
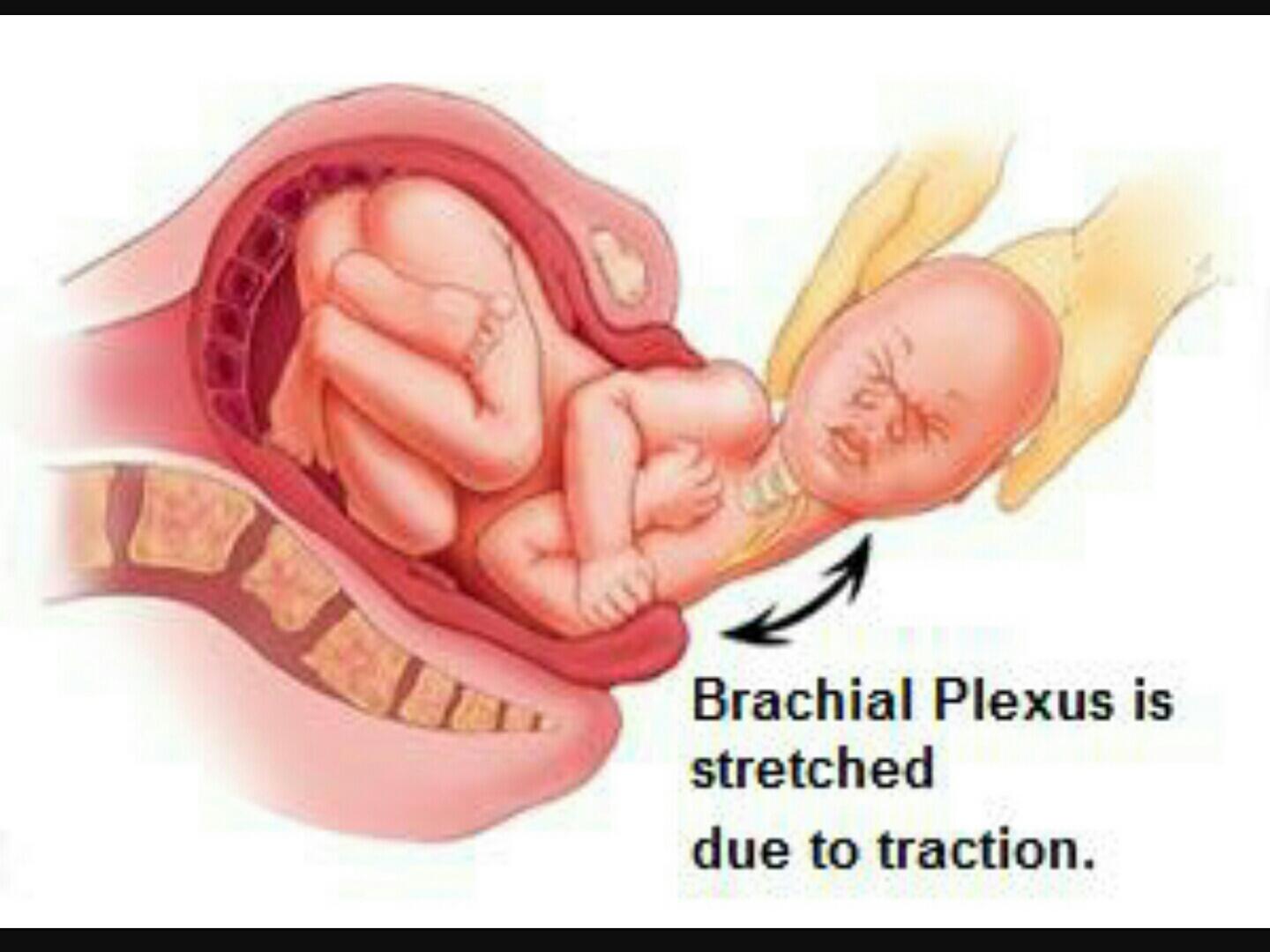
BIRTH INJURIES
Definition:
an impairment of infant’s body or structure
due to adverse influences which occurred at birth.
Larger babies are more liable.
Most cases are self-limited.
