
Morphomteric Analysis
التحليل المورفومتري

morphometric analysis
quantitative description and analysis of landforms as practiced in
geomorphology that may be applied to a particular kind of
landform or to
and large regions generally. With
regard to drainage basins, many quantitative measures have been
developed to describe valley side and channel slopes, relief, area,
drainage network type and extent, and other variables. Attempts
to correlate statistically parameters defining drainage basin
characteristics and basin hydrology, as in studies of sediment
yield, are generally designated as morphometric analyses.

is defined as the measurement of the
shape. Morphometric studies in the field of hydrology
were first initiated by R.E. Horton and A.E. Strahler in
the 1940s and 1950s. The main purpose of this work
was to discover holistic
properties from the
measurement of various stream attributes.
One of the first attributes to be quantified was the
hierarchy of stream segments according to an ordering
classification system (Next figure).
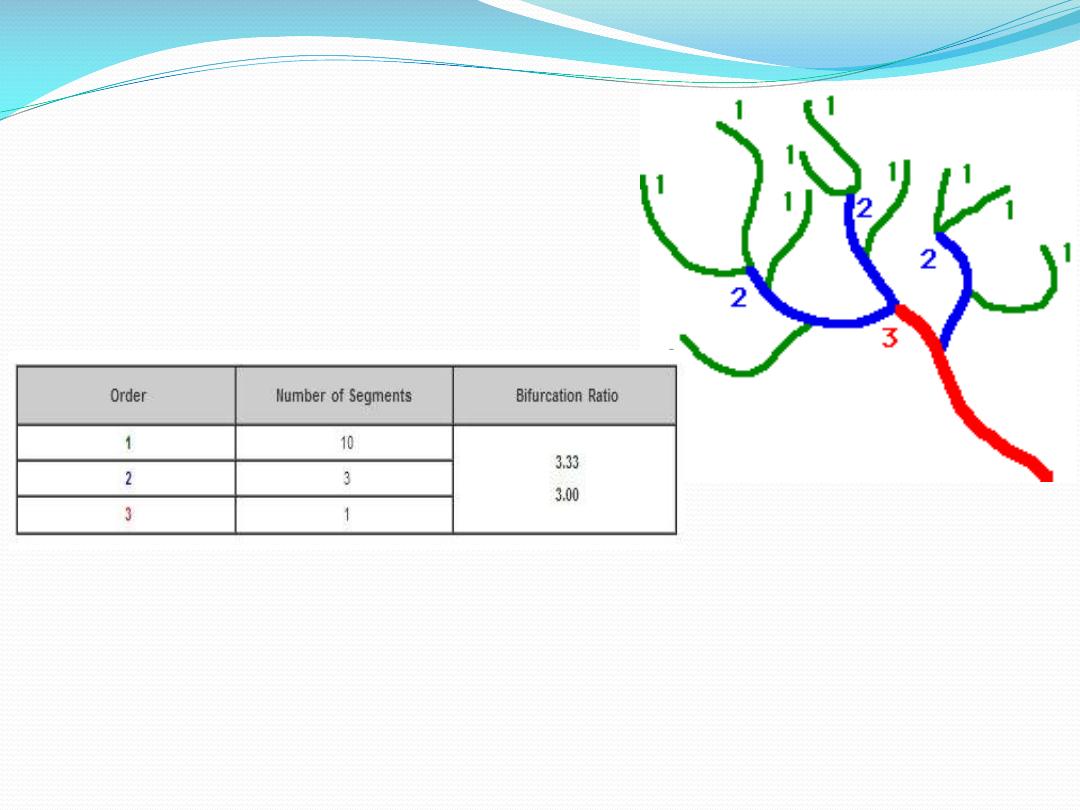
Example of stream ordering and the calculation of bifurcation ratio.

In this system, channel segments were ordered numerically
from a stream's
to a point somewhere down
stream. Numerical ordering begins with the tributaries at
the stream's headwaters being assigned the order 1. A
stream segment that resulted from the joining of two 1st
order segments was given an order of 2. Two 2nd order
streams formed a 3rd order stream, and so on. Analysis of
this data revealed some interesting relationships. For
example, the ratio between the number of stream segments
in one order and the next, called the
was consistently around three. R.E. Horton called this
association the

Horton applied morphometric analysis to a variety of stream attributes
and from these studies he proposed a number of laws of drainage
composition. Horton's
suggested that a
geometric relationship existed between the number of stream
indicated that the mean basin area of successive ordered streams
formed a linear relationship when graphed. The results described
above and the outcomes of other related analyses convinced
researchers that these findings suggested that some underlying factor
(or factors) was governing the structure of the various stream attributes
in a similar predictable way. Studies of other natural branching
networks have revealed patterns similar to the stream order model. For
example, the bifurcation ratio of three has also been discovered in the
rooting systems of plants, the branching structure of woody plants, and
the veination in leaves and the human circulatory system.

In addition to the mathematical relationships found in
stream ordering, various aspects of drainage network
forms were also found to be quantifiable. One such
relationship was
. Drainage density is
a measure of the length of
per unit area
of drainage basin. Mathematically it is expressed as:
Drainage Density (Dd) = Stream Length / Basin Area

The
measurement of
drainage density provides
a
hydrologist or geomorphologist with a useful numerical
measure of landscape dissection and
potential. On a
highly permeable landscape, with small potential for
runoff, drainage densities are sometimes less than 1
kilometer per square kilometer. On highly dissected
surfaces densities of over 500 kilometers per square
kilometer are often reported. Closer investigations of the
processes responsible for drainage density variation have
discovered that a number of factors collectively influence
stream density. These factors include climate, topography,
soil
capacity, vegetation, and geology

Laws

Length of Stream
Ls‾ = ∑ Ls / Ns ....…………...... ( 1 )
Length of Stream
Br = Ns / Ns + 1 .…......…....... ( 2 )
Ls‾
=
معدل طول اجلداول
(
كم
.)
Ls
=
طول اجلداول
(
كم
.)
Ns
=
عدد اجلداول

Drainage Density
D = ∑ Ls / A ......…………….... ( 3 )
Stream Frequency
F = ∑ Ns / A .........……………... (4)
A= basin area

Read my paper
