Dr. Jamal Al-Saidy
M.B.Ch.B. .F.I.C.M.S
Dislocation Of Knee
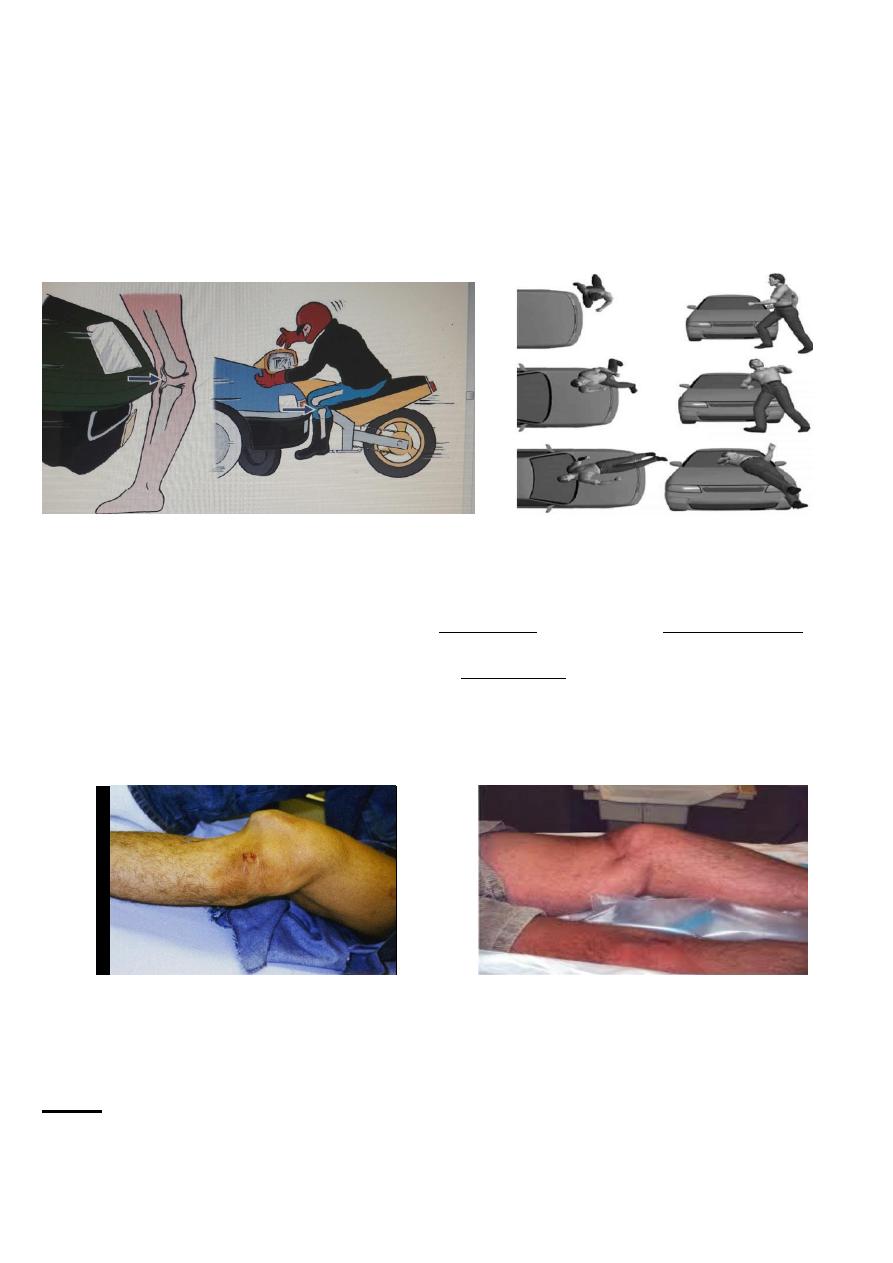
The knee can be dislocated only by considerable violence, as in a road accident. The cruciate ligaments and
one or both lateral ligaments are torn.
mechanism of injury
Clinical features
Rupture of the joint capsule produces a leak of the haemarthrosis, leading to severe bruising and swelling,
this may be the only clue on inspection, especially if the dislocated joint has reduced spontaneously.
Otherwise, the diagnosis is straightforward as there is gross deformity.
The circulation in the foot must be examined because the popliteal artery may be torn or obstructed.
Repeated examination is necessary(compartment syndrome).
Distal sensation and movement should be tested.