Risk factors:
1. Primi-parity.
2. Small maternal stature.
3. Prolonged or rapid labor.
4. Oligohydramnios.
5. Macrosomia.

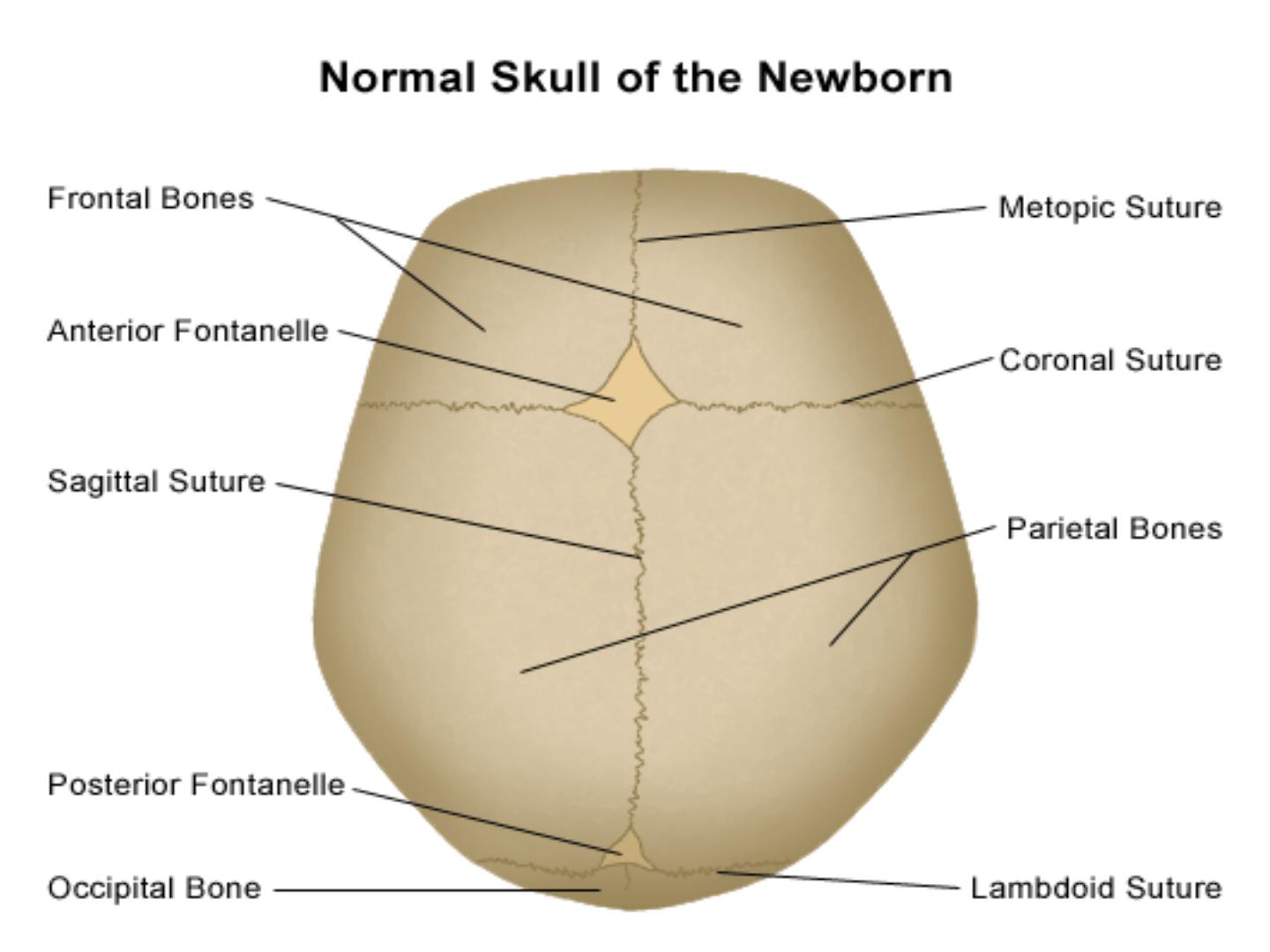
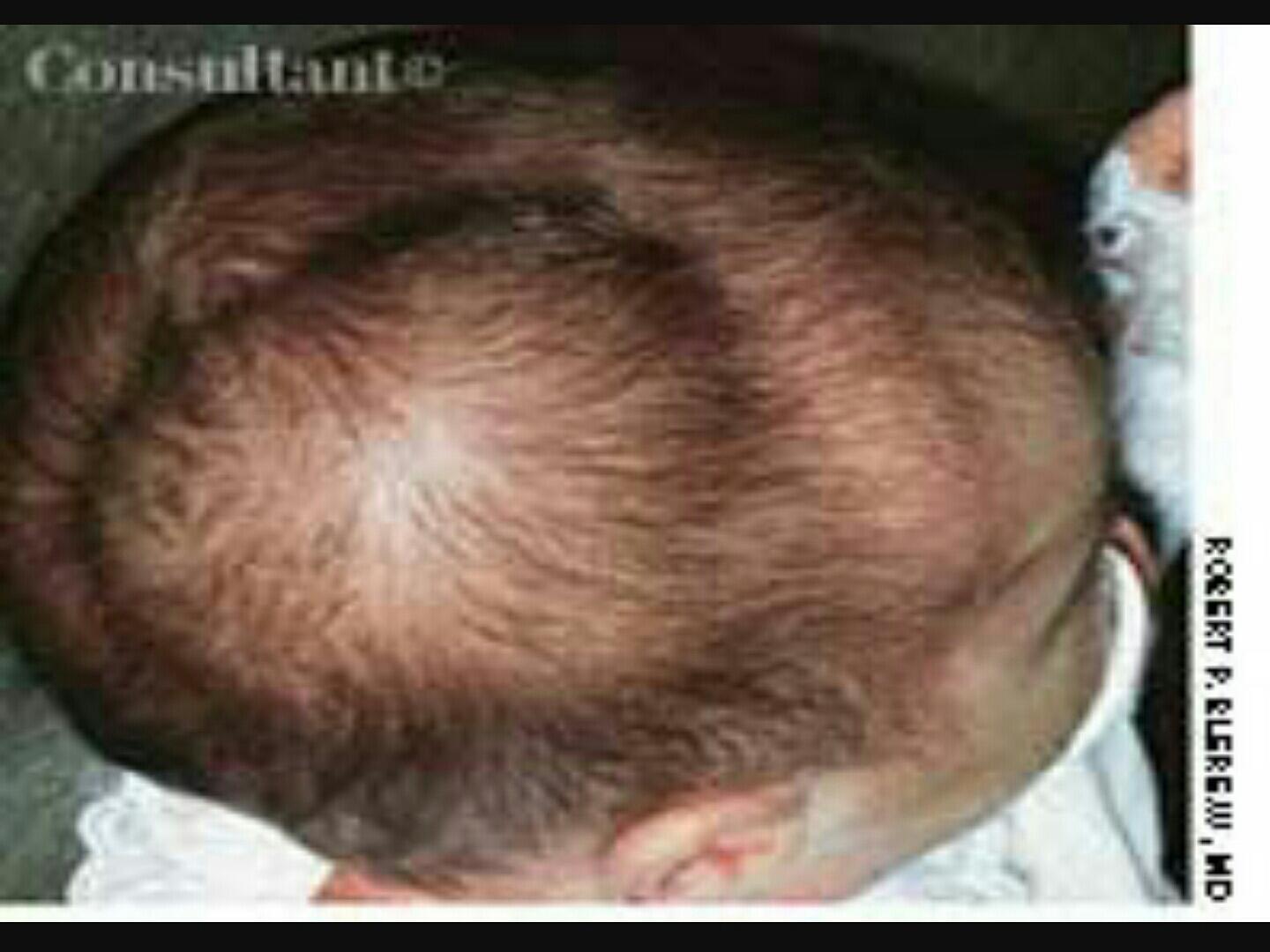
