Infectious Arthritis
Bacterial Arthritis
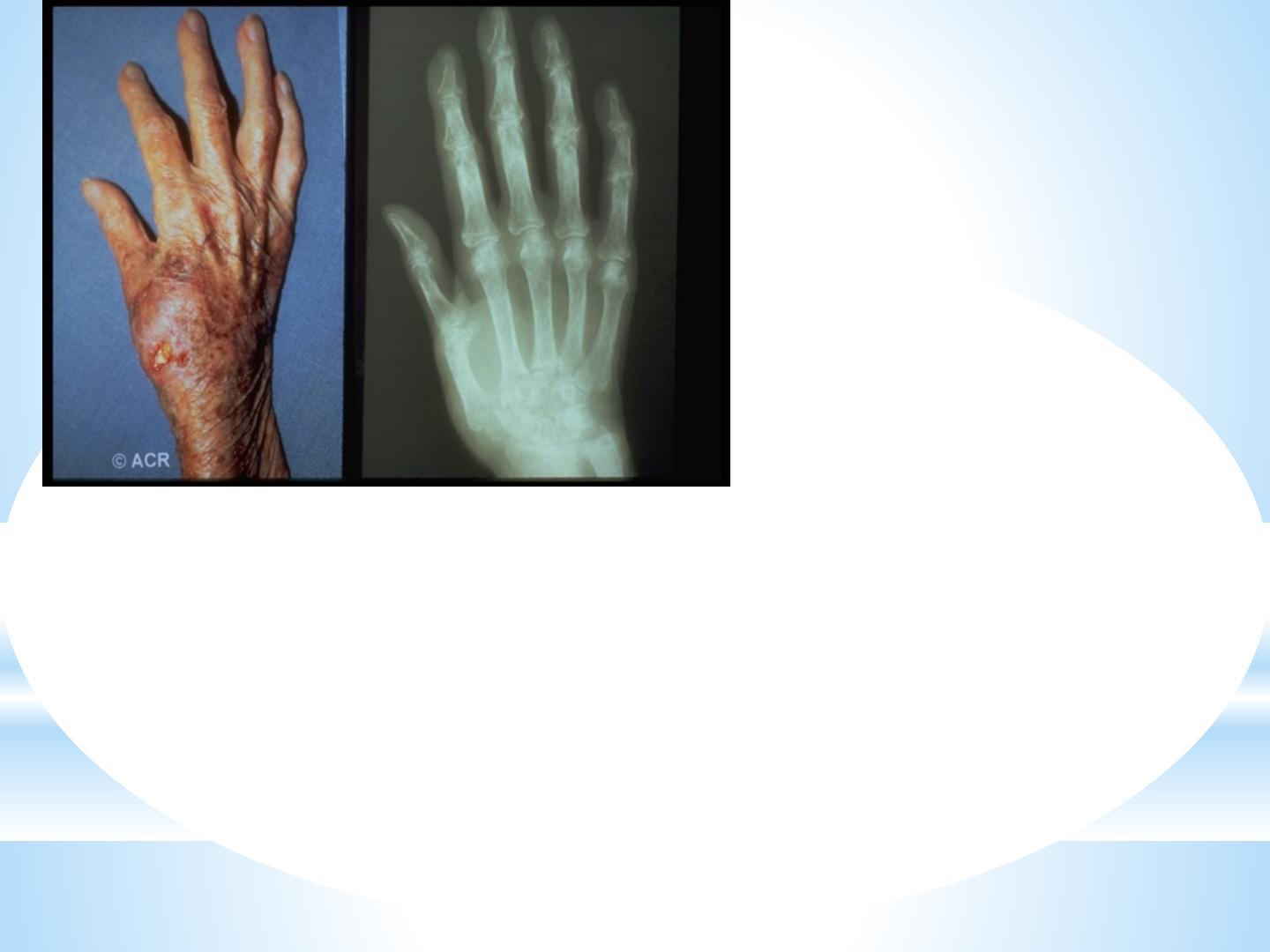
Non gonococcal septic arthritis: It is considered as medical emergency,
because it is most rapidly progressive, destructive joint disease, if not
treated rapidly, it will carry high morbidity and even significant rate of
mortality.

Routs of spread:
1- Haematogenous. Most common.
2- Penetrating wounds, Intra-articular
injec., post surgery in and around
the joint.
3- adjacent infected wound or adjacent
osteomeylitis.

