under watercaele chest tube
Contraindications of chest tube
• Risk of hemorrhage: where possible, any
coagulopathy or platelet defect should be
corrected.
• The differential diagnosis between a
pneumothorax and bullous disease is important.
• Lung densely adherent to the chest wall is an
absolute contraindication to chest drain
insertion.
diaphragmatic hernia
Indication of chest tube :-
1- draining of air /fluid/puss/blood…..
2- postoperatively
3- for pleurodesis (drug Therapy ).
4-pneumothorax, hemo thorax, post thoracotomy
Name of this investigation..??
Coronary angiography.
3 causes of unilateral Leg swelling ..???
1- DVT
2-lymphodema.
3- cellulitis.
Dx ?? Management ??
Dx:- Truncal varicose vein of the leg
Mx :- surgery
Differential Diagnosis …???
1- bronchogenic carcinoma.
2- hydatid cyst .
3- lung abcsess.
Spot Dx ….
Water lily sign of a ruptured Hydatid cyst.
Differential diagnosis ??
1- chronic limb ischemic ulcer .
2- diabetic foot.
3- gangrene
Diagnoses ??
Type of surgical managements ??
Dx :- H. cyst of the lung
Surgery :; removal of the cyst & edge suturing
(marsupialization )
Diagnosis ..?? Classification ..??
Dx: arterial aneurysm
Classification ::--
According to wall : true / false
According to shape : fusiform / saccular
According to cause : atherogenic /traumatic /
infection ….
Spot Dx…? Classify CHD…?
Dx :-TOF .
Classification of congenital heart disease ::-
Cyanotic / A cyanotic
A 25 year man sustained RTA & pelvic injury
1-what is this finding?
2-What is the diagnosis?
1- bleeding per urethra
2- urethral injury.
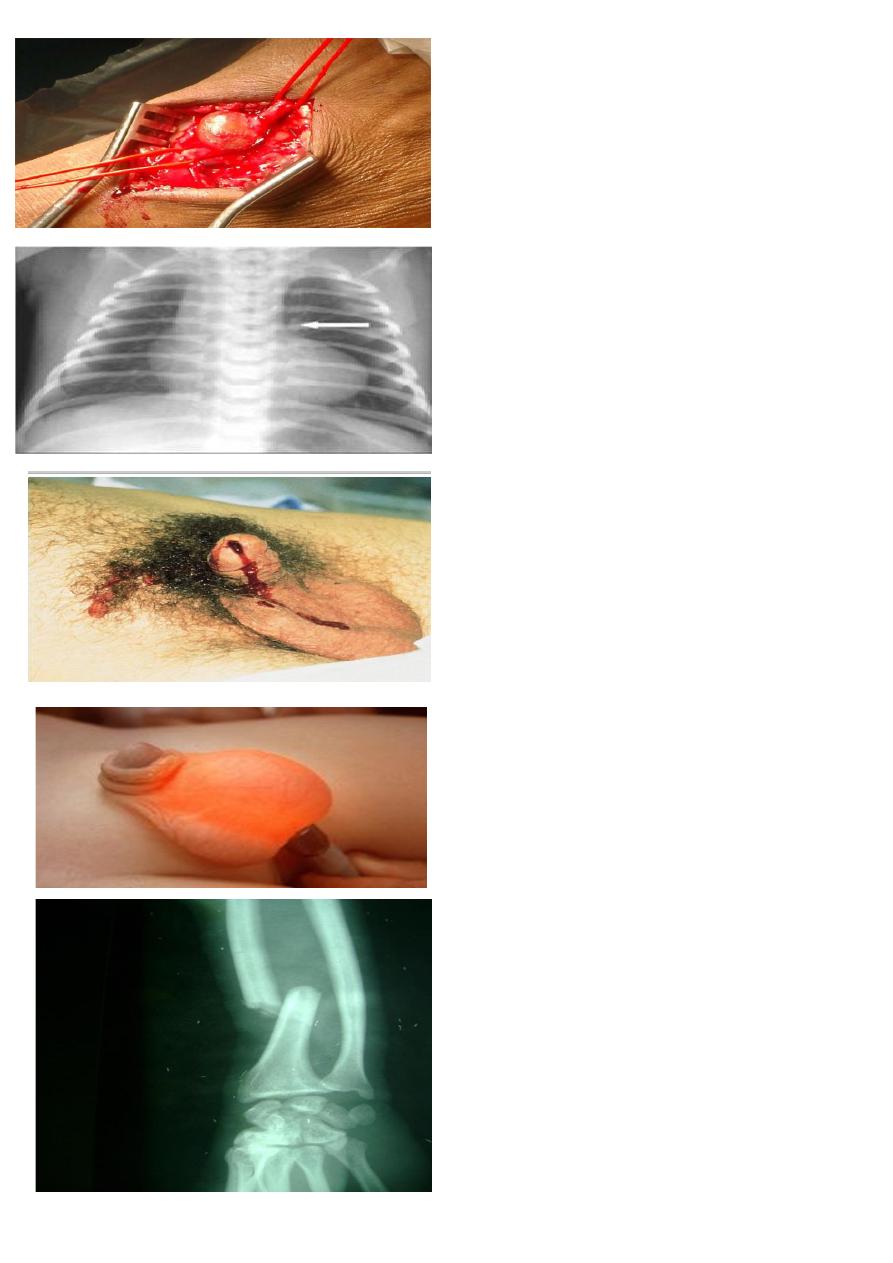
A case of 1 year child having this lesion :
1- What is this test?
2- what is the diagnosis?
1- translumination test
2- hydrocele
A 30 Years old man presented with pain and
deformity in forearm following fall on ground
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- what is the best method of treatment?
1-galliazi fracture dislocation
2- internal fixation
1- what is clinical test? What to confirm or exclude ?
2- what is this method of treatment?
1-ortolani and Barlow's test ,,, DDH
2-pelvic harness splint.
1-what is the radiological diagnosis?
2- what structure in danger in this injury?
1- Supracondylar fracture
2-brachial artery
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- best time for surgery?
1-hypospedues
2-before school age
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- what is the whitish structure?
1-Rt inguinal hernia
2-vas deference.
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- mention two complications of such condition.
1-Thryoglossal cyst
2-infection, fistula
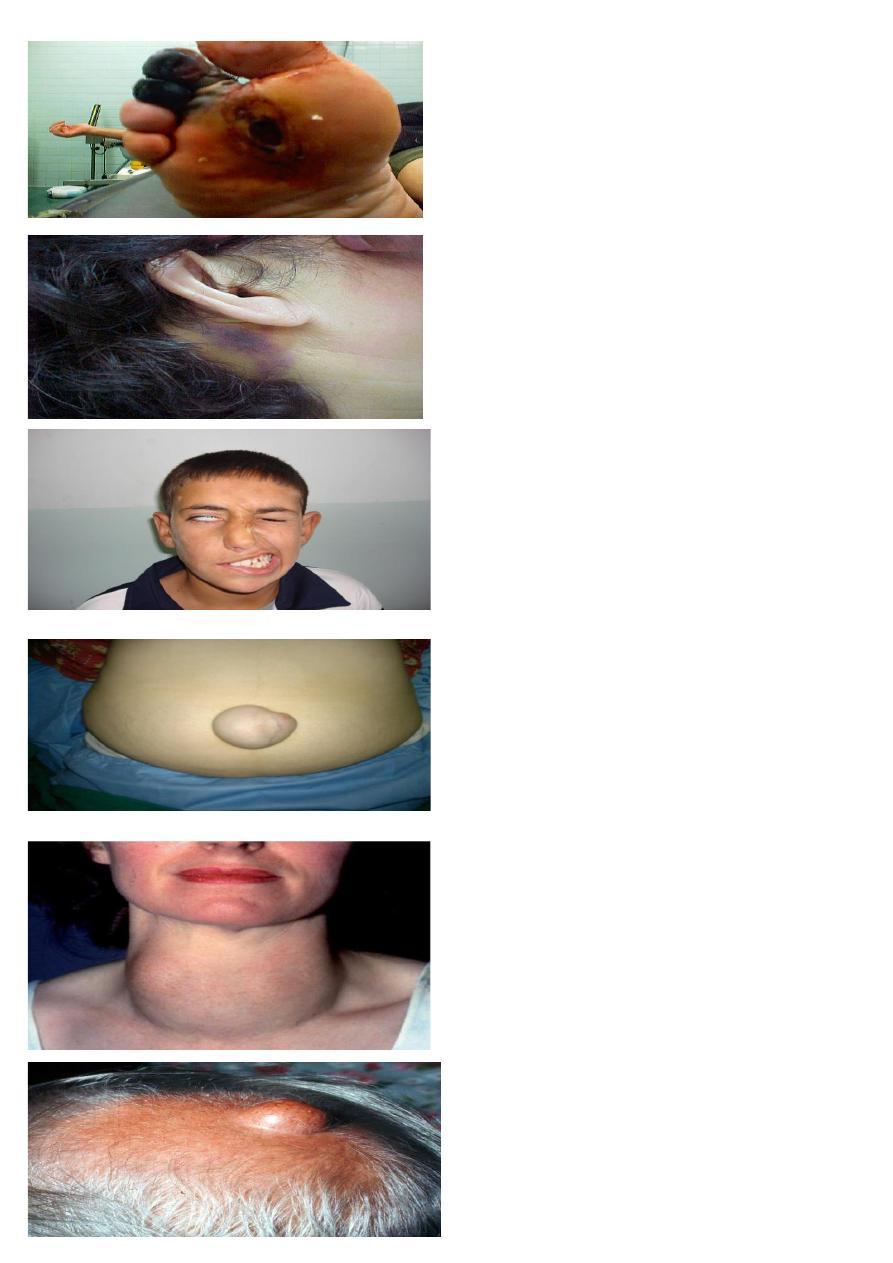
1- describe the lesion at second and third toys.