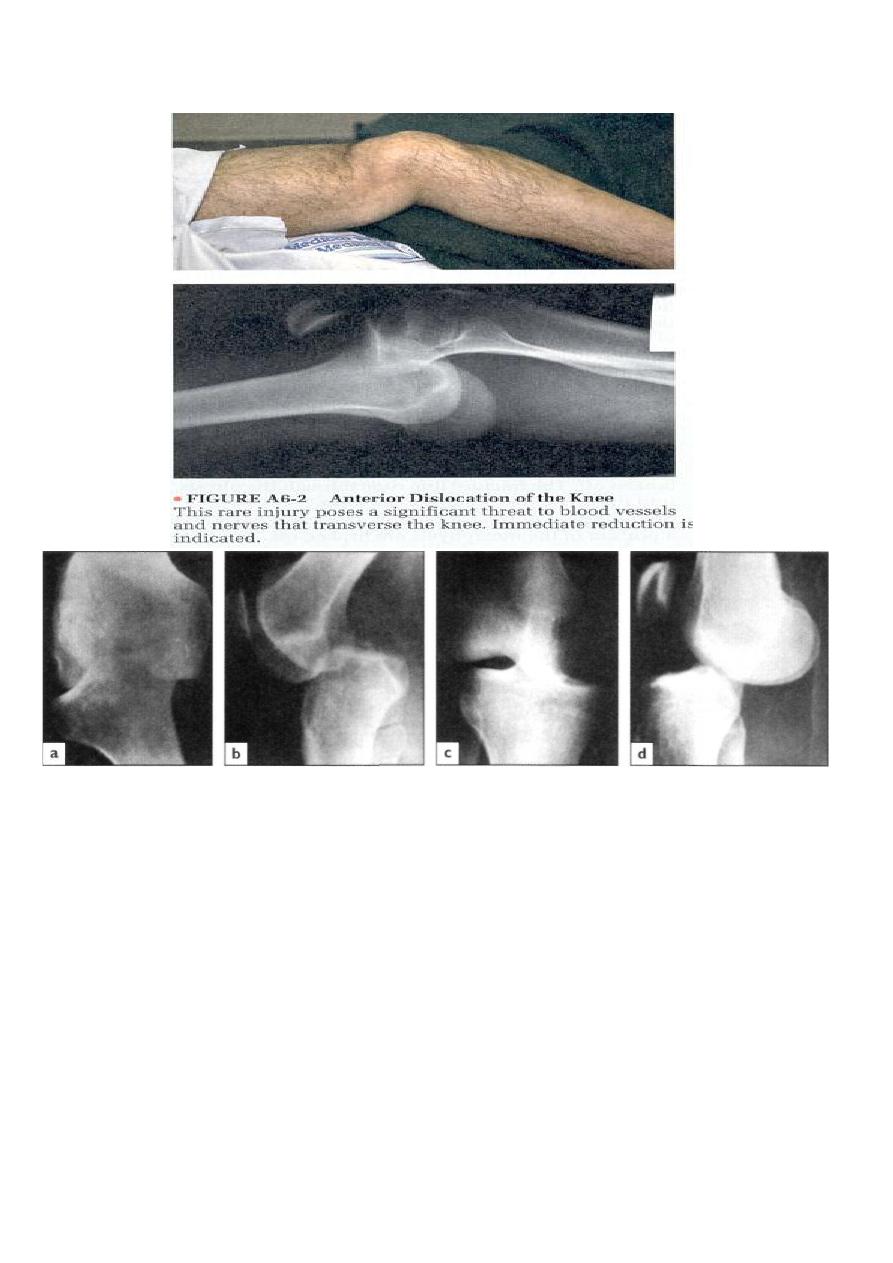
X-ray
Usually anterior, in addition to the dislocation, the films occasionally reveal a fracture of the tibial spine
(cruciate ligament avulsion). If there is any doubt about the circulation, an arteriogram should be obtained.
Dr. Jamal Al-Saidy
M.B.Ch.B. .F.I.C.M.S
Dislocations of the knee :-
(a, b) Posterolateral dislocation (c, d) anteromedial dislocation.