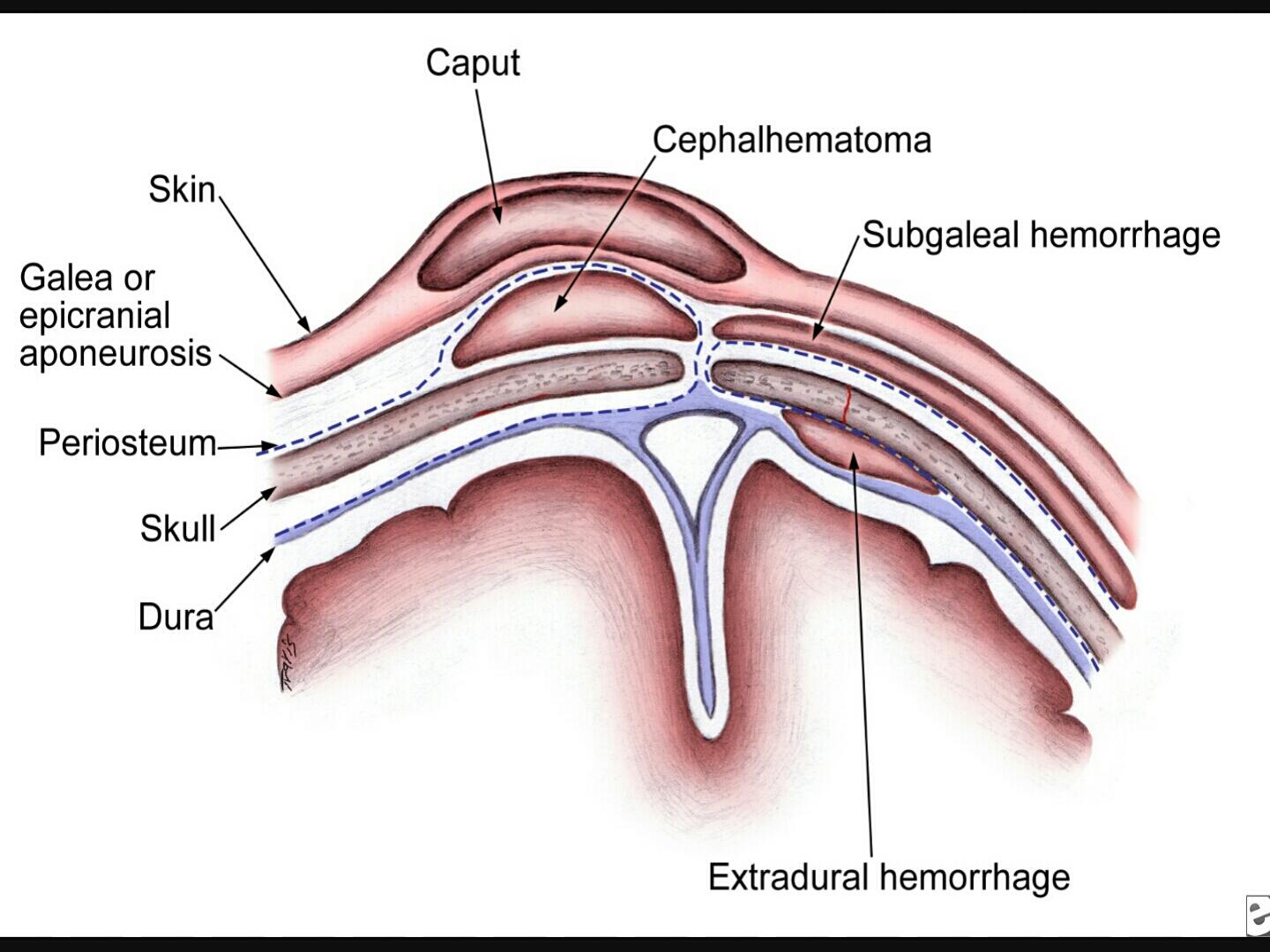
CEPHALHEMATOMA:
-Sub-periosteal hemorrhage.
-Common site is the parietal bones.
-It is limited by the suture lines.
-It may cause anemia and jaundice.
-Linear skull fractures may underlie
cephalhematoma (<20%).