2- what you call this ulcer?
1-black discoloration of second and third toe
2-neuropathic ulcer
A young female sustained RTA
1- What does this sign called?
2- What is the underling problem?
1-battile sign
2- med cranial fossa bleeding
1- what nerve is injured in this patient?
2- What is the skin sensation loss in such
condition? ENUMRATE 3 SYMPTOM .
1-Rt facial nerve
2-no ,,, loss of taste, hyperacusis, decrease of
salivation and tears secretion
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- what is the dangerous complication?
1-umbilical hernia
2-strangulation
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- Enumerate two local complications.
1-multi nodular goiter
2-dyspnoea, dysphagia, SVC obstruction
1- Spot diagnosis
2- Enumerate two regions in the body that such
lesion cannot occur.
1-sabecous cyst
2-palm, sole.
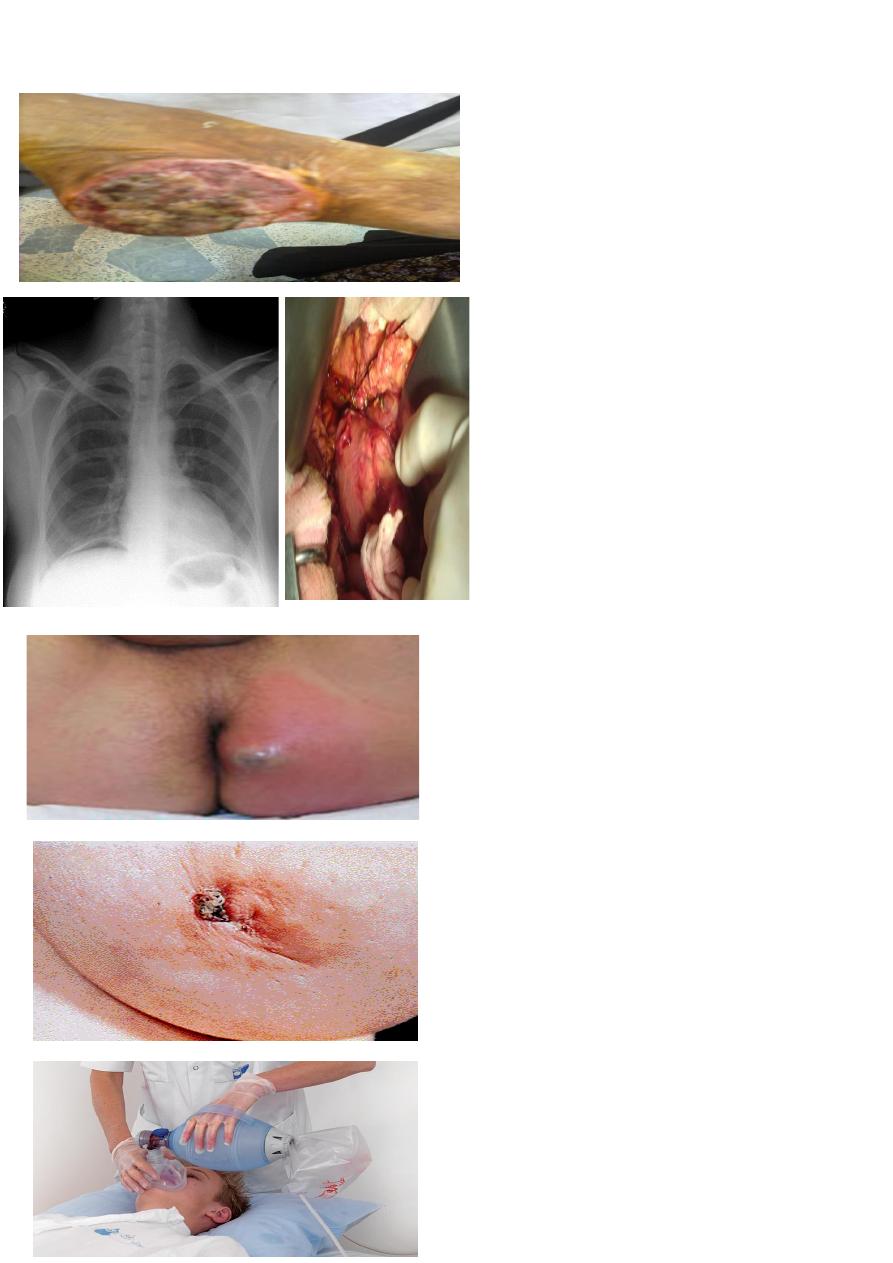
A Lady with her heel burned before 20 years.
1- What does this ulcer called?
2- What is the treatment?
1-margolin ulcer
2-below knee amputation
1- what does the x ray show?
2- what is the cause?
1-air under diaphragm
2-perforated duodenal ulcer
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- what is the best treatment?
3-What complication could happened later?
1-lt ischiorectal abscess
2- surgical drainage
3- Fistula formation
1- What are the changes seen at the nipple?
2- Give two deferential diagnosis?
1-niple distraction
2- paget disease, eczema
1- Mention the name of this equipment.
2- Mention the indication of use.
1-ambu bag
2-vintelation and oxygenation
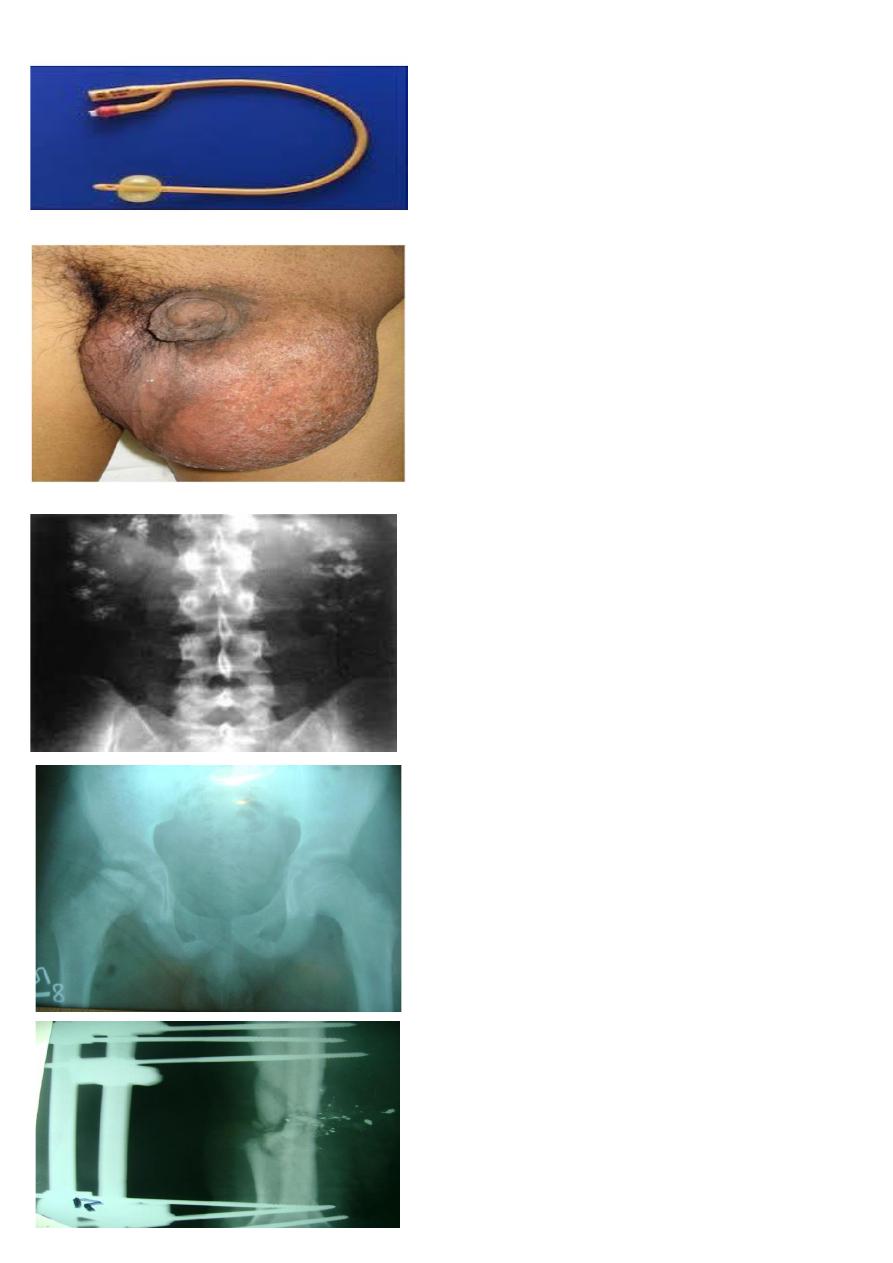
1- What is this equipment?
What is the benefit
of the balloon
2- Give 2 therapeutic uses.
3- GIVE 2 complication .
A- FOLYES CATHETER ,
self-retaining
B- RETENSION OF UTINE, COLLECTION OF
URINE. INSTELLATION OF MEDICATION.
c- injury to urethra, obstruction, infection .
1- Give two differential diagnosis?
2- Mention two physical examination you can
use it in such condition.
A- INGUINAL HERNEA, HYDROCELE
B- INVAGENATION TEST. 3 FINGURE
OCLUSION TEST
1- What are the finding in this plane X ray?