Treatment
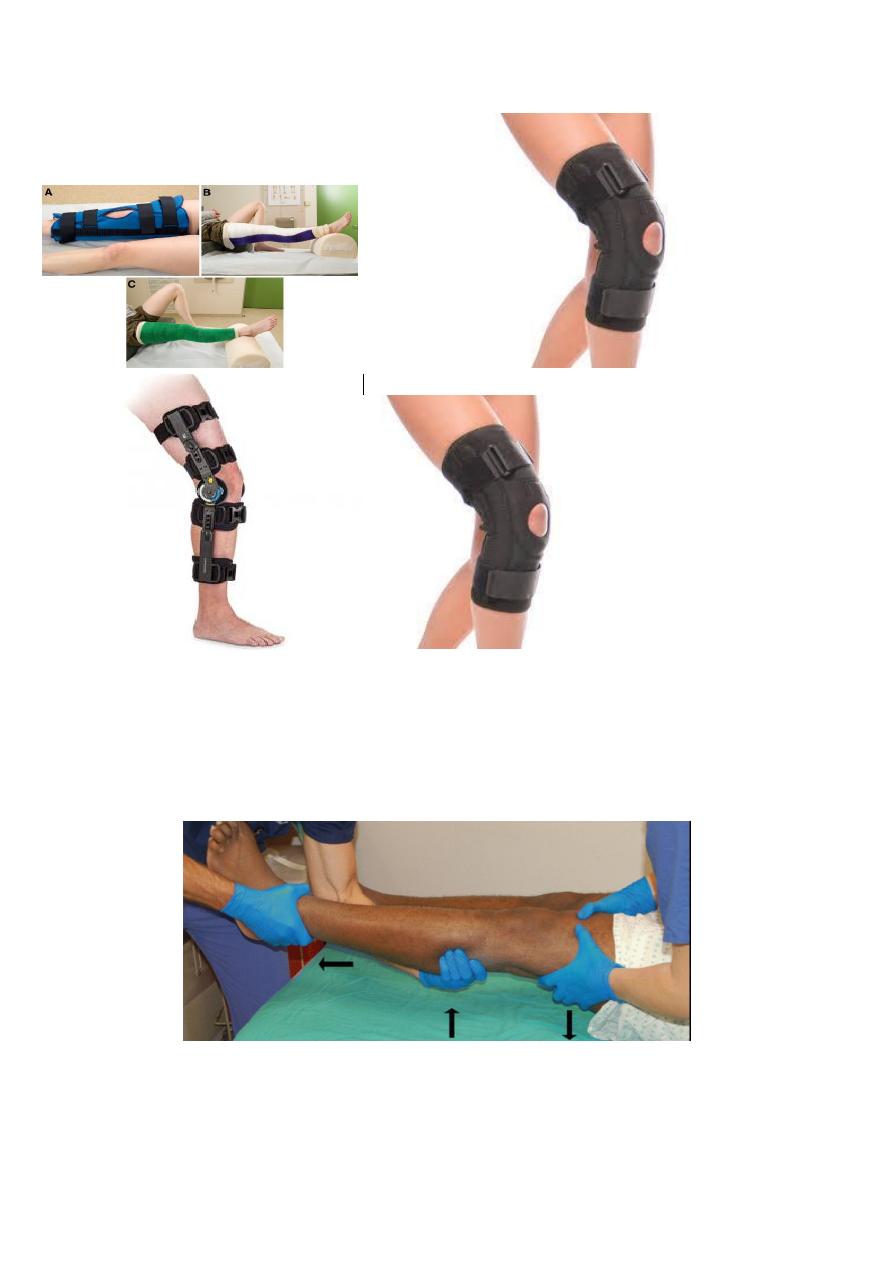
Reduction under anaesthesia is urgent; this is usually achieved by pulling directly in the line of the leg, but
hyperextension must be avoided because of the danger to the popliteal vessels. If reduction is achieved, the
limb is rested on a back-splint and the circulation is checked repeatedly during the 48 hours. Because of
swelling, a plaster cylinder is dangerous.
A vascular injury will need immediate repair and the limb is then splinted with an anterior external fixator
and also if the joint is unstable and if possible, repair or reconstruction of the capsule and collateral
ligaments should be undertaken at the same time.
Occasionally closed reduction fails because the torn medial ligament lies between the femur and the tibial
condyles; open reduction must then be performed, the ligament is sutured back into place and the capsule is
repaired. Similarly, if there is an open wound.
The cruciate ligaments can be reconstructed after knee movement has recovered, usually some 6–12 months
later.