Risk Factors:
•
Old aged people.
•
Already abnormal joints for e.g. joints
affected by RA.
•
Prosthetic joint.
•
DM.
•
Immuno-suppressed state {either to therapy
or to disease itself} .
•
Transplanted organs.
•
Haemodialysis.
•
I.V. drugs abusers.
Microbiology:
•
Staph. Aureus (adults, especially with
RA,DM).
•
G-ve bacilli, strep. Group B,C,G (elderly, drug
abusers).
•
Staph. Aureus, H. influnzae in children.
•
Staph. Aureus, G-ve bacilli, group B strep. Are
common pathogens in neonate and infants.
Clinical Features:
•
mono-articular in 80-90% .
•
patient with pre-existing arthritis, involvement
of more than one joint, is not uncommon.
•
tendency is to affect large joint, especially the
knee and hip joint.
•
The patient is feverish, the infected joint, is
swollen, hot and tender, with rest pain and
pain with movement.
•
the skin overlying is red, and the joint is held
in loose pack position.
Lab Investigation:
Joint aspiration:
•
Joint aspiration is a must whenever septic
arthritis is suspected. Synovial fluid should be
send for bacteriological study., synovial fluid
of infected joint looks, purulent, turbid or
blood stained. With high cell counts
sometimes up to 100000/mm
2
, predominantly
polymorphinuclear cell up to 90%..
•

Gram stain of infected fluid is +ve in more than
50%.
Synovial fluid culture is +ve in around 90% of
cases of septic arthritis.
Blood culture is +ve in about half cases of
patients with septic arthritis

*
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), It is
useful in detecting bacterial DNA in joint,
especially when it unable to do the culture or
in false -ve culture .
*
Although ESR , CRP , peripheral leukocytosis,
fever are raised in most of cases, it could be
minimal or even absent in elderly or immune
compromised patient or early in the disease
course.

*
Treatment:
*
- Patient should be hospitalized.
*
- In suspected septic arthritis, samples of synovial fluid and
blood should be obtained and sent for microbiological studies
[direct gram stain smear and for culture and sensitivity tests].
*
- If gram stain study is non revealing, and no clue is found
after searching for extra-articular as source of
infection, Broad spectrum antibiotic should be started
immediately, covering both staph. and streptococci, usually
flucloxacilline 2 gm I.V. 6 hourly, until identification and
sensitivity to definite antibiotic is available. I.V. anti-microbial
duration is for 2-3 weeks followed by oral treatment to 6
weeks in total, "usually the duration should be continue, till
complete eradication".

If patient is allergic to penicillin, If penicillin-
allergic:
Clindamycin (450–600 mg 4 times daily in
younger patients)
Intravenous vancomycin (1 g twice daily if age >
65 years)
• If high risk of Gram-negative sepsis (recurrent
urinary tract
infection):
Intravenous gentamicin (5 mg/kg once daily) or
vancomycin
(750–1000 mg twice
.

*
Analgesia and immobilization in proper position of
infected joint, during the initial few days, will ensure
pain relief, and patient comfort.
*
The infected joint's space must be drained
adequately .
*
* Most cases require that the infected prosthesis
required removal by orthopedic team.
*
* Physical therapy should be initiated as soon as the
patient can tolerate, regular gentle passive
movement, then an active movement as the condition
is stabilized.