2- What endocrine disease can cause such
condition?
A-MULTIPLE BILATERAL RENAL STONES
B- HYPERPARATHYROIDEZEM
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What is the main symptom of such condition?
A-PERTHES DISEASE
B- LIMBING
Patient with bullet injury to his RT leg
1-What is the holding method used.
2-What serious infection might complicate such
injury.
A-EXTERNAL FIXATION
B- GAS GANGEREN
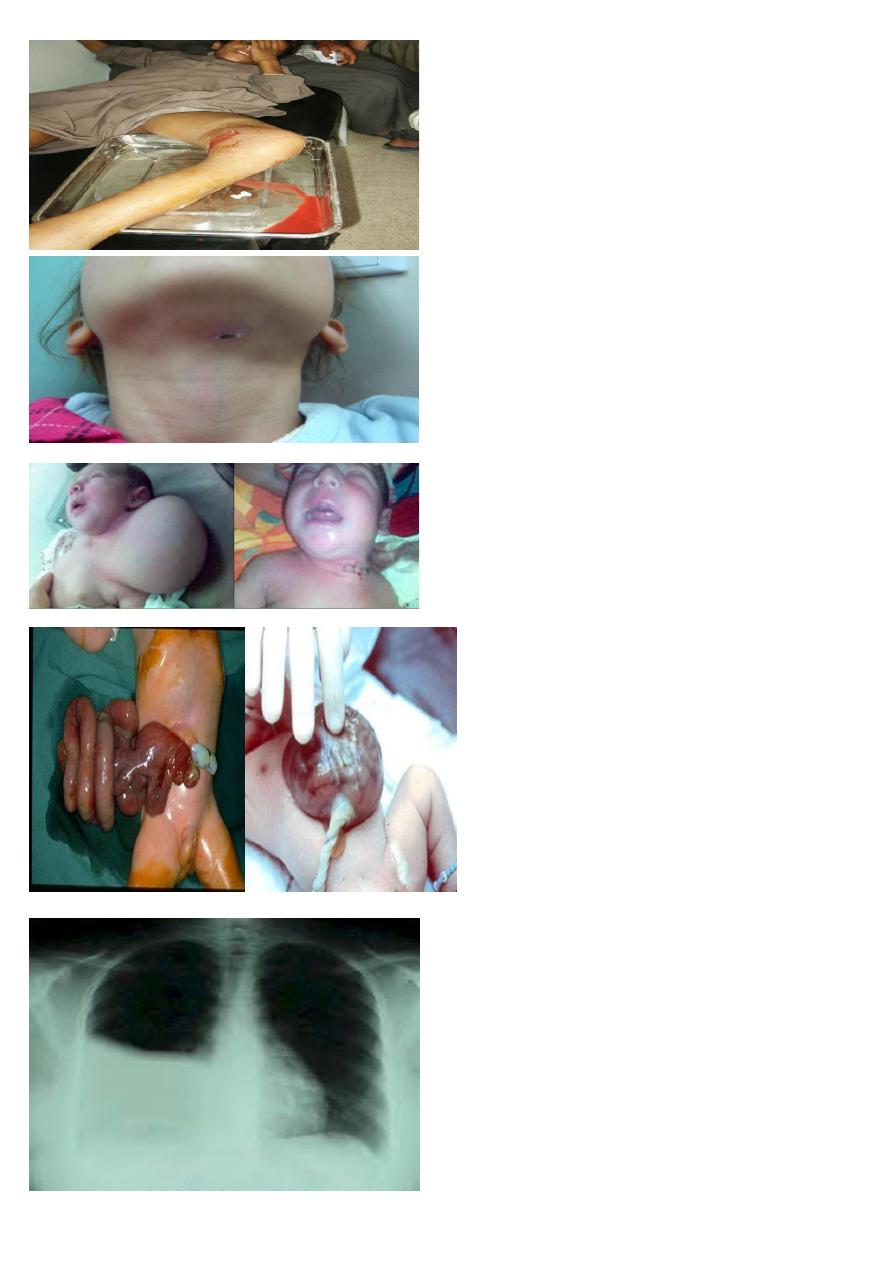
Pain, fever, swelling at lower thigh for 15 days
1- What is the most probable diagnosis?
2- What is the most serious early complication ?
A-KNEE JOINT SEPTIC ARTHRITIS
B- SEPTIC SHOCK
Chronic discharging lesion
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What investigation may help?
A-THYROGLOSSAL FISTULA
B- FISULOGRAPHY
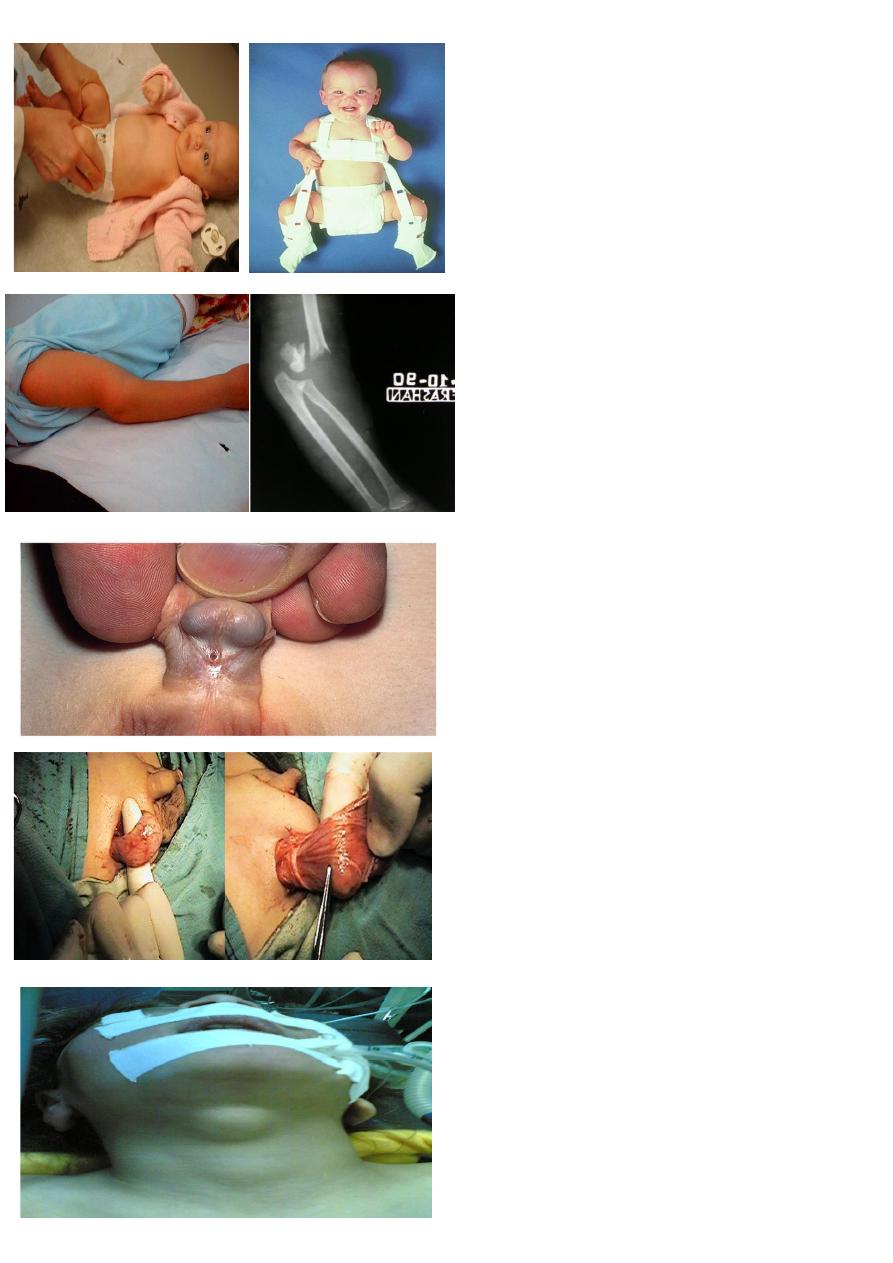
1- Name the disease.
2- What physical examination is pathognomonic
her?
A-CYSTIC HYGROMA
B- Brilliant TRANSLUMENATION TEST
1- What is the anomaly in slide 1
2- What is the anomaly in slide 2
A-GASTROSCISES
B-AMPHALCELE
Stab wound to Rt chest
1-What is the diagnosis?
2-What is the immediate interference?
