubertal gyn. Complaint ? discharge ( V.Vaginitis )
Q. The commonest pre-pubertal gyn . bleeding ? F. body / severe . V. Vaginitis .
Q. What are the Indications of R/R in gynecology ?
- Virgins
- Congenital imperforate hymen .
- Traumatic . complete perineal tears & fistula .
. differentiates rectocele from enterocele .
- Neoplastic - routine in all tumors e.g. cancer cervix .
- masses in D. pouch e.g. endometrioma .
- Miscellaneous Bleeding / rectum .
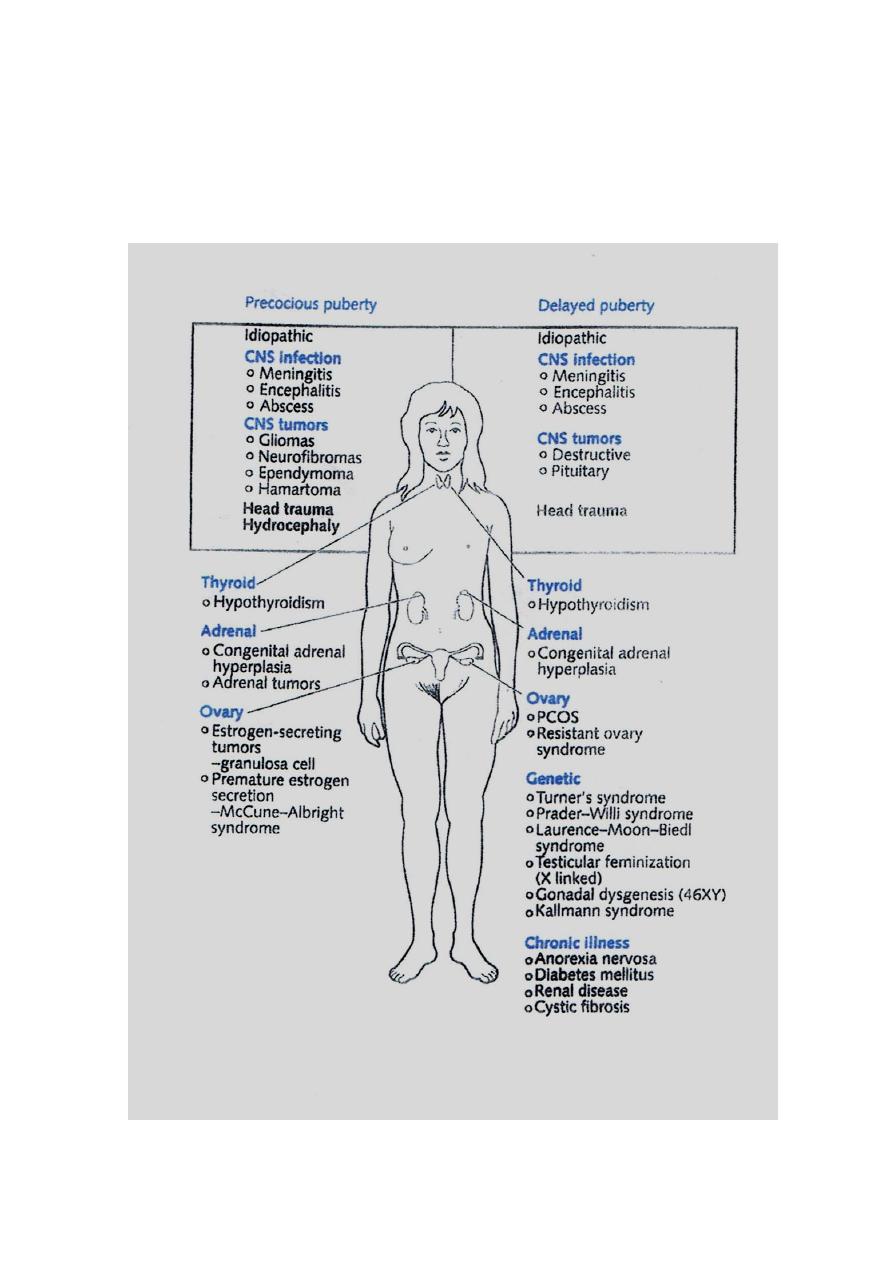
(1) Delayed puberty
Definition :
• No menarche by 16
• No secondary sexual characters by 14
• No menarche for 5 years after completed thelarche .
Etiology
- Constitutional , malnutrition , chronic illness .
- Hypergoadotrophic ovarian failure .
- Hypogonadotrophic hypothalamic – pituitary failure .
- Normogonadotrophic end-organ-insensitivity .
( Mullerian agenesis , TFS , imperforate hymen )
Investigations
LH , FSH to differentiate the 3 types
- Hyper-gonadotrophic ( FSH > 30mIU/mL ) karyotyping
- Hypo-gonadotrophic ( FSH < 10mIU / mL ) CT skull .
5
- Normo-gonadtrophic ultrasound pelvis .