Dr. Jamal Al-Saidy
M.B.Ch.B. .F.I.C.M.S
knee splint
Closed Reduction
Dr. Jamal Al-Saidy
M.B.Ch.B. .F.I.C.M.S
Complications
EARLY
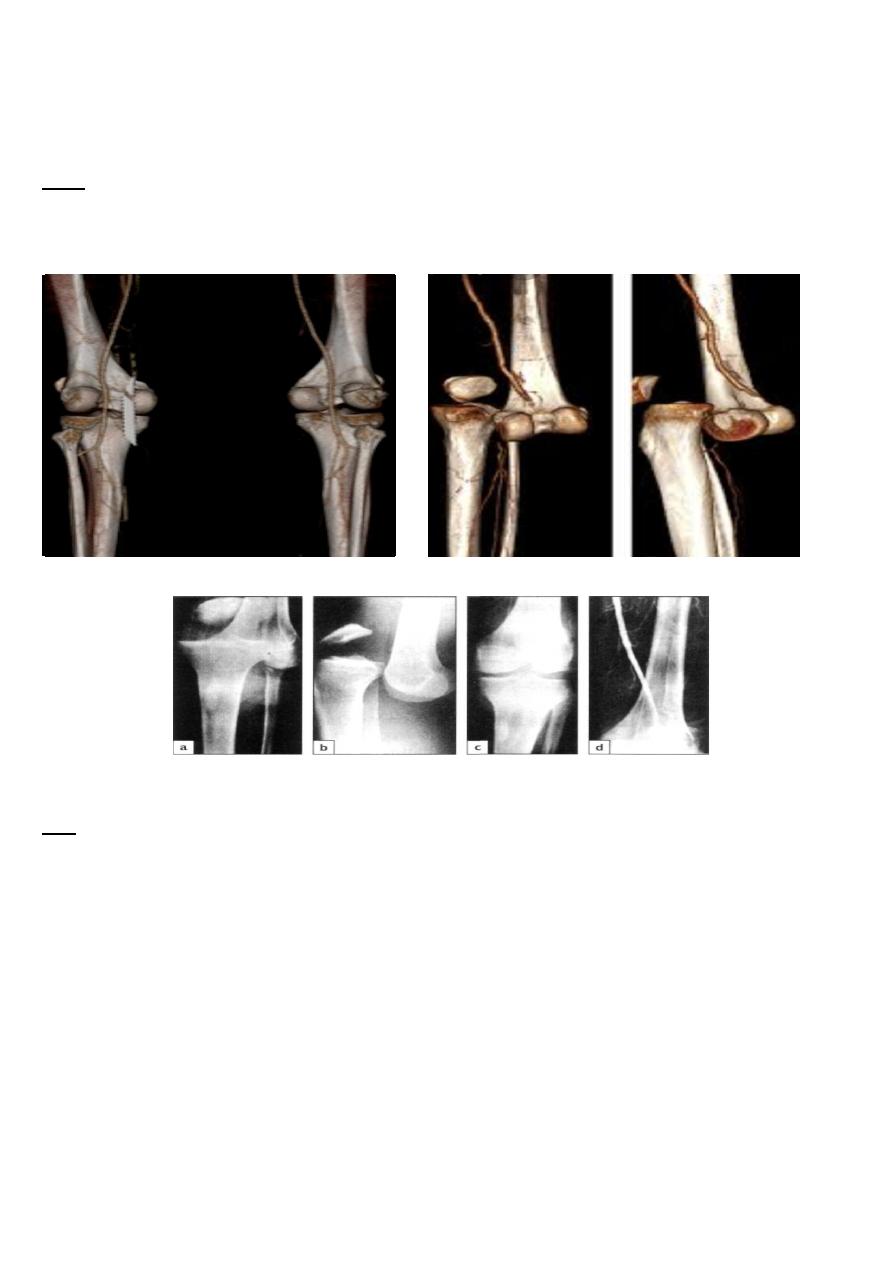
Arterial damage :- Popliteal artery damage occurs in nearly 20 per cent of patients and needs immediate
repair.
Nerve injury :- The lateral popliteal nerve may be injured, but fortunately it usually recovers by itself.
Knee dislocation and vascular trauma
(a, b) This patient was admitted with a dislocated knee. After reduction (c) the x-ray looked satisfactory,
but the circulation did not. (d) An arteriogram showed vascular cut-off just above the knee; had this not been recognized and treated ,
amputation might have been necessary.
LATE
o Joint instability
o Stiffness :- Loss of movement, due to prolonged immobilization, is a common problem and may be even
more troublesome than instability.
THANK YOU
Dr. Jamal Al-Saidy
M.B.Ch.B. .F.I.C.M.S
Assistant Professor and Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