A-RT HEMOTHORAX
B- CHEST TUBE THORACOSTOMY
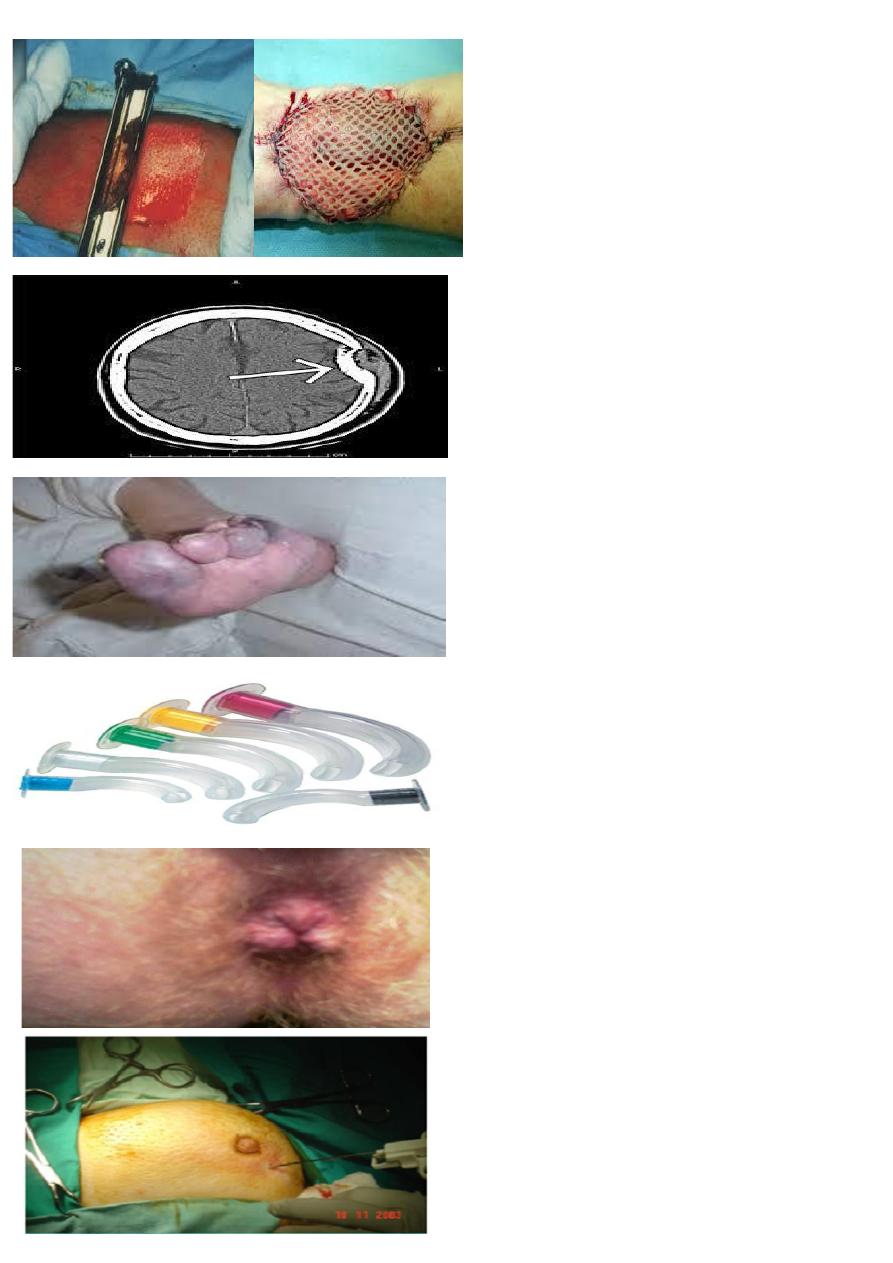
1- What type of graft is this?
2- Enumerate two late complications?
A-PARTIAL THICKNESS SKIN GRAFT
B- CONTRACTURE. HYPOPIGMENTION,
LOSS OF ELASTISITY
1- What is the finding in this CT?
2- By what chart you follow this patient?
A-DEPRESSED FRACTURE
B- GCS
Patient with atrial filtration
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What are the cardinal clinical findings?
A-ACUTE LIMB ISCHAMIA DUE TO EMBOLI
B- PULSLESS, PARASTHESIA, PROGRESSIVE
LOSS OF TEMP, PAIN, PARALYSES
1- Mention the name of this equipment
2- What is the benefit of its use?
A- MOUTH GAG
B- FACELETATE BREATHING IN UNCOSOUS
PATIENT
1- Describe the lesion
2- Enumerate 3 complications for such condition
A-THIRD DEGREE PILE
B-BLEEDING. THROMBOSIS, STRANGULATION
1-What skin changes indicative of breast cancer in
this image?
2- What is the procedure used for biopsy her?
A-PEUDE OARANGE
B-TRUE CUT BIOPSY
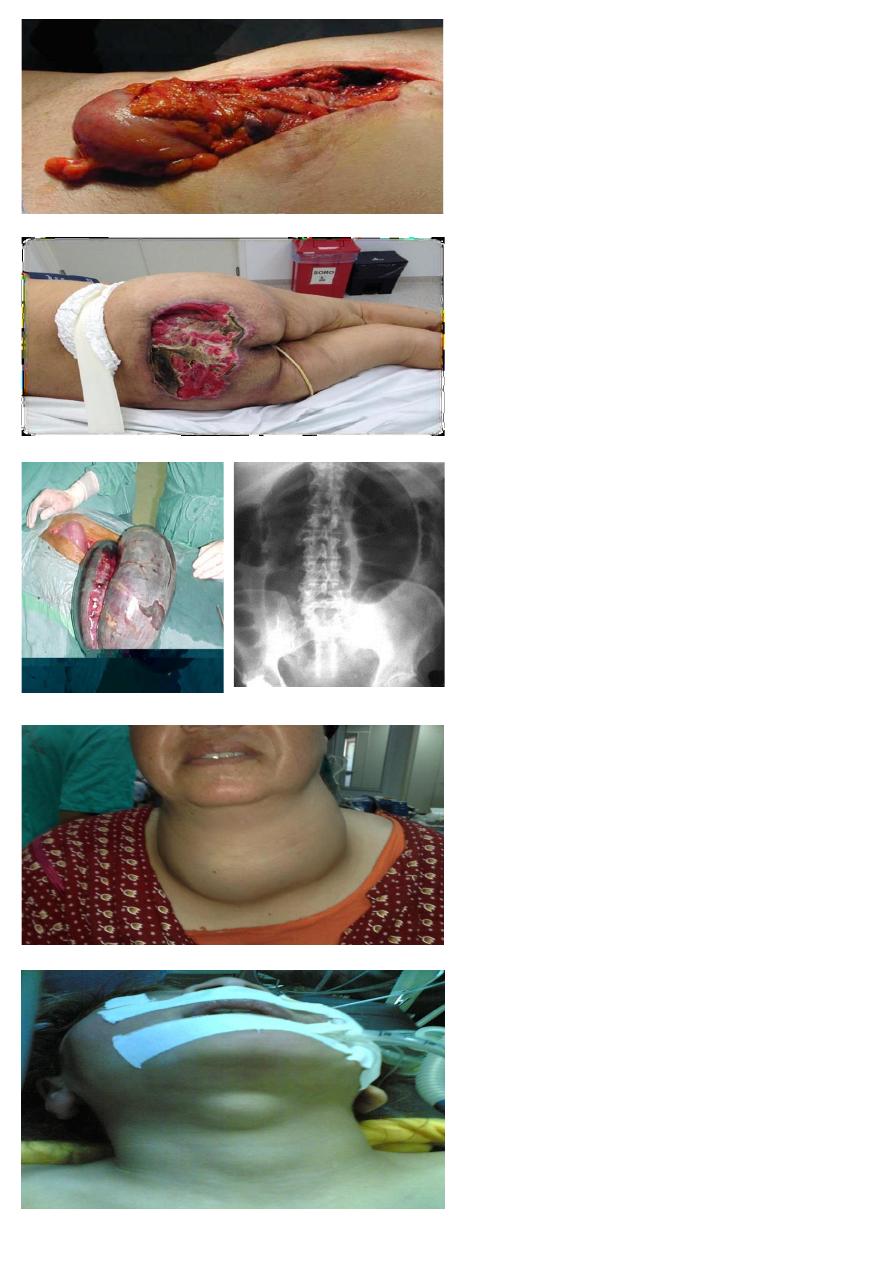
At emergency unit this patient in his 8th day post
laparotomy.
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- Mention the name of suturing to be used for its
treatment.
A-BURST ABDOMEN
B-TENSION SUTURE
80 year old, bedridden patient had this lesion in the
buttock and lower back area.
1- What does this lesion called?
2- Enumerate 3 predisposing factors.
A-BED SORE
B- ANAEMIA, MALNEUTRITION, CONTACT
WITH URINE AND STOOL. SWETTING.
1- what is show in x-ray ?What is the diagnosis?
2- Mention the surgical procedure needed in such
condition
3-mention the cardinal symptom .
A-
inverted omega sign , SIGMOID VUVOLUS
B- RESECTION WITH COLOSTOMY
c-
rapid abdominal distension ,constipation ,colic,
vomiting
1- When does goiter not move with swallowing?
2- What are the local complication her
A-MALIGNANCY.REDIELS THYROIDITIS,
VERY LARGE MASS
B- PRESSURE ON TRACHEA, ESOPHAGUS AND
SUPERIOR VENA CAVA
mass at med neck move with tongue protrusion
1- what is the diagnosis? What complications could
happen if not treated?
2- Name the operation, what structure to be excised
to prevent recurrence?
1-thyroglossal cyst, infection and fistula formation
2-sistrunk operation, the center of hyoid bone
.