-Resolution occurs over weeks ending with
calcification.
-NO TREATMENT.
-Aspiration should NEVER be done.
-Brain CT scan done if neurological manifestations
are present.
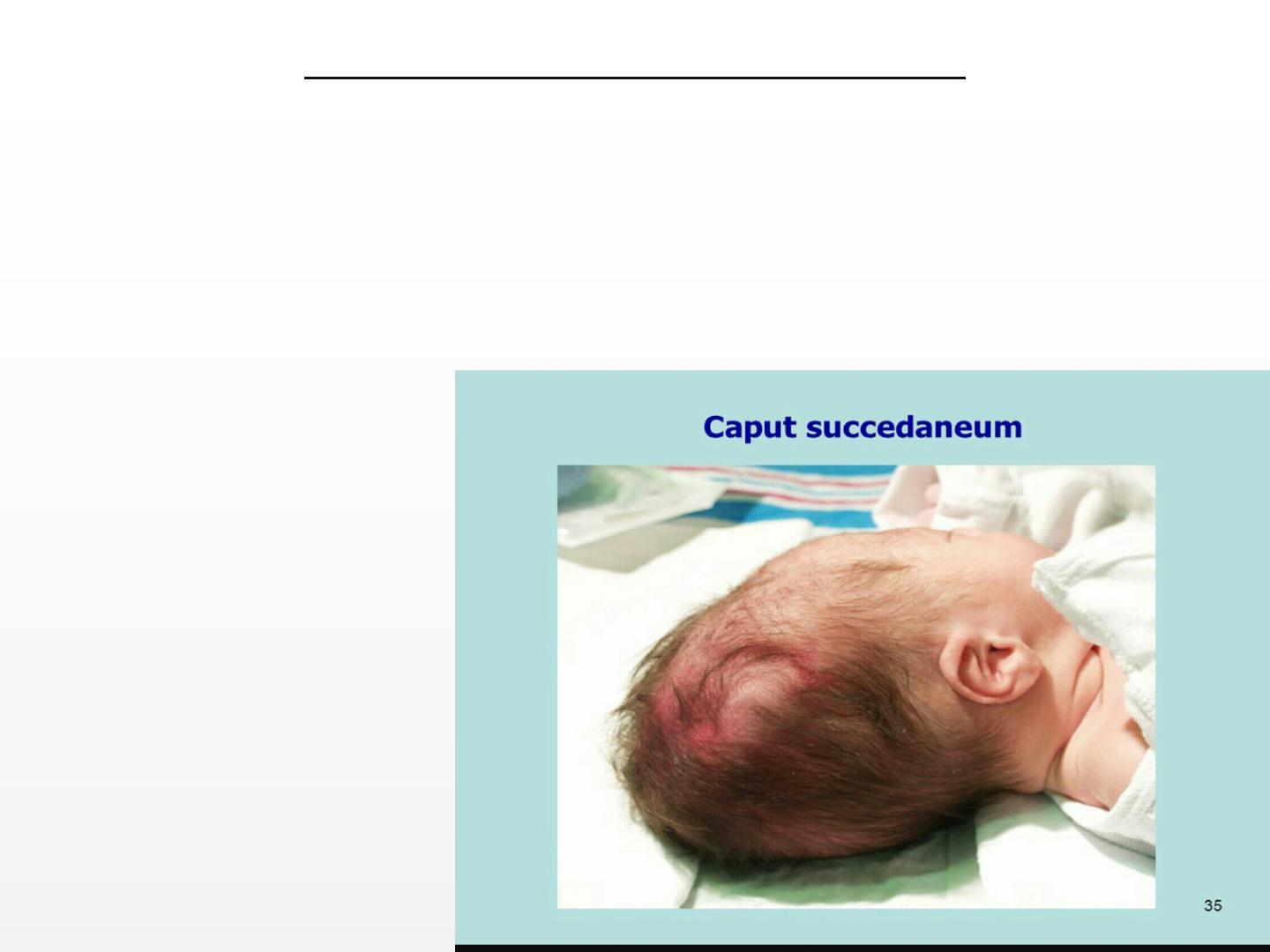