*
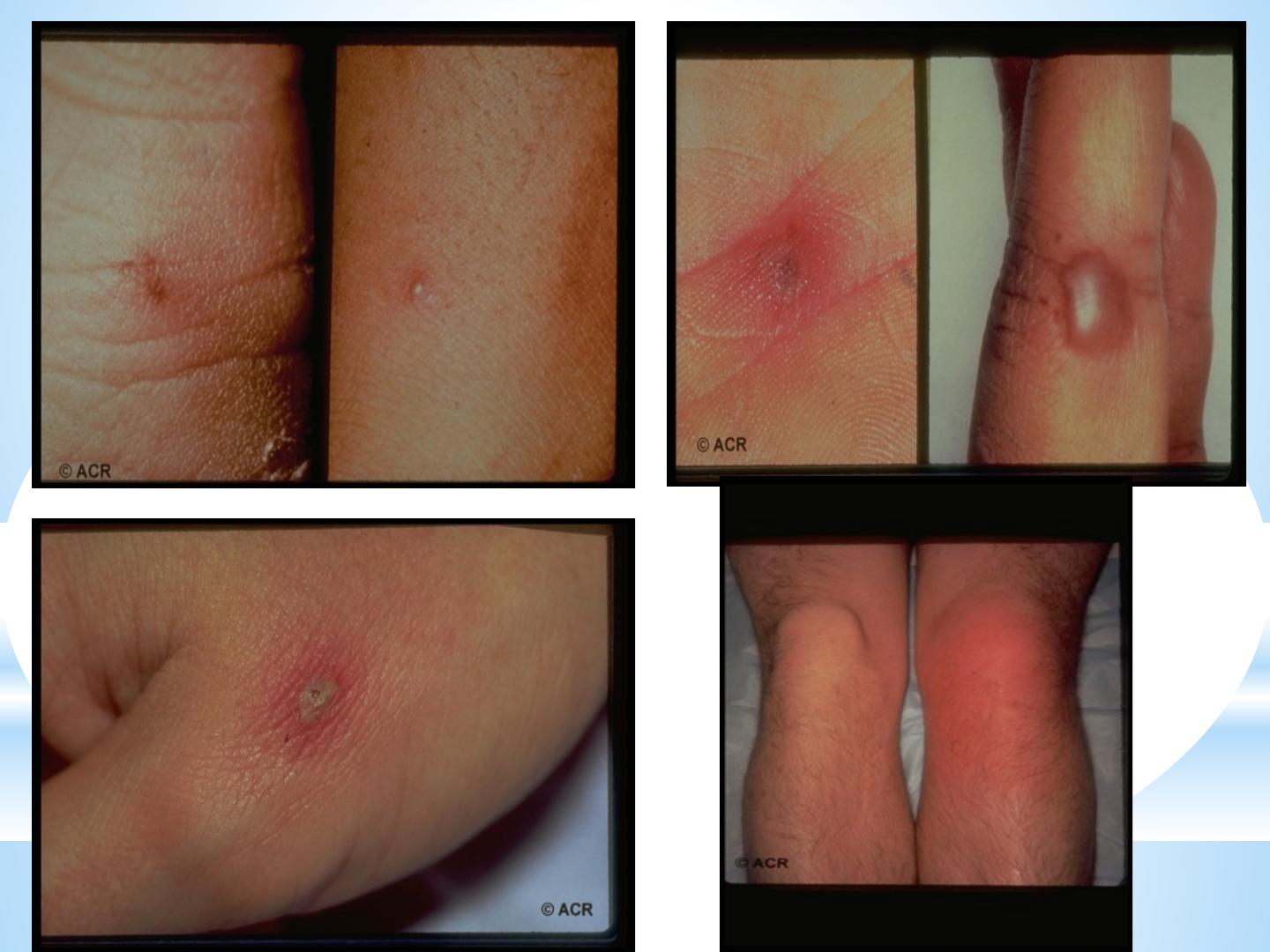
Gonococcal joint infection.
*
occurs in young healthy adult, women appear to be more susceptible to
disseminated gonococcal infection.
*
Disseminated gonococcal infection occurs in bout 3% of untreated gonorrhea.
*
*
Patient presented with migratory arthralgia/arthritis, low grade fever,
tenosynovitis with or without painful pustular skin lesions, preceding the mono or
oligo G. septic arthritis. Synovial fluid G-stain usually of -ve result and synovial
fluid culture +ve only in 30% making the importance to obtain a culture from the
genital tract which is +ve in 70-90%, It response very well to prompt antibiotic
treatment, and residual joint damage is unusual.
*
*
Because the resistance to penicillin is on the raise, it is wise to use 3
rd
generation
cephalosporin as initial treatment for disseminated gonococcal infection.

Viral arthritis. –
Polyarthritis or arthralgia can occur before, during or
after many viral illnesses. Arthritis in most cases it is
due to direct infection of synovial tissue, direct toxic
effect, or by provoking an immunologic reaction that
involve the joints (immune complex deposition)
- The arthritis is usually self-limited, human
parvovirus (mainly B-19) arthropathy is the most
common, Diagnosis is confirmed by arise in specific IgM.
.