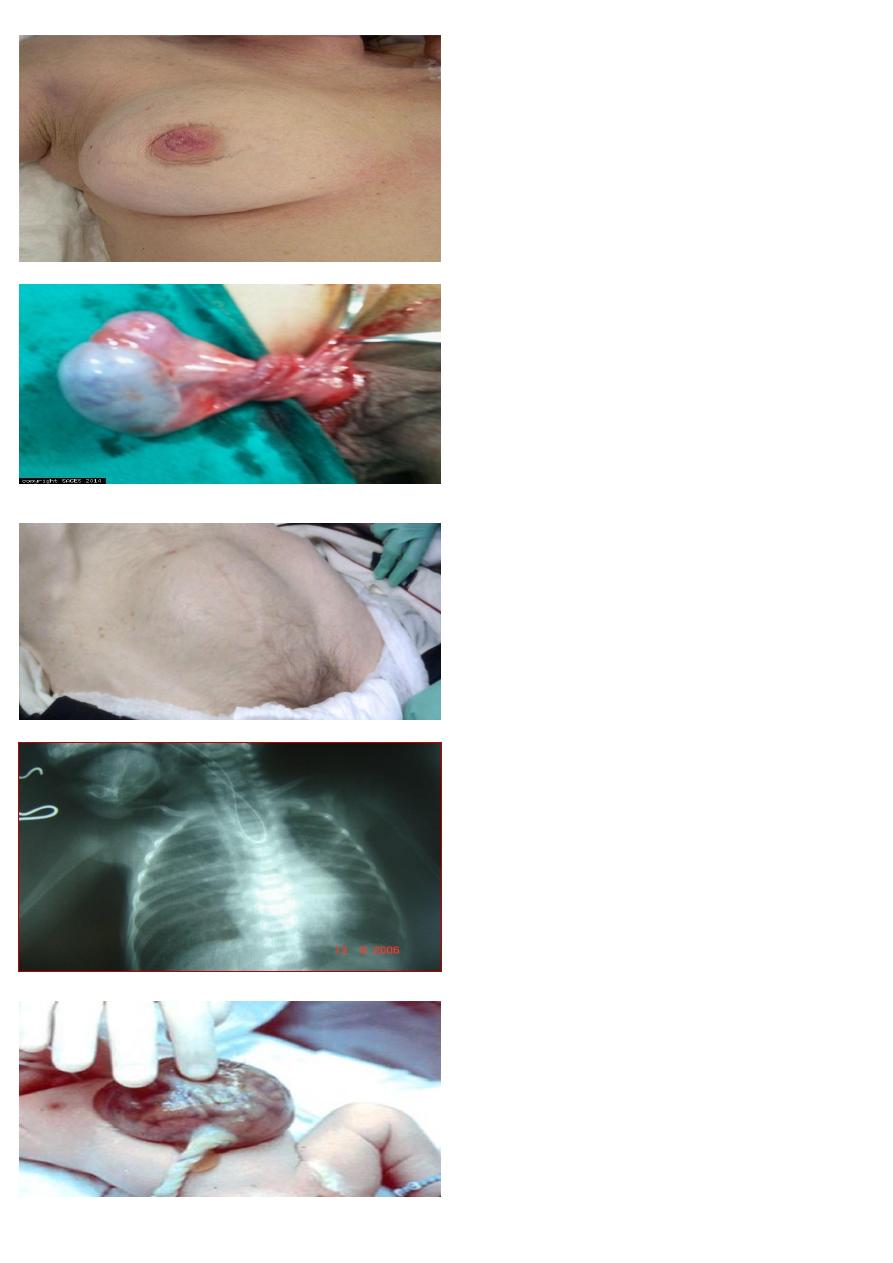
A 60 year old woman is referred to you with a rash
on her nipple.
1- What are the deferential diagnosis?
2- who to prove the diagnosis?
1-paget disease, nipple eczema
2-biopsy
10 years old boy with sudden sever scrotal pain
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- what is the treatment in such case? What to do to
other testis?
1-torsion testis
2-detwisting with fixation, fixation of other testis.
70 years old man fail to pass urine
1- What we call the condition? What is the most
common cause?
2- What is the first aid to be done
1-retension of urine, BPH,
2-drainge by catheter
.newly born baby with excessive salivation
1- what does the x ray shows
2- enumerate the types of such condition
1-failure of NG to pass to stomach
2-esophagial atresia with fistula to trachea , atresia
without fistula to trachea.
1- what is the diagnosis
2- who to differentiate it from other abdominal wall
defect?
1-amphalocele
2- covered by amnion, defect at the umbilicus
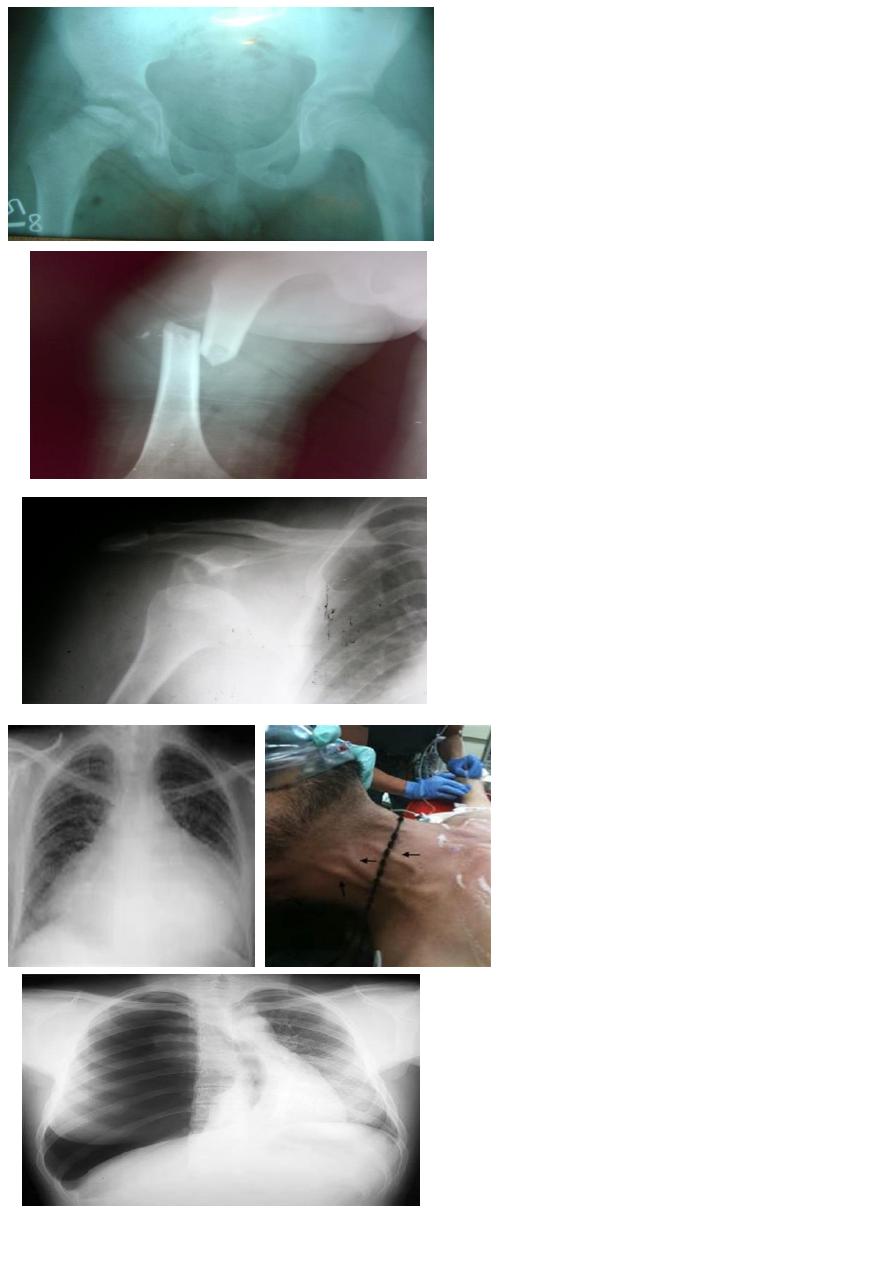
8 years old boy with recurrent painful limping
1- what is the radiological changes?
2- what is the diagnosis?
1- Fragmentation and flattening of femoral head
2-perthes disease
20 Years old man presented following car accident.
1- What is the diagnosis . what is the type of
displacement?
2- what is the best treatment
1-tranverse femoral fracture with over lapping
displacement
2-open reduction and internal fixation
a fall on out stretched hand
1- What is the diagnosis
2- What is the most common early neurological
complication ?
1-anterior dislocation of shoulder
2-axillary n damage
Severe chest trauma by car accident
1- What does the x ray show?
2- What make the neck veins distended
1-increase cardiac shadow
2-obstraction of superior vena cava
1- comment on the x-ray
2- the best response to you for urgent treatment.