CAPUT
SUCCIDINUM
:
-Subcutaneous collection of fluid.
-Poorly defined margins.
-Crosses the midline and sutures.
-Resolves spontaneously.
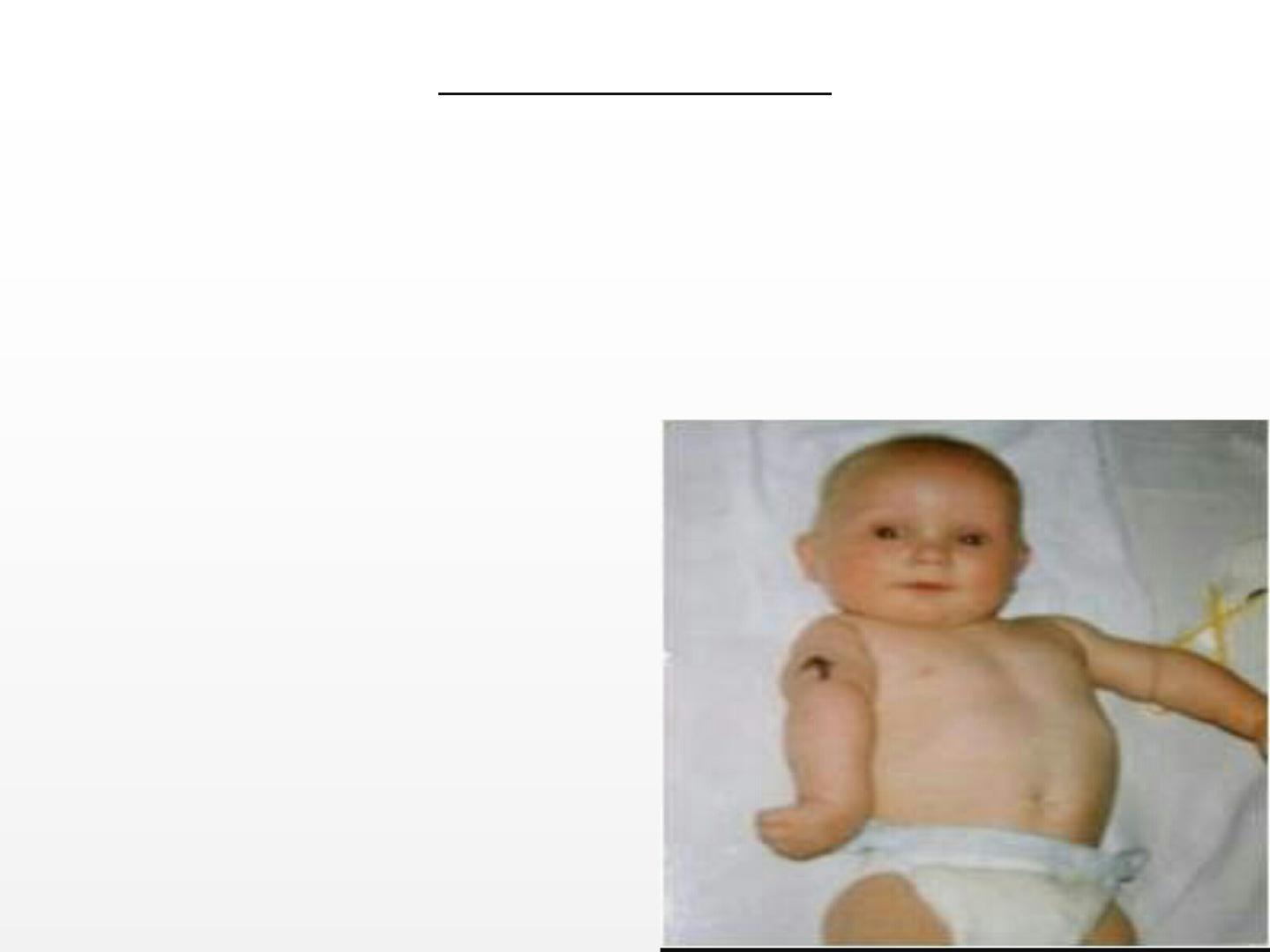
ERBS PALSY:
-
I
t involves C5,C6 nerve roots.