Treatment
: acc to cause
6
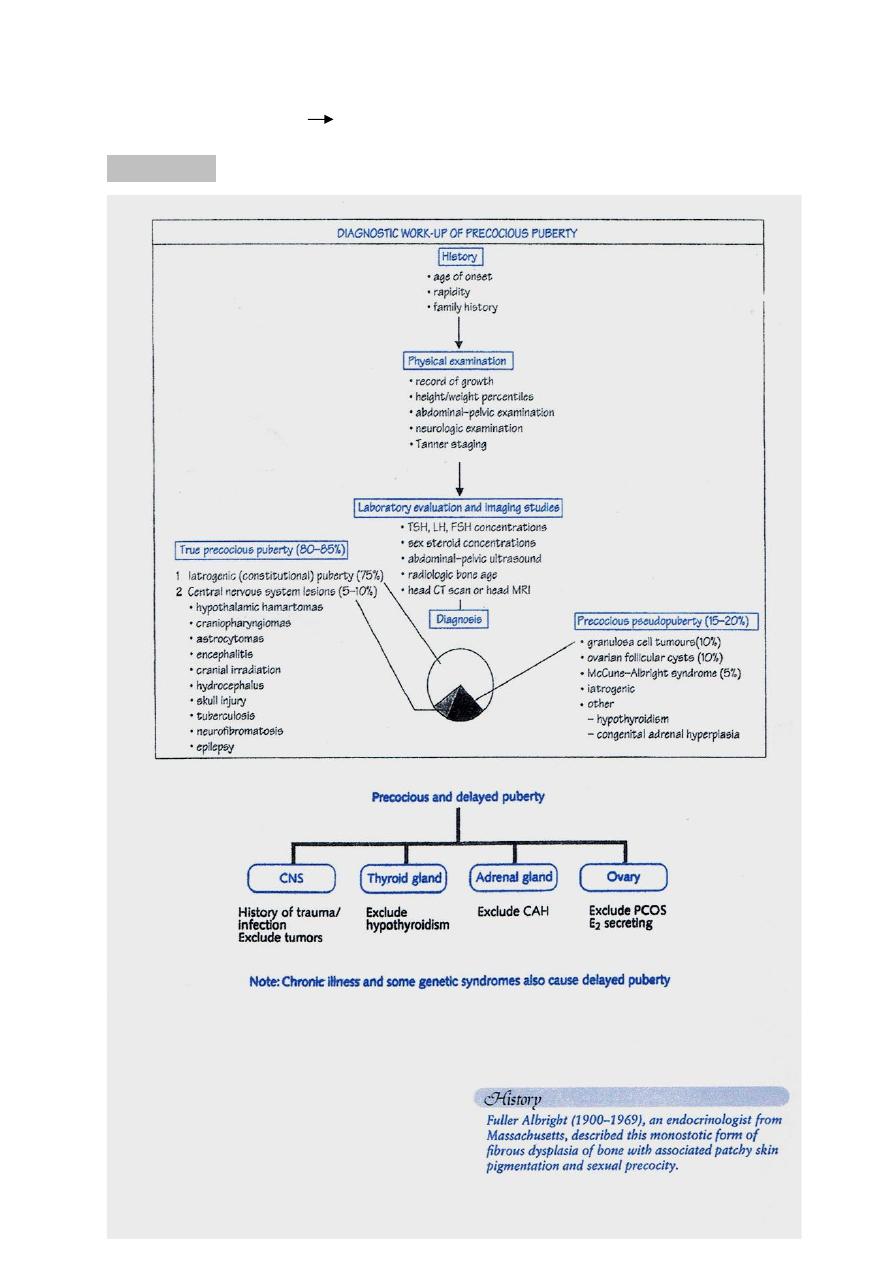
Precocious puberty
Definition
Appearance of any pubertal changes that its mean by 2 SD
Approximetely : < 8 years for breast & < 10 years for menarche
Etiology
* Isolated ( Incomplete ) = premature :
1. Thelarche ( 1 or 2 ) } No in E .. no ttt
2. Adrenarche } Just local tissue sensitivity
3. Pubarche } other pubertal changes occur normally .
Complete
Isosexual ( E ) ….
Heterosexual
( An ) rare
True ( central ) PP
False ( Peripheral ) PP
1. Idiopathic / Consituational
in 90% of cases early
maturation of HPO axis
2. Organic brain lesion
trauma / tumors /
meningitis
stimulation of HPO axis
1. Est. secreting ovarian tumors
2. latrogenic
3. Hypothyroidism
4. McCune Albright $ … Triad ;
- Precocios Puberty
- Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia .
- Café-au lait patches
1. And Sce. Tumors :
- Ovarian
- Adrenal
2. Latrogenic
3. Cushing
4. Adreno-genital $
( congenital adrenal
hyperplasia )
- Normal ovulation
- Pregnancy can occur
- No in Gn no ovulation
- Only feminization .
Assessment
First … History & Examination suggestive of any above disease
1) Bone age
2) Hormonal assay
3) FSH & LH
* Retarded hypothyroidism
* Normal Isolated PP
* Advanced ( tall child but ..)
- Isosexual or
- Heterosexual PP
* Androgens heterosexual :
- CT abdomen : adrenal tumor
- Pelvis U/S : ovarian tumor
- 170H progesterone : CAH
* Estrogens isosexual
* High True CT bran
* Low False :
- Pelvic U/S
- T3 , T4
- Bone scan ( McC . Alb )

7
Treatment :
* Of the cause e.g. surgery for ovarian tumor , thyroxin for Juv.
Hypothyroid .
* Isosexual anti-estrogens ttt till age of 12 ye ……… as in endometriosis .
* Heterosexual anti-androgen ………………………….. as in hirsutism .
Dr. ASEEL AL-HELFY