1- Translucency of right chest, deviation of
mediastinum to left
2-urgent decompression by needle or formal
chest tube
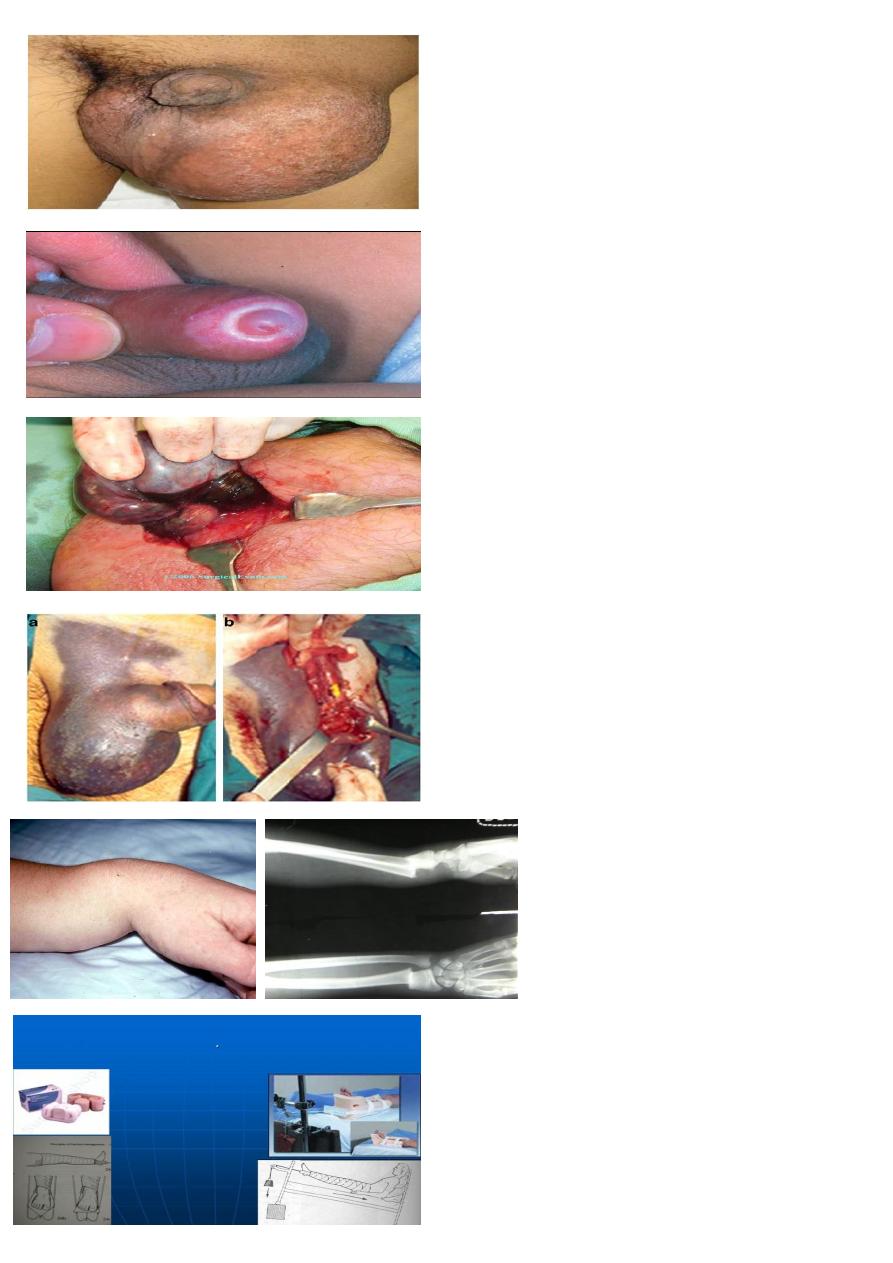
Mass at left scrotum increase in size by cough
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- what is the most dangerous complication?
1- lt is inguinal hernia
2- strangulation
1- What is this disorder?
2- What is the surgical treatment
1 phimosis
2- circumcision
Young boy presented with an extremely painful
scrotal condition for two days.
1. What is the diagnosis?
2. How should you proceed?
1-torsion testis
2- orchiectomy
A male fall a stride
1- what is the diagnosis?
2- what is the late complication?
1 rapture urethra
2 urethral stenosis
1-What is the deformity ?
2-Mention the way of treatment.
1 collies fracture
2 closed reduction
1- What we call this traction ?
2 How much the weight which should be used with it?
1-skin traction
2- 5 kg
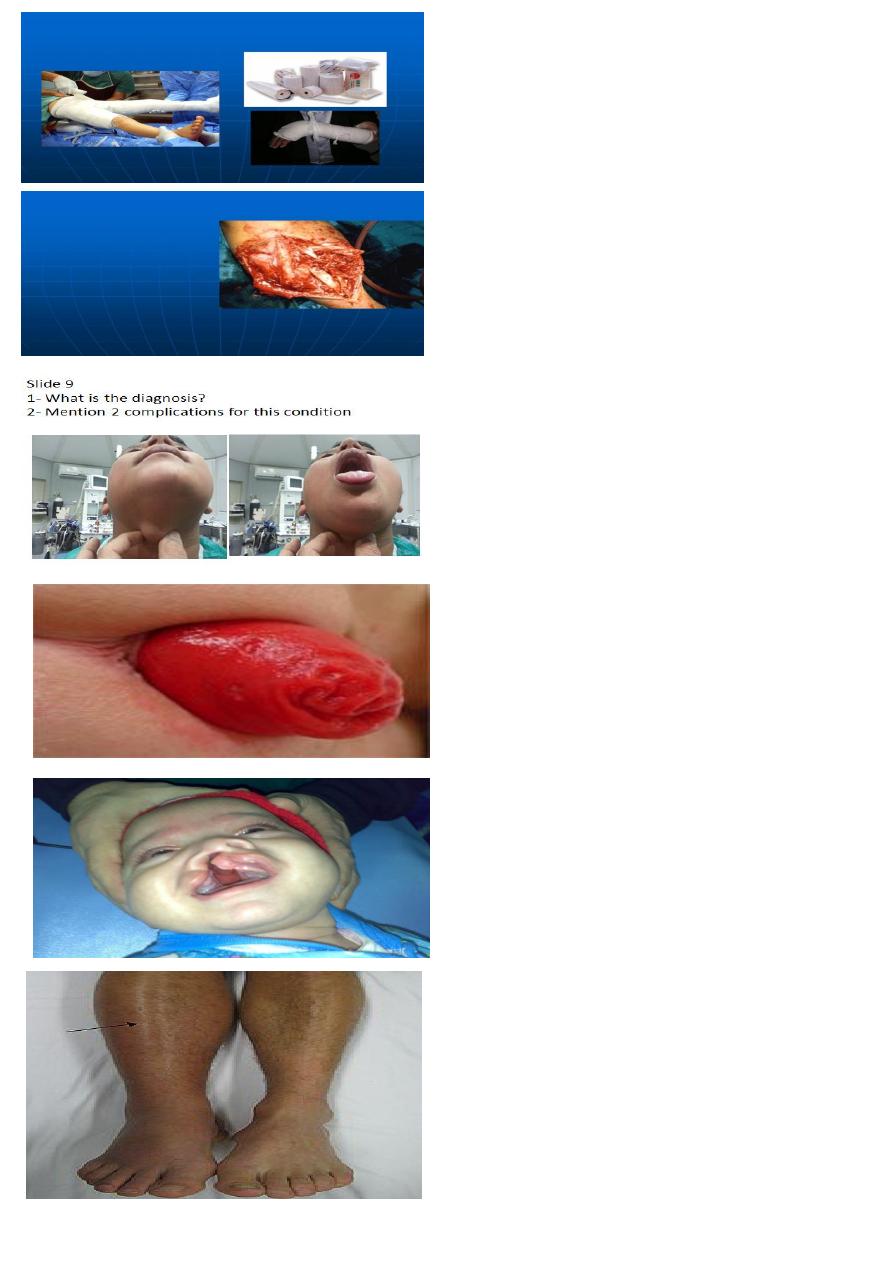
1- What we call this material?
2- Mention two of its complications.
1 POP
2 compartment syndrome, joint stiffness
1- What we call this type of fracture ?.
2- What is the suitable way of fixation ?
1 compound fracture
2 external fixation
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- Mention 2 complications for this condition
1 thyroglossal cyst
2 infection, fistula formation
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What is the deferential diagnosis?
1 complete rectal prolapse
2 intussusception
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What is the best time for operation?
1 cleft lip and palate
2 6 months
50 year old male, 10 days post thoracotomy had
swelling and pain at right leg
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What is the investigation of choice?
1 DVT
2 Doppler ultrasound
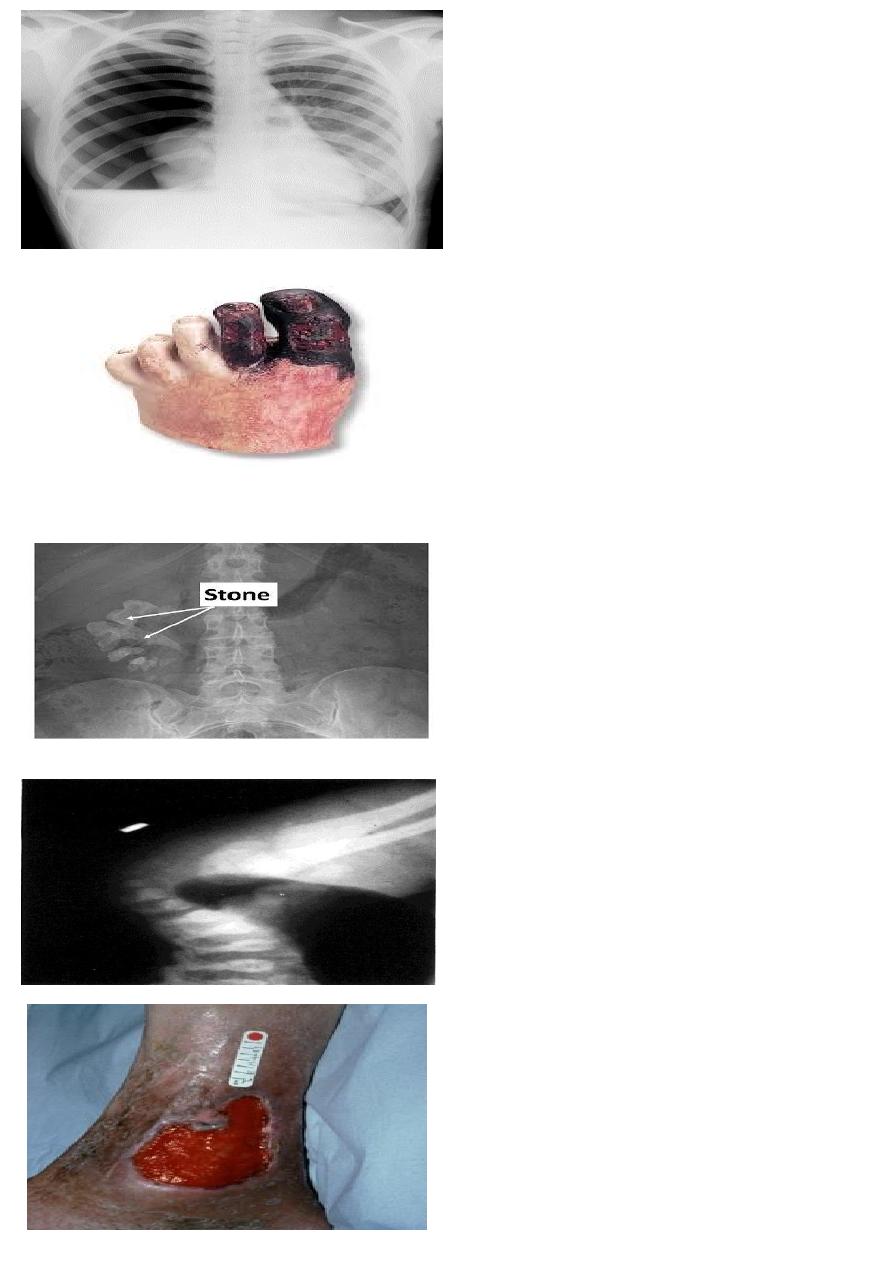
Stab wound to right chest
1- What is the finding?