-The limb is held limply on the side of the body with
the forearm pronated (waiter tip position).
-Grasp reflex is present.
-Recovery >80% .
-
Physical therapy should
be started by 7-10 days.
.
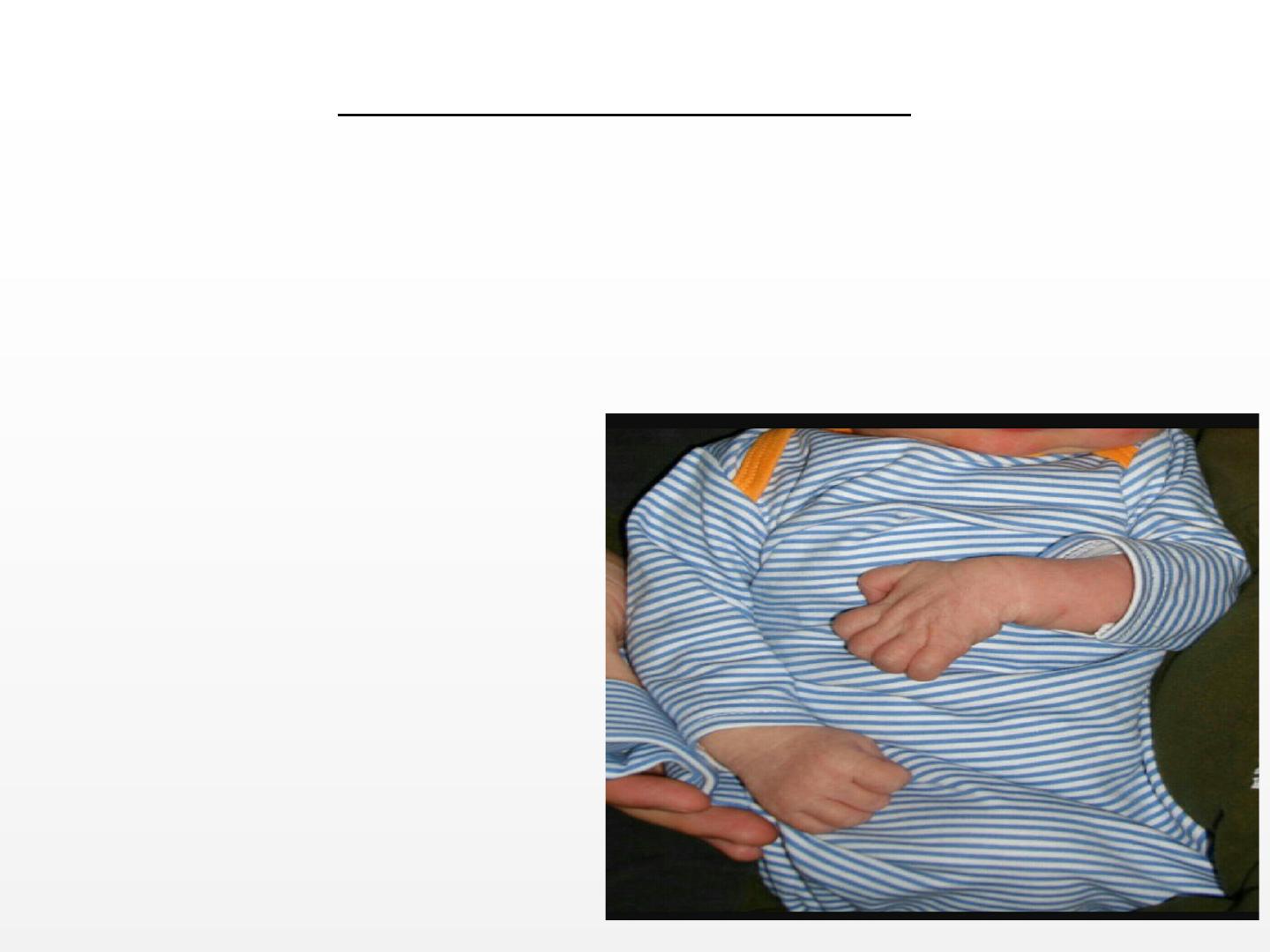
KLUMPKES PALSY:
-C7,C8,T1 are involved.
