Fifth Stage – Gynecology – Dr Wasn – Lecture 2
INTER SEX
Chromosomal abnormalities
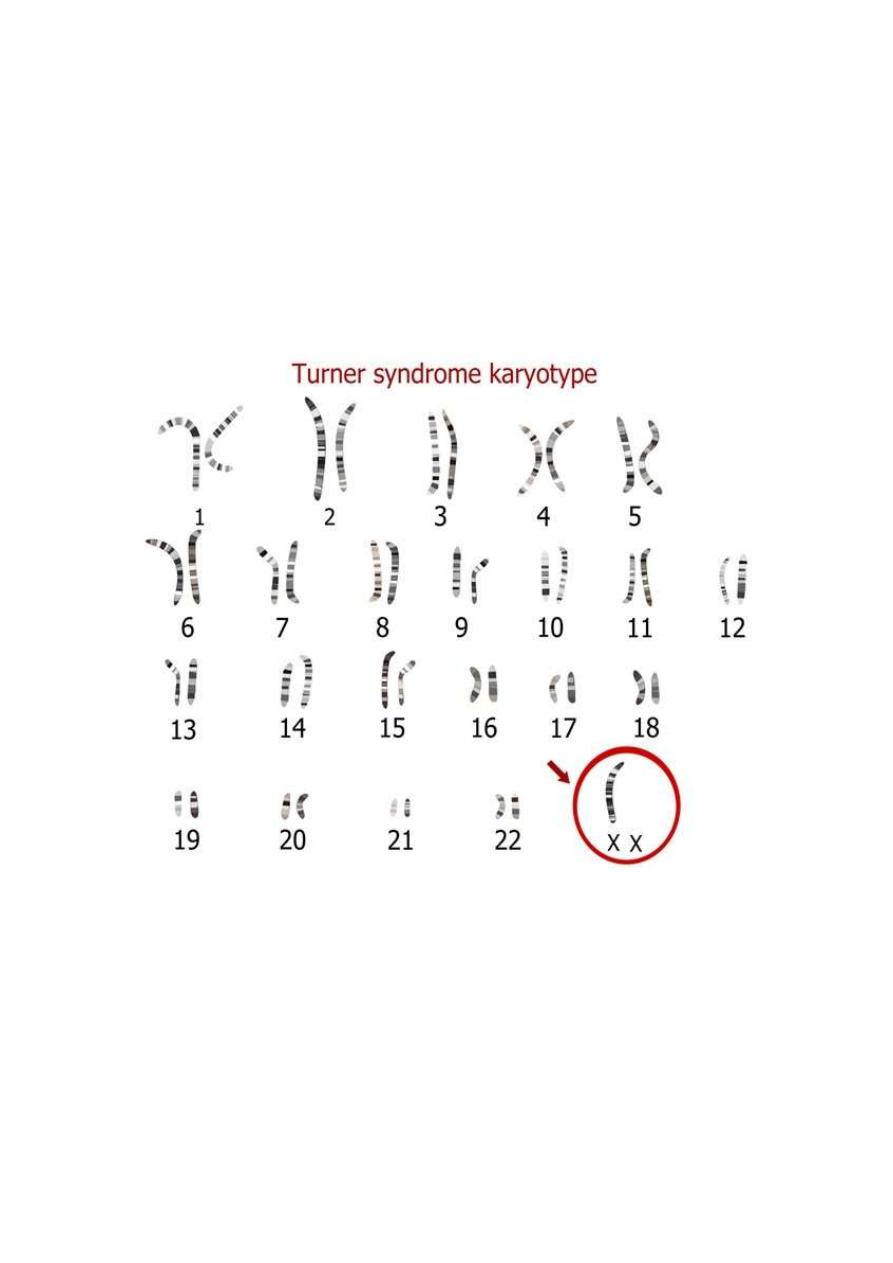
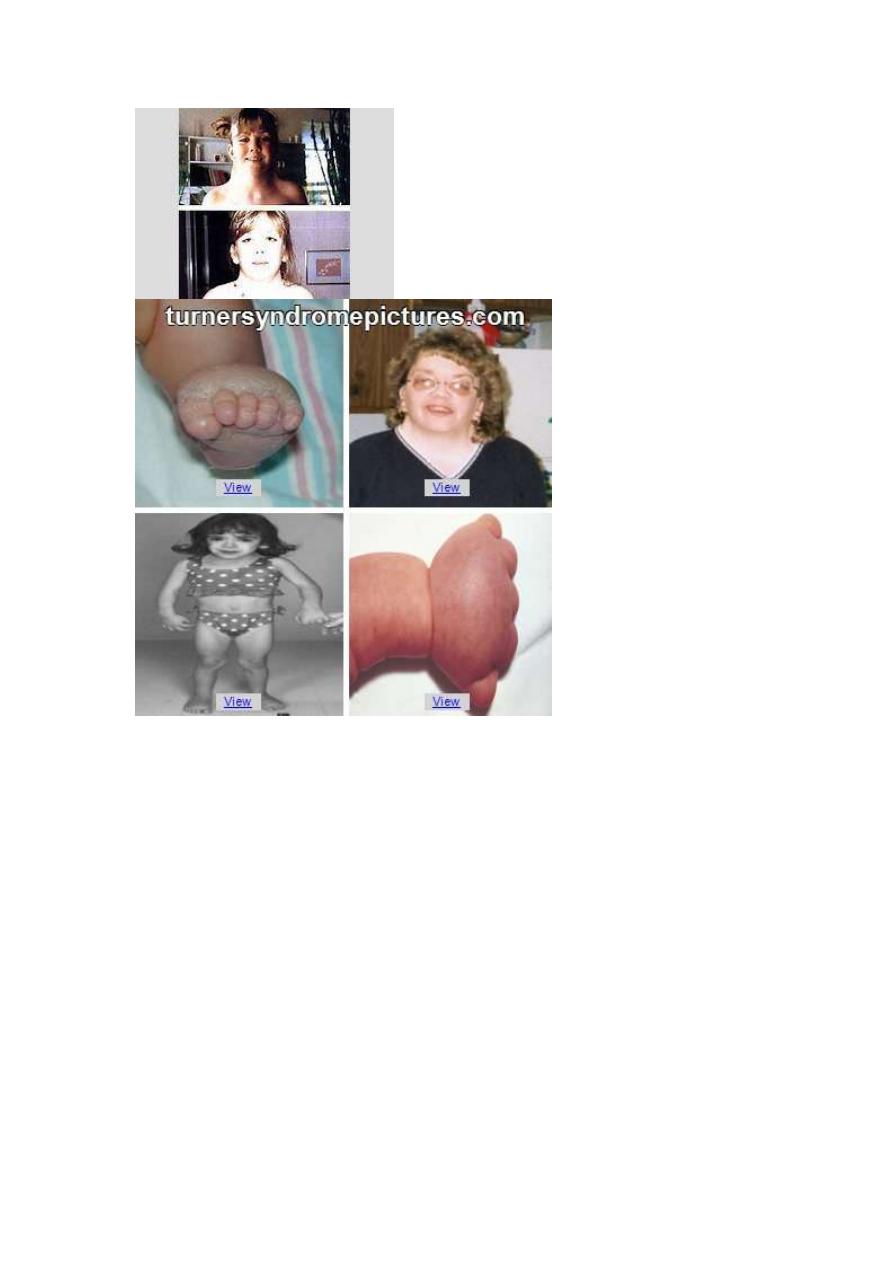
Turner syndrome
. complete or partial absence of X chromosome (45x0)
. most common chromosomal abnormalities in females 1 in
2500 live female birth
. clinical features: short stature, webbing of the neck and wide
carrying angle .inverted widely spaced nipples, shield chest
,puffy hand and feet in baby due to lymphedema ,low hair line
,cubitus valgus ,short forth metacarpal .high arched palate
,micrognathia,defective dental delvopment
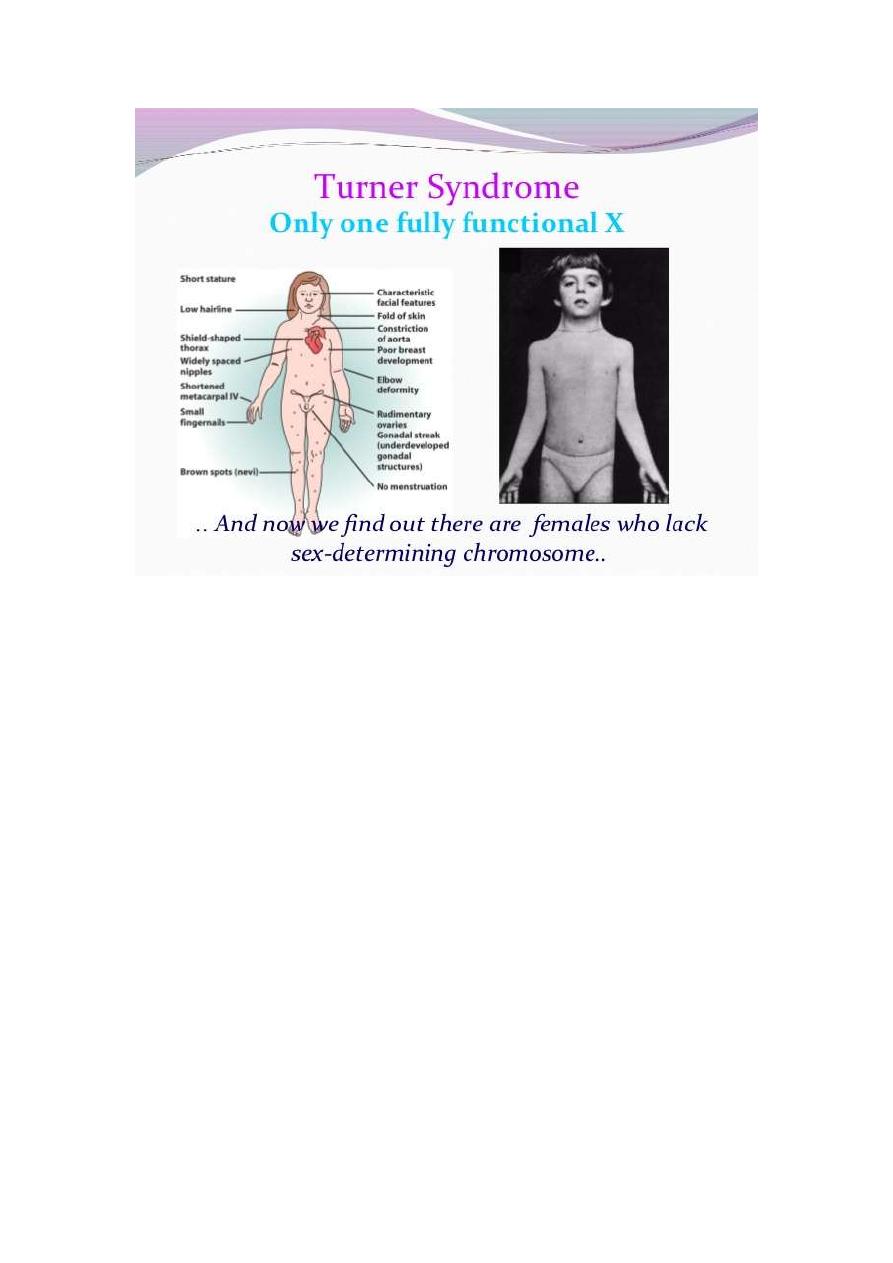
Normal intelligence
. associated medical conditions: coarctation of the aorta,
inflammatory bowel disease, sensorineural and conductive
deafness, renal anomalies and endocrine dysfunctions such as
autoimmune thyroid disease
. only ovarian stroma present (streak gonads) do not function
to produce estrogen or oocyte
. diagnosis clinically short stature during childhood or during
puberty (10%) due to delay puberty and absence of normal
physical changes of puberty
. treatment is focused on growth during childhood and on
induction of puberty in adolescent