Polyarthritis may follow hepatitis B, C, HIV, rubella, rubella
vaccine, mumps, infectious mononucleosis and chicken pox.
- In hepatitis B infection, sudden immune complex mediated
symmetrical polyarticular arthritis of small joints of the hands
occur in approximately 1/3 of the patients, often in prodromal
phase and mostly resolving before the onset of jaundice.
- Many patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report
persistent arthralgia or arthritis especially in the presence of
type II mixed cryoglobulinaemea. Raynaud’s phenomena,
Vasculitis, Sicca syndrome, Myalgia and Fibromyalgia can be a
manifestation. So screening for hepatitis C is essential for DDX in
undiagnosed rheumatic complaint

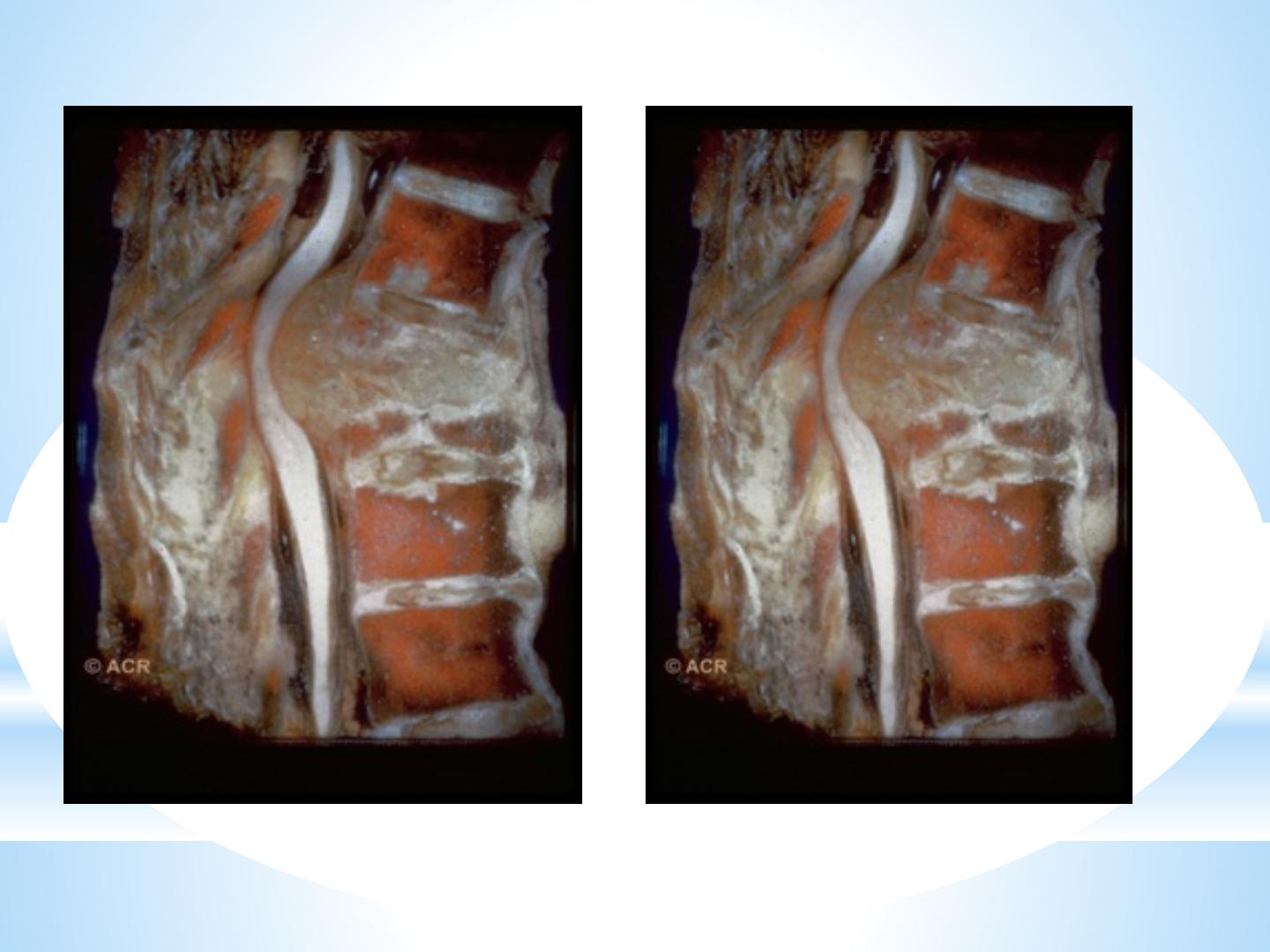
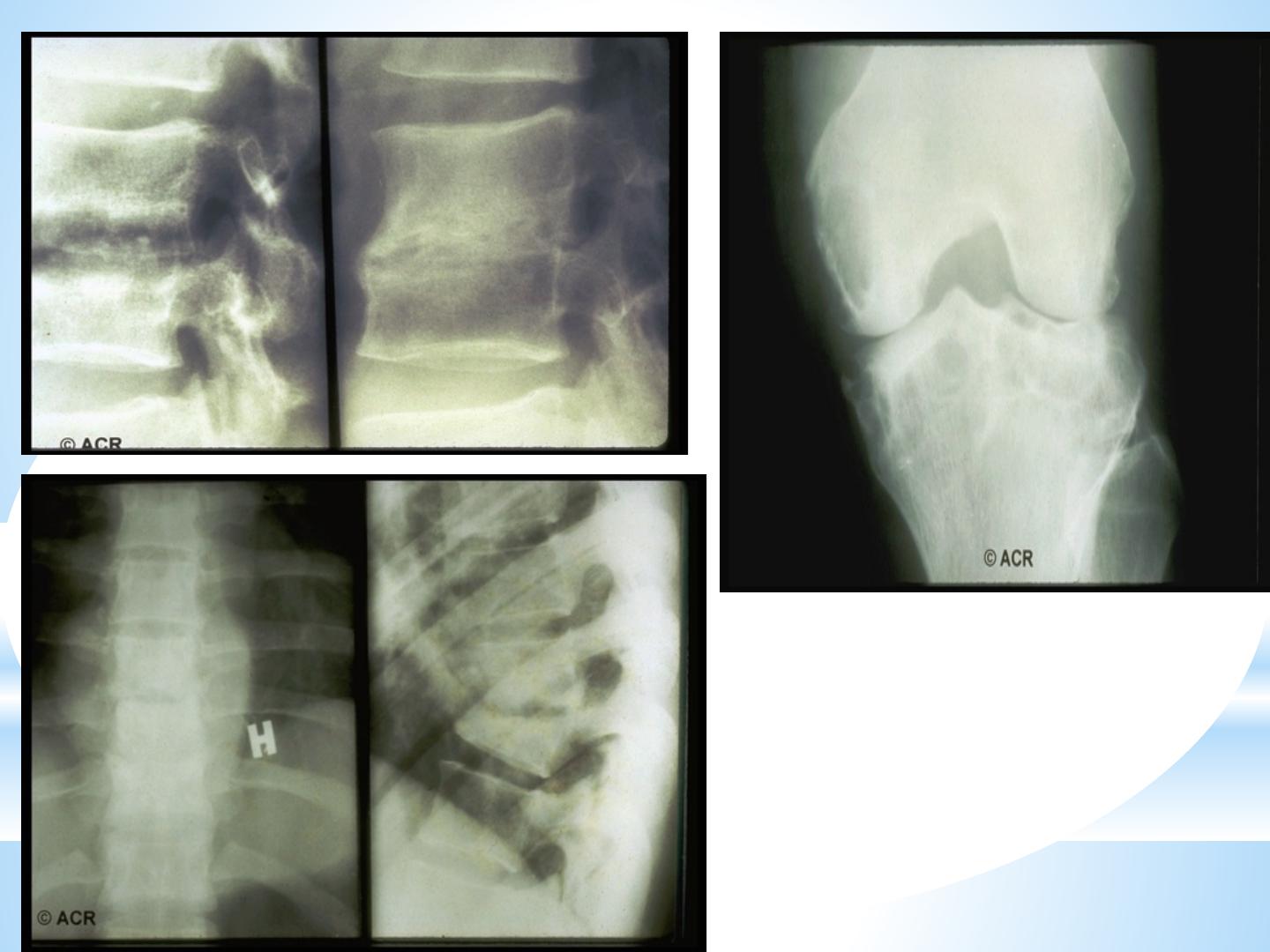
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis usually targeting the spine (Pott’s
disease) or large joints such as the hip, knee or
ankle.
Patient with TB arthritis usually present with
insidious, chronic, mildly inflammatory
monoarthritis with pain, swelling, fever eventual
deformity, often over several years.
Some patients develop a reactive poly-arthritis
(Poncet’s disease).

Plain x-ray findings non-specific .
and the organism (mycobacteria) are seldom to be shown in
synovial fluid. diagnosis is confirmed by culture of synovial fluid,
synovial tissue, bone biopsy, histopathological study and PCR
Treatment similar to pulmonary TB .some cases, surgical
intervention may be required( debridement or joint replacement)
In spinal involvement may require surgical stabilisation and
decompression
.