-The small muscles of the hand and wrist are affected.
-Loss of sweating and sensation may also be seen.
-Grasp reflex is absent.
-Bad prognosis.
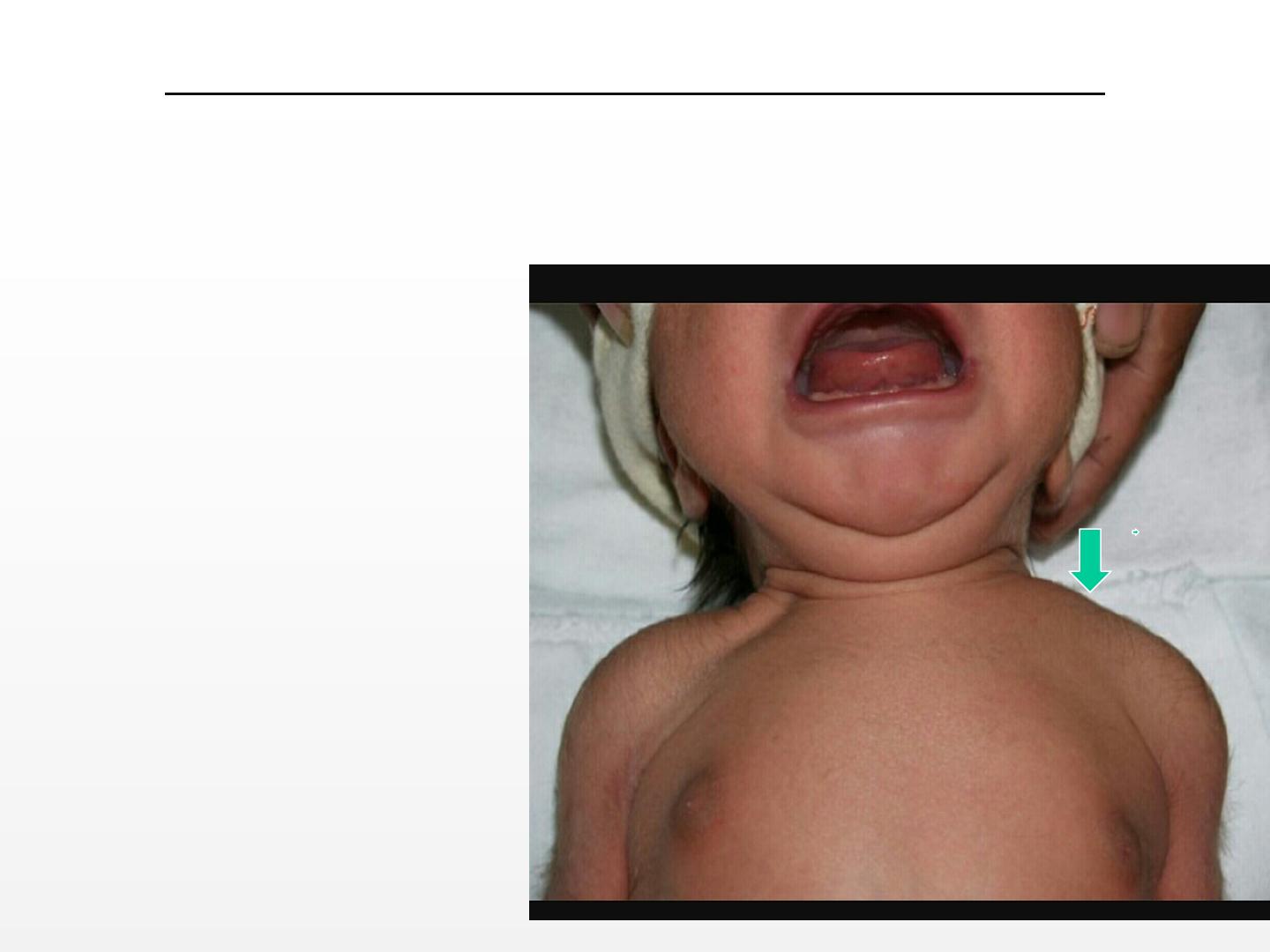
FRACTURE OF THE CLAVICLE:
-Most common bone injury.
-Asymptomatic, or features of fracture, or pseudo-paralysis.