2- What is the urgent treatment?
1 Rt pneumohemo thorax
2 chest tube
Heavy smoker young male
1- What is the finding?
2- What is the underlying cause?.
3. what is the predisposing factor ?
1 dry gangrene
2- burger disease
3- D.M , smoking , atherosclerosis , obesity .
1-What is this investigation called?
2-What such stone called?
1 KUB
2 staghorn stone
1-Name the X ray procedure?
2- What is used for?
1 upside position with mark
2 differentiate between high and low imperforated
anus.
1- what is the cause of such ulcer
2- what is the remote complication
1-chronic varicosity
2-margolin ulcer
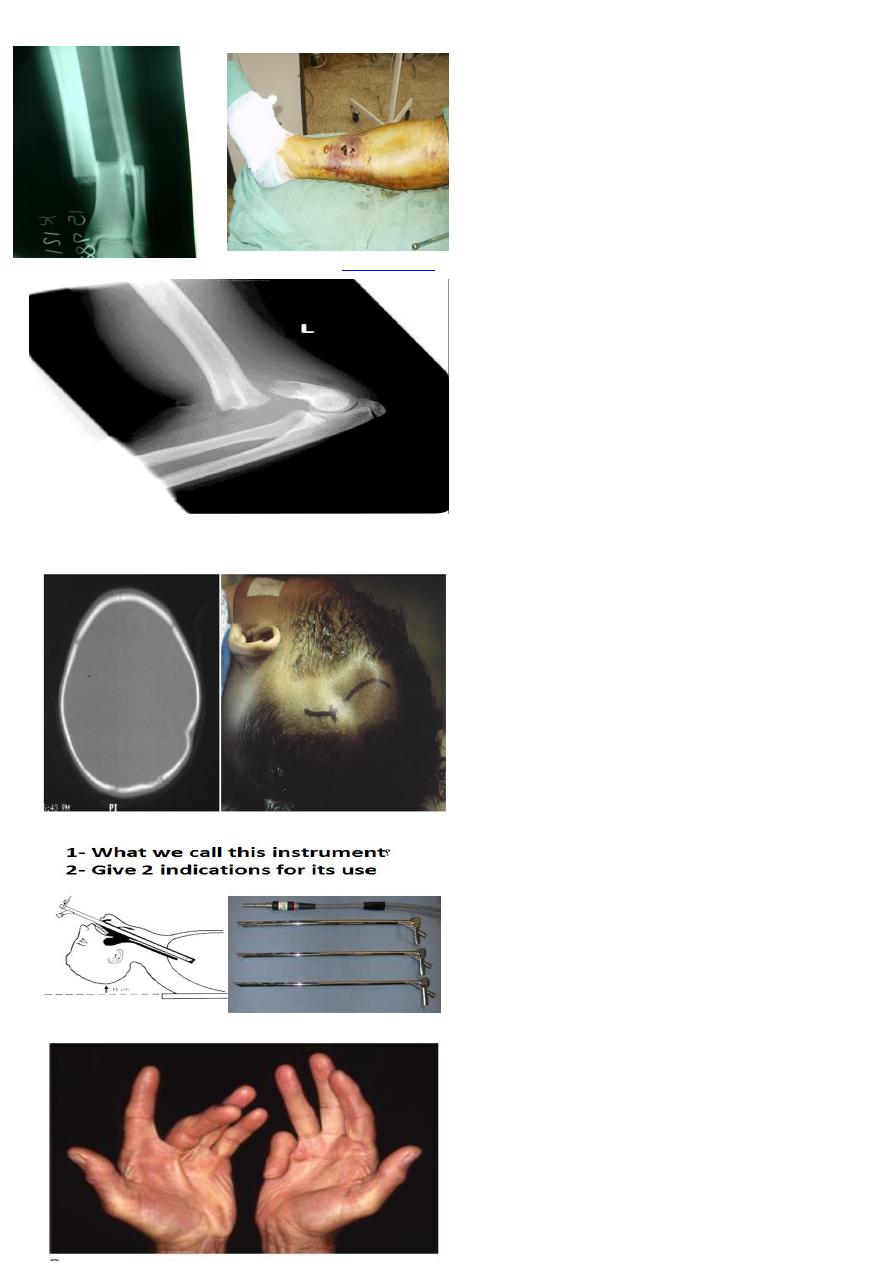
Bullet injury to lower leg
1- What is the most dangerous infection suspected?
2- What is the best treatment for such fracture?
1- tetanus
2- Antibiotic and anti tetanus.
3- MUA for displaced fractures.
What does the x ray shows?
what structure is in dangerous in such trauma?
1. Transvers supracondylar fracture with
displacement and overlap.
2. Brachial artery (risk of injury ).
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- What is the treatment?
1-ping pong fracture.
2-
Treatment :
• Fracture will elevate spontaneously if less than
3cm in diameter.
• If the fracture is more than 5cm in diameter, it
may need surgical elevation.
1. rigid bronchoscope
2. a. diagnostic ( cough , hemoptysis, atelectasis)
b. therapeutic for ( to remove F.B , blood ..etc)
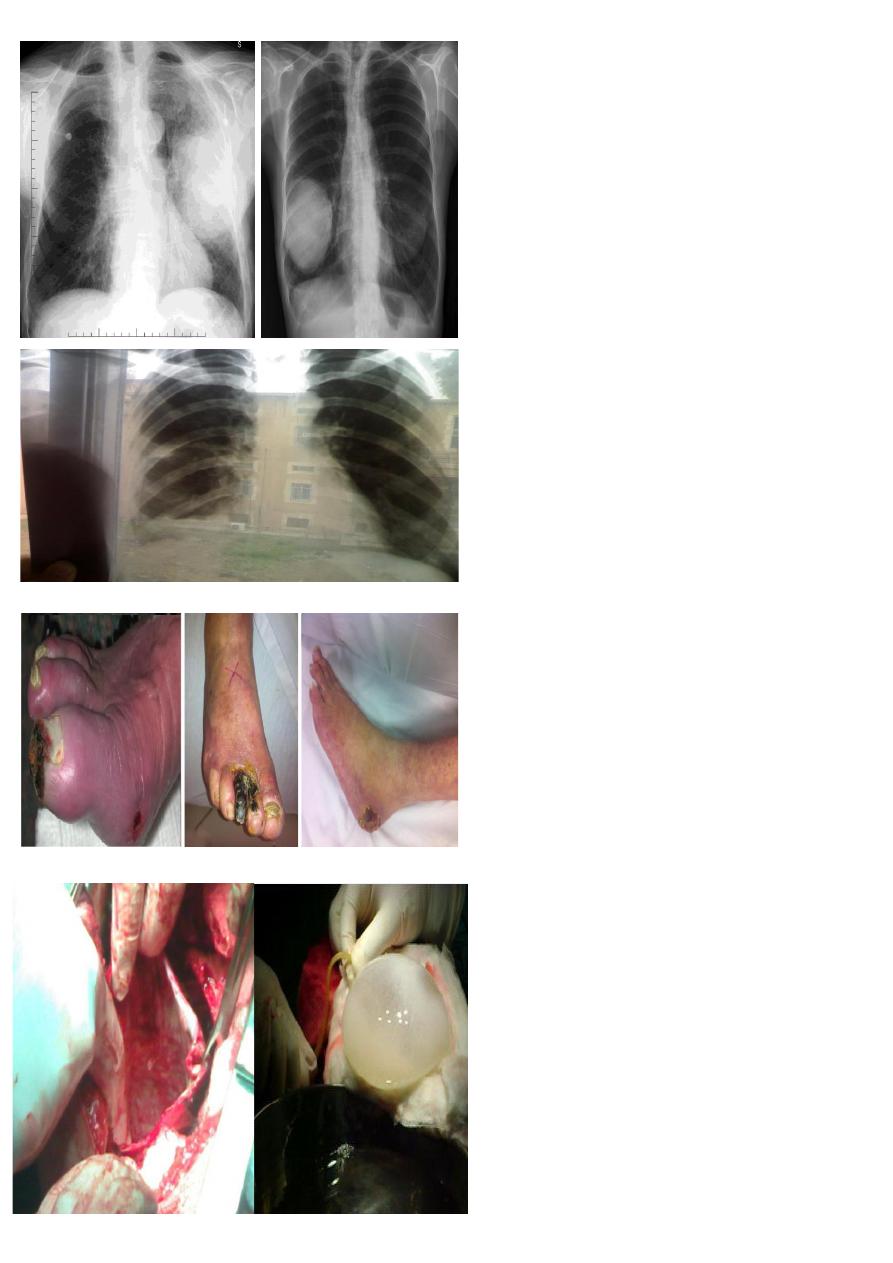
1- what does the picture shows?
2- give 2 conditions leads to such deformity
1. Dupuytren's contracture .
B. D.M & liver disease and alcoholism .
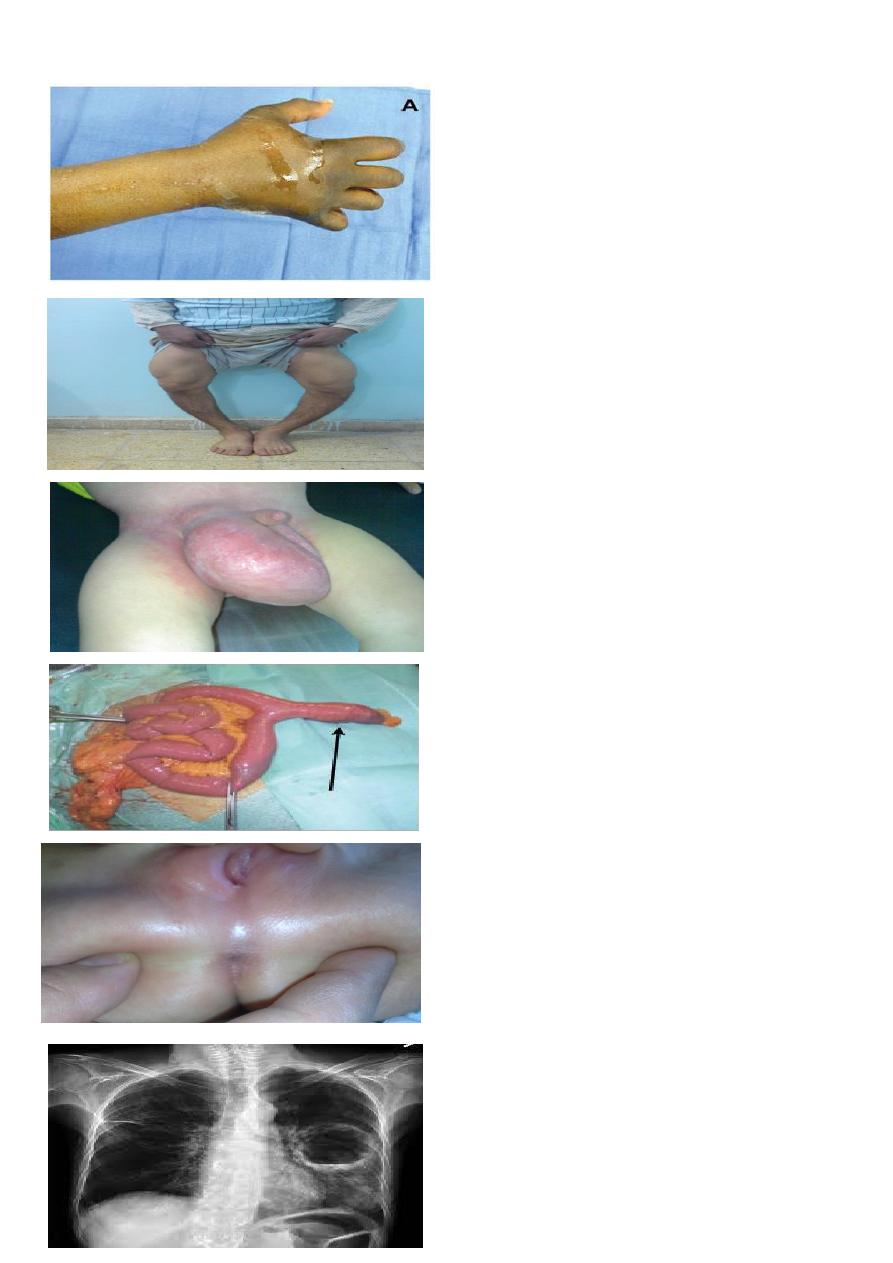
1- Spot diagnosis?
2- What is the best treatment?
1. compartment syndrome hand.
2. Fasciotomy .
1- What is the deformity?
2- Give 2 causes for it?
1. geno Varus deformity .
2. idiopathic , OA , RA .
1- Give 2 differential diagnoses
2-Why the skin is so red?
1. Inguinal Hernia , hydrocele, hematocele.
2. Indicate inflammation .
1- What is the intraoperative finding?
2- Enumerate two common presentations.
1. Meckel's diverticulum.
2. Bleeding per rectum (painless – bright
red – profuse)
Infection (lead to abdominal pain).
1- What is the diagnosis?
2- how many types of such condition you know?
1. Imperforated anus .
2. High type (above pubococcygeal line ) and low
type ( below the line ).
1- What is the finding in this x ray?
2- Give 2 deferential diagnoses
1. large left sided pulmonary cavity with a small
dependent air-fluid level. The wall is relatively
thin.
2. Hydatid cyst , bronchogenic cyst or CA.
1- What does this barium meal show?
2- Give 2 causes for such finding
1. Gastric outlet obstruction .
2. Peptic ulcer D , gastric polyp, pyloric stenosis.
1. What diagnostic features can you see?
2. What is the diagnosis?.
1.
obvious subcutaneous irregular nodules there are
also pigmented cutaneous markings .
2.
neurofibromatosis type I.
1- mention two finding?
2- what is the diagnosis?
1. Moon face , buffalo hump.
2. Cushing's syndrome.
after head injury, patient asked to look to
right
1- What is the finding?
2- What is the cause?
1.
The neurologic examination reveals an inability
to abduct the right eye with horizontal gaze to the
right, a finding that is consistent with an isolated
right Abducent nerve palsy.
2.
Right sixth cranial nerve palsy
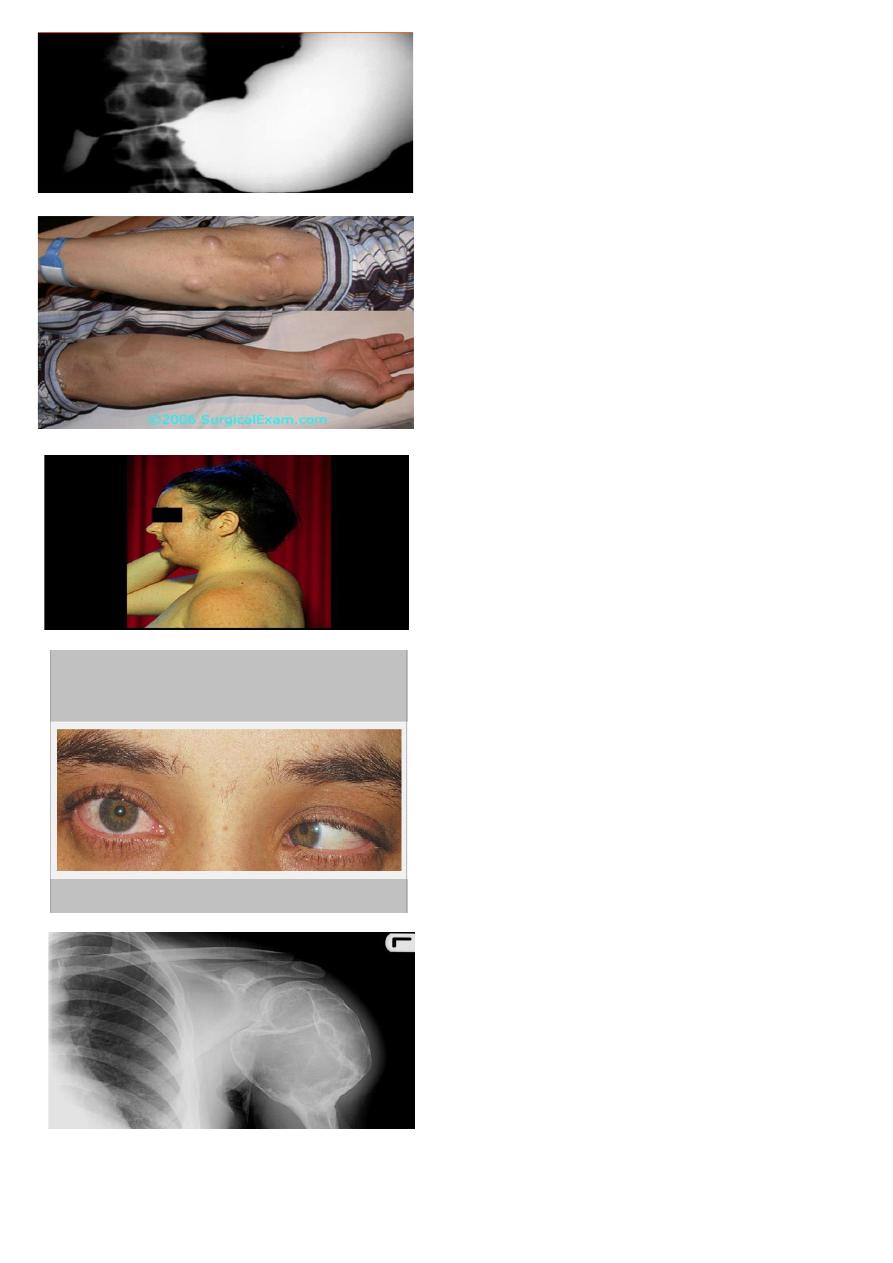
1- What is the diagnosis
2- What complication can result from it.
1.Giant cell tumor ( bubble soap
appearance).
2.infection lead to pathologic fracture , limited
joint movement & metastasis to lung .