. pregnancy is possible with ovum donation


47 XXX
Common
Sexual development occurs normally
Normal or tall height
Academic performance is usually below average, there may be
motor and speech delay and attention deficit
Premature ovarian failure and may present with secondary
amenorrhea
XY gonadal dysgenesis
.xy karyotype
. absence of SRY gene in 10% but most cases the cause is
unknown
. complete gonadal dysgenesis (Swyer syndrome) the gonad
remains as a streak gonad and does not produce any hormones
. uterus, vagina and fallopian tubes develop normally due to
absence of AMH (so Mullerian structures do not regress)
.no virilization of the fetus and phenotype female due to
absence of testosterone
. failure of spontaneous puberty due to non-function gonad
. the dysgenetic gonad has a high risk of malignancy so should
be removed when the diagnosis is made
. diagnosis: karyotype, laparoscopic biopsy of the gonad
. puberty is induced by estrogen
. pregnancy is reported with oocyte donation

Mixed gonadal dysgenesis
Is more complex, the karyotype may be 46 xx, mosaicism xx/xy
is present in 20%
Both functioning ovarian and testicular tissue can be present
(ovatesticular DSD
Anatomical finding vary according to functional gonad: virilize
baby and ambiguous or normal male genitalia. mullerian
structure are absent on one side of functioning testes, but
unicornute uterus may be present if there is an ovary
46XY DSD
. complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS) occurs in
individuals where virilesation of external genitalia does not
occur due to partial or complete inability of androgen receptor
to respond to androgen stimulation
.in the fetus with CAIS testes form normally due to the action of
SRYgen ,the testes secrete AMH leading to regression of
Mullerian ducts .

.CAIS woman do not have a uterus
. female external genitalia due to failure of viliralazation
because inability of androgen receptor to respond to
testosterone
. testes present at some point in their line of descend from
abdomen
.during puberty :normal breast development(circulating
testosterone is peripherally converted to estrogen
Minimal axillary and pubic hair
Primary amenorrhea
Sometime Inguinal hernia in young girl (testes
in inguinal canal)
. infertile
. gonadectomy is recommended because risk of malignancy
. long term hormonal replacement therapy
. vaginal dilator or surgical vaginal reconstruction surgery for
penetrative intercourse
In partial androgen insensitivity limited virilization and the
diagnosis at birth with ambiguous genitalia
5-Alpha-reductase deficiency
. XY karyotype
. normal function testes produce both testosterone and AMH
.the fetus unable to convert testosterone to
dihydrotestosterone in the peripheral tissue and cannot virilize
normally
Presentation: ambiguous genitalia at birth or increase
virilization at puberty due to large increase of testosterone with
the onset of puberty
.assigned female sex of rearing
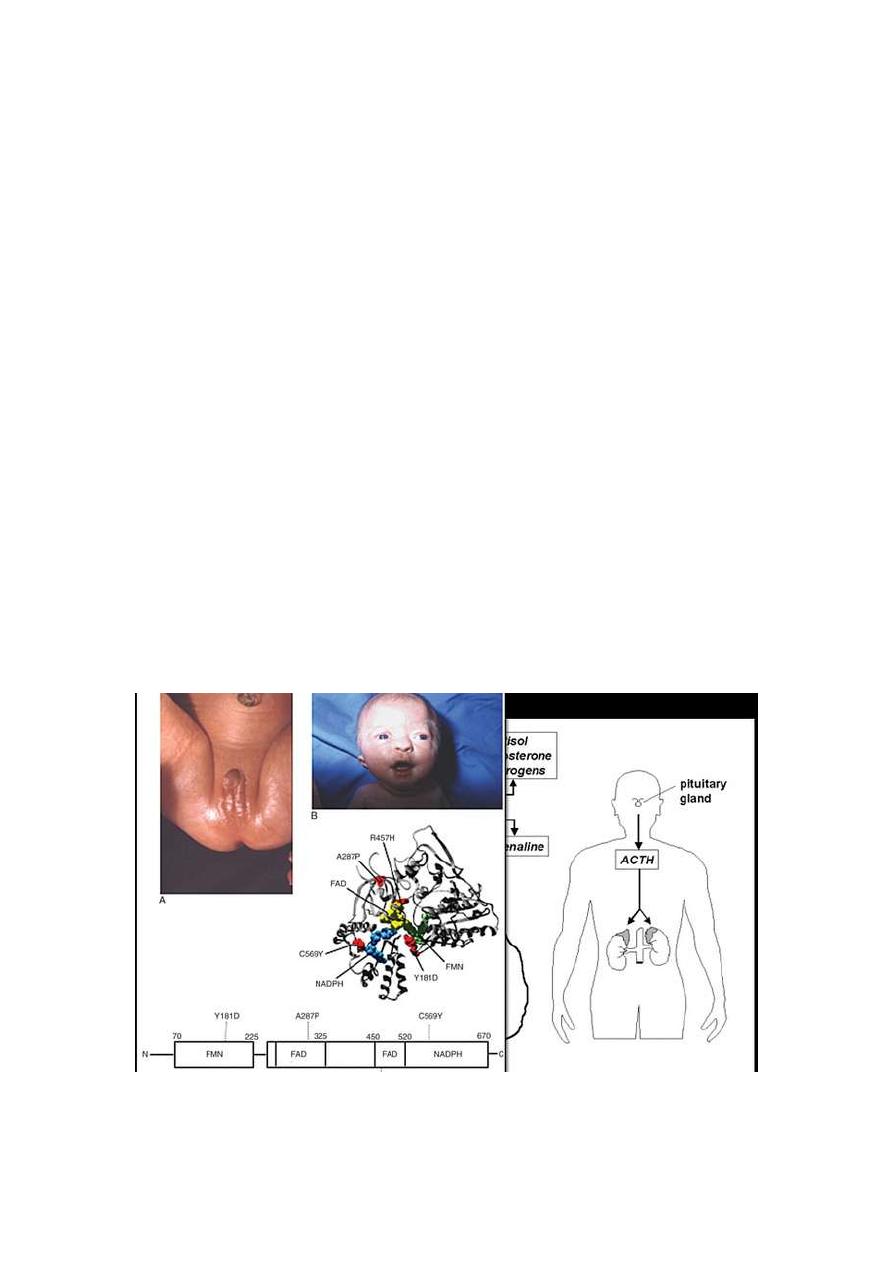
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
.it is due to an enzyme deficiency in the corticosteroid
production pathway in the adrenal gland with over 90%being
deficiency in 21-hydroxylase ,which convert progesterone to
deoxycorticosterone ,and 17-hydroxyprogestrone to
deoxycortisol
.adrenal hyperplasia as response to reduce level of cortisol
. increase progesterone production, this lead to increase
androgen precursor and then elevated testosterone.
. raised androgen levels in female fetus will lead to virilization
of external genitalia: the clitoris is enlarged and the labia are
fused and scrotal in appearance ,the upper vagina join to the
urethra and open as one common channel onto perineum
. two third of children with 21 OH CAH will have salt losing
variety ,which also affect the ability to produce aldosterone
which is life threatening condition
.life long steroid replacement such as hydrocortisone along
with fludrocortisone for salt loser
.surgical correction of external genitalia (feminizing genital
surgery

Q1 a mother bring her 15
th
year old daughter complaining of
primary amenorrhea .past medical history negative apart from
inflammatory bowel disease and on examination short stature
with micrognathia
.what is the professional diagnosis
.what are other clinical features that support our diagnosis
.how do you investigate this patient
.
.Is surgery help this girl
. A worried mother ask you about the future of her daughter
regarding menstruation and possibility of marriage and
pregnancy
Q2 you are obstetrician on call
30 year old female with negative past medical history gave
birth to a baby with ambiguous genitalia
.the female was surprised and become depressed so decide to
go home and and come back later for investigation .Do you
agree ?
.how to investigate the fetus
.give three possible differential diagnosis to this infant

.