-A callus at 7-10 days.
-Treatment: Analgesics,
Pinn the sleeve to
the shirt of infant.
-Complete recovery is
expected.
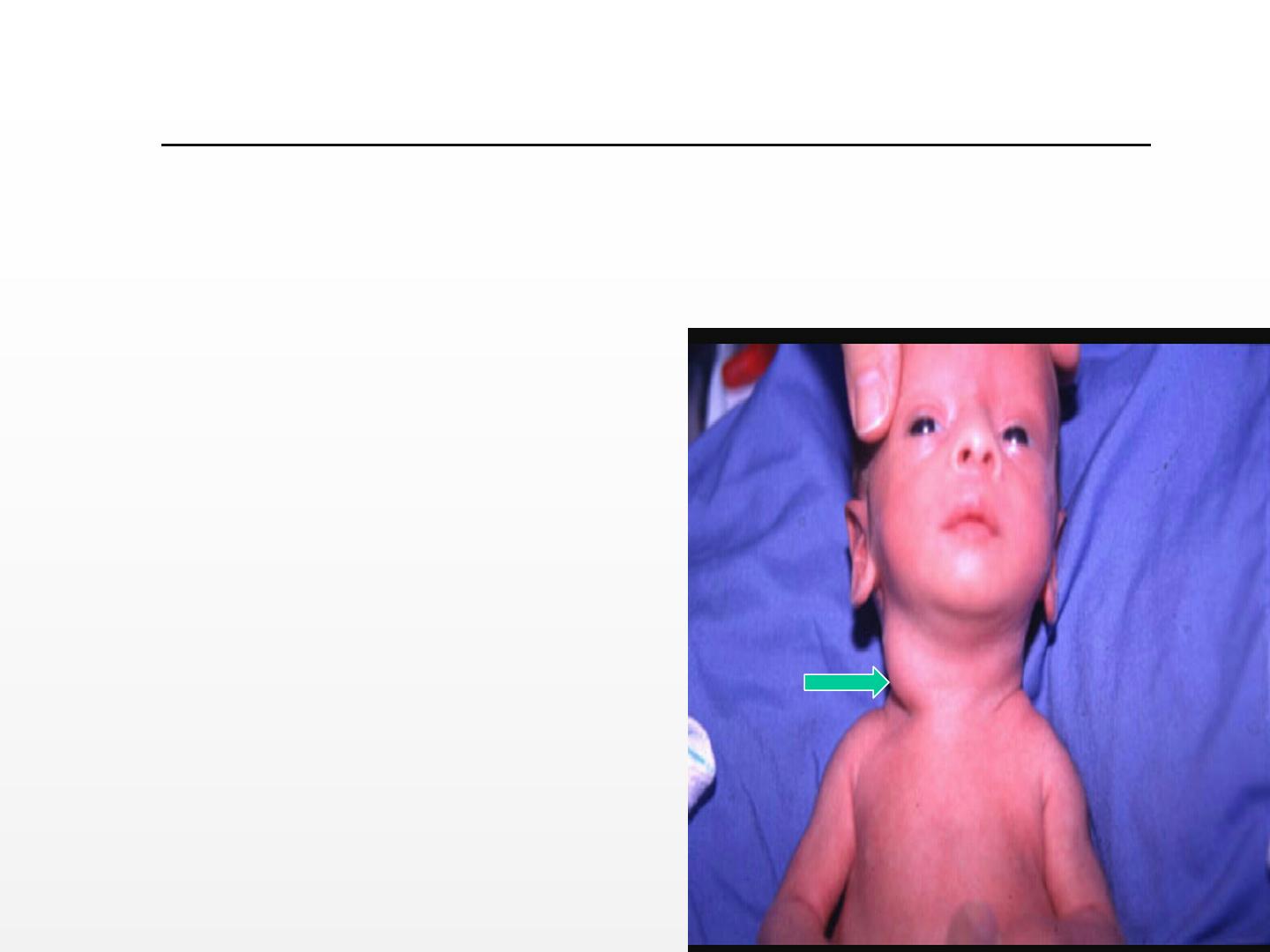
• STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID TUMOR (MASS):
- 1-2 cm mass.
-Appears at 2-3 weeks.
-Usually unilateral.
-80% recover in 3-4 months
by physiotherapy.
-Plastic surgery is needed
if it persists for>6months.

RUPTURED ORGANS:
e.g. liver, spleen, and adrenal glands.
All are seen due to pressure on these organs during
delivery, commonly in breech presentation &
large babies.
ADRENAL HEMORRHAGE:
It is common in I.D.M. It presents as:
-Shock.
-Abdominal mass.
-Cyanosis.
Treatment: supportive, surgical repair, treatment of adrenal
failure.
:
